#ada compliance for schools
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Inclusive Digital Experience
ADA Site Compliance creates an inclusive digital experience for schools, ensuring all students can engage with educational content regardless of their abilities!
#ada compliance for schools#digital accessibility in education#u.s. department of justice#ada title ii#world wide web consortium (w3c)#technical accessibility standards#accessibility features#accessible digital content#accessibility consultants#digital content creation#ada title ii 504 compliance#wcag 2.1 standards#ada compliance deadline 2027#universal design in education#school website#inclusive digital experience#assistive technologies#accessible digital content creation#website accessibility solutions#ADA site compliance#ADASiteCompliance#adasitecompliance.com
0 notes
Text
Schools don't have to overturn ADA compliance based on White House central government DEI edicts.
That isn't the American way things work, but people elected to school boards may not be familiar with Schoolhouse Rock.
My letter to school board members:
The Trump executive orders can't legally change any law regarding civil rights and nothing issued from the White House requires any changes to school or district policies or practices. These confusing, irrational, and rudely worded orders are however probably causing a lot of stress for parents and families, and probably the kids too, and that's wrong. Schools should NOT be places with toxic atmospheres that traumatize kids, that should be obvious. You have my support in our community to protect our schools so they are a welcoming place for all students and everyone has safe access to education with all rights honored.
Please feel free to copy or repurpose the contents of my letter.
The wording of the response I got from the president of the school board makes it clear that they do actually believe these "anti-DEI" edicts from the White House can overturn, for example, Section 504 law in the schools.
Ty Holmes in an email to Chloe Humbert Feb 2, 2025, 12:26 PM: "Regarding DEI and recent executive orders, we recognize that these matters are still unfolding at the federal level. At this time, I do not believe there is an immediate impact on our district. However, as clarity emerges through the legal and governmental process, we will continue to navigate any changes with thoughtfulness and a focus on our students' and staff members well-being."
What are they even saying? This is pretty scary that our local Scranton School District has a school board director that seems to be anticipating Trump putting the stops on Section 504, and who knows what else. And what's this about the staff member well-being I have to wonder. This response raises far more questions than answers. It seriously undermines my trust in the ability of the Scranton School Board to adhere to actual laws, and not just go along with whatever comes out of the "central government" to do targeted harm.
ACLU - ReNika Moore, January 24, 2025 The Supreme Court’s decision in Students for Fair Admissions, Inc. v. Harvard left colleges and universities with several pathways to advance educational equity. The decision had no bearing on K-12 education, where schools must continue to identify and address barriers to equitable learning environments. At a minimum, schools are required to comply with federal and state civil rights laws that ensure educational opportunities are provided on an equal basis. This means reviewing policies and practices to ensure they don’t unnecessarily limit opportunities based on race or other protected characteristics. Schools must also work to foster a climate where all students can access and thrive in their educational pursuits. Now, more than ever, educational institutions must resist intimidation and reaffirm their commitment to identifying and removing barriers to equal opportunity. Programs labeled as DEIA encompass a broad range of lawful initiatives that create fairer workplaces and schools. The executive orders attempt to conflate these lawful efforts with discrimination, weaponizing enforcement to bully institutions into abandoning critical programs and taking steps to try to eliminate protections against discrimination by government contractors. However, no court has declared DEIA efforts inherently illegal, and President Trump cannot override decades of legal precedent.
If you think that Trump's central government discriminatory chaos edicts aren't going to affect your blue enclaves because they're not legal, I suggest you think again.
Scranton is a blue city in a blue county in northeastern Pennsylvania, with a Dem governor in PA, and local Dem reps in the state government and a mayor who worked on Dem political campaigns including the Obama campaign and worked in the Obama administration. And Ty Holmes is the first Black Scranton School District School Board Director.
More info on the Scranton School Director:
OPINION: Chris Kelly Opinion: Want a Scranton School Board seat? Take the DeNaples challenge Chris Kelly, The Times-Tribune, Scranton, Pa. Wed, April 28, 2021 at 8:17 AM EDT "I expected it, but it's sad because you don't get to serve 25 years if you have questionable morals," Holmes told me in a telephone interview on Tuesday. "If people don't take that into consideration because of who I'm married to or what their perception of someone is that automatically I'm a corrupt person, that's ridiculous." Holmes' wife Margie — a teacher at Bancroft Elementary — is Louis DeNaples' niece, which makes "Uncle Louie" Holmes' actual uncle — by marriage. To some, this connection is disqualifying. These critics affix "the Scarlet D" to Holmes and dismiss him outright as the latest in a decadeslong line of corrupt flunkies DeNaples has installed in positions of power to do his bidding at public expense.
#politics#government#pennsylvania#504#section 504#ADA#public schools#public education#school boards#Scranton#Lackawanna County#local politics#trump administration#DEI#DEIA#ada compliance#Scranton School District#obama administration#Ty Holmes#Paige Cognetti#supreme court#schoolhouse rock
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Complete Guide to DOJ’s Title II Updates for Educational Institutions

The Department of Justice's Title II digital accessibility mandate is reshaping how educational institutions approach their online presence. With the first compliance deadline approaching in 2026, universities and public schools must act now to ensure their digital resources are accessible to all.
The New Digital Accessibility Landscape
Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act has expanded beyond physical accessibility to encompass digital spaces. This update affects all state and local government entities, including:
- Public schools and universities
- Community colleges
- Public libraries
- State and local courts
- Public healthcare facilities
The mandate requires these institutions to make their websites, applications, and electronic content accessible according to WCAG 2.1 Level AA standards. Non-compliance can result in lawsuits, loss of federal funding, and reputational damage.
Key Requirements for Educational Institutions
The DOJ's update focuses on four core principles of digital accessibility:
1. Perceivable Content: All digital content must be available to users regardless of their abilities, requiring alternatives like image descriptions and video captions.
2. Operable Navigation: Websites must be fully navigable via keyboard and provide clear pathways for all users.
3. Understandable Content: Information must be presented clearly and consistently across all platforms.
4. Robust Compatibility: Digital resources must work seamlessly with various assistive technologies.
Important Exceptions to Note
While compliance is crucial, certain exceptions exist:
- Archived content not actively used
- Pre-existing documents non-essential to current operations
- Third-party content without formal agreements
Action Plan for Compliance
To meet these requirements effectively, institutions should:
1. Start with a comprehensive accessibility audit
2. Implement WCAG 2.1 standards across all digital platforms
3. Ensure all documents are accessible
4. Train staff on accessibility best practices
5. Plan for compliance deadlines (April 2026 for large entities, April 2027 for smaller ones)
Moving Forward
Digital accessibility isn't just about compliance - it's about creating an inclusive educational environment that serves all students effectively. With proper planning and implementation, institutions can transform this mandate into an opportunity for innovation in education.
