#Big Data Analytics Market Share
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

#Big Data Analytics Market#Big Data Analytics Market Share#Big Data Analytics Market Size#Big Data Analytics Market Research#Big Data Analytics Industry#What is Big Data Analytics?
0 notes
Text
Hadoop Big Data Analytics Market Demand, Key Trends, and Future Projections 2032
The Hadoop Big Data Analytics Market size was valued at USD 11.22 billion in 2023 and is expected to Reach USD 62.86 billion by 2032 and grow at a CAGR of 21.11% over the forecast period of 2024-2032
The Hadoop Big Data Analytics market is expanding rapidly as businesses increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making. With the exponential growth of structured and unstructured data, organizations seek scalable and cost-effective solutions to process and analyze vast datasets. Hadoop has emerged as a key technology, offering distributed computing capabilities to manage big data efficiently.
The Hadoop Big Data Analytics market continues to thrive as industries recognize its potential to enhance operational efficiency, customer insights, and business intelligence. Companies across sectors such as healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing are leveraging Hadoop’s open-source framework to extract meaningful patterns from massive datasets. As data volumes continue to grow, businesses are investing in Hadoop-powered analytics to gain a competitive edge and drive innovation.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3517
Market Keyplayers:
Cloudera Inc. (Cloudera Data Platform)
Hortonworks, Inc. (Hortonworks Data Platform)
Hadapt, Inc. (Hadapt)
Amazon Web Services LLC (Amazon EMR)
Outerthought (Outerthought Hadoop)
MapR Technologies, Inc. (MapR Converged Data Platform)
Platform Computing (Platform Symphony)
Karmasphere, Inc. (Karmasphere Analytics)
Greenplum, Inc. (Greenplum Database)
Hstreaming LLC (Hstreaming)
Pentaho Corporation (Pentaho Data Integration)
Zettaset, Inc. (Zettaset Orchestrator)
IBM Corporation (IBM BigInsights)
Microsoft Corporation (Azure HDInsight)
Teradata Corporation (Teradata Analytics Platform)
SAP SE (SAP HANA)
Oracle Corporation (Oracle Big Data Appliance)
Dell Technologies (Dell EMC Isilon)
SAS Institute Inc. (SAS Viya)
Qlik Technologies (Qlik Sense)
Market Trends Driving Growth
1. Increasing Adoption of AI and Machine Learning
Hadoop is being widely integrated with AI and machine learning models to process complex data structures, enabling predictive analytics and automation.
2. Growth in Cloud-Based Hadoop Solutions
The demand for cloud-based Hadoop solutions is rising as businesses look for flexible, scalable, and cost-effective data management options. Leading cloud providers are offering Hadoop-as-a-Service (HaaS) to simplify deployment.
3. Real-Time Data Processing and Streaming Analytics
Organizations are increasingly focusing on real-time data analysis for instant decision-making, leading to the adoption of Hadoop-powered stream processing frameworks like Apache Kafka and Spark.
4. Industry-Specific Hadoop Implementations
Sectors like banking, healthcare, and retail are implementing Hadoop to enhance fraud detection, patient care analytics, and customer behavior analysis, respectively.
5. Growing Demand for Data Security and Governance
With the rise in cybersecurity threats and data privacy regulations, businesses are adopting Hadoop for secure, compliant, and well-governed big data storage and processing.
Enquiry of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/enquiry/3517
Market Segmentation:
By Component
Software
Services
By Application
Risk & Fraud Analytics
Internet of Things (IoT)
Customer Analytics
Security Intelligence
Distributed Coordination Service
Merchandising Coordination Service
Merchandising & Supply Chain Analytics
Others
By End-User
BFSI
IT & Telecommunication
Retail
Government & Defense
Manufacturing
Transportation & Logistics
Healthcare
Others
Market Analysis and Current Landscape
Surging data volumes from IoT, social media, and enterprise applications.
Growing enterprise investment in big data infrastructure.
Advancements in cloud computing, making Hadoop deployments more accessible.
Rising need for cost-effective and scalable data storage solutions.
Challenges such as Hadoop’s complex deployment, data security concerns, and the need for skilled professionals persist. However, innovations in automation, cloud integration, and managed Hadoop services are addressing these issues.
Future Prospects: What Lies Ahead?
1. Advancements in Edge Computing and IoT Analytics
Hadoop is expected to play a key role in processing data from IoT devices at the edge, reducing latency and improving real-time insights.
2. Expansion of Hadoop in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
As Hadoop-as-a-Service gains popularity, more SMEs will adopt big data analytics without the need for large-scale infrastructure investments.
3. Enhanced Integration with Blockchain Technology
Hadoop and blockchain integration will help improve data security, traceability, and regulatory compliance in industries like finance and healthcare.
4. Automation and No-Code Hadoop Solutions
The emergence of no-code and low-code platforms will simplify Hadoop deployments, making big data analytics more accessible to non-technical users.
5. Continued Growth in Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Hadoop Deployments
Organizations will increasingly adopt hybrid cloud and multi-cloud strategies, leveraging Hadoop for seamless data processing across different cloud environments.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/hadoop-big-data-analytics-market-3517
Conclusion
The Hadoop Big Data Analytics market is poised for sustained growth as businesses continue to harness big data for strategic decision-making. With advancements in AI, cloud computing, and security frameworks, Hadoop’s role in enterprise data analytics will only strengthen. Companies investing in scalable and innovative Hadoop solutions will be well-positioned to unlock new insights, improve efficiency, and drive digital transformation in the data-driven era.
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
#Hadoop Big Data Analytics market#Hadoop Big Data Analytics market Analysis#Hadoop Big Data Analytics market Scope#Hadoop Big Data Analytics market Share#Hadoop Big Data Analytics market Growth
0 notes
Text
Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Size, Growth Outlook 2035
The global healthcare big data analytics market size valued at approximately USD 81.8 billion in 2022. It is projected to reach USD 474.1 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.7% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The adoption of big data analytics in healthcare has revolutionized the industry by enabling evidence-based decision-making and personalized patient care. The growing use of AI and machine learning in predictive analytics has helped in early disease detection, drug discovery, and population health management. Additionally, healthcare providers and insurance companies are leveraging data analytics to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize resources.
Market Size and Growth Analysis
The global healthcare big data analytics market size valued at approximately USD 81.8 billion in 2022. It is projected to reach USD 474.1 billion by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.7% during the forecast period. The rapid adoption of cloud-based analytics solutions, AI-driven diagnostics, and real-time patient monitoring systems is expected to drive this growth.
Market Dynamics
5.1 Growth Drivers
Several factors are fueling the growth of the healthcare big data analytics market. The rising adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) across hospitals and healthcare institutions has significantly increased the volume of healthcare data, necessitating advanced analytics solutions. Additionally, the growing prevalence of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and cardiovascular conditions, has led to a higher demand for predictive analytics in patient care.
