#EDR Module
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
Microchip's Connected Thermometer Demonstration
https://www.futureelectronics.com/m/microchip . Microchip's Connected Thermometer Board demonstrates the implementation of a Bluetooth-connected digital thermometer using Microchip's PIC16F1519 MCU and RN42 Bluetooth Module. Connectivity is demonstrated on this board by the use of Microchip's fully qualified RN42 Bluetooth2.1 + EDR Module. This demo design can also be easily implemented using any of Microchip's Bluetooth Low Energy. https://youtu.be/2Qn7d26pnz0
#Microchip#Connected Thermometer#Bluetooth connected#digital thermometer#PIC16F1519#MCU#RN42#capacitive touch sensing#EDR Module#Wi-Fi connectivity modules#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
Microchip's Connected Thermometer Demonstration
https://www.futureelectronics.com/m/microchip . Microchip's Connected Thermometer Board demonstrates the implementation of a Bluetooth-connected digital thermometer using Microchip's PIC16F1519 MCU and RN42 Bluetooth Module. Connectivity is demonstrated on this board by the use of Microchip's fully qualified RN42 Bluetooth2.1 + EDR Module. This demo design can also be easily implemented using any of Microchip's Bluetooth Low Energy. https://youtu.be/2Qn7d26pnz0
#Microchip#Connected Thermometer#Bluetooth connected#digital thermometer#PIC16F1519#MCU#RN42#capacitive touch sensing#EDR Module#Wi-Fi connectivity modules#Youtube
0 notes
Text
The Role of Black Box Data in Trucking Accident Investigations

Source
In the aftermath of a trucking accident, determining the cause is crucial for ensuring accountability and improving safety standards. One of the most valuable tools used in accident investigations is the black box, or the event data recorder (EDR). Just like the black box in airplanes, this device captures essential data that can help investigators understand what happened before, during, and after a crash. This article explores the importance of black box data in trucking accident investigations, its role in enhancing safety, and how it helps legal professionals in handling claims.
What is a Black Box in Trucks?
A black box, also known as an event data recorder (EDR), is an electronic device installed in commercial trucks that records critical information about the vehicle’s performance. This device is typically embedded within the truck’s engine control module (ECM) and captures data related to speed, braking patterns, engine performance, and even driver behavior. The data is stored in a crash-resistant format and can be retrieved after an accident.
While the name "black box" might suggest a mysterious device, it is a key element in understanding trucking accidents. Black boxes are used to collect vital metrics, such as:
Speed of the truck at the time of the accident
Whether the driver was braking or accelerating before the collision
Engine RPM (revolutions per minute) during the incident
Steering inputs and whether the driver was attempting to avoid the accident
Vehicle location and direction of travel
In the event of an accident, investigators can retrieve this data to reconstruct the sequence of events leading to the crash.
How Black Box Data Helps in Trucking Accident Investigations
1. Providing Objective Evidence
One of the most significant advantages of black box data is that it provides objective, unbiased evidence. In many trucking accidents, there are conflicting accounts of what occurred. Eyewitness testimonies can vary, and the truck driver’s version of events may not always be accurate. Black box data, however, provides a factual record of the truck’s operation, which can help investigators identify what actually happened. This data can be crucial in proving liability or defending against false claims.
2. Understanding Driver Behavior
Black boxes not only record the truck’s performance but also the driver’s actions. For example, the device can capture whether the driver was speeding, whether they applied the brakes, or whether they made any erratic maneuvers before the accident. By analyzing this data, investigators can determine whether driver error played a significant role in the crash.
Additionally, this data can also provide insight into whether the driver was fatigued or distracted, which are major factors in many trucking accidents. While black boxes may not directly detect fatigue or distraction, they can reveal behaviors that suggest these factors, such as sudden swerves or failure to apply brakes in time.
3. Reconstructing the Accident Sequence
In some cases, the physical evidence at the scene of the accident may not provide enough information to fully reconstruct the crash. This is where black box data becomes invaluable. It allows investigators to piece together the events leading up to the crash. For example, if a truck was speeding at the time of the accident, the black box data can confirm this, helping to understand the role that excessive speed played in the crash. Similarly, if the driver made a last-second attempt to avoid the collision, the data can show whether they braked, swerved, or attempted another evasive maneuver.
The combination of black box data and physical evidence can create a more accurate picture of how the accident occurred, which can be vital in legal proceedings.
Legal Implications of Black Box Data
1. Strengthening Legal Claims
For victims of trucking accidents, black box data can be critical in proving negligence or fault. If the truck driver or the trucking company was at fault for the crash, the data can be used as evidence in court. It can show that the driver was speeding, failed to brake in time, or was not paying attention, all of which are key factors in determining liability.
In many cases, trucking companies and drivers may deny fault, claiming that the accident was unavoidable. However, black box data can provide an objective, technical account of the incident, challenging these claims and helping attorneys build a stronger case. If you are involved in a trucking accident, consulting with a qualified The Stuckey Firm truck accident lawyer can help you understand how to use this data to support your claim.
