#Armstrong number Program in Python
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Python: 100 Simple Codes

Python: 100 Simple Codes
Beginner-friendly collection of easy-to-understand Python examples.

Each code snippet is designed to help you learn programming concepts step by step, from basic syntax to simple projects. Perfect for students, self-learners, and anyone who wants to practice Python in a fun and practical way.
Codes:
1. Print Hello World
2. Add Two Numbers
3. Check Even or Odd
4. Find Maximum of Two Numbers
5. Simple Calculator
6. Swap Two Variables
7. Check Positive, Negative or Zero
8. Factorial Using Loop
9. Fibonacci Sequence
10. Check Prime Number
===
11. Sum of Numbers in a List
12. Find the Largest Number in a List
13. Count Characters in a String
14. Reverse a String
15. Check Palindrome
16. Generate Random Number
17. Simple While Loop
18. Print Multiplication Table
19. Convert Celsius to Fahrenheit
20. Check Leap Year
===
21. Find GCD (Greatest Common Divisor)
22. Find LCM (Least Common Multiple)
23. Check Armstrong Number
24. Calculate Power (Exponent)
25. Find ASCII Value
26. Convert Decimal to Binary
27. Convert Binary to Decimal
28. Find Square Root
29. Simple Function
30. Function with Parameters
===
31. Function with Default Parameter
32. Return Multiple Values from Function
33. List Comprehension
34. Filter Even Numbers from List
35. Simple Dictionary
36. Loop Through Dictionary
37. Check if Key Exists in Dictionary
38. Use Set to Remove Duplicates
39. Sort a List
40. Sort List in Descending Order
===
41. Create a Tuple
42. Loop Through a Tuple
43. Unpack a Tuple
44. Find Length of a List
45. Append to List
46. Remove from List
47. Pop Last Item from List
48. Use range() in Loop
49. Use break in Loop
50. Use continue in Loop
===
51. Check if List is Empty
52. Join List into String
53. Split String into List
54. Use enumerate() in Loop
55. Nested Loop
56. Simple Class Example
57. Class Inheritance
58. Read Input from User
59. Try-Except for Error Handling
60. Raise Custom Error
===
61. Lambda Function
62. Map Function
63. Filter Function
64. Reduce Function
65. Zip Two Lists
66. List to Dictionary
67. Reverse a List
68. Sort List of Tuples by Second Value
69. Flatten Nested List
70. Count Occurrences in List
===
71. Check All Elements with all()
72. Check Any Element with any()
73. Find Index in List
74. Convert List to Set
75. Find Intersection of Sets
76. Find Union of Sets
77. Find Difference of Sets
78. Check Subset
79. Check Superset
80. Loop with Else Clause
===
81. Use pass Statement
82. Use del to Delete Item
83. Check Type of Variable
84. Format String with f-string
85. Simple List Slicing
86. Nested If Statement
87. Global Variable
88. Check if String Contains Substring
89. Count Characters in Dictionary
90. Create 2D List
===
91. Check if List Contains Item
92. Reverse a Number
93. Sum of Digits
94. Check Perfect Number
95. Simple Countdown
96. Print Pattern with Stars
97. Check if String is Digit
98. Check if All Letters Are Uppercase
99. Simple Timer with Sleep
100. Basic File Write and Read
===
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Armstrong Number in Python
Summary: Discover the concept of Armstrong Numbers in Python, their unique properties, and how to implement a program to check them. Learn about basic and optimised approaches for efficient computation.

Introduction
In this article, we explore the concept of an Armstrong Number in Python. An Armstrong number, also known as a narcissistic number, is a number that equals the sum of its own digits, each raised to the power of the number of digits.
These numbers are significant in both programming and mathematical calculations for understanding number properties and algorithmic efficiency. Our objective is to explain what an Armstrong number is and demonstrate how to implement a program to check for Armstrong numbers using Python, providing clear examples and practical insights.
Read: Explaining Jupyter Notebook in Python.
What is an Armstrong Number?
An Armstrong number, also known as a narcissistic number, is a particular type of number in which the sum of its digits, each raised to the power of the number of digits, equals the number itself. This property makes Armstrong numbers unique and exciting in mathematics and programming.
Definition of an Armstrong Number
An Armstrong number is defined as a number equal to the sum of its digits; each raised to the power of the total number of digits. For example, if a number has 𝑛 digits, each digit d is raised to the 𝑛th power and the sum of these values results in the original number.
Explanation with a Simple Example
Consider the number 153. It has three digits, so we raise each digit to the third power and sum them:
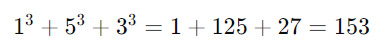
Since the result equals the original number, 153 is an Armstrong number. Another example is 370:

