#AI Coding Tools for non-programmer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
No Coding Skills? AI Tools Help Non-Programmers Code Easily
The world of programming has always been a daunting space for non-programmers. Writing complex lines of code requires a steep learning curve and technical expertise. However, advancements in artificial intelligence have transformed this landscape, making it easier for non-programmers to dive into coding with the help of AI tools. AI-powered coding assistants have revolutionized how people interact with programming languages, enabling those with no prior coding experience to create applications, automate processes, and build software solutions. Whether you are an entrepreneur, a student, or a business professional, AI coding tools can simplify your development journey.

How AI Coding Tools Make Coding Accessible
Coding was once an exclusive skill reserved for software engineers, but AI coding tools have made it more accessible than ever. These tools utilize machine learning and natural language processing to understand and generate code based on user input. Non-programmers can now build applications using AI-assisted features, reducing the reliance on manual coding expertise.
AI-Powered Coding Assistant: A Game Changer for Non-Programmers
The best AI coding assistants provide a seamless experience by suggesting code snippets, auto-correcting syntax errors, and even generating full scripts based on simple text prompts. This means non-programmers can now experiment with coding without the frustration of debugging and syntax complexities. An AI coding tool for non-programmers works like a virtual mentor, guiding users through each step of the development process. Whether it's website development, app creation, or automation tasks, these tools simplify coding tasks and make programming accessible to everyone.
Benefits of Using AI Coding Tools
AI-powered coding tools bring numerous advantages to users without a technical background. From reducing coding errors to accelerating development time, these tools enhance productivity and open new opportunities for creativity.
Learn to Code with AI Tools
For beginners, AI coding tools serve as an educational resource. Instead of spending months learning syntax and programming logic, users can quickly grasp fundamental coding concepts by interacting with AI-driven code generators. This makes learning to code with AI tools a time-efficient and practical approach. AI also assists in providing explanations for complex programming structures. Users can receive real-time feedback, helping them understand how different functions work and how they can optimize their code.
AI Code Generator: Bridging the Skill Gap
AI code generators allow non-programmers to create fully functional programs without manually writing extensive code. These tools can translate user instructions into executable scripts, making coding as easy as typing natural language commands. The efficiency and accuracy of AI-generated code minimize the barriers to software development.

Popular AI Coding Tools for Beginners
For those new to coding, the right AI-powered coding assistant can make a significant difference. Many AI coding tools cater specifically to beginners by providing intuitive interfaces and automated coding support.
Best AI Coding Assistant for Non-Programmers
Choosing the best AI coding assistant depends on the user’s needs. Some AI coding tools offer drag-and-drop interfaces for easy application building, while others focus on generating clean, efficient code.
A few popular AI tools include:
AI-assisted website builders that require no manual coding.
AI-powered app development platforms that simplify complex programming.
AI-enhanced automation tools that allow users to automate workflows with minimal effort.
Each tool is designed to help non-programmers build functional software without extensive coding knowledge.
Overcoming Challenges with AI Coding for Beginners
While AI coding tools are incredibly beneficial, there are still challenges that beginners might face. Understanding how AI interprets user input and refining prompts for better results requires practice. Additionally, while AI-generated code is highly efficient, human oversight is essential to ensure accuracy and security.
The Future of AI-Powered Coding
The integration of AI into coding is still evolving, but the future looks promising. As AI continues to improve, these tools will become even more sophisticated, making programming more accessible to a broader audience. The future of AI coding for beginners will involve more intuitive platforms, smarter AI suggestions, and seamless integration with existing software development processes.
Conclusion
AI coding tools have broken down the barriers that once made programming exclusive to tech professionals. With the right AI-powered coding assistant, non-programmers can now create applications, automate workflows, and experiment with coding without deep technical knowledge.
By leveraging the best AI coding assistant, beginners can quickly learn programming concepts and build functional projects with ease. As AI technology advances, the accessibility and efficiency of AI coding tools will continue to grow, empowering more individuals to code effortlessly.

FAQs
What is an AI coding tool for non-programmers?
An AI coding tool for non-programmers is software that uses artificial intelligence to assist users in generating, debugging, and optimizing code without requiring deep programming knowledge.
How do AI-powered coding assistants help beginners?
AI-powered coding assistants help beginners by providing real-time code suggestions, explanations, and automatic corrections, making it easier for users to learn and apply coding concepts.
Can I build an app without coding skills using AI?
Yes, AI coding tools allow users to build applications without extensive coding knowledge. Many platforms offer drag-and-drop functionality and AI-assisted code generation to simplify the process.
Is AI-generated code reliable?
AI-generated code is generally accurate and efficient, but it should always be reviewed by a human to ensure security, correctness, and optimization.
Which is the best AI coding assistant for non-programmers?
The best AI coding assistant depends on your needs. Popular options include AI-powered website builders, automation platforms, and AI-driven code generators that cater to beginners and professionals alike.
0 notes
Text
On paper, the first candidate looked perfect. Thomas was from rural Tennessee and had studied computer science at the University of Missouri. His résumé said he’d been a professional programmer for eight years, and he’d breezed through a preliminary coding test. All of this was excellent news for Thomas’ prospective boss, Simon Wijckmans, founder of the web security startup C.Side. The 27-year-old Belgian was based in London but was looking for ambitious, fully remote coders.
Thomas had an Anglo-Saxon surname, so Wijckmans was surprised when he clicked into his Google Meet and found himself speaking with a heavily accented young man of Asian origin. Thomas had set a generic image of an office as his background. His internet connection was laggy—odd for a professional coder—and his end of the call was noisy. To Wijckmans, Thomas sounded like he was sitting in a large, crowded space, maybe a dorm or a call center.
Wijckmans fired off his interview questions, and Thomas’ responses were solid enough. But Wijckmans noticed that Thomas seemed most interested in asking about his salary. He didn’t come across as curious about the actual work or about how the company operated or even about benefits like startup stock or health coverage. Odd, thought Wijckmans. The conversation came to a close, and he got ready for the next interview in his queue.
Once again, the applicant said they were based in the US, had an Anglo name, and appeared to be a young Asian man with a thick, non-American accent. He used a basic virtual background, was on a terrible internet connection, and had a single-minded focus on salary. This candidate, though, was wearing glasses. In the lenses, Wijckmans spotted the reflection of multiple screens, and he could make out a white chatbox with messages scrolling by. “He was clearly either chatting with somebody or on some AI tool,” Wijckmans remembers.
On high alert, Wijckmans grabbed screenshots and took notes. After the call ended, he went back over the job applications. He found that his company’s listings were being flooded with applicants just like these: an opening for a full-stack developer got more than 500 applications in a day, far more than usual. And when he looked more deeply into the applicants’ coding tests, he saw that many candidates appeared to have used a virtual private network, or VPN, which allows you to mask your computer’s true location.
Wijckmans didn’t know it yet, but he’d stumbled onto the edges of an audacious, global cybercrime operation. He’d unwittingly made contact with an army of seemingly unassuming IT workers, deployed to work remotely for American and European companies under false identities, all to bankroll the government of North Korea.
With a little help from some friends on the ground, of course.
christina chapman was living in a trailer in Brook Park, Minnesota, a hamlet north of Minneapolis, when she got a note from a recruiter that changed her life. A bubbly 44-year-old with curly red hair and glasses, she loved her dogs and her mom and posting social justice content on TikTok. In her spare time she listened to K-pop, enjoyed Renaissance fairs, and got into cosplay. Chapman was also, according to her sparse online résumé, learning to code online.
It was March 2020 when she clicked on the message in her LinkedIn account. A foreign company was looking for somebody to “be the US face” of the business. The company needed help finding remote employment for overseas workers. Chapman signed on. It’s unclear how fast her workload grew, but by October 2022 she could afford a move from chilly Minnesota to a low-slung, four-bedroom house in Litchfield Park, Arizona. It wasn’t fancy—a suburban corner lot with a few thin trees—but it was a big upgrade over the trailer.
Chapman then started documenting more of her life on TikTok and YouTube, mostly talking about her diet, fitness, or mental health. In one chatty video, shared in June 2023, she described grabbing breakfast on the go—an açaí bowl and a smoothie— because work was so busy. “My clients are going crazy!” she complained. In the background, the camera caught a glimpse of metal racks holding at least a dozen open laptops covered in sticky notes. A few months later, federal investigators raided Chapman’s home, seized the laptops, and eventually filed charges alleging that she had spent three years aiding the “illicit revenue generation efforts” of the government of North Korea.
For maybe a decade, North Korean intelligence services have been training young IT workers and sending them abroad in teams, often to China or Russia. From these bases, they scour the web for job listings all over, usually in software engineering, and usually with Western companies. They favor roles that are fully remote, with solid wages, good access to data and systems, and few responsibilities. Over time they began applying for these jobs using stolen or fake identities and relying on members of their criminal teams to provide fictional references; some have even started using AI to pass coding tests, video interviews, and background checks.
But if an applicant lands a job offer, the syndicate needs somebody on the ground in the country the applicant claims to live in. A fake employee, after all, can’t use the addresses or bank accounts linked to their stolen IDs, and they can’t dial in to a company’s networks from overseas without instantly triggering suspicion. That’s where someone like Christina Chapman comes in.
As the “facilitator” for hundreds of North Korea–linked jobs, Chapman signed fraudulent documents and handled some of the fake workers’ salaries. She would often receive their paychecks in one of her bank accounts, take a cut, and wire the rest overseas: Federal prosecutors say Chapman was promised as much as 30 percent of the money that passed through her hands.
Her most important job, though, was tending the “laptop farm.” After being hired, a fake worker will typically ask for their company computer to be sent to a different address than the one on record—usually with some tale about a last-minute move or needing to stay with a sick relative. The new address, of course, belongs to the facilitator, in this case Chapman. Sometimes the facilitator forwards the laptop to an address overseas, but more commonly that person holds onto it and installs software that allows it to be controlled remotely. Then the fake employee can connect to their machine from anywhere in the world while appearing to be in the US. (“You know how to install Anydesk?” one North Korean operative asked Chapman in 2022. “I do it practically EVERYDAY!” she replied.)
In messages with her handlers, Chapman discussed sending government forms like the I-9, which attests that a person is legally able to work in the US. (“I did my best to copy your signature,” she wrote. “Haha. Thank you,” came the response.) She also did basic tech troubleshooting and dialed into meetings on a worker’s behalf, sometimes on short notice, as in this conversation from November 2023:
Worker: We are going to have laptop setup meeting in 20 mins. Can you join Teams meeting and follow what IT guy say? Because it will require to restart laptop multiple times and I can not handle that. You can mute and just follow what they say ...
Chapman: Who do I say I am?
Worker: You don’t have to say, I will be joining there too.
Chapman: I just typed in the name Daniel. If they ask WHY you are using two devices, just say the microphone on your laptop doesn’t work right ... Most IT people are fine with that explanation.
