#Cardiomyopathy
Photo

Energy Production Failure
The heart on the left is healthy but the one on the right exhibits the tell-tale signs of dilated cardiomyopathy, including overall enlargement, and thinning and weakening of the muscle walls. In most cases of such cardiomyopathy, the cause is unknown, but recent research indicates dysfunctional energy production, already known to accompany the condition, may actually be an underlying cause. Analysis of gene activity in heart tissue from patients with dilated cardiomyopathy and healthy controls showed expression of mitochondrial metabolism genes, especially two key transcription factors – KDM8 and TBX15 – was disrupted in patient samples. When scientists then deleted KDM8 in mouse hearts, they found the knock-on disruption of TBX15 and other metabolism genes preceded physical signs of cardiomyopathy by months. Knowing that impaired energy production can initiate rather than simply follow myocardial degeneration suggests maintaining it may be a way to slow or stop heart failure.
Written by Ruth Williams
Image from work by Abdalla Ahmed and colleagues, Paul Delgado-Olguín lab
Department of Translational Medicine, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Image copyright held by the original authors
Research published in Nature Cardiovascular Research, February 2023
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
#science#biomedicine#cardiac#heart#cardiomyopathy#transcription factors#heart failure#immunofluorescence
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
On Christmas Eve, a man resurfaces, placing a bouquet of purple foxgloves on her bed. She has known him since childhood: they grew up together—lovers, friends, brother and sister, partners in crime. They are, for each other, almost everything a man and a woman can be.
[...]
Actually, he tells her, the digitalin contained in the flowers makes the heartbeat stronger, slower, steadier. It’s good for you.
She sleeps with the flowers that night. The man carefully undresses her, removing the petals one by one, then placing them on her naked skin like the scales of a fish, a sort of organic jigsaw puzzle that he painstakingly perfects into a ceremonial gown, whispering don’t move from time to time, even though she has long been asleep, in a luxuriant catalepsy, nursed and ornamented like a queen. It was still night when she awoke, but the children in the apartment above hers were already running around excitedly, shouting, their footsteps hammering the floorboards, rushing into the living room to tear the wrapping paper from the presents that had appeared during the night around the ectoplasmic Christmas tree. Her friend had gone. She shook the petals from her body and made them into a salad that she seasoned with truffle oil and balsamic vinegar.
~ The Heart, Maylis de Kerangal, Sam Taylor (Translation)
#maylis de kerangal#heart#heart disease#cardiomyopathy#heart transplant#foxglove#flower#flower petals#body
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
instagram
#heartattack#heartdiseaseawareness#heartdisease#hearthealth#heart#heartstopper#cardiacarrest#cardiac#cardiacrehabilitation#hearthealthy#heartfailure#heartfailuresurvivor#cardiomyopathy#cardiacarrhythmia#pericarditis#cad#coronaryarterydisease#Instagram
