#Global Machine Safety Market
Text
#Global Machine Safety Market Size#Industry Analysis By Segmentations#Top Key Players#Trends#Future Development & Forecast 2022-2030
0 notes
Text
These claims of an extinction-level threat come from the very same groups creating the technology, and their warning cries about future dangers is drowning out stories on the harms already occurring. There is an abundance of research documenting how AI systems are being used to steal art, control workers, expand private surveillance, and seek greater profits by replacing workforces with algorithms and underpaid workers in the Global South.
The sleight-of-hand trick shifting the debate to existential threats is a marketing strategy, as Los Angeles Times technology columnist Brian Merchant has pointed out. This is an attempt to generate interest in certain products, dictate the terms of regulation, and protect incumbents as they develop more products or further integrate AI into existing ones. After all, if AI is really so dangerous, then why did Altman threaten to pull OpenAI out of the European Union if it moved ahead with regulation? And why, in the same breath, did Altman propose a system that just so happens to protect incumbents: Only tech firms with enough resources to invest in AI safety should be allowed to develop AI.
[...]
First, the industry represents the culmination of various lines of thought that are deeply hostile to democracy. Silicon Valley owes its existence to state intervention and subsidy, at different times working to capture various institutions or wither their ability to interfere with private control of computation. Firms like Facebook, for example, have argued that they are not only too large or complex to break up but that their size must actually be protected and integrated into a geopolitical rivalry with China.
Second, that hostility to democracy, more than a singular product like AI, is amplified by profit-seeking behavior that constructs increasingly larger threats to humanity. It’s Silicon Valley and its emulators worldwide, not AI, that create and finance harmful technologies aimed at surveilling, controlling, exploiting, and killing human beings with little to no room for the public to object. The search for profits and excessive returns, with state subsidy and intervention clearing the way of competition, has and will create a litany of immoral business models and empower brutal regimes alongside “existential” threats. At home, this may look like the surveillance firm and government contractor Palantir creating a deportation machine that terrorizes migrants. Abroad, this may look like the Israeli apartheid state exporting spyware and weapons it has tested on Palestinians.
Third, this combination of a deeply antidemocratic ethos and a desire to seek profits while externalizing costs can’t simply be regulated out of Silicon Valley. These are fundamental attributes of the industry that trace back to the beginning of computation. These origins in optimizing plantations and crushing worker uprisings prefigure the obsession with surveillance and social control that shape what we are told technological innovations are for.
Taken altogether, why should we worry about some far-flung threat of a superintelligent AI when its creators—an insular network of libertarians building digital plantations, surveillance platforms, and killing machines—exist here and now? Their Smaugian hoards, their fundamentalist beliefs about markets and states and democracy, and their track record should be impossible to ignore.
310 notes
·
View notes
Text
The phone or computer you’re reading this on may not be long for this world. Maybe you’ll drop it in water, or your dog will make a chew toy of it, or it’ll reach obsolescence. If you can’t repair it and have to discard it, the device will become e-waste, joining an alarmingly large mountain of defunct TVs, refrigerators, washing machines, cameras, routers, electric toothbrushes, headphones. This is “electrical and electronic equipment,” aka EEE—anything with a plug or battery. It’s increasingly out of control.
As economies develop and the consumerist lifestyle spreads around the world, e-waste has turned into a full-blown environmental crisis. People living in high-income countries own, on average, 109 EEE devices per capita, while those in low-income nations have just four. A new UN report finds that in 2022, humanity churned out 137 billion pounds of e-waste—more than 17 pounds for every person on Earth—and recycled less than a quarter of it.
That also represents about $62 billion worth of recoverable materials, like iron, copper, and gold, hitting e-waste landfills each year. At this pace, e-waste will grow by 33 percent by 2030, while the recycling rate could decline to 20 percent. (You can see this growth in the graph below: purple is EEE on the market, black is e-waste, and green is what gets recycled.)
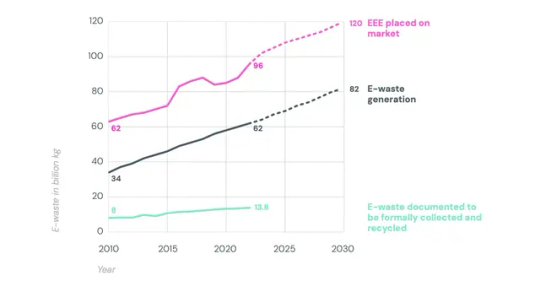
“What was really alarming to me is that the speed at which this is growing is much quicker than the speed that e-waste is properly collected and recycled,” says Kees Baldé, a senior scientific specialist at the United Nations Institute for Training and Research and lead author of the report. “We just consume way too much, and we dispose of things way too quickly. We buy things we may not even need, because it's just very cheap. And also these products are not designed to be repaired.”
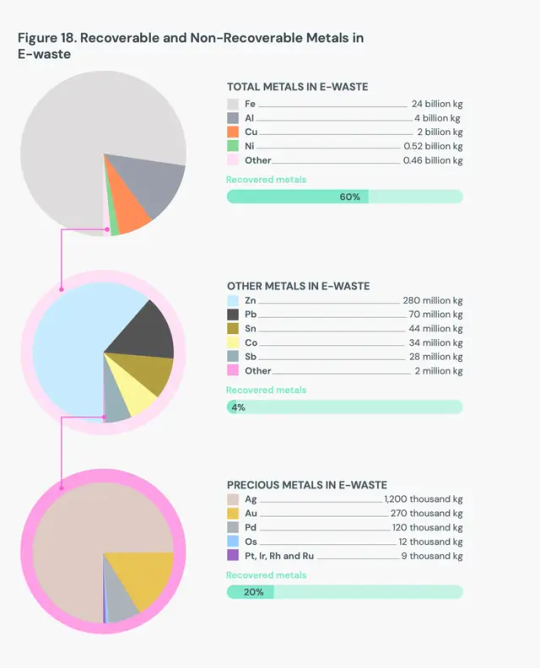
Humanity has to quickly bump up those recycling rates, the report stresses. In the first pie chart below, you can see the significant amount of metals we could be saving, mostly iron (chemical symbol Fe, in light gray), along with aluminum (Al, in dark gray), copper (Cu), and nickel (Ni). Other EEE metals include zinc, tin, and antimony. Overall, the report found that in 2022, generated e-waste contained 68 billion pounds of metal.
E-waste is a complex thing to break down: A washing machine is made of totally different components than a TV. And even for product categories, not only do different brands use different manufacturing processes, but even different models within those brands vary significantly. A new washing machine has way more sensors and other electronics than one built 30 years ago.
Complicating matters even further, e-waste can contain hazardous materials, like cobalt, flame retardants, and lead. The report found that each year, improperly processed e-waste releases more than 125,000 pounds of mercury alone, imperiling the health of humans and other animals. “Electronic waste is an extremely complex waste stream,” says Vanessa Gray, head of the Environment and Emergency Telecommunications Division at the UN’s International Telecommunication Union and an author of the report. “You have a lot of value in electronic waste, but you also have a lot of toxic materials that are dangerous to the environment.”
