#BalanceSheet
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
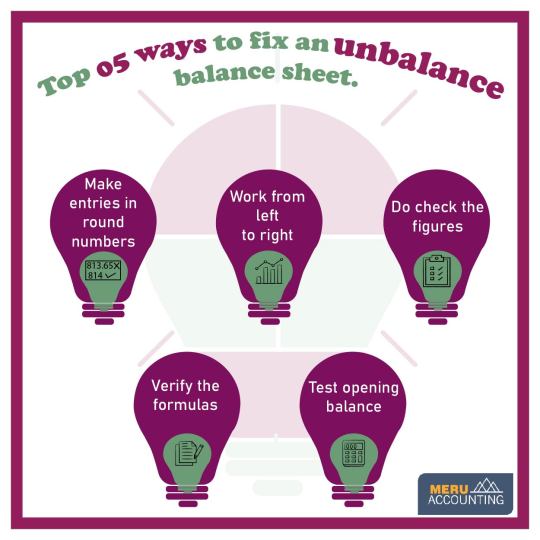
Is your balance sheet out of whack? Discover the top 5 strategies to restore financial equilibrium!
#MeruAccounting#bookkeepingcompany#bookkeepers#bookkeepingservices#bookkeepingtips#bookkeeping#accounting#accountingservices#balancesheet
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
📘📊 Master ACCOUNTANCY with Ease — Only at EDUCATION HUB! 🧾💼
Are Journal Entries, Ledgers & Balance Sheets giving you sleepless nights? Let’s turn confusion into clarity at Education Hub, where Commerce Coaching means real understanding! 💯

✅ What You’ll Learn with Us: 🔹 Golden Rules of Accounting with practical examples 🔹 Step-by-step Journal Entries & Ledger posting 🔹 Create accurate Trial Balance & Balance Sheets 🔹 Format-based learning + smart tricks for faster revisions 🔹 Weekly tests, past-year papers, and visual concept notes
🎯 For Class 11 & 12 Commerce Students (CBSE/ISC/State Board)
🎁 BONUS: Comment “ACCOUNT MASTER” and get a FREE PDF Guide with Formats + Practice Questions
🎓 Enroll Now – Available in Offline & Online Modes 📞 Book your FREE Trial Class today and make Accountancy your strength!
#EducationHub#Accountancy#CommerceCoaching#JournalEntries#Ledgers#BalanceSheet#CBSEClass11#CBSEClass12#AccountMaster
0 notes
Text
What is a Balance Sheet?

A balance sheet is a financial snapshot of a company at a specific point in time. It shows what the company owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the owner’s share (equity).
Think of it like a personal financial statement: your assets could be your savings and valuables, your liabilities are loans or debts, and your equity is the difference between the two — what you really own.
In business, the balance sheet follows this simple formula:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Assets include cash, inventory, buildings, and equipment. Liabilities are debts and obligations like loans or bills to pay. Equity is the owner’s investment plus retained profits.
Balance sheets help investors, managers, and lenders understand a company’s financial health. They reveal how well a company can pay its debts and how much value it holds.
In short, the balance sheet is like a financial report card that helps people see how a company is doing at a glance.
1 note
·
View note
Text
📊 Understanding Financial Statements for US Small Businesses: A Simple Guide 💼
Running a small biz means juggling a lot — customers, operations, growth plans. But there’s one thing you can’t skip: understanding your financial health. Financial statements are like your business’s GPS, showing you where you are and what your next move should be.
Not a numbers person? No worries — here’s a simple breakdown of the 3 main financial statements every US small business owner should know:
1️⃣ Income Statement (Profit & Loss)
Think of this as your biz’s report card. It shows:
💰 Revenue: Money you make from sales
📉 Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): What it costs to make your product or service
💸 Operating Expenses: Rent, salaries, marketing, etc.
📈 Net Income/Loss: Profit or loss after everything
Why it matters? It tells you if you’re making money or not — and where to tweak if things aren’t looking good.
2️⃣ Balance Sheet
This is a snapshot of your business’s financial health right now:
🏦 Assets: What you own (cash, inventory, equipment)
💳 Liabilities: What you owe (loans, bills)
📊 Equity: What’s left after subtracting liabilities from assets
Why it matters? It shows if your business is stable and able to cover debts and obligations.