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
हृदय रोगों की समझ: एक संक्षिप्त जानकारी

हृदय रोग एक विविधता है जो हृदय और रक्त वाहिकाओं को प्रभावित करती है। इन स्थितियों को पहचानना और प्रतिकूलन के लिए यह अत्यधिक महत्वपूर्ण है। यहाँ कुछ सामान्य प्रकार के हृदय रोग हैं:
कोरोनरी धमनी रोग (CAD): इसका कारण कोरोनरी धमनियों में प्लाक बढ़ जाना है, जिससे हृदय मांसपेशी को कम रक्त प्रवाह प्राप्त होता है।
हृदय अटैक (मायोकार्डियल इन्फार्क्शन): यह तब होता है जब हृदय के किसी हिस्से में रक्त प्रवाह को बंद कर दिया जाता है, अक्सर एक रक्त थक्का के कारण, जिससे हृदय मांसपेशी को क्षति होती है।
अरिथमिया: ये अनियमित हृदय ध्वनि हैं जो हृदय को बहुत तेज (ताच्यकार्डिया), बहुत धीमे (ब्रदीकार्डिया), या अनियमित बना सकती हैं (एट्रियल फिब्रिलेशन)।
हृदय प्रतिरोध: यह स्थिति उत्कृष्ट रूप से रक्त को पारित करने के लिए हृदय को पर्याप्त रूप से पंप करने में असमर्थ होने पर होती है।
वाल्व्युलर हृदय रोग: यह हृदय के वाल्वों में क्षति या दोष होने पर होता है, जिससे हृदय के माध्यम से रक्त प्रवाह प्रभावित होता है।
कार्डिओमायोपैथी: यह हृदय की मांसपेशी की बीमारियों को संदर्भित करता है, जिससे हृदय को बड़ा, मोटा या कठोर बना दिया जाता है।
जन्मजात हृदय दोष: ये वह हृदय स्थितियाँ हैं जो जन्म से होती हैं, हृदय की संरचना और कार्य प्रभावित करती हैं।
इन स्थितियों का समय पर पता लगाना और प्रबंधन करना हृदय स्वास्थ्य के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
व्यक्तिगत सलाह और परामर्श के लिए, Dr. Md. Farhan Shikoh, MBBS, MD (Medicine), DM (Cardiology) से संपर्क करें, एक प्रमुख हृदय विशेषज्ञ, सुकून हार्ट केयर, सैनिक मार्केट, मुख्य सड़क, रांची, झारखंड - 834001 में स्थित। अपॉइंटमेंट के लिए कॉल करें 6200784486 या उनकी वेबसाइट पर जाएं drfarhancardiologist.com और अधिक जानकारी प्राप्त करें।
साथ मिलकर हम एक स्वस्थ ह्रदय की ओर कदम बढ़ाते हैं।
#HeartHealth#Cardiology#HeartDisease#HealthyHeart#HeartCare#CoronaryArteryDisease#Arrhythmia#HeartFailure#ValvularHeartDisease#Cardiomyopathy#CongenitalHeartDefects#HeartAttack#HeartSpecialist#HealthyLiving#HeartAwareness#Healthcare#Ranchi#Jharkhand#DrFarhanShikoh#SukoonHeartCare
0 notes
Text
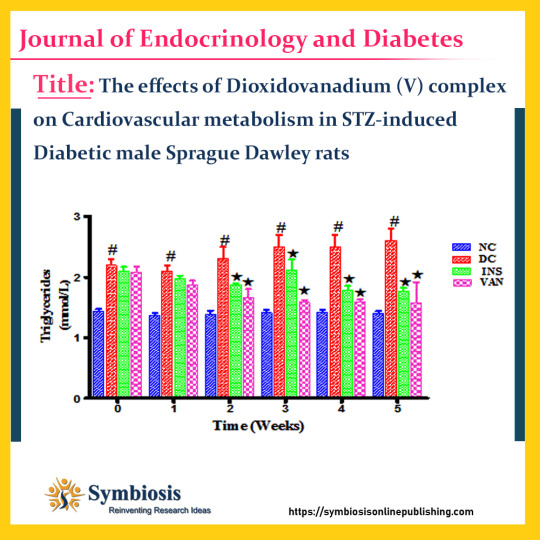
insulin is an effective #hyperglycemia agent, however hyperinsulinemia, as result of prolonged administration, has been shown to lead to #cardiovasculardisease (CVD) in DM. As a result, research into alternative therapies for the management of #diabetes is needed. In our laboratory, a novel vanadium complex has been synthesized and has been shown to improve #glycemic control and #liverfunction.
Visit @ https://symbiosisonlinepublishing.com/endocrinology-diabetes/endocrinology-diabetes154.php
#symbiosisonlinepublishing#endocrinologia#endocrinesystem#endocrinologist#endocrine#liverhealth#dioxidovanadium#cardiovascularhealth#Cardiovascular#diabetesmellitus#cardiomyopathy#diabetics#liverfunction#research#ResearchStudy#journal#medical#medicaljournal#openaccess
0 notes
Text
What Is The Main Cause & Cure Of Atrial Fibrillation?
The main cause of cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation is a form of scar tissue (also called "electrical noise"), and the cure for it is to make sure you take care of your heart health.