Challenges and Restraints
Despite the promising growth, the healthcare big data analytics market faces several challenges. Data privacy and security concerns remain a major restraint, as healthcare data is highly sensitive and prone to cyber threats. Ensuring compliance with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) adds complexity to data management strategies
Regional Analysis
The healthcare big data analytics market exhibits strong regional variations in adoption and growth. North America leads the market, driven by the presence of established healthcare IT infrastructure, significant government funding, and widespread adoption of EHRs. The United States, in particular, has been at the forefront of AI-driven healthcare analytics, with major investments from both public and private sectors. Europe follows closely, with increasing digital health initiatives and regulations supporting data interoperability. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate due to the rising demand for quality healthcare services, expanding healthcare infrastructure, and growing investments in AI-based analytics solutions. Countries like China, India, and Japan are leading the regional growth, driven by government policies supporting healthcare digitalization.
Market Segmentation
The healthcare big data analytics market is segmented based on component, type, application, deployment model, and end-user.
By Component:
Software – AI-driven analytics platforms, EHR-integrated analytics, and predictive modeling tools
Services – Consulting, data management, implementation, and training services
Hardware – Data storage devices, servers, and networking solutions
By Type:
Descriptive Analytics – Used for historical data analysis and reporting
Predictive Analytics – Helps forecast diseases, patient outcomes, and treatment effectiveness
Prescriptive Analytics – Provides recommendations for clinical and operational decision-making
By Application:
Clinical Analytics – Patient management, disease prediction, precision medicine
Financial Analytics – Cost management, fraud detection, revenue cycle optimization
Operational Analytics – Hospital workflow optimization, resource allocation, supply chain management
By Deployment Model:
Cloud-Based Solutions – Scalable, cost-effective, and widely adopted due to remote access capabilities
On-Premise Solutions – Provides greater data security and control but requires high infrastructure investment
By End-User:
Hospitals and Healthcare Providers – Use analytics for patient care optimization and operational efficiency
Insurance Companies – Leverage analytics for risk assessment, fraud detection, and claims processing
Pharmaceutical Companies – Apply analytics for drug discovery, clinical trials, and market research
Government and Regulatory Bodies – Utilize data analytics for population health management and policy-making
Competitive Landscape and Key Market Players
The healthcare big data analytics market is highly competitive, with major companies investing in AI, machine learning, and cloud technologies to enhance their offerings. Some of the leading companies in the market include:
Allscripts Healthcare solution
Cerner Corporation
Health Analyst
Epic System Corporation
IBM Corporation
Recent Developments
The healthcare big data analytics market has witnessed significant developments in recent years. The increasing integration of AI and machine learning in healthcare analytics has led to improved predictive capabilities and automation in data processing. Cloud-based analytics solutions have gained momentum, enabling remote access to healthcare data and enhancing collaboration among healthcare providers
Future Outlook and Opportunities
The future of healthcare big data analytics looks promising, with continuous advancements in AI, IoT, and blockchain technology driving innovation in healthcare data management. The adoption of real-time analytics, wearable health monitoring devices, and personalized medicine is expected to grow, leading to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
For more information please visit @marketresearchfuture
#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Size#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Share#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Growth#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Analysis#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Trends#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Forecast#Global Healthcare Big Data Analytics Market Segments
1 note
·
View note
Text
#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market size#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market share#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market trends#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market analysis#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market forecast#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market outlook#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market overview#Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market report
0 notes
Text
The Big Data Analytics in Retail Market is expected to reach USD 5.26 billion in 2023 and grow at a CAGR of 21.20% to reach USD 13.76 billion by 2028. SAP SE, Oracle Corporation, IBM Corporation, Hitachi Vantara Corporation, Qlik Technologies Inc. are the major companies.
#big data analytics in retail market report#big data analytics in retail market growth#big data analytics in retail market forecast#big data analytics in retail market trends#big data analytics in retail market analysis#big data analytics in retail market size#big data analytics in retail market share
0 notes
Text
Keir Starmer appoints Jeff Bezos as his “first buddy”

Picks and Shovels is a new, standalone technothriller starring Marty Hench, my two-fisted, hard-fighting, tech-scam-busting forensic accountant. You can pre-order it on my latest Kickstarter, which features a brilliant audiobook read by Wil Wheaton.

Turns out Donald Trump isn't the only world leader with a tech billionaire "first buddy" who gets to serve as an unaccountable, self-interested de facto business regulator. UK PM Keir Starmer has just handed the keys to the British economy over to Jeff Bezos.
Oh, not literally. But here's what's happened: the UK's Competitions and Markets Authority, an organisation charged with investigating and punishing tech monopolists (like Amazon) has just been turned over to Doug Gurr, the guy who used to run Amazon UK.
This is – incredibly – even worse than it sounds. Marcus Bokkerink, the outgoing head of the CMA, was amazing, and he had charge over the CMA's Digital Markets Unit, the largest, best-staffed technical body of any competition regulator, anywhere in the world. The DMU uses its investigatory powers to dig deep into complex monopolistic businesses like Amazon, and just last year, the DMU was given new enforcement powers that would let it custom-craft regulations to address tech monopolization (again, like Amazon's).
But it's even worse. The CMA and DMU are the headwaters of a global system of super-effective Big Tech regulation. The CMA's deeply investigated reports on tech monopolists are used as the basis for EU regulations and enforcement actions, and these actions are then re-run by other world governments, like South Korea and Japan:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/10/an-injury-to-one/#is-an-injury-to-all
The CMA is the global convener and ringleader in tech antitrust, in other words. Smaller and/or poorer countries that lack the resources to investigate and build a case against US Big Tech companies have been able to copy-paste the work of the CMA and hold these companies to account. The CMA invites (or used to invite) all of these competition regulators to its HQ in Canary Wharf for conferences where they plan global strategy against these monopolists:
https://www.eventbrite.co.uk/e/cma-data-technology-and-analytics-conference-2022-registration-308678625077
Firing the guy who is making all this happening and replacing him with Amazon's UK boss is a breathtaking display of regulatory capture by Starmer, his business secretary Jonathan Reynolds, and his exchequer, Rachel Reeves.
But it gets even worse, because Amazon isn't just any tech monopolist. Amazon is a many-tentacled kraken built around an e-commerce empire. Antitrust regulators elsewhere have laid bare how Amazon uses that retail monopoly to take control over whole economies, while raising prices and crushing small businesses.
To understand Amazon's market power, first you have to understand "monopsonies" – markets dominated by buyers (monopolies are markets dominated by sellers – Amazon is both a monopolist and a monopsonist). Monopsonies are far more dangerous than monopolies, because they are easier to establish and easier to defend against competitors. Say a single retailer accounts for 30% of your sales: there isn't a business in the world that can survive an overnight 30% drop in sales, so that 30% market share might as well be 100%. Once your order is big enough that canceling it would bankrupt your supplier, you have near-total control over that supplier.
