#Fixed Angle and Swinging Bucket Rotor
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Ultra Centrifuge operate at speed up to 80000 RPM with temperature and vacuum controls) (Use for preparative and analytic works such as fractionate subcellular organelles – DNA – RNA – Virus) and use (Fixed angle Rotor – Swinging Bucket Rotor – Vertical Tube Rotor) #geneticteacher
0 notes
Text
Key Factors to Consider While Picking a Lab Centrifuge
Choosing the appropriate centrifuge for your laboratory can make all the difference when it comes to yielding good efficiency, dependability, and suitability for various applications. In this guide, we outline the key consideration factors that would help you make informed choices as you pick the right centrifuge for your needs.
Understanding Centrifuges and Their Role in the Lab
A lab centrifuge becomes indispensable in those laboratories where the separation of fluids, gasses, or liquids, based on density, becomes necessary. Various models of centrifuges are used in the laboratory, starting with blood, DNA, RNA, or other cellular components separations. The correct model will depend on your specific application, throughput, and long-term requirements.
Neuation offers a range of models with the aim of solving diversified laboratory needs, namely,
iFuge CS2P NXT
iFuge FX2P
iFuge L1000
iFuge L400 NXT
iFuge L400P
Below are the key factors to consider when picking the perfect centrifuge for your lab:
1. Type of Samples
Different centrifuges are optimized for specific sample types. Blood, DNA, RNA, and other biological materials may require varying speeds, rotor configurations, and temperature controls. Identifying your sample types will guide you in choosing the right model. For example, high-speed centrifuges are typically needed for molecular biology applications, whereas clinical labs may prefer low-speed models for blood sample separation.
2. Volume and Throughput
The main factor for consideration should be the volume and the number of samples you will be processing at any one time. Some centrifuges are designed for smaller volumes but at high throughput, whereas others handle larger volumes with a limited number of samples to be processed at one time. The iFuge L1000, for example, offers a large capacity of 4 x 250 mL for laboratories dealing in bulk sample processing.
3. Rotor Types
Centrifuge rotors are highly variable concerning the type of sample that one intends to process and the required application. The main types of rotors include:
Fixed-Angle Rotators: Can be operated at high speeds for faster separation of samples, thus generally used in units such as iFuge FX2P.
Buckets on swing-out rotors: Buckets on swing-out rotors work satisfactorily for applications that involve sedimentation and gradient separation. Models accommodating such include iFuge CS2P NXT and iFuge L1000.
Specialized Rotors: These are designed for specific tasks, such as cell culture or microplate centrifugation.
4. Maximum Speed and RCF
The centrifuge speed, conventionally measured in RPM, and the RCF are critical in such separations. The applications will fall into one category or another based on the speed and the RCF of a centrifuge, enabling its functionality in sample separations. As an example, the iFuge FX2P is for very demanding applications because of its unusually high maximum speed of 20,000 RPM at an RCF of 28,000g.
5. Refrigerated vs. Non-Refrigerated
For sensitive, temperature-dependent samples, a refrigerated centrifuge is required. Models include the iFuge CS2P NXT and the iFuge L1000, which boast of refrigeration that ensures sensitive samples are protected even on extended centrifugation. Variants, without refrigeration, include types like the iFuge L400P, best used when the separation of samples is rather basic, where temperature control is not of major concern.

6. Imbalance Detection and Lid Lock Features
Safety is the most important feature of any laboratory equipment. The presence of features like imbalance detection and secure lid locking prevents an accident in centrifugation. This, along with all other models in the Neuation series including iFuge CS2P NXT and iFuge FX2P has imbalance detection and lid locks that ensure safe operation of these.
7. Space Considerations
For space-saving without giving up performance, compact models include the iFuge L400 NXT and the iFuge CS2P NXT. These could be a good option for space-constrained laboratories, while major equipment such as the iFuge L1000 would be better suited to bigger laboratories.
8. User Interface and Ease of Maintenance
Centrifuges with user-friendly interfaces also minimize the learning curve for laboratory technicians and ensure smooth operation. In that regard, the iFuge FX2P and iFuge CS2P NXT models allow for intuitive digital setting of parameters with ease. Besides, ease of maintenance will be a factor to consider in ensuring long-term performance and cost efficiency.
9. Cost-Efficiency and After-Sales Support
Balancing performance with cost efficiency is relevantly important at a purchase decision. The iFuge L400 NXT and the iFuge L400P strike a reasonable balance between cost and performance; hence, these are excellent choices for labs with constrained budgets. Besides, a centrifuge from a reputable brand like Neuation assures one of reliable after-sales support in regard to maintenance, repairs, and calibration.
Sample type, throughput, rotor type, speed, refrigeration, and general safety features are considerations that will go into a purchasing decision when it comes to a lab centrifuge. For each of these requirements, Neuation, a brand of Accumax, has an extensive range of centrifuges. Be it high-volume processing, sensitive biological samples, or budget-friendly options, Accumax provides your laboratory with specific needs-oriented centrifuges with precision and reliability.
Read More:- Key Factors to Consider While Picking a Lab Centrifuge.