#atrial fibrillation#heart problems#heart rhythm#blood thinners#hypertension#heart surgery#kidney disease#cardiomyopathy
0 notes
Text
i just got diagnosed with Cardiomyopathy lol
0 notes
Link
The Enigma: Right-Sided Heart Failure Right-sided heart failure is a condition that affects the ability of the right side of the heart to pump blood effectively. It is an important topic to understand as it can have significant implications for a person's overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the anatomy and physiology of the heart, explore the mechanisms and pathophysiology of right-sided heart failure, and discuss its clinical presentation and diagnosis, as well as treatment and management approaches. We will also touch upon the potential complications and prognosis, provide preventive tips, and address frequently asked questions. By shedding light on this condition, we hope to raise awareness and promote early detection and proper management ofright-sidedd heart failure. [caption id="attachment_59982" align="aligncenter" width="800"] sided heart failure[/caption] Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart The heart plays a crucial role in the circulatory system, pumping oxygen-rich blood to the body's tissues and organs. It consists of four chambers: two atria (left and right) and two ventricles (left and right). The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body's tissues and pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation. Right-sided heart failure occurs when the right ventricle is unable to effectively pump blood, leading to a backup of blood in the veins and fluid accumulation in the body's tissues. This can occur due to various reasons, including underlying heart conditions, such as left-sided heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, or heart valve disorders. Understanding Heart Failure Heart failure is a condition where the heart's ability to pump blood is impaired. It can be categorized into left-sided heart failure and right-sided heart failure, depending on the affected side of the heart. Right-sided heart failure specifically refers to the inability of the right side of the heart to pump blood efficiently. It often occurs as a result of left-sided heart failure, where the weakened left ventricle causes increased pressure and fluid buildup in the lungs, leading to strain on the right side of the heart. Other causes of right-sided heart failure include pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs), heart valve diseases, congenital heart defects, and chronic lung diseases. The symptoms of right-sided heart failure may include fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles (edema), fluid retention in the abdomen (ascites), and shortness of breath. Risk factors for developing right-sided heart failure include a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and smoking. Additionally, conditions that directly affect the right side of the heart can also contribute to tonight-sided heart failure. Pulmonary hypertension, for example, is a condition characterized by high blood pressure in the lungs. This increased pressure puts strain on the right ventricle, impairing its ability to pump blood efficiently. Heart valve diseases, such as tricuspid regurgitation or stenosis, can also affect the right side of the heart and lead to right-sided heart failure. Certain congenital heart defects, such as atrial septal defect or ventricular septal defect, can cause communication between the left and right sides of the heart, leading to increased blood flow and pressure on the right side, eventually resulting in right-sided heart failure. Chronic lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pulmonary fibrosis, can also exert pressure on the right side of the heart, causing it to weaken over time. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis The clinical presentation of right-sided heart failure can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include fatigue, swelling in the lower extremities (edema), fluid retention in the abdomen (ascites), and shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or when lying flat (orthopnea). Diagnosing right-sided heart failure involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The healthcare provider will inquire about the symptoms experienced, risk factors, and any previous heart conditions. During the physical examination, they may look for signs of fluid retention, such as swollen ankles and distended neck veins. Diagnostic tests commonly used to identify right-sided heart failure include: Echocardiogram: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the heart and assess its structure and function. It can help determine the size and function of the right ventricle and detect any abnormalities. Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart and can provide information about any rhythm abnormalities or signs of right ventricular strain. Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can reveal signs of fluid buildup in the lungs or an enlarged heart, which may indicate right-sided heart failure. Blood tests: Blood tests may be conducted to assess kidney and liver function, as well as check for elevated levels of certain biomarkers associated with heart failure. Cardiac catheterization: In some cases, a cardiac catheterization may be performed to measure pressures within the heart chambers and assess blood flow. Treatment and Management Approaches The primary goals of treating right-sided heart failure are to improve symptoms, slow disease progression, and enhance the patient's quality of life. The specific treatment approach will depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options for right-sided heart failure may include: Medications: Several medications can be prescribed to manage right-sided heart failure. Diuretics help reduce fluid retention and relieve symptoms of edema. ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) may be used to dilate blood vessels and lower blood pressure. In some cases, beta-blockers or inotropic agents may be prescribed to improve heart function and reduce symptoms. Lifestyle modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve the management of right-sided heart failure. Patients are often advised to follow a low-sodium diet to reduce fluid retention. Regular exercise, as recommended by a healthcare professional, can help strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also important steps in managing the condition. Fluid and salt restriction: Limiting fluid intake and reducing salt consumption can help prevent fluid overload and minimize symptoms of right-sided heart failure. Oxygen therapy: In cases where oxygen levels are low, supplemental oxygen therapy may be prescribed to improve breathing and oxygenation of the blood. Device therapy: In some advanced cases, device therapy such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be recommended to help regulate heart rhythm and improve cardiac function. Surgical interventions: In severe cases, of of right-sided heart failure, surgical interventions such as heart valve repair or replacement, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), or ventricular assist device (VAD) implantation may be considered. Complications and Prognosis Untreated or poorly managed right-sided heart failure can lead to several complications, including: Fluid buildup: The accumulation of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema) can cause severe breathing difficulties and increase the risk of respiratory infections. Organ damage: Inadequate blood flow and oxygenation can affect the function of vital organs, such as the kidneys and liver, leading to organ damage or failure. Arrhythmias: The weakened heart muscle and altered electrical conduction can result in abnormal heart rhythms, which can be life-threatening. Right-sided heart enlargement: Prolonged right-sided heart failure can cause the right ventricle to enlarge, further impairing its ability to pump blood effectively. FAQ's What are the common symptoms of right-sided heart failure? Common symptoms of right-sided heart failure include fatigue, swelling in the legs and ankles (edema), fluid retention in the abdomen (ascites), and shortness of breath. Can right-sided heart failure occur without any underlying heart conditions? While right-sided heart failure often occurs as a result of left-sided heart failure or other heart conditions, it can also be caused by pulmonary hypertension, heart valve diseases, congenital heart defects, or chronic lung diseases. How is right-sided heart failure diagnosed? Diagnosis of right-sided heart failure involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as an echocardiogram, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and blood tests. Are there any specific medications used to treat right-sided heart failure? Medications commonly used to treat right-sided heart failure include diuretics, ACE inhibitors or ARBs, beta-blockers, and inotropic agents. The specific medication regimen will depend on the individual's condition and underlying causes. Can lifestyle changes alone improve right-sided heart failure? Lifestyle changes, such as following a low-sodium diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption, can significantly improve the management of right-sided heart failure. However, medical treatment and close monitoring are often necessary. Are there any dietary restrictions for individuals with right-sided heart failure? Individuals with right-sided heart failure are often advised to follow a low-sodium diet to reduce fluid retention. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations. Can right-sided heart failure be reversed or cured completely? While right-sided heart failure cannot be completely cured, it can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. Early detection and proper management can slow disease progression and improve symptoms. What are the potential complications of untreated right-sided heart failure? Untreated or poorly managed right-sided heart failure can lead to complications such as fluid buildup in the lungs(pulmonary edema), organ damage, arrhythmias, and right-sided heart enlargement. Are there any ongoing research or advancements in the treatment of right-sided heart failure? Yes, there is ongoing research and advancements in the treatment of right-sided heart failure. These include new medications, surgical techniques, and device therapies that aim to improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with this condition. Patients need to stay informed and work closely with their healthcare providers to explore the most up-to-date treatment options. Conclusion: Right-sided heart failure is a condition that affects the ability of the right side of the heart to pump blood effectively. Understanding its mechanisms, clinical presentation, and management approaches is crucial for early detection and proper care. By following a heart-healthy lifestyle, seeking timely medical advice, and adhering to recommended treatment plans, individuals with right-sided heart failure can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential to ensure optimal management and long-term well-being. By raising awareness and promoting preventive measures, we can work towards a healthier future with a reduced burden of right-sided heart failure.
#cardiomyopathy#chronic_lung_disease#congestive_heart_failure#cor_pulmonale#pulmonary_embolism#pulmonary_hypertension#right_heart_dysfunction#right_ventricular_failure#right_ventricular_hypertrophy#tricuspid_regurgitation
0 notes
Text
ICD-10 code B33.24 for Viral cardiomyopathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
For more details:
🌐 www.transorze.com
☎️ 9495833319
#thiruvananthapuram#trivandrum#virals#cardiomyopathy#infectious#infectiousdisease#parasitic#diseases#AAPC#CPC#NSDC#WHO#medical#coding#medicalcoding#training#health#learning#transorzesolutions#transorze
0 notes
Text

ICD-10 code B33.24 for Viral cardiomyopathy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
For more details:
🌐 www.transorze.com
☎️ 9495833319
#thiruvananthapuram#trivandrum#virals#cardiomyopathy#infectious#infectiousdisease#parasitic#diseases#AAPC#CPC#NSDC#WHO#medical#coding#medicalcoding#training#health#learning#transorzesolutions#transorze
0 notes
Text
Cardiomyopathy
The cardiomyopathies may be primary (idiopathic) or secondary (where the cause is known). An important part of the management of childhood cardiomyopathies involves search for a primary cause.