Difference Between Armstrong Numbers and Other Numerical Concepts
Armstrong numbers are distinct because they involve the specific property of digit manipulation. Unlike prime numbers, which are based on divisibility, or perfect numbers, which relate to the sum of divisors, Armstrong numbers focus solely on digit power sums. This unique characteristic sets them apart from other numerical concepts in mathematics.
How to Determine an Armstrong Number?
To determine whether a number is an Armstrong number, we need to verify if the sum of its digits, each raised to the power of the number of digits, equals the number itself. This concept may seem complex at first, but with a clear understanding of the process, it becomes straightforward.
Let's break down the steps and explore the mathematical method used to identify Armstrong numbers.
Mathematical Formula
The formula to check if a number is an Armstrong number is:

Here, d1,d2,…,dm represent the digits of the number, and 𝑛 is the total number of digits.
Step-by-Step Breakdown
Determine the Number of Digits: First, find the total number of digits, nnn, in the given number. This is crucial as each digit will be raised to the power of nnn.
Extract Each Digit: Extract each digit of the number. This can be done using mathematical operations like modulus and division.
Raise Each Digit to the Power of nnn: For each digit, calculate its power by raising it to nnn.
Sum the Powered Digits: Add the results of the previous step together to get the sum.
Compare the Sum with the Original Number: Finally, compare the sum with the original number. If they are equal, the number is an Armstrong number.
Example Calculation
Let's determine if 153 is an Armstrong number:
Number of digits (n): 3
Extracted digits: 1, 5, 3
Raised to the power of n:
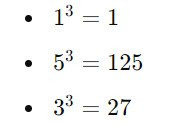
Sum of powered digits: 1+125+27=1531
Comparison: The sum, 153, equals the original number, confirming that 153 is an Armstrong number.
This systematic approach helps in accurately identifying Armstrong numbers, making the concept both interesting and accessible.
Also Check: Data Abstraction and Encapsulation in Python Explained.
Armstrong Number Algorithm

An Armstrong number, also known as a narcissistic number, is a number that is equal to the sum of its own digits each raised to the power of the number of digits. To determine if a number is an Armstrong number, we follow a specific algorithm.
This section outlines the steps involved and discusses the efficiency and complexity of the algorithm.
Outline of the Algorithm
To check if a number is an Armstrong number, follow these steps:
Determine the Number of Digits:
First, calculate the number of digits (n) in the given number. This step helps in raising each digit to the appropriate power.
Calculate the Sum of Digits Raised to the Power of n:
For each digit in the number, raise it to the power of n and sum these values. This step involves iterating through each digit, performing the power operation, and accumulating the results.
Compare the Sum with the Original Number:
Finally, compare the calculated sum with the original number. If they are equal, the number is an Armstrong number.
Key Steps in the Algorithm
Extracting Digits: We extract each digit from the number, which can be done using modulus and division operations.
Power Calculation: Raise each extracted digit to the power of the total number of digits.
Summation: Accumulate the results of the power calculations to form the total sum.
Comparison: Compare the accumulated sum with the original number to determine if it is an Armstrong number.
Efficiency and Complexity
The Armstrong number algorithm is efficient for small to moderately sized numbers. The primary operations involve basic arithmetic, such as modulus, division, and exponentiation, making the algorithm computationally light. The time complexity is O(d), where d is the number of digits in the number.
This is because the algorithm processes each digit exactly once. For large numbers, the time complexity may increase, but it remains manageable due to the simplicity of the calculations involved.
Implementing Armstrong Number in Python
To determine whether a number is an Armstrong number, we need to implement a straightforward approach in Python. Armstrong numbers, also known as narcissistic numbers, are numbers that equal the sum of their own digits each raised to the power of the number of digits.
Here, we’ll explore a basic implementation in Python and discuss how to optimise it for better performance.
Basic Implementation
Let’s start with a simple Python program to check if a number is an Armstrong number:

