Text
The Gameplay of The Last of Us: A Masterclass in Survival, Storytelling, and Immersion

Introduction
The Last of Us (2013), developed by Naughty Dog and published by Sony Computer Entertainment, is widely regarded as one of the greatest video games of all time. While its narrative and character development receive immense praise, its gameplay is equally groundbreaking. Blending survival horror, stealth, and thirdperson action, The Last of Us creates a tense, immersive experience that complements its emotional storytelling.
1. Core Gameplay Mechanics
1.1. Survival Horror Elements
At its core, The Last of Us is a survival horror game. Resources are scarce, enemies are deadly, and every encounter carries weight. Players must scavenge for supplies such as:
Ammunition (pistols, rifles, bows)
Crafting materials (scissors, tape, alcohol)
Health kits (medications and bandages)
Unlike traditional action games, bullets are limited, forcing players to make every shot count. This scarcity heightens tension, making combat encounters feel desperate rather than empowering.
1.2. Stealth and Avoidance
Direct confrontation is often dangerous, so stealth is a crucial mechanic. Players can:
Crouchwalk to avoid detection
Listen Mode (using Joel’s heightened hearing to detect enemies through walls)
Distract enemies with thrown bottles or bricks
Human enemies communicate with each other, calling out Joel’s position if spotted. Infected enemies, like Clickers (blind but deadly), require even more caution—forcing players to move silently or use shivs for instant kills.
1.3. Crafting and Upgrades
Scavenged materials allow players to craft:
Health kits (essential for survival)
Molotov cocktails (effective against groups)
Smoke bombs (for escape or stealth kills)
Nail bombs (deadly traps)
Weapons can also be upgraded at workbenches, improving reload speed, damage, and stability. These upgrades are permanent, rewarding exploration.
2. Combat: Brutal, Tactical, and Weighted
2.1. Human vs. Infected Encounters
Combat differs drastically depending on the enemy type:
Humans use cover, flank, and throw grenades.
Runners (fast, aggressive infected) swarm the player.
Clickers kill instantly if they grab Joel, requiring stealth or heavy weapons.
Bloaters (lategame infected) are heavily armored and throw spore bombs.
Each enemy type demands different strategies, keeping combat dynamic.
2.2. Melee Combat
When ammo runs low, melee weapons become vital. Players can:
Use fists (weak but unlimited)
Swing pipes or bats (strong but breakable)
Craft shivs (onehit kills on Clickers)
Melee combat is visceral, with brutal animations that emphasize the game’s harsh world.
2.3. Environmental Kills
The environment can be weaponized:
Glass shards create noise distractions.
Bricks stun enemies for quick kills.
Explosive traps can be set using nail bombs.
This interactivity makes each encounter feel dynamic.
3. Exploration and Level Design
3.1. SemiOpen Environments
While linear in structure, levels often feature optional areas with:
Hidden supplies
Collectibles (notes, comics, artifacts that expand lore)
Puzzles (e.g., floating pallets to escort Ellie across water)
These moments slow the pace, allowing tension to build before intense combat sections.
3.2. Immersive Storytelling Through Gameplay
The game avoids cutscenes for many key moments, instead using gameplay to tell the story:
Joel lifting Ellie onto a dumpster to reach higher ground.
Ellie covering Joel with a sniper rifle in a desperate fight.
The Winter chapter, where players control Ellie, changing gameplay dynamics.
These sequences deepen player investment in the characters.
4. AI and Companionship
4.1. Ellie’s AI: A Revolutionary Companion
Unlike most games, Ellie feels like a real ally:
She stays hidden during stealth sections.
She assists in combat, throwing bricks or stabbing enemies.
She reacts to the environment, commenting on discoveries.
Her presence enhances immersion rather than feeling like a burden.
4.2. Enemy AI: Smart and Unpredictable
Enemies adapt:
They flank if Joel stays in cover too long.
They call for backup if alerted.
They panic when alone, adding realism.
This makes fights feel organic rather than scripted.
5. Difficulty and Pacing
5.1. Dynamic Pacing
The game balances:
Highintensity combat (e.g., hotel basement with a generator)
Quiet exploration (e.g., abandoned houses with notes)
Emotional downtime (e.g., giraffe scene)
This rhythm prevents fatigue and keeps players engaged.
5.2. Difficulty Options
Players can adjust:
Combat difficulty (affecting enemy aggression)
Resource scarcity (harder modes give fewer supplies)
Permadeath mode (in the Part II remake)
These options cater to both casual and hardcore players.
6. The Last of Us Part II’s Gameplay Evolution
While this article focuses on the first game, Part II (2020) refined mechanics:
Prone mechanics allow deeper stealth.
Dodging makes melee more fluid.
Enhanced enemy AI (dogs track scent, humans call out names when allies die).
These improvements build on the original’s foundation.
Conclusion: Why The Last of Us’ Gameplay Stands the Test of Time
The Last of Us isn’t just a narrative masterpiece—it’s a gameplay triumph. By blending survival horror, stealth, and emotional storytelling, it creates an experience that remains unmatched. Every mechanic serves its themes of desperation and human connection, making players feel the weight of Joel and Ellie’s journey.
Whether through tense combat, smart AI, or immersive exploration, The Last of Us proves that gameplay and storytelling are inseparable—and that’s why it remains a benchmark for the medium.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Indian Politics: A Dynamic Democracy Navigating Challenges and Aspirations

India, the world’s largest democracy, boasts a vibrant yet complex political landscape shaped by its diversity, historical legacy, and evolving socio-economic priorities. Governed by a parliamentary system enshrined in its 1950 Constitution, Indian politics reflects both democratic ideals and persistent challenges, from corruption to identity-based divisions. This essay explores the structure, key players, contemporary issues, and future prospects of Indian politics in 2025.