Sometimes, she got jumpy. “I hope you guys can find other people to do your physical I9s,” she wrote to her bosses in 2023, according to court documents. “I will SEND them for you, but have someone else do the paperwork. I can go to FEDERAL PRISON for falsifying federal documents.” Michael Barnhart, an investigator at cybersecurity company DTEX and a leading expert on the North Korean IT worker threat, says Chapman’s involvement followed a standard pattern—from an innocuous initial contact on LinkedIn to escalating requests. “Little by little, the asks get bigger and bigger,” he says. “Then by the end of the day, you��re asking the facilitator to go to a government facility to pick up an actual government ID.”
By the time investigators raided Chapman’s home, she was housing several dozen laptops, each with a sticky note indicating the fake worker’s identity and employer. Some of the North Korean operatives worked multiple jobs; some had been toiling quietly for years. Prosecutors said at least 300 employers had been pulled into this single scheme, including “a top-five national television network and media company, a premier Silicon Valley technology company, an aerospace and defense manufacturer, an iconic American car manufacturer, a high-end retail store, and one of the most recognizable media and entertainment companies in the world.” Chapman, they alleged, had helped pass along at least $17 million. She pleaded guilty in February 2025 to charges relating to wire fraud, identity theft, and money laundering and is awaiting sentencing.
Chapman’s case is just one of several North Korean fake-worker prosecutions making their way through US courts. A Ukrainian named Oleksandr Didenko has been accused of setting up a freelancing website to connect fake IT workers with stolen identities. Prosecutors say at least one worker was linked to Chapman’s laptop farm and that Didenko also has ties to operations in San Diego and Virginia. Didenko was arrested in Poland last year and was extradited to the United States. In Tennessee, 38-year-old Matthew Knoot is due to stand trial for his alleged role in a scheme that investigators say sent hundreds of thousands of dollars to accounts linked to North Korea via his laptop farm in Nashville. (Knoot has pleaded not guilty.) And in January 2025, Florida prosecutors filed charges against two American citizens, Erick Ntekereze Prince and Emanuel Ashtor, as well as a Mexican accomplice and two North Koreans. (None of the defendants’ lawyers in these cases responded to requests for comment.) The indictments claim that Prince and Ashtor had spent six years running a string of fake staffing companies that placed North Koreans in at least 64 businesses.
before the hermit kingdom had its laptop farms, it had a single confirmed internet connection, at least as far as the outside world could tell. As recently as 2010, that one link to the web was reserved for use by high-ranking officials. Then, in 2011, 27-year-old Kim Jong Un succeeded his father as the country’s dictator. Secretly educated in Switzerland and said to be an avid gamer, the younger Kim made IT a national priority. In 2012, he urged some schools to “pay special attention to intensifying their computer education” to create new possibilities for the government and military. Computer science is now on some high school curricula, while college students can take courses on information security, robotics, and engineering.
The most promising students are taught hacking techniques and foreign languages that can make them more effective operatives. Staff from government agencies including the Reconnaissance General Bureau— the nation’s clandestine intelligence service—recruit the highest-scoring graduates of top schools like Kim Chaek University of Technology (described by many as “the MIT of North Korea”) or the prestigious University of Sciences in Pyongsong. They are promised good wages and unfettered access to the internet—the real internet, not the intranet available to well-off North Koreans, which consists of a mere handful of heavily censored North Korean websites.
The earliest cyberattacks launched by Pyongyang were simple affairs: defacing websites with political messages or launching denial-of-service attacks to shut down US websites. They soon grew more audacious. In 2014, North Korean hackers famously stole and leaked confidential information from Sony’s film studio. Then they targeted financial institutions: Fraudulent trades pulled more than $81 million from the Bank of Bangladesh’s accounts at the New York Federal Reserve. After that, North Korean hackers moved into ransomware—the WannaCry attack in 2017 locked hundreds of thousands of Windows computers in 150 countries and demanded payments in bitcoin. While the amount of revenue the attack generated is up for debate—some say it earned just $140,000 in payouts—it wreaked much wider damage as companies worked to upgrade their systems and security, costing as much as $4 billion, according to one estimate.
Governments responded with more sanctions and stronger security measures, and the regime pivoted, dialing back on ransomware in favor of quieter schemes. It turns out these are also more lucrative: Today, the most valuable tool in North Korea’s cybercrime armory is cryptocurrency theft. In 2022, hackers stole more than $600 million worth of the cryptocurrency ether by attacking the blockchain game Axie Infinity; in February of this year, they robbed the Dubai-based crypto exchange Bybit of $1.5 billion worth of digital currency. The IT pretender scam, meanwhile, seems to have been growing slowly until the pandemic dramatically expanded the number of remote jobs, and Pyongyang saw the perfect opportunity.
In 2024, according to a recent report from South Korea’s National Intelligence Service, the number of people working in North Korea’s cyber divisions—which includes pretenders, crypto thieves, and military hackers—stood at 8,400, up from 6,800 two years earlier. Some of these workers are based in the country, but many are stationed overseas in China, Russia, Pakistan, or elsewhere. They are relatively well compensated, but their posting is hardly cushy.
Teams of 10 to 20 young men live and work out of a single apartment, sleeping four or five to a room and grinding up to 14 hours a day at weird hours to correspond with their remote job’s time zone. They have quotas of illicit earnings they are expected to meet. Their movements are tightly controlled, as are those of their relatives, who are effectively held hostage to prevent defections. “You don’t have any freedom,” says Hyun-Seung Lee, a North Korean defector who lives in Washington, DC, and says some of his old friends were part of such operations. “You’re not allowed to leave the apartment unless you need to purchase something, like grocery shopping, and that is arranged by the team leader. Two or three people must go together so there’s no opportunity for them to explore.”
The US government estimates that a typical team of pretenders can earn up to $3 million each year for Pyongyang. Experts say the money is pumped into everything from Kim Jong Un’s personal slush fund to the country’s nuclear weapons program. A few million dollars may seem small next to the flashy crypto heists— but with so many teams operating in obscurity, the fraud is effective precisely because it is so mundane.
in the summer of 2022, a major multinational company hired a remote engineer to work on website development. “He would dial in to meetings, he would participate in discussions,” an executive at the company told me on condition of anonymity. “His manager said he was considered the most productive member of the team.”
One day, his coworkers organized a surprise to celebrate his birthday. Colleagues gathered on a video call to congratulate him, only to be startled by his response—but it’s not my birthday. After nearly a year at the company, the worker had apparently forgotten the birth date listed in his records. It was enough to spark suspicion, and soon afterward the security team discovered that he was running remote access tools on his work computer, and he was let go. It was only later, when federal investigators discovered one of his pay stubs at Christina Chapman’s laptop farm in Arizona, that the company connected the dots and realized it had employed a foreign agent for nearly a year.
For many pretenders, the goal is simply to earn a good salary to send back to Pyongyang, not so much to steal money or data. “We’ve seen long-tail operations where they were going 10, 12, 18 months working in some of these organizations,” says Adam Meyers, a senior vice president for counter adversary operations at the security company CrowdStrike. Sometimes, though, North Korean operatives last just a few days— enough time to download huge amounts of company data or plant malicious software in a company’s systems before abruptly quitting. That code could alter financial data or manipulate security information. Or these seeds could lay dormant for months, even years.
“The potential risk from even one minute of access to systems is almost unlimited for an individual company,” says Declan Cummings, the head of engineering at software company Cinder. Experts say that attacks are ramping up not just in the US but also in Germany, France, Britain, Japan and other countries. They urge companies to do rigorous due diligence: speak directly to references, watch for candidates making sudden changes of address, use reputable online screening tools, and conduct a physical interview or in-person ID verification.
But none of these methods are foolproof, and AI tools are constantly weakening them. ChatGPT and the like give almost anyone the capacity to answer esoteric questions in real time with unearned confidence, and their fluency with coding threatens to make programming tests irrelevant. AI video filters and deepfakes can also add to the subterfuge.
At an onboarding call, for instance, many HR representatives now ask new employees to hold their ID up to the camera for closer inspection. “But the fraudsters have a neat trick there,” says Donal Greene, a biometrics expert at the online background check provider Certn. They take a green-colored card the exact shape and size of an identity card—a mini green screen—and, using deepfake technology, project the image of an ID onto it. “They can actually move it and show the reflection,” says Greene. “It’s very sophisticated.” North Korean agents have even been known to send look-alikes to pick up a physical ID card from an office or to take a drug test required by prospective employers.
Even security experts can be fooled. In July 2024, Knowbe4, a Florida-based company that offers security training, discovered that a new hire known as “Kyle” was actually a foreign agent. “He interviewed great,” says Brian Jack, KnowBe4’s chief information security officer. “He was on camera, his résumé was right, his background check cleared, his ID cleared verification. We didn’t have any reason to suspect this wasn’t a valid candidate.” But when his facilitator—the US-based individual giving him cover—tried to install malware on Kyle’s company computer, the security team caught on and shut him out.
Back in london, Simon Wijckmans couldn’t let go of the idea that somebody had tried to fool him. He’d just read about the Knowbe4 case, which deepened his suspicions. He conducted background checks and discovered that some of his candidates were definitely using stolen identities. And, he found, some of them were linked to known North Korean operations. So Wijckmans decided to wage a little counter exercise of his own, and he invited me to observe.
I dial in to Google Meet at 3 am Pacific time, tired and bleary. We deliberately picked this offensively early hour because it’s 6 am in Miami, where the candidate, “Harry,” claims to be.
Harry joins the call, looking pretty fresh-faced. He’s maybe in his late twenties, with short, straight, black hair. Everything about him seems deliberately nonspecific: He wears a plain black crewneck sweater and speaks into an off-brand headset. “I just woke up early today for this interview, no problem,” he says. “I know that working with UK hours is kind of a requirement, so I can get my working hours to yours, so no problem with it.”
So far, everything matches the hallmarks of a fake worker. Harry’s virtual background is one of the default options provided by Google Meet, and his connection is a touch slow. His English is good but heavily accented, even though he tells us he was born in New York and grew up in Brooklyn. Wijckmans starts with some typical interview questions, and Harry keeps glancing off to his right as he responds. He talks about various coding languages and name-drops the frameworks he’s familiar with. Wijckmans starts asking some deeper technical questions. Harry pauses. He looks confused. “Can I rejoin the meeting?” he asks. “I have a problem with my microphone.” Wijckman nods, and Harry disappears.
A couple of minutes pass, and I start to fret that we’ve scared him away, but then he pops back into the meeting. His connection isn’t much better, but his answers are clearer. Maybe he restarted his chatbot, or got a coworker to coach him. The call runs a few more minutes and we say goodbye.