That makes recycling e-waste a dangerous occupation. In low- and middle-income countries, informal e-waste recyclers might go door-to-door collecting the stuff. To extract valuable metals, they melt down components without proper safety equipment, poisoning themselves and the environment. The new report notes that in total, 7.3 billion pounds of e-waste is shipped uncontrolled globally, meaning its ultimate management is unknown and likely not done in an environmentally friendly way. Of that, high-income countries shipped 1.8 billion pounds to low- and middle-income countries in 2022, swamping them with dangerous materials.
High-income countries have some of this informal recycling, but they also have formal facilities where e-waste is sorted and safely broken down. Europe, for example, has fairly high formal e-waste recycling rates, at about 43 percent. But globally, recycling is happening nowhere near enough to keep up with the year-over-year growth of the waste. Instead of properly mining EEE for metals, humanity keeps mining more ore out of the ground.
Still, the report found that even the small amount of e-waste that currently gets recycled avoided the mining of 2 trillion pounds of ore for virgin metal in 2022. (It takes a lot of ore to produce a little bit of metal.) The more metals we can recycle from e-waste, the less mining we’ll need to support the proliferation of gadgets. That would in turn avoid the greenhouse gases from such mining operations, plus losses of biodiversity.
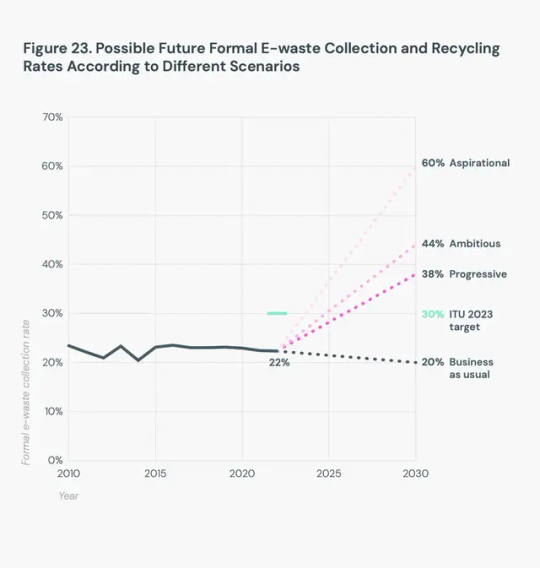
The complexity of e-waste, though, makes it expensive to process. As the chart above shows, even an ambitious scenario of a formal e-waste collection rate in 2030 is 44 percent. “There is no business case for companies to just collect e-waste and to make a profit out of this in a sustainable manner,” says Baldé. “They can only survive if there is legislation in place which is also compensating them.”
The report notes that 81 countries have e-waste policies on the books, and of those, 67 have provisions regarding extended producer responsibility, or EPR. This involves fees paid by manufacturers of EEE that would go toward e-waste management.
Of course, people could also stop throwing so many devices away in the first place, something right-to-repair advocates have spent years fighting for. Batteries, for instance, lose capacity after a certain number of charge cycles. If a phone can’t hold a charge all day anymore, customers should be able to swap in a new battery. “Manufacturers shouldn't be able to put artificial limitations on that ability,” says Elizabeth Chamberlain, director of sustainability at iFixit, which provides repair guides and tools. That includes limiting access to parts and documentation. “Repair is a harm-reduction strategy. It's not the be-all-end-all solution, but it's one of many things we need to do as a global society to slow down the rate at which we're demanding things of the planet.”
At the core of the e-waste crisis is the demand: A growing human population needs phones to communicate and fridges to keep food safe and heat pumps to stay comfortable indoors. So first and foremost we need high-quality products that don’t immediately break down, but also the right to repair when they do. And what absolutely can’t be fixed needs to move through a safe, robust e-waste recycling system. “We are consuming so much,” says Baldé, “we cannot really recycle our way out of the problem.”
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tainted CPAP machines and ventilators went to children, the elderly and at least 700,000 veterans despite internal warnings. Company insiders said the devices posed an “unacceptable” risk.
The first complaints landed at the offices of Philips Respironics in 2010, soon after the company made a fateful decision to redesign its bestselling breathing machines used in homes and hospitals around the world.To silence the irritating rattle that kept users awake at night, Philips packed the devices with an industrial foam — the same kind used in sofas and mattresses. It quickly became clear that something had gone terribly wrong.
The reports coming into Philips described “black particles” or “dirt and dust” inside machines that pump air to those who struggle to breathe. One noted an “oily-like” substance. Others simply warned of “contamination.”
Yet Philips withheld the vast majority of the warnings from the Food and Drug Administration, even as their numbers grew from dozens to hundreds to thousands and became more alarming each year.
. . .
Instead, as the complaints continued to pile up in company files, Philips waged aggressive global marketing campaigns to sell more machines, including new models fitted with the hazardous foam.The sales pitch worked: The devices went to infants, the elderly and at least 700,000 veterans. The company also promoted machines meant for some of the sickest people in the country, rolling out a new ventilator filled with the foam in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
. . .
All the while, people using Philips machines were suffering from illnesses that no one could explain: vomiting, dizziness and headaches, along with newly diagnosed cancers of the lungs, throat, sinuses and esophagus. One man in Philadelphia coughed so hard that he broke his ribs, and a Florida woman with a hacking cough was hospitalized for days and placed on oxygen.
. . .
Studies published in scholarly journals showed the foam broke apart in heat and moisture. The company used it anyway, even though the machines send air for hours at a time into the lungs of users.
. . .
As news of the problem spread, customers and others stepped forward by the thousands, describing emergency room visits and sudden illnesses in reports submitted to Philips and the government. The reports detailed nearly 2,000 cases of cancer, 600 liver and kidney illnesses and 17,000 respiratory ailments.
. . .
The company acknowledges that the foam tested positive for genotoxicity — its own experts described “uncontrolled cellular replication” — but said that a third-party assessment still concluded the machines are unlikely to cause harm.
The three experts consulted by the news organizations said that’s not possible. While safety thresholds for chemical emissions vary and findings can be open to interpretation, genotoxicity means that one or more chemicals are changing cells, the building blocks of the human body.
“You can’t make the argument that it’s safe. That’s bad science,” said the engineer familiar with the Philips testing. “It’s a real-life failure that shows you have a problem. There’s no ambiguity. There is unacceptable risk. Full stop.”
The company’s ventilators also tested positive for genotoxicity; Philips said the devices are still being assessed.
. . .
More details about the health risks are expected to emerge through the ongoing federal lawsuits in Pittsburgh. Earlier this month, the company reached a settlement in one of the cases, agreeing to pay at least $479 million to reimburse customers and others for the costs of the defective machines.
Other legal challenges are still ongoing, including more than 600 personal injury claims and a class-action suit seeking ongoing medical monitoring and research on the dangers posed by the devices.
------
They knew the foam would break down when they decided to use it. Tests within the company after complaints came in showed how dangerous the devices were, but they refused to even change the design for new sales, much less recall the old ones. For every official complaint, how many more people were harmed that weren't reported?
They didn't recall them until 3,700 official complaints had been made. Until after they sold over 5 million life-threatening machines. There's no way to know how many people they killed.
If they think the products are so great, then they won't mind being forced to use them.
Companies will keep doing this until the financial cost of hurting people is greater than the profits from doing so.