1. Political Framework and Democratic Structure
India operates as a federal parliamentary republic, with power divided among the Legislature, Executive, and Judiciary. The President serves as the ceremonial head, while the Prime Minister leads the government. The bicameral Parliament consists of the Lok Sabha (Lower House) and Rajya Sabha (Upper House), representing the people and states, respectively .
The 2024 general elections saw Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secure a third term, albeit reliant on alliances with regional parties like the Telugu Desam Party (TDP) and Janata Dal (United) . This underscores the growing influence of regional parties, which dominate states such as West Bengal (Trinamool Congress) and Tamil Nadu (DMK) .
2. Key Political Parties and Electoral Dynamics
India’s multi-party system features national and regional players. The BJP and Indian National Congress (INC) remain dominant nationally, while regional parties advocate state-specific agendas. The 2024 elections highlighted voter turnout at 67%, with youth and digital campaigns playing pivotal roles . However, challenges like electoral fraud allegations and the criminalization of politics persist, with many legislators facing criminal charges .
The BJP’s consolidation since 2014 has reshaped politics, emphasizing Hindu nationalism, economic reforms, and centralization. Critics argue this has marginalized minorities and weakened federalism, while supporters credit it with infrastructure growth and global stature .
3. Challenges in Indian Politics
A. Corruption and Governance
Corruption remains systemic, exemplified by scandals like the 2G Spectrum scam. Initiatives like the Lokpal Act and digital governance (e.g., Digital India) aim to enhance transparency, yet implementation gaps endure .
B. Identity Politics
Caste and religion often dictate electoral strategies. The BJP’s policies, such as revoking Jammu and Kashmir’s autonomy (Article 370), have intensified debates on secularism and minority rights .
C. Security and Internal Conflict
The 2025 Pahalgam terror attack, attributed to Pakistan-based militants, reignited India-Pakistan tensions and scrutiny of intelligence failures . Meanwhile, Naxalite insurgencies in Chhattisgarh and ethnic violence in Manipur underscore internal security challenges .
D. Economic Disparities
Despite being a $3.7 trillion economy, wealth inequality and unemployment persist. Welfare schemes like MNREGA and PM-KISAN aim to alleviate poverty, yet informal sector workers (94% of the workforce) remain vulnerable .
4. Recent Developments and Policy Shifts
A. BJP’s Third Term Agenda
Modi’s 2024–2029 agenda focuses on “Atmanirbhar Bharat” (self-reliant India), defense modernization, and Hindu cultural revival. The Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025, sparked protests in West Bengal, reflecting tensions over religious property rights .
B. Foreign Policy and Global Partnerships
The 2025 U.S.-India COMPACT initiative strengthened defense and trade ties, including co-production of Javelin missiles and a $500 billion trade target by 2030 . India’s leadership in the G20 and Quad alliances underscores its rising global influence .
C. Social Reforms
The Women’s Reservation Bill (pending) and appointments like Rekha Gupta as Delhi’s Chief Minister signal incremental progress in gender representation .
5. The Road Ahead: Opportunities and Reforms
A. Youth and Digital Engagement
With 65% of the population under 35, youth-driven movements and digital platforms (e.g., MyGov) are reshaping political participation .
B. Judicial and Electoral Reforms
Calls to decriminalize politics and abolish sedition laws (IPC 124A) highlight the need for judicial accountability . The Election Commission’s use of EVMs and VVPATs aims to ensure fair elections .
C. Sustainable Development
Initiatives like the Green Hydrogen Mission and amendments to nuclear liability laws (CLNDA) aim to balance energy security and climate goals .
Conclusion
Indian politics, a tapestry of democracy and diversity, faces a critical juncture in 2025. While the BJP’s dominance reflects a shift toward majoritarianism, regional parties and civil society push for pluralism and equity. Addressing corruption, enhancing inclusivity, and fostering youth leadership will determine whether India realizes its potential as a global democratic exemplar. As historian Ramachandra Guha noted, India’s democracy is “a marathon, not a sprint”—a testament to its resilience amid evolving challenges .
References: Insights synthesized from constitutional frameworks , electoral dynamics , policy initiatives , and contemporary events .
1 note
·
View note
Text
Digitisation of Bharatham
India's journey towards digitization has been remarkable, transforming the country's economy, governance, and society. The Digital India initiative, launched in 2015, aimed to connect rural areas with high-speed internet networks, promote digital literacy, and make government services available electronically.

Key Components of Digital India
Digital Infrastructure: Development of secure and stable digital infrastructure, including high-speed internet connectivity and digital platforms.
Governance and Services: Delivery of government services digitally, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Digital Literacy: Promotion of digital literacy among citizens, enabling them to access and utilize digital services effectively.
Impact on Economy
India's digital economy has grown significantly, contributing 11.74% to the country's GDP in 2022-23. It's expected to contribute nearly one-fifth of the national income by 2029-30, outpacing agriculture and manufacturing. Digital platforms, artificial intelligence, and cloud services are driving this growth.
Digitalization in Various Sectors
Banking and Finance: Over 95% of banking payment transactions are digital, although revenue-generating activities like loans and investments remain largely offline.
Retail: Shifting to omni-channel models, with e-tailers adding physical stores and utilizing AI chatbots and digital inventory tools.
Education: Adopting offline, online, and hybrid models, with most institutions favoring hybrid approaches.
Hospitality and Logistics: Embracing AI, metaverse, and digital tools, with large firms fully digitalizing operations.Challenges and Opportunities
While India's digital transformation has been impressive, concerns over data breaches and cybersecurity persist. Nevertheless, the country's digital economy is poised for continued growth, with opportunities emerging in areas like:Global Capability Centers: India hosts 55% of the world's GCCs, providing services like R&D, IT support, and business process management.
Digital Employment: The digital economy employs 14.67 million workers, with digital platforms contributing to increasing job opportunities for women.Global Ranking
India ranks third in terms of economy-wide digitalization, behind the US and China. However, in terms of individual user digitalization, India ranks 12th among G20 countries.Overall, India's digitization journey has transformed the country's economy and society, offering numerous opportunities for growth and development. As the digital economy continues to expand, it's essential to address challenges and harness the potential of digital technologies to drive sustainable growth and inclusive development.