0 notes
Text
Laboratory Equipment: Essential Tools for Research and Development

Microscopes are indispensable tools for laboratories as they enable researchers to see structures and features too small for the naked eye. Different types of microscopes like compound, stereo, and electron microscopes allow examination of cells, tissues and various samples at different levels of magnification. Compound microscopes have interchangeable objectives and ocular lenses that provide low to high magnifications from 40X to 1000X. Stereo microscopes give low magnifications from 6X to 120X and are ideal for viewing three-dimensional samples. Electron microscopes have resolutions down to the nanometer level and are crucial for cellular and molecular analysis. Microscopes continue advancing with techniques like fluorescence and confocal microscopy for live cell imaging. Laboratory Equipment: Pipettes and Dispensers Handling small liquid volumes accurately is critical in many experimental procedures. Pipettes available in various fixed and adjustable volumes are used to transfer samples, reagents, drugs and more between tubes, plates or vessels. Manual pipettes come in single channel and multichannel varieties for quickly dispensing set volumes. Electronic pipettes automate repetitive pipetting with adjustable speed and greater reproducibility. Dispensers are also available for liquid handling, dispensing adhesive liquids, organic solvents and even highly viscous materials. Automated liquid handlers are large capital equipment that can pipette thousands of samples in parallel for high throughput experiments. Centrifuges Centrifugation is a fundamental separation technique used across all types of laboratories. Benchtop centrifuges are simple bi-phasic models suitable for routine pelleting of cells, small particles and precipitates. They provide RCFs (relative centrifugal forces) from 1000 to 12000g. Preparative centrifuges have larger rotors and capacities for voluminous sample processing. Ultracentrifuges enable high speed sedimentation by developing enormous RCFs over 100,000g. Models for ultracentrifugation employ zonal, swinging bucket or fixed angle rotors depending on the separation goals. Selecting the right centrifuge based on sample type, size and desired separations is key for optimizing results. Laboratory Equipment: Spectrophotometers and Colorimeters Quantifying analytes through detection and measurement of light absorbance or transmittance is done using spectrophotometers and colorimeters. They are indispensable in analytical chemistry, biochemistry and molecular biology labs. Single beam spectrophotometers detect absorbance of a sample against a blank reference. Double or triple beam instruments allow simultaneous measurement of multiple samples and references. Colorimeters are compact single wavelength devices ideal for dedicated absorbance assays. Modern multi-mode readers combine varied features like fluorescence, luminescence, absorbance in a single box for versatility. Automated instruments speed up high throughput absorbance measurements in microplates. Advancements in detector and optic materials continue enhancing sensitivity and accuracy. Laboratory Equipment: Water Purification Systems Pure water is imperative for numerous analytical procedures and as a solvent in chemical reactions. Laboratories install point-of-use or centralized water purification systems to generate different grades of water for their needs. Reverse osmosis systems yield high purity water from tap or well sources. Ion exchange columns further polish RO water to Type I standards. Advanced systems integrate UV oxidation to minimize microbial growth and sub-micron filtration for generating ultra pure or Milli-Q water. Water qualities are certified through resistivity, TOC and particle testing. Laboratories also require simple dispensers of purified water right at the bench. Mobile cart-based purifiers deliver purified water anywhere as needed. Integrated systems optimize space and centralize management of water purification.
0 notes
Text
Laboratory Centrifuges Market Segments, Gross Margin and Revenue and Forecast by 2030
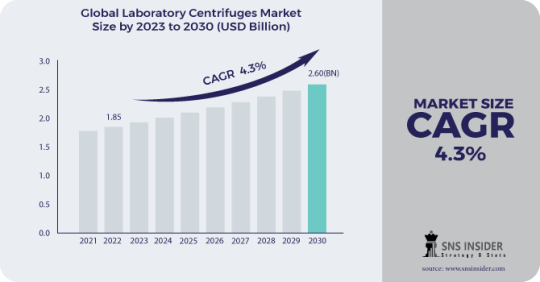
The Laboratory Centrifuges Market Size was valued at USD 1.85 Bn in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 2.60 Bn by 2030, and grow at a CAGR of 4.3% over the forecast period 2023-2030.
The global Laboratory Centrifuges market research report provides a complete overview on the existing and future state of the industry. The study conducted utilizing extensive primary and secondary research, has all of the necessary market data. The research also covers data from segments such as type, industry, channel, and others, as well as market volume and value for each. The research also looks into the market's major players, distributors, and the overall structure of the supply chain. It also evaluates the factors and features that may have an impact on the market's sales growth.
Book Your Free Sample Report @ https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/1140
Major market player included in this report are:
The coronavirus pandemic had different impact on the global economies across the globe. The market is fast evolving, according to the Laboratory Centrifuges research report, and the influence is being examined in the current scenario and covers future projections. The study gives precise estimates for the industry's market size, share, production capacity, demand, and growth for the forecast period. This is the most recent report on the COVID-19 scenario.
Becton Dickinson and Company, Danaher Corporation, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., QIAGEN, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Agilent Technologies, Inc., INC., Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH, Neuation, Hitachi Koki Co., Ltd., and Harvard Bioscience, Inc.