2. Protection Against Data Manipulation
In some instances, trucking companies may try to alter or tamper with the black box data to avoid responsibility. As a result, it is crucial to have a legal professional who can ensure that the data is preserved and analyzed properly. A skilled attorney can work with accident investigators to retrieve and examine the data, ensuring that it is not manipulated or destroyed. Legal experts can also work with accident reconstruction specialists to interpret the data in the context of the crash.
By ensuring that the black box data is protected and used properly, attorneys can safeguard the rights of the accident victims and prevent any attempts to cover up the truth.
The Role of the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA)
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) plays a critical role in regulating the trucking industry and ensuring that trucking companies comply with safety standards. The FMCSA mandates the installation of event data recorders in many commercial trucks, which has helped improve transparency in accident investigations.
The FMCSA also establishes guidelines for the use of black box data in accident investigations. These guidelines ensure that the data is accurately recorded and can be used in legal proceedings. By adhering to these regulations, trucking companies can avoid legal penalties, while victims of accidents can ensure that the data is available to support their claims.
Additionally, the FMCSA has guidelines for data retention, ensuring that black box information is kept for a sufficient period after an accident. This can be crucial for accident investigations, as the data may be erased or overwritten if not preserved quickly enough.
Conclusion
Black box data is an essential tool in trucking accident investigations. It provides objective, reliable information that helps investigators reconstruct accidents, identify causes, and determine liability. Whether it’s verifying driver behavior, understanding truck performance, or ensuring that evidence is preserved, black box data plays a pivotal role in ensuring fairness and transparency in the aftermath of a crash.
For those involved in trucking accidents, working with a knowledgeable truck accident lawyer can ensure that this data is used effectively in building a strong legal case. With the right legal support, you can leverage the full potential of black box data to secure justice and compensation.
0 notes
Text
Modulator Fm, ecran mare color LCD 1.3", Hands-free, Bluetooth 5.0 + EDR, USB Mp3 Player, Aux, microfon incorporat
https://www.cu-reduceri.ro/
0 notes
Photo

HP EliteDesk 800 G2 Mini Intel Core i5 6th 65W Designed for every demand Blast through your most demanding challenges with the uncompromising performance of 6th Gen Intel® Core™ processors,[2] Intel® HD 530 Graphics, and optional high-end discrete graphics and HP Turbo Drive.[3] Seriously secure Help protect your PC and maintain maximum uptime with a suite of solutions that help stop security breaches, including HP BIOSphere[4] with SureStart. Make durability a reality Get the reassurance of a PC that goes through 120,000 hours of HP Total Test Process and is designed to pass MIL-STD testing.[5] Add an optional Dust Management Solution for enhanced reliability in dusty environments. Expand with ease Extend the life of your investment with a toolless chassis and a range of expansion slots, bays, ports, and connectors for the most demanding business needs. SPECIFICATIONS: General Platform Technology Intel vPro Platform Type Personal computer Product Form Factor Mini desktop Built-in Devices Speaker, hood sensor Embedded Security Trusted Platform Module (TPM 1.2) Security Chip Localization Language: English / region: United States Processor / Chipset CPU Intel Core i5 (6th Gen) 6500T Clock Speed 2.5 GHz Max Turbo Speed 3.1 GHz Number of Cores Quad-Core CPU Upgradability: Upgradable Processor Main Features: Intel Turbo Boost Technology 2 CPU Socket: LGA1151 Socket Chipset Type: Intel Q170 Cache Memory Installed Size: 6 MB Cache Per Processor: 6 MB RAM Installed Size: 8 GB Technology: DDR4 SDRAM - non-ECC Effective Memory Speed: 2133 MHz Rated Memory Speed: 2133 MHz Memory Specification Compliance PC4-17000 Form Factor: SO-DIMM 260-pin Slots 2 (total) / 1 (empty) Features Unbuffered, dual channel memory architecture Configuration Features: 1 x 8 GB Hard Drive Type: HDD Capacity: 1 x 500 GB Interface Type: SATA 6Gb/s Spindle Speed: 7200 rpm Storage Controller Type: 1 x SATA Controller Interface Type: SATA 6Gb/s Optical Storage Type: No optical drive Graphics Controller Graphics Processor: Intel HD Graphics 530 Dynamic Video Memory Technology Video Interfaces: VGA, DisplayPort HDCP Compatible: Yes Max Monitors Supported: 3 Audio Output Sound Output Mode Stereo Max Sampling Rate 192 kHz Compliant Standards High-Definition Audio, DTS Studio Sound Input Device Type Mouse, keyboard Keyboard Keyboard Name HP Business Slim Keyboard Interface USB Localization & Layout US Mouse Interface USB Networking Ethernet Controller Intel I219-LM Wireless LAN Supported Yes Wireless NIC Intel Dual Band Wireless-AC 8260 Data Link Protocol Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n, Bluetooth 2.1 EDR, IEEE 802.11ac, Bluetooth 4.1 Remote Management Protocol DMI Features Wake on LAN (WoL), PXE