0 notes
Text
Top Ten Heart-Healthy Foods for Cardiovascular Well-Being

In a world where heart health often takes center stage, the importance of adopting heart-healthy habits cannot be overstated. With the guidance of cardiologists and the wealth of information available, focusing on a balanced diet has emerged as a cornerstone of cardiovascular well-being.
The Role of Nutrition in Cardiovascular Health
A. Cardiologist Insights on Dietary Impact
The insight of cardiologists echoes loudly: what we consume profoundly impacts our heart health. From addressing conditions like cardio myopathy to identifying symptoms of heart attacks in women, medical experts emphasize the role of nutrition in preventing and managing cardiovascular disease.
B. Building Resilience Against Cardiovascular Disease
Understanding the interplay between nutrition and heart health becomes crucial. A well-rounded approach encompasses the prevention of heart failure symptoms, ischemic heart disease, and other cardiovascular conditions, encouraging a comprehensive view of cardiovascular well-being.
Heart-Friendly Nutrients: A Closer Look
A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Guardians of Cardiovascular Wellness
The powerful cardiovascular benefits of omega-3 fatty acids are akin to a protective shield for the heart. Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, these fatty acids play an essential role in reducing the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD) and supporting overall heart function.
B. Antioxidants: Shielding the Heart from Oxidative Stress
Antioxidants, found in abundance in colorful berries, provide the heart with a robust defense against oxidative stress—a factor implicated in cardiovascular disease. These natural compounds neutralize harmful free radicals, promoting cardiovascular wellness and contributing to the prevention of conditions like congenital heart disease and rheumatic heart disease.
C. Fiber: Supporting Digestion and Heart Health
The connection between fiber and heart health is intricately woven. Foods rich in fiber, such as oats, legumes, and whole grains, not only support digestion but also assist in managing cholesterol levels, thereby reducing the risk of coronary heart disease and other cardiovascular complications.
Top Ten Heart-Healthy Foods
A. Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Powerhouses for Heart Function
Fatty fish, encompassing varieties like salmon, trout, and herring, are renowned for their omega-3 fatty acid content. These nutrients promote cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and lowering the risk of arrhythmias.
B. Berries: Bursting with Antioxidants and Fiber
Berries—blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries—stand as vibrant sources of antioxidants and fiber. Their ability to enhance the circulatory system's function while aiding in blood pressure management solidifies their role in a heart-healthy diet.
C. Oats: Soluble Fiber Champions
Oats, revered for their soluble fiber content, work to lower cholesterol levels, supporting cardiovascular wellness. By reducing the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, oats become a staple in the diet of those seeking to strengthen their heart's defenses.
D. Leafy Greens: Nutrient-Dense Allies for Cardiovascular Well-Being
Leafy greens, ranging from spinach to kale, pack a nutritional punch. Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, these greens contribute to heart health by reducing hypertension, bolstering the cardiovascular system, and mitigating the risk of cardiovascular disease.
E. Nuts: Nutrient-Packed Snacking for Heart Health
Nuts, including almonds, walnuts, and pistachios, offer a heart-healthy trio of unsaturated fats, fiber, and antioxidants. Their consumption is linked to improved cholesterol levels, lowered ischemic heart disease risk, and cardiovascular well-being.
F. Legumes: Plant-Based Protein and Fiber Boost
Legumes, encompassing beans, lentils, and chickpeas, exemplify plant-based powerhouses. Their potent combination of protein, fiber, and micronutrients contributes to blood sugar regulation, lowered hypertension risk, and improved cardiovascular fitness.
G. Whole Grains: Complex Carbohydrates for Sustained Energy
Whole grains—quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat—embody complex carbohydrates that offer lasting energy and numerous health benefits. Their capacity to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease and provide heart-friendly nutrients elevates them to heart-healthy essentials.