Market Segmentation
By Product
Equipment
Accessories
By Rotor Design
Fixed-angle Rotors
Swinging-bucket Rotors
Vertical Rotors
Other Rotor
By Model Type
Benchtop Centrifuges
Floor-standing Centrifuges
By Intended Use
Preclinical Centrifuges
General Purpose Centrifuges
Clinical Centrifuges
By Application
Diagnostics
Microbiology
Cellomics
Genomics
Proteomics
Blood Component Separation
By End-User
Hospitals
Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Companies
Academic & Research Institutions
The market segmentation by product type, application, end-user, and geography is discussed in the Laboratory Centrifuges research study. The research looks into the industry's growth goals and programs, as well as cost awareness and production procedures. The report also covers a broad review of the core industry, including classification, definition, and thus the supply and demand chain's structure. Global marketing data, competitive climate surveys, growth rates, and information on critical development status are all covered by global research.
Regional Analysis
The Laboratory Centrifuges market is separated into geographical regions based on places such as North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East and Africa. Production and consumer ratios, market size and market share, import and export ratios, supply and demand, consumer demand ratios, technological advancements, research and development, infrastructure development, economic growth, and a strong market presence in every region are all covered by research.
Get Exclusive Discount this Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/discount/1140
Competitive Outlook
TheLaboratory Centrifuges market research highlights the most significant acquisitions, collaborations, and product launches in the industry. To provide deeper insights into prominent players, the study report employs advanced research methods such as SWOT and Porter's Five Forces analysis. The research provides an overview of the worldwide competitive environment as well as key insights into the major competitors and their plans to expand their businesses. It also contains vital information on financial conditions, worldwide positioning, product portfolios, income and gross profit margins, as well as technological and research advances.
Contact Us:Akash AnandHead of Business Development & [email protected]: +44 20 8144 2758
0 notes
Link
Fixed Angle and Swinging Bucket Rotor is one of the important equipment for any research institute or laboratory. Go through this blog post to know more about Rotors and different types of Rotors are available in market.
0 notes
Text
Learn about Two Kinds of Rotors – Fixed Angle and Swinging Bucket
In the areas of molecular biology, biochemistry, medicine, industry, and food sciences, centrifugation is the most utilized methods of laboratory for the materials separation in world wide. This is all about masses and the gravity, the substances present inside the solution that is heterogeneous will be parted in a given time period depending on the density and size. The dense and small substances in the solution go down and settle at the bottom. However, it doesn’t occur all the time. Sometimes the particles present in the solution doesn’t settle, instead get suspended in it. The force of the centrifuges makes this procedure in efficient and sufficient manner. The centrifuge uses have been proved to be strong and is spread entirely in the field of sciences. This centrifuge became normal thing of lab apparatuses since the earlier years. The centrifugation uses centripetal force application and it is put in driving the partition of substances in the heterogeneous solution into pellet and supernatant. The force of gravity is amplified by the modern centrifuge which will make the solution to spin at speed rate in the higher range for incrementing the sedimentation rate. The substances having the high ranging material density does sediment far away from the centrifugation axis. Likewise, the particles suspended in the solution have the high range of particle density and happens to be settling at the bottom in solution.
When an intensity of ten thousand grams is associated with a tolerably sensible and easy to-use bit of apparatus, the strategy would frequently take hours or days under the average gravity can be abridged to only minutes. More often than not to get some answers concerning cycles per-minute. The more events it will turn, the speed will be very fast and increasingly it is essential that the imperativeness being associated. Another technique for imparting the gravitational power or the turning of the rotor is relative transmitting power. Accordingly, it is really undeniable to see how this clear device can empower researchers to easily seclude tissues, cells, organelles, and macromolecules for taking up further examination.
youtube
youtube
Differences between the swinging bucket rotor and fixed angle rotor
A centrifuge consists of a part called as rotor. This is utilized for housing the tubes where the partition is actually happening. Normally, you can find two kinds of important rotors of centrifuge – one is fixed angle rotor and other one is swinging bucket rotor. The rotor, fixed angle will handle the pipes at stable degree of 45 that is approximately relative to the rotation axis. The other one, swinging bucket rotor will swing out whenever the centripetal power is enforced. And handles the cells at the degree of appropriately ninety, this is relative to the rotation angle. Make sure to remember that more dense substances will be parting nearer the centripetal force angle. Thus, the materials that are pelleted are settled at the centrifuge tube bottom which is conical in shape in the swinging bucket rotors. On the other side, the progressing tubes in a fixed angle rotor forms the sedimentation towards the side. If sedimentation happens and solids gets suspended in the tube angle then this kind of situation will lead to problems. Everything being proportionate, swinging bucket rotors be able to offer a predominant zone of sedimentation settles on them the obvious choice for centrifuging tests. in any case, the rotors of fixed angle offer beneficial highlights that much of time settle on them a continuously charming choice. To begin with, due to their clear and beneficial chamber isolating, the rotors of fixed angle can hold a progressively important measure of barrels appeared differently in relation to its accomplice of swinging-bucket. Making it progressively sensible for high-throughput applications. Next, due to the rigid structure of the metal compound material, the fixed angle rotors can withstand much higher gravitational forces. Which is major while confining characteristic macromolecules, for instance, protein, RNA, and DNA.
Regardless of your application and rotor structure, the centrifugation is an astonishing resource for segment of scaled down scale and full scale in game plans. Various sorts and size rotators are used every day for normal inspection in lawful examinations, sustenance faultiness, pharmaceutical headway, and wastewater the officials.
youtube
0 notes
Text
Guide To Centrifugation by Neuation Technologies
Centrifuge is a device that applies centrifugal force to separate mixture in the fluid by putting an object in rotational movement around a fixed axis thereby separating fluids of different densities or liquid from solids.