Our team at Documenta11y specializes in helping educational institutions navigate these requirements and implement sustainable accessibility solutions. Start your accessibility journey today to ensure your institution is ready for the future of inclusive education.Need expert guidance on digital accessibility compliance? Contact Documenta11y for a consultation on making your educational resources accessible to all.
#Accessibility Audit for Schools#Accessibility in Learning Systems#Accessible Education#Accessible Websites for Schools#ADA Title II Requirements#Compliance Deadlines for Title II#Digital Accessibility for Schools#Digital Campus Compliance#Digital Inclusion in Education#Document accessibility solutions#Documenta11y#DOJ Digital Accessibility#Educational Accessibility Guidelines#Higher Education Accessibility#Inclusive Digital Learning#Inclusive Education Tools#K-12 Accessibility Compliance#Public University Accessibility#Title II Compliance#WCAG 2.1 Standards
0 notes
Text
Ableism in “A Court of Thorns and Roses”
Since I’ve been seeing a ton of posts about how Nesta is being ableist toward her father and his disability, let’s discuss it.
So what is ableism?
“Ableism is the discrimination of and social prejudice against people with disabilities based on the belief that typical abilities are superior. At its heart, ableism is rooted in the assumption that disabled people require ‘fixing’ and defines people by their disability.”
What does ableism look like?
Ableism can take many forms including:
Lack of compliance with disability rights laws like the ADA
Segregating students with disabilities into separate schools
The use of restraint or seclusion as a means of controlling students with disabilities
Segregating adults and children with disabilities in institutions
Failing to incorporate accessibility into building design plans
Buildings without braille on signs, elevator buttons, etc.
Building inaccessible websites
The assumption that people with disabilities want or need to be ‘fixed’
Using disability as a punchline, or mocking people with disabilities
Refusing to provide reasonable accommodations
Based on the description of Nesta’s actions and context, she does not fit the specific examples of ableism listed. Here’s why:
Lack of Compliance with Disability Rights Laws: Nesta’s actions do not involve legal issues or non-compliance with disability rights laws.
Segregating Students or Adults with Disabilities: There’s no indication that Nesta is involved in segregating individuals with disabilities into separate schools or institutions.
Use of Restraint or Seclusion: Nesta’s actions do not involve using restraint or seclusion to control someone with a disability.
Failing to Incorporate Accessibility into Building Design: There’s no mention of issues related to building design or accessibility in your description.
Buildings Without Braille or Inaccessible Websites: Nesta’s actions do not relate to the accessibility of physical spaces or websites.
Assumption that Disabilities Need Fixing: Nesta’s actions are driven by her frustration with her father’s neglect, not an assumption that his disability needs fixing.
Using Disability as a Punchline or Mocking: There is no indication that Nesta is mocking or using her father’s disability as a punchline.
Refusing to Provide Reasonable Accommodations: Nesta’s actions are not about refusing accommodations but rather about expressing frustration with her father’s inaction.
But what about ‘everyday’ or minor ableism? What does that look like?
Choosing an inaccessible venue for a meeting or event, therefore excluding some participants
Using someone else’s mobility device as a hand or foot rest
Framing disability as either tragic or inspirational in news stories, movies, and other popular forms of media
Casting a non-disabled actor to play a disabled character in a play, movie, TV show, or commercial
Making a movie that doesn’t have audio description or closed captioning
Using the accessible bathroom stall when you are able to use the non-accessible stall without pain or risk of injury
Wearing scented products in a scent-free environment
Talking to a person with a disability like they are a child, talking about them instead of directly to them, or speaking for them
Asking invasive questions about the medical history or personal life of someone with a disability
Assuming people have to have a visible disability to actually be disabled
Questioning if someone is ‘actually’ disabled, or ‘how much’ they are disabled
Asking, “How did you become disabled?”
Nesta’s actions do not fit most of these examples of ableism based on the context provided. Here’s a breakdown:
Choosing an Inaccessible Venue: Nesta’s actions do not involve selecting venues or events, so this does not apply.
Using Someone Else’s Mobility Device: There’s no mention of Nesta using or misusing her father’s mobility device in this way.
Framing Disability as Tragic or Inspirational: Nesta’s actions are not about framing disability in a media context; they are about her personal frustration and family dynamics.
Casting a Non-Disabled Actor: This example pertains to media and casting, which does not relate to Nesta’s situation.
Movie Without Audio Description or Closed Captioning: This is related to media accessibility, not relevant to Nesta’s scenario.
Using the Accessible Bathroom Stall: Nesta’s actions do not involve the use of accessible facilities inappropriately.
Wearing Scented Products in a Scent-Free Environment: This is unrelated to Nesta’s situation.
Talking to a Person with a Disability Like a Child: Nesta’s actions do not involve speaking to her father in a condescending manner.
Asking Invasive Questions: There’s no indication that Nesta is asking invasive questions about her father’s disability.
Assuming People Have to Have a Visible Disability: Nesta’s actions are based on her father’s behavior and neglect, not assumptions about visible disabilities.
Questioning if Someone is ‘Actually’ Disabled: Nesta’s actions do not involve questioning the legitimacy of her father’s disability.
Asking, “How Did You Become Disabled?”: This question is not part of Nesta’s interaction with her father.
Even considering the description provided, Nesta’s frustration and actions stem from her father’s neglect and inaction, not from a belief that his disability makes him inferior or requires fixing. Her actions are driven by the burden placed on her family and his refusal to contribute, rather than discrimination or social prejudice based on his disability. Therefore, her behavior is more about addressing family dynamics and neglect rather than ableism.
You can find all the information and examples listed at: https://www.accessliving.org/newsroom/blog/ableism-101/#:~:text=Ableism%20is%20the%20discrimination%20of,defines%20people%20by%20their%20disability.
#anti acotar#anti acosf#anti inner circle#anti feysand#anti rhysand#anti azriel#anti cassian#anti morrigan#anti amren#anti nessian#pro nesta#nesta archeron deserves better#papa archeron#what is ableism
24 notes
·
View notes
Note
Do you have any favorite headcanon about cybertronians culture or "biology" you like or would want to use in your writing?
HMMMMMMMMM Interesting questions. Sorry for the ramble, I hope it makes sense but it really got me thinking. This became less headcanons and more just a rant fdkjvbefjvskndjnfjfdknvkjasvfn
As far as culture, I like leaning into what's been established a little.
Example: I like the fraught nature of Velocitron prioritizing speed and creating a system that revolves around it. I'm pretty sure the extent of it discussed is political, but I think it would also stem culturally (and maybe it is in the comics but I haven't gotten there yet).
Music having faster rhythms and beats, childhood games centered around racing, courting rituals based on showing off your speed or racing together.
And on the flip side, Velocitron does devalue slower, bulkier bots which creates this caste-type system. I like the idea of those mechs having their own culture, which is stemmed from their physicality but also their political situation of being outcasted.
Like, since Velocitron is all about who is the fastest, I think an interesting cultural attitude is created where you are constantly trying to be better than others, but if you are already limited being able to go fast, proving you are better isn't as important when society tells you differently. It shifts the value of the Importance of Self to the Importance of Community. That in itself creates a shift in culture.