Explanation of the Code:
Function Definition: The function is_armstrong_number takes an integer number as its parameter.
Convert Number to String: We convert the number to a string using str(number) to easily access each digit.
Count Digits: We determine the number of digits using len(digits).
Initialise Sum Variable: We initialise sum_of_powers to zero to accumulate the sum of each digit raised to the power of num_digits.
Calculate Sum of Powers: We loop through each digit in the string, convert it back to an integer, raise it to the power of num_digits, and add it to sum_of_powers.
Check Armstrong Condition: Finally, we compare sum_of_powers with the original number to determine if it is an Armstrong number.
Optimised Approach
While the basic implementation is easy to understand, it may not be the most efficient for larger numbers. Here are some optimisations:
Use List Comprehension: Python’s list comprehension can make the code more concise. Here’s an optimised version:
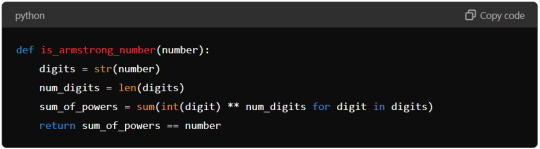
This version uses a single line to calculate sum_of_powers using list comprehension, making the code more compact and potentially faster.
2. Precompute Powers: For very large numbers, precomputing powers for digits (0 through 9) and reusing them can reduce computation time.
3. Avoid String Conversion: If working with extremely large numbers, you might want to avoid converting numbers to strings repeatedly. However, this is a trade-off between readability and performance.
By employing these optimisations, you can enhance the efficiency of the Armstrong number checking algorithm, especially for larger inputs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Armstrong Number in Python?
An Armstrong Number in Python is a number that equals the sum of its digits each raised to the power of the number of digits. For example, 153 is an Armstrong Number because 1^3+5^3+3^3=153.
How can I check for an Armstrong Number in Python?
To check for an Armstrong Number in Python, calculate the sum of each digit raised to the power of the total number of digits. If this sum equals the original number, it’s an Armstrong Number.
What is the efficiency of the Armstrong Number algorithm in Python?
The Armstrong Number algorithm in Python is efficient for small to moderate numbers with a time complexity of O(d), where d is the number of digits. The primary operations include basic arithmetic and exponentiation.
Further See: Understanding NumPy Library in Python.
Conclusion
In this article, we've explored Armstrong Numbers in Python, highlighting their unique property of being equal to the sum of their digits raised to their respective powers. We demonstrated how to implement and optimise a Python program to check for Armstrong Numbers. Understanding this concept and its implementation enhances both mathematical knowledge and programming skills.
0 notes
Video
youtube
Arm Strong number program java.mp4
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
Python - Chat GPT + Python Programming - Armstrong Number
#youtube#Python - Chat GPT + Python Programming - Armstrong Number పైథాన్ - చాట్ GPT + పైథాన్ ప్రోగ్రామింగ్ - ఆర్మ్స్ట్రాంగ్ నంబర్
0 notes
Text
डाटा साइंस
डाटा साइंस आज के समय में डाटा ही धन है क्योंकि आजकल हम सुबह से लेकर सोने तक डेटा का उपयोग करते हैं आप जिस मोबाइल का उपयोग करते हैं उसमें केवल डाटा ही तो है हर व्यक्ति गूगल सर्च के माध्यम से डाटा ही तो प्राप्त करता है इस प्रकार से डाटा धन से भी ज्यादा मूल्यवान हो चुका है हम 1 मिनट भी मोबाइल फोन लैपटॉप के बिना नहीं रह सकते क्योंकि इन चीजों पर हम पूरी तरह से निर्भर हो चुके हैं अब इनके बिना जीवन की…

View On WordPress
#a python program example#python program advanced#python program algorithm#python program and solution#python program answers#python program application#python program ask in interview#python program challenges#python program class 11#python program class 12#python program code#python program course#python program for factorial of a number#python program for prime number#python program to add two numbers#python program to check armstrong number#python programmer#python programming#python programming b tech#python programming for beginners#python programming in hindi#python programming language#python programming tutorial
0 notes
Link
Armstrong number Program in Python
Using modulus operator and if statement you can write this code. And remaining concept are apply same like C programming only change syntax.
0 notes
Photo






