#FinancialStatements
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why is financial statement preparation so important?
It’s the process of organizing a company’s financial data into structured reports, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These documents show your profits, losses, assets, and expenses over a specific period.
Why It Matters
Informed Decisions Well-prepared financial statements give business owners insights into spending, savings, and profitability. This helps in making smart, data-driven decisions.
Legal and Tax Compliance Accurate financial records ensure you meet government regulations and file taxes correctly, reducing the risk of fines or audits.
Attracting Investors and Loans Clear financials help build trust with banks and investors. They’re often a requirement when applying for funding or business partnerships.
Business Planning and Growth Financial statements reveal trends and performance, making it easier to plan for the future and set realistic goals.
Financial Statement Preparation isn’t just about staying organized; it’s about staying in control. Whether you’re a startup or an established business, proper financial reporting is the foundation for stability and growth.
0 notes
Text
📊 Understanding Financial Statements for US Small Businesses: A Simple Guide 💼
Running a small biz means juggling a lot — customers, operations, growth plans. But there’s one thing you can’t skip: understanding your financial health. Financial statements are like your business’s GPS, showing you where you are and what your next move should be.
Not a numbers person? No worries — here’s a simple breakdown of the 3 main financial statements every US small business owner should know:
1️⃣ Income Statement (Profit & Loss)
Think of this as your biz’s report card. It shows:
💰 Revenue: Money you make from sales
📉 Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): What it costs to make your product or service
💸 Operating Expenses: Rent, salaries, marketing, etc.
📈 Net Income/Loss: Profit or loss after everything
Why it matters? It tells you if you’re making money or not — and where to tweak if things aren’t looking good.
2️⃣ Balance Sheet
This is a snapshot of your business’s financial health right now:
🏦 Assets: What you own (cash, inventory, equipment)
💳 Liabilities: What you owe (loans, bills)
📊 Equity: What’s left after subtracting liabilities from assets
Why it matters? It shows if your business is stable and able to cover debts and obligations.
3️⃣ Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow = your business’s lifeline. Even if you’re profitable, no cash means trouble. This shows:
🔄 Operating Activities: Cash from daily operations
🛠️ Investing Activities: Cash spent or earned from buying/selling assets
💵 Financing Activities: Cash from loans, repayments, or investments
Why it matters? Positive cash flow means you can pay bills and invest in growth. Keep an eye on this to avoid surprises.
How They Work Together
Income Statement = Are you profitable?
Balance Sheet = What do you own vs. owe?
Cash Flow = Can you cover your bills today?
For example, you could be profitable but have negative cash flow if customers pay late — so watch all three!
🔗 For more tips and guides, learn more here.
#SmallBusiness#FinancialStatements#AccountingTips#CashFlow#ProfitAndLoss#BalanceSheet#BizGrowth#EntrepreneurLife#accounting#united states#bookkeeping#business#small business#Counto
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Analyze a Company’s Financial Statements?
Grasping the art of analyzing a company’s financial statements ranks among the most crucial skills for investors, business owners, and financial analysts. These documents unveil the financial health, profitability, operational efficiency, and future prospects of a business. However, given the depth and complexity involved, determining what to focus on—and understanding its significance—can seem daunting. This guide simplifies the process into a clear, structured approach for financial reporting, equipping you with the tools to assess a company’s financials with confidence and precision.
What Are Financial Statements?
Financial statements are official records of a company’s financial activities. Typically prepared quarterly and annually, these statements form the foundation for business analysis. They are designed to provide shareholders, regulators, creditors, and analysts with a transparent view of a company's financial health and performance. The three primary financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Each statement serves a distinct purpose in highlighting various facets of the business. The income statement details profitability, the balance sheet outlines financial position, and the cash flow statement offers insights into liquidity and cash movements. Analyzing them collectively provides a comprehensive view of the company.
The Income Statement: Understanding Profitability
Commonly known as the profit and loss statement, the company's income statement outlines the company’s revenues and expenses over a specific period. Its primary function is to ascertain whether the company is profitable and what factors influence its performance.
The analysis begins with the top line—revenue. Revenue growth can signify expansion, customer demand, or new income streams. It is crucial to assess whether this revenue is sustainable, recurring, or based on one-time events.
From revenue, expenses are deducted to determine net income. Major expenses include the cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, interest, and taxes. Ideally, a robust company will exhibit growing revenue and controlled expenses, resulting in a strong net income and operating income .
A key indicator here is the operating margin—how much profit the company generates from its core operations. An increasing operating margin often indicates enhanced efficiency and a more profitable business model. Another important measure is the gross profit margin, along with earnings per share (EPS), which reflects how much profit is attributable to each outstanding share.
The Balance Sheet: Assessing Financial Position
While the income statement measures performance over time, the balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a given moment. It details what the company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the value that belongs to shareholders (equity).
1. Understanding Assets and Liabilities
Assets are divided into current assets, such as cash and inventory, and non-current assets, including property or long-term investments. Liabilities are similarly categorized into short-term and long-term obligations. The difference between total assets and total liabilities equals shareholders’ equity, reflecting the company’s net worth.