support, auto-uplink (auto MDI/MDI-X) Compliant Standards IEEE 802.2, IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u, IEEE 802.3i, IEEE 802.1Q, IEEE 802.3ab, IEEE 802.1p, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11i, Wi-Fi CERTIFIED, IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.3az Expansion / Connectivity Bays 1 (total) / 0 (free) x internal 2.5" x 1/8H Slots 1 (total) / 0 (free) x CPU | 2 (total) / 1 (free) x SO-DIMM 260-pin | 1 (total) / 0 (free) x M.2 Card (x1 mode) | 1 (total) / 1 (free) x M.2 Card (x4 mode) Interfaces 1 x headphones - mini-jack (1 in front) | 1 x headphones/microphone - mini-jack (1 in front) | 1 x USB-C 3.0 (1 in front) | 6 x USB 3.0 (2 front, 4 rear) | 1 x VGA | 2 x DisplayPort | 1 x LAN (Gigabit Ethernet) - RJ-45 Miscellaneous Theft/Intrusion Protection Security lock slot (cable lock sold separately) Security Slot Type Kensington security slot VESA Mounting Interface 100 x 100 mm Compliant Standards ACPI, CCC, CECP, SEPA, low halogen Manufacturer Selling Program HP Smart Buy Power Device Type Power adapter Voltage Required AC 120/230 V (50/60 Hz) Power Provided 65 Watt Efficiency 89% Power Factor Correction Yes (active) Operating System / Software OS not provided Environmental Standards ENERGY STAR Certified Yes
#REFURBISHED#REFURBISHED_DESKTOP#6TH_GEN#CORE_I5#ELITEDESK_800_G2#HP#INTEL#MICRO#SMALL_FORM_FACTOR#TPC_P055_DM
0 notes
Text
Firmware And Hypervisors Support To Secure IBM Cloud VPC

Do you know your hypervisor and firmware?
IBM Cloud VPC is built for secure cloud computing, and numerous platform planning, development, and operational characteristics assure that. However, since cloud security is usually a shared duty between the cloud service provider and the client, you must thoroughly grasp the levels of security your workloads operate on here with us. Its’ve included a few IBM Cloud VPC security components to help the virtual server clients safeguard their computing.
Start with the hypervisor
Any virtual server architecture needs a hypervisor to safeguard client workloads and cloud native applications. Everything from hardware and firmware to system software and configuration must be safeguarded from outside manipulation.
Firmware and hypervisor software are the lowest changeable code layers and good targets for supply chain and other privileged assaults. Endpoint security tools like antivirus and EDR software struggle to identify kernel-mode rootkits (bootkits), privileged threats. They rush before any defense mechanism that may conceal them. Thus, supply chain security is essential.
Qualification and testing before deployment are among IBM Cloud VPC’s procedures to ensure hardware, firmware, and software quality, integrity, and supply chain.
IBM Cloud VPC’s 3rd-generation solutions ensure platform integrity with ubiquitous code signing. This procedure digitally signs and authenticates firmware at origin before installation. Before processor initiation, a platform security module validates the firmware image’s integrity during system startup. The platform security module hardware becomes the system’s source of trust when the firmware authenticates the hypervisor and device software.
Configuring and testing devices
IBM Cloud Virtual Servers for VPC provide several profile choices (vCPU + RAM + bandwidth provisioning bundles) to satisfy clients’ workload needs. Profile types are regulated by product specifications. These product specs describe the server’s hardware, firmware, and configuration. Software encompasses host firmware and component devices. The server fleet uses these versioned product profiles produced and managed by a hardware leadership team.
New hardware and software in the IBM Cloud VPC environment are mapped to a product specification, which describes their configuration. The intake verification procedure confirms that the server’s physical composition fulfills the requirements before entering the fleet. The server is quarantined for examination and repair if its physical composition doesn’t fit the standard.
Device configuration and verification
This verification has two dimensions:
IBM Cloud Virtual Servers for VPC it must be signed by an authorized source before installation. This keeps servers running on certified firmware. IBM Cloud works with numerous vendors to sign it and set components to reject fraudulent firmware.
Only IBM Cloud-approved it may be installed: The regulated specification is updated periodically to include qualifying firmware and delete old versions. This firmware check is done after server intake and before firmware updates.
The product specs also control server settings: Some solutions need special UEFI setups, features, or constraints. Configurations are automated on servers based on the product specification. IBM Cloud’s monitoring and compliance infrastructure scans servers live.
Versioning and promoting specifications
As said, product specifications are key to IBM Cloud virtual server for VPC administration. Product specifications comprise server profile settings and are approved by the IBM Cloud product leader and governance-focused leadership team. They oversee the server’s authorized components, configuration, and firmware. Product leaders concentrate on value and market uniqueness, while the governance-focused leadership team seeks commonality.