Amazon boasts about this. They call it "the flywheel": Amazon locks in shoppers (by getting them to prepay for a year's worth of shipping in advance, via Prime). The fact that a business can't sell to a large proportion of households if it's not on Amazon gives Amazon near-total power over that business. Amazon uses that power to demand discounts and charge junk fees to the businesses that rely on it. This allows it to lower prices, which brings in more customers, which means that even more businesses have to do business with Amazon to stay afloat:
https://vimeo.com/739486256/00a0a7379a
That's Amazon's version, anyway. In reality, it's a lot scuzzier. Amazon doesn't just demand deep discounts from its suppliers – it demand unsustainable discounts from them. For example, Amazon targeted small publishers with a program called the "Gazelle Project." Jeff Bezos told his negotiators to bring down these publishers "the way a cheetah would pursue a sickly gazelle":
https://archive.nytimes.com/bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/10/22/a-new-book-portrays-amazon-as-bully/
The idea was to get a bunch of cheap books for the Kindle to help it achieve critical mass, at the expense of driving these publishers out of business. They were a kind of disposable rocket stage for Amazon.
Deep discounts aren't the only way that Amazon feeds off its suppliers: it also lards junk-fee atop junk-fee. For every pound Amazon makes from its customers, it rakes in 45-51p in fees:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/29/aethelred-the-unready/#not-one-penny-for-tribute
Now, just like there's no business that can survive losing 30% of its sales overnight, there's also no business that can afford to hand 45-51% of its gross margin to a retailer. For businesses to survive at all on Amazon, they have to jack their prices up – way up. However, Amazon has an anticompetitive deal called "most favoured nation status" that forces suppliers to sell their goods on Amazon at the same price as they sell them elsewhere (even from their own stores). So when companies raise their prices in order to pay ransom to Amazon, they have to raise their prices everywhere. Far from being a force for low prices, Amazon makes prices go up everywhere, from the big Tesco's to the corner shop:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/25/greedflation/#commissar-bezos
Amazon makes so much money off of this scam that it doesn't have to pay anything to ship its own goods – the profits from overcharging merchants for "fulfillment by Amazon" pay for all the shipping, on everything Amazon sells:
https://cdn.ilsr.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/AmazonMonopolyTollbooth-2023.pdf
Amazon competes with its own sellers, but unlike those sellers, it doesn't have to pay a 45-51% rake – and it can make its competitor-customers cover the full cost of its own shipping! On top of that, Amazon maintains the pretense that its headquarters are in Luxembourg, the tax- and crime-haven, and pays a fraction of the taxes that British businesses pay to HMRC (and that's not counting the 45-51% tax they pay to Jeff Bezos's monoposony).
That's not the only way that Amazon unfairly competes with British businesses, though: Amazon uses its position as a middleman between buyers and sellers to identify the most successful products sold by its own customers. Then it copies those products and sells them below the original inventor's costs (because it gets free shipping, pays no tax, and doesn't have to pay its own junk fees), and drives those businesses into the ground. Even Jeff "Project Gazelle" Bezos seems to understand that this is a bad look, which is why he perjured himself to the American Congress when he was questioned under oath about it:
https://www.bbc.com/news/business-58961836
Amazon then places its knockoff products above the original goods on its search results page. Amazon makes $38b selling off placement on these search pages, and the top results for an Amazon search aren't the best matches for your query – they're the ones that pay the most. On average, Amazon's top result for a search is 29% more expensive than the best match on the site. On average, the top row of results is 25% more expensive than the best match on the site. On average, Amazon buries the best result for your search 17 places down the results page:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/03/subprime-attention-rent-crisis/#euthanize-rentiers
Amazon, in other words, acts like the business regulator for the economies it dominates. It decides what can be sold, and at what prices. It decides whose products come up when you search, and thus which businesses deserve to live and which ones deserve to die. An economy dominated by Amazon isn't a market economy – it's a planned economy, run by Party Secretary Bezos for the benefit of Amazon's shareholders.
Now, there is a role for a business regulator, because some businesses really don't deserve to live (because they sell harmful products, engage in deceptive practices, etc). The UK has a regulator that's in charge of this stuff: the Competition and Markets Authority, which is now going to be run by Jeff Bezos's hand-picked UK Amazon boss. That means that Amazon is now both the official and the unofficial central planner of the UK economy, with a free hand to raise prices, lower quality, and destroy British businesses, while hiding its profits in Luxemourg and starving the exchequer of taxes.
The "first buddy" role that Keir Starmer just handed over to Jeff Bezos is, in every way, more generous than the first buddy deal Trump gave Elon Musk.
Starmer's government claims they're doing this for "growth" but Amazon isn't a force for growth, it's force for extraction. It is a notorious underpayer of its labour force, a notorious tax-cheat, and a world-beating destroyer of local economies, local jobs, and local tax bases. Contrary to Amazon's own self-mythologizing, it doesn't deliver lower prices – it raises prices throughout the economy. It doesn't improve quality – this is a company whose algorithmic recommendation system failed to recognize that an "energy drink" was actually its own drivers' bottled piss, which it then promoted until it was the best-selling energy drink on the platform:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/10/20/release-energy/#the-bitterest-lemon
There's a reason that the UK, the EU, Japan and South Korea found it so easy to collaborate on antitrust cases against American companies: these are all countries whose competition law was rewritten by American technocrats during the Marshall Plan, modeled on the US's own laws. The bedrock of US competition law is 1890's Sherman Act, whose author, Senator John Sherman, declared that:
If we will not endure a King as a political power we should not endure a King over the production, transportation, and sale of the necessaries of life. If we would not submit to an emperor we should not submit to an autocrat of trade with power to prevent competition and to fix the price of any commodity.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/20/we-should-not-endure-a-king/
Jeff Bezos is the autocrat of trade that John Sherman warned us about, 135 years ago. And Keir Starmer just abdicated in his favour.

Check out my Kickstarter to pre-order copies of my next novel, Picks and Shovels!

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2025/01/22/autocrats-of-trade/#dingo-babysitter

Image: UK Parliament/Maria Unger (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Keir_Starmer_2024.jpg
CC BY 3.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
--
Steve Jurvetson (modified) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Jeff_Bezos%27_iconic_laugh.jpg
CC BY 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en
#pluralistic#cma#competition and markets authority#dmu#digital markets unit#guillotine watch#silicon roundabout#Marcus Bokkerink#doug gurr#industrial policy henhouse foxes#dingo babysitters#ukpoli#labour#competition#antitrust#trustbusting#marshall plan#Jonathan Reynolds#regulatory capture#keir starmer
315 notes
·
View notes
Note
This is the data from the app I use shows
Cait has gained +27,900 followers during the last 30 days and daily +930 but for Sam is daily +432 and during the Last 30 days +12,960 followers
What you see is a snapshot from the last month with the average number of new followers. It's a nice indication, but for marketeers not really interesting as it doesn't break the numbers down to daily growth in real time that can be connected and explained to a certain event happening.