2. Analyzing Liquidity and Solvency
Analyzing a balance sheet involves evaluating the company’s liquidity and solvency. Liquidity ratios, such as the current ratio and quick ratio, help assess whether the company can cover its short-term obligations. A current ratio above 1 suggests the company has more current assets than liabilities, which is generally a positive sign.
3. Leverage Ratios and Financial Risk
Leverage ratios, like the debt-to-equity ratio, provide insights into how much of the company is financed by debt versus shareholder equity. A high debt-to-equity ratio may indicate financial risk, especially in uncertain markets, while a lower ratio points to a more conservative capital structure.
The Cash Flow Statement: Tracking Liquidity
A company can appear profitable on the income statement and still struggle to generate cash. That’s where the cash flow statement becomes invaluable. It shows how cash moves in and out of the business through operations, investments, interest expense and financing activities.
Importance of Operating Cash Flow
Operating cash flow is one of the most important areas to focus on. It reveals whether the business is generating enough cash from its core operations to sustain itself. A positive operating cash flow suggests the company can fund its own growth, pay dividends, and manage debts without needing to raise external capital.
Reviewing Investing and Financing Activities
Investing activities detail how the company spends its cash, typically on capital expenditures like equipment or acquisitions. Financing activities include debt repayments, dividend payments, and stock issuance or buybacks. Reviewing all three sections helps paint a picture of how management is allocating resources and whether those decisions are creating long-term value.
Financial Ratios: Making Sense of the Numbers
Financial statements contain a huge volume of data. Financial ratios help condense that data into meaningful indicators. They allow you to quickly assess profitability, efficiency, liquidity, and leverage, and are essential for comparing performance across companies or industries.
Profitability and Efficiency Ratios
Profitability ratios like return on equity (ROE) and return on assets (ROA) measure how efficiently a company is turning investments into profits. Higher ratios typically indicate a well-managed, profitable business. Efficiency ratios show how effectively a company uses its assets. For instance, the inventory turnover ratio indicates how quickly inventory is sold and replaced. A higher turnover suggests efficient operations, while a low turnover may signal declining demand or poor stock management.
Solvency and Liquidity Ratios
Solvency ratios like the interest coverage ratio demonstrate whether a company can meet its long-term obligations. An interest coverage ratio below 1.5 might raise red flags, signaling potential difficulties in servicing debt. Liquidity ratios, such as the current ratio and quick ratio, reveal the company’s short-term financial health. They are particularly important for businesses in volatile industries or those with fluctuating cash flows.
Interpreting Trends Over Time
Reviewing financial statements in a single period provides value, but trends observed through horizontal analysis are even more telling. Comparing quarterly or annual reports side by side helps identify consistent performance, improvement, or warning signs.
Contextual Analysis and Industry Benchmarks
For example, a declining gross margin could indicate rising production costs or pricing pressure. Consistently increasing free cash flow may reflect strong financial discipline. Recognizing patterns allows investors to assess whether recent performance is an anomaly or part of a larger trend. Context also matters. Comparing results against industry benchmarks and peers can reveal how well a company is positioned in its sector. A company with lower margins than its competitors might be struggling with cost control, or it may operate in a more competitive niche.
Qualitative Factors to Consider
Financial analysis should not be purely numerical. Understanding the story behind the numbers is just as important. Management commentary in earnings reports can offer insights into company strategy, risks, and future outlook. It’s also worth evaluating the quality of leadership, their track record, and how consistently they’ve delivered on guidance.
Evaluating Business Model and Competitive Advantage
Other qualitative aspects to review include the company’s business model, competitive advantage, regulatory environment, and customer base. A company with strong brand recognition and recurring revenue streams may weather economic downturns better than peers with cyclical revenue and effective equity financing.
Evaluating Red Flags and Risks
Analyzing financial statements also means being alert to warning signs. Frequent one-time charges, inconsistent cash flow, or excessive debt levels can signal potential trouble in income statement analysis. Overly aggressive revenue recognition, large amounts of goodwill, or frequent changes in accounting methods may also warrant closer inspection.
Importance of Audit Reports and Notes
Audit reports and notes to the financial statements often contain critical information about risks, contingencies, and accounting policies. Skimming over these details could mean missing material issues that impact the company’s long-term health.
The Importance of Comparative Analysis
Financial data becomes even more powerful when placed side-by-side with that of competitors. Comparative analysis allows you to understand whether performance metrics are unique to the company or part of a broader industry trend.
Peer Analysis and Valuation
If one telecom company shows declining revenue while the rest of the industry is growing, it might suggest internal operational issues rather than macroeconomic conditions. Peer analysis also helps gauge valuation. A company trading at a much higher P/E ratio than competitors may be overpriced unless it’s justified by significantly stronger growth prospects.
How to Approach a Financial Statement Review?
Start with a structured approach. Begin by reading the income statement to assess profitability, then examine the balance sheet to understand financial health. Finish with the cash flow statement to determine if the company is generating sufficient liquidity. Use financial ratios to supplement the analysis, providing comparative context and highlighting trends.
Utilizing Historical Data for Comprehensive Analysis
It’s useful to review at least three to five years of financial data when possible. This time horizon helps smooth out anomalies and provides a better sense of how the company performs over full economic cycles. For newer companies or startups, consider forward-looking metrics, projected cash flows, and market potential.