Centrifuge is a relatively simple instrument but yet tricky to maintain. Most of the centrifuge related blunders are due to user handling error and many machines have been destroyed by the scientists who are in it for simple pelleting. Therefore, it is crucial to understand what we do during centrifugation and avoid damaging the instrument and it’s in for the prolonged stay in the lab
Balance
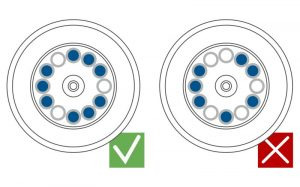
Centrifugation produces centrifugal force to effectively separate and sediment the sample component based on size and density. Rotors spin very rapidly generating extreme force and therefore it is crucial to properly balance rotors during spin especially when rotors are loaded partially with tubes and plates. Any imbalance in the rotor including placement of the centrifuge on an uneven or slanted work surface can cause abnormal vibration that can in turn damage the rotor. An unbalanced centrifuge is as dangerous as unstable chemical reaction and can start domino effect of catastrophes all the way from instrument failure, to sample breakage, user injury and overall large-scale destruction in the laboratory and can be major safety hazard in the laboratory environment
Precise balancing at high speed becomes more crucial as the centrifugal force generated during centrifugation is directly proportional to sample mass and acceleration. At higher RCF even slight change in sample mass can lead to substantial force imbalance which in turn could be a catastrophe.
It doesn’t matter if the centrifuge has a fixed angle or swing bucket rotor, two important factors to consider when balancing include sample volume and symmetrical arrangement of tubes. It is important to ensure that the sample volumes are equal in all tubes and the tubes are placed directly opposite each other in the centrifuge. If the solution is not of similar density (eg acetone and water), tubes should be equal mass rather than volume to be correctly balanced. In the case of a swing bucket rotor it is to make sure that all slots contain a rotor bucket appropriate to the machine and are of the same weight.
Time, Speed and centrifugation
The choice of centrifugation speed depends on the size of the particle in the sample, smaller the particle size higher centrifugation speed for example bacterial cells are pelleted at higher speeds (2000-10000 g) than mammalian cells. Relative centrifugal force (RCF) generated by a spinning rotor is expressed relative to earth's gravitational force and therefore is also known as G-force . The G force acting on a particle is exponential to the speed of rotation due to this square dependence of RCF in RPM, centrifugation speed of 10000RPM for 5 minutes and 500 RPM for 10 minutes are not interchangeable. The former produces a much larger RCF than the latter. RCF is proportional to the radius of the rotor and to the square of RPM
RPM and RCF are not the same
RPM (Revolution per minutes) and RCF (Relative centrifugal force or g-force) are commonly used to describe centrifugal speed. RCF refers to the acceleration applied to your sample for example 10,000 g means 10,000 times earth’s gravitational force. RPM is not a useful unit because the force varies with radius of the machine (Bigger the radius, the more acceleration is applied to your sample for the same RPM) therefore RPM speed setting needs to be converted to RCF to ensure that the correct centrifugal force is applied.
Centrifugation and the temperature
Centrifugation generates heat because of the movement of molecules and friction with air which in turn can increase the temperature within a centrifuge which can affect stability of the sample. Temperature inside the centrifuge is primarily influenced by three factors: Rotor material, Rotor shape and speed of rotation.
Rotor materials such as steel and aluminium have a high density and high thermal conductivity which means it can transfer heat efficiently and get chilled quickly. Material like polymer and carbon fibre are low density material (Heat Insulator) and helps in maintaining constant temperature.
Rotor Shape determines the airflow within a centrifuge. Optimizing the airflow within a centrifuge through rotor shape is essential to maintaining the temperature.
Speed of Centrifuge, Centrifugation is proportional to the rise in temperature – at higher speed, more heat is generated. The degree of warming is very much depending on the maximum speed and shape of the rotor. It is important to understand the maximum speed of the centrifuge and the range of speed that maintains the temperature range that will not change the outcome of the experiment. This information is supplied by the manufacturer to help users understand the limitation and work around it.
Acceleration and Deceleration
Many Centrifuge offers the option to control deceleration setting (brakes) to bring it to stop faster and what is the effect on sample outcome.
Braking can be particularly useful during centrifugation involving Nucleic acid extraction or bacterial cell pelleting which are not affected by sudden stopping. Experiments that are more sensitive to abrupt deceleration such as isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and gradient centrifugation, braking can cause separated layers to remix.
The Interphase separation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) is very sensitive to vibration and too fast acceleration or deceleration would disturb the gradient and lead to a milky/Non-existent interphase, making it difficult to extract PBMC. To prevent remixing the protocol requires acceleration/deceleration be shut off completely so that the centrifuge accelerates slowly and high forces cannot disturb the gradient and accumulate in the appropriate phase according to their density. When the brake is shut off, the centrifuge simply runs down until the rotor stops by itself.
Thus, centrifuge with different Acceleration/Deceleration ramps offers users the option of adjusting acceleration and deceleration speed and optimizing their protocols quite easily
Know where your pellet is?