Trigger warning for disturbing medical details, descriptions of suffering, and an image of a permanent feeding tube, in the article.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
In 5-7 years, what is the world-dominating vision for the RideBoom company?
Global Expansion: RideBoom may aim to expand its services to more countries and cities worldwide, establishing a strong presence on a global scale. This expansion could include entering emerging markets and regions where ride-hailing services are still developing.
Diversification of Services: To become a dominant player in the transportation industry, RideBoom may diversify its services beyond traditional ride-hailing. They might explore additional offerings such as food delivery, logistics, parcel delivery, or even autonomous vehicle services.
Enhanced Technology: RideBoom may invest heavily in advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics to optimize their operations. This could involve developing more sophisticated algorithms for matching drivers with passengers, improving route optimization, and providing personalized user experiences.
Sustainable and Electric Mobility: With increasing environmental concerns and a shift towards sustainable transportation, RideBoom may focus on expanding its fleet of electric vehicles or promoting the use of environmentally friendly options. They might offer incentives for drivers to switch to electric vehicles, invest in charging infrastructure, or explore partnerships with electric vehicle manufacturers.
Integration with Public Transportation: RideBoom could aim to integrate its services with public transportation systems, providing seamless multi-modal travel options. This integration might involve partnerships with public transit agencies, allowing users to plan, book, and pay for both ride-hailing and public transportation through a single app.
Enhanced Safety Measures: RideBoom may continue to prioritize safety and invest in innovative safety features. This could involve implementing advanced driver screening processes, enhancing driver and passenger identity verification, and utilizing technologies like real-time monitoring and emergency response systems.
Remember, these are speculative possibilities, and the actual vision and strategy of RideBoom may be different. To get accurate and up-to-date information about RideBoom's long-term plans, it's best to refer to official company statements, press releases, or announcements.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
How is AI transforming every aspect of human life?
AI is transforming every aspect of human life by revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, learn, and live. Here are some key areas where AI is making a significant impact:

What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that can perform tasks requiring human-like cognitive abilities. It involves machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and other advanced techniques.
How does it impact every industry?
AI has the potential to revolutionize every industry by automating processes, analyzing vast amounts of data, and making intelligent predictions. It improves efficiency, enhances decision-making, and drives innovation across sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and transportation.
How does it impact every individual?
AI impacts individuals by providing personalized experiences, virtual assistants, and smart devices. It enhances daily life through voice recognition, recommendation systems, and virtual customer support. AI-powered technologies make our lives easier, more convenient, and efficient.
AI is transforming every aspect of human life by revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, learn, and live. Here are some key areas where AI is making a significant impact:
1. Healthcare:
AI is enhancing medical diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized treatment plans. It helps analyze vast amounts of patient data, identify patterns, and provide accurate predictions for disease prevention and early intervention.
According to Accenture, AI in healthcare could potentially save up to $150 billion annually for the U.S. healthcare economy by 2026.
The global AI in healthcare market is projected to reach $45.2 billion by 2026, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 44.9% from 2019 to 2026.
2. Education:
AI is revolutionizing education by enabling personalized learning experiences, adaptive tutoring, and intelligent assessment systems. It helps tailor educational content to individual student needs, track progress, and provide timely feedback for better learning outcomes.
The global AI in education market is expected to reach $3.68 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 38.17% from 2018 to 2025.
A study by the American Institutes for Research found that AI-powered tutoring systems have a positive impact on student learning outcomes, resulting in an average percentile gain of 28 points.
3. Transportation:
AI is driving advancements in autonomous vehicles, optimizing traffic management systems, and improving transportation efficiency and safety. It enables self-driving cars, real-time navigation, and predictive maintenance, revolutionizing the way we commute and travel.
The global autonomous vehicle market is projected to reach $556.67 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 39.47% from 2019 to 2026.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, AI-powered advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) have the potential to reduce traffic fatalities by up to 94%.
4. Communication:
AI-powered language translation, natural language processing, and speech recognition technologies are transforming communication. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and language translation tools facilitate seamless cross-cultural communication and enhance accessibility.
The global AI in communication market is expected to reach $3.5 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 34.7% from 2019 to 2026.
AI-powered language translation technologies have advanced significantly, with Google Translate handling more than 100 billion words daily in over 100 languages.
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant leverage AI to understand and respond to user commands, making voice-based communication more convenient and efficient.
5. Entertainment:
AI is reshaping the entertainment industry with personalized content recommendations, virtual reality experiences, and computer-generated imagery. It enhances user experiences, facilitates content curation, and enables immersive storytelling.
The global AI in the entertainment market is projected to reach $5.5 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 25.4% from 2019 to 2026.
AI algorithms are used in content recommendation systems of streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify, which account for a significant portion of their user engagement and revenue.
AI-powered computer-generated imagery (CGI) has transformed the visual effects industry, enabling the creation of realistic and immersive experiences in movies, video games, and virtual reality.
6. Finance:
AI is revolutionizing the financial industry with automated trading, fraud detection, risk assessment, and personalized financial advice. It enables efficient data analysis, real-time market insights, and improved decision-making processes.
A report by PwC estimates that AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with the financial sector being one of the largest beneficiaries.
AI-driven automated investment platforms, also known as robo-advisors, managed over $1 trillion in assets globally in 2020.
7. Smart Homes:
AI-powered smart home devices and virtual assistants, such as voice-activated speakers and smart thermostats, make our daily lives more convenient and efficient. They automate tasks, provide personalized recommendations, and create a connected and intelligent living environment.
The global smart home market is expected to reach $246.97 billion by 2027, with a CAGR of 11.6% from 2020 to 2027.
Voice-activated smart speakers, powered by AI assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, have seen widespread adoption. As of 2021, there were over 200 million smart speakers in use worldwide.
8. Manufacturing:
AI-driven robotics and automation technologies optimize manufacturing processes, increase productivity, and improve product quality. AI-enabled machines and robots perform complex tasks, enhance precision, and enable predictive maintenance.
The global AI in manufacturing market is expected to reach $16.7 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 49.5% from 2019 to 2026.
According to Deloitte, companies that invest in AI and advanced automation technologies in manufacturing can experience productivity gains of up to 30%.
AI-powered predictive maintenance can reduce equipment downtime by up to 50% and maintenance costs by up to 10-40%.
9. Agriculture:
AI is transforming agriculture by optimizing crop management, monitoring soil conditions, and predicting weather patterns. It enables precision farming techniques, reduces resource waste, and improves agricultural productivity.
The global AI in agriculture market is projected to reach $4 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 22.5% from 2021 to 2026.
AI-powered agricultural robots and drones are expected to reach a market value of $1.3 billion by 2026.
The use of AI in agriculture can increase crop yields by up to 70%, according to a study by the International Data Corporation (IDC).
10. Cybersecurity:
AI is strengthening cybersecurity measures by detecting and preventing cyber threats, identifying anomalous behavior, and improving data protection. AI algorithms analyze large datasets to detect patterns and anomalies, enhancing security measures.
According to Gartner, by 2022, 90% of security budgets will be allocated to addressing AI-powered cyber threats.
The global AI in cybersecurity market is projected to reach $38.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 23.3% from 2021 to 2026.