1969
On July 20, one of man’s crowning achievements occurred when American astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on the moon, and uttered the immortal words “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.” The opposition to the war continued to increase with more and more attending anti-war demonstrations and demanding that the U.S. withdrew from Vietnam. The music came from artists such as the Doors, Led Zeppelin, Janis Joplin, and the Beatles. The most famous music festival of modern times, Woodstock, took place on a New York farm on August 15-18, with more than 400,000 avid music fans attending to see the Who, Jimi Hendrix, Crosby, Stills & Nash and others perform live. Fashions reflected the anti-war sentiment with military jackets adorned with peace signs, and trends such as long, unkempt wild hair and headbands showed the feelings of anti-establishment experienced by the youth.
Major events
• The first man is landed on the moon on the Apollo 11 mission by the United States. Neil Armstrong and Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin became the first humans to set foot on the moon.
• The second manned moon mission, Apollo 12, successfully launches and lands on the moon.
• The Isle of Wight Festival attracts an audience of approximately 150,000 people; the Atlanta International Pop Festival attracts 100,000; and Woodstock attracts more than 350,000.
• The Beatles record Abbey Road, their final album together.
• The first communications are sent through the ARPANET on October 29, 1969.
• The U.S. Air Force closes its Blue Book Project, concluding that there is no evidence of UFOs.
• 250,000 people march on Washington in protest against the Vietnam War.
• The RMS Queen Elizabeth II enters service.
• Golda Meir becomes Prime Minister of Israel.
• Robin Knox-Johnston becomes the first person to sail around the world solo without stopping.
• The U.S. institutes the draft lottery to determine draft into U.S. forces for Vietnam War.
• The very first U.S. troop withdrawals are made from Vietnam.
• The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is established.
• On June 28, the police raids Stonewall Inn, a gay club located in New York City, inciting the Stonewall Riots.
• The Civil war in Biafra leaves 3 million people starving and needing international aid.
• Members of a cult led by Charles Manson murder seven people—including actress Sharon Tate—on August 9-10 in Los Angeles, California.
• Richard Nixon becomes President of the United States.
• Hurricane Camille hits the Mississippi coast, killing 248 people.
• Britain deploys troops in Northern Ireland following increasing violence.
• The Australian light aircraft carrier HMAS Melbourne slices the destroyer USS Frank E. Evans in half, killing 82 crew members.
• The trial of the “Chicago Seven” begins. They are accused of inciting riot at the 1968 Democratic National Convention.
• Charles de Gaulle resigns as president of France.
• A bomb is exploded in a bank in Milan, Italy.
• Rising inflation is a worldwide problem.
• The U.S. Supreme Court rules on Stanley v. Georgia that “the State may not prohibit mere possession of obscene materials for personal use."
• Militant black students at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, use force to take over the Willard Straight Hall, demanding a black studies program.
• Police forces in the U.S. crack down on student protests.
• A free concert organized by the Rolling Stones is held at the Altamont Speedway in Livermore, California, with problems caused by the use of Hells Angels as bouncers, resulting in a number of deaths.
• Monty Python’s Flying Circus and Sesame Street make their debuts on television.
• Brian Jones, former guitarist of the Rolling Stones, is found dead at his home on July 3, after apparently drowning in his swimming pool.
• John Lennon’s album Two Virgins, featuring himself and Yoko Ono naked, is confiscated at the Newark Airport.
• The Beatles make their last public performance on the roof of Apple Records.
Top 10 highest-grossing films in the U.S.
1. Butch Cassidy and the Sundance Kid (dir. George Roy Hill)
2. Midnight Cowboy (dir. John Schlesinger)
3. Easy Rider (dir. Dennis Hopper)
4. Hello, Dolly! (dir. Gene Kelly)
5. Bob & Carol & Ted & Alice (dir. Paul Mazursky)
6. Paint Your Wagon (dir. Joshua Logan)
7. True Grit (dir. Henry Hathaway)
8. Cactus Flower (dir. Gene Saks)
9. Goodbye, Colombus (dir. Larry Peerce)
10. On Her Majesty’s Secret Service (dir. Peter R. Hunt)
Billboard’s number-one music albums (in chronological order)
1. “The Beatles” by The Beatles
2. “TCB” by Diana Ross & the Supremes and The Temptations
3. “Wichita Lineman” by Glen Campbell
4. “Blood, Sweat & Tears” by Blood, Sweat & Tears
5. “Hair” by Hair Original Cast
6. “At San Quentin” by Johnny Cash
7. “Blind Faith” by Blind Faith
8. “Green River” by Creedence Clearwater Revival
9. “Abbey Road” by The Beatles
