#time and labor software
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
school is school but i made a fish spin so life is good

#so in graphic design class i have access to all of the adobe software#so after i finish my assignment each day i rush onto animate#and teach myself to animate#so far this is the fruit of my labors#tomorrow im going to color it and give it eyes#im also gonna work on making it overall more detailed and prettier#id work on it at home#but NONE of the FIVE computers in my house are new enough to run adobe software#the plan is to save up some money and buy a new laptop and one of those drawing-pad thingies with a pen#and then i can animate in my free time too!#doodley dude#three pigeons in a trench coat
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Video game price and budget discourse is genuinely poison, but it’s especially infuriating because when people link the massive budgets to prices they seem to think there is anywhere budgets to come down other than labor. They’re not building Video Game out of steel, it’s Just People.
#quick math question what does 4 years of labor cost for a team of 10 people making 60k/year#a comically low number for software dev but video games pay low on purpose#the other complaint I’ve seen is game timelines should be shorter#I for one would like to see my husband from time to time so I don’t endorse that one#mind you the other complaint is scale I.e. games are too big and too long and that one has A Point but doesn’t fix the problem#at least some big games will exist#anyway I’m mostly vague posting about people on twitter who don’t follow me lmao
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top Tips for Producing Accurate Electrical Estimates
Producing accurate electrical estimates is essential for contractors aiming to submit competitive bids and successfully manage project budgets. Careful planning, attention to detail, and the right tools can significantly improve estimate quality. Here are key tips to help achieve accurate electrical estimates.
Thoroughly Review Project Documents
Start by carefully examining all available project documents including blueprints, electrical drawings, and specifications. Understanding the full scope and details ensures no materials or work items are missed. Clarify any ambiguous or incomplete information with designers or clients before beginning the estimate.
Use Digital Takeoff Tools
Digital takeoff software allows precise measurement and quantification of materials directly from electronic plans. Using these tools reduces manual errors and speeds up the process compared to traditional paper takeoffs. Accurate quantity takeoffs form the foundation of a reliable estimate.
Keep Pricing Data Updated
Material costs and labor rates frequently fluctuate due to market conditions. Regularly update pricing databases by consulting suppliers or using real-time industry resources. Accurate current pricing helps prevent cost overruns and ensures your bids reflect true market conditions.
Adjust Labor Units for Project Conditions
Standard labor units estimate time needed for installation under typical conditions. However, factors such as site accessibility, complexity, crew experience, and project schedule impact actual labor requirements. Adjust labor hours accordingly to reflect these realities.
Include Indirect and Miscellaneous Costs
Don’t overlook indirect costs such as equipment rentals, permits, testing, cleanup, and project management time. Including these expenses ensures your estimate reflects the total project cost and helps avoid surprises later.
Collaborate with Field Teams
Consult with electricians and project managers to validate labor productivity assumptions and identify potential challenges. Their practical insights can help refine estimates and improve accuracy.
Review and Verify Estimates
Double-check all calculations and quantities. Have a second estimator or project manager review the estimate to catch mistakes or omissions. Peer review is a valuable quality control step.
Document Assumptions Clearly
Maintain clear documentation of all assumptions made during estimating, such as productivity rates, pricing sources, and scope interpretations. This documentation supports transparency and helps explain estimates to clients or internal teams.
Stay Informed on Codes and Regulations
Electrical codes and standards change periodically. Staying current ensures your estimates incorporate compliance costs and avoid costly rework due to nonconformance.
Invest in Ongoing Training and Software Updates
Regular training for estimators on best practices and new technologies, along with keeping estimating software updated, contributes to consistent estimate quality.
FAQs
How often should I update labor and material pricing? Ideally, update pricing at least quarterly or whenever there are significant market changes to maintain estimate accuracy.
What is the biggest cause of inaccurate electrical estimates? Incomplete project documentation and failure to adjust for site-specific conditions often lead to inaccurate estimates.
Can software alone guarantee accurate estimates? Software is a powerful tool but accuracy depends on quality data input and estimator expertise.
How detailed should an electrical estimate be? The level of detail depends on project size and client requirements but should always cover all major materials, labor, indirect costs, and contingencies.
Conclusion
Producing accurate electrical estimates requires a combination of detailed review, precise measurement, realistic labor evaluation, and ongoing collaboration. Following these tips can improve your estimating process and contribute to successful project outcomes.
#how to produce accurate electrical estimates#tips for electrical estimating accuracy#best practices for electrical estimating#improving electrical bid accuracy#electrical takeoff accuracy tips#updating material pricing#adjusting labor units#estimating indirect electrical costs#reviewing electrical estimates#validating labor productivity#electrical estimating collaboration tips#avoiding mistakes in electrical estimating#documenting estimating assumptions#training for estimators#electrical estimating software tips#electrical code updates and estimating#bid preparation accuracy#electrical estimating checklist#estimating electrical subcontractor work#checking electrical estimate calculations#refining electrical estimates#managing estimating risks#electrical cost forecasting tips#estimating complex electrical projects#electrical estimating quality control#improving estimating workflows#electrical project cost accuracy#real-time pricing in estimating#estimator review processes#tips for winning electrical bids
0 notes
Text
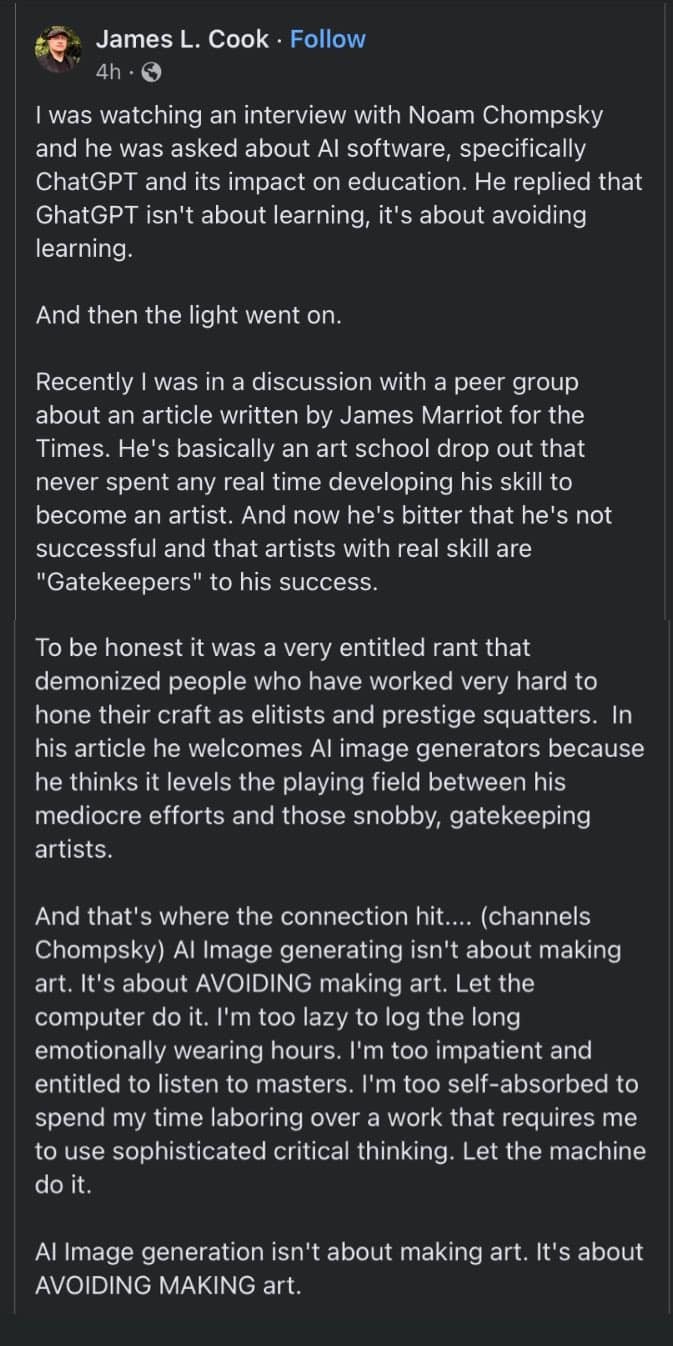
Image description from the notes by @summery-captain:
"A post by James L. Cook, reading: "I was watching an interview with Noam Chompsky and he was asked about AI software, specifically Chat GPT and its impact on education. He replied that Chat GPT isn't about learning, it's about avoiding learning.