Our next applicant calls himself “Nic.” On his résumé he’s got a link to a personal website, but this guy doesn’t look much like the profile photo on the site. This is his second interview with Wijckmans, and we are certain that he’s faking it: He’s one of the applicants who failed the background check after his first call, although he doesn’t know that.
Nic’s English is worse than Harry’s: When he’s asked what time it is, he tells us it’s “six and past” before correcting himself and saying “quarter to seven.” Where does he live? “I’m in Ohio for now,” he beams, like a kid who got something right in a pop quiz.
Several minutes in, though, his answers become nonsensical. Simon asks him a question about web security. “Political leaders ... government officials or the agencies responsible for border security,” Nic says. “They’re responsible for monitoring and also securing the borders, so we can employ the personnel to patrol the borders and also check the documents and enforce the immigration laws.”
I’m swapping messages with Wijckmans on the back channel we’ve set up when it dawns on us: Whatever AI bot Nic seems to be using must have misinterpreted a mention of “Border Gateway Protocol”—a system for sending traffic across the internet—with national borders, and started spewing verbiage about immigration enforcement. “What a waste of time,” Wijckmans messages me. We wrap up the conversation abruptly.
I try to put myself in the seat of a hiring manager or screener who’s under pressure. The fraudsters’ words may not have always made sense, but their test scores and résumés looked solid, and their technical-sounding guff might be enough to fool an uninformed recruiter. I suspect at least one of them could have made it to the next step in some unsuspecting company’s hiring process.
Wijckmans tells me he has a plan if he comes across another pretender. He has created a web page that looks like a standard coding assessment, which he’ll send to fake candidates. As soon as they hit the button to start the test, their browser will spawn dozens of pop-up pages that bounce around the screen, all of them featuring information on how to defect from North Korea. Then loud music plays—a rickroll, “The Star-Spangled Banner”—before the computer starts downloading random files and emits an ear-splitting beep. “Just a little payback,” he says.
Wijckman’s stunt is not going to stop the pretenders, of course. But maybe it will irritate them for a moment. Then they’ll get back to work, signing on from some hacking sweatshop in China or through a laptop farm in the US, and join the next team meeting—a quiet, camera-off chat with coworkers just like me or you.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Playing the devil's advocate on AI and generative art
As someone who has long been making and enjoying generative art ("generative" as in all kinds of computer generation), and has written lessons about how to write programmes that do it, I'm always regretful that the current AI discourse leans so heavily on the argument that images made by a computer cannot be art because they lack the human touch, or whatever.
Because generative art is a mature field and this is a well-trodden discourse! People have written and argued about it for decades, whether computer-generated imagery can be considered art, and whether beauty is in the form or in the perception, and so on.
Here's some generative art I've made - not a single pixel was placed directly by my hand, and it was all programmed with Processing / turtle libraries:
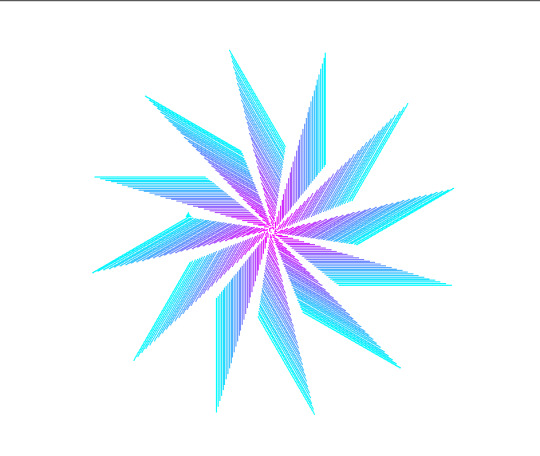



You might be tempted to point out that you can see my creative voice in the output. And you're right - I iteratively adjusted the code to make it produce an effect I liked. The results are, effectively, curated.
The only problem is...the above also describes the output of any generative AI. The AI user is choosing their prompts based on taste, refining their prompts if they don't like what they get, picking the best images for display. So now I have to ask, where does the difference lie? Is it in the time I spent programming the tools? What if I snagged the code from someone else and modified it to produce something I liked better? Is it that in your view, there's a clean divide between Tool and Input and because I made the Tool, that makes it art? Are fiber arts a kind of art, then, when the maker didn't invent the patterns but may have modified them for their purposes?
I think being an art critic or appreciator (two sides of the same coin) means revelling in non-answers. People aren't going to agree on whether this is art, whether it's beautiful, etc. and in my opinion that's fine, because beauty is a phenomenon. It emerges from the viewer's engagement with the piece. You can think something is not beautiful, and really it should not dictate what others think is beautiful.
So, I know the genie's out of the bottle and there's no take backs on cultural shifts, but I do wish people would focus on worker's rights, the use of human work without consent, and the environmental impacts of AI training data centres...not on whether we can categorically call everything made by a computer ugly.
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't really think they're like, as useful as people say, but there are genuine usecases I feel -- just not for the massive, public facing, plagiarism machine garbage fire ones. I don't work in enterprise, I work in game dev, so this goes off of what I have been told, but -- take a company like Oracle, for instance. Massive databases, massive codebases. People I know who work there have told me that their internally trained LLM is really good at parsing plain language questions about, say, where a function is, where a bit oif data is, etc., and outputing a legible answer. Yes, search machines can do this too, but if you've worked on massive datasets -- well, conventional search methods tend to perform rather poorly.
From people I know at Microsoft, there's an internal-use version of co-pilot weighted to favor internal MS answers that still will hallucinate, but it is also really good at explaining and parsing out code that has even the slightest of documentation, and can be good at reimplementing functions, or knowing where to call them, etc. I don't necessarily think this use of LLMs is great, but it *allegedly* works and I'm inclined to trust programmers on this subject (who are largely AI critical, at least wrt chatGPT and Midjourney etc), over "tech bros" who haven't programmed in years and are just execs.
I will say one thing that is consistent, and that I have actually witnessed myself; most working on enterprise code seem to indicate that LLMs are really good at writing boilerplate code (which isn't hard per se, bu t extremely tedious), and also really good at writing SQL queries. Which, that last one is fair. No one wants to write SQL queries.
To be clear, this isn't a defense of the "genAI" fad by any means. chatGPT is unreliable at best, and straight up making shit up at worst. Midjourney is stealing art and producing nonsense. Voice labs are undermining the rights of voice actors. But, as a programmer at least, I find the idea of how LLMs work to be quite interesting. They really are very advanced versions of old text parsers like you'd see in old games like ZORK, but instead of being tied to a prewritten lexicon, they can actually "understand" concepts.
I use "understand" in heavy quotes, but rather than being hardcoded to relate words to commands, they can connect input written in plain english (or other languages, but I'm sure it might struggle with some sufficiently different from english given that CompSci, even tech produced out of the west, is very english-centric) to concepts within a dataset and then tell you about the concepts it found in a way that's easy to parse and understand. The reason LLMs got hijacked by like, chatbots and such, is because the answers are so human-readable that, if you squint and turn your head, it almost looks like a human is talking to you.
I think that is conceptually rather interesting tech! Ofc, non LLM Machine Learning algos are also super useful and interesting - which is why I fight back against the use of the term AI. genAI is a little bit more accurate, but I like calling things what they are. AI is such an umbrella that includes things like machine learning algos that have existed for decades, and while I don't think MOST people are against those, I see people who see like, a machine learning tool from before the LLM craze (or someone using a different machine learning tool) and getting pushback as if they are doing genAI. To be clear, thats the fault of the marketing around LLMs and the tech bros pushing them, not the general public -- they were poorly educated, but on purpose by said PR lies.
Now, LLMs I think are way more limited in scope than tech CEOs want you to believe. They aren't the future of public internet searches (just look at google), or art creation, or serious research by any means. But, they're pretty good at searching large datasets (as long as there's no contradictory info), writing boilerplate functions, and SQL queries.
Honestly, if all they did was SQL queries, that'd be enough for me to be interested fuck that shit. (a little hyperbolic/sarcastic on that last part to be clear).
ur future nurse is using chapgpt to glide thru school u better take care of urself
154K notes
·
View notes
Text
How Vibe Coding Is Empowering a New Wave of Digital Creators
In an era where technology and creativity intersect more than ever, a new paradigm known as Vibe Coding is reshaping how people, especially non-programmers and junior developers, engage with software development. From AI-powered tools that assist in writing complex code to platforms enabling intuitive interaction with development environments, Vibe Coding is leading the charge in democratizing digital creation.
This movement is opening the doors for a broader, more diverse pool of creators to express ideas through code—without needing years of technical training.

The Rise of Vibe Coding in the Digital Age
What Is Vibe Coding?
Vibe Coding is a movement that merges intuitive design, creativity, and the power of artificial intelligence to simplify coding. It's not just about writing efficient algorithms; it's about empowering individuals—regardless of their technical background—to create, iterate, and build with digital confidence. By using AI coding tools for non-programmers, even those unfamiliar with traditional development methods can participate in building digital products.
Vibe Coding for Creative Programmers emphasizes fluid, flexible approaches to software creation. It favors accessibility and imagination over syntax memorization, making it a perfect match for today's digital creatives.
Why It's More Than Just Code
Unlike traditional programming, Vibe Coding treats code like a medium for artistic and functional expression. This new wave isn't just for professional developers. It's about giving musicians, artists, educators, and junior programmers the tools to build without the friction of a steep learning curve. AI coding for junior devs turns what once felt like an intimidating process into an approachable and even fun experience.
Vibe Coding aligns closely with how modern creators work—visually, intuitively, and interactively. The result? More inclusive tech spaces and a richer array of digital innovations.
AI Coding for Junior and Non-Programmers
Lowering the Barriers with AI
One of the most significant shifts in modern coding practices is the integration of AI as a creative and functional partner. For those who have never written a line of code, AI coding for non-programmers offers a powerful starting point. Through natural language processing and smart suggestions, AI systems can translate plain English into working code.
By using the best AI tool for coding, newcomers can now build simple applications, automate workflows, or create websites—tasks that once required expert knowledge. These tools are becoming the virtual training wheels for a new generation of creators.
Empowering Junior Devs with Vibe Coding
AI coding for junior programmers is especially impactful because it helps them learn while building. These systems act as an AI-powered coding assistant, offering real-time feedback, fixing errors, and even explaining concepts on the go. Instead of spending hours searching forums for help, junior developers can progress with confidence, learning through doing.
Vibe Coding provides junior devs with a sandbox where experimentation is encouraged, and failure is just part of the journey—not a blocker.

Creative Freedom Through AI Coding Tools
Unlocking Creativity for Non-Programmers
Creativity has always been at the heart of innovation. With AI coding tools for non-programmers, we are witnessing the rise of digital artists who build interactive experiences without needing to master a programming language. Tools now translate vision into code in real-time, allowing creators to bring their ideas to life faster and more effectively.