0 notes
Text
Cellbiology

I. Introduction to Cell Biology
Cell biology is the study of the structure, function, and behavior of cells, which are the basic units of life. Cells are the building blocks of all living organisms, and they are responsible for carrying out the functions necessary for life.
II. Cell Structure
A cell consists of several organelles, each with its own unique structure and function. The main components of a cell include:
1. Plasma Membrane: The plasma membrane is the outermost layer of the cell that separates the cell from its environment. It is semi-permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while keeping others out.
2. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane where many of the cell's metabolic reactions take place.
3. Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell where DNA is stored.
4. Mitochondria: The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell where energy is produced.
5. Endoplasmic Reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that is responsible for protein synthesis and transport.
6. Ribosomes: The ribosomes are small organelles found throughout the cytoplasm where protein synthesis takes place.
7. Lysosomes: The lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes and are responsible for cellular digestion and recycling.
8. Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is a complex organelle that is responsible for protein modification and transport.
III. Cell Function
Cells perform a wide range of functions necessary for life, including:
1. Metabolism: Cells carry out metabolic reactions to produce energy and synthesize the molecules needed for life.
2. Protein Synthesis: Cells synthesize proteins using the genetic information stored in DNA.
3. Cell Division: Cells divide to produce new cells, which is necessary for growth, repair, and reproduction.
4. Cell Signaling: Cells communicate with each other through cell signaling pathways, which allow them to coordinate their behavior and respond to their environment.
5. Cell Movement: Cells move using various mechanisms, such as muscle contraction and cytoskeletal rearrangement.
IV. Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is the series of events that a cell goes through from one cell division to the next. The cell cycle consists of three main stages:
1. Interphase: During interphase, the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division.
2. Mitosis: During mitosis, the replicated DNA is divided equally between two daughter cells.
3. Cytokinesis: During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm divides and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
V. Cell Signaling
Cell signaling is the process by which cells communicate with each other and respond to their environment. Cell signaling pathways involve a series of molecular interactions that allow cells to transmit and receive signals.
A. Types of Cell Signaling
There are several types of cell signaling, including:
1. Endocrine Signaling: Endocrine signaling involves the release of hormones into the bloodstream, which then bind to receptors on target cells.
2. Paracrine Signaling: Paracrine signaling involves the release of signaling molecules that diffuse through the extracellular space and bind to receptors on nearby cells.
3. Autocrine Signaling: Autocrine signaling involves the release of signaling molecules that bind to receptors on the same cell.
4. Juxtacrine Signaling: Juxtacrine signaling involves the release of signaling molecules that bind to receptors on adjacent cells.
VI. Cell Movement
Cell movement is the ability of cells to change their position in response to various stimuli. There are several types of cell movement, including:
1. Muscle Contraction: Muscle contraction involves the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other to produce force.
2. Cytoskeletal Rearrangement: Cytoskeletal rearrangement involves the reorganization of the cytoskeleton to produce force and movement.
3. Cell Migration: Cell migration involves the movement of cells from one location to another in response to various stimuli.
VII. Cell Death
Cell death is the process by which cells die and are removed from the body. There are several types of cell death, including:
1. Apoptosis: Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death that involves the activation of a series of molecular pathways that lead to the death of the cell.
2. Necrosis: Necrosis is a form of cell death that involves the uncontrolled death of cells, often as a result of injury or infection.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, cell biology is the study of the structure, function, and behavior of cells.
1 note
·
View note
Text
The Communist Manifesto

The Communist Manifesto, written by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels in 1848, is a foundational document of modern communism
.I. Introduction
The manifesto begins by introducing the concept of class struggle and the idea that all societies have been divided into opposing classes. Marx and Engels argue that in capitalist societies, the bourgeoisie (those who own the means of production) exploit the proletariat (the working class).
II. Section 1: Bourgeois and Proletarians
Marx and Engels describe the rise of the bourgeoisie and the development of capitalism. They argue that the bourgeoisie have created a global market and have exploited the proletariat, reducing them to a state of alienation.
A. The Rise of the Bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie emerged as a result of the Industrial Revolution, which created new technologies and new forms of production. The bourgeoisie accumulated wealth and power, becoming the dominant class in society.
B. The Exploitation of the Proletariat
Marx and Engels argue that the bourgeoisie exploit the proletariat by paying them less than the value of their labor. This creates a surplus value, which the bourgeoisie use to accumulate wealth and power.
C. Alienation
Marx and Engels argue that the proletariat are alienated from their labor, their fellow workers, and their humanity. This alienation is a result of the capitalist system, which reduces workers to mere commodities.
III. Section 2: Proletarians and Communists
This section outlines the principles of communism and the role of the Communist Party. Marx and Engels argue that communists seek to abolish private property and establish a classless society.
A. The Principles of Communism
Marx and Engels argue that communism is based on the principles of equality, justice, and the abolition of private property. They argue that communism will create a classless society, in which there is no exploitation or oppression.
B. The Role of the Communist Party
Marx and Engels argue that the Communist Party has a crucial role to play in the revolutionary process. The party must educate and organize the proletariat, and lead them in the struggle against the bourgeoisie.
IV. Section 3: Socialist and Communist Literature
Marx and Engels critique various forms of socialism and communism, arguing that they are inadequate or misguided.
A. Reactionary Socialism
Marx and Engels argue that reactionary socialism seeks to restore the old feudal order, and is therefore reactionary and counter-revolutionary.
B. Conservative or Bourgeois Socialism
Marx and Engels argue that conservative or bourgeois socialism seeks to reform the capitalist system, rather than abolish it. They argue that this approach is inadequate, and that only a revolutionary transformation of society can create a truly just and equal society.