And then the light went on.
Recently I was in discussion with a peer group about an article written by James Marriot for the Times. He's basically an art school drop out that never spent any real time developing his skill to become an artist. And now he's bitter that he's not successful and that artists with real skill are 'gatekeepers' to his success.
To be honest it was a very entitled rant that demonized people who have worked very hard to hone their craft as elitists and prestige squatters. In his article he welcomes AI generators because he thinks it levels the playing field between his mediocre efforts and those snobby, gatekeeping artists.
And that's where the connection hit... (channels Chompsky) AI image generating isn't about making art. It is about AVOIDING making art. Let the computer do it. I'm too lazy to log the long emotionally wearing hours. I'm too impatient to listen to masters. I'm too self-absorbed to spend my time laboring over a work that requires me to use sophisticated critical thinking. Let the machine do it.
AI imagine generation isn't about making art. It's about AVOIDING MAKING art." End of imagine description
62K notes
·
View notes
Text
Benefits of Implementing ERP Software for Engineering Firms

The engineering industry is one of the biggest industries in the world, and it plays an important role in growing the economy as well. The engineering sector is growing day by day and is highly competitive. Hence, efficiency, accuracy, and streamlined operations are crucial for success in this sector. Businesses face several challenges in this sector, like the complexities of a project, resource management, and deadline restrictions. ERP software for engineering firms is the best way to overcome all of these challenges as it integrates and automates business processes.
Here is the list of top benefits of utilizing ERP systems for the engineering industry:
1. Project Management:
The projects in engineering sectors have a detailed documentation process, different teams, and complicated workflows. ERP system for engineering firms help in various ways, like centralizing project data, enabling limitless collaboration, and getting real-time updates. Because of this software, every team member has all the updates, which in turn reduces miscommunication and delays in the project.
2. Resource Management:
For all engineering projects, it is essential to allocate all resources carefully, like equipment, materials, and labor. With the utilization of ERP software, the monitoring of resources can be performed easily. It helps in checking resource availability, optimizing usage, and forecasting requirements. This ultimately results in improving cost efficiency.
3. Quality Management:
Ensures engineering projects meet industry standards and regulations.
Quality Control: Offers tools for monitoring and managing the quality of materials, processes, and completed projects.
4. Data Management:
Using ERP software, engineering firms can make sure that they can get a unified database to eliminate data silos and ensure consistency through all departments. A centralized data management system is beneficial for decision-making as well it provides critical information when required.
5. Time and Budget Management:
When the whole system gets automated with ERP software, it reduces time and cost on repetitive tasks like data entry, procurement, and inventory management. The utilization of ERP systems in engineering firms helps in reducing manual errors and improving productivity. Hence, the firms can focus on other important things like innovation and project execution.
6. Client Relationship Management:
Most ERP systems include customer relationship management tools that are very helpful in managing client interactions. This tool allows the firm to track communication history, project milestones, and client preferences. Because of this feature, firms can improve customer satisfaction and build long-term relationships.
7. Scalability and Flexibility
ERP solutions may scale with the company as it grows, allowing for more projects, clients, and resources. Customization: ERP solutions can typically be tailored to an engineering firm’s specific demands and operations.
8. Financial Management
Accounting combines financial accounting with project management to provide a complete picture of the company’s financial health. Reporting: Creates detailed financial reports, such as profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
How PMTRACK ERP Helps:
Managing development processes, monitoring complex projects, and ensuring seamless collaboration across divisions are becoming increasingly important for company success. Engineering organizations in Pune, India, and around the world have distinct issues in successfully managing their operations.
Implementing a bespoke Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution provides transformative benefits by streamlining processes, improving project management, and ultimately generating profitability.
For businesses considering ERP adoption, selecting the correct ERP software vendor is critical. PMTRACK ERP, a reputable ERP solution provider in Pune, India, specializes in engineering ERP systems tailored to the demands of engineering and manufacturing companies.
ERP software is used to connect project management with financial accounting, inventory control, and procurement procedures. This integration gives project managers real-time information about project costs, resource availability, and schedules, resulting in better-informed decisions and more effective project execution.
Engineering firms that use an ERP system can improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve project delivery, and ultimately boost client satisfaction and profitability.
Summary:
ERP software provides several advantages to engineering firms in Pune, India, ranging from better project management and financial control to higher client satisfaction and scalability. Engineering organizations can employ a comprehensive ERP solution to improve operations, decrease inefficiencies, and drive long-term growth.
PMTRACK ERP, one of the leading ERP solution providers in Pune, India, provides comprehensive, industry-specific ERP solutions that are suitable for engineering organizations’ unique requirements. Firms that collaborate with an experienced engineering ERP software company in India receive a trusted partner in negotiating the complexity of their business, setting them up for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
#efficiency#accuracy#and streamlined operations are crucial for success in this sector. Businesses face several challenges in this sector#like the complexities of a project#resource management#Here is the list of top benefits of utilizing ERP systems for the engineering industry:#1. Project Management:#The projects in engineering sectors have a detailed documentation process#different teams#and complicated workflows. ERP system for engineering firms help in various ways#like centralizing project data#enabling limitless collaboration#and getting real-time updates. Because of this software#every team member has all the updates#which in turn reduces miscommunication and delays in the project.#2. Resource Management:#For all engineering projects#it is essential to allocate all resources carefully#like equipment#materials#and labor. With the utilization of ERP software#the monitoring of resources can be performed easily. It helps in checking resource availability#optimizing usage#and forecasting requirements. This ultimately results in improving cost efficiency.#3. Quality Management:#Ensures engineering projects meet industry standards and regulations.#processes#and completed projects.#4. Data Management:#Using ERP software
0 notes
Text
"As the U.S. government continues to provide Israel with both weapons and diplomatic cover — most recently, by voting against a UN resolution demanding a ceasefire, coincidentally also on December 11 — activists like DBNY see collective direct action as their best means of curbing the violence. They also describe their organizing as a direct response to solidarity requests from Palestinian labor unions urging workers around the world to halt the flow of weapons to Israel.
... Since September, DBNY has been taking the fight to Easy Aerial’s doorstep. Each week, activists with the group distribute flyers to the more than 11,000 people who work for over 450 businesses in the 300-acre complex, including art studios, food vendors and entertainment companies. The flyers in English and Spanish provide background on Easy Aerial, Crye Precision and the Brooklyn Navy Yard itself .... In addition to the weekly flyering, DBNY has organized demonstrations to coincide with the corporation’s board meetings and public events. Activists have also been directly petitioning the corporation’s executives, board members and staff, demanding they evict Easy Aerial and Crye Precision from the Brooklyn Navy Yard.