These platforms aren’t just technical—they’re inspirational. They provide templates, libraries, and smart guidance to support creativity, whether it's designing an interactive story, building a portfolio, or crafting a music app.
The Role of AI-Powered Coding Assistants
The best AI for coding doesn’t just write code—it collaborates. AI-powered coding assistants now help with:
Suggesting more efficient logic
Writing reusable functions
Identifying bugs before execution
Offering alternative approaches based on user goals
This revolution is critical in making development less about rote syntax and more about creative solutions. The best AI for coding becomes a partner in progress, guiding users to learn better practices while achieving their project goals.
AI Tools Leading the Charge
Click-Coder: Code Without Boundaries
Click-Coder is one of the standout tools revolutionizing Vibe Coding. Designed for both seasoned developers and absolute beginners, Click-Coder uses natural language input to generate real code that can be modified in real-time. Its intuitive drag-and-drop interface and AI engine remove the complexity of traditional coding, making it ideal for educational settings and design-first creators.
With features like project walkthroughs, live previews, and instant code explanations, Click-Coder transforms how we think about building digital products. It’s especially beneficial for junior devs who are still developing their problem-solving frameworks.
DeepPrompt and CodeMuse: Game Changers in AI Coding
DeepPrompt is another leading AI tool that uses deep learning to enhance coding workflows. With contextual understanding of your codebase, it provides suggestions that are both syntactically correct and contextually relevant—helping both beginners and experienced coders streamline their work.
CodeMuse focuses on creative coding projects. It helps artists and storytellers build interactive content using minimal technical knowledge. With pre-trained models and creative libraries, CodeMuse is tailored for those using code as a canvas.
Key Benefits of These AI Tools
Accessibility: No prior experience needed
Speed: Rapid prototyping and iteration
Support: Real-time suggestions and error correction
Education: In-line explanations help users learn as they build
Creativity: Encourage experimentation and innovation across disciplines
How Vibe Coding Is Transforming Tech Education
Coding as a Language of Creativity
Vibe Coding is not just about technical proficiency—it’s about storytelling, exploration, and personal expression through digital media. As educational systems adopt these AI tools, students are learning to see code as a medium for creativity rather than just a technical skill.
Schools and coding bootcamps now use AI coding for junior programmers to nurture problem-solving and critical thinking from an early stage. The focus has shifted from memorizing syntax to building meaningful projects that foster innovation.
Bridging the Gap Between Art and Tech
Historically, art and programming have been seen as separate domains. Vibe Coding is bridging that divide, allowing creators from all backgrounds to participate in tech. Whether you’re building generative art, designing user experiences, or composing digital music, AI-assisted tools ensure that coding doesn’t become a barrier to entry.
By blending design thinking, AI, and intuitive tools, Vibe Coding encourages a fusion of disciplines that’s essential for the future of technology.

FAQs
What is Vibe Coding, and how is it different from traditional coding?
Vibe Coding emphasizes creativity, ease of use, and accessibility. Unlike traditional coding, which often requires deep technical knowledge, Vibe Coding empowers users to build through intuitive interfaces and AI support.
Can non-programmers really build apps with AI coding tools?
Yes. Many AI coding tools for non-programmers allow users to create apps using simple natural language commands or visual interfaces, removing the need for extensive coding knowledge.
Is AI coding for junior devs a good way to learn programming?
Absolutely. AI-powered coding assistants help junior devs understand the logic behind code by offering real-time suggestions and explanations, making the learning curve much less steep.
Which is the best AI tool for coding right now?
While the best tool depends on your needs, Click-Coder is highly recommended for beginners and creative professionals. DeepPrompt and CodeMuse are also excellent for context-aware suggestions and creative coding respectively.
How does Vibe Coding fit into the future of education?
Vibe Coding supports project-based learning and encourages creative problem-solving. It’s already being integrated into tech education to help students build confidence and fluency in digital creation.
Conclusion
Vibe Coding is more than a trend—it’s a cultural and technological shift that redefines who gets to be a creator in the digital world. By leveraging AI coding tools for non-programmers and junior developers, it's unlocking the door to innovation for artists, storytellers, designers, and hobbyists. As tools like Click-Coder, Deep Prompt, and Code Muse continue to evolve, the future of coding looks more inclusive, more creative, and far more accessible than ever before. Whether you’re just starting your tech journey or looking to re imagine how you code, Vibe Coding offers a compelling, intuitive path forward.
0 notes
Text
Best AI Courses in India You Can Join Today— No Coding Needed

Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming a big part of our daily life. It is used in mobile phones, smart TVs, online shopping websites, digital assistants, and many apps. Because of this, many people now want to learn AI and build a career in this field.
But one question comes to mind – Do I need to learn coding to study AI?
The answer is No. There are many AI courses in India that you can join even if you don’t know how to code. These courses are made for beginners, students from non-technical backgrounds, working professionals, and even freshers.
In this blog, Digital Bano will tell you about some of the best AI courses in India that you can join without coding knowledge. You can study these courses online from your home. They are simple to understand and do not require a technical background. You just need basic computer knowledge and interest in learning.
Why Learn AI?
Here are some simple reasons to learn AI:
Good Career: Many companies are hiring AI professionals.
High Salary: AI jobs give good salary packages.
Growing Field: AI is the future. If you learn it now, your skills will be useful for many years.
No Coding Jobs Available: You can work in AI without being a software developer.
AI is not only for engineers or coders. It is also useful for students of commerce, arts, and even business owners. Today, people from different fields are learning how to use AI in their work and daily life.
What You Will Learn in AI Courses Without Coding
These courses are designed to teach you AI in a very simple way. Some things you will learn include:
What is AI and how it works
Real examples of AI in business, marketing, and daily life
AI tools like ChatGPT, Canva AI, and others
How to use AI for content writing, videos, presentations, and more
Projects and case studies (practical learning)
Ethics and rules of using AI
Some courses may also include basic data analysis, charts, or understanding patterns using simple drag-and-drop tools.
Best AI Courses in India – No Coding Needed
Let’s look at some of the top AI courses available in India for beginners.
1. AI For Everyone – by Andrew Ng (Coursera)
Mode: Online
Time: 6 to 8 hours
Fees: Free (you pay only if you want a certificate)
Good For: Students, business owners, job seekers
This is a simple course that explains what AI is, how it can help in business, and what it can and cannot do. No technical knowledge is needed. It is one of the best starting points.
2. Post Graduate Program in AI & ML – Simplilearn (in partnership with Purdue University)
Mode: Online
Time: 12 months
Fees: Around ₹1.5 to ₹2 Lakhs
Good For: Working professionals, graduates
This course is more advanced, but it also has tracks for non-programmers. You will learn AI tools and concepts used in real companies. The course is useful if you want to work in the corporate or IT industry.
3. AI in Business – Great Learning
Mode: Online
Time: 2 hours
Fees: Free
Good For: Business students, beginners, office workers
This course teaches how companies use AI in sales, marketing, and customer support. It is very easy to understand. It gives you an idea of how AI helps improve business decisions.
4. AI Tools and Platforms – Udemy
Mode: Online
Time: Self-paced (learn anytime)
Fees: Around ₹499 to ₹1,299
Good For: Content creators, marketers, beginners
In this course, you will learn how to use AI tools like Canva AI, ChatGPT, Pictory, and others for business, social media, and projects. You can use these tools to write content, make posters, edit videos, and more.
5. AI Bootcamp – Skill-Lync
Mode: Online
Time: 4 weeks
Fees: Around ₹2,000
Good For: Students, freshers
This course is for beginners. You will work on small projects and understand how AI works in simple ways. No coding is required. It is great for students who want to explore new skills.
Note: You Can Read Also These Blogs For More Information About Your Better Future:
Best courses after 12th
Captcha Typing Jobs
Courses After 12th Commerce
Jobs You Can Get After These Courses
After completing any of these courses, you can apply for roles like:
AI Product Manager
AI Content Writer
Prompt Engineer (write smart inputs for AI tools)
AI Business Analyst
Chatbot Designer
AI Marketing Specialist
Social Media Executive using AI tools
All of these jobs do not need programming knowledge. You need to be creative and understand how to use tools smartly. These jobs are available in digital marketing companies, media houses, IT firms, startups, and big brands.
Even freelancers and YouTubers are using AI to grow faster and work smarter.
Why AI Courses in India Are Growing Fast
Many Indian companies now use AI to save time and money
Schools and colleges have started teaching AI
AI tools are easy to use, even by non-technical people
Online learning has become common after COVID
Government is supporting AI learning programs
Now anyone with interest and the internet can learn AI from home. You don’t need to travel or attend a classroom.
Things to Remember Before Choosing a Course
Check if the course is for beginners
See if they give a certificate
Look at the reviews from other students
Choose a course that gives projects or hands-on learning
Try free courses if you are just starting out
Make sure the language of the course is easy for you to understand
Start with a short course. Once you are comfortable, you can move to advanced learning.
Final Words
AI is the future of technology. You can become a part of this future without being a coder. Many AI courses in India are now made for people who are new to the tech world. These courses are simple, affordable, and useful.
So if you are a student, fresher, or professional, now is the right time to learn AI. Pick a course that matches your interest, and start learning today.
0 notes
Text
Future Trends in Data Science: 2025 and Beyond
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, data science is becoming even more crucial in shaping business decisions and technological advancements. For those looking to build a career in this dynamic field, finding the best data science training in KPHB is the first step toward staying relevant in 2025 and beyond.
1. AI and Machine Learning Will Drive Innovation
One major trend is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in everyday applications.Data science solutions powered by artificial intelligence are revolutionizing industries from personalized shopping experiences to predictive healthcare. In 2025, we can expect even deeper integration of AI with automation, enabling real-time decision-making and self-learning systems.
2. Edge Computing Will Gain Momentum
The rise of edge computing is another emerging trend. Instead of sending data to centralized servers, edge computing allows data processing at the source—such as IoT devices—reducing latency and improving efficiency. This is especially vital in fields like autonomous driving and smart cities.
3. Data Ethics and Privacy Will Be Crucial
Data ethics and privacy are also becoming increasingly important. As data becomes more powerful, regulations like GDPR and India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act will push companies to prioritize ethical data usage, transparency, and user consent.
4. No-Code Tools Will Empower Non-Tech Users
No-code and low-code platforms are making data science more accessible. These tools empower non-programmers to perform complex data analysis, expanding the field’s reach across different roles and industries.
5. Interdisciplinary Skills Will Be in Demand
The need for interdisciplinary skills—combining domain expertise with data analytics—is shaping the modern data scientist’s role. Professionals who can bridge business understanding with technical knowledge will lead the next wave of innovation.
Start Your Journey with the Right Training
If you aspire to stay ahead in this evolving landscape, consider enrolling at SSSIT Computer Education, where our expert-led training equips you with the latest tools, techniques, and real-world projects to launch a successful career in data science.