Keep in mind that specs change: As firmware versions change or server hardware expands to handle more vendor devices, these definition files change. Because of this, IBM Cloud VPC standard is versioned to track server lifecycle changes. Each server deployment records its specification version and the planned vs actual condition.
Specifications must be promoted: A specification update may not be immediately effective in production. Instead, it undergoes development, integration, and staging before production. The rollout speed may vary depending on the devices or fixes.
IBM Cloud VPC firmware updates in waves: Although some changes need downtime, it may be updated live. The clients seldom experience this owing to live migration. As it upgrades are produced, consumers may take time to migrate. A specification update promoted via the pipeline initiates the update through runtime systems. Change severity determines update speed.
IBM Cloud VPC virtual servers provide a hardware root of trust
IBM Cloud Virtual Servers for VPC have platform security module root of trust hardware. Before the main processor boots, the platform security module hardware verifies the platform firmware image’s validity and integrity. Verifies picture authenticity and signature with an authorized certificate. Platform security module saves platform firmware image copies. If the host firmware image is not signed with the permitted certificate, the platform security module replaces it with one of its images before initializing the main processor.
After initializing the main processor and installing the system firmware, the firmware authenticates the hypervisor’s bootloader in secure boot to create the next trust link. The firmware checks that the bootloader was signed with a valid key before loading. Enrolling public keys in the server’s key database authorizes them. After clearing and loading, the bootloader checks the kernel before running. Finally, the kernel checks all modules before loading them. System boot stops for every component that fails validation.
Secure boot and the platform security module combine to prevent supply chain threats and server privileges from injecting malicious software. IBM Cloud Virtual Servers for VPC can only boot firmware, bootloaders, kernels, and kernel modules certified with IBM Cloud certificates and those of previously authorized operating system providers.
The aforementioned firmware configuration procedure checks firmware secure boot keys against the permitted list. Boot keys in the permitted keys database, banned keys, exchange key, and platform key.
Secure boot allows adding kernel and kernel module signing keys to the first stage bootloader (shim), also known as the system owner key. Thus, IBM Cloud’s operating system setup ensures that only permitted keys are registered in the mok facility.
After a server passes all tests and is permitted to start, an audit chain is built from the platform security module hardware to kernel modules.
How to use Verified hypervisors on IBM Cloud VPC virtual servers?
Hypervisor verification is enabled by default for supported IBM Cloud VPC Virtual Servers. To guarantee your virtual server instances operate on hypervisor-verified supported servers, choose a generation 3 virtual server profile (bx3d, cx3d, mx3d, or gx3). Customers may use generation 3 virtual servers to take use of these features, which are now available.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Firmware#Hypervisors#IBMCloudVPC#cloudcomputing#software#hardware#VirtualServers#VPC#News#Technews#Technology#Technologytrends#Technologynews#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Next - Gen cyber security

Introduction
Welcome and Orientation
Overview of the Next-Gen Cyber Security Skills course in Bangalore
Introduction to instructors and fellow participants
Setting goals and expectations for the course
Module 1: Foundations of Cyber Security
Understanding Cyber Security
Definition and importance of cyber security in today’s world
Current landscape and emerging threats
Cyber Security Terminology
Key terms and concepts crucial for the Bangalore cyber security course
Overview of common attack vectors and defenses
Cyber Security Frameworks and Standards
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
ISO/IEC 27001
CIS Controls and their relevance to Bangalore’s cyber security environment
Module 2: Network Security
Network Security Fundamentals
Basic networking concepts vital for Bangalore cyber security professionals
Understanding firewalls, VPNs, and IDS/IPS
Securing Network Infrastructure
Techniques for network segmentation and isolation
Secure network design and architecture
Wireless Network Security
Wireless security protocols (WPA3, WPA2)
Securing wireless access points in a Bangalore context
Module 3: Application Security
Introduction to Application Security
Common vulnerabilities (OWASP Top Ten)
Secure coding practices essential for Bangalore developers
Web Application Security
Addressing Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and SQL Injection
Integrating secure development lifecycle (SDLC) practices
Mobile Application Security
Addressing mobile-specific threats and vulnerabilities
Best practices for securing mobile apps in the Bangalore market
Module 4: Endpoint Security
Endpoint Protection
Anti-virus and anti-malware solutions
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools
Securing Operating Systems
Hardening Windows and Linux systems
Effective patch management and software updates
BYOD and IoT Security
Managing Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies in Bangalore
Securing Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Module 5: Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Fundamentals of IAM
Authentication vs. Authorization
Identity lifecycle management and its application in Bangalore businesses
Access Control Mechanisms
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Identity Management Solutions
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Federation
Identity as a Service (IDaaS) platforms and their relevance
Module 6: Cloud Security
Cloud Security Basics
Understanding cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Shared responsibility model for cloud security
Securing Cloud Environments
Best practices for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud in Bangalore
Cloud security posture management
Cloud Compliance and Governance
Regulatory requirements and compliance standards applicable in Bangalore
Data protection and privacy in the cloud
Module 7: Threat Intelligence and Incident Response
Cyber Threat Intelligence
Gathering and analyzing threat data
Using threat intelligence platforms effectively
Incident Response Planning
Developing an incident response plan
Incident detection and analysis
Handling Security Incidents
Containment, eradication, and recovery strategies
Post-incident activities and lessons learned
Module 8: Security Operations and Monitoring
Security Operations Center (SOC)
Roles and responsibilities of SOC teams
Setting up and managing a SOC in Bangalore
Monitoring and Logging
Importance of logging and monitoring
Using SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools
Threat Hunting
Proactive threat hunting techniques
Leveraging advanced analytics and AI for threat detection
Module 9: Compliance and Legal Aspects
Understanding Cyber Security Regulations
Key regulations (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc.)