H. Avocado: Heart-Healthy Monounsaturated Fats
Avocado's creamy texture and monounsaturated fats align seamlessly with heart health goals. Rich in potassium and antioxidants, avocados support blood pressure management and contribute to the prevention of cardiovascular disease.
I. Tomatoes: Lycopene-Rich Support for Heart Health
Tomatoes, particularly notable for their lycopene content, offer cardiovascular protection through their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Contributing to the reduction of coronary heart disease risk, tomatoes are a heart-boosting addition.
J. Dark Chocolate: Indulgence with Heart-Boosting Properties
Dark chocolate's indulgence is coupled with heart-boosting flavonoids and antioxidants. Enjoyed in moderation, it promotes blood flow, supports healthy blood pressure, and offers a delightful treat with cardiovascular benefits.
Incorporating Heart-Healthy Foods into Your Diet
A. Creating Balanced Meals Around Heart-Boosting Ingredients
Crafting meals that revolve around heart-healthy foods can be both nutritious and delicious. Incorporate a variety of these ingredients into your dishes, ensuring a balanced intake of essential nutrients that promote cardiovascular well-being.
B. Heart-Focused Meal Planning and Preparation
Meal planning becomes a strategic tool in cultivating heart health. By intentionally selecting heart-healthy foods and minimizing processed options, you can design meals that align with your cardiovascular goals. Dedicate time to preparation, ensuring your meals are both convenient and nutritious.
The Cardiovascular Benefits of a Balanced Diet
A. Reducing Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease
A diet rich in heart-healthy foods directly addresses risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease. From hypertension to atherosclerotic heart disease, the nutrients in these foods act as allies in minimizing risks and maintaining a robust cardiovascular system.
B. Cardiovascular Fitness and Longevity
The synergy between a balanced diet and cardiovascular fitness cannot be overstated. The heart-boosting properties of these foods contribute to improved circulation, lower inflammation levels, and overall heart resilience, ultimately promoting longevity and an enhanced quality of life.
Educating About Heart-Healthy Nutrition
A. Spreading Awareness About Cardiovascular Wellness
Sharing knowledge about the impact of diet on cardiovascular health is a form of advocacy. By raising awareness about the link between heart-healthy foods and overall well-being, you empower others to make informed choices and take proactive steps toward optimal heart health.
B. Empowering Individuals to Make Informed Dietary Choices
Equipping individuals with the tools to make informed dietary decisions is a gift that resonates beyond the individual level. By disseminating information about heart-boosting foods, you contribute to a collective effort to combat cardiovascular disease and improve public health.
Conclusion
A. Nourishing Your Heart: A Lifelong Commitment
Prioritizing heart-healthy foods is a commitment to nurturing your cardiovascular system. With each bite of omega-3-rich fish, every indulgence in antioxidant-packed berries, you're making a positive investment in your heart's well-being.
B. Embracing Heart-Healthy Foods for a Thriving Cardiovascular System
As you embark on this journey of incorporating heart-healthy foods into your diet, remember that the choices you make impact not only your cardiovascular system but your overall health and vitality. By embracing these nourishing options, you're taking significant strides toward a thriving and resilient heart.
#HeartHealthMatters, #CardioWellness, #HealthyHeartChoices, #NutritionForLife, #HeartSmartEating, #NourishYourHeart, #HeartHealthyHabits, #EatForYourHeart, #WellnessThroughNutrition, #HeartwiseLiving
Read the full article
#cardiomyopathy#cardiologistnearme#cardiovascular#cardiovascularsystem#circulatorysystem#hearthealthy#hearthealthyfoods#symptomsofheartattacksinwomen
0 notes
Text
https://wwwivateayurved.blogspot.com/2023/07/understanding-rheumatic-heart-disease.html
#HeartDisease#CardiovascularDisease#CoronaryArteryDisease#HeartAttack#Angina#Atherosclerosis#HighBloodPressure#Arrhythmia#HeartFailure#ValvularHeartDisease#RheumaticHeartDisease#IschemicHeartDisease#Cardiomyopathy#PeripheralArteryDisease#Stroke#Cholesterol#BloodPressure#HeartHealth#RiskFactors#LifestyleModifications#Exercise#DietAndNutrition#QuitSmoking#StressManagement#Medications#InterventionalProcedures#SurgicalTreatments#Rehabilitation#CardiacRehabilitation#PreventiveCare
0 notes
Text
A Rare cause of Troponin elevation: Focal Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy by Arzu Canan in Journal of Clinical Case Reports Medical Images and Health Sciences

CASE PRESENTATION
A 61-year-old woman with acute encephalopathy and acute cholecystitis, was found to have elevated troponin (high-sensitive troponin: 978 ng/L; >52 ng/L: abnormal), regional wall motion abnormality of mid anterior and septal segments and 50% LVEF on transthoracic echocardiography (Movie 1), without EKG changes. Patient denied chest pain, shortness of breath or palpitation. Subsequent CTA demonstrated no coronary artery disease.