In summary:
AI is transforming every aspect of human life, from healthcare and education to transportation, communication, entertainment, finance, and beyond. Its applications are vast and diverse, revolutionizing industries, improving efficiency, and enhancing the overall human experience. As AI continues to advance, it holds immense potential to shape a future where intelligent technologies seamlessly integrate into our daily lives, making them more convenient, productive, and enriching.
#aiinnovation#artificialintelligence#airevolution#futuretechnology#transformativetech#aiadvancements#ai applications#aiprogress#aiinsociety#emergingtech#techtrendsin2023#aiimpact#aiintegration#aiforgood
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Aquatic Robot Market to Eyewitness Huge Growth by 2030

Latest business intelligence report released on Global Aquatic Robot Market, covers different industry elements and growth inclinations that helps in predicting market forecast. The report allows complete assessment of current and future scenario scaling top to bottom investigation about the market size, % share of key and emerging segment, major development, and technological advancements. Also, the statistical survey elaborates detailed commentary on changing market dynamics that includes market growth drivers, roadblocks and challenges, future opportunities, and influencing trends to better understand Aquatic Robot market outlook.
List of Key Players Profiled in the study includes market overview, business strategies, financials, Development activities, Market Share and SWOT analysis:
Atlas Maridan ApS. (Germany), Deep Ocean Engineering Inc. (United States), Bluefin Robotics Corporation (United States), ECA SA (France), International Submarine Engineering Ltd. (Canada), Inuktun Services Ltd. (Canada), Oceaneering International, Inc. (United States), Saab Seaeye (Sweden), Schilling Robotics, LLC (United States), Soil Machine Dynamics Ltd. (United Kingdom)
Download Free Sample PDF Brochure (Including Full TOC, Table & Figures) @ https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/sample-report/177845-global-aquatic-robot-market
Brief Overview on Aquatic Robot:
Aquatic robots are those that can sail, submerge, or crawl through water. They can be controlled remotely or autonomously. These robots have been regularly utilized for seafloor exploration in recent years. This technology has shown to be advantageous because it gives enhanced data at a lower cost. Because underwater robots are meant to function in tough settings where divers' health and accessibility are jeopardized, continuous ocean surveillance is extended to them. Maritime safety, marine biology, and underwater archaeology all use aquatic robots. They also contribute significantly to the expansion of the offshore industry. Two important factors affecting the market growth are the increased usage of advanced robotics technology in the oil and gas industry, as well as increased spending in defense industries across various countries.
Key Market Trends:
Growth in AUV Segment
Opportunities:
Adoption of aquatic robots in military & defense
Increased investments in R&D activities
Market Growth Drivers:
Growth in adoption of automated technology in oil & gas industry
Rise in awareness of the availability of advanced imaging system
Challenges:
Required highly skilled professional for maintenance
Segmentation of the Global Aquatic Robot Market:
by Type (Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV), Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV)), Application (Defense & Security, Commercial Exploration, Scientific Research, Others)
Purchase this Report now by availing up to 10% Discount on various License Type along with free consultation. Limited period offer.
Share your budget and Get Exclusive Discount @: https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/request-discount/177845-global-aquatic-robot-market
Geographically, the following regions together with the listed national/local markets are fully investigated:
• APAC (Japan, China, South Korea, Australia, India, and Rest of APAC; Rest of APAC is further segmented into Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Thailand, New Zealand, Vietnam, and Sri Lanka)
• Europe (Germany, UK, France, Spain, Italy, Russia, Rest of Europe; Rest of Europe is further segmented into Belgium, Denmark, Austria, Norway, Sweden, The Netherlands, Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, and Romania)
• North America (U.S., Canada, and Mexico)
• South America (Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Rest of South America)
• MEA (Saudi Arabia, UAE, South Africa)Furthermore, the years considered for the study are as follows:
Historical data – 2017-2022
The base year for estimation – 2022
Estimated Year – 2023
Forecast period** – 2023 to 2028 [** unless otherwise stated]
Browse Full in-depth TOC @: https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/reports/177845-global-aquatic-robot-market
Summarized Extracts from TOC of Global Aquatic Robot Market Study Chapter 1: Exclusive Summary of the Aquatic Robot market
Chapter 2: Objective of Study and Research Scope the Aquatic Robot market
Chapter 3: Porters Five Forces, Supply/Value Chain, PESTEL analysis, Market Entropy, Patent/Trademark Analysis
Chapter 4: Market Segmentation by Type, End User and Region/Country 2016-2027
Chapter 5: Decision Framework
Chapter 6: Market Dynamics- Drivers, Trends and Challenges
Chapter 7: Competitive Landscape, Peer Group Analysis, BCG Matrix & Company Profile
Chapter 8: Appendix, Methodology and Data Source
Buy Full Copy Aquatic RobotMarket – 2021 Edition @ https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/buy-now?format=1&report=177845
Contact US :
Craig Francis (PR & Marketing Manager)
AMA Research & Media LLP
Unit No. 429, Parsonage Road Edison, NJ
New Jersey USA – 08837
Phone: +1 201 565 3262, +44 161 818 8166
[email protected]
#Global Aquatic Robot Market#Aquatic Robot Market Demand#Aquatic Robot Market Trends#Aquatic Robot Market Analysis#Aquatic Robot Market Growth#Aquatic Robot Market Share#Aquatic Robot Market Forecast#Aquatic Robot Market Challenges
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Finance: How Fintech Is Winning the Cybersecurity Race

In the cyber age, the financial world has been reshaped by fintech's relentless innovation. Mobile banking apps grant us access to our financial lives at our fingertips, and online investment platforms have revolutionised wealth management. Yet, beneath this veneer of convenience and accessibility lies an ominous spectre — the looming threat of cyberattacks on the financial sector. The number of cyberattacks is expected to increase by 50% in 2023. The global fintech market is expected to reach $324 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 25.2% from 2023 to 2028. This growth of the fintech market makes it even more prone to cyber-attacks. To prevent this there are certain measures and innovations let's find out more about them
Cybersecurity Measures in Fintech
To mitigate the ever-present threat of cyberattacks, fintech companies employ a multifaceted approach to cybersecurity problems and solutions. Here are some key measures:
1. Encryption
Encrypting data at rest and in transit is fundamental to protecting sensitive information. Strong encryption algorithms ensure that even if a hacker gains access to data, it remains unreadable without the decryption keys.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification (e.g., passwords, fingerprints, or security tokens) before gaining access to their accounts.
3. Continuous Monitoring
Fintech companies employ advanced monitoring systems that constantly assess network traffic for suspicious activities. This allows for real-time threat detection and rapid response.
4. Penetration Testing
Regular penetration testing, performed by ethical hackers, helps identify vulnerabilities in systems and applications before malicious actors can exploit them.
5. Employee Training
Human error is a significant factor in cybersecurity breaches. Companies invest in cybersecurity training programs to educate employees about best practices and the risks associated with cyber threats.
6. Incident Response Plans
Having a well-defined incident response plan in place ensures that, in the event of a breach, the company can respond swiftly and effectively to mitigate the damage.