Compliance requirements for organizations in Bangalore
Legal Considerations in Cyber Security
Data breach laws and notification requirements
Intellectual property and cyber crime laws
Auditing and Assessment
Conducting security audits and assessments
Preparing for compliance audits
Module 10: Capstone Project and Certification
Capstone Project
Real-world scenario-based project
Applying learned skills to solve complex problems
Exam Preparation
Review of key concepts and practice exams
Tips and strategies for passing the certification exam
Certification and Next Steps
Receiving course completion certificate
Exploring advanced certifications and career paths
Conclusion and Course Wrap-Up
Final Q&A Session
Addressing any remaining questions
Sharing additional resources and tools
Networking and Alumni Community
Joining the course alumni network
Continued learning and professional development opportunities in Bangalore
This Next-Gen Cyber Security course in Bangalore will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in the evolving field of cyber security
0 notes
Text
Buy HC05 Bluetooth Module at Affordable Price in Ainow
HC05 Bluetooth Module
The Bluetooth Transceiver HC05 bluetooth Module with enable/disable button Breakout is the latest Bluetooth wireless serial cable! This version of the popular Bluetooth uses the HC05 module. These modems work as a serial (RX/TX) pipe. Any serial stream from 9600 to 115200bps can be passed seamlessly from your computer to your target. The remote unit can be powered from 3.3V up to 6V for easy battery attachment. All signal pins on the remote unit are 3V-6V tolerant. No level shifting is required. Do not attach this device directly to a serial port. You will need an RS232 to TTL converter circuit or Arduino XBee USB Adapter if you need to attach this to a computer. You can either solder a 6-pin header or individual wires. The unit comes without a connector. Please see related male and female pins below. And now, we provide HC-05/06, HC05 bluetooth module could be set to Master or Slave by a user. HC-06 just be Master or Slave, that could be customized.
HC05 bluetooth module Applications:
Embedded Projects
Industrial Applications
Computer and portable Devices
GPS receiver.etc.
Note: Product Image may vary in terms of design and colour of the board
Features :
CSR Bluetooth Chip Solution-Bluetooth Spec v2.0 EDR Compliant
Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) compliant with V2.0.E.2 of the specification for both 2Mbps and 3Mbps modulation modes
Full Speed Bluetooth Operation with Full Piconet Support and Scatternet Support
Incredible small size with 3.3V input, and RoHS Compliant-UART interface and with baud rate setup function
Support for 8Mbit External Flash Onboard Support for 802.11Co-Existence. A range of operation: 8 – 10 meter.

0 notes
Text
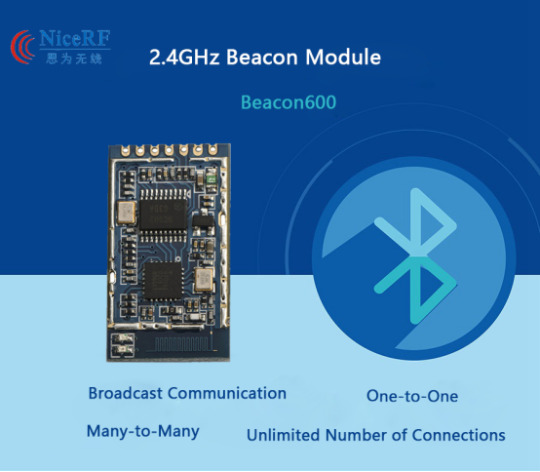
2.4GHz High-Performance Bluetooth Module: Effortlessly Handles Many-to-Many Communication with Flexible Operating Modes
The operating modes of Bluetooth modules encompass two technologies: Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). Each technology has various operating modes, such as master mode, slave mode, master-slave mode, and advertising mode. Among these, master mode and slave mode are the two fundamental roles that devices play in Bluetooth communication, defining their behavior and responsibilities in the connection and data transmission process.