3️⃣ Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow = your business’s lifeline. Even if you’re profitable, no cash means trouble. This shows:
🔄 Operating Activities: Cash from daily operations
🛠️ Investing Activities: Cash spent or earned from buying/selling assets
💵 Financing Activities: Cash from loans, repayments, or investments
Why it matters? Positive cash flow means you can pay bills and invest in growth. Keep an eye on this to avoid surprises.
How They Work Together
Income Statement = Are you profitable?
Balance Sheet = What do you own vs. owe?
Cash Flow = Can you cover your bills today?
For example, you could be profitable but have negative cash flow if customers pay late — so watch all three!
🔗 For more tips and guides, learn more here.
#SmallBusiness#FinancialStatements#AccountingTips#CashFlow#ProfitAndLoss#BalanceSheet#BizGrowth#EntrepreneurLife#accounting#united states#bookkeeping#business#small business#Counto
1 note
·
View note
Text
Understanding the Types of Financial Statements: What They Reveal About a Business

Financial statements assist investors, regulators, and management in their decision-making processes. These serve as the documents that are used to view the company’s transparent view of its financial status and also its compliance with the Companies Act 2013 and Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS). Additionally, financial statements are required for GST regulations, taxation, and financial expectations of investors. This guide will provide the information regarding the types of financial statements that are used in India and also what they offer to the companies.
Types of Financial Statements
Financial statements are standardized reports that summarize a business’s financial activities. In India, they are mandatory for registered companies and include:
Income Statement
Balance Sheet
Cash Flow Statement
Statement of Changes in Equity
Let’s delve into each, with examples tailored to Indian businesses.
Income Statement
This is also known as a statement of revenue and expense or a profit and loss statement. Income statement concentrates on the total revenue and expenses of the company over the duration of the accounting term. As a result, it assists in knowing the comprehensive financial performance within the specified accounting period.
Interestingly, revenue is calculated by adding together the money made from a company's operational and non-operating operations. Revenues are generated and shown on a company's income statement, but they are not receivables. However, overall expenses are the costs incurred as a result of the primary and secondary operations of such a business.
Key Components:
Revenue: Total income from sales (e.g., GST-inclusive sales in INR).
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs related to production.
Gross Profit: Revenue – COGS.
Operating Income: Gross Profit – Operating Expenses (salaries, rent).
EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes): Operating Income + Non-operating items.
EBITDA: EBIT + Depreciation + Amortization (non-cash expenses).
Net Income: Final profit after taxes and interest.
Example: ABC Manufacturing Pvt. Ltd., a Pune-based auto parts maker, reports:
Revenue: ₹50 crore (post-GST).
COGS: ₹30 crore (raw materials, labor).
Gross Profit: ₹20 crore.
Operating Expenses: ₹10 crore (marketing, admin).
Operating Income: ₹10 crore.
EBITDA: ₹12 crore (adds ₹2 crore depreciation on machinery).
Net Income: ₹7 crore (after ₹3 crore in taxes and interest).
This shows ABC’s core profitability and efficiency in managing costs.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet represents the information related to the company’s assets, finances, and also investment by the owners in that company.
Simply said, a company's balance sheet should display all of its financial data, including its income, expenditure, left over, and whether or not it has spent more than it has earned.
Key Components:
Assets: Resources owned (e.g., cash, Inventory, Accounts Receivable).
Current Assets: Convertible to cash within a year (e.g., ₹5 crore in Inventory).
Non-Current Assets: Long-term investments (e.g., machinery worth ₹20 crore).
Liabilities: Debts owed (e.g., loans, Accounts Payable).
Current Liabilities: Due within a year (e.g., ₹3 crore in Accounts Payable).
Non-Current Liabilities: Long-term debt (e.g., ₹15 crore bank loan).
Equity: Owner’s stake, including Retained Earnings and share capital.
Example: XYZ Retail Ltd., a Delhi-based chain, reports:
Assets: ₹100 crore (₹25 crore cash, ₹30 crore Inventory, ₹45 crore property).
Liabilities: ₹60 crore (₹15 crore Accounts Payable, ₹45 crore long-term debt).