Emerging Technologies in Fintech Cybersecurity
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so do cybersecurity technologies in fintech. Here are some emerging technologies that are making a significant impact:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI and machine learning algorithms are used to analyse vast amounts of data and identify patterns indicative of cyber threats. This allows for proactive threat detection and quicker response times.
2. Blockchain
Blockchain technology is employed to enhance the security and transparency of financial transactions. It ensures that transaction records are immutable and cannot be altered by malicious actors.
3. Biometrics
Fintech companies are increasingly adopting biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, to provide a higher level of security than traditional passwords.
4. Quantum-Safe Encryption
With the advent of quantum computing, which poses a threat to current encryption methods, fintech companies are exploring quantum-safe encryption techniques to future-proof their security measures.
Conclusion
In the realm of fintech, where trust and security are paramount, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. Fintech companies must remain vigilant, employing a combination of advanced digital transformation solutions, employee training, and robust incident response plans to protect sensitive financial data from cyber threats. As the industry continues to evolve, staying one step ahead of cybercriminals will be an ongoing challenge, but one that fintech firms must embrace to ensure their continued success and the safety of their customers' financial well-being.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
CAT Footwear Invader Mid Vent
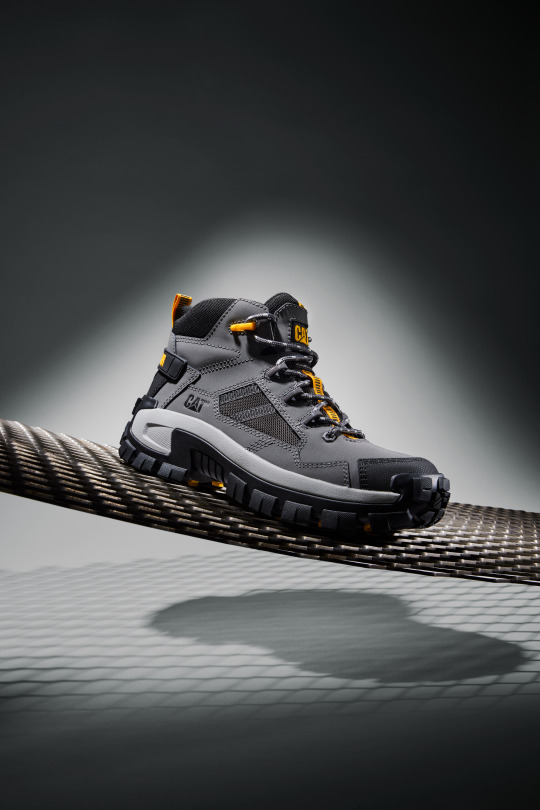

In September 2023, Cat Footwear will launch its new Invader
Mid Vent - a shoe that boasts unbeatable traction, unmatched style, and unwavering confidence.
Cat Footwear, a leading footwear brand under Wolverine World Wide, Inc., is growing its Invader collection by adding the Invader Mid Vent as its newest inclusion. Other styles within the collection include the Invader Steel Toe, the Invader Hi Steel Toe, and the Invader Hiker
Waterproof Boot.
The Invader Mid Vent features a ReViveTech Engineered Comfort footbed, an 100% Post Industrial Recycled Lining with an NXT footbed cover, a resilient EVA midsole, a nylon shank, a
composite toe, and an industrial-grade rubber outsole.
The new design also features an aggressive lug pattern that provides unbeatable traction inspired by the Cat® machine, and its overbuilt styling offers a distinct look.
“The Invader Mid Vent delivers on both the Outdoor Utility and Overbuilt Style macro trends in the marketplace, with hiking silhouettes leading the way. Insights show that more and more
consumers are wearing their work/safety products indoors AND outdoors,” said Kelly Ballou, VP of Global Marketing. “With visible traction and overbuilt styling cues, the Invader collection ladders up to Cat ® Inc. and the machines they’re known for.”
The Invader Mid Vent will be available in 4 colorways and retail for $135. For more information, visit the Cat Footwear website.





2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clinical Development Solutions
In the rapidly evolving field of healthcare, clinical development plays a crucial role in bringing novel treatments and therapies to patients worldwide. Clinical Development Solutions (CDS) is at the forefront of this exciting journey, pioneering innovative approaches to accelerate the development and approval of life-saving drugs and medical devices. With a dedicated team of experts and cutting-edge technologies, CDS is committed to transforming the landscape of clinical research and improving patient outcomes.
At CDS, we understand the challenges and complexities of clinical development. Our comprehensive suite of solutions is designed to address these challenges head-on, providing tailored strategies and support throughout the entire drug development lifecycle. From early-phase clinical trials to post-marketing studies, we offer a wide range of services that enable pharmaceutical and biotech companies to navigate the regulatory landscape efficiently and effectively.
One of the key strengths of CDS lies in our expertise in clinical trial design and optimization. We work closely with our clients to design robust and scientifically rigorous trials that generate high-quality data while minimizing risks. By leveraging our extensive knowledge and experience, we can identify the most appropriate patient populations, endpoints, and study designs to maximize the chances of success. Our statistical and data management teams ensure that the collected data is accurate, reliable, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
In addition to trial design, CDS also excels in patient recruitment and retention strategies. We understand the importance of enrolling a diverse and representative patient population to ensure the generalizability of study results. Through our innovative patient-centric approaches, such as digital recruitment platforms and targeted engagement campaigns, we connect with potential study participants and enhance their overall trial experience. By fostering strong relationships with patients and investigators, we improve retention rates and reduce dropout rates, ultimately leading to faster and more reliable study results.
CDS is at the forefront of adopting emerging technologies to drive efficiency and innovation in clinical development. We harness the power of big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to uncover valuable insights from complex datasets. These advanced analytics enable us to identify trends, predict outcomes, and optimize trial protocols, thus accelerating the development timeline and reducing costs. Our investment in digital health technologies and wearable devices further enhances data collection and remote monitoring capabilities, enabling more flexible and patient-friendly trial designs.
In the realm of regulatory affairs, CDS provides comprehensive support to ensure compliance with global regulations and standards. Our regulatory experts have in-depth knowledge of regional requirements, including those of the FDA, EMA, and other regulatory authorities worldwide. From preparing regulatory submissions to managing post-marketing safety surveillance, we guide our clients through every step of the regulatory process, ensuring timely approvals and post-approval compliance.
CDS is also committed to fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing within the clinical research community. We organize scientific symposia, webinars, and training programs to facilitate the exchange of ideas and best practices. By promoting interdisciplinary collaboration and staying up to date with the latest industry advancements, we continuously enhance our capabilities and stay at the forefront of clinical development.
In conclusion, Clinical Development Solutions is a leading provider of innovative solutions in clinical development. Through our expertise, technology-driven approaches, and commitment to patient-centricity, we strive to transform the drug development landscape and improve patient outcomes. By partnering with CDS, pharmaceutical and biotech companies can navigate the complexities of clinical research with confidence, bringing new therapies to patients faster and more efficiently. Together, let us shape the future of healthcare through innovation and collaboration.