Resources for Financial Statement Analysis
To analyze financial statements effectively, you’ll need access to accurate and timely data. Most publicly traded companies publish their financials on their investor relations websites and file them with regulatory bodies like the SEC. Platforms such as EDGAR, Yahoo Finance, and Morningstar are great starting points.
Advanced Tools and Research Platforms
Investment research platforms like Bloomberg Terminal, Refinitiv, or Seeking Alpha can offer deeper insights, analyst commentary, and financial modeling tools. For more advanced analysis, accounting software or spreadsheet modeling might be necessary to track ratios, create forecasts, or build valuation models.
Building Confidence in Financial Analysis
Maximizing financial statement analysis takes time and practice. But with consistency through ratio analysis, investors can develop a keen eye for interpreting data, spotting trends, and making informed decisions. Whether you're investing in a new company, reviewing an existing holding, or conducting due diligence, the ability to break down financial statements is a core skill that unlocks a deeper understanding of business performance.
As with any discipline, the more you engage with financial data, the more intuitive it becomes. With a clear process, critical thinking, and an eye for detail, analyzing financial statements transforms from a daunting task into a powerful decision-making tool for navigating the markets and managing investment risk.
#financialstatements#investing#stockmarket#financialanalysis#fundamentalanalysis#accounting#investmentstrategies#financialratios
0 notes
Text

Let us handle the numbers, so you can focus on growing your business.
Contact Us: (519) 376-6464 Visit: https://blackboxinc.ca/ Email: [email protected]
#BlackBoxConsultancy#AccountingServices#Bookkeeping#PayrollServices#FinancialReports#FinancialStatements#VirtualCFO#SmallBusinessSupport#FinancialFreedom
0 notes
Text
Income Statement vs. Cash Flow Statement: Understanding the Differences

Financial statements are the compass directing choices for investors, entrepreneurs, and legislators in India's vibrant commercial climate. Two important instruments that play different but related duties are the Cash Flow Statement and the Income Statement (Profit & Loss Account). The Income Statement shows profitability; the Cash Flow Statement checks liquidity. Understanding these assertions is non-negotiable for Indian companies negotiating GST complexity, Ind AS requirements, and strict Compliance under the Companies Act 2013.
Income Statement
It is generally one of the three principal financial statements, alongside the cash flow statement and the balance sheet. All publicly traded firms are required to create and disseminate this specific financial statement as part of their annual reports. A company's income statement is sometimes referred to as the statement of revenue and expense or the profit and loss statement. The statement primarily emphasizes the overall income and expenditures of a company within a specific accounting quarter. Thus, it aids in conveying a company's whole financial performance throughout a certain accounting period. Revenue is defined as the total money derived from a firm's operational and non-operating operations. However, revenues are distinct from receivables, as they are generated and documented on a company's income statement. Conversely, total expenses constitute the costs incurred during the firm's core and secondary operations.
Key Components of the Income Statement
Revenue (Sales/Turnover) – Total income earned from business operations.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) – Direct costs related to the production of goods/services.
Gross Profit – Revenue minus COGS.
Operating Expenses – Includes administrative, selling, and other business expenses.
Operating Profit (EBIT) – Earnings before interest and taxes.
Other Income & Expenses – Interest income, investment income, or one-time gains/losses.
Net Profit Before Tax (PBT) – Earnings before deducting taxes.
Tax Expenses – Corporate tax payable to the government.
Net Profit After Tax (PAT) – The final earnings available to shareholders.
Relevance of Income Statement in the Indian Context
The Income Statement forms the basis for corporate tax calculations under the Income Tax Act, 1961.
As per the Companies Act, 2013, businesses must prepare and report their financials as per Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in India (Indian GAAP).
Investors use net profit and earnings per share (EPS) from the Income Statement to evaluate stock performance.
Banks and financial institutions assess operating profits before granting loans.
Cash Flow Statement
It is a financial statement that provides comprehensive information on all cash inflows a firm receives from its ongoing operations and external investment sources. It encompasses all financial outflows over a designated period for firm operations and investments. Financial statements from a corporation provide investors and analysts with an overview of all transactions occurring within the entity, each of which contributes to its success. The cash flow statement is considered the most basic of all financial statements, since it delineates the cash created by the firm through three primary avenues: sales, acquisitions, and funding. Net cash flow is defined as the aggregate of all three components. The three distinct components of the cash flow statement assist investors in assessing the value of a company's shares or the organization overall.
Key Components of the Cash Flow Statement
Operating Cash Flows (CFO) – Cash generated from core business activities (e.g., cash sales, payments to suppliers, salaries, etc.).
Investing Cash Flows (CFI) – Cash spent or received from investments (e.g., purchase/sale of assets, investments in securities, etc.).
Financing Cash Flows (CFF) – Cash movements related to financing activities (e.g., issuing shares, taking loans, repaying debt, paying dividends, etc.).
Net Cash Flow – The total increase or decrease in cash over a period.
Relevance of Cash Flow Statement in the Indian Context
A company may report profits but still face cash shortages if its cash flows are weak.
Helps businesses manage cash cycles effectively, especially in industries like manufacturing and retail.