Equity: ₹40 crore (₹30 crore share capital + ₹10 crore Retained Earnings).
This highlights XYZ’s liquidity and leverage.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement can be described as the statement that shows the company’s overall capital inflow in the nature of cash equivalents via core activities, investment dealings, and funding operations. Additionally, it represents the overall cash outlay through the activities outlined above.
The Cash Flow Statement tracks cash inflows/outflows across three activities:
Operating: Core business activities (e.g., cash from sales).
Investing: Asset purchases/sales.
Financing: Loans, dividends, equity changes.
Key Metrics:
Net Income (from Income Statement).
Adjustments for non-cash items (Depreciation, Amortization).
Changes in working capital (Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Accounts Payable).
Example: Mumbai Tech Solutions Ltd. reports:
Operating Cash Flow: ₹12 crore (Net Income ₹10 crore + ₹2 crore depreciation – ₹3 crore increase in Accounts Receivable).
Investing Cash Flow: -₹8 crore (new software licenses).
Financing Cash Flow: ₹5 crore (loan taken).
Net Cash Flow: ₹9 crore.
This reveals how the company funds growth and manages liquidity.
Statement of Changes in Equity
The Statement of Changes in Equity is the financial adjustment between the opening and closing balance of the shareholder’s equity. This financial statement assists in abstracting the transactions associated with the shareholder’s equity throughout an accounting period. This report documents changes in share capital, including the issuance of new shares and dividend payments, as well as movements in retained earnings and other reserves.
Key Components:
Opening Equity Balance.
Net Income added to Retained Earnings.
Dividends paid.
New share issuances.
Example: Chennai Pharma Ltd.
Opening Equity: ₹50 crore.
Net Income: ₹15 crore (added to Retained Earnings).
Dividends Paid: ₹5 crore.
Closing Equity: ₹60 crore.
This clarifies how profits are reinvested or distributed.
Questions to understand your ability
What does the Income Statement do?
A) Tracks cash coming in and going out. B) Shows the company’s financial status at one point. C) Lists throughout the specified time frame the revenues, expenses, and profits of a corporation. D) Shows how the company's equity changes over time.
Answer: C) Lists throughout the specified time frame the revenues, expenses, and profits of a corporation. Reason: - The Income Statement is all about revealing how much a company made, spent, and how much it earned as profit during a specific time—like a quarter or year.
Which of these is a non-current asset on the Balance Sheet?
A) Cash B) Inventory C) Machinery D) Accounts Receivable
Answer: C) Machinery Reason: - Non-current assets are things that a company owns and plans to use for more than a year. Machinery is a prime example—it lasts longer than a year.
What’s the main thing the Cash Flow Statement tracks?
A) Revenues and expenses B) Assets, liabilities, and equity C) Cash moving in and out from operating, investing, and financing activities D) Changes in equity
Answer: C) Cash moving in and out from operating, investing, and financing activities Reason: - Tracking cash—from sales, out for investments, or in and out for financing—the Cash Flow Statement shows how money moves. All of it is about liquidity.
How do you calculate Net Income in the Income Statement?
A) Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses – Taxes and Interest B) Revenue – Operating Expenses – Depreciation C) Revenue – EBIT – Taxes D) Operating Income + Depreciation
Answer: A) Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses – Taxes and Interest Reason: - Net Income is what’s left after you subtract the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), expenses, taxes, and interest from the revenue. It’s the bottom line.
What’s included in the Statement of Changes in Equity?
A) Revenue from sales B) Non-current liabilities C) Net income added to retained earnings and dividends paid D) Machinery purchases
Answer: C) Net income added to retained earnings and dividends paid Reason: - This statement explains how a company’s equity changes over time. Net income increases retained earnings, and paying dividends takes money out of the equity pool.
Conclusion
In the competitive market of India, financial statements are absolutely essential instruments. The Income Statement reveals profitability; the Balance Sheet evaluates stability; the Cash Flow Statement guarantees liquidity; the Statement of Changes in Equity records ownership movements. Taken together, they enable stakeholders to follow rules like Ind AS, make wise judgments, and propel environmentally friendly development. Whether you are examining a family-owned SME or a listed behemoth like Reliance, understanding these ideas can help you to release the actual potential of a company.