V. Section 4: Position of the Communists in Relation to the Various Opposition Parties
This section outlines the Communist Party's stance on various opposition parties, including the bourgeoisie, the petty bourgeoisie, and other socialist groups.
A. The Bourgeoisie
Marx and Engels argue that the bourgeoisie are the main enemy of the proletariat, and that they must be overthrown in order to create a socialist society.
B. The Petty Bourgeoisie
Marx and Engels argue that the petty bourgeoisie are a contradictory class, who are both exploited by the bourgeoisie and seek to exploit the proletariat. They argue that the petty bourgeoisie must be won over to the side of the proletariat in order to create a successful revolution.
VI. Conclusion
The manifesto concludes by calling for the overthrow of the bourgeoisie and the establishment of a communist society. Marx and Engels famously declare, "The proletarians have nothing to lose but their chains. They have a world to win."
VII. Key Concepts
1. Class struggle: The idea that all societies have been divided into opposing classes, and that the ruling class exploits the subordinate class.
2. Alienation: The idea that the proletariat are alienated from their labor, their fellow workers, and their humanity.
3. Private property: The idea that the ownership of private property is a key feature of capitalist societies, and that it must be abolished in order to create a socialist society.
4. Communism: The idea that communism is a system in which there is no private property, no exploitation, and no oppression.
5. Proletariat: The class of workers who are exploited by the bourgeoisie.
6. Bourgeoisie: The class of owners of the means of production who exploit the proletariat.
VIII. Influence and Legacy
The Communist Manifesto has had a profound impact on modern politics and society. It has influenced socialist and communist movements worldwide, and continues to be studied and debated by scholars and activists today.Influence on Socialist and Communist Movements
The Communist Manifesto has influenced socialist and communist movements worldwide, including the Russian Revolution, the Chinese Revolution, and the Cuban Revolution.
0 notes
Text
Dracula

Introduction
Bram Stoker's Dracula, published in 1897, is a masterpiece of Gothic horror that has captivated readers for over a century. The novel tells the story of Count Dracula, a bloodthirsty vampire who moves from Transylvania to England, preying on humans to satisfy his thirst for blood. This review will delve into the world of Dracula, exploring its themes, characters, and the reasons behind its enduring popularity.
The Plot
The novel begins with Jonathan Harker, a young solicitor who travels to Transylvania to finalize the sale of a property to Count Dracula. Unbeknownst to Harker, he is entering a world of horror and superstition. Upon his arrival at the castle, he discovers that he is a prisoner, and soon learns that Dracula is a vampire.Harker manages to escape from the castle, but Dracula follows him to England, where he begins to prey on Harker's fiancée, Mina, and her friend, Lucy. As the novel progresses, the characters become increasingly entangled in a web of horror and suspense.
The Themes
One of the primary themes of Dracula is the fear of the unknown. Stoker masterfully crafts a sense of unease and uncertainty, leaving the reader questioning what is real and what is imagined. The novel also explores the idea of good vs. evil, with Dracula representing the ultimate evil and the characters who oppose him embodying goodness and virtue.
Another significant theme is the role of women in society. During the Victorian era, women were expected to conform to traditional roles and expectations. Stoker's female characters, particularly Mina and Lucy, challenge these norms, demonstrating independence, courage, and determination.
The Characters
The characters in Dracula are well-developed and complex, adding depth and richness to the narrative. Count Dracula is a masterful creation, embodying the perfect blend of charm, intelligence, and terror. His powers of persuasion and manipulation are matched only by his supernatural abilities.The human characters are equally well-crafted. Jonathan Harker is a brave and resourceful hero, while Mina is a strong and determined woman who plays a crucial role in the defeat of Dracula. The character of Van Helsing, a wise and experienced vampire hunter, adds a sense of authority and expertise to the narrative.
The Style and Structure
Stoker's writing style is descriptive and evocative, painting vivid pictures of the settings and characters. The novel is structured as a series of letters, diaries, and newspaper articles, which adds to the sense of realism and immediacy.The use of epistolary format allows the reader to experience the story through multiple perspectives, creating a sense of intimacy and immediacy. Stoker's use of language is masterful, conjuring up a sense of atmosphere and tension that draws the reader into the world of the novel.
The Impact and Legacy
Dracula has had a profound impact on popular culture, influencing countless adaptations, interpretations, and reimaginings. From films and stage plays to books and comics, the character of Count Dracula has become an iconic figure, symbolizing the ultimate evil.The novel has also had a significant influence on the genre of horror, inspiring generations of writers and filmmakers. Stoker's use of suspense, tension, and the supernatural has become a hallmark of the horror genre, and his influence can be seen in everything from Stephen King to Anne Rice.
Conclusion
Bram Stoker's Dracula is a masterpiece of Gothic horror that continues to captivate readers to this day. Its themes of fear, good vs. evil, and the role of women in society are timeless and thought-provoking. The characters are well-developed and complex, and the writing style is descriptive and evocative.As a work of horror, Dracula is unparalleled, conjuring up a sense of atmosphere and tension that draws the reader into the world of the novel. Its impact on popular culture is immeasurable, and its influence can be seen in countless adaptations, interpretations, and reimaginings.In conclusion, Dracula is a must-read for fans of horror, suspense, and supernatural fiction. Its enduring popularity is a testament to the power of Stoker's storytelling, and its influence will continue to be felt for generations to come.
0 notes
Text
A Spiritual Sojourn to Mookambika

As I embarked on my journey to Mookambika, a revered temple town in Karnataka, India, I couldn't help but feel a sense of excitement and trepidation. The promise of a spiritual awakening and the allure of unspoiled natural beauty beckoned me to this sacred destination.
The Journey Begins
My travels took me from the bustling city of Bangalore to the quaint town of Kollur, home to the famous Mookambika Temple. The 400-kilometer journey was a scenic one, winding through rolling hills, verdant forests, and picturesque villages. As I traversed the Western Ghats, the air grew thick with the scent of blooming flowers and the sounds of nature provided a soothing accompaniment.