#clinical development#development solutions#biometric solution providers#clinical development consultant#clinical development service#drug development solutions#clinical product development#clinical development solution company#clinical development specialist#Clinical Development Services in Hyderabad#Clinical Services in Hyderabad#clinical development services agency in hyderabad india#best clinical development agency in india#project management solutions provider#project management service provider#biometric service provider near me#Clinical Trial Services In Hyderabad#specialized clinical pharmacist#clinical pharmaceutical company
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Global AI Accelerator Chip Market Expected to Grow Substantially Owing to Healthcare Industry

Global AI Accelerator Chip Market Expected to Grow Substantially Owing to Increased Use of AI Accelerator Chips in Healthcare Industry.
The global AI accelerator chip market is expected to grow primarily due to its growing use in the healthcare industry. The cloud sub-segment is expected to flourish immensely. The market in the North American region is predicted to grow with a high CAGR by 2031.
NEW YORK, March 17, 2023 - As per the report published by Research Dive, the global AI accelerator chip market is expected to register a revenue of $332,142.7 million by 2031 with a CAGR of 39.3% during the 2022-2031 period.
Dynamics of the Global AI Accelerator Chip Market
Growing use of AI accelerator chips across the global healthcare industry is expected to become the primary growth driver of the AI accelerator chip market in the forecast period. Additionally, the rise of the cyber safety business is predicted to propel the market forward. However, according to market analysts, lack of skilled AI accelerator chip workforce might become a restraint in the growth of the market.
The growing use of AI accelerator chip semiconductors is predicted to offer numerous growth opportunities to the market in the forecast period. Moreover, the increased use of AI accelerator chips to execute AI workloads such as neural networks is expected to propel the AI accelerator chip market forward in the coming period.
COVID-19 Impact on the Global AI Accelerator Chip Market
The Covid-19 pandemic disrupted the routine lifestyle of people across the globe and the subsequent lockdowns adversely impacted the industrial processes across all sectors. The AI accelerator chip market, too, was negatively impacted due to the pandemic. The disruptions in global supply chains due to the pandemic resulted in a decline in the semiconductor manufacturing industry. Also, the travel restrictions put in place by various governments reduced the availability of skilled workforce. These factors brought down the growth rate of the market.
Key Players of the Global AI Accelerator Chip Market
The major players in the market include:
- NVIDIA Corporation
- Micron Technology Inc.
- NXP Semiconductors N.V.
- Intel Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Advanced Micro Devices Inc. (AMD)
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Alphabet Inc. (Google Inc.)
- Graphcore Limited.
- International Business Machines Corporation
These players are working on developing strategies such as product development, merger and acquisition, partnerships, and collaborations to sustain market growth.
For instance, in May 2022, Intel Habana, a subsidiary of Intel, announced the launch of 2nd generation AI chips which according to the company, will provide a 2X performance advantage over the previous generation NVIDIA A100. This product launch will help Intel Habana to capitalize on this rather nascent market and will consolidate its lead over the competitors further.
What the Report Covers:
Apart from the information summarized in this press release, the final report covers crucial aspects of the market including SWOT analysis, market overview, Porter's five forces analysis, market dynamics, segmentation (key market trends, forecast analysis, and regional analysis), and company profiles (company overview, operating business segments, product portfolio, financial performance, and latest strategic moves and developments.)
Segments of the AI Accelerator Chip Market
The report has divided the AI accelerator chip market into the following segments:
Chip Type: Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC), Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA), Central Processing Unit (CPU), and others
Processing Type: edge and cloud
Application: Natural Language Processing (NLP), computer vision, robotics, and network security
Industry Vertical: financial services, automotive and transportation, healthcare, retail, telecom, and others
Region: North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA
SegmentSub-SegmentChip TypeCentral Processing Unit (CPU)
– Most dominant market share in 2021
- The use of CPU for improving the performance of a computer while running graphics and video editors are expected to push the growth of this sub-segment further.Processing TypeCloud – Significant revenue growth in 2021
Cloud acceleration chip helps content creators, publishers, and other entities to offer material to end users promptly which is predicted to propel the growth rate of the market higher.ApplicationNatural Language Processing (NLP) – Highest market share in 2021
Increased use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) due to its ability to make computer-human interactions more natural is expected to propel the sub-segment forward.Industry VerticalHealthcare– Huge market revenue in 2021
The growing use of AI by major healthcare companies to complement medical imaging is anticipated to offer numerous growth opportunities to the sub-segment in the forecast period.RegionNorth America – Most profitable by 2031
The development of new technologies in artificial intelligence (AI) accelerators in this region is predicted to propel the market in the forecast period.
Read the full article
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Global Machine Safety Market Size#Industry Analysis By Segmentations#Top Key Players#Trends#Future Development & Forecast 2022-2030
0 notes
Text
Almost two and half years into Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, Moscow’s war machine still runs on energy revenues—despite unprecedented Western sanctions that took a bite out of, but hardly battered, the Kremlin’s cash cow.
Russian exports of oil, natural gas, and coal continue apace with their biggest markets in Asia, especially China and India. Even Europe, which has largely sworn off Russian gas since the invasion, is stealthily buying a lot more of the stuff off tankers to meet its own energy needs, indirectly helping finance the invader that it spends so much time, energy, and money trying to combat.
Russian energy export revenues before the war were about 1 billion euros ($1.1 billion) a day, and the whole gamut of sanctions had brought that down to about 660 million euros ($720 million) by this June—but those levels have stayed remarkably steady for the past 18 months. Russia recorded a rare current accounts surplus just last month, a sign of that export health. The sanctions battle, like the war itself, seems to have stalemated.
“The glass is neither half full, nor half empty. The sanctions are working, but not as well as we expected,” said Petras Katinas, an energy analyst at the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA).
Some aspects of Russia’s energy exports have fallen off a cliff, such as its exports of natural gas via pipelines, which have all but disappeared from the lucrative European market. But the country’s exports of oil and refined oil products, which make up the biggest chunk of its sales, have stayed essentially the same after an initial hit in the first months after the introduction of Western sanctions, and state earnings even crept a little higher thanks to a rise in global oil prices.
The main Western effort to curb Russian energy earnings was a balancing act meant to keep the global market supplied while limiting the Kremlin’s take by capping Russian oil sales at $60 a barrel. Some countries wanted an even lower price cap of about $30 a barrel to really cut Moscow’s earnings, but that idea—as demonstrated when Ukraine floated it again this spring—was politically and diplomatically a lot tougher.
Still, the original price cap worked great at first, until Russia—with a little help from its friends in OPEC—goosed the global price of oil higher, which dragged the price of discounted Russian oil above the cap as well. That’s pretty much where it has been for the past year.
More importantly, Russia has found a reliable way to sidestep that formal limit on its crude oil exports by using a fleet of so-called shadow tankers that don’t have to follow Western restrictions on insurance, safety, and the like. About 4 out of every 5 barrels of seaborne crude that Russia sells are now carried on shadow tankers, Katinas said, meaning that they are entirely outside the reach of Western measures. (Those shadow tankers aren’t beyond the reach of the Iran-backed Houthi insurgents in Yemen, though: One got blown up trying to take Russian oil to China this week.)
“The strategy was good, but the tactics were poor—there was little enforcement,” Katinas said.