#FinancialStatements#IncomeStatement#BalanceSheet#CashFlowStatement#EquityStatement#IndianAccountingStandards
0 notes
Text
How to Read Financial Statements: A Guide for Small Business Owners
How to Read Financial Statements: A Guide for Small Business Owners
Written by: D. Marshall Jr The Key to Business Success: Understanding Your Numbers Imagine driving a car with no dashboard, no speedometer, no fuel gauge, and no warning lights. You wouldn’t know how fast you’re going, how much gas is left, or if something is about to break down. Running a business without understanding financial statements is just like that, you’re operating blind. Financial…
#BalanceSheet#BusinessGrowth#CashFlowManagement#EntrepreneurTips#FinancialStatements#FinancialSuccess#IncomeStatement#ProfitAndLoss#SmallBusinessFinance#SmallBusinessTips
0 notes
Text
Understanding Financial Statements A Beginner's Guide
Balance Sheet Basics! The balance sheet is your company’s financial snapshot, showing assets, liabilities, and equity. It’s the equation that keeps your business in balance: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Why is this so important? Find out in our beginner's guide!
read the full article here
0 notes
Text

The Role of Management Accounts in Business Growth
https://digi-tax.co.uk
#Accounting#Accountant#Services#Bookkeeping#Annual#Business#AccountingTips#AccountingHelp#Accountancy#Financial#Reporting#Tax#BalanceSheet#DigiTax
0 notes
Text
CA Articles can relate😁🥲
#career#education#students#exams#student#castudents#ca classes#ca coaching#result#meme#balancesheet#caclasses#caaspirants
1 note
·
View note
Text

Elevate Your Financial Literacy: Enroll now for our online Balance Sheet Finalization Certification course from Tyariexamki.com and become a Certified Professional. ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ star rating Course
For more information Visit us:- https://www.tyariexamki.com/CourseDetail/62/Balance-Sheet-Finalization-Online-Certification-Course
#balancesheet#account#balancesheeteducation#income tax education#online courses#balance sheet finalization online certification course
1 note
·
View note
Text
From Transactions to Reports: A Comprehensive Overview of Financial Accounting
📊 Dive into the financial world with our blog on "From Transactions to Reports: A Comprehensive Overview of Financial Accounting." 💰 Explore the journey from individual transactions to insightful reports, uncovering the secrets behind the double-entry system, GAAP principles, and accrual accounting. 📈 Learn the art of balancing debits and credits, as we demystify the core financial statements - Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Cash Flow Statement. 💡 Discover how these reports serve as the pulse of business, influencing strategic decisions and ensuring regulatory compliance. 🌐 Stay informed, stay ahead in the financial landscape!

#FinancialAccounting#DoubleEntrySystem#GAAP#BalanceSheet#IncomeStatement#CashFlowStatement#AccrualAccounting#BusinessFinance#DecisionMaking#FinancialReports#LearnWithUs#AccountingJourney#FinancialInsights
0 notes
Text
#MeruAccounting#bookkeepingservices#accountingservices#reconciliation#balancesheet#financialstatements#bookkeeping#accounting#bookkeepingtips#bookkeepers#bookkeepingcompany#india#uk
0 notes
Text
having a fav glup shitto that's so obscure people don't know it exists is pain
#star wars#ku'dar mu'bat#balancesheet#(a talking spider drifting through space in its nest)#i have a fic in progress where its nest plays an important role#just wait#spreading the ku'dar mu'bat and balancesheet agenda#my fav little guys
0 notes
Text
Federal Reserve's Actions Boost Stocks & Lower Borrowing Costs #balancesheet #bondprices #federalreserve #inflationexpectations #InterestRates
0 notes
Text
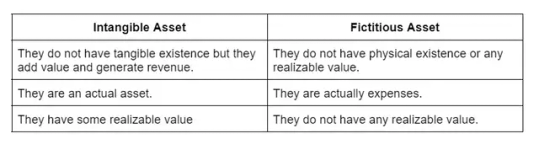
Title: "Distinguishing Fictitious Assets from Intangible Assets: A Financial Insight"
Understanding the difference between fictitious assets and intangible assets is essential for financial clarity. Fictitious assets have no tangible value but may represent deferred expenses or losses, affecting a company's balance sheet. In contrast, intangible assets include valuable non-physical assets like patents, copyrights, and trademarks, influencing a company's worth. This guide provides insights into the classification, accounting, and impact of fictitious and intangible assets on financial statements and the valuation of a business. Explore the intricacies of asset categorization, and enhance your financial knowledge to make informed decisions in the world of accounting and corporate finance.