Arrival in Kollur
Upon arrival in Kollur, I was struck by the town's tranquil atmosphere. The streets were lined with quaint shops and eateries, offering a range of local delicacies and souvenirs. As I made my way to the temple, the sound of chanting and the fragrance of incense wafted through the air, heightening my anticipation.
The Mookambika Temple
The Mookambika Temple, dedicated to the goddess Parvati, is a stunning example of ancient Indian architecture. The temple's intricate carvings, vibrant frescoes, and imposing towers left me in awe. As I stepped inside, I was enveloped by an aura of serenity, and the divine energy of the temple seemed to permeate every pore.
A Spiritual Awakening
As I participated in the temple's rituals and offerings, I felt a deep sense of connection to the divine. The temple's priests, with their warm smiles and gentle guidance, helped me navigate the intricacies of the puja ceremony. As I prayed and meditated, I felt a sense of peace and clarity wash over me, as if the goddess herself was bestowing her blessings upon me.
Exploring Kollur
Beyond the temple, Kollur offered a range of experiences that allowed me to soak in the local culture. I strolled along the banks of the Souparnika River, watching as the sun dipped below the horizon. I sampled local delicacies, such as the famous Kollur idlis and dosas. And I marveled at the stunning natural beauty of the surrounding hills and forests.
A Lasting Impression
As I prepared to leave Kollur and return to the chaos of city life, I felt a sense of gratitude and peace. My journey to Mookambika had been a transformative one, offering me a glimpse into the spiritual heart of India. The memories of this trip will stay with me forever, a reminder of the power of faith, nature, and culture to uplift and inspire
0 notes
Text
Ghosts and Roads: A Spooky Connection

As the sun sets and darkness falls, many of us have experienced the thrill of driving down a deserted road, wondering if we're truly alone. The idea of ghosts and roads has long fascinated humans, sparking tales of paranormal activity and unexplained occurrences.
From eerie fog-shrouded highways to haunted byways, certain roads around the world have gained notoriety for their ghostly encounters. These routes often have a dark history, marked by tragic accidents, untimely deaths, or mysterious disappearances.
One such example is the infamous Route 66 in the United States, where numerous drivers have reported strange sightings and experiences. Similar tales can be found on India's NH-17, where locals claim to have seen ghostly apparitions and heard strange noises.
While the existence of ghosts remains a topic of debate, the psychological impact of driving on certain roads cannot be denied. The isolation, darkness, and fatigue can play tricks on our minds, making us more susceptible to the power of suggestion.
Whether you believe in ghosts or not, the allure of haunted roads continues to captivate our imagination. So the next time you find yourself driving down a deserted road at night, keep your eyes peeled for unexpected surprises – or perhaps, a ghostly passenger.
0 notes
Text

This invention is not a mith ,it do not have a defence structure that is to work with network. A aluminium can that need to be inserted in a big can on top of it we can have a CONVEX lens that help to boil water. Tech; to find the focal length, point it to the ground and ignite something. FL need to be less that the length of the can. Their will be two output on top of the bottle. Try it ...
1 note
·
View note
Text
Introduction to human body
I. Introduction (approx. 1,000 words)
- Overview of the human brain
- Importance of understanding brain function
II. Brain Structure (approx. 10,000 words)
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brainstem
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
- Basal ganglia
III. Brain Functions (approx. 15,000 words)
- Sensory perception
- Motor control
- Cognitive processing
- Emotional regulation
- Memory formation
- Language processing
- Problem-solving
- Decision-making
IV. Neurotransmitters and Hormones (approx. 5,000 words)
- Overview of neurotransmitters
- Major neurotransmitters (e.g., dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine)
- Hormones and their roles in brain function
V. Brain Development and Plasticity (approx. 5,000 words)
- Brain development from embryonic stage to adulthood
- Neuroplasticity and its importance
VI. Conclusion (approx. 1,000 words)
- Summary of key points
- Future directions in brain research
Introduction
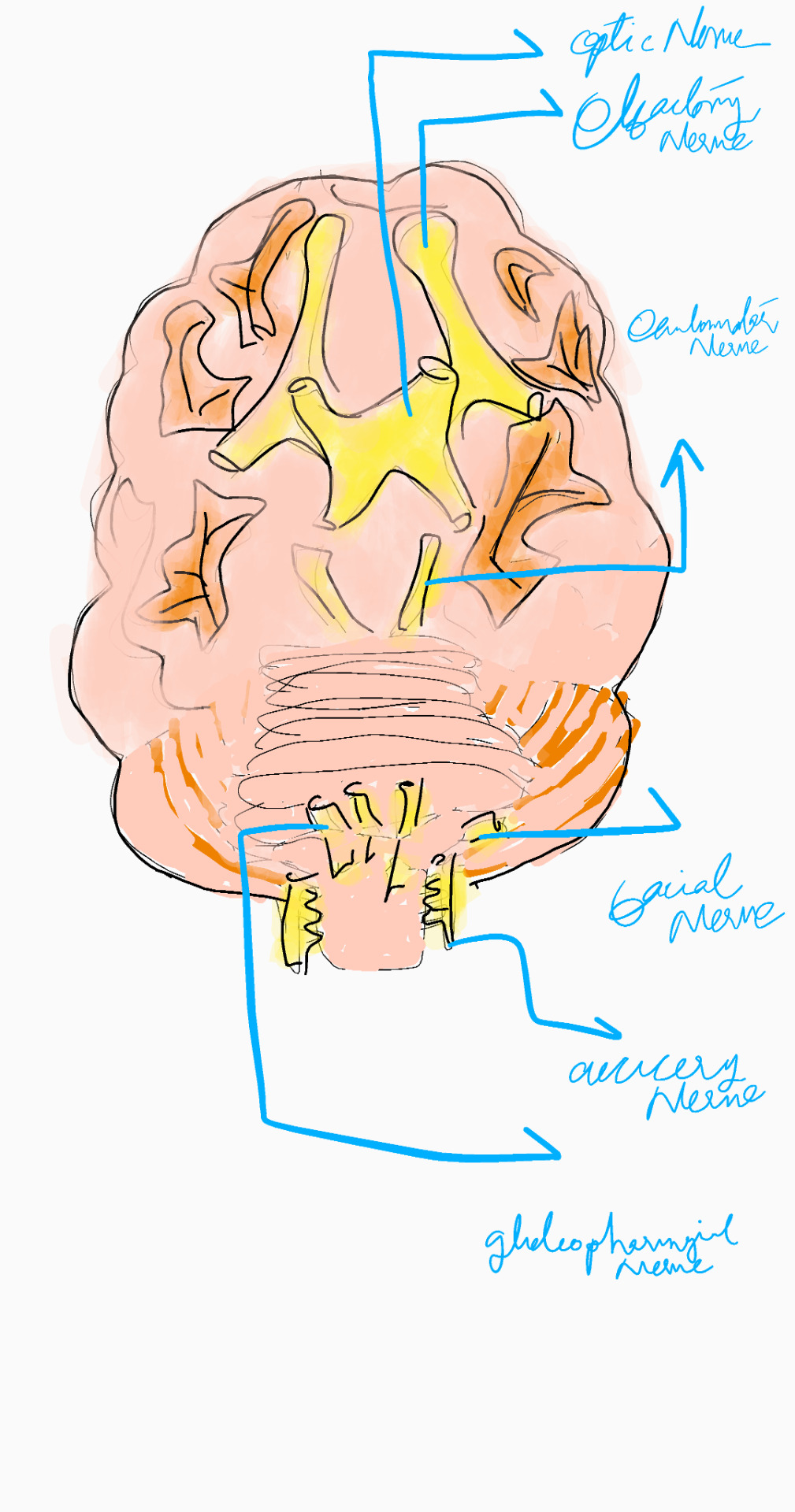
The human brain is a mysterious and intricate organ, responsible for controlling every aspect of our lives. From the moment we wake up to the moment we sleep, our brain is constantly working, processing information, and enabling us to interact with the world around us. Despite its importance, the brain remains a largely unexplored territory, with much of its functionality still unknown.