Number are one thing, the other thing is to try and find an explanation for it. That is what marketeers do to adjust and imporve a marketing strategy.
If we take for instant the numbers of Cait's IG. We know she doesn't post much, is not a real influencer of anything. Just sometimes a post of a product, something she endorses.
Now we have seen her wrap posts on 25th October, the video has 279k likes, almost 2M870k views, and 11k comments, the slides post has 307k likes and 7k comments, which both are outstanding compared to the other posts
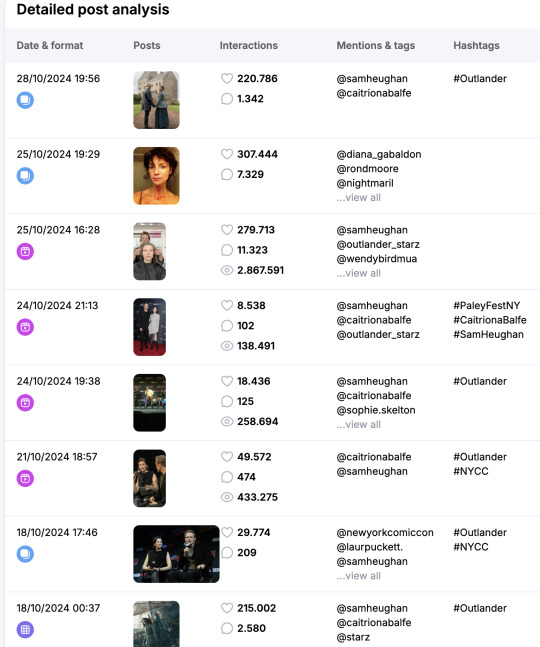
Note, the other posts are all accepted posts, originally posted by the OL_Starz account, (and one by Paleyfest) the top one and the bottome one are on SH's IG accepted as a post as well. This is important, as the likes and comments are coming from more accounts, not only her IG. But the wrap video and post with slides are on her IG and not on others, so these likes and comments are solely hers.
This all translates very obviously in her followers growth.


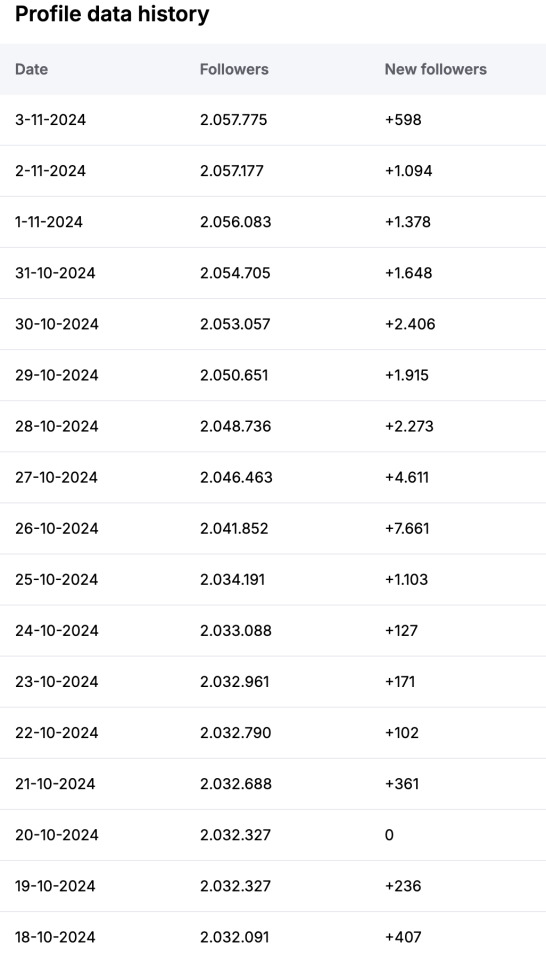
you are correct about the gain of almost 28k new followers over the month, but as you can see the biggest amount are gained starting on the day she posted the wrap video and slides. Which not only gained likes and comments but followers as well.
I think this is crystal clear, and I think anyone with a couple of brain cells can understand how marketeers would/could use these analytics if this is about a product, or say an influencer on IG.
This isn't really the case for Cait's IG, as she is not an active influencer, not even an active social media user. She occasionally posts about the projects she has worked on and work events.
Her growth for the next month will most likely be a lot lower, unless there is some big news she can share. We've seen f.i the last big growth when she was promoting her movie with Orlando Bloom in Toronto (I shared those numbers at some point). So all I can conclude from this analysis is that to me this looks normal and completely organic.
As for Sam, what we've been talking about in the other post is the huge fluctuation within 10-15 hours. That is not normal. Sure you can come up with all kind of explanations. Fact is that along all the time that I have watched his followers growth over quite some years now, I have never seen this huge fluctuations within such a short time interval and it is a weird phenomena. I do not see this on other accounts I've watched. Note that his follower growth is more interesting (to him) from a marketing pov as he is actively advertising his product (at nausea).
So that is why analytics are interesting, and why I find it interesting. [and for the people in the back, no you don't have to watch it 24/7 to get the numbers and educate yourself about what they mean or not, or when one sees a striking change which is interesting to watch as well as try to find a good reason for it, not just put a wet finger in the air, or google for 10 minutes and then claim you educated yourself!] (I suggest try to ask Google who is Caitriona's husband for a change)
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
US Customs and Border Protection experienced a sharp rise in reports about potential tariff evasion after President Donald Trump abruptly imposed new duties on over 100 countries earlier this year, according to data the agency shared with WIRED. From March through May, CBP’s official e-Allegations tipline received 542 complaints about alleged duty dodging, an almost 160 percent increase from the same three months in 2024.
Importers have long tried to evade tariffs and lower their costs by mislabeling the origin, value, and nature of the products they bring into the country. But the new data suggests that Trump’s policies may have pushed more firms to adopt these kinds of legally risky tactics. Over the same recent period, CBP fielded 242 tips about other types of potential violations, such as the import of counterfeit or unsafe items, an increase of just 42 percent. Submissions can be made anonymously, and trade experts say they often come from a company’s former employees or competitors.
Trade attorney Jennifer Diaz says her law firm files “tons of e-Allegations” on behalf of clients, and she has found that CBP often does take them seriously. It takes up to half a year for the agency to vet a claim, but the wait can be worth it. When CBP catches wrongdoing, it can “help level the playing field,” says Diaz, including by wiping out artificially low prices from a market.