Indian banks scrutinize a firm’s cash flow position before extending credit lines.
Foreign and domestic investors assess free cash flows to determine a company’s financial stability.
Differences Between Income Statement and Cash Flow Statement
Aspect
Income Statement
Cash Flow Statement
Accounting Basis
Accrual Accounting (Records revenues & expenses when incurred)
Cash Accounting (Records actual cash transactions)
Purpose
Shows profitability
Shows cash liquidity
Key Metric
Net Profit (PAT)
Net Cash Flow (CFO, CFI, CFF)
Non-Cash Items
Includes depreciation, amortization, and accruals
Excludes non-cash items
Financial Health Indicator
Measures long-term profitability
Measures short-term liquidity
Focus
Revenue & expenses
Cash inflows & outflows
Why Do Profit and Cash Flow Differ?
A company may report high profits but still face cash shortages due to several reasons:
Due to credit sales Revenue may be booked, but cash is yet to be received.
Depreciation & amortization reduce net profit but have no cash impact.
Loan repayments reduce cash but are not part of the income statement.
Expenses incurred in cash may not yet reflect as COGS.
Which One Matters More?
Both statements are important, but their relevance depends on the stakeholder’s perspective:
Investors prefer the income statement to assess profitability and earnings growth.
Lenders & creditors focus more on the cash flow statement to ensure repayment capability.
Management uses both to make strategic decisions.
Questions to Understand your ability
Which accounting method does the Income Statement follow?
a) Cash Accounting b) Accrual Accounting c) Hybrid Accounting d) Deferred Accounting
Correct Answer: b) Accrual Accounting Reason: The Income Statement follows the accrual accounting method, where revenue and expenses are recorded when they are incurred, not when cash is received or paid.
What is the primary purpose of the Cash Flow Statement?
a) To show profitability b) To show cash liquidity c) To report tax expenses d) To calculate net profit
Correct Answer: b) To show cash liquidity Reason: The Cash Flow Statement focuses on showing cash inflows and outflows, which helps assess the company’s liquidity, unlike the Income Statement which focuses on profitability.
Which of the following is NOT included in the Income Statement?
a) Depreciation b) Interest income c) Purchase of machinery d) Tax expenses
Correct Answer: c) Purchase of machinery Reason: The purchase of machinery is part of the Cash Flow Statement under investing activities. The Income Statement includes items like depreciation, interest income, and tax expenses.
Why might a company show a high profit but face cash shortages?
a) Depreciation and amortization b) Loan repayments c) Credit sales d) All of the above
Correct Answer: d) All of the above Reason: A company may show a high profit but still face cash shortages because of factors like credit sales (where cash isn't received yet), depreciation (non-cash expense), and loan repayments (affecting cash flow but not profit).
Which statement is more relevant for lenders and creditors?
a) Income Statement b) Cash Flow Statement c) Balance Sheet d) Statement of Changes in Equity
Correct Answer: b) Cash Flow Statement Reason: Lenders and creditors are more concerned with a company’s ability to repay debts, which is directly related to cash flow, making the Cash Flow Statement more important to them.
Conclusion
Making wise financial decisions depends on a knowledge of the Income Statement and Cash Flow Statement. The Income Statement shows profitability; the Cash Flow Statement guarantees liquidity and financial stability. Maintaining healthy financial flows and following Ind AS is absolutely vital for companies doing business in India if they want to have sustainable development. Analyzing both statements taken together offers a whole picture of a company's financial situation regardless of your position—investment, business, or financial specialist.
0 notes
Text
Professional Audit Company in Tajikistan
Looking for a trusted audit company in Tajikistan? Our expert team ensures accurate audits of your financial statements, helping you stay compliant with local and international regulations. Contact us today for detailed audit services!
#AuditCompany#TajikistanAudit#AuditServices#BusinessAudit#FinancialStatements#Compliance#TajikistanBusiness#AuditExperts#AuditSolutions#BusinessFinance
0 notes
Text
Financial statement automation simplifies the process of generating balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports. By integrating with existing accounting systems, automation tools reduce manual data entry, minimize errors, and provide real-time financial insights. This approach enhances efficiency, ensures regulatory compliance, and allows finance teams to focus on analysis rather than repetitive tasks. Businesses benefit from faster reporting, improved accuracy, and cost savings over time. While implementation may require an initial investment, the long-term gains in productivity and reliability make automation a valuable solution for organizations managing financial data at any scale.
#FinanceTech#AutomatedReporting.#AIinFinance#RegulatoryCompliance#AccountingSoftware#FinancialStatements
0 notes
Text
How to Read Financial Statements: A Guide for Small Business Owners
How to Read Financial Statements: A Guide for Small Business Owners
Written by: D. Marshall Jr The Key to Business Success: Understanding Your Numbers Imagine driving a car with no dashboard, no speedometer, no fuel gauge, and no warning lights. You wouldn’t know how fast you’re going, how much gas is left, or if something is about to break down. Running a business without understanding financial statements is just like that, you’re operating blind. Financial…
#BalanceSheet#BusinessGrowth#CashFlowManagement#EntrepreneurTips#FinancialStatements#FinancialSuccess#IncomeStatement#ProfitAndLoss#SmallBusinessFinance#SmallBusinessTips
0 notes
Text
Why Financial Statements Matter for Your Business

Financial statements are the backbone of every successful business. They tell the story of your company’s financial health and are essential for informed decision-making. At SAI CPA Services, we specialize in preparing accurate and insightful financial statements tailored to your needs.