Beacon600 is the latest 2.4GHz beacon module which is compatible with BLE. This module integrates the MCU and process the SPI protocol. It provides generic UART interface, users can connect the module with smart phone with BLE. This module has the same structure of BLE, and works as Broadcast mode of Bluetooth. It is easier and cost-effective compare with Bluetooth.

Master Mode
Initiating Connections: The master device is responsible for scanning nearby Bluetooth devices and actively initiating pairing and connection requests.
Controlling the Connection: Once the connection is established, the master device controls the connection parameters, such as the connection interval and the start and stop of data transmission.
Multiple Device Connections: A master device can theoretically connect to multiple slave devices simultaneously.
Master Mode
Initiating Connections: The master device is responsible for scanning nearby Bluetooth devices and actively initiating pairing and connection requests.
Controlling the Connection: Once the connection is established, the master device controls the connection parameters, such as the connection interval and the start and stop of data transmission.
Multiple Device Connections: A master device can theoretically connect to multiple slave devices simultaneously.
Slave Mode
Passive Connection Reception: The slave device cannot initiate connection requests. Instead, it waits to be discovered and connected by the master device.
Responding to Connections: Upon receiving a connection request from the master device, the slave device responds and establishes the connection.
Data Interaction: Once the connection is established, the slave device can exchange data with the master device, although the communication parameters are primarily controlled by the master.
Dependence on Master Clock: During communication, the slave device's clock is synchronized with the master's clock, ensuring synchronous data transmission between both devices.
In some cases, devices support a master-slave mode, allowing them to switch between master and slave roles to adapt to different application scenarios or take on different communication responsibilities as needed. This flexibility enhances the applicability and functionality of Bluetooth devices, particularly in IoT and wearable device scenarios.
Master-Slave Mode
Bluetooth modules can switch between the roles of master and slave as needed. This means the same Bluetooth module can act like a master device, scanning for and connecting to other slave devices, controlling the data transmission process, and can also switch to the slave role, waiting to be discovered and connected by other master devices.
This mode significantly enhances the flexibility and versatility of Bluetooth devices in various application scenarios. For instance, in IoT devices, one device might need to act as a central node collecting data at certain times, while also being able to function as a terminal device reporting data to another central node.
Broadcast Communication Mode
One-to-One Communication
In one-to-one communication, Bluetooth devices establish a dedicated connection. This connection ensures reliable data transmission, and in point-to-point communication, Bluetooth's transfer speed and stability are guaranteed.
Many-to-Many Communication
The Bluetooth module integrates an MCU internally and communicates through Bluetooth broadcasting and scanning protocols. It supports transparent UART transmission and has no limits on the number of connections, which is particularly evident in BLE.
Broadcast Mode
Broadcast mode refers to the Bluetooth module periodically sending data packets (advertisement packets) in a non-connected manner. These packets can be received by any device within range and in listening mode. In broadcast mode, the Bluetooth module does not establish one-to-one connections but instead uses a one-to-many approach to broadcast information to all interested receivers.
Beacon600 Bluetooth module is low power, cost-effective, and powerful, suitable for a variety of wireless communication applications. It offers flexible parameter configuration and efficient data transmission capabilities.
For details, please click:https://www.nicerf.com/products/ Or click:https://nicerf.en.alibaba.com/productlist.html?spm=a2700.shop_index.88.4.1fec2b006JKUsd For consultation, please contact NiceRF (Email: [email protected]).
0 notes
Text
Features ESP32-WROOM-32UE - Campus Component
ESP32-WROOM-32 UE are two powerful, generic Wifi+BT+BLE MCU modules that target a wide variety of applications, ranging from low-power sensor networks to the most demanding tasks, such as voice encoding, music streaming and MP3 decoding. ESP32-WROOM-32 UE with an IPEX antenna. They both feature a 8 MB external SPI flash. The integration of Bluetooth®, Bluetooth LE and Wi-Fi ensures that a wide range of applications can be targeted, and that the module is all-around: using Wi-Fi allows a large physical range and direct connection to Internet through a Wi-Fi router, while using Bluetooth allows the user to conveniently connect to the phone or broadcast low energy beacons for its detection.
The sleep current of the ESP32 chip is less than 5 μA, making it suitable for battery powered and wearable electronics applications. The module supports a data rate of up to 150 Mbps, and 20 dBm output power at the antenna to ensure the widest physical range. As such the module does offer industry-leading specifications and the best performance for electronic integration, range, power consumption, and connectivity.