Whether CBP is equipped to handle the surge in tips is unclear. Congress has yet to finalize legislation known as the One Big Beautiful Bill Act that would increase border staffing and resources for countering smuggling. As of April, CBP was on track to conduct roughly the same number of audits and issue about as many penalties for alleged trade violations as it had in recent years, according to public data.
Last year, a US Department of Treasury inspector general audit report concluded that CBP had not adequately tracked the outcomes of e-Allegations tips and called for new training and oversight measures to be put in place. From October 2018 through September 2020, CBP confirmed 68 out of over 900 duty evasion tips it received, the report found. But out of an estimated $65 million in unpaid duties, CBP did not know how much it ended up collecting. The agency responded that it was already rolling out improvements.
Data on tips and penalties are important because, unless Trump’s tariffs are sufficiently enforced, they may fall short of the president’s stated goals of increasing revenue and US manufacturing. Some companies also could grow frustrated with his administration if illegal conduct by their competitors goes unpunished. Businesses reluctant to engage in evasion could lose market share to those more willing to gamble as tariffs go up. Violators can face a variety of charges and be on the hook for multiples of the amount they evaded.
CBP spokesperson Trish Driscoll declined to comment on the number of duty evasion investigations happening at US ports and whether they have increased, citing law enforcement sensitivities. In general, she says that the agency uses a combination of “advanced data analytics, risk-based targeting, inspections, audits, investigations, and coordination with government agencies to identify patterns of evasion.”
Since Trump began announcing sweeping new tariffs in February, importers have been filling online forums with questions and advice about tactics that could help them reduce their tariff burdens. Consultants who help importers previously told WIRED that clients have received unsolicited offers from foreign business partners to skirt tariffs using dodgy tactics.
Companies can legally obtain lower tariff rates by shifting their manufacturing operations to other jurisdictions or changing the components, materials, and features of their products. But those maneuvers can be costly. More quick and affordable options, though, may violate the law. They include lying about the price of an item or shipping products to the US through a country subject to lower tariffs. Another common tactic is to misrepresent the type of item being imported on customs declarations, since tariffs can vary by product.
Whistleblowers can earn a reward of up to $250,000 through the e-Allegations program. They can receive higher sums by filing what’s known as a qui tam lawsuit under the False Claims Act, though that process includes jumping through extra legal hoops. The lawsuits are initially filed under seal, so it may not be evident for years whether there has been an increase recently, says Gregg Shapiro, an attorney who specializes in the False Claims Act.
Even given the recent increase in tips, many tariff violations may be going unreported, according to trade experts. CBP processes roughly 10 million customs declarations every three months, covering goods with a collective value in the hundreds of billions of dollars. During the seven months from last October through this April, the agency collected about $82 billion in tariffs and related fees. About $14 billion in assessed tariffs stemmed from Trump’s new policies, but the total lost to evasion will likely never be known.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Commercial Loan Brokering: Trends to Watch!
The commercial loan brokering industry is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, changing market dynamics, and shifting borrower expectations. As businesses continue to seek financing solutions, brokers must stay ahead of emerging trends to remain competitive. Here are some key developments shaping the future of commercial loan brokering:
1. Rise of AI and Automation
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are revolutionizing loan processing. From AI-driven underwriting to automated document verification, these technologies are streamlining workflows, reducing manual effort, and speeding up loan approvals. Brokers who leverage AI-powered tools can offer faster and more efficient services.
2. Alternative Lending is Gaining Momentum
Traditional banks are no longer the only players in commercial lending. Alternative lenders, including fintech platforms and private lenders, are expanding options for businesses that may not qualify for conventional loans. As a result, brokers must build relationships with non-bank lenders to provide flexible financing solutions.
3. Data-Driven Decision Making
Big data and analytics are transforming how loans are assessed and approved. Lenders are increasingly using alternative data sources, such as cash flow analysis and digital transaction history, to evaluate creditworthiness. Brokers who understand and utilize data-driven insights can better match clients with the right lenders.
4. Regulatory Changes and Compliance Requirements
The commercial lending landscape is subject to evolving regulations. Compliance with federal and state laws is becoming more complex, requiring brokers to stay updated on industry guidelines. Implementing compliance-friendly processes will be essential for long-term success.
5. Digital Marketplaces and Online Lending Platforms
Online lending marketplaces are making it easier for businesses to compare loan offers from multiple lenders. These platforms provide transparency, efficiency, and better loan matching. Brokers who integrate digital platforms into their services can enhance customer experience and expand their reach.
6. Relationship-Based Lending Still Matters
Despite digital advancements, relationship-based lending remains crucial. Many businesses still prefer working with brokers who offer personalized service, industry expertise, and lender connections. Building trust and maintaining strong relationships with both clients and lenders will continue to be a key differentiator.
7. Increased Focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) Lending
Sustainability-focused lending is gaining traction, with more lenders prioritizing ESG factors in their financing decisions. Brokers who understand green financing and social impact lending can tap into a growing market of businesses seeking sustainable funding options.
Final Thoughts
The commercial loan brokering industry is undergoing a transformation, with technology, alternative lending, and regulatory changes shaping the future. Brokers who embrace innovation, stay informed on market trends, and continue building strong relationships will thrive in this evolving landscape.
Are you a commercial loan broker? What trends are you seeing in the industry? Share your thoughts in the comments below!

#CommercialLoanBroker#BusinessFinancing#LoanBrokerTrends#AlternativeLending#Fintech#SmallBusinessLoans#AIinLending#DigitalLending#ESGLending#BusinessGrowth#LoanBrokerage#FinanceTrends#CommercialLending#BusinessFunding#FinancingSolutions#4o
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The CFA Charter in the Age of Algorithms: Can Certification Outlast Clout?

Evidently, in the last few years, there has been a visible change in the entire financial landscape. The former traditional heroes of the investment banking industry, CFA charterholders, and certified analysts are now being challenged by a new group- the “finfluencers,” who have emerged rather more as a digital class than as an institution or a regulatory body. These are the social media-savvy financial influencers reshaping how young investors and aspiring finance professionals consume their financial educations via platforms like YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok. The big question is can rigorous, structured qualifications like the CFA Charter withstand this wave of simplified, fast-paced content?
Finfluencers: Fast Fame, Greater Reach
Finfluencers are financial influencers, not necessarily with credentials and degrees. Most of them self-taught traders, people interested in personal finances, or early investors who share some tips, tricks, and general opinions on the market with others online. They cover things from stock market explainers to cryptocurrency predictions, budgeting hacks, and passive income strategies.
The allure is straightforward. Finfluencers cover complex finance concepts in widely understandable, digestible parcels that speak to the digitally born Gen Z and millennials. They do not use academic language but tap into everyday analogies and personal accounts to bring understanding. In this case, when such a message goes viral with high speed through social media algorithms, it provides them with unparalleled reach.