The Three Key Financial Statements
Balance Sheet: Gives you a snapshot of your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
Income Statement: Tracks your revenues and expenses, showing profitability over time.
Cash Flow Statement: Highlights the inflow and outflow of cash, ensuring you stay financially stable.
Why You Need Them
Informed Decisions: Understand your financial position to make strategic choices.
Compliance: Meet regulatory requirements with accurate reporting.
Growth Planning: Identify trends and opportunities to grow your business.
Whether you're a small business owner or running a large organization, financial statements are indispensable tools. Let SAI CPA Services handle the complexities, so you can focus on building your dream.
📞 Contact us today for expert financial statement preparation!
908-380-6876
1 Auer Ct, 2nd Floor
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
#saicpaservices#financial services#accounting#book keeping#cpa#finanace#new jersey#financialstatements#businessgrowth#startup#smallbusinesssuccess#financial planning
1 note
·
View note
Text
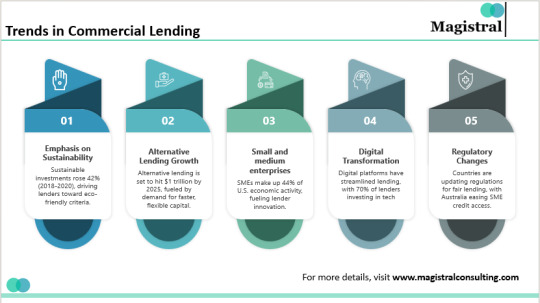

Commercial Lending Process: Insights, Trends, and Global Opportunities
#magistralconsulting#commerciallending#globalopportunities#financialstatements#creditrating#underwriting#digitaltransformation
0 notes
Text
How to Keep Your Financial Records Clean and Accurate for Your US Small Business 💼📊
Keeping your financial records in order is key to running a healthy business. Whether you’re handling daily ops, planning ahead, or just keeping track of cash flow, solid record-keeping saves time and headaches later. Here’s how to stay organized and compliant — simplified. 👇
Why Accurate Financial Records Matter
Tax Compliance: Makes tax season easier and helps avoid penalties.
Transparency: Clear records show you’re on top of your game for audits or funding.
Better Decisions: Know how your business is really doing to make smart moves.
Set Up Your Accounting System
Manual: Spreadsheets work at first, but watch for messiness.
Outsource: Hire pros if numbers aren’t your thing.
Track Every Transaction
Record all sales & revenue, no matter the payment method.
Track all expenses (rent, supplies, salaries).
Update bank & credit card transactions regularly.
Categorize Everything
Income: Sales and fees.
Expenses: Rent, utilities, salaries, supplies.
Assets & Liabilities: Equipment, loans, debts.
Organize Your Docs
Keep receipts & invoices safe (digital or paper).
Store bank statements regularly.
Hold on to contracts & agreements.
Reconcile Accounts Regularly
Match bank statements with records.
Check credit card expenses for accuracy.
Review payroll records closely.
Manage Payroll & Benefits
Track wages, bonuses, commissions.
Document tax deductions and benefits.
Stay on top of payroll tax filings.
Keep Track of Taxes
Collect & remit sales tax as required.
Monitor income, deductions, credits for accurate tax returns.
Document deductible expenses to save money.
Generate Financial Statements Often
Balance Sheet: What you own vs. owe.
Income Statement: Profit and loss summary.
Cash Flow: Money in and out.
Stay Organized & On Track
Use digital tools to keep records neat.
Create a filing system for documents.
Review records weekly or monthly.
Summary: Accurate financial records aren’t just about taxes—they’re essential for smart business management and growth. Whether using software or outsourcing, keeping things clean saves time, prevents costly mistakes, and sets your business up for success.
Want to keep your finances sharp? Learn more with Counto — your partner for smart, simple small business accounting. 🚀
#Counto#SmallBusinessTips#FinancialRecords#AccountingTips#TaxCompliance#SmallBusinessFinance#Bookkeeping#BusinessGrowth#Payroll#FinancialStatements#BusinessTaxes#StartupTips#USSmallBusiness#EntrepreneurLife#accounting#business#united states#small business
1 note
·
View note
Text

📊 Simplifying Financial Statement Analysis: Key Points 💡
Make your financial statement analysis easy with expert accounting assignment help from TutorHelpDesk! Whether it’s balance sheets, income statements, or cash flow analysis, we’ve got you covered! Connect with top accounting experts to ensure A-grade success in your assignments.