While the response from the Brooklyn Navy Yard Development Corporation to DBNY has been official silence paired with harassment from hired security — including drone surveillance — the response from workers has been 'overwhelmingly positive,' according to the activists. 'Most of them have been shocked and disgusted to learn that they work alongside war criminals.'
... Ultimately, DBNY hopes to replicate the recent successes of other activists targeting weapons manufacturers supplying the Israeli military. Boycott, Divestment, Sanctions Boston, for example, was able to force the closure of Elbit Systems’s offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts, in August, following a year of demonstrations, as reported by Cambridge Day.
According to DBNY, until the Brooklyn Navy Yard ceases to host businesses trading in 'blood money' from targeting people in Gaza and the United States alike, all New Yorkers and visitors should boycott the complex. To that end, the activists have created a petition demanding the eviction of Easy Aerial and Crye Precision, as well as pledging a boycott until that time.
'We also urge all tenants and workers to take autonomous actions at the Brooklyn Navy Yard and by joining our campaign to disrupt, strike and boycott all genocide profiteers,' said the DBNY spokesperson."
Demilitarize Brooklyn Navy Yard: IG, Linktree Resources for locating genocide profiteers near you ACT UP Civil Disobedience Guide Small Group Direct Action Advice
862 notes
·
View notes
Note
whats wrong with ai?? genuinely curious <3
okay let's break it down. i'm an engineer, so i'm going to come at you from a perspective that may be different than someone else's.
i don't hate ai in every aspect. in theory, there are a lot of instances where, in fact, ai can help us do things a lot better without. here's a few examples:
ai detecting cancer
ai sorting recycling
some practical housekeeping that gemini (google ai) can do
all of the above examples are ways in which ai works with humans to do things in parallel with us. it's not overstepping--it's sorting, using pixels at a micro-level to detect abnormalities that we as humans can not, fixing a list. these are all really small, helpful ways that ai can work with us.
everything else about ai works against us. in general, ai is a huge consumer of natural resources. every prompt that you put into character.ai, chatgpt? this wastes water + energy. it's not free. a machine somewhere in the world has to swallow your prompt, call on a model to feed data into it and process more data, and then has to generate an answer for you all in a relatively short amount of time.
that is crazy expensive. someone is paying for that, and if it isn't you with your own money, it's the strain on the power grid, the water that cools the computers, the A/C that cools the data centers. and you aren't the only person using ai. chatgpt alone gets millions of users every single day, with probably thousands of prompts per second, so multiply your personal consumption by millions, and you can start to see how the picture is becoming overwhelming.
that is energy consumption alone. we haven't even talked about how problematic ai is ethically. there is currently no regulation in the united states about how ai should be developed, deployed, or used.
what does this mean for you?
it means that anything you post online is subject to data mining by an ai model (because why would they need to ask if there's no laws to stop them? wtf does it matter what it means to you to some idiot software engineer in the back room of an office making 3x your salary?). oh, that little fic you posted to wattpad that got a lot of attention? well now it's being used to teach ai how to write. oh, that sketch you made using adobe that you want to sell? adobe didn't tell you that anything you save to the cloud is now subject to being used for their ai models, so now your art is being replicated to generate ai images in photoshop, without crediting you (they have since said they don't do this...but privacy policies were never made to be human-readable, and i can't imagine they are the only company to sneakily try this). oh, your apartment just installed a new system that will use facial recognition to let their residents inside? oh, they didn't train their model with anyone but white people, so now all the black people living in that apartment building can't get into their homes. oh, you want to apply for a new job? the ai model that scans resumes learned from historical data that more men work that role than women (so the model basically thinks men are better than women), so now your resume is getting thrown out because you're a woman.
ai learns from data. and data is flawed. data is human. and as humans, we are racist, homophobic, misogynistic, transphobic, divided. so the ai models we train will learn from this. ai learns from people's creative works--their personal and artistic property. and now it's scrambling them all up to spit out generated images and written works that no one would ever want to read (because it's no longer a labor of love), and they're using that to make money. they're profiting off of people, and there's no one to stop them. they're also using generated images as marketing tools, to trick idiots on facebook, to make it so hard to be media literate that we have to question every single thing we see because now we don't know what's real and what's not.
the problem with ai is that it's doing more harm than good. and we as a society aren't doing our due diligence to understand the unintended consequences of it all. we aren't angry enough. we're too scared of stifling innovation that we're letting it regulate itself (aka letting companies decide), which has never been a good idea. we see it do one cool thing, and somehow that makes up for all the rest of the bullshit?
#yeah i could talk about this for years#i could talk about it forever#im so passionate about this lmao#anyways#i also want to point out the examples i listed are ONLY A FEW problems#there's SO MUCH MORE#anywho ai is bleh go away#ask#ask b#🐝's anons#ai
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
I first posted this in a thread over on BlueSky, but I decided to port (a slightly edited version of) it over here, too.
Entirely aside from the absurd and deeply incorrect idea [NaNoWriMo has posited] that machine-generated text and images are somehow "leveling the playing field" for marginalized groups, I think we need to interrogate the base assumption that acknowledging how people have different abilities is ableist/discriminatory. Everyone SHOULD have access to an equal playing field when it comes to housing, healthcare, the ability to exist in public spaces, participating in general public life, employment, etc.
That doesn't mean every person gets to achieve every dream no matter what.
I am 39 years old and I have scoliosis and genetically tight hamstrings, both of which deeply impact my mobility. I will never be a professional contortionist. If I found a robot made out of tentacles and made it do contortion and then demanded everyone call me a contortionist, I would be rightly laughed out of any contortion community. Also, to make it equivalent, the tentacle robot would be provided for "free" by a huge corporation based on stolen unpaid routines from actual contortionists, and using it would boil drinking water in the Southwest into nothingness every time I asked it to do anything, and the whole point would be to avoid paying actual contortionists.
If you cannot - fully CAN NOT - do something, even with accommodations, that does not make you worth less as a person, and it doesn't mean the accommodations shouldn't exist, but it does mean that maybe that thing is not for you.
But who CAN NOT do things are not who uses "AI." It's people who WILL NOT do things.
"AI art means disabled people can be artists who wouldn't be able to otherwise!" There are armless artists drawing with their feet. There are paralyzed artists drawing with their mouths, or with special tracking software that translates their eye movements into lines. There are deeply dyslexic authors writing via text-to-speech. There are deaf musicians. If you actually want to do a thing and care about doing the thing, you can almost always find a way to do the thing.
Telling a machine to do it for you isn't equalizing access for the marginalized. It's cheating. It's anti-labor. It makes it easier for corporations not to pay creative workers, AND THAT'S IS WHY THEY'RE PUSHING IT EVERYWHERE.
I can't wait for the bubble to burst on machine-generated everything, just like it did for NFTs. When it does some people are going to discover they didn't actually learn anything or develop any transferable skills or make anything they can be proud of.
I hope a few of those people pick up a pencil.
It's never too late to start creating. It's never too late to actually learn something. It's never too late to realize that the work is the point.