#best data science training in hyderabad#best data science training in kukatpally#best data science training in KPHB#Best data science training institute in Hyderabad
0 notes
Text
first: i am a programmer. "having a machine execute my thoughts for me" is literally the point for me. i don't care about "laziness" when making art, whether via code, drawing software, or AI software. in fact, it's common in programmer culture to consider "laziness" a virtue because finishing the creative process in the least amount of steps possible is a rewarding experience in and of itself.
second: it is entirely possible to customize the output of an AI software by writing your own python code, by hooking up several AIs together, by fiddling with models and samplers and parameters, and so on. you can type a sentence into a box and click "generate" but this is the skill floor, not the ceiling.
third: can you explain how, by generating an image, i am "using an external tool and not exercising my self imagination and skills", but taking out my phone and pointing it out at a pretty sunset and pressing a single button to get a picture of a pretty sunset (you know, photography) is fine? what about tools like Visions of Chaos, which takes a (potentially dead simple) mathematical formula as input and produce fractals as output, without me making decisions about the result? (fractal art being an established form of art, mind you)
fourth: there are entire mediums and art movements about giving up your thoughts and letting an external process take over as a mean of self-expression. there is of course (non-AI) algorithmic art, which includes fractal art and procedural art. what about found objects and specifically marcel duchamp's readymades? can you tell me how marcel duchamp's fountain showed his "skill" and "expressed his thoughts and emotions" even though it is quite literally a piece of slop he didn't design at all, but took from a factory and signed?
fifth: your narrow definition of art was rejected by the entire dada movement over 100 years ago and keeps being rejected by conceptual artists, which is why if you go to a modern museum right now in 2025 you have a pretty good chance of seeing art that uses AI (example: the Centre Pompidou or the Museum of Modern Art), because the art world doesn't really care about "skill" and "laziness" and a lot of people, like them and me, just have a different definition of art than you do.
As gen-AI becomes more normalized (Chappell Roan encouraging it, grifters on the rise, young artists using it), I wanna express how I will never turn to it because it fundamentally bores me to my core. There is no reason for me to want to use gen-AI because I will never want to give up my autonomy in creating art. I never want to become reliant on an inhuman object for expression, least of all if that object is created and controlled by tech companies. I draw not because I want a drawing but because I love the process of drawing. So even in a future where everyone’s accepted it, I’m never gonna sway on this.
48K notes
·
View notes
Text
Create Manual and Automated Test Cases with Genqe

In the fast-paced world of software development, where release cycles are shrinking and quality expectations are growing, testing plays a pivotal role. To ensure applications are robust, scalable, and bug-free, both manual and automated testing are indispensable. However, managing these two streams efficiently — especially within the same environment — can be a daunting task for most QA teams.
This is where Genqe, a powerful AI-driven testing tool, makes a significant difference. Genqe allows teams to seamlessly create, manage, and execute both manual and automated test cases from a unified platform, all while reducing the time and effort traditionally required.
In this comprehensive article, we’ll explore how you can use Genqe to create effective manual and automated test cases, the unique features that make Genqe stand out, and best practices to elevate your QA strategy.
What Is Genqe?
Genqe is a next-generation test automation platform designed to simplify and accelerate the testing process. It offers a no-code interface, AI-powered test generation, and deep integrations with modern DevOps pipelines. Unlike many tools that specialize in only one form of testing (manual or automated), Genqe supports both — allowing QA teams to transition smoothly between manual exploration and automated verification.
Manual Test Cases in Genqe
Manual testing is still vital — especially during the initial stages of feature development, UX assessments, or when dealing with highly exploratory or one-off test scenarios.
Creating Manual Test Cases in Genqe
Here’s how you can use Genqe to write and manage manual test cases:
Intuitive Test Case Authoring Genqe provides a user-friendly interface to write test cases in a structured format:
Test Title
Preconditions
Test Steps
Expected Results
Priority and Tags
This makes it easy for testers, product managers, or even developers to document test scenarios clearly and consistently.
Test Step Reusability Reuse steps across different test cases. For example, a login sequence used in multiple flows can be saved as a reusable component, saving time and maintaining consistency.
Test Case Versioning Genqe automatically maintains a version history of test cases, so you can track changes, revert to previous versions, or audit the evolution of a test over time.
Team Collaboration With built-in commenting and status tracking, testers and developers can collaborate directly within the tool — making it easy to assign test cases, track execution status (e.g., Passed, Failed, Blocked), and link test cases to requirements or user stories.
Automated Test Cases in Genqe
Manual testing is great, but it doesn’t scale — especially when you need to validate core functionality across multiple environments or rapidly evolving UIs. That’s where Genqe’s automation capabilities shine.
1. No-Code Automated Test Creation
Genqe empowers even non-programmers to build robust automation using a visual, no-code interface. Testers simply interact with the web application (click, type, select), and Genqe records these actions as steps in a test case.
Each step can be customized with conditions, validations, and input data — making it easy to simulate real-world behavior without touching a line of code.
2. AI-Powered Test Generation
Genqe leverages artificial intelligence to scan your application’s UI and suggest tests automatically. This includes:
Form validations
Navigation checks
Button functionality
Input boundary tests
This not only accelerates the test writing process but also helps uncover edge cases that may be overlooked during manual planning.
3. Dynamic Data Injection
Automated tests in Genqe can be data-driven. You can inject dynamic values into test steps — like random emails, usernames, dates — or upload data sheets for broader test coverage.
This feature is especially useful for flows like sign-up, checkout, or search functionality, where variations in input play a critical role.
4. Robust Assertions and Validations
Genqe supports both visual and functional assertions:
Validate that specific text or elements appear on the page
Confirm successful navigations or redirects
Check field states (enabled, disabled, visible, hidden)
Compare screenshots for visual regression
These assertions are easily configurable and can be reused across different test cases.
5. Test Scheduling and CI/CD Integration
Automated tests can be scheduled to run:
At specific intervals (e.g., nightly, weekly)
On deployment triggers via integrations with CI/CD pipelines (GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab, etc.)
This ensures that test coverage remains up-to-date and regressions are caught early.
6. Cross-Browser and Device Testing
Genqe allows you to run tests across multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari) and devices (desktop, tablet, mobile). You can even test responsive layouts to ensure a consistent UX regardless of screen size.
Managing Both Manual and Automated Tests Together
One of Genqe’s biggest strengths is that it treats both manual and automated test cases as first-class citizens — allowing teams to manage, link, and report on both within a single platform.
Unified Test Management Dashboard
All test cases — manual or automated — can be filtered, searched, tagged, and grouped by feature, sprint, or release. This unified view helps teams:
Understand test coverage gaps
Identify redundant test cases
Track execution history
Assign test ownership
Transitioning from Manual to Automated
Genqe supports test case promotion, allowing teams to convert manual test cases into automated flows. For example, a manual login test can be turned into an automated test simply by replaying it with Genqe’s test recorder.
This enables incremental automation — you don’t have to automate everything at once, and you retain the flexibility to mix testing styles based on context.
Best Practices for Using Genqe for Manual & Automated Testing
✅ Write Clear, Descriptive Steps
Both manual and automated tests benefit from clarity. Use action verbs and specific conditions. For example:
“Click the ‘Submit’ button after entering a valid email address.”
✅ Use Tags and Components
Group your test cases using tags like Regression, Smoke, Login, etc. This helps in filtering, scheduling, and reporting.
✅ Reuse Test Steps
Modularize common steps (like authentication) and reuse them across multiple test cases to save time and ensure consistency.
✅ Link Tests to Requirements or Defects
Track traceability by linking test cases to user stories, bugs, or tasks — all directly within Genqe.
✅ Monitor Test Reports
Genqe offers detailed execution logs, screenshots, error traces, and performance metrics. Use these insights to debug issues quickly and improve test reliability.
Benefits of Using Genqe for Manual & Automated Testing
Unified Workflow: Manage all your test types from a single place.
Team Collaboration: Share, assign, and review tests with built-in roles and permissions.
No-Code Simplicity: Empower every stakeholder to contribute to quality.
AI Boost: Use smart test suggestions to accelerate coverage.
CI-Ready: Keep up with modern development workflows.
Final Thoughts
In today’s development lifecycle, where releases are frequent and product complexity is high, having an effective test strategy that includes both manual and automated testing is non-negotiable.
Genqe simplifies this strategy by offering a single, powerful platform to create, execute, and manage both types of test cases — without the usual complexity. Whether you’re writing exploratory manual tests, building automation without code, or scheduling cross-browser regression suites, Genqe has you covered.
If your QA process still feels fragmented, slow, or hard to scale — it’s time to embrace a smarter way.
Start building better manual and automated tests with Genqe today — and make quality everyone’s responsibility.
0 notes
Text
5 Essential AI Courses to Take in 2025 — No Matter Your Industry
Your fastest path to mastering AI skills that top companies are hiring for
AI Isn't Optional Anymore — It's the New Literacy

If there's one capability that will determine achievement in 2025 and beyond, it's artificial intelligence. No longer the exclusive province of Silicon Valley engineers, AI is now part of the everyday arsenal in marketing, education, finance, design, and healthcare.
A recent report from McKinsey estimates AI has the potential to inject more than $13 trillion into the economy by 2030. That's not a niche—it's a revolution. And those who know how to tap it will have a huge career advantage.
The best part? You don't require a computer science degree to get started. Nowadays, top AI education is a click away. The next five courses are some of the most prestigious and useful available, supported by giants like Google, Stanford, and DeepLearning.AI.
Google AI Essentials (Coursera) Best For: Complete beginners looking for a reliable, hands-on primer Google AI Essentials aims to equip you with a solid understanding of how AI works and how to apply it in your role, even if tech is not your background. It touches on practical uses of AI and even includes exercises to create your first AI-powered tools with Google's suite.
With a Google and Coursera certificate, this course is unique on a résumé and enables professionals to begin applying AI quickly in content writing, admin tasks, or data analysis.
AI For Everyone by Andrew Ng (Coursera) Best For: Entrepreneurs, managers, and non-technical teams Teased out by Coursera co-founder and former Google Brain boss Andrew Ng, a legendary in the field, the course is not about code but strategy for AI—how to think about the role of AI in business and society.
It’s perfect for decision-makers who want to speak the language of AI without writing a single line of code. You’ll learn how to identify which problems AI can solve, and how to build teams around those solutions.
Machine Learning Specialization (Stanford + DeepLearning.AI) Best For: Learners who want depth, and a Stanford-backed certificate If you're willing to dive deeper, this three-course specialisation—again taught by Andrew Ng—teaches the principles of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and ML engineering best practices.
This is one of the best-known ML programmes in the world and provides you with a solid grounding to transition into AI work or create your own projects. It's an essential if you're keen on the technical aspects.