Not to mention the ADA Compliance angle of there are areas of Velocitron that just have structures that allow for bigger, slower bots. I think I wrote something along the lines of Breakdown complaining that going to a convention medic on Velocitron as a bigger bot often ends up with misdiagnosed problems because they are so focused on the idea that you must be fast and smaller that they offer reformatting without looking at what the root of the problem is. (I know many fat people have this issue of doctors suggesting "losing weight" when addressing medical concerns without digging in deeper which is bullshit but aside from the point).
A SIDE THOUGHT: I would love to read (or maybe write???) Cybertronian folk stories/myths. I think that would be a fun avenue of culture to explore. It would be a way to delve into multiple aspects of culture and each city and colony would naturally have different ones or even rival ones. For example, taking the Velocitron culture into consideration, there could be conflicting folk stories alla a tortoise and hare situation. Speedy, conventional mechs would have a story framed around the "hare" being the winner where a slowly, bulkier mechs would have it framed around the "tortoise" being the winner. Idk i think that is so cool and interesting and gahhh.
BIOLOGY THOUGH x---x science was my worst subject in school already and i struggle with anything related to it. Writing such topics is a fun challenge but very difficult for me to broach, especially when we add mechanical components into it. I am writing a fic with the basis of scavenging the parts of deceased/offlined mechs and using them to rebuild another.
#IDK IF THIS IS WHAT YOU HAD IN MIND BUT I SPEND LIKE AN HOUR ON HOLD SPINNING THIS AROUND IN MY BRAIN#anonymous#asks#transformers#cybertronian culture#id love to hear other people's thoughts and opinions because the possibilities are really endless#there are so many aspects of culture to go down#i could talk about this forever#can you tell i used to be a history/literature major?
51 notes
·
View notes
Note
My job now wants to give us bathroom passes and has a hall monitor to check passes if you are allowed to go to the bathroom
I’m 27 I’m not in grade school…thinking I should quit
There's gonna be some issues with both OSHA and ADA compliance there I think, legally they can do it within reason but it can open the door to all kinds of lawsuits if they do.
Thanks to the internet and those blessed meme things, many employees live by the meme-philosophy: Boss makes a dollar, I make a dime, that's why I poop on company time. However, under the law, employers are legally allowed to restrict bathroom breaks, at least, within reason.
Generally, reasonable restrictions will not prohibit employees from using the restroom when the need arises. However, in production, or client facing industries, employers may require an employee to wait for a co-worker to relieve their position before taking a bathroom break. Additionally, if an employee has a medical condition that necessitates frequent bathroom breaks, employers may need to be flexible as frequent bathroom breaks is an easily achievable reasonable accommodation in nearly all situations.
Giving Bathroom Restrictions the Business
While there is no federal law that specifies the number or length of bathroom breaks an employer must provide, restricting bathroom use unreasonably can lead to lawsuits and even all-out labor disputes with picketers and media. OSHA does provide rules that require employers to provide employee restrooms, and allow employees access to those restrooms.
Generally, unreasonable restrictions on bathroom usage will be viewed as a violation of an employee's rights because it subjects employees to detrimental effects to their health, including urinary tract and bladder infections, kidney stones, and other ailments. Furthermore, depending on a company's policy, restrictions on the length of bathroom usage may also have a discriminatory impact on women, or aging individuals, who sometimes need a little extra time in the restroom.
What's Reasonable?
What is considered reasonable will vary from job to job, and likely depend on state law as well. If an employee's bathroom usage interferes with their ability to do their job, or with the production line, or client services, then the law may not protect that employee.
Alternatively, if an employee needs to use the restroom, an employer should not have a policy that denies that employee the ability to do so. Even where an employee has an essential job, such as on a production line, an employer may be required to provide prompt and temporary relief of duties for the employee.
Does an Employer Have to Pay for Bathroom Breaks?
Generally, under the Fair Labor Standards Act, short breaks between 5 to 20 minutes are considered mutually beneficial for employer and employee, and as such, should be paid. However, if the breaks extend beyond 20 minutes, an employer can refuse to pay for that time.
____________________
This will be location specific for you I think.
An employer does not have to pay you for a break during which you are completely relieved of your job duties. Your employer can require you to stay on the business premises during your break. Only the following breaks are required:
Minors younger than 16 must be given a 30-minute break if they are employed five hours or more in a day.
All employees must be allowed toilet breaks when needed.
A union contract may require breaks and those requirements are enforced by the union.
Certain other limited categories of workers, such as airline pilots, may be entitled to mandatory breaks under applicable regulations. Check with the appropriate regulatory agency.
_________________________
Half dozen other sites I've looked at and even the state labor website say 'when needed' so they can't restrict bathroom breaks, not unreasonably at least.
Can't give you little bathroom pass cards at the start of the week and that's as many times as you can pee or anything like that at least.
19 notes
·
View notes
Note
Thoughts?
https://www.tumblr.com/immaturityofthomasastruc/726947568371826688/does-anyone-else-feel-just-a-bit-uncomfortable?source=share
I mean. Yeah. It's.
Let's look at the 'disabled rep' within Canon.
We have Tomoe, who is blind but..... only in character description. She seems to be able to see just fine? Like Gabriel shows her his Cataclysmed arm and she knows what he's talking about instead of going 'bitch I'm blind?'. Also she's a major villain.
We have Gabriel and Nathalie count. Gabriel in Season 5 is getting fucked up by Cataclysm and it effects his ability to complete tasks, so yes it counts as disabled. Nathalie has been fucked up by the Peacock for three seasons now, in ways that her health is impacting her ability by making her weak and faint often. There's the point in Season 4/5 where she can't even walk unaided. Absolutely disabled. Also a pair of villains.
There's Lila who claims disabilities, but they're all fake. She's just trying to get attention. Also another Villain. But she's a liar who's faking so it's /good/ that Marinette screams at her to try and prove she's not actually disabled, right?
Then we have Rose, our only disabled Hero character. Whose disability is an incredibly vague illness. But she's the 'good' disabled where she's functional 95% of the time and she's soooo nice about everything and she doesn't want help at all when she's having a hard time because it's such an inconvenience to others isn't it?
Also not a character, but it's canon that the school isn't actually following the most basic of compliance for whatever the French ADA is called because there's no wheelchair access to even get into the fucking place they literally don't allow handicapped people into the school. This isn't just 'they forgot to model a wheelchair ramp for the school' this is something that is said directly in Canon.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text

The ADA is 33 years old today.
(Americans with Disabilities Act)
Cities have not complied.
Venues have not complied.
Stores have not complied.
Schools have not complied.