#AI#writing#just fucking do it#if you want to be a writer then write#literally no one can do it for you#especially not machine-generated text machines#the work is the point
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Tech’s benevolent-dictator-for-life to authoritarian pipeline

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/12/10/bdfl/#high-on-your-own-supply

Silicon Valley's "authoritarian turn" is hard to miss: tech bosses have come out for autocrats like Trump, Orban, Milei, Bolsonaro, et al, and want to turn San Francisco into a militia-patrolled apartheid state operated for the benefit of tech bros:
https://newrepublic.com/article/180487/balaji-srinivasan-network-state-plutocrat
Smart people have written well about what this means, and have gotten me thinking, too:
https://www.programmablemutter.com/p/why-did-silicon-valley-turn-right
Regular readers will know that I make a kind of hobby of collecting definitions of right-wing thought:
https://pluralistic.net/2021/09/29/jubilance/#tolerable-racism
One of these – a hoary old cliche – is that "a conservative is a liberal who's been mugged." I don't give this one much credence, but it takes on an interesting sheen when combined with this anonymous gem: "Conservatives say they long for the simpler times of their childhood, but what they miss is that the reason they lived simpler lives back then wasn't that the times were simpler; rather, it's because they were children."
If you're a tech founder who once lived in a world where your workers were also your pals and didn't shout at you about labor relations, perhaps that's not because workers got "woke," but rather, because when you were all scrapping at a startup, you were all on an equal footing and there weren't any labor relations to speak of. And if you're a once-right-on tech founder who used to abstractly favor "social justice" but now find yourself beset by people demanding that you confront your privilege, perhaps what's changed isn't those people, but rather the amount of privilege you have.
In other words, "a reactionary tech boss is a liberal tech boss who hired a bunch of pals only to have them turn around and start a union." And also: "Tech founders say things were simpler when they were running startups, but what they miss is that the reason no one asked their startup to seriously engage with the social harms it caused is the because the startup was largely irrelevant to society, while the large company it turned into is destroying millions of peoples' lives today."
The oft-repeated reactionary excuse that "I didn't leave the progressive movement, they left me," can be both technically true and also profoundly wrong: if progressives in your circle never bothered you about your commercial affairs, perhaps that's because those affairs didn't matter when you were grinding out code in your hacker house, but they matter a lot now that you have millions of users and thousands of employees.
I've been in tech circles since before the dawn of the dotcoms; I was part of a movement of people who would come over to your house with a stack of floppies and install TCP/IP and PPP networking software on your computer and show you how to connect to a BBS or ISP, because we wanted everyone to have as much fun as we were having.
Some of us channeled that excitement into starting companies that let people get online, create digital presences of their own, and connect with other people. Some of us were more .ORG than .COM and gave our lives over to activism and nonprofits, missing out on the stock options and big paydays. But even though we ended up in different places, we mostly started in the same place, as spittle-flecked, excited kids talking a mile a minute about how cool this internet thing would be and helping you, a normie, jump into it.
Many of my peers from the .ORG and .COM worlds went on to set up institutions – both companies and nonprofits – that have since grown to be critical pieces of internet infrastructure: classified ad platforms, online encyclopedias, CMSes and personal publishing services, critical free/open source projects, standards bodies, server-to-server utilities, and more.
These all started out as benevolent autocracies: personal projects started by people who pitched in to help their virtual neighbors with the new, digital problems we were all facing. These good people, with good impulses, did good: their projects filled an important need, and grew, and grew, and became structurally important to the digital world. What started off as "Our pal's project that we all pitch in on," became, "Our pal's important mission that we help with, but that also has paid staff and important stakeholders, which they oversee as 'benevolent dictator for life.'"
Which was fine. The people who kicked off these projects had nurtured them all the way from a napkin doodle to infrastructure. They understood them better than anyone else, had sacrificed much for them, and it made sense for them to be installed as stewards.
But what they did next, how they used their powers as "BFDLs," made a huge difference. Because we are all imperfect, we are all capable of rationalizing our way into bad choices, we are all riven with insecurities that can push us to do things we later regret. When our actions are checked – by our peers' social approval or approbation; by the need to keep our volunteers happy; by the possibility of a mass exodus of our users or a fork of our code – these imperfections are balanced by consequences.
Dictators aren't necessarily any more prone to these lapses in judgment than anyone else. Benevolent dictators actually exist, people who only retain power because they genuinely want to use that power for good. Those people aren't more likely to fly off the handle or talk themselves into bad places than you or me – but to be a dictator (benevolent or otherwise) is to exist without the consequences that prevent you from giving in to those impulses. Worse: if you are the dictator – again, benevolent or otherwise – of a big, structurally important company or nonprofit that millions of people rely on, the consequences of these lapses are extremely consequential.
This is how BDFL arrangements turn sour: by removing themselves from formal constraint, the people whose screwups matter the most end up with the fewest guardrails to prevent themselves from screwing up.
No wonder people who set out to do good, to help others find safe and satisfying digital homes online, find themselves feeling furious and beset. Given those feelings, can we really be surprised when "benevolent" dictators discover that they have sympathy for real-world autocrats whose core ethos is, "I know what needs to be done and I could do it, if only the rest of you would stop nagging me about petty bullshit that you just made up 10 minutes ago but now insist is the most important thing in the world?"
That all said, it's interesting to look at the process by which some BDFLs transitioned to community-run projects with checks and balances. I often think about how Wikipedia's BDFL, the self-avowed libertarian Jimmy Wales, decided (correctly, and to his everlasting credit), that the project he raised from a weird idea into a world-historic phenomenon should not be ruled over by one guy, not even him.
(Jimmy is one of those libertarians who believes that we don't need governments to make us be kind and take care of one another because he is kind and takes care of other people – see also John Gilmore and Penn Jillette:)
https://www.cracked.com/article_40871_penn-jillette-wants-to-talk-it-all-out.html
Jimmy's handover to the Wikimedia Foundation gives me hope for our other BDFLs. He's proof that you can find yourself in the hotseat without being so overwhelmed with personal grievance that you find yourself in sympathy with actual fascists, but rather, have the maturity and self-awareness to know that the reason people are demanding so much of you is that you have – deliberately and with great effort – created a situation in which you owe the world a superhuman degree of care and attention, and the only way to resolve that situation equitably and secure your own posterity is to share that power around, not demand that you be allowed to wield it without reproach.
#pluralistic#autocracy#authoritarian turn#silicon valley#tech#big tech#bdfl#benevolent dictatorships#accountability#unaccountability#henry farrell
488 notes
·
View notes
Note
This got long and I apologize but I really needed to put this into words somewhere.
I recorded my own podfic. The finished project will probably be under 1 hour of audio, is straightforward (one "character"), and due to the nature of the content, I genuinely feel that my attempt would be better than anything someone else could've done on my behalf.
I'm confident in the emotion/tone in the recording, I'm satisfied with the room acoustics, and I think my diction was generally coherent, but I keep hitting other roadblocks and secondguessing myself.
I was a semi-professional singer for years, but my voice in this recording occasionally isn't the oily smooth quality that many people demand from narrators (there aren't sudden jarring mistakes like voice register breaks, but yeah, I got a little gravelly or fatigued in some emotionally difficult sections and didn't notice at the time when I recorded it). Re-recording isn't a viable option because I needed a specific set of circumstances and logistics to do this the first time.
Also, although I have about 7 years of sound editing experience and a variety of software tools, editing the audio is very challenging on this because my mouth is anatomically prone to adding a plethora of weird non-speech noises that range from distracting to disgusting. Despite trying a slew of "magic" plugins/tools (even some AI stuff, to my shame), they did little or nothing in my case and the only truly effective option is to edit them out one by one. I know exactly how to do that, but it's going to mean HUNDREDS of spots to manually edit and consequently MANY hours of effort…for something that will probably only get a few listeners due to its niche content.