Understanding the brain is a complex task, as it consists of billions of neurons, trillions of connections, and an intricate network of blood vessels. However, advances in neuroscience and technology have enabled us to study the brain in greater detail, revealing its remarkable capabilities and complexities.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the human brain, exploring its structure, functions, and intricacies. We will delve into the brain's development, its various regions, and the roles they play in controlling our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Additionally, we will discuss the brain's remarkable ability to adapt and change, its potential for growth and development, and the latest research and discoveries in the field of neuroscience.
Brain Structure
The human brain is a complex and intricate organ, consisting of several regions that work together to control various aspects of our lives. The brain can be broadly divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
A. Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, responsible for processing sensory information, controlling movement, and managing higher-level cognitive functions such as thought, emotion, and memory. The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere.
B. Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located at the base of the brain, below the cerebrum. It plays a crucial role in coordinating movement, balance, and posture.
C. Brainstem
The brainstem connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord, and regulates basic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
D. Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is located in the front of the brain, and is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, planning, and problem-solving.
E. Parietal Lobe
The parietal lobe is located near the center of the brain, and processes sensory information related to touch and spatial awareness.
F. Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is located on the sides of the brain, and plays a key role in processing auditory information and memory.
G. Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is located at the back of the brain, and is primarily responsible for processing visual information.
Brain Functions
The brain is responsible for a wide range of functions, including:
A. Sensory Perception
- Interpreting visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, and gustatory information
- Enabling us to perceive and understand the world around us
B. Motor Control
- Coordinating voluntary movements, such as walking, talking, and writing
- Regulating involuntary movements, like heartbeat and digestion
C. Cognitive Processing
- Facilitating thought, problem-solving, and decision-making
- Enabling us to learn, remember, and adapt
D. Emotional Regulation
- Processing emotions, such as happiness, sadness, and fear
- Influencing our mood, motivation, and behavior
E. Memory Formation
- Storing and retrieving information
- Enabling us to learn and remember new skills, knowledge, and experiences
Neurotransmitters and Hormones
Neurotransmitters and hormones play a crucial role in regulating various brain functions, including mood, motivation, and metabolic processes.
A. Neurotransmitters
- Chemical messengers that transmit signals between neurons
- Examples: dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine, and norepinephrine
- Influence mood, motivation, movement, and other physiological processes
B. Hormones
- Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands
- Examples: insulin, thyroxine, cortisol, and oxytocin
- Regulate metabolic processes, growth, and development
Brain Development and Plasticity
The brain is a dynamic and adaptive organ, capable of reorganizing itself throughout life.
A. Brain Development
- From embryonic stage to adulthood
- Critical periods of development
- Neuronal migration and synaptogenesis
B. Neuroplasticity
- Brain's ability to reorganize and adapt
- Synaptic plasticity and neuronal rewiring
- Role of experience and learning in shaping brain structure and function
C. Neurogenesis
- Growth of new neurons in adult brain
- Role of exercise, diet, and stress in promoting neurogenesis
D. Brain Injury and Recovery
- Effects of injury on brain structure and function
- Mechanisms of recovery and compensation
- Role of rehabilitation and therapy in promoting recovery
Conclusion
In conclusion, the human brain is a complex and fascinating organ, responsible for controlling every aspect of our lives. From its intricate structure to its dynamic functions, the brain is a marvel of nature. We have explored the brain's development, functions, and plasticity, as well as its many mysteries still waiting to be unraveled.
As we continue to advance our understanding of the brain, we may uncover new ways to improve brain health, treat neurological disorders, and enhance cognitive function. The study of the brain is an ongoing journey, and one that holds great promise for improving human life.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the human brain, and inspires further exploration and discovery.
Please let me know if you'd like me to make any changes or if you're satisfied with the conclusion!