And disabled people usually can't afford to sue them into compliance with federal law.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
I put in my ADA, I had an ADA cause I had ADHD, my only accommodation for all of grad school and most of undergrad was that the professors had to give me actual descriptions of the project and when they were due at the start of the term. I had meetings with professors who had inadequate syllabi to get this information and at least one of them still didn't give it to me. That man no longer works for that university because we all complained about him and I referenced my fucking accommodations which is a mandatory compliance.
Sometimes college professors like to hop on my posts lamenting the sorry state of syllabi these days and joke about how they haven't thought that far ahead in the course themselves, or talk about how they struggle to complete a schedule for their students.
With all due respect, that's your job. If you can't do your job, you should have a different job. If you need help, ask your colleagues or your department chair or *someone* because I know that professors aren't given a hell of a lot of education on how to educate, so you probably *need* help.
But every single time I make one of those posts I get anywhere from ten to thirty messages, replies, reblogs, and asks say "oh man, that's exactly why I had to drop out of school; I couldn't keep up with the assignments because I didn't know when they were due until the week they were due."
I have been a college student in three separate decades, and "not having a schedule of assignments in the syllabus" is new to my experience. That shit didn't fly in the 2000s or 2010s and I think it likely has to do with professors being overly reliant on apps.
AT A MINIMUM your syllabus should have:
Contact information (including preferred method of contact) for the professor
Office Hours
Grading Policy
Assignment schedule.
Your assignment schedule doesn't necessarily need to have the exact page numbers of every reading or a full assignment sheet for each project, but it should have things like:
December 1st - Major Project 3 second draft due December 9th - Quiz 10 December 12th - Major Project 3 final draft due December 15th - Final Exam
If you end up presenting a more thorough schedule with readings and homework later, that is acceptable to present a week or two into the semester but it is absolutely insane to me that students these days don't know what homework they're going to have to get done over Thanksgiving break during the first couple weeks of class.
If I had three professors at once who didn't give me a schedule, how on earth would I know if I was going to have to read three chapters of a novel, take a midterm and turn in two stats homework assignments, and complete a history research paper the same week that I'm planning to travel to see family? If I'm aware of this from the beginning of the semester I can make sure not to pick up extra shifts, or I can plan to leave a day later to accommodate the midterm, or I can start working on the paper early to complete it before the due date but if I don't know what's going to be due when, I'm going to have a big problem.
If you don't give your students a schedule you are communicating that you don't care about their schedule, and that you think it's their responsibility to contort their life (and their job, and their other classes) around your class, and honestly my advice to students in that situation is "drop in the first week and pick up another class". That's actually part of why I recommend signing up for one more class than you can really manage - if you get a professor whose class looks like it's going to be a disaster because they don't have a schedule, you can bail before the withdrawal period and get a refund for the class.
I'm only in one class this semester but the professor's response has fully dropped me into "Fuck it, I guess I'll fail" mode and I don't even know if I can pull myself out of my current D grade because I don't know how many assignments we have left in the semester.
This is a shitty way to run a class. If you can't do better than this, you shouldn't be running a class.
#I don't really have a lot to add I'm just still bitter about it.#My last year my last quarter actually of undergrad I wrote the term paper on the structure of#syllabi and the authoritative positioning it upholds#i used to practice creating syllabi because i wanted to be a professor too but that's a separate thing
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
How ADA Signs in Baltimore Build Community and Compliance

Introduction
Baltimore is a city built on respect, resilience, and diversity. Ensuring everyone can navigate businesses and public buildings safely is fundamental. ADA signs in Baltimore are at the heart of this mission—making spaces welcoming and usable for all.
What Makes a Sign “ADA Compliant”?
ADA compliant signs must meet specific U.S. federal standards in design, placement, and construction. In Baltimore, these signs are more common than people realize—from restroom doors in Fells Point cafes to directional signs in Hopkins hospitals.
They include:
Raised, tactile text for the visually impaired
Braille dots beneath wording
High-contrast colors with non-glare backgrounds
Compliance is non-negotiable for facilities open to the public—and in many cases, even for employee-only areas.
Where Are ADA Signs Required in Baltimore?
The Americans with Disabilities Act requires compliant signage in many locations:
Entrances and exits
Restrooms
Elevators and stairwells
Accessible parking spots and loading areas
Emergency evacuation routes
In Baltimore, most office buildings, schools, hospitals, government offices, and retail locations must display ADA signs at key points to help everyone navigate safely.
Designing ADA Signs for Baltimore Spaces
There’s a myth that ADA signs must be bland or generic. In fact, Baltimore signmakers offer creative options that reflect your brand while meeting every ADA standard:
Incorporate logos and unique fonts that remain legible
Use branded colors, as long as contrast and readability guidelines are observed
Select from a range of materials: brushed metal, acrylic, high-density plastics
Add custom graphics, wayfinding maps, and more
Why Baltimore Businesses Invest in ADA Signs
Legal Compliance: Avoid lawsuits and expensive retrofits or fines
Ethical Obligation: Serve the entire community—including seniors, people with disabilities, and families with children
Positive Business Image: Customers prefer—and revisit—businesses they can comfortably access
The Process of Getting ADA Signs in Baltimore
Site Survey: A professional sign company will evaluate your property and identify compliance gaps.
Design: Work with designers who blend ADA specs with your branding goals.
Fabrication: Signs are produced using advanced methods (engraving, digital printing, etc.).
Installation: Correct mounting height, angle, and location are crucial for compliance.
Several Baltimore-based sign companies offer consultations, audits, design, and installation, making the process seamless.
Stories from Local Baltimore Businesses
Business owners regularly share how updating ADA signs improved not just compliance but reputation. From small cafes in Hampden to downtown office buildings, adding or upgrading ADA signage brought peace of mind and new customers.
Common ADA Sign Solutions in Baltimore
Braille and tactile room identifiers for hotels, schools, offices
Custom restroom or all-gender restroom signs that respect inclusivity
Accessible parking and pathway signs highlighting routes for wheelchairs and strollers
Updating Your ADA Signage
As ADA regulations evolve, businesses in Baltimore should regularly review their signage. Working with a local vendor who follows updates in federal and Maryland accessibility rules ensures you’re always up to code.
Final Thoughts
Accessible, attractive ADA signs in Baltimore do more than satisfy legal mandates. They build trust, foster community, and say loudly: everyone deserves respect and access. For every detail—from design to installation—partner with local professionals to make your space truly welcoming for all.
0 notes
Text
U.S. Department Of Justice

Public Schools Need A Digital ADA Accessibility Makeover Within 2-3 Years
According to a new federal mandate from the U.S. Department of Justice, public schools must make all digital content accessible to students with disabilities.
The U.S. Department of Justice has issued under Title II of the ADA that stipulates compliance with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) by 2027.
This means schools must ensure that websites, mobile apps, and other digital platforms used for education are usable by students with a wide range of impairments.
The United States Department of Justice has endorsed the WCAG 2.1 to provide clear guidance for ADA compliance for web content and mobile apps.