I really don't want to outsource the labor to finish this, partly because I have zero money to pay anyone to do it but also because it's extremely personal writing and I don't want anyone to hear it before it's finished. But I also don't want to actually scrap the project because I do think the overall voicing was authentic and I've wanted to do something like this for a long time. It helps my motivation if I only work on a tiny portion of audio each week, but at that rate (because life and employment are things), it will easily take YEARS to finish it.
I welcome your thoughts but don't have a specific question here. Thank you for letting me unload.
*hugs* I'm glad you were able to get this off your chest anon. It sounds like it's weighing on you a lot.
I think this is a labour of love that you're doing, and I think that you should put in as much effort as you want to put into it. If that means not editing out the random noises, then that's totally fine! This project is important to you for a lot of reasons, and you're doing all of this with the expectation that very few people will be interested in listening to it.
That tells me that you're doing this for you. Not for anyone else. Those concerns about narration quality or popping plosives or whatever else seem to me (just based on this ask) like they're more like intrusive thoughts. You're trying to protect yourself from a negative response, and you're identifying all of the issues that a potential listener might have with your recording.
But with something as personal as what you describe, I think the protection is more likely tied to how important this work is to you. I know that, for myself at least, when something I've made means as much to me as this work seems to mean to you, it's really hard to hear even a little bit of negative feedback.
I'll let the podficcers and listeners share their thoughts in the notes, of course, but I think you're better off deciding whether or not you want to post this publicly and whether or not you want to allow comments on it. This one might just be for you, and that's okay. You're the most important audience member you have. 💗
168 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is AWAY using it's own program or is this just a voluntary list of guidelines for people using programs like DALL-E? How does AWAY address the environmental concerns of how the companies making those AI programs conduct themselves (energy consumption, exploiting impoverished areas for cheap electricity, destruction of the environment to rapidly build and get the components for data centers etc.)? Are members of AWAY encouraged to contact their gov representatives about IP theft by AI apps?
What is AWAY and how does it work?
AWAY does not "use its own program" in the software sense—rather, we're a diverse collective of ~1000 members that each have their own varying workflows and approaches to art. While some members do use AI as one tool among many, most of the people in the server are actually traditional artists who don't use AI at all, yet are still interested in ethical approaches to new technologies.
Our code of ethics is a set of voluntary guidelines that members agree to follow upon joining. These emphasize ethical AI approaches, (preferably open-source models that can run locally), respecting artists who oppose AI by not training styles on their art, and refusing to use AI to undercut other artists or work for corporations that similarly exploit creative labor.
Environmental Impact in Context
It's important to place environmental concerns about AI in the context of our broader extractive, industrialized society, where there are virtually no "clean" solutions:
The water usage figures for AI data centers (200-740 million liters annually) represent roughly 0.00013% of total U.S. water usage. This is a small fraction compared to industrial agriculture or manufacturing—for example, golf course irrigation alone in the U.S. consumes approximately 2.08 billion gallons of water per day, or about 7.87 trillion liters annually. This makes AI's water usage about 0.01% of just golf course irrigation.
Looking into individual usage, the average American consumes about 26.8 kg of beef annually, which takes around 1,608 megajoules (MJ) of energy to produce. Making 10 ChatGPT queries daily for an entire year (3,650 queries) consumes just 38.1 MJ—about 42 times less energy than eating beef. In fact, a single quarter-pound beef patty takes 651 times more energy to produce than a single AI query.
Overall, power usage specific to AI represents just 4% of total data center power consumption, which itself is a small fraction of global energy usage. Current annual energy usage for data centers is roughly 9-15 TWh globally—comparable to producing a relatively small number of vehicles.
The consumer environmentalism narrative around technology often ignores how imperial exploitation pushes environmental costs onto the Global South. The rare earth minerals needed for computing hardware, the cheap labor for manufacturing, and the toxic waste from electronics disposal disproportionately burden developing nations, while the benefits flow largely to wealthy countries.
While this pattern isn't unique to AI, it is fundamental to our global economic structure. The focus on individual consumer choices (like whether or not one should use AI, for art or otherwise,) distracts from the much larger systemic issues of imperialism, extractive capitalism, and global inequality that drive environmental degradation at a massive scale.
They are not going to stop building the data centers, and they weren't going to even if AI never got invented.
Creative Tools and Environmental Impact
In actuality, all creative practices have some sort of environmental impact in an industrialized society:
Digital art software (such as Photoshop, Blender, etc) generally uses 60-300 watts per hour depending on your computer's specifications. This is typically more energy than dozens, if not hundreds, of AI image generations (maybe even thousands if you are using a particularly low-quality one).
Traditional art supplies rely on similar if not worse scales of resource extraction, chemical processing, and global supply chains, all of which come with their own environmental impact.
Paint production requires roughly thirteen gallons of water to manufacture one gallon of paint.
Many oil paints contain toxic heavy metals and solvents, which have the potential to contaminate ground water.
Synthetic brushes are made from petroleum-based plastics that take centuries to decompose.
That being said, the point of this section isn't to deflect criticism of AI by criticizing other art forms. Rather, it's important to recognize that we live in a society where virtually all artistic avenues have environmental costs. Focusing exclusively on the newest technologies while ignoring the environmental costs of pre-existing tools and practices doesn't help to solve any of the issues with our current or future waste.
The largest environmental problems come not from individual creative choices, but rather from industrial-scale systems, such as:
Industrial manufacturing (responsible for roughly 22% of global emissions)
Industrial agriculture (responsible for roughly 24% of global emissions)
Transportation and logistics networks (responsible for roughly 14% of global emissions)
Making changes on an individual scale, while meaningful on a personal level, can't address systemic issues without broader policy changes and overall restructuring of global economic systems.
Intellectual Property Considerations
AWAY doesn't encourage members to contact government representatives about "IP theft" for multiple reasons:
We acknowledge that copyright law overwhelmingly serves corporate interests rather than individual creators
Creating new "learning rights" or "style rights" would further empower large corporations while harming individual artists and fan creators
Many AWAY members live outside the United States, many of which having been directly damaged by the US, and thus understand that intellectual property regimes are often tools of imperial control that benefit wealthy nations
Instead, we emphasize respect for artists who are protective of their work and style. Our guidelines explicitly prohibit imitating the style of artists who have voiced their distaste for AI, working on an opt-in model that encourages traditional artists to give and subsequently revoke permissions if they see fit. This approach is about respect, not legal enforcement. We are not a pro-copyright group.
In Conclusion
AWAY aims to cultivate thoughtful, ethical engagement with new technologies, while also holding respect for creative communities outside of itself. As a collective, we recognize that real environmental solutions require addressing concepts such as imperial exploitation, extractive capitalism, and corporate power—not just focusing on individual consumer choices, which do little to change the current state of the world we live in.
When discussing environmental impacts, it's important to keep perspective on a relative scale, and to avoid ignoring major issues in favor of smaller ones. We promote balanced discussions based in concrete fact, with the belief that they can lead to meaningful solutions, rather than misplaced outrage that ultimately serves to maintain the status quo.