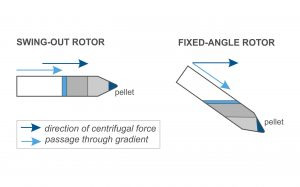
One of the applications of centrifuge is to pellet down bacterial cells, mammalian cells or nucleic acid. Angle of rotor determines the position of pellet. To Ensure and know where your pellet is, a good lab practice is to always spin the tube with lid hinges placed in the same orientation (for example lid hinges facing outward). In the case of a swing rotor, the pellets are formed at the bottom of the tube.
Hope this article will help you in choosing the right centrifuge product which custom fits your application.
Original Source: https://neuation.com/guide-to-centrifugation/
0 notes
Text
Bucket rotors are sold separately from centrifuges
Bucket rotors are sold separately from centrifuges. The TX-1000 swinging bucket rotor is compatible with the ST40/40R and Heraeus Megafuge X3/X3R centrifuges. The rotors come with 18 tubes each.
bucket adapters allow you China metal casting to use the same centrifuge with different tubes. These tubes are designed with a diameter of 13 mm and are compatible with a variety of Eppendorf centrifuges. They also feature an extra writing area and smearing-resistant writing panel.
This bucket adapter fits the 5417 and 5430 centrifuges. It can hold up to 30 1.5/2mL tubes. The rotor has a 14,000 rpm spin speed. This rotor is sold used but is still in good condition. It comes with a cover.
bucket adapters come in many sizes. There are swing bucket rotors and fixed angle rotors. The rotors are autoclavable at 121degC. The rotors are easy to clean and disassemble, with color-coded buckets. They can also be used with biohazardous samples and can be sealed with aerosol-tight covers.
0 notes
Text
Laboratory Centrifuges Market is projected to expand at a steady CAGR over the forecast by 2031 | NuAire, QIAGEN N.V., Sartorius AG
Global Laboratory Centrifuges Market report from Global Insight Services is the single authoritative source of intelligence on Laboratory Centrifuges Market. The report will provide you with analysis of impact of latest market disruptions such as Russia-Ukraine war and Covid-19 on the market. Report provides qualitative analysis of the market using various frameworks such as Porters’ and PESTLE analysis. Report includes in-depth segmentation and market size data by categories, product types, applications, and geographies. Report also includes comprehensive analysis of key issues, trends and drivers, restraints and challenges, competitive landscape, as well as recent events such as M&A activities in the market.
A laboratory centrifuge is a piece of laboratory equipment, typically powered by electricity, that is used to separate substances of different densities by spinning them in a tube. Centrifuges can be used to separate cells from blood, to separate different types of cells, or to purify proteins.
Request Sample Report – https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-sample/GIS20526/
Key Trends
The main trend in laboratory centrifuges technology is the development of more compact and portable centrifuges. This is being driven by the need for more mobile and flexible lab equipment, as well as the need to save space in crowded laboratories. Another trend is the development of centrifuges that can accommodate a wider range of sample sizes and types. This is in response to the increasing diversity of samples being processed in laboratories.
Key Drivers
One of the key drivers of the laboratory centrifuges market is the increasing demand for these devices from the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. This is due to the fact that centrifuges play an important role in the purification and isolation of biomolecules and cells. Additionally, centrifuges are also used in the food and beverage industry for the clarification of juices and other liquids.
Key Market Segments
By Product
Equipment
Accessories
Others
By Rotor Design
Swinging Bucket Rotors
Fixed Angle Rotors
Vertical Rotors
Others
By Intended Use
General-Purpose Centrifuges
Clinical Centrifuges
Preclinical Centrifuges
Get Customized Report as Per Your Requirement – https://www.globalinsightservices.com/request-customization/GIS20526/
Key Market Players
NuAire
QIAGEN N.V.
Sartorius AG
Cardinal Health
Centurion Scientific
Antylia Scientific
Heal Force
With Global Insight Services, you receive:
10-year forecast to help you make strategic decisions
In-depth segmentation which can be customized as per your requirements
Free consultation with lead analyst of the report
Excel data pack included with all report purchases
Robust and transparent research methodology
Ground breaking research and market player-centric solutions for the upcoming decade according to the present market scenario
About Global Insight Services:
Global Insight Services (GIS) is a leading multi-industry market research firm headquartered in Delaware, US. We are committed to providing our clients with highest quality data, analysis, and tools to meet all their market research needs. With GIS, you can be assured of the quality of the deliverables, robust & transparent research methodology, and superior service.
Contact Us:
Global Insight Services LLC
16192, Coastal Highway, Lewes DE 19958
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone: +1–833–761–1700
0 notes
Text
High Speed Centrifuge operate at speed up to 30000 RPM with temperature control (Use for sensitive biological samples such as bacterial cells and protein pellet) and use (Fixed angle Rotor – Swinging Bucket Rotor – Vertical Tube Rotor) #geneticteacher
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Buffers
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for processes and/or reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. Buffer solutions have a working pH range and capacity which dictate how much acid/base can be neutralized before pH changes, and the amount by which it will change.
What is a buffer composed of?