🎯 Achieve better results 👨🏫 Get personalized tutoring 📈 Excel in financial analysis
#AccountingHelp#FinancialAnalysis#AssignmentHelp#TutorHelpDesk#StudySmart#FinancialStatements#AccountingTutor#AcademicSuccess
0 notes
Text
General Business Accounting and Strategy

General Business Accounting
1. Financial Statements
2. Accounting Principles
3. Cost Accounting
4. Managerial Accounting
Business Strategy
1. Strategic Planning|
2. Financial Strategy +61-0872004783 +1-2817332789 +44-1173184885 [email protected] www.obgoutsourcing.com
#FinancialStatements#IncomeStatement#CostAccounting#StrategicPlanning#BusinessStrategy#FinancialPlanning#generalbusinessaccounting
0 notes
Text
Profit and Loss Statement: A Deep Dive into Revenue & Expenses

The Profit & Loss Statement is a crucial financial document that outlines a company's revenues, expenses, and profits or losses over a specific period, typically quarterly or annually. It helps businesses assess their financial performance, make informed decisions, and meet statutory requirements. This statement includes various components like revenue, costs, operating expenses, and net income, and can be prepared in different formats based on the business structure, such as for sole traders, partnerships, or companies.
What is Profit & Loss Statement?
The Profit & Loss Statement is an essential financial statement that outlines the costs, revenues, and expenses accumulated by a company during a set timeframe. This timeframe can be quarterly or on a yearly basis.
The profit & loss statement consists of all the indirect expenses and incomes that include gross profit/loss. These all are documented in this statement to determine the net profit or loss. It discloses the company’s net profit or loss over a particular timeframe for which it is formulated. This statement assists the companies in making rational decisions relating to their business practices and evaluating their financial performance.
A business's monthly or annual profits and losses are displayed in the profit and loss statement or account. For the reasons listed below, businesses utilize profit and loss statements, while others use "T Accounts." There are two primary reasons for preparing a profit and loss statement or account.
A profit and loss statement, or account, is used to know the profits and losses accumulated by the business as well as for meeting statutory specifications.
The Profit & Loss Statement: How Do You Prepare It?
The steps to create the profit and loss statement are as follows:
1.The first step is to prepare the ledger accounts. An account statement is required to be prepared for each ledger out of the journal book to identify the closing balance.
2.The second step is to create a trial balance. A trial balance presents an overview of all the ledger accounts. It specifies every ledger account with the closing balance forwarded from the individual ledger account statement.
3.The last one is to prepare the trading and profit and loss statement. The profit and loss statement is posted to all ledger accounts that reflect the kind of sales, purchases, indirect expenditures, direct expenses, and revenue.
Components of Profit & Loss Statements
Various components are present in the Profit & Loss Account. These components are used to document the expenses and income of the business within several categories.
Revenue/Income
Two key areas define the income of the company. First reported is the income from the main company activities, which covers typical course of business earnings. The second category describes the other revenue or miscellaneous income of the firm, which consists of the interest or dividend income resulting from the several investments made by the corporation.
Cost of Goods Sold
The direct cost of running like the labour cost, raw material cost or direct overheads of the company associated to the buying or producing the items is included in the Cost of items Sold (COGS) disclosed in the Profit & Loss Statement. Gross margin of the company is produced by deducting these costs from the income.
Operating Expenses
Operating expenditures are the indirect costs or expenses related to running a company in the manufacturing or production process. Administrative expenses include depreciation costs, staff costs, marketing and distribution expenses, selling costs, research and development costs, etc. comprise these outlay.
Operating Profit
After running expenditures, the positive balance from the gross margin is the operational profit. It also goes EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes). A good operational margin guarantees the investors and stakeholders of the profitability and solvency of the company.
Net Income
After subtracting all operating and non-operational expenditures, interest, and taxes, a company's net income—that is, net profit—is what results. It is the profit ready for sharing among the shareholders. Additionally, computed depending on the net profit of the company is the earnings per share.
Various Profit and Loss Account Formats
Two types of formats are used for the preparation of the Profit & Loss Account:
Format used for Sole Traders & Partnership Firms
Format used for P&L Account for Companies
Format used for Sole Traders & Partnership Firms
There is no prescribed format of Profit & Loss Account is provided for the sole traders and partnership firms. The P&L Account can be prepared in any way. Nonetheless, it must to show the net profit and gross profit independently. These organizations typically favor the "T shaped form" for creating P&L accounts.
T-shape Form: - T-shaped form Debit and credit are the two sides of a P&L account. The profit and loss statement are created after the trading account.
Trading and Profit & Loss Account
Particulars
Amount
Particulars
Amount
To Opening Stock
xxx
By Sales
xxx
To Purchases
xxx
By Closing Stock
xxx
To Direct Expenses
xxx
To Gross Profit
xxx
xxx
xxx
To Operating Expenses
xxx
By Gross Profit
xxx
To Operating Profit
xxx
xxx
xxx
To Non-operating expenses
xxx
By Operating Profit
xxx
To Exceptional Items
xxx
By Other Income
xxx
To Finance Cost
xxx
To Depreciation
xxx
To Net Profit Before Tax
xxx
xxx
xxx
Format used for P&L Account for Companies
As per Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013, companies are required to prepare the Profit & Loss Account. The format outlined in Schedule III is as follows: "Statement of Profit and Loss," which includes the name of the company and the period for which the statement is prepared, indicating the financial results for that specific time frame.
Note No.