The United States cracked down on part of that trade a couple of times—late last year on shadow tankers and earlier this year on Russian state-owned vessels—by sanctioning individual tankers; CREA estimates that tougher enforcement probably cost Russia about 5 percentof its oil export revenues since October 2023. But there is still a long way to go to ensure thorough enforcement of the existing limits on Russian oil trade: Full enforcement would have kept almost 20 billion euros ($21.8 billion) out of Russian President Vladimir Putin’s coffers, CREA estimates.
The Biden administration has toyed with additional efforts to tighten the screws on the shadow fleet, but it worries that stricter measures might send oil (and gasoline) prices higher just in time for a pivotal U.S. presidential election in November.
But there is a way to get there without causing much pain, if any, for global energy consumers, argue global economy experts Robin Brooks and Ben Harris of the Brookings Institution. There remain some 100-odd unsanctioned ships in the Sovcomflot state-owned fleet that are doing heavy lifting for Russian oil exports. Targeted sanctions on just 15 of the busiest of those tankers would cut into a good-sized chunk of Russia’s oil export earnings with little market impact. “With such a process in place, we anticipate little to no impact on global oil prices but suspect the action will meaningfully lower Russia’s revenue from the oil trade,” they wrote.
But it’s not just oil. Russian natural gas exports are not dead yet, either, despite lots of pain for state-owned energy company Gazprom and plenty of crowing in Europe about largely weaning itself off of what used to be its biggest energy supplier. Some European countries, including Hungary, Austria, and Slovakia, are still heavily reliant on the remnants of Russian gas that arrive via Ukraine or Turkey, for reasons that range from the geographic to the political.
What’s amazing about the sharp decline in exports of Russian natural gas to what was formerly the nation’s biggest market is that Russian natural gas is not sanctioned in Europe at all, yet it has suffered the most of all of Moscow’s energy streams.
“Gas is not sanctioned; it was the stupidity of Putin” that drove the Europeans off of it, Katinas said.
But this year, Russian gas is sneaking back into Europe in liquefied form, supercooled and shipped on tankers rather than compressed and routed through pipelines. European Union imports of Russian liquefied natural gas, or LNG, are up 24 percent over past year, especially to big Western European countries such as France, Spain, and Belgium; the bloc buys half of all Russian LNG exports.
There are plenty of reasons why—Spain’s main suppliers in North Africa have their own geopolitical squabbles that have disrupted exports, long-term contracts with Russia essentially lock in some European buyers for years, and Russian gas is nearby and fairly cheap compared to alternatives—but the biggest reason is simply concern over the security of supplies.
“There was lots of talk even last year about banning LNG imports, but then what prevailed were the fears about the implications for the security of supply,” said Anne-Sophie Corbeau, a gas expert at Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy. The trickle of Russian gas that still comes in through Ukraine will end later this year; Turkey, despite offers to do more, can hardly export significantly more gas to southern Europe since it isn’t a gas producer itself. And Europeans remember the shock and pain of the war’s first winter, when energy prices skyrocketed due to the upheavals in the gas market.
Last month, the European Union finally took its first step to deal with Russian LNG—not by banning the import of the fuel, but by making sure that European ports would not be waystations for Russian exports to Asia. That measure won’t even start until early next year. And there certainly won’t be any further EU efforts to target Russian gas this year, with Hungary at the helm of the rotating presidency of the EU council.
“We are not actually banning imports, but preventing other countries from getting Russian LNG,” Corbeau said. “It makes life more difficult for Russia’s Asia exports, but does nothing to keep LNG out of Europe.”
The good news, such as it is, is that LNG isn’t quite the cash cow for the Russian government that other energy sources are. Oil is sold in huge volumes and is taxed; pipeline gas, too, helps prop up the federal budget. But LNG has all sorts of tax breaks that mean much less of that Western money goes straight to the Ukrainian battlefront. In terms of how to target Russian energy earnings, Corbeau said, “first oil, then piped gas, then finally LNG.”
The bad news is that despite years of unprecedented sanctions on one of the world’s biggest energy providers, Russia’s cash machine is still working enough to continue underwriting the war. The relatively limited success in the battle against the country’s energy sector is mirrored by similar failings in cracking down on Russian trade in all sorts of other things, from Western machinery routed through Central Asia to the high-tech Chinese-made components needed for the war.
“We are not doing enough. We need to strengthen sanctions—we need to start enforcing sanctions, and start punishing companies that are violating them,” said Katinas. “There are just too many loopholes.”
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Evolving World of Anesthesia Machine Suppliers
Anesthesia machines are critical pieces of equipment in modern healthcare, enabling safe and effective administration of anesthesia during surgical procedures. As the demand for advanced anesthesia technology continues to grow, the role of anesthesia machine suppliers becomes increasingly important. These suppliers play a vital part in ensuring that healthcare providers have access to cutting-edge anesthesia machines that meet the evolving needs of patients and medical professionals.
The Global Anesthesia Machine Market
The global anesthesia machine market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. In 2023, the market was valued at USD 8.84 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 9.21% over the next five years. This growth is driven by several factors, including the rise in minimally invasive surgeries, increasing healthcare expenditure, and rapid technological advancements in anesthesia equipment.
Key Players in the Anesthesia Machine Supplier Landscape
The anesthesia machine market is dominated by several key players, each offering a range of innovative products and solutions. Some of the major players include:
- Medtronic
- GE Healthcare
- Philips
- Dräger
- Getinge
- Penlon
- Heyer Medical
These companies are at the forefront of technological transformation in the anesthesia equipment industry, continuously developing advanced devices that prioritize patient safety and comfort.
Technological Advancements in Anesthesia Machines
The anesthesia machine market has witnessed significant technological advancements in recent years. Modern anesthesia machines are no longer just tools; they have evolved into enablers of a patient-centric approach, ensuring that every breath matters. These advancements include:
- Integrated patient monitoring solutions: Combining anesthesia devices with patient monitoring solutions provides healthcare professionals with real-time, patient-relevant data at the point-of-care and in the ICU.
- ICU-quality ventilation therapy: Advanced anesthesia machines now offer ICU-quality ventilation therapy, such as lung-protective ventilation and minimal- and low-flow anesthesia, in the operating room.
- Innovative local anesthesia delivery devices: Recent advancements in local anesthesia delivery devices leverage concepts like the gate control hypothesis, using vibration to minimize pain during needle procedures.
These technological advancements aim to improve patient outcomes, enhance patient comfort, and contribute to the evolving landscape of anesthetic equipment.
The Importance of Anesthesia Machine Suppliers
Anesthesia machine suppliers play a crucial role in ensuring that healthcare providers have access to the latest and most advanced anesthesia technology. These suppliers not only provide cutting-edge anesthesia machines but also offer comprehensive support services, including:
- Installation and training: Anesthesia machine suppliers ensure that healthcare professionals are properly trained in the use and maintenance of the equipment, minimizing the risk of errors and complications.
- Maintenance and repair: Regular maintenance and prompt repair services are essential for ensuring the reliable performance of anesthesia machines. Suppliers offer comprehensive maintenance plans and quick turnaround times for repairs.
- Customization: Many anesthesia machine suppliers offer customization options to meet the specific needs of healthcare facilities, ensuring that the equipment is tailored to the unique requirements of each organization.
By partnering with reliable and experienced anesthesia machine suppliers, healthcare providers can be confident that they are investing in high-quality equipment that will deliver optimal patient outcomes and support the needs of their medical professionals.