Prompt Engineering for ChatGPT (DeepLearning.AI + OpenAI) Best For: Creators, marketers, copywriters, and researchers Prompt engineering is rapidly turning into the most sought-after AI skill. In this course, you learn how to effectively interact with large language models such as ChatGPT so you can obtain the most accurate and creative output.
You will discover how to frame prompts for various purposes—summarizing, content writing, programming assistance, and more. Whether you are writing articles, emails, code, or strategies, prompt mastery is a productivity shortcut to 10x.
AI Product Management (Duke University on Coursera) Ideal For: Future product managers and startup entrepreneurs AI isn't merely about creating tools—it's about creating the right tools. This Duke University course is designed to get you to market with AI-powered products.
You'll learn to design, test, and release AI systems with consideration for user requirements, data ethics, and risk. With case studies and frameworks from leading product leaders, it's ideal for professionals who want to drive AI innovation in their firm or startup.
Why These Courses Matter These aren't random YouTube tutorials. Each one is instructed by Stanford, Google, OpenAI, or top university experts. More significantly, they provide you with practical know-how that's applicable in almost every profession.
If you are a writer wanting to apply AI for quicker content generation or a manager seeking to revolutionize your company's process, these courses will make you AI-literate—quickly.
Final Thought AI is not just a passing trend—it’s the skill that will define career trajectories for the next decade. The sooner you get started, the further ahead you’ll be when everyone else starts catching up.
Choose one course today, block 30 minutes on your calendar, and start your journey. You’ll thank yourself in six months.
#ai revolution#learn ai#future careers#stanford courses#prompt engineering#ai education#career advice
1 note
·
View note
Text
Programmer here, in the pretty large tech division of a non-tech company. I'd say this is where the true believer holdouts remain
Management is still pushing hard for devs to adopt it-- not so they can lay us off, they claim, but so we can "automate easy tasks like unit tests" (if you don't know what a unit test is, it's like the safeguards that prevent life-ruining code from going out there. So that tells you how much management knows)
There's still quite a few people drinking the Kool-Aid. I think that they're seeing the benefit as "making things easier", because it shifts your brain from problem solving to information verification, and people are too willing to trust it.
My prediction for the next year is that we will start to see major data or security issues escape containment because of genAI code verified by genAI unit tests and overlooked in burnt-out code reviews (because surely having AI tools means we can do more work, right?!). The cracks will start to appear once the Kool-Aid drinkers realize they're spending more time fixing bugs than they'd be doing if they didn't use genAI in the first place.
I feel like the big push for AI is starting to flag. Even my relatively tech obsessed dad is kinda over it. What do you even use it for? Because you sure as hell dont want to use it for fact checking.
There's an advertisement featuring a woman surreptitiously asking her phone to provide her with discussion topics for her book club. And like... what. Is this the use case for commercial AI? This the best you could come up with? Lying to your friends about Moby Dick?
37K notes
·
View notes
Text
Generative AI Training in Pune: A 2025 Guide to the Future of Intelligent Learning
Generative AI is no longer just a buzzword—it's the future of technology, creativity, and automation. As industries worldwide rapidly adopt tools like ChatGPT, Midjourney, and AutoGPT, professionals and students alike are seeking to master these innovations. And when it comes to upskilling in India, Pune is quickly becoming a hub for cutting-edge AI education.
If you're searching for the most relevant, industry-ready Generative AI training in Pune, this 2025 guide is your roadmap to understanding what to look for, why Pune is a prime destination, and how one institution—the Boston Institute of Analytics—is leading the charge.
Why Pune Is Emerging as a Generative AI Education Hub?
Pune, known as the "Oxford of the East," has long been recognized for its thriving academic and tech ecosystem. In 2025, it’s also a hotbed for artificial intelligence research and innovation.
Here’s why:
1. Thriving IT and Startup Ecosystem
Home to major tech parks and over 5000 IT companies, Pune offers an ideal environment for Generative AI applications in automation, finance, healthcare, and marketing.
2. Academic and Research Excellence
With top universities and research institutions, Pune fosters a knowledge-driven culture that attracts learners from across India and abroad.
3. Strong Demand for AI Talent
Companies in Pune are increasingly investing in AI-driven transformation. From content generation to intelligent automation, the demand for skilled professionals in Generative AI is soaring.
What Is Generative AI and Why Is It Important in 2025?
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence models that can generate content—text, images, audio, video, and even code—based on prompts or training data. It includes technologies like:
Large Language Models (LLMs) – e.g., GPT-4, Claude, Gemini
Diffusion Models – used in tools like DALL·E, Midjourney
Agentic AI Systems – self-operating agents that complete tasks autonomously
Key Applications in 2025:
Automating marketing content and ad copy
AI-powered customer support
Code generation and debugging
Game development and 3D modeling
Business intelligence reporting
AI-based tutoring and content creation
As the world transitions toward AI-assisted productivity, Generative AI training in Pune is an essential step for both tech and non-tech professionals.
Who Should Enroll in a Generative AI Course in Pune?
The beauty of Generative AI is that it’s interdisciplinary—you don’t need to be a data scientist or a programmer to benefit. In fact, the best training programs in Pune cater to a wide range of learners:
Students and Freshers: Stand out in a competitive job market
Marketing and Design Professionals: Automate content, visuals, and workflows
Entrepreneurs: Build AI-driven products or services
IT Professionals and Developers: Integrate LLMs, APIs, and automation tools
Educators and Trainers: Use AI tools for course design, grading, and delivery
Features of a Good Generative AI Training Program
When choosing a Generative AI course in Pune, look for the following:
✅ Hands-On Projects
The best courses offer real-world projects such as chatbot development, AI-generated content platforms, or intelligent agents.
✅ Industry-Relevant Tools
Look for training that includes tools like:
ChatGPT & OpenAI APIs
Midjourney & DALL·E
LangChain & Pinecone
AutoGPT & Agentic AI systems
Google Gemini & Claude
✅ Certification & Portfolio Support
Reputable institutions provide globally recognized certifications and help you build a GitHub or portfolio showcasing your AI projects.
✅ Mentorship & Career Support
Courses that offer personalized mentorship, mock interviews, and job assistance give you a head-start in AI career roles.
Top Choice for Generative AI Training in Pune: Boston Institute of Analytics
Among the many options available, one name is setting benchmarks for Generative AI training in Pune—the Boston Institute of Analytics (BIA).
Why BIA?
With a presence in over 30 countries, BIA is globally respected for its AI, Data Science, and Business Analytics programs. In Pune, the institute offers one of the most comprehensive and career-focused Generative AI training programs.
What Makes BIA’s Pune Program Unique?
1. Industry Faculty
Courses are taught by AI professionals from global firms, not just academic trainers.
2. Live Projects with Impact
Work on actual client projects or simulations that replicate real workplace problems.
3. Affordable Pricing
Compared to other international programs, BIA offers top-tier training at a fraction of the cost—making it ideal for students and working professionals alike.
4. Community & Networking
Join a growing community of BIA alumni in Pune, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and beyond.
Career Opportunities After Generative AI Training
Completing a Generative AI course opens the door to a wide range of careers, including:
Generative AI Developer
Prompt Engineer
AI Product Manager
Automation Specialist
LLM Integration Engineer
AI Content Strategist
NLP Analyst
Conversational AI Designer
As organizations increasingly automate knowledge work, these roles will dominate recruitment drives in 2025 and beyond.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, Generative AI isn’t just a trend—it’s a revolution. And Pune, with its perfect mix of tech culture, educational legacy, and rising demand, is the ideal place to begin your journey.
If you’re looking to gain real skills, work on impactful projects, and get certified by a globally respected institute, then Boston Institute of Analytics is your best bet for Generative AI training in Pune.
#Generative AI course in Pune#Generative AI training in Pune#Agentic AI Course in Pune#Agentic AI Training in Pune
0 notes
Text
Top 5 AI Certifications That Are Actually Worth It in 2025
Published by Prism HRC – Leading IT Recruitment Agency in Mumbai
Let’s face it, in 2025, AI is not "nice to know." It’s everywhere. From chatbots and content marketing to finance and medicine, artificial intelligence is the force working behind the scenes. That also means employers are actively searching for professionals who understand AI or at least know how to work alongside it.
But with countless online courses out there, it’s tough to know which certifications actually carry weight. Which ones make your resume stand out to real hiring managers and recruiters?
We’ve curated the top five AI certifications that are genuinely worth your time, effort, and investment in 2025, whether you’re a fresher, a seasoned techie, or someone switching careers.

Google Professional Machine Learning Engineer
Why it’s worth it: This certification shows that you can design, develop, and deploy machine learning models on Google Cloud. It’s widely respected in the industry, especially if you’re eyeing cloud-based AI roles.
Who it’s for: Mid-level professionals, data scientists, ML engineers
What you'll learn:
Defining machine learning problems
Feature engineering
Model architecture and deployment
Tools like Vertex AI, BigQuery, and TensorFlow
Bonus tip: Just having Google’s name on your resume adds major credibility, especially if you're applying to MNCs or product companies.
IBM Applied AI Professional Certificate (via Coursera)
Why it’s worth it: This course is one of the most beginner-friendly yet hands-on AI certifications out there. It teaches you practical tools and includes real-world projects you can add to your portfolio.
Who it’s for: Freshers, career changers, and even non-programmers curious about AI
What you'll learn:
Foundations of AI
Python programming for AI
IBM Watson tools and services
How to build chatbots and deploy AI applications
Pro tip: The included labs and projects are great for showcasing your work on LinkedIn or GitHub.
Microsoft Certified: Azure AI Fundamentals
Why it’s worth it: A solid starting point for anyone looking to understand AI through the lens of Microsoft’s Azure platform. This course makes complex AI ideas approachable without diving into deep code.
Who it’s for: Newcomers, business analysts, marketers, and non-tech professionals exploring a switch to AI
What you'll learn:
Core machine learning and AI principles
Natural language processing, computer vision
Responsible AI practices
Use cases and tools in Azure
Why it stands out: If you’re applying to companies already using Microsoft tools, this certification puts you ahead of the pack.
Stanford Online: Machine Learning Specialization by Andrew Ng (on Coursera)
Why it’s worth it: Andrew Ng is a well-known name in the AI world, and his course has helped millions break into machine learning. The 2025 version is updated, relevant, and perfect for serious learners who want a deep understanding.
Who it’s for: Developers, tech enthusiasts, aspiring machine learning engineers
What you’ll learn:
Supervised learning and neural networks
Bias-variance tradeoff
Decision trees
Model evaluation and tuning
What makes it special: This isn’t just a theory-heavy course. It helps you understand how machine learning actually works, and that knowledge is rare and respected.

DeepLearning.AI’s Generative AI with LLMs Specialization
Why it’s worth it: Let’s be honest, generative AI is everywhere right now. Whether you’re playing with ChatGPT or building AI tools at work, this course puts you in sync with the future.