Figures for the current reporting period
INCOME
a) Revenue From operations
b) Other Income
Total Income
EXPENSES
a) Cost of materials consumed
b) Purchases of Stock-in-Trade
c) Changes in inventories of finished goods, Stock-in -Trade and work-in-progress
d) Employee benefits expense
e) Finance costs
f) Depreciation and amortization expenses
g) Other expenses
Total Expenses
Profit/(loss) prior to taxes and special items
Exceptional Items
Profit/ (loss) before tax
Tax Expense:
Current tax
Deferred tax
Profit (Loss) for the period from continuing operations
Profit/(loss) from discontinued operations
Tax expenses of discontinued operations
Profit/(loss) from Discontinued operations (after tax)
Profit/(loss) for the period
Other Comprehensive Income
A. (i) Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss
(ii) Income tax pertaining to goods unlikely to be classed as profit or loss
B. (i) Things scheduled for reclassification as profit or loss
(ii) income tax relating to items that will be reclassified to profit or loss
Total Comprehensive Income for the period Comprising Profit (Loss) and other comprehensive income for the period)
Earnings per equity share (
for ongoing operations):
(1) Basic
(2) Diluted
Earnings per equity share (for halted operations):
(1) Basic
(2) Diluted
Earning per equity share (for ongoing & halted operation)
(1) Basic
(2) Diluted
Questions to Understand your Ability
What is the primary purpose of the Profit & Loss Statement?
A) To outline the total revenue generated by a company. B) To display the company's net profit or loss over a specific period. C) To show the company's assets and liabilities. D) To provide a detailed list of the company’s inventory.
Correct Answer: B) To display the company's net profit or loss over a specific period. Reason: The Profit & Loss Statement primarily shows the financial performance of a company by reporting the net profit or loss over a specific period (quarterly or annually).
Which of the following is included under Operating Expenses in the Profit & Loss Statement?
A) Income from investments. B) Interest paid on loans. C) Depreciation and administrative costs. D) Sales revenue.
Correct Answer: C) Depreciation and administrative costs. Reason: Operating expenses include indirect costs related to running the business, such as depreciation, staff costs, and administrative expenses.
What does EBIT stand for in the context of the Profit & Loss Statement?
A) Earnings Before Interest and Taxes. B) Earnings Before Interest and Taxation. C) Earnings Before Income Taxes. D) Earnings Before Investment Taxes.
Correct Answer: A) Earnings Before Interest and Taxes. Reason: EBIT is a measure of a company's profitability that excludes interest and tax expenses, showing the operating profit before these deductions.
What does the "Cost of Goods Sold" (COGS) refer to in a Profit & Loss Statement?
A) The total revenue generated from sales. B) The direct costs of producing the goods sold, such as labor and raw materials. C) The operating expenses related to marketing and distribution. D) The costs associated with administrative expenses.
Correct Answer: B) The direct costs of producing the goods sold, such as labor and raw materials. Reason: COGS refers to the direct costs of production, including labor, raw materials, and direct overheads, directly tied to the production of goods sold.
Which format is used for the preparation of the Profit & Loss Account for companies under the Companies Act, 2013?
A) T-Form. B) Sole Trader's Format. C) Schedule III Format. D) Fixed-Account Format.
Correct Answer: C) Schedule III Format. Reason: Companies are required to prepare their Profit & Loss Account according to the format specified in Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013, which provides a structured format for reporting financial performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Profit & Loss Statement is a vital financial document that helps businesses assess their performance over a specific period, including revenue, expenses, and net income. It aids in decision-making and ensures statutory compliance. The statement can be prepared using different formats, such as for sole traders, partnership firms, and companies, with each format providing a clear overview of the company’s financial position and profitability.
0 notes
Text
How to Simplify ROC Compliance Filing for Your Delhi Company
Navigating the complexities of ROC (Registrar of Companies) compliance filing can be a daunting task for any business owner. In Delhi, where the regulatory environment is as dynamic as it is stringent, simplifying ROC compliance is crucial for ensuring your company's legal standing and operational efficiency. This article will guide you through the essentials of ROC compliance filing, outline the challenges and solutions, and provide insights into leveraging technology and professional ROC compliance filing in Delhi to streamline the process.
Understanding ROC Compliance Filing in Delhi: A Beginner's Guide
ROC compliance filing is a mandatory process for companies registered in Delhi, ensuring adherence to the legal requirements set forth by the Companies Act, 2013. This process involves the submission of various documents and forms to the Registrar of Companies to maintain transparency, accountability, and proper governance.

Key Aspects of ROC Compliance:
Annual Returns: Annual financial statements, auditor reports, and company details must be filed annually.
Director Reports: Detailed reports about the company's activities, financial performance, and governance.
Board Resolutions: Documentation of key decisions made by the company's board of directors.
Why It Matters:
Legal Compliance: Avoid legal penalties and maintain good standing.
Transparency: Ensure that stakeholders have access to accurate and timely information.
Operational Efficiency: Streamline company operations through regular and accurate reporting.
What’s Included in the ROC Compliance Filing Package in Delhi
When opting for a ROC compliance filing service in Delhi, it’s essential to understand what the package includes. A comprehensive ROC compliance package typically covers the following services:

Preparation and Filing of Annual Returns: Drafting and submitting necessary forms like MGT-7 and AOC-4.