Also, I'd like to thank you for your patience and collaboration throughout this project. It's been a pleasure working with you to create this comprehensive article about the human brain!
1 note
·
View note
Text

Child care
Introduction (approx. 1,000 words)
- Definition of child care
- Importance of quality child care
- Brief overview of the article's contents
II. Types of Child Care (approx. 2,000 words)
- Center-based care
- Home-based care
- Family child care
- In-home care
- Nanny care
III. Benefits of Child Care (approx. 2,500 words)
- Cognitive development
- Social-emotional development
- Physical development
- Language and literacy skills
- Preparation for school
IV. Child Care Settings (approx. 2,500 words)
- Child care centers
- Home-based settings
- Group child care
- Drop-in centers
- Parent-child playgroups
V. Child Care Providers (approx. 2,000 words)
- Qualifications and training
- Roles and responsibilities
- Characteristics of effective providers
- Provider-child relationships
VI. Child Development and Child Care (approx. 3,000 words)
- Infant care (0-12 months)
- Toddler care (1-3 years)
- Preschool care (3-5 years)
- School-age care (5-12 years)
VII. Safety and Health in Child Care (approx. 2,000 words)
- Health and safety standards
- Injury prevention
- Illness management
- Nutrition and meal planning
VIII. Child Care Policies and Regulations (approx. 1,500 words)
- Licensing and accreditation
- Staff qualifications and training
- Child-staff ratios
- Program standards
IX. Conclusion (approx. 1,000 words)
- Recap of key points
- Importance of quality child care
- Future directions in child care
Introduction
Child care is a vital component of modern society, providing young children with a safe, nurturing environment while their parents or guardians are at work or pursuing other responsibilities. Quality child care is essential for children's cognitive, social-emotional, physical, and language development. It also plays a critical role in preparing them for formal education and lifelong learning.
The importance of child care cannot be overstated. With more women participating in the workforce and single-parent households on the rise, child care has become a necessity for many families. Moreover, research has shown that high-quality child care is linked to better academic achievement, social skills, and emotional well-being.
Types of Child Care
Child care comes in various forms, each catering to different needs, ages, and preferences. Understanding the types of child care is essential for parents, caregivers, and educators to make informed decisions. Let's explore the most common types:
1. Center-Based Care: These are dedicated facilities that provide care and education to children in a group setting. They often have structured programs, qualified staff, and age-appropriate activities.
2. Home-Based Care: This type of care takes place in the child's own home or the caregiver's home. It offers a more personalized and flexible environment, often with smaller child-to-adult ratios.
3. Family Child Care: A variation of home-based care, where the caregiver provides care for multiple children in their own home.
4. In-Home Care: One-on-one care provided in the child's own home, often by a nanny or au pair.
5. Nanny Care: A dedicated caregiver who provides individualized care for a child or children in their own home.
6. Group Child Care: A small group of children, often from multiple families, cared for together in a home or center.
7. Drop-In Centers: Flexible, short-term care for children, usually on a hourly or daily basis.
8. Parent-Child Playgroups: Informal gatherings of parents and children, focusing on socialization and play-based learning.
Each type of child care has its unique advantages and disadvantages. Some prioritize socialization, while others focus on personalized attention. When choosing a child care option, consider factors like cost, location, and the child's individual needs.
Benefits of Child Care
Quality child care provides numerous benefits for young children, their families, and society as a whole. Some of the most significant advantages include:
1. Cognitive Development: Child care stimulates early learning, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
2. Social-Emotional Development: Child care helps children develop essential life skills like communication, empathy, and self-awareness.
3. Physical Development: Child care promotes healthy habits, gross and fine motor skills, and overall physical well-being.
4. Language and Literacy Skills: Child care exposes children to diverse language experiences, laying the foundation for future reading and writing abilities.
5. Preparation for School: Child care eases the transition to formal education, helping children adapt to structured environments and academic expectations.
6. Parental Support: Child care enables parents to pursue education, career goals, or other responsibilities, knowing their children are safe and supported.
7. Socialization: Child care provides opportunities for children to interact with peers, make friends, and develop essential social skills.
8. Early Intervention: Child care professionals may identify potential developmental delays or special needs, allowing for early intervention and support.
9. Community Building: Child care centers and programs often serve as hubs for family engagement, community resources, and social connections.
10. Economic Benefits: Child care contributes to workforce productivity, employer satisfaction, and overall economic growth.
By understanding the benefits of child care, we can better appreciate the critical role it plays in supporting young children's development, families' well-being, and society's prosperity.
Child Care Settings
Child care takes place in various settings, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and considerations. Let's explore the most common child care settings:
1. Child Care Centers: Dedicated facilities that provide care and education to children in a group setting.
2. Home-Based Settings: Care provided in the child's own home or the caregiver's home.
3. Group Child Care Homes: A small group of children cared for together in a home.
4. Drop-In Centers: Flexible, short-term care for children, usually on an hourly or daily basis.
5. Parent-Child Playgroups: Informal gatherings of parents and children, focusing on socialization and play-based learning.
6. School-Based Care: Care provided before or after school hours, often on school premises.
7. Community-Based Care: Care provided in community centers, churches, or other public spaces.
8. Corporate Child Care: On-site care provided by employers for their employees' children.
9. Military Child Care: Care provided for military families, often on bases or through subsidized programs.
10. Temporary Care: Short-term care for children during special events, conferences, or emergencies.
When choosing a child care setting, consider factors like location, cost, staffing, curriculum, and the child's individual needs.