Is There A Trust-Gap?
Finfluencers, like with most other professions, could reach a wide audience lacking all the credentials and depth. In fact, misinformation among financial content creators is a major concern. In March 2024, swings of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) against unregistered investment advisers who misled their followers with false or exaggerated claims surged. A few finfluencers were fined or banned from offering investment advice without proper registration.
That is a glaring example of the growing trust deficit. The determinants include severe fines that barely catch the eye of talents on the online stock market. Finfluencers whose motivations tilt virality over responsibly, thus leaving virulent investment strategies or incomplete financial insights for public consumption; thus, unlike CFA Institute, which stands for a strong Code of Ethics and Standards of Professional Conduct, these influencers remain unaccountable.
CFA: The Gold Standard of Finance
The CFA Charter, therefore, stands tall in this very setting as a mark of trustworthiness, depth, and professionalism. The three levels of the CFA examination process test candidates on a wide range of subjects including equities, derivatives, ethics, portfolio management, and alternative investments. The process is not geared toward anything viral; it is designed to develop expertise over the long term.
CFA charterholders are not simply financial analysts; they are also often the decision-makers in asset management firms, hedge funds, and investment banking. Their pronouncements are data-supported, model-supported, and framework-supported.
How The CFA Charter is Adapting
Surprisingly, the CFA Institute is not ignorant to digital evolution. They have just launched new micro-credential programs an updated curriculum concentrating on the real world and fintech as a result of the increasing interest among young candidates. The latest modules include blockchain, decentralized finance (DeFi), and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing.
This is to say that values are updated to adapt and remain relevant without compromise to traditional ethics and analytical rigor. These movements are important to remain vibrant in a world loaded with information but as rare as real insight.
Location and Global Awareness
The overall growth of the financial influencer will find its acme in the rapidly developing financial markets. In India, where the digital tentacles are outspreading so fast, platforms such as YouTube and Instagram are becoming the most important conduits for financial literacy. Cities like Mumbai, India's financial capital, are experiencing a dual surge: a rise in fintech content creators alongside a rise in CFA aspirants.
The appetite for structured learning continues unabated. Increases in enrollments for courses like CFA course mumbai have been noted as finance students scramble for credibility in an age of omnipresent but often misleading online content.

Are Influencers and Analysts Able to Work Together?
Finfluencers and CFA professionals have the ability and potential to work together. Some charterholders have started to build their personal brands via LinkedIn and YouTube, a blend of credibility yet relatability. They use digital tools to help facilitate an understanding of finance while maintaining professionalism. This voice is desperately needed!
With enough regulations, cooperation, and transparency in disclosures, these finfluencers can move towards becoming aware educators. Charterholders with a CFA can escape the insular space of the boardrooms and reach the general population. Merging entertainment and expertise is the golden intersection.
Effect of Regulation and AI
The roles of both finfluencers and analysts are poised for change as AI tools like ChatGPT, portfolio optimization bots, and sentiment analysis engines become entrenched. While content creation is becoming easier, verifying the quality has become harder. Across the world, regulatory scrutiny is increasing on financial content posted on social media, which has led platforms to introduce disclaimers and to flag or, in some cases, discontinue specific hashtags regarding investment tips.
This new way signals more demand for verified professional advice. Everybody will keep searching on social media for financial education, but for those decisions that truly matter, CFA qualifications do provide some level of protection.
Conclusion: Coexistence Through Evolution
The arrival of finfluencers has brought a certain democratization to finance. Labels such as investing, saving, and creating wealth are on more lips than ever. However, with that democratization comes responsibility: with volatile markets and complex products, something like the CFA Charter provides a safety net-an anchor in the sea of fast-moving and oftentimes, untested advice.
What is ironically true for cities like Mumbai, where the wave of financial content promotes the 'fast', holds just as much for the 'slow'. The well-trodden paths remain a strong second option. CFA Training Program in Mumbai continues to attract serious-minded candidates who value substantive knowledge, ethical standards, and career credibility.
A balance between virality and tangible value will, in the long run, favor whoever can harness both sets of skills. Whoever merges insight and clout will thrive in the next ten years—finfluencers, CFA candidates, or whichever other designation may come by. That's a journey already worthy of pursuit!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Big Data Analytics in Retail Market#Big Data Analytics in Retail Market Share#Big Data Analytics in Retail Market Size#Big Data Analytics in Retail Market Research#Big Data Analytics in Retail Industry#What is Big Data Analytics in Retail?
0 notes
Text
The Social Credit System in China is a government-led initiative aimed at promoting trustworthiness in society by scoring individuals, businesses, and government institutions based on their behavior. While it’s often portrayed in Western media as a dystopian surveillance system, the reality is more nuanced. The system is still fragmented, evolving, and complex, blending both digital surveillance and bureaucratic rating mechanisms.
Here’s a detailed look at its structure, goals, mechanisms, and implications:
⸻
1. Origins and Goals
The Social Credit System (社会信用体系) was officially proposed in 2001 and formally outlined in 2014 by the State Council. Its main objectives are:
• Strengthen trust in market and social interactions.
• Encourage law-abiding behavior among citizens, businesses, and institutions.
• Prevent fraud, tax evasion, default on loans, and production of counterfeit goods.
• Enhance governance capacity through technology and data centralization.
It’s inspired by a mix of Confucian values (trustworthiness, integrity) and modern surveillance capitalism. It’s not a single unified “score” like a credit score in the West but rather a broad framework of reward-and-punishment mechanisms operated by multiple public and private entities.
⸻
2. Key Components
A. Blacklists and Redlists
• Blacklist: If an individual or business engages in dishonest or illegal behavior (e.g., court judgments, unpaid debts, tax evasion), they may be added to a “dishonest” list.
• Redlist: Those who follow laws and contribute positively (e.g., charitable donations, volunteerism) may be rewarded or publicized positively.
Examples of punishments for being blacklisted:
• Restricted from purchasing plane/train tickets.
• Difficulty in getting loans, jobs, or business permits.
• Public exposure (like having one’s name posted in public forums or apps).
Examples of rewards for positive behavior:
• Faster access to government services.
• Preferential treatment in hiring or public procurement.
• Reduced red tape for permits.
B. Fragmented Local Systems
Rather than one central system, there are hundreds of local pilots across China, often using different criteria and technologies. For example:
• Rongcheng (in Shandong Province) implemented a points-based system where citizens start at 1,000 points and gain or lose them based on specific actions.
• Hangzhou introduced systems where jaywalking, loud behavior on buses, or failing to show up in court could affect a personal credit profile.
Some local systems are app-based, while others are more bureaucratic and paper-based.
⸻
3. Surveillance and Technology Integration
A. Data Sources:
• Public records (tax, court, education).