These guidelines, established by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), are recognized globally and offer a comprehensive framework for creating accessible digital experiences. Although W3C released an updated version of these guidelines in 2023, public schools must adhere to the WCAG 2.1 standards from 2018.
Public schools nationwide face a formidable challenge: ensuring all students can access digital resources by 2027. However, navigating the complexities of digital accessibility can be overwhelming for schools.
Meeting the 2027 deadline for compliance while creating an inclusive online environment requires expertise and precision. At ADA Site Compliance, we simplify the process.
Our team ensures your school’s digital platforms adhere to accessibility standards, preventing legal issues and fostering a welcoming environment for all students. Let us help you create a truly inclusive digital experience.
Schools Face Steep Climb to ADA Compliance
Public educational institutions across the U.S. have two or three years, depending on their size, to ensure their web content and mobile apps meet technical accessibility standards adopted in April under Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Smaller school districts have until April 26, 2027, to achieve compliance, while larger districts exceeding populations of 50,000 have till April 24, 2026, to meet compliance.
Attaining ADA compliance is an uphill battle for many educational institutions.
This requirement has placed significant pressure on school districts, many grappling with limited resources and poor technological expertise.
The standards cover a wide range of accessibility features, including providing alternative text for images, ensuring keyboard navigation, and maintaining adequate color contrast.
That’s why some experts say they should start preparing now. The transition to a fully accessible digital infrastructure is a technical upgrade and comprehensive overhaul of existing systems and practices.
Revamping their digital infrastructure to create inclusive online learning environments necessitates strategic planning, substantial investments, and continuous professional development for staff.
Schools must adopt a phased approach to ensure compliance within the given timeframe. This involves thorough audits of current digital assets, identifying accessibility gaps, and implementing necessary modifications.
These principles are not just technical requirements; they are essential for enhancing the educational experience of students with disabilities and fostering a more equitable learning environment for all.
Accessibility: More Than Just Website Compliance
The shift towards accessibility isn’t solely a technological endeavor for schools. It also demands a cultural change within educational institutions, fostering an environment where inclusivity is a core value.
Professional development opportunities will play a crucial role in this transformation.
Staff must have the knowledge and skills to create and maintain accessible digital content. This includes understanding universal design, becoming proficient with assistive technologies, and staying updated with the latest accessibility standards.
Additionally, schools must allocate budgetary resources to support this initiative. This might include hiring accessibility consultants, investing in accessible technology, and ensuring ongoing maintenance and updates to digital content.
Collaboration with stakeholders, including parents, students, and disability advocacy groups, is essential to address diverse needs and gather feedback on accessibility improvements.
Consequences of non-compliance
The consequence of non-compliance with WCAG is the risk of facing potential legal ramifications with time. The legal fees associated with non-compliance can get expensive, much more than the cost of attaining web compliance.
While the Department of Justice has outlined specific exemptions—such as archival information, legacy papers, content from third parties, social media postings, and password-protected files—it’s important to note that these exceptions are limited and may not apply universally.
Educators must thus thoroughly analyze their digital assets to determine which information falls under these exemptions.
Benefits of accessibility to educational institutions
According to CAST, a leading accessibility organization, this regulatory reform is a significant milestone in the quest for accessibility. By integrating accessibility standards into digital content, educational institutions can offer a more equitable learning environment for students with disabilities.
Furthermore, universal design principles benefit all users by making content easier to understand and navigate. Lindsay Jones, CEO of CAST, underscores that accessibility is not just about compliance; it’s about providing a better user experience for the entire school community.
This emphasis on enhancing user experience is the true driving force behind accessibility.
The Ripple Effect of ADA-Compliance on Student Success
Compliance with ADA Title II 504 is more than just a legal obligation; it’s a commitment to fostering an inclusive and supportive learning environment. Schools that prioritize accessibility adhere to legal standards and are dedicated to educational equity.
This proactive stance can lead to numerous benefits:
Enhanced Student Engagement: Accessible digital content ensures all students can fully participate in educational activities. This inclusivity can lead to higher levels of engagement and academic success.
Improved Academic Outcomes: Studies have shown that when students have access to resources that cater to their individual needs, their academic performance improves. By removing barriers, schools can help all students reach their full potential.
Positive Institutional Reputation: Schools known for their inclusive practices attract a diverse student body and staff. This positive reputation can enhance the institution’s standing in the community and attract more resources and partnerships.
Legal and Financial Safeguards: Proactively addressing accessibility reduces the risk of legal challenges and the associated financial costs. Schools can avoid costly lawsuits and fines by complying with ADA Title II 504.
Equal access for everyone: ADA compliance ensures that students with disabilities have the same access to educational resources as their peers, which is fundamental for their academic success and overall well-being.
Universal design approach: Accessible digital environments benefit all students, as they promote a universal design approach that can accommodate diverse learning needs and preferences.
Digital accessibility extends beyond the classroom: Accessible online learning platforms and resources prepare students for the future, equipping them with the skills to navigate an increasingly digital world.
A Roadmap to ADA Compliance: Nine Essential Steps for Schools
As schools work towards meeting these compliance deadlines, they must also consider the ongoing training and support for educators and staff to use and create accessible digital content.
To effectively comply with ADA Title II 504 within the given timeframe, schools can adopt these nine practical steps:
Conduct Regular Accessibility Audits: Regularly conduct audits of school websites and mobile apps to identify and address accessibility issues. Use both automated tools and manual testing to ensure a thorough evaluation.
Invest in Training: Educate staff about the importance of digital accessibility and provide training on creating and maintaining accessible content. This includes understanding how to use accessibility features in various software and platforms.
Utilize Accessible Technology: Integrate and support using assistive technologies that can aid students with disabilities. Ensure website compatibility with screen readers, voice recognition software, and other assistive tools.
Engage with the Community: Involve students, parents, and community members in the accessibility planning process. Their feedback can provide valuable insights and ensure that the solutions implemented meet the needs of all users.
Incorporate Accessibility in Procurement: When acquiring new digital tools or platforms, ensure they meet WCAG 2.1 standards. Include accessibility requirements in procurement processes to avoid future compliance issues.
Develop an Accessibility Plan: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps to achieve compliance. This plan should include timelines, responsible parties, and measurable goals.
Policy Development: Develop and enforce policies prioritizing accessibility in all digital content creation and management processes. Make accessibility a core component of the school’s digital strategy.
Fostering collaborations: Collaborating with students, parents, and advocacy groups can provide valuable insights and help identify areas that need attention.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates: Accessibility is not a one-time effort. Continuously monitor digital content for compliance and stay updated with the latest accessibility standards and best practices. Implement regular updates to address new accessibility challenges as they arise.
By following these nine steps, public schools can meet the requirements of ADA Title II 504 and also create a more inclusive and supportive learning environment for all students.
As technology evolves, so should our commitment to accessibility, ensuring no student is left behind.
Conclusion
The journey toward compliance with ADA Title II 504 is challenging but an opportunity for schools to enhance their digital offerings and ensure that all students, regardless of their abilities, have equitable access to educational resources.