If this resonates with you, please feel free to join our discord. :)
Works Cited:
USGS Water Use Data: https://www.usgs.gov/mission-areas/water-resources/science/water-use-united-states
Golf Course Superintendents Association of America water usage report: https://www.gcsaa.org/resources/research/golf-course-environmental-profile
Equinix data center water sustainability report: https://www.equinix.com/resources/infopapers/corporate-sustainability-report
Environmental Working Group's Meat Eater's Guide (beef energy calculations): https://www.ewg.org/meateatersguide/
Hugging Face AI energy consumption study: https://huggingface.co/blog/carbon-footprint
International Energy Agency report on data centers: https://www.iea.org/reports/data-centres-and-data-transmission-networks
Goldman Sachs "Generational Growth" report on AI power demand: https://www.goldmansachs.com/intelligence/pages/gs-research/generational-growth-ai-data-centers-and-the-coming-us-power-surge/report.pdf
Artists Network's guide to eco-friendly art practices: https://www.artistsnetwork.com/art-business/how-to-be-an-eco-friendly-artist/
The Earth Chronicles' analysis of art materials: https://earthchronicles.org/artists-ironically-paint-nature-with-harmful-materials/
Natural Earth Paint's environmental impact report: https://naturalearthpaint.com/pages/environmental-impact
Our World in Data's global emissions by sector: https://ourworldindata.org/emissions-by-sector
"The High Cost of High Tech" report on electronics manufacturing: https://goodelectronics.org/the-high-cost-of-high-tech/
"Unearthing the Dirty Secrets of the Clean Energy Transition" (on rare earth mineral mining): https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/apr/18/clean-energy-dirty-mining-indigenous-communities-climate-crisis
Electronic Frontier Foundation's position paper on AI and copyright: https://www.eff.org/wp/ai-and-copyright
Creative Commons research on enabling better sharing: https://creativecommons.org/2023/04/24/ai-and-creativity/
218 notes
·
View notes
Text
Oh hey since I mentioned sci hub again
I'd love to hear people's stories about small things that radicalized them in benign ways. I'll start.
I was already pretty leftist at this point, but being associated with academia so long means I've gotten free access to a variety of scientific journals, software, and more for... Basically my entire adult life. On campus, all of those systems have automatic logins. But off campus, usually there's janky, half-functional systems associated with actually inputting your credentials into these sites. Scientific journals especially are really and at tracking logins, and oftentimes have to link back to your uni's generic login page, which they're bad at pinging. Software installation usually requires
So instead of using services that the university had already paid for, for me to freely use, like adobe, journal logins, and Microsoft products, I started using free equivalents. Sci hub, gimp, libre office, Ubuntu... Not because I was invested in open source and free access mentalities at the time, but because they were literally quicker and simpler to use.
And then I started thinking about all of the little bits of tech infrastructure I was using to access my "free" stuff.
Someone coded those systems.
Some tiny portion of a server is devoted to handling those pings an login requests.
Someone spent hours upon days of work moving office 365 and adobe from actual pieces of software that fully live on your computer into stripped down versions of themselves that now have to verify
Someone made the payment system for Nature.
So. Much. Wasted. Labor. Just to block people from already existing services. That have alternatives. That are as good. For free. And they can be free largely because they don't have all of the bullshit associated with locking them down and keeping them proprietary.
Tech and science are of course what I have the most experience in, but I feel like once you start realizing that in one sector, you start seeing it everywhere.
Anyways this is a barely focused unmedicated ADHD ramble but I'd love to hear other examples
520 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Accurately Calculate Electrical Labor Costs
Accurately calculating electrical labor costs is a vital part of preparing an effective estimate. Labor often represents a significant portion of any electrical project budget, and even small miscalculations can lead to financial loss, delays, or underbidding. To avoid these risks, estimators must adopt a structured, data-driven approach. This involves understanding the tasks involved, applying proper labor units, adjusting for real-world site conditions, and using historical performance data where possible.
Understanding Labor Units in Electrical Estimating
Labor units are standardized measurements that represent the time required to install a specific electrical component. For example, installing a single-gang switch might be assigned a labor unit of 0.3 hours. These values come from industry databases, such as NECA or manufacturer-provided data, and are commonly integrated into estimating software.
Using labor units provides consistency across estimates and allows contractors to benchmark productivity over time. However, these units are based on ideal conditions and may require adjustment to reflect actual project variables.
Steps to Calculate Electrical Labor Costs
Perform a Detailed Takeoff Start by identifying and counting every component that will be installed—light fixtures, switches, receptacles, panels, conduit runs, and wire pulls. Group these by system to simplify the labor application process.
Apply Standard Labor Units Assign the appropriate labor unit to each item based on type and installation complexity. Labor units can vary depending on mounting method, ceiling height, voltage level, or fixture type.
Adjust for Project Conditions Real-world conditions rarely match the assumptions used in standardized units. Factors like difficult access, high ceilings, tight timelines, or occupied buildings can significantly affect productivity. Estimators typically use efficiency or difficulty factors to adjust labor units accordingly. For instance, a 10% increase might be added to labor hours for installations in hard-to-reach areas.
Factor in Crew Productivity Each electrical contractor may have different crew efficiency based on experience, training, and available tools. Reviewing past projects provides insight into how quickly your team completes specific tasks, helping to fine-tune estimates for future jobs.
Include Setup, Testing, and Cleanup Time In addition to installation, don’t forget to include time for setup, equipment staging, system testing, and cleanup. These indirect labor hours can account for 5–10% of the total labor cost and are often overlooked in basic estimates.
Apply Labor Rates Once total labor hours are calculated, multiply them by your actual hourly rate. This should include base wage, payroll taxes, insurance, and any applicable benefits. Some companies add a labor burden multiplier to streamline this calculation (e.g., 1.35 times the base rate).
Review and Validate Cross-check your total labor hours against similar past projects to identify any discrepancies. This validation process ensures your estimate aligns with known performance benchmarks and avoids surprises during project execution.
Common Factors That Affect Labor Costs
Project Size and Complexity: Larger projects may have economies of scale, but more complex installations often require longer labor hours.
Weather and Season: Outdoor electrical work is slower in cold or rainy conditions.
Location: Union vs. non-union areas, local labor laws, and regional wage variations can influence rates and crew availability.
Material Availability: Delays in receiving components can extend labor hours if crews are waiting or rescheduled.
Coordination with Other Trades: Working around HVAC, plumbing, or drywall crews can slow progress and should be factored in.
Avoiding Common Labor Estimating Mistakes
Some estimators either overestimate to cover uncertainty or underestimate to win a bid—both approaches are risky. Accurate labor estimating relies on data, field feedback, and real-time adjustments. Mistakes often arise from using outdated labor units, failing to adjust for field conditions, or misjudging crew performance.
To minimize these errors, estimators should document assumptions, apply realistic adjustment factors, and involve field supervisors when reviewing estimates. Collaboration between office and field teams enhances estimating precision and builds accountability.
FAQs
What is a labor burden rate and why does it matter? The labor burden rate includes wages plus taxes, insurance, and benefits. It reflects the true cost of labor to your business and ensures estimates are financially accurate.
Can labor units be customized for my company? Yes. Many estimating platforms allow you to edit or build custom labor units based on your historical project data and crew productivity.
Should I use average labor hours or exact values? Use exact values where possible, but averages can help when data is limited. Always adjust for known site conditions or installation challenges.
Conclusion
Calculating electrical labor costs accurately is essential for producing reliable, profitable estimates. By combining standardized labor units with field-specific adjustments and company data, estimators can create labor forecasts that reflect real-world performance. The result is not only stronger bids but smoother project delivery and greater client satisfaction.