10. “Led Zeppelin II” by Led Zeppelin
Source: [x]
132 notes
·
View notes
Link
A number is said to be an Armstrong if the sum of each digit’s cube of a given number equals the original number.
0 notes
Link
C++ Tutorial for Absolute Beginners . Become An Expert ##100%FREEUdemyDiscountCoupons ##UdemyFreeDiscountCoupons #Absolute #Beginners #Expert #Tutorial C++ Tutorial for Absolute Beginners . Become An Expert C++ is general purpose, compiled, object-oriented programming language and its concepts served as the basis for several other languages such as Java, Python, Ruby, Perl etc. C++ is not just a powerful programming language. It's also the basis of many other popular languages, so this knowledge will serve you well, even when you're not using C++. 1) This is by far the most comprehensive C++ Programming course you'll find here, or anywhere else. 2) This C++ Programming tutorial Series starts from the very basics and covers advanced concepts as we progress. This course breaks even the most complex applications down into simplistic steps. 3) It is aimed at complete beginners, and assumes that you have no programming experience whatsoever. 4) This C++ Programming tutorial Series uses Visual training method, offering users increased retention and accelerated learning. The goal of this course is to provide you with a working knowledge of C++. We'll start with the basics, including syntax, operators, loops, and functions. This Course will explain you how to use data structures and create your own Functions. This Course will show you the details of the powerful object and template systems so you can create useful classes and objects. Finally, we will cover the unique and powerful Standard Template Library, which provides you with some of the most flexible container classes available anywhere. Bonus - C++ Example Codes and Exercise Example 1: Write a C++ program to Make Simple calculator Example 2: C++ program to Arrange 10 Numbers In Ascending Order Example 3: C++ program to calculate (n, x). 1+ (nx/1!) - (n(n-1)x^2/2!).... Example 4: Write a C++ program for Matrices Example 5: Write a C++ program that gets two strings from input and stores them in variable Example 6: Write a C++ program to Solve Quadratic equation Example 7: C++ program for Calculation of the Surface and The Volume of a Cone Example 8: C++ Program to show Fibonacci Series Example 9: C++ Program to Find Perfect Number Example 10: C++ program to find prime numbers in a given range Example 11: C++ program to find Armstrong number Example 12: C++ program to convert a string into upper-case or lower-case Example 13: C++ program to find HCF and LCM of two numbers Example 14: C++ Program for Printing 1 to 1000 without loop Example 15: C++ example for pass by reference Example 16: C++ Program to print half Pyramid Example 17: Write a C++ program that can print a temperature conversion Who this course is for: Amateur programmers willing to understand the basics of coding Students, final year pass outs, Graduates and post graduates C programmers and database analysts with basic coding abilities A genuine interest to learn. Anyone looking to begin their programing journey 👉 Activate Udemy Coupon 👈 Free Tutorials Udemy Review Real Discount Udemy Free Courses Udemy Coupon Udemy Francais Coupon Udemy gratuit Coursera and Edx ELearningFree Course Free Online Training Udemy Udemy Free Coupons Udemy Free Discount Coupons Udemy Online Course Udemy Online Training 100% FREE Udemy Discount Coupons https://www.couponudemy.com/blog/c-tutorial-for-absolute-beginners-become-an-expert/
0 notes
Text
Python Program to Check Armstrong Number Using Functions
Python Program to Check Armstrong Number Using Functions
Let’s have a glance at how to check Armstrong’s number using the function in Python programming language.
What is Armstrong’s number? Armstrong number is a number that is equivalent to the sum of cubes of its digits. For example 0, 1, 153, 370, 371 and 407 are the Armstrong numbers. Let’s try to understand why 407 is an Armstrong number.
(4*4*4)+(0*0*0)+(7*7*7)=407
Python Program to Check…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Learn more about Armstrong Number in Python
Learn how to identify Armstrong numbers using Python with this step-by-step guide. This tutorial covers the basics of Armstrong numbers, along with practical code examples to help you understand the concept and implement it in your own projects.
0 notes
Text
Armstrong Number in Python
Learn how to identify Armstrong numbers using Python with this step-by-step guide. This tutorial covers the basics of Armstrong numbers, along with practical code examples to help you understand the concept and implement it in your own projects.
0 notes
Video
youtube
Python - Chat GPT + Python Programming - Armstrong Number
#youtube#Python - Chat GPT Python Programming - Armstrong Number Chatgpt courses programming harisystems coding webdevelopment artificialintelligenc
0 notes