To effectively maintain a pH range, a buffer must consist of a weak conjugate acid-base pair, meaning either a. a weak acid and its conjugate base, or b. a weak base and its conjugate acid. The use of one or the other will simply depend upon the desired pH when preparing the buffer. For example, the following could function as buffers when together in solution:
Acetic acid (weak organic acid w/ formula CH3COOH) and a salt containing its conjugate base, the acetate anion (CH3COO-), such as sodium acetate (CH3COONa)
Pyridine (weak base w/ formula C5H5N) and a salt containing its conjugate acid, the pyridinium cation (C5H5NH+), such as Pyridinium Chloride.
Ammonia (weak base w/ formula NH3) and a salt containing its conjugate acid, the ammonium cation, such as Ammonium Hydroxide (NH4OH)
Buffers are a class of solution-stabilizing molecules which existed long before contemporary lab technology. Natural buffer substances like bicarbonate and carbonic acid are manufactured by organisms and molecular interactions, functioning to maintain pH equilibrium.
After natural buffer systems were discovered, their balancing effects became indispensable in scientific exploration. Synthetic buffers were developed over decades to produce reliable reactions in experimental models, enhancing biochemical reactions and medicinal products.
New buffers are introduced every year, built from the fundamentals developed over a century ago. This article explores buffers beginning with the foundation which made them inseparable from biochemistry. We’ll then follow the construction and replacement of buffering systems among individual studies as procedures are continually refined.
Basic reagents are used in combination to produce the most potent buffer solutions. Once buffers transitioned into biochemistry, researchers began to establish what chemical mixtures were most productive for equalizing the pH of certain reactions.
Between the 1960s and 80s, a project for determining the best buffers resulted in a list that remains crucial in modern laboratories. “Good’s buffers” were produced or collected by Norman Good and his colleagues, and selected on a number of criteria that qualified application to research in the biological field. Some of the requirements were pKa between 6 and 8, high water solubility, stability and a lack of exchange with membranes or biochemical reactions. Good also prioritized substances that could be prepared easily and safely.
One of the lab world’s most valuable buffer agents, Tris – was first recognized by Good in the early 1960s. Known in therapeutics as THAM, Tris quickly adopted scientific roles. Tris and other reagents identified by Good continue to act as the equalizing agents within buffer mixtures by adjusting pH to a specified range.
How are Goggles Made
Goggles are a form of eye protection that is designed to shield the wearer from injuries to the eye due to hazardous conditions in the workplace, home, or other venues such as while playing sports. According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), approximately 2,000 work-related eye injuries requiring medical treatment are reported in the U.S. every day, the majority of which could have been prevented or been less severe had the proper eye protection been worn. Furthermore, the Department of Labor reports that eye injuries result in an estimated $300 million annually in lost production time, medical expenses, and workers’ compensation.
This article will describe how goggles are made and will discuss the common types of safety eyewear used as Personal Protection Equipment (PPE). You can learn more about other types of PPE in our related guides and articles, a list of which may be found at the end of this article.
Face masks
When her Danish colleagues first suggested distributing protective cloth face masks to people in Guinea-Bissau to stem the spread of the coronavirus, Christine Benn wasn’t so sure.
“I said, ‘Yeah, that might be good, but there’s limited data on whether face masks are actually effective,’” says Benn, a global-health researcher at the University of Southern Denmark in Copenhagen, who for decades has co-led public-health campaigns in the West African country, one of the world’s poorest.
That was in March. But by July, Benn and her team had worked out how to possibly provide some needed data on masks, and hopefully help people in Guinea-Bissau. They distributed thousands of locally produced cloth face coverings to people as part of a randomized controlled trial that might be the world’s largest test of masks’ effectiveness against the spread of COVID-19.
Face masks are the ubiquitous symbol of a pandemic that has sickened 35 million people and killed more than 1 million. In hospitals and other health-care facilities, the use of medical-grade masks clearly cuts down transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. But for the variety of masks in use by the public, the data are messy, disparate and often hastily assembled. Add to that a divisive political discourse that included a US president disparaging their use, just days before being diagnosed with COVID-19 himself. “People looking at the evidence are understanding it differently,” says Baruch Fischhoff, a psychologist at Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, who specializes in public policy. “It’s legitimately confusing.”
Endotoxin Removal from Bench to Process Scale
Endotoxin or lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are highly toxic components of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria and are often present in significant amounts in bacterial cell expression systems such as E.coli.
A number of methods have been adopted for the removal of endotoxin based on adsorption, in particular ion exchange chromatography. Although downstream processing can significantly reduce endotoxin levels in the product, efficient and cost effective removal of residual endotoxin from biopharmaceutical preparations remains a challenge.
Astrea Bioseparations Ltd. ('Astrea') has developed a novel affinity chromatography adsorbent, EtoxiClear, that is highly stable, robust and non-toxic, with a high affinity for bacterial endotoxin and low protein binding. EtoxiClear is a cost effective and scalable technology designed for use in endotoxin removal applications including process development, sample/buffer preparation and product polishing steps used during cGMP manufacture of biological molecules.
This application note describes the use of EtoxiClear? to effectively remove endotoxin from a purified immunoglobulin protein solution at both bench scale and process scale; utilising Astrea’s new 100 mm diameter Evolve? Process Column.
A Basic Tool for the Small Clinical Lab
No matter how elementary or advanced, every clinical laboratory has one essential device—a centrifuge. Whether it stands on the benchtop or floor and is refrigerated or not, a laboratory centrifuge fractionates liquid specimens by creating spin-induced high g-forces, and has long been a standard tool for both clinical and research applications. With broad utility, laboratory centrifuges are true workhorses, usually providing trouble-free service for many thousands of cycles over many years of steady use.