ESP32-WROOM-32UE Features:-
MCU :
ESP32-D0WD-V3 embedded, Xtensa® dual-core 32-bit LX6 microprocessor, up to 240 MHz
448 KB ROM for booting and core functions
520 KB SRAM for data and instructions
16 KB SRAM in RTC
802.11b/g/n
Bit rate: 802.11n up to 150 Mbps
A- Wi-Fi :
MPDU and A-MSDU aggregation
0.4 μs guard interval support
Center frequency range of operating channel: 2412 ~ 2484 MHz
Bluetooth :
Bluetooth V4.2 BR/EDR and Bluetooth LE specification
Class-1, class-2 and class-3 transmitter
AFH
CVSD and SBC
Hardware :
Interfaces: SD card, UART, SPI, SDIO, I2C, LED PWM, Motor PWM, I2S, IR, pulse counter, GPIO, capacitive touch sensor, ADC, DAC
40 MHz crystal oscillator
4 MB SPI flash
Operating voltage/Power supply: 3.0 ~ 3.6 V
Operating temperature range: –40 ~ 85 °C
Buy ESP32-WROOM-32UE 8MB Flash, 448kB ROM, 536kB SRAM 2.4GHz ~ 2.5GHz Bluetooth V4.2 BR/EDR 40MHz crystal oscillator avaliable at the lowest price from Espressif Systems Distributor in India | Campus Component.
0 notes
Text
RN42 Bluetooth Module: A Comprehensive Guide
The RN42 Bluetooth module was developed by Microchip Technology. It’s designed to provide Bluetooth connectivity to devices and is commonly used in various applications, including wireless communication between devices.
Features Of RN42 Bluetooth Module
The RN42 Bluetooth module comes with several key features that make it suitable for various wireless communication applications. Here are the key features of the RN42 module:
Bluetooth Version:
The RN42 module is based on Bluetooth version 2.1 + EDR (Enhanced Data Rate).
Profiles:
Supports a range of Bluetooth profiles including Serial Port Profile (SPP), Human Interface Device (HID), Audio Gateway (AG), and others. The availability of profiles makes it versatile for different types of applications.
Frequency Range:
Operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band, the standard frequency range for Bluetooth communication.
Data Rates:
Offers data rates of up to 3 Mbps, providing a balance between speed and power consumption.
Power Supply Voltage:
Operates with a power supply voltage in the range of 3.3V to 6V, making it compatible with a variety of power sources.
Low Power Consumption:
Designed for low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-powered applications and energy-efficient designs.
Antenna Options:
Provides options for both internal and external antennas, offering flexibility in design based on the specific requirements of the application.
Interface:
Utilizes a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) interface for serial communication, facilitating easy integration with microcontrollers and other embedded systems.
Security Features:
Implements authentication and encryption mechanisms to ensure secure wireless communication.
Read More: RN42 Bluetooth Module
#rn42-bluetooth-module#bluetooth-module#rn42#bluetooth-low-energy#ble#microcontroller#arduino#raspberry-pi#embedded-systems#IoT#internet-of-things#wireless-communication#data-transmission#sensor-networking#wearable-technology#mobile-devices#smart-homes#industrial-automation#healthcare#automotive#aerospace#telecommunications#networking#security#software-development#hardware-engineering#electronics#electrical-engineering#computer-science#engineering
0 notes
Link
https://www.futureelectronics.com/m/panasonic. Panasonic PAN9026 Series is a dual band 2.4/5 GHz 802.11 a/b/g/n Wi-Fi Radio Module with integrated Bluetooth BDR/EDR/LE, specifically designed for highly integrated and cost-effective applications. https://youtu.be/eNDBttgGR2U
1 note
·
View note
Video
youtube
https://www.futureelectronics.com/m/panasonic. Panasonic PAN9026 Series is a dual band 2.4/5 GHz 802.11 a/b/g/n Wi-Fi Radio Module with integrated Bluetooth BDR/EDR/LE, specifically designed for highly integrated and cost-effective applications. https://youtu.be/eNDBttgGR2U
0 notes
Text
New European Drawer Rack set for Space Station
ESA - Columbus Module logo.
May 18, 2020
Stork capture
When the Japanese HTV-9 cargo vehicle launches to the International Space Station on 20 May it will carry a part of Europe in its pressurised module. The second iteration of the European Drawer Rack (EDR-2) is destined for the European Columbus laboratory and will provide even greater opportunities for science in space.
Columbus over Earth
Columbus has been flying 400 km above our heads as part of the International Space Station for 12 years. Its collection of facilities enables European scientists to run experiments across scientific disciplines including biology, metallurgy and physics, as well as research in radiation and testing new technology in microgravity. A facility for the future As the International Space Station enters its 20th year of operations, EDR-2 is part of a comprehensive upgrade of Columbus to offer faster, easier and more flexible access to researchers on Earth. The rack was developed by an industrial team led by Thales Alenia Space Italy, based in Turin, Italy. As the name implies, the facility offers room to run experiments by supplying power, data communication, cooling, nitrogen and venting waste gasses.
European Drawer Rack-2
Rob Postema from ESA’s exploration systems team says: “The rack is based on a simplified architecture to accommodate many types of sub-facilities with different dimensions and masses. We can even use it to support experiments nearby the experiment rack, so long as these are within the Columbus cabin.” The standard-sized racks that fit in all Space Station laboratories are the size of large fridges, and fly in the Japanese HTV to the International Space Station. Once on board they become easier to manipulate for the astronauts in weightlessness.