Who it’s for: Developers, content creators, product managers, and tech professionals working with AI APIs
What you’ll learn:
Prompt engineering strategies
How large language models function
Fine-tuning LLMs
Building ethically sound GenAI applications
Hot tip: If you're interviewing for product, content, or R&D roles related to AI, this certification will make you stand out.
Before you go
Let’s cut through the noise. There are tons of AI courses out there, but only a few actually help you grow. These five certifications offer real skills, portfolio projects, and recruiter-approved credibility.
If you’re planning to enter AI, grow in your current role, or shift from another domain, one of these certifications could be the best decision you make in 2025.
Still unsure which AI path is right for your career?
Prism HRC can help you make the smart move. We match skilled talent with companies hiring in AI, data, and cloud, and we know exactly what certifications employers are asking for right now.
Based in Gorai-2, Borivali West, Mumbai Website: www.prismhrc.com Instagram: @jobssimplified LinkedIn: Prism HRC
#AIcertifications#machinelearning#BCAjobs#techcareers2025#upskill2025#learnAI#BestITRecruitmentAgencyinMumbai#AIforbeginners#AIjobsindia#careertransitiontech#generativeAI#LLMcertifications#microsoftazure#ibmwatson
0 notes
Text




Document Control Number: USPTO 13/573,002 Art Unit: 2468
TITLE: The WORLD GAME (s) GREAT REDESIGN Document Control Number: USPTO 13/573,002 Art Unit: 2468
Patent Application Type: Adaptive procedural template
TITLE: The Heart Beacon Cycle Time - Space Meter
SUBTITLE: Adaptive Procedural Template framework, control grid / matrix telemetry, metrics, meters for the World Game's Great Redesign
USE CASE: Taffiff Trade Wars = Trade Reference Currency TRC = GDP pacing items statistical mean index Milton Friedman's K% rule #GDP pacing item index based economy #tariffs time - space calculation tool (s) IDMaps - SonarHops Distance Estimation Service / Trade of GDP Gross Domestic Product Economic Pacing Items
#tokens #blockchain #crypto #bitcoin #GDP #tokenization #commodity #RWA Real world Assets
THESIS: Foundation Technology trinity:
EPOCH (s) = Time intervals, cycles ex: Blockchain, AI dbase = TIME Chain
SPACE (ex: IRS memo #1421 "Bitcoin transaction akin to land acquisition"
SYNTAX: data elements mapped to symbols for A.I. / man - machine interface
THESIS: All artifacts internet, programmable net of money are formed using:
Epoch time cycle intervals ex: created by silicon microchip oscillations
Syntax parsed, processed during epoch time cycle intervals
All things internet, internet of money, blockchains (time chains) are formed with unicast, multicast, anycast protocols. workflow logic, procedures, process filters
BACKGROUND: an invention may be an improvement to an existing invention. USPTO 13/573,002's basis for invention is US Army CECOM Communication - Electronics Command's "Greatest Invention" a system of systems structured data digital dashboard geo-temporal - spatial synchronization, standardization program matching brevity codes to symbols, symbol sets critical for A.I. Artificial Intelligence man - machine interface used for OOTW Operations Other Than War: a German Army suggestion circa 2003. Supreme Court SCOTUS Alice in Wonderland Precedent: Packets, frames, layers, blocks, shards, graphs, hash graphs “bots”, “motes”, … or Satoshi's traversing the net, stored in a blockchain cube are abstractions, abstract ideas, terms. The afore mentioned terms are non-existent, fictitious, imaginary metaphorical fabrications are non - compliant with US Supreme Court SCOTUS Alice Corp Vs CLS Bank 2014 ruling “claims may not direct towards abstract ideas”. Physical is the opposite of abstract.
USE CASE: The main use case of the (technically non-existent) blockchain derived from the video game industry adapted to the cryptocurrency industry is about adding micropayments / microtransactions with the intent to add a pay by event / action / (token) transaction additional income stream / control grid layer of control. Source: https://intelligenteconomist.com/microtransactions/
Use Case: avoid duplication of DoD / NATO decades of work in concert with ISO, ITU, IEEE, DoD / NATO maps data element OPSCODE brevity codes, tokens to (Mil standard 2525C, D) symbols supporting A.I. man - machine interface for consensus, concurrence among an engineering system of federated, distributed systems PRECEDENT: BRICS / Eurasian Economic Union Commodity Basket backed currency / “new global reserve currency based on Real World Assets, commodities” “The matter of creating the international reserve currency based on the basket of currencies of our countries is under review” Source: Fintech Magazine
Nobel Prize winning Economist Milton Friedman “only a crisis brings real change”
USE CASE: Tariff space - time metrics, meters, calculation tool (s), algorithms
Milton Friedman (July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on analysis, monetary history and theory and the complexity of stabilization policy. Friedman promoted a macroeconomic viewpoint known as monetarism and argued that a steady, small expansion of the money supply was the preferred policy, compared to rapid, unexpected changes. See: Book: Capitalism and Freedom QUOTE: “Only a crisis - actual or perceived - produces real change. When that crisis occurs, the actions that are taken depend on the ideas that are lying around. That, I believe, is our basic function: to develop alternatives to existing policies, to keep them alive and available until the politically impossible becomes the politically inevitable.” Milton Friedman Nobel Prize winning Economist who described a GDP Gross Domestic Product commodity RWA Real World Asset based K% rule to monetize a currency, implement GDP based rules automated inflation control to manage the global economy.
USE CASE: Real World Assets commodity index backed stablecoin currency: commodity tokens / RWA Real World Assets index backed currency / algorithmic stable coin, tariff space - time calculation tool, DeFI / TradeFi algorithmically regulated programmable economy, control grid, permission access, price discovery derived from many stablecoin time (block) chains, that employ equilibrium algorithms (s) where stablecoin features, attributes: use of geo-spatial temporal event, activity intensity fencing to establish payment boundaries, geo-spatial areas of effect, geo-spatial temporal areas of support where a coin may have a set time limit based on time - stamp servers heartbeat, geo-spatial area of authorized use, select (federated) group of crowd funders, harvest, move crop commodities, goods backing the value of the coin from / to a given area's commons market, federation
The Terra TRC Trade Reference Currency is a global complementary currency designed to provide an inflation-resistant international standard of value; to stabilize the business cycle on a global level; and to realign stockholder’s interests with long-term sustainability. From a legal viewpoint, the Terra is standardized “countertrade” (international barter), which is routinely used for over one trillion dollars worth of transactions per year. Legislation on countertrade exists in about two hundred countries, including all the major trading nations. https://www.lietaer.com/2010/01/terra/ #currency #trade #commodities
French Money of Peace: Le Fédériste“ "L'Europa monnaie de la paix" January 1st 1933 QUOTE: "There is only one revolution tolerable to all men, all societies, all political systems: Revolution by design and invention". Richard Buckminster Fuller author of The World (Peace) (simulation) Game book, futurist, environmentalist: http://bfi.org
QUOTE: "Build a new model that makes the old model obsolete" Richard Buckminster Fuller Author of the book Our Spaceship Earth
QUOTE: "The world desperately needs a universal time chain (blockchain) with a distributed time-stamping server with globally recognized immutability to preserve digital truth." "A provable and immutable global time chain is urgently needed, not to replace human conscience but to protect and preserve it." The global economy has begun to degenerate from a relatively free form of capitalism into a digital feudal system,"
QUOTE: "Avoiding danger is no safer in the long run than outright exposure. The fearful are caught as often as the bold." The Yale Book of Quotations Helen Adams Keller (June 27, 1880 – June 1, 1968) deaf and blind author, activist and lecturer.
USPTO 13/573,002 CLAIMS
The object, purposes of the invention is based on the assertion: All internet, programmable internet of money artifacts, building blocks are formed using:
Epoch time cycle intervals created by silicon microchip oscillations, sound wave oscillations intrinsic of, foundation tech for quantum computing at room temperature
Syntax parsed, processed, transmitted during epoch time cycle intervals
All things internet, internet of money, blockchains (time chains) are formed by unicast, multicast, anycast protocols. Programmable money’s improvements are in cryptography for example, blockchains are formed like all things internet, internet of money through use of unicast, multicast, anycast of workflow filters... additionally, The method of claims rely on use of an adaptive procedural template’s tools, processes, procedures enabling micropayments / micro-transactions pay by event / action / (token) transaction income based on this invention’s object of claims
Method of claim 1 is to comply with Supreme Court SCOTUS US SC 573 US 134 2347 Alice Corp Vs CLS Bank ruling with use of a physical, non-abstract little league baseball tournament meme to describe, list steps, procedures, processes intrinsic to internet, internet of foundation technology framework adaptive procedural template to support for example: DeFi programmable money digital tokenized assets by providing system time epoch cycles, geospatial location survey points, workflow roles, rules, scoring system, rewards, penalties, rulings, schedules, event, alerts, sync deltas control grid, access, permission, price discovery, equilibrium algorithms (s) for DeFi, TradeFi based trade federations to establish for example, a one world government, economic, financial system of system’s universal unit of value, statistical mean value for many cryptocurrencies, commodities, currencies, stocks derived from price discovery algorithms which are then heartbeat message beacon broadcasted across time - space
Method of claim 2 relies on through use of an adaptive procedural template framework tools, procedures, processes to describe internet, internet of money, programmable money foundation technology, metrics, meters, SLA Service Level Agreements to form a syntax lexicon namespace derived from NATO / DoD brevity OPSCODE FFIRN, FFUDNS tokens structured data exchange mapped to symbols describing A.I. man – machine interface symbols, big data elements, sets, fields, to form a consistent, universal syntax structured data exchange library – lexicon using UTZ / UTC time stamped data with organization <Org_ID>. data class type, </URN Uniform Resource Name type to form a syntax, code, date element Rosetta Stone referred to in military discussions as The "Grail": i.e., synchronized, common, shared situational awareness data dashboard view (s) of time stamped, brevity code / tokens, digital assets that are filtered, prioritized from heartbeat message bus filtered, parsed, processed from a federated system of systems via use of heartbeat message event bus sync delta epoch data updates Universal Time Zone UTZ synchronized, stochastically harmonized updates using an improvement described by the University of Bologna / Hungary’s ,Chinese University’s firefly inspired heartbeat synchronization algorithm that matches, synchronizes stochastic harmonizes via firefly inspired heartbeat synchronization pulses intrinsic analogous to Network Centric Warfare’s Battlefield Digitization’s closest OPTEMPO Operational Tempos epoch time intervals, cycles i.e., 05, 10, 15, 30 micro, milli seconds, minutes, hours days, years posted to digital dashboards.