#how to calculate electrical labor costs accurately#step by step guide to electrical labor estimating#electrical labor cost estimation for contractors#using labor units in electrical estimating#how to adjust labor hours for job conditions#what affects electrical labor cost#how to factor labor burden in estimating#estimating labor for conduit and wiring installation#how to price labor in electrical projects#best way to estimate electrician work hours#applying labor units in electrical bids#calculating real labor hours in electrical jobs#how to estimate crew productivity#what is a labor burden multiplier in estimating#how to include testing and cleanup time in labor costs#how much labor to install electrical panel#how to price labor for electrical rough-in#estimating labor in commercial electrical jobs#calculating labor for residential wiring projects#understanding electrical labor databases#tips for estimating labor in electrical bids#estimating electrical labor for design build projects#software that calculates electrical labor hours#how many man hours per light fixture install#how to validate electrical labor estimates#what is the industry standard for electrical labor units#how crew experience affects labor estimating#factoring weather in electrical labor costs#avoiding mistakes in labor cost estimation
0 notes
Text
DAY 6274
Jalsa, Mumbai Aopr 20, 2025 Sun 11:17 pm
🪔 ,
April 21 .. birthday greetings and happiness to Ef Mousumi Biswas .. and Ef Arijit Bhattacharya from Kolkata .. 🙏🏽❤️🚩.. the wishes from the Ef family continue with warmth .. and love 🌺
The AI debate became the topic of discussion on the dining table ad there were many potent points raised - bith positive and a little indifferent ..
The young acknowledged it with reason and able argument .. some of the mid elders disagreed mildly .. and the end was kind of neutral ..
Blessed be they of the next GEN .. their minds are sorted out well in advance .. and why not .. we shall not be around till time in advance , but they and their progeny shall .. as has been the norm through generations ...
The IPL is now the greatest attraction throughout the day .. particularly on the Sunday, for the two on the day .. and there is never a debate on that ..
🤣
.. and I am most appreciative to read the comments from the Ef on the topic of the day - AI .. appreciative because some of the reactions and texts are valid and interesting to know .. the aspect expressed in all has a legitimate argument and that is most healthy ..
I am happy that we could all react to the Blog contents in the manner they have done .. my gratitude .. such a joy to get different views , valid and meaningful ..
And it is not the end of the day or the debate .. some impressions of the Gen X and some from the just passed Gen .. and some that were never ever the Gen are interesting as well :
The Printing Press (15th Century)
Fear: Scribes, monks, and elites thought it would destroy the value of knowledge, lead to mass misinformation, and eliminate jobs. Reality: It democratized knowledge, spurred the Renaissance and Reformation, and created entirely new industries—publishing, journalism, and education.
⸻
Industrial Revolution (18th–19th Century)
Fear: Machines would replace all human labor. The Luddites famously destroyed machinery in protest. Reality: Some manual labor jobs were displaced, but the economy exploded with new roles in manufacturing, logistics, engineering, and management. Overall employment and productivity soared.
⸻
Automobiles (Early 20th Century)
Fear: People feared job losses for carriage makers, stable hands, and horseshoe smiths. Cities worried about traffic, accidents, and social decay. Reality: The car industry became one of the largest employers in the world. It reshaped economies, enabled suburbia, and created new sectors like travel, road infrastructure, and auto repair.
⸻
Personal Computers (1980s)
Fear: Office workers would be replaced by machines; people worried about becoming obsolete. Reality: Computers made work faster and created entire industries: IT, software development, cybersecurity, and tech support. It transformed how we live and work.
⸻
The Internet (1990s)
Fear: It would destroy jobs in retail, publishing, and communication. Some thought it would unravel social order. Reality: E-commerce, digital marketing, remote work, and the creator economy now thrive. It connected the world and opened new opportunities.
⸻
ATMs (1970s–80s)
Fear: Bank tellers would lose their jobs en masse. Reality: ATMs handled routine tasks, but banks actually hired more tellers for customer service roles as they opened more branches thanks to reduced transaction costs.
⸻
Robotics & Automation (Factory work, 20th century–today)
Fear: Mass unemployment in factories. Reality: While some jobs shifted or ended, others evolved—robot maintenance, programming, design. Productivity gains created new jobs elsewhere.
The fear is not for losing jobs. It is the compromise of intellectual property and use without compensation. This case is slightly different.
I think AI will only make humans smarter. If we use it to our advantage.
That’s been happening for the last 10 years anyway
Not something new
You can’t control that in this day and age
YouTube & User-Generated Content (mid-2000s onward)
Initial Fear: When YouTube exploded, many in the entertainment industry panicked. The fear was that copyrighted material—music, TV clips, movies—would be shared freely without compensation. Creators and rights holders worried their content would be pirated, devalued, and that they’d lose control over distribution.
What Actually Happened: YouTube evolved to protect IP and monetize it through systems like Content ID, which allows rights holders to:
Automatically detect when their content is used
Choose to block, track, or monetize that usage
Earn revenue from ads run on videos using their IP (even when others post it)
Instead of wiping out creators or studios, it became a massive revenue stream—especially for musicians, media companies, and creators. Entire business models emerged around fair use, remixes, and reactions—with compensation built in.
Key Shift: The system went from “piracy risk” to “profit partner,” by embracing tech that recognized and enforced IP rights at scale.
This lead to higher profits and more money for owners and content btw
You just have to restructure the compensation laws and rewrite contracts
It’s only going to benefit artists in the long run
Yes
They can IP it
That is the hope
It’s the spread of your content and material without you putting a penny towards it
Cannot blindly sign off everything in contracts anymore. Has to be a lot more specific.
Yes that’s for sure
“Automation hasn’t erased jobs—it’s changed where human effort goes.”
Another good one is “hard work beats talent when talent stops working hard”
Which has absolutely nothing to with AI right now but 🤣
These ladies and Gentlemen of the Ef jury are various conversational opinions on AI .. I am merely pasting them for a view and an opinion ..
And among all the brouhaha about AI .. we simply forgot the Sunday well wishers .. and so ..