By embracing this mandate, schools can foster a more inclusive learning environment that supports the diverse needs of their student population. However, meeting the 2027 deadline for compliance while creating an inclusive online environment requires expertise and precision.
At ADA Site Compliance, we simplify the process. Our team ensures your school’s digital platforms adhere to accessibility standards, preventing legal issues and fostering a welcoming environment for all students. Let us help you create a truly inclusive digital experience!
#ada compliance for schools#digital accessibility in education#u.s. department of justice#ada title ii#world wide web consortium (w3c)#technical accessibility standards#accessibility features#accessible digital content#accessibility consultants#digital content creation#ada title ii 504 compliance#wcag 2.1 standards#ada compliance deadline 2027#universal design in education#school website#inclusive digital experience#assistive technologies#accessible digital content creation#website accessibility solutions#ADA site compliance#ADASiteCompliance#adasitecompliance.com
0 notes
Text
Modern ADA Signs in Dallas for Public & Private Spaces
Create an inclusive environment with ADA signs in Dallas tailored to your space. At SpeedPro Addison, we specialize in ADA signage solutions for schools, offices, hospitals, and more. Invest in ADA braille signs in Addison that combine compliance with modern aesthetics. Schedule your order today.
0 notes
Text
Educational Lawyers
Understanding the Role and Importance of Educational Lawyers
Education is often referred to as the great equalizer, a tool that empowers individuals, uplifts communities, and shapes the future of nations. But when disputes, discrimination, or complex legal issues arise within the educational system, it can feel anything but empowering. This is where educational lawyers step in. These legal professionals play a critical role in protecting the rights of students, parents, teachers, administrators, and institutions alike. From special education disputes to Title IX investigations and school discipline hearings, educational lawyers ensure that the principles of fairness, due process, and access to education are upheld.
What Do Educational Lawyers Do?
Educational lawyers handle a broad spectrum of legal matters related to education at every level—from elementary schools to universities. Their work is often categorized into two main areas: student rights and school administration.
When working with students and families, educational lawyers help resolve issues such as discrimination, special education disputes, bullying, school discipline, and access to appropriate educational services. They ensure that schools comply with state and federal education laws, particularly those designed to protect vulnerable populations, such as students with disabilities or those affected by poverty or systemic inequality.
On the administrative side, educational lawyers advise school boards, administrators, and educators on employment law, regulatory compliance, policy development, and risk management. They may also represent institutions in litigation or during investigations brought by state or federal agencies.
Special Education and Disability Rights
One of the most common areas where educational lawyers provide support is in special education law. The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) mandates that public schools provide students with disabilities a free and appropriate public education (FAPE) in the least restrictive environment. However, disagreements often arise between parents and school districts about what services a child needs, how those services should be delivered, or whether a school is in compliance.
Educational lawyers assist families by reviewing Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), attending IEP meetings, advocating for appropriate services, and filing complaints or due process hearings when necessary. They ensure that the school upholds its legal obligations and that the student receives the education they are entitled to under the law.
Discrimination and Civil Rights Violations
Discrimination based on race, color, national origin, sex, disability, or religion is prohibited in educational settings under various federal laws, including Title VI, Title IX, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). When students or employees experience harassment, unequal treatment, or retaliation, educational lawyers can intervene.
For example, under Title IX, students are protected from sex-based discrimination, including sexual harassment or assault. Educational lawyers often help victims navigate complaint procedures, understand their rights, and ensure that institutions follow proper protocols during investigations. Conversely, they may represent individuals accused of violations to ensure due process is followed.
Bullying and Student Discipline
Bullying is a serious issue that can severely affect a student's mental health, academic performance, and overall well-being. While schools have policies in place to prevent and address bullying, there are times when they fail to act appropriately or ignore the issue altogether. Educational lawyers can step in to advocate for the student, demanding corrective measures or even pursuing legal action if the school's inaction violates the student’s rights.
Similarly, when students are suspended, expelled, or otherwise disciplined, educational lawyers ensure that due process is followed. This is especially critical when discipline may disproportionately affect students based on race, disability, or socioeconomic status. Legal intervention can ensure that disciplinary actions are fair, legally justified, and not a barrier to continued education.
Higher Education Legal Issues
In the context of colleges and universities, educational lawyers handle a range of legal matters including academic dismissal, financial aid disputes, campus safety issues, intellectual property, and faculty employment concerns. They also deal with compliance issues related to FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act), which protects the privacy of student records, and Clery Act requirements around campus crime reporting.
When disputes arise between students and institutions—such as allegations of misconduct, grade disputes, or denial of accommodations—educational lawyers help navigate internal grievance processes and represent clients in appeals or legal proceedings if necessary.
Teacher and Employee Rights
Educators and school staff are also protected under employment laws that prohibit discrimination, wrongful termination, harassment, and violations of employment contracts. Educational lawyers work with these professionals to address workplace issues, negotiate employment terms, and represent them in union disputes or administrative hearings.
Teachers may also face accusations related to professional misconduct, licensure issues, or performance reviews. In such cases, having legal representation is crucial to protecting their reputation, certification, and career.
Policy Development and Regulatory Compliance
Educational institutions operate in a heavily regulated environment. Educational lawyers help ensure that schools and districts stay compliant with changing state and federal laws, from curriculum mandates to accessibility requirements. They may review or draft policies, conduct legal audits, and advise on risk mitigation strategies.
This is especially important in today’s climate, where legal challenges often intersect with social issues such as gender identity, political expression, and digital privacy. Having sound legal guidance helps institutions implement policies that are both legally compliant and socially responsible.
Navigating Complex Legal Frameworks
Education law is a multifaceted field that pulls from constitutional law, administrative law, civil rights law, and employment law. Educational lawyers must have a deep understanding of federal and state statutes, court decisions, and regulatory guidelines. For example, understanding the intricacies of the IDEA, Section 504, and the ADA requires not only legal knowledge but also familiarity with educational psychology, behavioral supports, and the workings of school systems.
Their role often involves translating complex legal language into practical strategies for parents, students, or administrators—bridging the gap between policy and practice.
When Legal Help Becomes Essential
There are many situations in which hiring an educational lawyer can make a significant difference in outcomes. Parents of students with disabilities, for example, may not know how to advocate effectively for services, especially when up against a large school district. Students facing suspension or expulsion may not be aware of their rights or the long-term consequences of disciplinary records. Teachers wrongfully terminated or disciplined may feel powerless against the system. Educational lawyers bring clarity, confidence, and legal leverage to these scenarios.
It is also important to understand that educational legal issues don’t always lead to court. Many disputes are resolved through negotiation, mediation, or administrative hearings. Educational lawyers are skilled at choosing the right path—one that preserves relationships when possible and fights for justice when necessary.