0 notes
Text
Financial Reporting, Financial Analysis, Auditing: A Comprehensive Guide

Discover the ins and outs of Financial Reporting, Financial Analysis, and Auditing in this detailed guide. Gain valuable insights from experts in the field and find answers to your burning questions.
Introduction Welcome to the world of Financial Reporting, Financial Analysis, and Auditing. These three pillars of financial management are vital for businesses and organizations worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deep into each aspect, offering expert insights and practical knowledge to help you understand their significance and application.
Financial Reporting: Unveiling the Numbers Financial Reporting is the cornerstone of transparency in any organization. It involves the preparation and presentation of financial statements that reflect the true financial health of a company. Let's explore this in detail.
The Importance of Financial Reporting Financial reporting is not just about numbers; it's about trust. Stakeholders, including shareholders, investors, and regulatory authorities, rely on these reports to make informed decisions. Transparent reporting builds confidence and attracts investment.
Elements of Financial Reporting Balance Sheets: These provide a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific time, detailing assets, liabilities, and equity. Income Statements: Also known as profit and loss statements, they showcase revenue, expenses, and net income over a period. Cash Flow Statements: These track cash inflows and outflows, ensuring a company's liquidity. Financial Analysis: Deciphering the Data Financial Analysis is the art of dissecting financial reports to gain insights into a company's performance and potential. Let's dive into this crucial aspect.
The Role of Financial Analysis Financial analysts use various techniques to assess a company's profitability, stability, and growth prospects. Their findings guide investment decisions and strategic planning.
Tools for Financial Analysis Ratio Analysis: Examining key ratios like the debt-to-equity ratio and gross margin ratio. Trend Analysis: Identifying patterns and trends in financial data over time. Comparative Analysis: Benchmarking a company against competitors in the same industry. Auditing: Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance Auditing is the process of examining financial statements and transactions to verify their accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Let's uncover the world of auditing.
The Significance of Auditing Auditing instills confidence in financial reporting. Independent auditors provide an unbiased assessment of a company's financial statements, ensuring integrity and credibility.
Types of Audits External Audits: Conducted by independent firms, these ensure compliance with accounting principles and legal regulations. Internal Audits: Performed by a company's internal team, focusing on risk management and process improvement. FAQs Q: What's the primary goal of Financial Reporting? A: The main goal is to provide accurate and transparent financial information to stakeholders.
Q: How can I interpret a company's balance sheet? A: Look at the assets, liabilities, and equity to assess solvency and financial structure.
Q: What is the difference between Financial Reporting and Financial Analysis? A: Financial Reporting is about presenting financial data, while Financial Analysis involves interpreting that data for decision-making.
Q: Why is Auditing necessary if we already have Financial Reporting? A: Auditing ensures the accuracy of the reported financial information, offering an external validation.
Q: Can you recommend any tools for financial analysis? A: Tools like Excel, financial modeling software, and industry-specific software can be helpful.
Q: Is financial analysis only for large corporations? A: No, financial analysis is valuable for businesses of all sizes to make informed decisions.
Conclusion In this comprehensive guide, we've explored the crucial realms of Financial Reporting, Financial Analysis, and Auditing. These pillars form the foundation of financial management, driving transparency, informed decision-making, and trust in the corporate world. As you embark on your journey in finance, remember that knowledge is power, and understanding these concepts is key to success.
#FinancialReporting#FinancialAnalysis#Auditing#FinanceTips#BusinessInsights#InvestmentStrategies#AccountingStandards#CorporateTransparency#FinancialManagement#InvestorRelations#FinancialStatements#FinancialHealth#FinancialProfessionals#EconomicAnalysis#AuditProcess#FinancialData#Profitability#FinancialPlanning#BalanceSheet#CashFlowAnalysis
0 notes