Method of claim 3 relies on the use of an adaptive procedural template tools, processes, procedures to provide an alternative to formal mergers and acquisitions for example, tether, untether to autonomous DAO Distributed Autonomous Organization i.e., trade federations using agile, adhoc NetOps supporting federations for example; Ripple's consensus protocol based on federation / federated on demand liquidity drawn from a distributed (global) (trade) federation i.e., 1907 Knickerbocker Banker's Crisis JP Morgan protocol on demand AI directed response - financial system revaluation where Battlefield Digitization Network effects: splits, joins, adds, drops are used as needed as a temporary alternative to formal merger and organization, corporate acquisitions
Method of claim 4 relies on the use of an adaptive procedural template processes, procedures to broadcast, unicast, anycast data synchronization deltas “sync deltas” via micro to macro-cycle system of systems data updates at agreed upon times observing set durations of events, time, temporal epoch leases, price discover algorithms i.e., tariff space - time metrics, meters, data harvests for example stocks, commodity real world digital assets, currency arbitrage trade exchange adjustments using heartbeat epoch time beacon’s intrinsic temporally consistent, synchronized, time bounded i.,e heartbeat start, stop, TTL Time to Live epochs providing discrete time interval start, stop, TTL Time To Live epoch windows embedded in </108> system heartbeats, messages in a control matrix among for example HFT stock market systems participating to establish algorithmic regulation via use of algorithmic price discovery, Nash Equilibrium algorithms to derive a uniform, universal statistical mean value index, discrete, time bounded trade windows, stock trade circuit breaker via heartbeat beacon message, event bus broadcasted , uni, multicast among many stock, commodity, ETF Exchange Traded Fund systems
Method of claim 5 relies on the use of the adaptive procedural template’s firefly inspired heartbeat synchronization message event bus algorithm – protocol, software application neutral monitors geo-spatial, temporally distributed events reported across a DAO Distributed Autonomous Organization among federated groups synchronized across time-space to achieve common, synchronized goals in conjunction with use of adaptive procedural template list items that are intrinsic to algorithms / protocols such as Princeton’s John Nash Equilibrium algorithms and count minimum sketch or streaming K algorithms algorithmically regulating through use of epoch time intervals for HFT stock, commodity, digital token, tokenized RWA Real World Assets, cryptocurrency trade, arbitrage micro transaction epoch temporal time windows in federated systems supporting economic, fiscal control grid matrix among a federated system of systems Method of claim 6 relies on the use of an adaptive procedural template framework to establish, support, maintain economist Milton Friedman’s K% rule where a Central Bank Digital Currency CBDC. stablecoin or conventional FIAT, commodity index backed currency is derived from sampling lead GDP Gross Domestic Product economic indicators among a global event message bus sync delta data, event changes updating for example, a RWA Real World Asset based commodity index backed collective, consistent value unit based currency via use of filtered, stochastically harmonized, temporally synchronized telemetry polled from a universal event bus applying firefly-heartbeat algorithm events, state changes leveraging heartbeat message - event functions to update a statistical mean value index as a standard, consistent unit of value using algorithmic price discovery heartbeat beacon broadcasted among many systems
Method of claim 7 relies on the use of an adaptive procedural template’s tools, processes, procedures, algorithms to derive from price discovery algorithm from Real World Assets a commodity index backed algorithmic stablecoin comprised of: commodity tokens / RWA Real World Assets index where algorithmic price discovery is derived from many stablecoin time (block) chains, that employ equilibrium algorithms (s) where a stablecoin may include attributes, processes, procedures: i.e., use of geo-spatial temporal event, activity intensity fencing to establish payment boundaries, geo-spatial areas of effect, geo-spatial temporal areas of support where a coin may have a set time limit based on time - stamp servers heartbeat, geo-spatial area of authorized use, select (federated) group of crowd funders, harvest, move crop commodities, goods backing the value of the coin from / to a given area's commons market, federation for example, a trade federation supported by Economist Bernard Lietaer’s TRC Trade Reference Currency: TERRA RWA Real World Assets, commodities, commodity basket , index based featuring demurrage fees, charges to support supplier to consumer logistics transfer, travel of for example GDP Gross Domestic Product pacing items as a global complementary currency designed to provide an inflation-resistant international standard of value; to stabilize the business cycle on a global level; and to realign stockholder’s interests with long-term sustainability, management of trade tariffs
Method of claim 8 relies on referencing an adaptive procedural template to establish, maintain trade tariffs SLA Service Level Agreements i.e., ecologically sustainable economic econometric epoch time cycles supporting universal standard measures, meters, metrics sync delta cyclic update temporal change, linear sequential, geo-spatial temporal intensity radius hop count metrics and meters where closer is shorter, closer is cheaper, given less CO2 carbon dioxide credits are used given less trade demurrage fees levied as a method of climate control agreed upon by a trade federation (s)
Method of claim 9 relies on the use of an adaptive procedural template’s tools, processes, procedures to establish, maintain a global system of systems telemetry data synchronization, stochastic harmonization, based on sound - light waveform based quantum computing to establish for example, temporal speed limits, discrete time intervals to derive, provide systemic metrics, meters, synchronization, stochastic harmonization among many system of systems Distributed Autonomous Systems DAS
Method of claim 10 relies on the use of adaptive procedural template tools, processes, procedures, algorithms and specifically sound waves (see water drop in pond meme, graphic) to measure trough, crest wave cycles that when statistically sampled represent a digital approximation of physical waves as the basis for establishing common, shared, universal method and means to measure, meter, communicate telemetry across a plurality of quantum computing system of systems using a system (s) for example: comprised of curved electrodes to concentrate sound waves similar to a magnifying lens to focus a point of light at room temperature rather than use of liquid hydrogen to cool a space for quantum particles event sampling with electron microscopes
Method of claim 11 relies on the use of an adaptive procedural template framework’s tools, processes, procedures, algorithms to apply the electric dipole effect electric meters, metrics where closer is cheaper given less infrastructure needed given energy attenuates over distances • data over energy link where energy pulses as a method and means to transmit data / electricity via wired, and wireless air – ground pathways as demonstrated by inventor, scientist Nicola Telsa circa 1900 near Colorado Springs CO
Metaphorical blockchain’s = timechain actual foundation tech, net of $ building blocks
0 notes
Text
Programming
Programming: The Language of the Digital Age
Programming is the backbone of the digital world. It’s the process of writing instructions that computers follow to perform specific tasks. From mobile apps and websites to artificial intelligence and space technology, programming drives innovation in nearly every field.
At its core, programming is about problem-solving. Programmers use languages like Python, JavaScript, Java, and C++ to create solutions that automate tasks, process data, and build interactive systems. Each language has its strengths — Python is popular for its simplicity and is widely used in AI and data science, while JavaScript powers the web.
Learning to program develops logical thinking, creativity, and attention to detail. It encourages a mindset of experimentation and continuous learning, as technologies constantly evolve. Today, with the rise of user-friendly tools and online platforms, programming is more accessible than ever — even beginners can build applications or automate tasks without a formal computer science background.
In the job market, programming is a highly sought-after skill. Software development, data analysis, cybersecurity, and game design all rely on coding expertise. Additionally, non-technical roles in marketing, business, and education increasingly benefit from basic programming knowledge.
Beyond careers, programming empowers individuals to create. Whether it’s building a personal blog, developing a game, or contributing to open-source projects, coding gives people the tools to bring ideas to life.
As the world becomes more digitized, programming is not just a technical skill — it’s a form of digital literacy. It enables people to understand and shape the technologies that influence our lives. Whether you’re writing your first “Hello, World!” or building complex systems, programming offers endless opportunities to learn, build, and innovate.
In short, programming is more than code — it’s the language of creation in the 21st century.
0 notes
Text
Python for Everyone: From Students to Professionals
Python has evolved into more than just a programming language—it's a bridge between ideas and innovation. In 2025, Python remains the go-to language for beginners, experienced developers, researchers, and even non-programmers. Its readability, simplicity, and vast ecosystem make it a perfect fit for anyone looking to solve problems through code. Whether you're a student exploring your first line of code or a professional seeking career growth, Python opens doors across industries.
Why Python Appeals to Everyone
Beginner-Friendly and Easy to Learn
Python’s syntax is simple and mirrors everyday English, making it beginner-friendly and easy to understand. Unlike many other programming languages that require steep learning curves, Python makes it possible to write meaningful code within hours of learning. For students, this lowers the barrier to entry. You can grasp concepts like loops, functions, and data structures without getting overwhelmed. Professionals from non-technical backgrounds also find it easier to automate tasks or perform data analysis using Python.
Highly Versatile
Python isn’t tied to one niche. It powers websites, analyzes massive data sets, drives artificial intelligence models, automates business processes, and much more.
Web developers use Django or Flask.
Data scientists rely on Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib.
AI engineers build models using TensorFlow or PyTorch.
Finance professionals automate reports with Python scripts.
Educators use Python to teach logic and problem-solving.
Whatever your field, Python has tools to support your goals.
A Language with Real-World Applications
Python’s applications are not just theoretical. It's used in mission-critical environments by top companies like Google, Netflix, NASA, and Microsoft. For students, this means that the skills you learn today are directly applicable in the workplace. For professionals, Python adds value by automating tasks, improving productivity, and enabling innovation.
Thriving Community and Abundant Resources
Python boasts one of the largest programming communities in the world. From open-source contributions and discussion forums to YouTube tutorials and university-level courses, learners at all stages have access to guidance, support, and updates. Need help fixing a bug?Curious about how to build a machine learning model? The answer is often just a search away.
How Students Benefit from Learning Python
Improves logical thinking and problem-solving skills
Encourages project-based learning through simple games or calculators
Prepares students for college and career opportunities
Python is commonly used in academic disciplines like mathematics, biology, and economics.
Python is even being introduced in schools as part of STEM education, making it an early gateway to technology and innovation.
How Professionals Use Python to Advance Their Careers
Professionals in finance, marketing, HR, and engineering are all leveraging Python to:
Automate routine tasks like report generation or data entry
Analyze and visualize business data for better decision-making
Create internal tools for managing workflows
Venture into high-demand areas like data science and AI to unlock new opportunities.
Adding Python to your skillset boosts your resume, helps in career transitions, and enables you to take on more complex roles.
Getting Started the Right Way
While there are many online tutorials and self-study options, structured learning offers a faster and more focused path. Enrolling in a python training course in Ahmedabad gives you access to a planned curriculum, guided mentorship, and real-time feedback—all critical for mastering the language. Choosing the right python training institute in Ahmedabad ensures you're learning not just syntax, but also best practices, project development, and real-world applications. Many institutes also offer placement support, helping you transition into a tech career smoothly.
Python is truly for everyone. It empowers students to learn the logic behind technology and equips professionals to solve real-world problems creatively. Its simplicity combined with robust capabilities makes it the most inclusive language of our time. Whether you're starting fresh or upskilling for the future, Python is a smart investment in your personal and professional growth. With the right mindset and the right training, your Python journey in 2025 can take you places you never imagined.
0 notes