• Private platforms (e.g., Alibaba, Tencent’s financial and social data).
• Facial recognition and CCTV: Often integrated with public security tools to monitor individuals in real-time.
B. AI and Big Data:
While the idea of a real-time, fully integrated AI-run system is more a long-term ambition than a reality, many systems use:
• Predictive analytics to flag high-risk individuals.
• Cross-agency data sharing to consolidate behavior across different parts of life.
However, this level of integration remains partial and uneven, with some cities far more advanced than others.
⸻
4. Criticisms and Concerns
A. Lack of Transparency
• Citizens are often unaware of what data is being used, how scores are calculated, or how to appeal decisions.
• There’s minimal oversight or independent auditing of the systems.
B. Social Control
• Critics argue the system encourages conformity, discourages dissent, and suppresses individual freedoms by rewarding obedience and penalizing perceived deviance.
• It may create a culture of self-censorship, especially on social media.
C. Misuse and Arbitrary Enforcement
• Cases have emerged where individuals were blacklisted due to clerical errors or as a result of political pressure.
• There are concerns about selective enforcement, where some citizens (e.g., activists) face harsher consequences than others.
⸻
5. Comparisons to Western Systems
It’s important to note:
• Western countries have private credit scores, employment background checks, social media tracking, and predictive policing—all of which can impact someone’s life.
• China’s system differs in that it’s state-coordinated, often public, and spans beyond financial behavior into moral and social conduct.
However, similar behavioral monitoring is increasingly used in tech-based social systems globally (e.g., Uber ratings, Airbnb reviews, Facebook data profiles), though usually without state-enforced punishments.
⸻
6. Current Status and Future Trends
Evolving System
• As of the mid-2020s, China is moving toward greater standardization of the credit system, especially for businesses and institutions.
• The National Credit Information Sharing Platform is becoming more central, aiming to integrate local experiments into a coherent framework.
Smart Cities and Governance
• The social credit system is increasingly linked with smart city infrastructure, predictive policing, and AI-powered surveillance.
• This aligns with the Chinese government’s broader vision of “digital governance” and technocratic legitimacy.
⸻
7. Key Takeaways
• Not one unified “score” like in fiction; it’s more like a patchwork of overlapping systems.
• Used as a governance tool more than a financial one.
• Integrates traditional values with modern surveillance.
• Viewed domestically as a way to restore trust in a society that has undergone rapid transformation.
• Internationally, it raises serious questions about privacy, freedom, and state overreach.
Needed clarification 😅
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Harnessing the Power of Digital Marketing in E-commerce: Strategies That Convert

In the fast-evolving world of e-commerce, leveraging effective digital marketing strategies is not just an option—it's a necessity. At The Big Shoutout, we've mastered the art of turning browsing into buying, driving both traffic and conversions. This post explores cutting-edge strategies that can transform your e-commerce business.
The Importance of SEO in E-commerce: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the backbone of digital visibility. For e-commerce businesses, SEO not only helps you appear first in search results but also ensures you are visible to the right audience. Our approach involves a thorough keyword analysis tailored to your niche, enhancing site structure for better crawlability, and creating content that engages and converts.
Leveraging Social Media for Brand Engagement: Social media platforms are invaluable for e-commerce brands looking to engage directly with their customer base. At The Big Shoutout, we specialize in creating targeted social media campaigns that resonate with your demographic, encourage sharing, and drive sales. We'll dive into successful case studies where we've transformed likes and shares into tangible sales growth.
Email Marketing: The Direct Line to Sales: Often underestimated, email marketing holds a significant ROI potential for e-commerce. Whether it's through personalized offers, cart abandonment strategies, or new product launches, our targeted email campaigns build a direct connection with your customers and keep them returning.
Paid Advertising: Maximizing ROI: Pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns can be a game-changer if executed correctly. We focus on optimizing ad spend to achieve the highest return, targeting users who are most likely to convert, and analyzing data to refine our strategies continually.
Conclusion: Digital marketing in the e-commerce space is about combining creativity with analytics. At The Big Shoutout, we bring these elements together to help your business thrive in a competitive market. Want to see how we can boost your digital presence? Visit us at The Big Shoutout - About Us to start transforming your e-commerce strategy today.
#digital marketing#ig story#black entrepreneurship#black community#online marketing#social media marketing#insta#marketing#DigitalMarketing#Ecommerce#MarketingStrategies#OnlineBusiness#SEO#SocialMediaMarketing#ContentMarketing#EcommerceTips#BusinessGrowth#MarketingTrends
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
What are the skills needed for a data scientist job?
It’s one of those careers that’s been getting a lot of buzz lately, and for good reason. But what exactly do you need to become a data scientist? Let’s break it down.
Technical Skills
First off, let's talk about the technical skills. These are the nuts and bolts of what you'll be doing every day.
Programming Skills: At the top of the list is programming. You’ll need to be proficient in languages like Python and R. These are the go-to tools for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization. If you’re comfortable writing scripts and solving problems with code, you’re on the right track.
Statistical Knowledge: Next up, you’ve got to have a solid grasp of statistics. This isn’t just about knowing the theory; it’s about applying statistical techniques to real-world data. You’ll need to understand concepts like regression, hypothesis testing, and probability.
Machine Learning: Machine learning is another biggie. You should know how to build and deploy machine learning models. This includes everything from simple linear regressions to complex neural networks. Familiarity with libraries like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch will be a huge plus.
Data Wrangling: Data isn’t always clean and tidy when you get it. Often, it’s messy and requires a lot of preprocessing. Skills in data wrangling, which means cleaning and organizing data, are essential. Tools like Pandas in Python can help a lot here.
Data Visualization: Being able to visualize data is key. It’s not enough to just analyze data; you need to present it in a way that makes sense to others. Tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Tableau can help you create clear and compelling visuals.
Analytical Skills
Now, let’s talk about the analytical skills. These are just as important as the technical skills, if not more so.
Problem-Solving: At its core, data science is about solving problems. You need to be curious and have a knack for figuring out why something isn’t working and how to fix it. This means thinking critically and logically.
Domain Knowledge: Understanding the industry you’re working in is crucial. Whether it’s healthcare, finance, marketing, or any other field, knowing the specifics of the industry will help you make better decisions and provide more valuable insights.
Communication Skills: You might be working with complex data, but if you can’t explain your findings to others, it’s all for nothing. Being able to communicate clearly and effectively with both technical and non-technical stakeholders is a must.
Soft Skills
Don’t underestimate the importance of soft skills. These might not be as obvious, but they’re just as critical.
Collaboration: Data scientists often work in teams, so being able to collaborate with others is essential. This means being open to feedback, sharing your ideas, and working well with colleagues from different backgrounds.
Time Management: You’ll likely be juggling multiple projects at once, so good time management skills are crucial. Knowing how to prioritize tasks and manage your time effectively can make a big difference.