ESA astronaut installing standard-sized Space Station rack
A facility for science and technology The first three experiments planned for installation in EDR-2 include a metal 3D printer, an instrument investigating granular materials and a facility looking into heat transfer. ESA intends to use the 3D printer to produce metal parts through additive manufacturing – a process considered the next important step in building structures and parts in space.
Preparing VIP-GRAN experiment for parabolic flight
The VIP-GRAN experiment will investigate how particles behave in microgravity to understand the underlying physics in detail. This involves looking at how particles jam together as they flow through small openings.
Working in Columbus
The Heat Transfer Host will continue ESA’s investigations into convection – how heat is transferred through air and liquids. Investigating the process in space allows researchers to look at the core mechanics without gravity getting in the way. This should improve future satellite cooling systems as well as confirm or fine-tune computer models that can be applied on Earth to improve cooling for electronics such as smartphones and computers. These experiments are the first in a long line planned for the new facility. More than double The EDR-2 will not replace the original European Drawer Rack but run in parallel, increasing the possibilities of research and technology demonstration in space. EDR-2 will benefit from other Columbus upgrades to modernise data management and improve data-rates for scientists operating their experiments from laboratories on Earth.
European Drawer Rack-2
The EDR-2 and most of its experiments will be operated from CADMOS, the French User Support Operations Centre located in Toulouse, France. A full-scale Engineering Model of EDR-2 is available at CADMOS to test instruments and prepare experiment operations, as well as run control versions of experiments on Earth. Watch the launch of EDR-2 in HTV-9 on NASA television or via JAXA. Live coverage starts at 19:00 CEST (17:00 GMT) with launch scheduled at 19:30 (17:30 GMT). HTV-9 is scheduled to arrive at the International Space Station on 25 May. Related links: European Drawer Rack: https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration/Columbus/European_Drawer_Rack CADMOS: http://www.medes.fr/en/our-activities-1/space-exploration/space-missions/physiology-experiments-cadmos.html Human and Robotic Exploration: http://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Human_and_Robotic_Exploration Images, Text, Credits: ESA/L. Parmitano, M. Cowan, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO/NASA/JAXA.
Greetings, Orbiter.ch
Full article
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mud Logging Recorder
Mud logging recorder
The Laversab sand logging recorder EDR is created for common data acquisition software on the rig, such as Mudlogging, Lithology, Pit Volume Totalizer (PVT), Depth Logging, and much more.
What is a mud logging recorder?
In the circumstance of an oilfield drilling operation, mud logging is the custom of producing a thorough record of the depth of a borehole, which is a vertical or horizontal rotating drilled from the floor. Another purpose of sand drilling is to determine whether geologic formations exposed by the borehole comprised hydrocarbons, among the chief components in petroleum and natural gas. By creating a detailed listing, or well log, oilfield operators can ascertain the viability of this borehole for the production of the raw gas that sustains our daily lives.
mud logging EDR
Nowadays, sand logging has expanded in scope to include a range of technical services and advanced technology that help to monitor boreholes and preserve their equilibrium. To that end, Laversab Oilfield has designed an Electronic Drilling Recorder (EDR) system that performs common data acquisition software onto the rig, including mud logging. Laversab's mud logging recorder can deliver surface parameters in real time to drillers, operators, and offsite stakeholders. Additionally, thanks to the LINKS EDR software, these persons may additionally access key performance indicators, tour sheets, daily reports, and other valuable information.
How is a sand logging recorder utilized?
Mud logging technicians in oilfield environments have many broad objectives, including identifying the positions of hydrocarbon-bearing formations and tracking natural gas entering the drilling sand flow. Well logs for boreholes within an oilfield can provide valuable real-time info about cuttings, or the types of minerals found. Although this job may be physically and mentally taxing, equipment such as a mud logging recorder offer accurate readings that help boost productivity and security.
In order to maximize the potency of a subway logging recorder, it has to have an application package capable of generating oilfield data at a minute's notice. That is where Laversab LINKS comes in: this rig-ready application, which is compatible with EDR systems made by either Laversab or other businesses, is able to obtain surface parameters and format them to well-site data transfer standard markup language (WITSML). Does this transmit well-site information to oilfield stakeholders, but WITSML archives it for future usage and computes both time-based and depth-based measurements as required.
The potential for volatility is ever-present in oilfield drilling circumstances. For this advice, receiving swift, accurate information regarding well-site requirements is paramount. Not only does having this information ease successful drilling, it aids in keeping a high level of safety around the website. When used along with a mud logging recorder, LINKS accounts for distributing surface parameters and managing key performance indicators, tour sheets, and daily reports. LINKS also has modules for lithology, swab, well planning, and ton-mile calculations.
1 note
·
View note
Text
[Media] Bin-Finder
Bin-Finder Detect EDR's exceptions by inspecting processes' loaded modules. https://github.com/Kudaes/Bin-Finder #infosec #pentesting #redteam

0 notes