Director KYC Compliance: Ensuring all directors are compliant with their KYC requirements.
Maintenance of Statutory Registers: Keeping up-to-date records such as register of members, directors, and charges.
Regular Updates: Providing timely updates on regulatory changes and compliance requirements.
Additional Services Might Include:
Tax Compliance: Integration with tax filing services for comprehensive financial management.
Advisory Services: Expert advice on corporate governance and compliance best practices.
Audit Support: Assistance during statutory audits and compliance reviews.
Common Challenges in ROC Compliance Filing and How to Overcome Them in Delhi
Navigating ROC compliance can present several challenges. Here’s how to address them effectively:
1. Complexity of Regulations:
Solution: Work with experienced professionals who stay updated with regulatory changes and can guide you through the complexities.
2. Documentation Errors:
Solution: Implement a thorough review process to ensure all documents are accurate and complete before submission.
3. Timeliness:
Solution: Set reminders for filing deadlines and use technology to automate reminders and track progress.
4. Compliance Costs:
Solution: Opt for bundled compliance packages to manage costs effectively and avoid surprises.
Essential Documents for ROC Compliance Filing in Delhi: What You Need
To ensure a smooth ROC compliance process, gather the following essential documents:

Company Financial Statements: Balance sheets, profit and loss accounts, and auditor reports.
Board Resolutions: Records of decisions taken by the board of directors.
Director Details: KYC documents, DIN (Director Identification Number) proofs.
Shareholder Information: Records of shareholding patterns and changes.
Statutory Registers: Registers of members, directors, and charges.
Document Checklist:
Financial Statements (AOC-4)
Annual Return Form (MGT-7)
Director KYC Form (DIR-3 KYC)
Board Meeting Minutes
Shareholder Resolutions
How Technology Can Aid in Simplifying ROC Compliance Filing in Delhi
Technology plays a pivotal role in streamlining ROC compliance filing. Here’s how:
1. Automation:
Solution: Use automated software to generate, file, and track compliance documents, reducing manual errors and saving time.
2. Cloud Storage:
Solution: Store all compliance-related documents securely in the cloud for easy access and management.
3. Compliance Management Tools:
Solution: Implement tools that provide real-time updates on compliance requirements and deadlines.
4. Data Analytics:
Solution: Utilize analytics to gain insights into compliance trends and areas for improvement.
Choosing the Right Professional for ROC Compliance Filing in Delhi
Selecting the right professional service provider for ROC compliance is crucial. Here’s why Taxgoal stands out:

1. Expertise and Experience:
Solution: Taxgoal offers a team of seasoned professionals with extensive experience in ROC compliance and corporate law.
2. Comprehensive Services:
Solution: Taxgoal provides a full suite of services, including filing, advisory, and document management.
3. Technology Integration:
Solution: Leverage Taxgoal’s advanced technology solutions for efficient and accurate compliance filing.
4. Client-Centric Approach:
Solution: Taxgoal prioritizes client needs, offering personalized services and support throughout the compliance process.
Best Practices for Timely and Accurate ROC Compliance Filing in Delhi
Adhering to best practices ensures timely and accurate ROC compliance:
1. Maintain Regular Records:
Keep financial and governance records up-to-date to avoid last-minute scrambles.
2. Set Up Internal Controls:
Implement internal controls to ensure accurate data collection and reporting.
3. Monitor Deadlines:
Regularly check compliance deadlines and set reminders to avoid missed submissions.
4. Engage Professionals:
Work with experienced professionals to navigate complex compliance requirements efficiently.
5. Review and Audit:
Periodically review and audit your compliance processes to identify and rectify any issues.
Conclusion
Simplifying ROC compliance filing in Delhi involves understanding the process, preparing the right documentation, leveraging technology, and choosing the right professional services. By implementing these strategies, companies can ensure timely and accurate compliance, thereby safeguarding their legal standing and operational efficiency.
Final Words
Navigating ROC compliance may seem challenging, but with the right approach and resources, it becomes a manageable and integral part of running a successful business. Embrace technology, follow best practices, and consider professional services like Taxgoal to streamline your compliance efforts and focus on growing your business.
#ROCCompliance#DelhiCompany#BusinessCompliance#CorporateFiling#RegulatoryCompliance#ROCFilingsDelhi#Taxgoal#ComplianceChallenges#DocumentManagement#TechInCompliance#ProfessionalServices#ComplianceBestPractices#CompanyRegistration#LegalCompliance#FinancialStatements#DirectorKYC#FilingDeadlines#ComplianceSolutions#BusinessGrowth#ComplianceSimplified
0 notes
Text

Unlock financial potential with expert corporate services
Accounting & Bookkeeping
Financial Statements
Tax Preparation
Budgeting and Forecasting
Contact us: +971 58 863 6832 | info@wesetupbusiness
Visit our website: https://wesetupbusiness.com/services
#WeSetupBusiness#CorporateFinance#AccountingServices#FinancialStatements#TaxPreparation#BudgetForecasting#BusinessGrowth#VAT#CorporateTax#BusinessSetupDubai#UAEBusienssSetup
0 notes