Benchtop centrifuge, also known as tabletop, centrifuges have smaller throughputs and cannot provide high-end g-forces compared with floor models, but can accommodate most applications. Tabletop models include low-speed clinical centrifuges used for diagnostics; high-speed instruments for whole-cell harvesting and some nucleic acid applications; multipurpose centrifuges that accept either fixed-arm or swinging bucket rotors; and cell washers, which are highly specialized for washing red blood cells. For those considering a replacement or initial purchase, here is a brief overview of several of the most popular benchtop models used in the small laboratory. All are manufactured by laboratory equipment companies with long-standing reputations for quality and reliability.
Low-Speed, Fixed-Angle Clinical Centrifuge Options
At the entry point of its centrifuge line, the Drucker Company (Philipsburg, PA) produces the Model 614B as its most affordable basic centrifuge. The device is designed for the small lab or doctor’s office and is a single-speed centrifuge (up to 3150 rpm) used for blood separations. The 45o rotor will hold six test tubes of up to 15 mL (17 mm × 125 mm). The unit has a lid safety switch and is UL/CSA compliant. It includes a 30-minute timer, a double-encased, brushless motor, and a clear lid with a safety switch. The motor housing and rotation chamber are designed to allow for cool operation. Standard accessories include three sets of tube holders to fit tubes of varying lengths.
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Waltham, MA) characterizes its Medilite centrifuge as ideal for routine low-speed centrifugation of blood and urine samples. Each Medilite centrifuge includes a 6- or 12-place 45o rotor and standard shields for aerosol containment. The device is designed with an integral 30-minute timer and accepts a variety of tube sizes up to 10 or 15 mL, depending on the rotor. This centrifuge also features a maintenance-free brushless motor, incorporates a power interrupter for user safety, and provides fixed speeds of 3100 or 2700 rpm.
0 notes
Link
FirstSource is providing different types of centrifuge rotors like Fixed angle or Swinging bucket rotors. If you want to know more about centrifuge rotors then go through this blog post.
0 notes
Text
Laboratory Centrifuge Industry Key Business Driving Factors and Development Opportunities, 2023
Global laboratory centrifuge market is anticipated to witness exponential growth in the forecast period. A laboratory centrifuge is driven by a motor that spins liquid samples at high speed. The factors that propel the growth of the market include an increase in occurrence and incidence of disease, increase in acceptance of automation techniques in hematology, new product launches, technical progressions, the surge in research activities in the field of biotechnology & life sciences, and surge in private & public healthcare investment.
On the other hand, there are factors that may hamper the growth of the market including reduced sales of the equipment owing to extended lifespan and the high cost of equipment. The market is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR in the upcoming period as the scope, product types, and its applications are increasing across the globe.
The market could be explored by product type, rotor design, intended use, application, end user and geography. Market could be explored by product type as Equipment (Microcentrifuges, Multipurpose Centrifuges, Minicentrifuges, Ultracentrifuges, Analytical Ultracentrifuges, Preparative Ultracentrifuges and Other Equipment), and Accessories (Tubes, Rotors, Centrifuge Bottles, Plates, Buckets and Other Accessories).
Market could be explored by model type as Floor-standing Centrifuges and Benchtop Centrifuges. The “Benchtop Centrifuges” segment led the laboratory centrifuge market in 2017 and will continue to lead in the forecast period. The key factors that may be attributed to the growth of the market include increased acceptance in the laboratory centrifuges market. Laboratory centrifuge market could be explored by rotor design as Vertical Rotors, Fixed-angle Rotors, Swinging-bucket Rotors, and Other Rotors (Batch Rotors, Continuous Flow Rotors, Drum Rotors, and Zonal Rotors).
Get Sample Copy of this Report @
https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/laboratory-centrifuge-market/request-sample
Based on intended use, market could span Clinical Centrifuges, General Purpose Centrifuges, and Preclinical Centrifuges. The key applications that could be explored in the market include Diagnostics, Proteomics, Genomics, Blood Component Separation, Microbiology, Cellomics and Other Applications (Nanotechnology Research and Biochemical Analysis).
The market could be explored based on the end user as Academic & Research Institutions, Hospitals, and Biotechnology & Pharmaceutical Companies. The “Hospitals” segment led the laboratory centrifuge market in 2017 and will continue to lead in the forecast period. The key factors that may be attributed to the growth of market includes rising occurrence of diseases, growing consciousness about initial diagnosis and treatment, growing demand for blood, availability of technologically advanced and novel centrifuges for blood separation, and rising number of hospitals, particularly in developing countries.
North America accounted for the major share of the laboratory centrifuge market in 2017 and will continue to lead in the forecast period. The factors that could be attributed to the growth include the presence of numerous laboratories and academic institutions and the well-established healthcare business. Furthermore, the rising number of research in Latin American nations. North America is followed by Asia-Pacific region owing to a vast population base with disease problem and rising clinical diagnostic facilities.