Cardiac MRI revealed LVEF 45%, focal akinesis of mid anterior and septal segments (Movie 2), and mild native T1 and T2 elevation without late gadolinium enhancement (Figure 1). Considering the concomitant medical stress and spontaneous troponin down titration (978 à 764 à711 ng/L), the patient was diagnosed with focal Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Follow-up echocardiogram two weeks later demonstrated full recovery of wall motion abnormalities and 59% LVEF (Movie 3).
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is usually associated with physical-emotional trigger and characterized by a variety of wall-motion abnormalities and transient LV dysfunction. Neurological disorders is a well-known trigger of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and is more compared to patients with acute coronary syndromes. Although common presentation is acute chest pain, incidental troponin elevation or EKG changes can be the only finding. The most common type is the apical involvement resulting in apical ballooning. Isolated mid ventricular or basal involvement can also be seen. Focal anterior wall involvement is the rarest form and may mimic acute myocardial stunning or focal myocarditis. Small group of patient can have abnormal LGE while the majority of cases do not demonstrate any abnormal enhancement which can be helpful in distinguishing from other entities in addition to clinical and other ancillary findings.
Figure 1:
(a) 2-chamber steady state free precession still image in diastolic phase demonstrates minimal wall thinning of the mid anterior segment.
(b) 2-chamber steady state free precession still image in systolic phase shows focal akinesia of mid anterior segment resulting in focal bulging (arrow). Note the normal contraction at the basal and apical segments.
(c) 2-chamber phase sensitive inversion recovery (PSIR) image shows no late gadolinium enhancement.
Movie Legends:
Movie 1: Parasternal long axis view from the initial transthoracic echocardiography demonstrates the focal wall motion abnormality in the mid septal segment.
Movie 2: 2-chamber (a) and 3-chamber (b) steady state free precession cine clips from cardiac MRI demonstrates the mid anterior and septal wall motion abnormality.
Movie 3: Parasternal long axis view from the follow-up transthoracic echocardiography demonstrates the resolution of previously identified wall motion abnormality in the mid septal segment. Also note that, overall LV function has improved.
For more information: https://jmedcasereportsimages.org/about-us/
For more submission : https://jmedcasereportsimages.org/
#echocardiography#encephalopathy#CTA#abnormality#transthoracic#Neurological#cardiomyopathy#EKG#LGE#phase sensitive inversion recovery#Arzu Canan#jcrmhs
0 notes
Text
𝑫𝒓𝒖𝒈 𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒂𝒍𝒔: These trials test new medications to see if they are safe and effective for treating heart disease.
𝑫𝒆𝒗𝒊𝒄𝒆 𝒕𝒓𝒊𝒂𝒍𝒔: These trials test new medical devices, such as pacemakers or stents, to see if they are safe and effective for treating heart disease.
Visit: https://symbiosisonlinepublishing.com/cardiology/
#cardiology#cardiologist#cardiologylife#clinicaljournal#clinicaltrials#peerreviewed#pubmed#openaccess#hemofiltration#bloodtransfusion#endocarditis#pericardium#cardiomyopathy#interventionalcardiology#vascularsurgery#systemichypertension#cardiacanesthesia#myocardialischemia#electrocardiography#hemodialysis#cardiovascularbiology#openaccessjournal#journals#journal#onlinepublication#onlinepublishing#symbiosis#symbiosisonlinepublishing
1 note
·
View note
Text
Do any of y’all know of any good studies regarding polygenic cardiomyopathies? I’ve found like 4 and I’m trying to do a GWAS and it’s kinda hard to figure which polymorphisms I should even be looking at.
0 notes