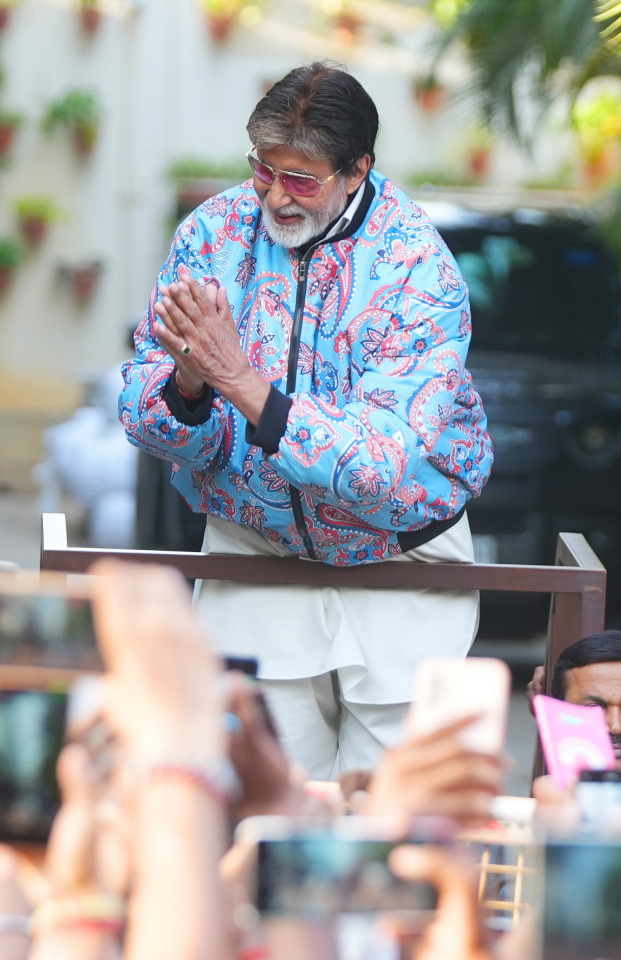
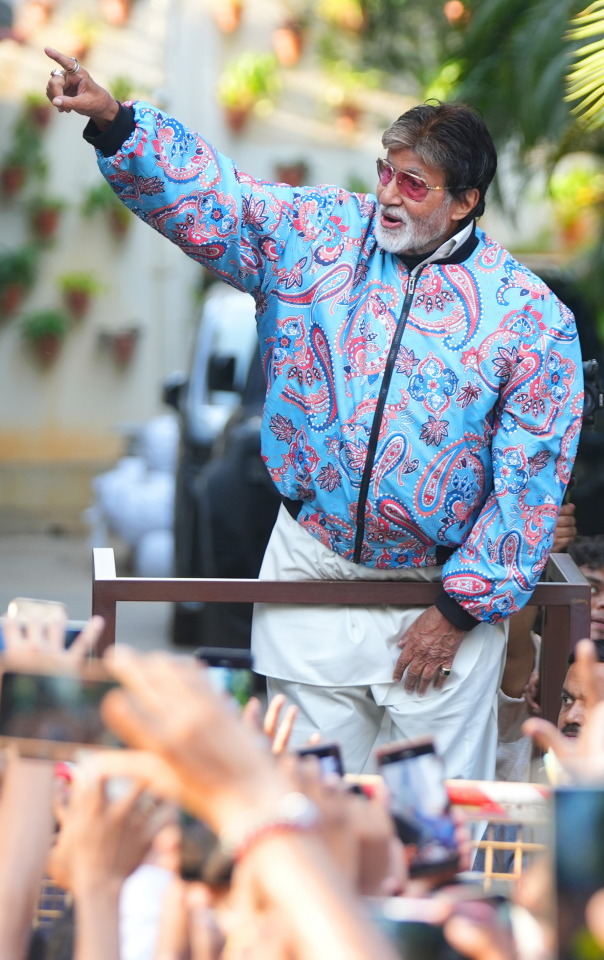
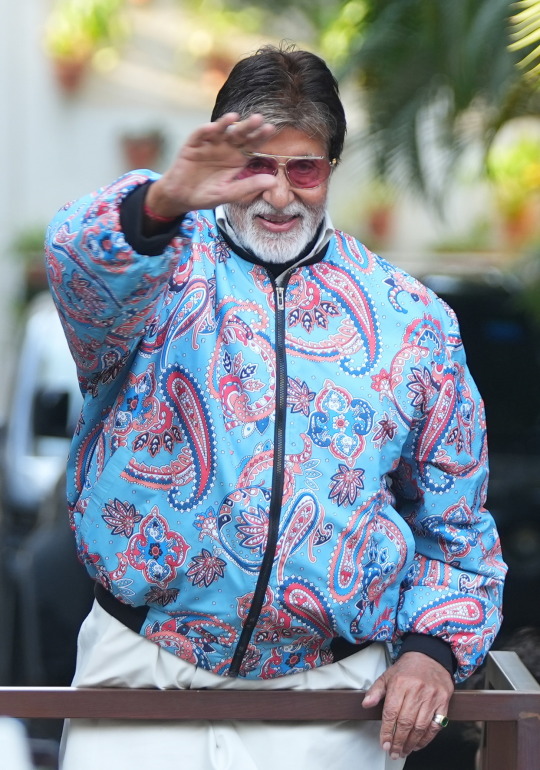
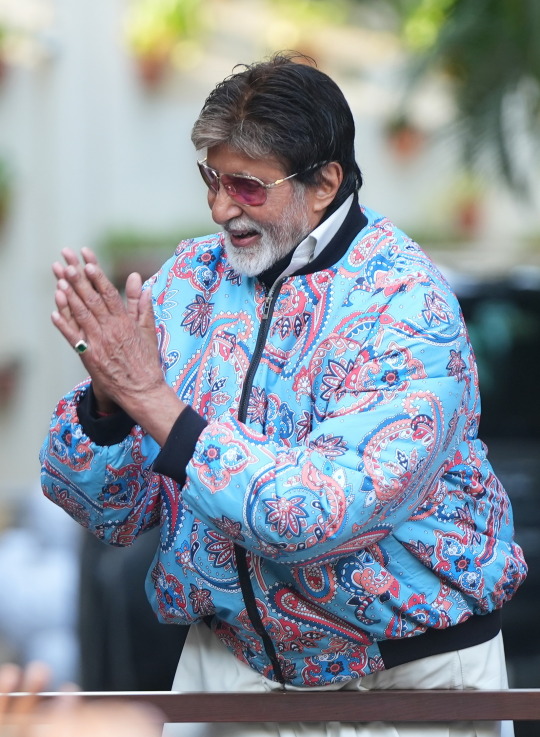














my love and the length be of immense .. pardon

Amitabh Bachchan
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Judd Legum and Rebecca Crosby at Popular Information:
Today, the National Security Agency (NSA) is planning a "Big Delete" of websites and internal network content that contain any of 27 banned words, including "privilege," "bias," and "inclusion." The "Big Delete," according to an NSA source and internal correspondence reviewed by Popular Information, is creating unintended consequences. Although the websites and other content are purportedly being deleted to comply with President Trump's executive orders targeting diversity, equity, and inclusion, or "DEI," the dragnet is taking down "mission-related" work. According to the NSA source, who spoke on the condition of anonymity because they are not authorized to speak to the media, the process is "very chaotic," but is plowing ahead anyway. A memo distributed by NSA leadership to its staff says that on February 10, all NSA websites and internal network pages that contain banned words will be deleted. This is the list of 27 banned words distributed to NSA staff:
Anti-Racism Racism Allyship Bias DEI Diversity Diverse Confirmation Bias Equity Equitableness Feminism Gender Gender Identity Inclusion Inclusive All-Inclusive Inclusivity Injustice Intersectionality Prejudice Privilege Racial Identity Sexuality Stereotypes Pronouns Transgender Equality
The memo acknowledges that the list includes many terms that are used by the NSA in contexts that have nothing to do with DEI. For example, the term "privilege" is used by the NSA in the context of "privilege escalation." In the intelligence world, privilege escalation refers to "techniques that adversaries use to gain higher-level permissions on a system or network." The purge extends beyond public-facing websites to pages on the NSA's internal network, including project management software like Jira and Confluence.
[...]
The government memory hole
Since Trump took office, thousands of web pages across various federal agencies have been altered or removed entirely. Federal agencies have taken down or edited resources about HIV, contraceptives, LGBTQ+ health, abortion, and climate change. Some web pages have later come back online “without clarity on what had been changed or removed.” An analysis by the Washington Post of 8,000 federal web pages “found 662 examples of deletions and additions” since Trump took office. The analysis found that words like diversity, equity, and inclusion were removed at least 231 times from the websites of federal agencies, including the Department of Labor, the Department of Education, the Department of Health and Human Services, and the Department of Transportation.
The NSA’s “Big Delete” is a form of authoritarian censorship under the MAGA regime led by the Trump-Musk-Vance axis of evil.
See Also:
NCRM: The 27 Words the NSA Is Scrubbing From Its Websites: Report
60 notes
·
View notes