Some of the key players that fuel the growth of the laboratory centrifuge market comprise Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Sartorius AG, LLC. (Subsidiary of GTCR firm), Eppendorf Group, QIAGEN N.V., Cole-Parmer Instrument Company, Andreas Hettich GmbH & Co.KG, Beckman Coulter, Inc. (Subsidiary of Danaher Corporation), Hitachi Koki Co., Ltd. (Subsidiary of Hitachi, Ltd.), KUBOTA Corporation, and Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH. The leading companies are taking up partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, and joint ventures in order to boost the inorganic growth of the industry.
Browse Related Category Market Reports @
https://www.millioninsights.com/industry/laboratory-equipment
0 notes
Text
Laboratory Centrifuge Market Equipment Suppliers and Price Analysis 2018-2023
Global laboratory centrifuge market is anticipated to witness exponential growth in the forecast period. A laboratory centrifuge is driven by a motor that spins liquid samples at high speed. The factors that propel the growth of the market include an increase in occurrence and incidence of disease, increase in acceptance of automation techniques in hematology, new product launches, technical progressions, the surge in research activities in the field of biotechnology & life sciences, and surge in private & public healthcare investment.
On the other hand, there are factors that may hamper the growth of the market including reduced sales of the equipment owing to extended lifespan and the high cost of equipment. The market is anticipated to expand at a significant CAGR in the upcoming period as the scope, product types, and its applications are increasing across the globe.
Request a Sample Copy of This Report @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/laboratory-centrifuge-market/request-sample
The market could be explored by product type, rotor design, intended use, application, end user and geography. Market could be explored by product type as Equipment (Microcentrifuges, Multipurpose Centrifuges, Minicentrifuges, Ultracentrifuges, Analytical Ultracentrifuges, Preparative Ultracentrifuges and Other Equipment), and Accessories (Tubes, Rotors, Centrifuge Bottles, Plates, Buckets and Other Accessories).
Market could be explored by model type as Floor-standing Centrifuges and Benchtop Centrifuges. The “Benchtop Centrifuges” segment led the laboratory centrifuge market in 2017 and will continue to lead in the forecast period. The key factors that may be attributed to the growth of the market include increased acceptance in the laboratory centrifuges market. Laboratory centrifuge market could be explored by rotor design as Vertical Rotors, Fixed-angle Rotors, Swinging-bucket Rotors, and Other Rotors (Batch Rotors, Continuous Flow Rotors, Drum Rotors, and Zonal Rotors).
Based on intended use, market could span Clinical Centrifuges, General Purpose Centrifuges, and Preclinical Centrifuges. The key applications that could be explored in the market include Diagnostics, Proteomics, Genomics, Blood Component Separation, Microbiology, Cellomics and Other Applications (Nanotechnology Research and Biochemical Analysis).
View Full Report with TOC @ https://www.millioninsights.com/industry-reports/laboratory-centrifuge-market
Market Segment:
Geographically, this report is segmented into several key Regions, with production, consumption, revenue (million USD), market share and growth rate of Laboratory Centrifuge in these regions, from 2012 to 2023 (forecast), covering
• North America (United States, Canada and Mexico)
• Europe (Germany, France, UK, Russia and Italy)
• Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, Korea, India and Southeast Asia)
• South America (Brazil, Argentina, Columbia)
• Middle East and Africa (Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria and South Africa)
Global Laboratory Centrifuge market competition by top manufacturers, with production, price, revenue (value) and market share for each manufacturer; the top players including
• Thermo Fisher Scientific?The U.S)
• Beckman Coulter?The U.S)
• Eppendorf AG?Germany?
• Kubota Corporation?Japan?
• Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH?Germany?
For More Details Visit @ million insights
0 notes
Text
Low Speed Centrifuge operate at speed up to 10000 RPM with temperature control (Use in cells and nucleus isolations) and use (Fixed Angle Rotor – Swinging Bucket Rotor) #geneticteacher
0 notes
Text
Different Parts of a Centrifuge

A centrifuge is a laboratory device that uses centrifugal force in order to separate the various components of a fluid. The end result is achieved after the fluid is spun at high speed inside the device.
Centrifuges are necessary equipment in most laboratories with application needs like clinical and blood banking, microbiology, tissue culture, molecular biology and genomics, drug discovery, and proteomics.
At the center of the centrifuge is the motor which creates the spin and attached to it is the rotor which houses the tubes contained with samples.
Centrifuge rotors are designed in a way that it can generate rotation speed that could bring about the separation of components in a particular sample. There are three main types of rotors used in a centrifuge, to wit: fixed-angle rotors, swinging bucket rotors or horizontal rotors, and vertical rotors.
The tubes or containers may be spun at different angles. Depending on the type of centrifuge, the tubes may either be loaded at the angle on which they will rotate or be loaded into a container that will adjust itself to a different angle upon startup.
When the centrifuge is started, its motor will run based on the given settings. During the cycle, the sample in the test tubes will separate into their various components so they are ready for analysis.
Hettich perfected a wide range of centrifuges for different applications and markets. Hettich’s centrifuges are thoroughly tested to ensure the safety of users while still being able to comply with international regulatory standards.
Furthermore, Hettich centrifuges are available in a variety of temperature control versions which are able to maintain a constant sample temperature during operation. HETTICH’s model varieties also support the option of built-in temperature control, internal heating, external cooling, and additional configurations to meet clinical, research, and industrial requirements.
0 notes