Conclusion
Educational lawyers are vital advocates within the educational ecosystem. They ensure that students receive the services they need, institutions comply with the law, and all parties are treated with fairness and dignity. Whether it’s addressing discrimination, supporting students with disabilities, guiding school policies, or defending educators, their work reinforces the values of justice, equity, and accountability in education.
Navigating the world of education can be overwhelming, especially when legal challenges arise. But with the guidance of a knowledgeable educational lawyer, individuals and institutions alike can better understand their rights and responsibilities—and move forward with greater confidence and clarity.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Title IX Attorneys
Understanding the Role of Title IX Attorneys in Education and Civil Rights
Title IX is a pivotal federal law that has transformed the landscape of education in the United States. Originally passed in 1972, Title IX of the Education Amendments prohibits sex-based discrimination in any school or educational program that receives federal funding. While many people associate Title IX primarily with women's athletics, its scope extends far beyond sports, touching on all aspects of educational access, equity, and safety. As schools and universities grapple with complex issues such as sexual harassment, gender identity, and due process rights, Title IX attorneys have become increasingly essential. These legal professionals play a critical role in protecting the rights of students, faculty, and institutions alike.
What Is Title IX and Why Does It Matter?
Title IX is a civil rights law that ensures no person in the United States is excluded from participation in, denied the benefits of, or subjected to discrimination under any educational program or activity receiving federal financial assistance, on the basis of sex. Over the years, the law has evolved through legislative amendments, executive guidance, and court interpretations. It covers a wide range of issues, including:
Sexual harassment and assault
Gender-based discrimination
Pregnancy and parenting discrimination
Retaliation for reporting discrimination
Equity in athletics and extracurricular programs
Discrimination based on gender identity and sexual orientation
Given the broad nature of the law, navigating Title IX can be complex for both complainants and respondents. Schools must maintain policies that comply with federal standards while protecting the rights of all parties involved. This is where Title IX attorneys come in—they offer specialized legal guidance to ensure fair treatment and compliance.
Who Do Title IX Attorneys Represent?
Title IX attorneys represent a diverse array of clients, including:
Students who have experienced sexual harassment or assault and are seeking justice
Students accused of misconduct who need defense and due process protection
Parents concerned about how their child’s case is being handled
Faculty and staff involved in Title IX proceedings
Educational institutions seeking compliance support or legal defense
The role of Title IX attorneys is not one-dimensional. Whether advocating for a survivor’s rights, defending a student against unfair accusations, or guiding an institution through an investigation, these legal professionals bring critical knowledge of federal regulations, legal precedent, and institutional policy.
Why Title IX Cases Are Legally Complex
Title IX cases are legally sensitive and procedurally unique. Unlike typical civil or criminal cases, Title IX proceedings within educational institutions follow a different framework. Some of the legal complexities involved include:
Jurisdictional Variability: Title IX applies to federally funded institutions, but interpretations of the law may vary based on regional case law and evolving federal guidance.
Administrative Procedures: Schools must follow specific processes for investigating and adjudicating Title IX complaints, and failing to do so can result in civil liability or federal investigation.
Due Process Requirements: Institutions must balance the rights of complainants and respondents, providing equal access to evidence, fair hearings, and the opportunity to appeal.
Intersection with Other Laws: Title IX often intersects with the Clery Act, FERPA, ADA, and state criminal laws, creating additional layers of complexity.
Because of these nuances, Title IX attorneys often need deep expertise not only in civil rights and education law but also in administrative and constitutional law.
Protecting Complainants and Survivors
For those who have experienced sexual assault or harassment, engaging with the Title IX process can be daunting. Title IX attorneys help ensure their clients are heard, protected, and supported throughout the process. Their roles may include:
Assisting with filing formal complaints
Preparing clients for interviews and hearings
Advocating for supportive measures such as academic accommodations or no-contact orders
Ensuring the institution follows proper investigative procedures
Filing appeals or lawsuits if the process is unjust or the outcome inadequate
An experienced attorney can also help survivors understand their rights and the range of legal options available—both within the Title IX framework and beyond it.
Defending the Accused and Upholding Due Process
Title IX attorneys are equally important for students or faculty accused of misconduct. Given the serious consequences—such as suspension, expulsion, or reputational harm—it’s critical that accused parties receive a fair opportunity to present their side. Legal representation ensures that:
Rights under federal law and school policy are preserved
Investigations are conducted without bias or procedural errors
Evidence is properly evaluated and cross-examined
Appeals are made effectively if the outcome is unfavorable
In recent years, concerns about due process violations in Title IX cases have gained national attention. Several federal court rulings have underscored the importance of fair treatment for all parties involved. Title IX attorneys advocate for that fairness.
Advising Educational Institutions
Educational institutions face significant risk when handling Title IX complaints. A poorly managed investigation can lead to federal audits, lawsuits, and damage to reputation. Title IX attorneys help institutions:
Develop and update compliant policies and procedures
Train staff and Title IX coordinators on their responsibilities
Conduct internal investigations or serve as third-party investigators
Respond to complaints filed with the U.S. Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights (OCR)
Mitigate risk through proactive legal guidance
These attorneys also provide crisis management support when high-profile cases arise, ensuring schools maintain transparency while adhering to legal obligations.
Recent Developments and Ongoing Changes
The legal landscape surrounding Title IX is far from static. Over the past decade, presidential administrations have issued differing guidance regarding how schools should handle sexual misconduct cases. For example:
The Obama-era guidelines emphasized survivor support and broadened definitions of harassment.
The Trump administration revised the rules to reinforce due process protections, including live hearings and cross-examinations.
The Biden administration has proposed new rules that aim to strike a balance between the two approaches and expand protections for LGBTQ+ students.
These shifts have made it more important than ever for both individuals and institutions to consult Title IX attorneys who stay current with evolving policies and case law.
When Litigation Arises
Although many Title IX matters are handled internally by schools, some escalate to litigation in state or federal courts. Common scenarios include:
A student sues a university for failing to prevent or properly address harassment
A wrongly accused individual sues for due process violations or defamation
An institution is investigated by the OCR for systemic discrimination
Title IX attorneys play a central role in navigating these legal challenges. Their ability to gather evidence, build legal arguments, and represent clients in court or before regulatory agencies is essential for achieving just outcomes.
Building a Culture of Equity and Accountability
Title IX attorneys are more than just legal representatives—they are advocates for a fair, safe, and inclusive educational environment. Their work contributes to building campus cultures where:
Victims feel safe to come forward
Accused parties are treated fairly
Schools are held accountable to federal standards
Legal disputes are handled with professionalism and care
By working with all parties involved, Title IX attorneys help promote trust, transparency, and equity in education.
Conclusion
Title IX remains one of the most powerful tools for promoting gender equity in education, but enforcing its provisions is no small task. The issues at stake are deeply personal, legally intricate, and socially impactful. Title IX attorneys bring clarity, expertise, and advocacy to this critical area of law. Whether representing students, faculty, or institutions, they help ensure that justice is not only sought—but served. As the conversation around Title IX continues to evolve, their role will remain indispensable in shaping a more equitable educational future for everyone.