Child Care Providers
Child care providers are the backbone of the child care system, playing a vital role in shaping young minds and supporting families. Let's explore the different types of child care providers:
1. Child Care Center Staff: Teachers, assistants, and directors who work in child care centers.
2. Family Child Care Providers: Caregivers who provide care in their own homes for multiple children.
3. In-Home Caregivers: Nannies, au pairs, and other caregivers who provide one-on-one care in the child's own home.
4. Group Child Care Home Providers: Caregivers who provide care for a small group of children in their own home.
5. Drop-In Center Staff: Caregivers who provide short-term care for children on an hourly or daily basis.
6. Parent-Child Playgroup Leaders: Facilitators who lead informal gatherings of parents and children.
7. School-Based Care Staff: Caregivers who provide before- or after-school care on school premises.
8. Community-Based Care Providers: Caregivers who provide care in community centers, churches, or other public spaces.
9. Corporate Child Care Staff: Caregivers employed by companies to provide on-site care for employees' children.
10. Military Child Care Providers: Caregivers who provide care for military families, often on bases or through subsidized programs.
Child care providers should possess certain qualities, such as:
- Patience
- Creativity
- Flexibility
- Communication skills
- Ability to build trust
- Knowledge of child development
- First aid and safety training
Child Development and Child Care
Child development and child care are intimately connected. Understanding how children grow and develop is essential for providing high-quality care. Let's explore the stages of child development and their implications for child care:
Infancy (0-12 months):
- Physical development: Lying, sitting, crawling, walking
- Cognitive development: Recognizing faces, objects, and sounds
- Language and literacy: Cooing, babbling, first words
- Social-emotional development: Trust, attachment, smiling
Toddlerhood (1-3 years):
- Physical development: Walking, running, climbing, balance
- Cognitive development: Problem-solving, exploration, memory
- Language and literacy: Vocabulary expansion, simple sentences
- Social-emotional development: Independence, tantrums, empathy
Preschool age (3-5 years):
- Physical development: Gross and fine motor skills, coordination
- Cognitive development: Curiosity, questioning, learning concepts
- Language and literacy: Complex sentences, storytelling
- Social-emotional development: Cooperation, friendship, self-awareness
School age (5-12 years):
- Physical development: Refining motor skills, sports, and games
- Cognitive development: Formal education, critical thinking
- Language and literacy: Reading, writing, communication
- Social-emotional development: Social skills, responsibility, self-esteem
Child care providers should tailor their care and activities to the unique needs and stages of development. This includes:
- Creating a nurturing environment
- Encouraging exploration and learning
- Supporting language and literacy development
- Fostering social-emotional growth
- Promoting physical development through play and activity
By understanding child development and adapting child care accordingly, providers can play a vital role in supporting young children's growth and laying the foundation for future success.
Safety and Health in Child Care
Ensuring the safety and health of children in child care settings is paramount. Providers must be vigilant and proactive in preventing accidents, injuries, and illnesses. Let's explore key aspects of safety and health in child care:
1. Physical Environment:
- Safe furniture and equipment
- Secure storage of hazardous materials
- Regular cleaning and disinfection
- Access to first aid kits
1. Supervision and Monitoring:
- Adequate staff-to-child ratios
- Continuous visual and auditory supervision
- Regular head counts and attendance tracking
1. Health and Hygiene:
- Handwashing and sanitizing
- Proper diaper changing and disposal
- Management of medications and allergies
- Exclusion policies for sick children
1. Emergency Preparedness:
- Fire evacuation plans
- First aid training for staff
- Natural disaster preparedness
- Emergency contact information
1. Nutrition and Food Safety:
- Healthy meal planning and preparation
- Safe food handling and storage
- Allergy awareness and accommodation
1. Mental Health and Well-being:
- Recognizing signs of stress and trauma
- Promoting social-emotional development
- Supporting children with special needs
1. Staff Training and Qualifications:
- First aid and CPR certification
- Child development and education courses
- Background checks and clearance
By prioritizing safety and health, child care providers can create a secure and nurturing environment for children to thrive.
Child Care Policies and Regulations
Child care policies and regulations are essential for ensuring the quality and safety of child care services. These policies and regulations vary by country, state, or region, but generally cover:
1. Licensing and Accreditation:
- Requirements for child care centers and home-based care
- Standards for staffing, facilities, and programs
- Accreditation processes and quality improvement
1. Staff Qualifications and Training:
- Education and experience requirements for staff
- Training in child development, first aid, and safety
- Staff-to-child ratios and supervision
1. Health and Safety:
- Immunization and health checks for children and staff
- Management of medications and allergies
- Emergency procedures and first aid
1. Program and Curriculum:
- Age-appropriate activities and learning goals
- Curriculum standards and assessment
- Diversity and inclusion policies
1. Parental Involvement and Communication:
- Parent-teacher conferences and progress reports
- Daily reports and communication logs
- Parenting resources and support
1. Enrollment and Admission:
- Age and eligibility requirements
- Enrollment procedures and waitlists
- Admission policies and priorities
1. Fees and Payments:
- Tuition rates and payment schedules
- Late payment fees and policies
- Financial assistance and subsidies
1. Compliance and Monitoring:
- Regular inspections and monitoring
- Compliance with regulations and standards
- Enforcement and penalties for non-compliance
By understanding and following child care policies and regulations, providers can ensure a high-quality and safe environment for children to grow and develop.
Conclusion
In conclusion, child care is a vital component of modern society, providing young children with a safe, nurturing environment while their parents or guardians are at work or pursuing other responsibilities. Quality child care is essential for children's cognitive, social-emotional, physical, and language development. This comprehensive guide has covered various aspects of child care, including types of care, benefits, settings, providers, child development, safety and health, policies and regulations, and conclusion.
By understanding the intricacies of child care, we can appreciate the significant impact it has on children's lives and society as a whole. It is crucial for parents, caregivers, and policymakers to work together to ensure access to high-quality child care for all families.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue researching and improving child care practices, addressing the needs of diverse families, and advocating for policies that support the well-being of children and their caregivers.
By doing so, we can create a brighter future for generations to come, where every child has the opportunity to thrive and reach their full potential.
This concludes our comprehensive guide to child care. I hope you found it informative and helpful. If you have any further questions or need additional clarification, please don't hesitate to ask.
1 note
·
View note