Adaptability: The field of data science is always evolving. New tools, techniques, and technologies are constantly emerging. Being adaptable and willing to learn new things is key to staying current and relevant in the field.
Conclusion
So, there you have it. Becoming a data scientist requires a mix of technical prowess, analytical thinking, and soft skills. It’s a challenging but incredibly rewarding career path. If you’re passionate about data and love solving problems, it might just be the perfect fit for you.
Good luck to all of you aspiring data scientists out there!
#artificial intelligence#career#education#coding#jobs#programming#success#python#data science#data scientist#data security
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
I think a lot of data-driven marketing/communications/media services are like this because you can gather a lot of data (for example, number of views) but that doesn't mean you are reading it correctly or using it advantageously and if your client doesn't know much about it, you can basically trick them into thinking they are successful (yay, you have 100 people looking at your website!) You can get pretty far into a grift before your client realizes they are not making the money you claim they should be. IE, you could say, I can increase your views by 100% in a year. But if none of those views turns into significant increase in purchases, then you're literally just losing money on advertising to uninterested people. But there is so much power in analytics now - you can gather tons of data, you can get really granular, it can be seductive. to clients who think that more data = smarter decisions. Signed, A Marketer lol
Big yikes! Yeah, I worry about this a lot too with book authors. I met a self-published author who had worked in marketing for 35 years and had a regular meetup group with other self-published authors in which they only discussed marketing/selling their books. They were all failing to actually sell.
I'm not a big fan of the huge number of author discussions and for-profit courses that tell you "things you could talk about on booktok to promote your book" with zero mention of ROI.
Anyway, that's why I don't really talk bout marketing at my group Authors of Nonfiction Books in Progress, and I don't encourage it unless someone has some real, tangible experience or data to share (data that will probably have a lot of caveats.) My book Carcass isn't out so I can't say if anything I do will result in sales, but I do plan on sharing in the group whatever successes and failures I have on that front. Also, I'm trad publishing so it's mostly the publisher's job to sell the book, not the author's. I'll promote my book for sure but I'm not getting them in Barnes & Nobles, that’s up to the publisher.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top investors in space in India
Why Venture Capitalists Are Betting Big on India’s Space Sector

A Thriving Ecosystem of Space Startups: India’s space ecosystem is no longer limited to government-run entities like the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Today, a surge of innovative space startups are taking the stage, offering cutting-edge solutions in satellite technology, launch services, space data analytics, and more. Companies like Skyroot Aerospace, Agnikul Cosmos, and Pixxel lead the charge, each carving out a unique niche. These startups are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, driving investor interest with the potential for high returns in a relatively untapped market.
Strong Government Support and Policy Reforms: One of the key reasons behind the surge in space venture capital in India is the proactive stance taken by the Indian government. Recent policy reforms have opened the doors for private players to participate in space activities, previously dominated by ISRO. Establishing IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center) is a significant step, providing a regulatory framework that encourages private sector involvement. Such government support has given investors in space in India the confidence to back ambitious projects, knowing there’s a clear path for private ventures.
Cost-Effective Innovation as a Competitive Edge: India’s reputation for cost-effective innovation is another major attraction for investors. Launching satellites at a fraction of the cost compared to global competitors has positioned India as a hub for affordable space technology. This competitive edge not only allows Indian space startups to thrive domestically but also makes them attractive on the international stage. Investors are keen to support companies that can deliver world-class technology with lower capital outlays, reducing investment risks while promising impressive returns.
Global Interest in Indian Talent and Expertise: India’s space sector is not just about affordability; it’s about world-class talent. The country boasts a deep pool of highly skilled engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs with expertise in aerospace and technology. This talent pool has been instrumental in driving innovation and attracting global attention. International investors are increasingly looking to partner with Indian space startups, recognizing the country’s unique blend of technical prowess and entrepreneurial spirit.
A Growing Market for Space-Based Services: The market for space-based services, including satellite communications, Earth observation, and data analytics, is expanding rapidly. In India, this growth is driven by rising demand from industries such as agriculture, telecommunications, logistics, and defense. With space technology playing a crucial role in optimizing these sectors, investors see an opportunity to capitalize on the potential for domestic and international applications. Space-based services represent a lucrative market, attracting space venture capital in India to back startups that can cater to these needs.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations: Indian space startups are not working in isolation; they are forming strategic partnerships with global companies and space agencies. Collaborations with NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and private companies have opened up new opportunities for technology sharing, funding, and market access. These partnerships have also strengthened investor confidence, as they reduce risks and validate the technology being developed by Indian companies. For investors in space in India, such collaborations signal a promising future, driving more venture capital into the sector.
A New Era of Commercial Space Exploration: The idea of commercial space exploration, once confined to science fiction, is now becoming a reality. From reusable rockets to satellite constellations, Indian space startups are exploring new frontiers that were once considered out of reach. This new era of commercial space exploration has piqued the interest of venture capitalists who see the potential for profitable exits through IPOs, acquisitions, and global partnerships. With private space missions no longer just a dream, space venture capital in India is ready to fuel the next big leap.
Encouraging Signs from Successful Fundraising Rounds: The confidence in India’s space sector is evident from the successful fundraising rounds by leading space startups. Companies like Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos have secured millions in funding from top-tier venture capital firms. These funding rounds not only provide the necessary resources for scaling but also act as a signal to other investors that the Indian space market is mature and ready for high-stakes investment. The momentum created by these early successes is a clear indicator of why investors in space in India are increasingly willing to place their bets.
Conclusion: A Promising Orbit for Investment India’s space sector is on an exciting trajectory. With a favorable policy environment, a surge of innovative startups, and a proven track record of cost-effective solutions, it’s no wonder that space venture capital in India is booming. As the country continues to explore new frontiers and expand its role in global space exploration, venture capitalists are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future. For those looking to invest in the final frontier, India’s space industry presents a unique opportunity to be part of a revolution that’s only just beginning.
#305, 3rd Floor, 5 Vittal Mallya Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka, 560001, India
5 Ring Road, Lajpat Nagar 4, 3rd Floor, New Delhi-110024
#Keywords#best venture capital firm in india#venture capital firms in india#popular venture capital firms#venture capital firm#seed investors in bangalore#deep tech investors india#startup seed funding india#funding for startups in india#early stage venture capital firms#invest in startups bangalore#funders in bangalore#startup investment fund#fintech funding#india alternatives investment advisors#best venture capital firms in india#business investors in kerala#venture capital company#semiconductor startups#semiconductor venture capital#investors in semiconductors#startup seed funding in India#deep tech venture capital#deeptech startups in india#semiconductor companies in india#saas angel investors#saas venture capital firms#saas venture capital#b2b venture capital#space venture capital in india
2 notes
·
View notes