1 note
·
View note
Text
From Blueprints to Mobile Screens: How Facility Management Software Modernizes Building Operations

Managing a facility means staying one step ahead—of maintenance issues, safety protocols, compliance audits, and even emergency situations. But when crucial building information is buried in binders, scattered across spreadsheets, or dependent on long-tenured staff who may be nearing retirement, that “one step ahead” becomes hard to maintain.
That’s where facility management software steps in—not just as a digital upgrade, but as a smarter way to operate.
The Shift Toward Smart Facility Management
For decades, facility management has relied on paper documentation, institutional memory, and reactive problem-solving. This worked when buildings were simpler and compliance demands were lower. But today’s facilities are far more complex. From advanced HVAC systems and fire safety protocols to ADA compliance and asset lifecycle tracking, there’s too much at stake to leave to chance.
A modern facility management solution helps organize, streamline, and digitize building operations. It centralizes everything from equipment data and maintenance schedules to floor plans and emergency procedures—making it easier for teams to manage operations proactively.
Centralizing What Matters Most
Many facility teams face the same challenge: important information is everywhere. Shut-off locations may be marked on an old blueprint. The last inspection report might be on someone’s desktop. The knowledge of how to fix a recurring boiler issue may live in the head of a single technician.
By using a unified facility management software, all that critical information can be centralized in a digital space that’s secure, searchable, and accessible to the right people at the right time.
This improves:
Decision-making speed
Maintenance coordination
Team accountability
Long-term asset management
The Power of Mobile Access in the Field
In fast-paced environments—like schools, hospitals, or government buildings—every minute counts. Whether it’s a routine maintenance task or an emergency response, the ability to access data in the field is no longer optional.
A facility management app puts that power directly in the hands of field teams. With a smartphone or tablet, technicians can:
Pull up floor plans on site
Locate shut-off valves instantly
Update work orders in real time
Reference manuals, permits, or repair logs
No more running back to the office or waiting for someone to find a document. Mobile access streamlines workflows and improves response times.
Emergency Preparedness and Compliance Simplified
Emergencies are unpredictable, but preparation is key. Without fast access to evacuation routes, utility shut-offs, or first responder entry points, a crisis can escalate quickly. Paper plans are often out-of-date or misplaced when you need them most.
Facility management software ensures your emergency documentation is always up to date and accessible—especially with mobile capabilities. Teams can act fast and with confidence, and first responders can be better informed on arrival.
The same applies to compliance. With regulations becoming more stringent across industries, storing inspection reports, certifications, and safety records in a digital, organized format simplifies audits and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
Bridging the Knowledge Gap
One of the most overlooked benefits of facility software is its ability to capture institutional knowledge. In many organizations, long-serving staff are the go-to source for building quirks, fix-it tricks, and system layouts. But when they retire or leave, that knowledge often disappears.
A solid facility management solution makes it easier to preserve this information. Notes, procedures, and histories can all be stored and accessed long after original staff members are gone—ensuring continuity and reducing training time for new employees.
Smarter Systems, Stronger Facilities
As facility challenges become more complex, so must the tools we use to manage them. Facility management software is more than a digital shift—it’s a necessary evolution. By helping teams centralize data, improve workflows, respond faster, and maintain compliance, it becomes a core part of a building’s long-term health and safety strategy.
ARC Facilities complements existing systems by digitizing and mobilizing building documentation—from architectural plans to shut-off maps—so teams can access vital information instantly. It’s a simple yet powerful way to improve field response, reduce risk, and make everyday operations more efficient.
0 notes
Note
“It’s fascist to eliminate DOE!” Americans are considered some of the most illiterate people and lack critical thinking skills on the planet since the DOE was made.
Boys are INTENTIONALLY throw under the bus since the public school system is purposely designed for girls style of learning. Fuck I’m 23 and I realize I only got any form of support because of my skintone.
And what we been getting, hmm, kids don’t know how to do taxes. We barely have any cooking lessons unless your lucky af. Most Americans can only read at a 3rd grade level and oh the big ones.
Teachers unions are corrupted af and we have rampant child sex abuse issues where 1 in 10 students REPORTED sexual misconduct. And how many headlines that boils down to “Teacher raped a male student” in one year alone?
And I’m African American, now I didn’t grow up in the inner cities. But I known the government don’t give two fucks about me(I live in the Chicago area too)
What wrong destroying the DOE? People call American schools a hell on earth and we been getting more stupid since the government interference. Oh shit I forgot, how many boys were overdrugged again? Sorry I don’t have Stockholm syndrome towards schools
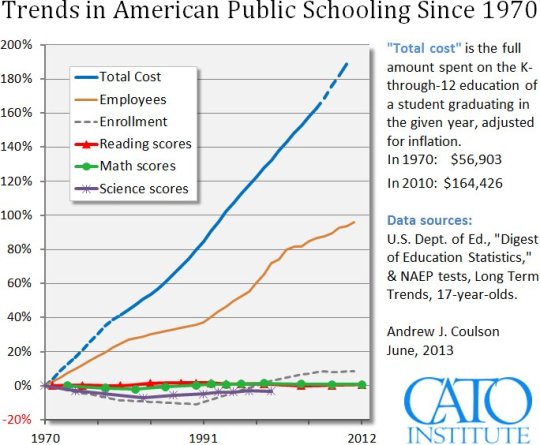
2013 not sure if there's anything more recent this was the one that popped up when I was looking for something different for that post
You'll notice that adjusted for inflation there is three times the money being spent per student now than there was in 1970 with a fairly static level on scoring, but you know that whole definition of insanity trying the same thing and expecting different results doesn't count when it comes to my tax dollars apparently.
There are understandable newer things that will increase the monetary need like ADA compliance, computers, and meal programs (which I wholeheartedly support, kids shouldn't go hungry drop the obama one tho I don't support that one it's garbage and kids were still hungry, how bad does it have to be for a kid to skip out on some of what might be all they eat that day) and various other improvements and such, big fan of air conditioning myself.
Still shouldn't triple the dollar number,
Also for the record the DOE was formed in 1979 so the numbers were already going up for spending when it came in.
Data presented to the Akron, Ohio, school board revealed not a single student from the school’s inaugural third-grade class — now entering eighth grade — has ever passed the state’s math test. “It is discouraging,” said Keith Liechty-Clifford, the district’s director of school improvement, in a model of understatement. State test scores in English and science are nearly as bad, and Black students at I Promise test in the bottom 5% of all Black students in Ohio.
Nice to see the people there making excuses instead of taking responsibility too, one more lesson in failure from this school.
I do hope they can figure it out though, I still have hopes for this one.
But if you've been around here for more than a few months you'll likely know I have hopes for everything to be better, I try to be very bright side oriented.
and in that vein, at least these kids get 3 hots 5 days a week maybe more so that's a W, less hungry kids is always a W
10 notes
·
View notes