Conclusion
The anesthesia machine supplier landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the growing demand for innovative anesthesia equipment. Key players in the market are continuously developing advanced devices that prioritize patient safety, comfort, and outcomes. By partnering with reliable anesthesia machine suppliers, healthcare providers can ensure that they have access to cutting-edge technology and comprehensive support services, ultimately contributing to the delivery of high-quality patient care.
0 notes
Text
Top Brands in Industrial Automation
Leading Company Segments of Industrial Automation
Industrial automation has brought changes in the manufacturing and processing industries, where the company's productivity and production quality have improved while the operating costs have been cut. Many leading market players deliver innovative technologies such as robotics, control systems, and automation software applications to popular brands about industrial automation, their contributions, and their offerings.
1. Siemens
Overview: Siemens is a well-established global organization specializing in industrial automation and electrification solutions and products. This company offers its customers automation solutions, which include but are not limited to the following: programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and industrial communication products.
Key Products:
• SIMATIC PLCs: Siemens called its SIMATIC series a highly reliable and adaptable product in various automation applications in simple machine and complicated process control.
• TIA Portal: The Totally Integrated Automation or TIA Portal is an assured engineering environment for scheming, programming, and commissioning automation systems.
• SINAMICS Drives: These drives regulate the electric motor's speed and torque, which is imperative in many industrial applications.
2. ABB
Overview: ABB is a well-established global company creating innovative technologies for the utility, industrial, and commercial sectors, emphasizing digitalization and energy management. It deals with various products and services that seek to improve the operations of organizations and reduce their impact on the environment.
Key Products:
• ABB Robotics: ABB is one of the world's largest industrial robot manufacturers in the automotive, electronics, and logistics industries. Their robots are highly precise and very flexible in their applications.
• Control Systems: One is ABB's Distributed Control System (DCS), ABB Ability™ System 800xA, which combines process automation, electrical control, and safety into a single system for increased power.
• Servo Motors and Drives: Servo motors are products of ABB that the company designs for various operations requiring precision and accuracy in using power.
3. Rockwell Automation
Overview: Rockwell Automation is an organization operating in America. The company mainly specializes in industrial automation and information technology. The company is now set on designing and integrating hardware and software solutions, a reformative wheel in industrial utilization.
Key Products:
• Allen-Bradley PLCs: Therefore, the main product of Rockwell is Allen-Bradley, which manufactures and supplies excellent quality PLCs needed by all departments.
• FactoryTalk Software: This set of software applications brings real-time monitoring, control, and analysis of the collected data, allowing companies to make the right decisions based on the data collected.
• Motion Control: Therefore, motion control solutions offered by Rockwell are to be implemented into high-performance machines that perform operations with enhanced precision and speed.
4. Mitsubishi Electric
Overview: Mitsubishi Electric is the market leader in industrial automation solutions, offering a wide range of products to satisfy almost all demands of different industries. It is so well known for automating bits and aspects, as necessitated by high quality in the organization.
Key Products:
• MELSEC PLCs: Mitsubishi's MELSEC PLCs are also acknowledged for reliability and scalability and thus can be used for small and large automation purposes.
• GOT HMIs: Some examples of excellent, friendly, and convenient interfaces are Mitsubishi Graphic Operation Terminals (GOT), which allow users to control and supervise systems in industries.
•Servo Systems: Mitsubishi continues to improve its servo systems, mainly when the speed is high. At the same time, it is used selectively and where the level of precision is comparatively high, thus being mostly applicable to the manufacturing and assembling industry.
5. Schneider Electric
Overview: Schneider Electric is a global company that markets its products worldwide and is in the energy and automation business. Product: The products from the company are supposed to force industries to become more efficient and have cleaner, less problematic production processes.
Key Products:
• Modicon PLCs: The Modicon PLCs of the Schneider Electric Company are highly reliable and multifunctional, which is why they are applied in many fields.
• EcoStruxure: Schneider's EcoStruxure employs IoT Cloud and big data analytics to create intelligent, sustainable automation solutions.
• Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs from Schneider help control motor speeds and are significant for energy conservation in industrial businesses.
Why RAM Automations – Industrial Automation Solutions & Services Company in India, UAE & Saudi Arabia?
As you may see, these manufacturers provide some of the best industrial automation solutions.
That is why, when working with our clients at RAM Automations, we ensure we can get all their products. Read our HMI tutorial and learn how our best hardware and advice improve your performance, whether it be PLC, robotics, or drives.
You are in business, and thus, you stand to benefit a lot from the growth and success of your business by choosing RAM Automations. Our team comprises professionals willing to assist you in selecting the best solutions to suit your needs by offering sound, dependable, and forward-compatible systems.
You can read more about Oxley and our wide range of industrial automation products here on the website, or contact us to learn how we can help you gain a competitive edge. As a ranging company at RAM Automations, we aim to deliver the best automation services to improve your industries.
0 notes
Text
Understanding Case Packer Machines: A Key to Efficient Packaging
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing and distribution environment, efficiency is paramount. One of the critical components that enhance productivity in packaging processes is case packer machine. This article delves into what a case packer machine is, its various types, benefits, and its role in modern packaging operations.
What is a Case Packer Machine?
A case packer machine is an automated device designed to pack products into cases or boxes. It can handle various products, including bottles, cans, jars, boxes, and bags. These machines are essential in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer goods, where large volumes of products need to be packaged efficiently.
Types of Case Packer Machines
Horizontal Case Packers: These machines load products horizontally into cases. They are typically used for products like bottles or jars, where they can handle varying sizes and shapes. Horizontal case packers often provide high speed and flexibility.
Vertical Case Packers: In contrast, vertical case packers load products into cases vertically. They are ideal for products like pouches or bags, allowing for a compact design and efficient use of space. These machines are often used for products that can be stacked.
Robotic Case Packers: Leveraging advanced robotics technology, these machines use robotic arms to pick and place products into cases. They offer unparalleled flexibility and precision, making them suitable for diverse product ranges and packaging formats.
Semi-Automatic Case Packers: These machines require some manual intervention, such as placing cases on the machine, but automate the packing process. They are cost-effective for smaller operations or businesses that may not need fully automated solutions.
Benefits of Using Case Packer Machines
Increased Efficiency: Automated packing reduces labor costs and speeds up the packaging process, allowing for higher production rates.
Consistency and Quality Control: Case packers ensure uniformity in packaging, reducing the risk of errors and enhancing the overall quality of packaged products.
Space Optimization: Many case packers are designed to be compact, helping manufacturers save valuable floor space in their production areas.
Enhanced Safety: By automating the packing process, case packers minimize the risk of workplace injuries associated with manual handling of heavy or sharp items.
Versatility: Many case packers can handle a variety of products and packaging styles, making them a flexible solution for manufacturers with diverse product lines.
The Role of Case Packer Machines in Modern Packaging
As consumer demands for speed and efficiency continue to rise, the role of vertical cartoner becomes increasingly crucial. These machines not only improve packaging speeds but also contribute to better supply chain management by ensuring products are packaged correctly and ready for distribution.
In a world where e-commerce and global distribution are expanding, having reliable and efficient case packing solutions is vital. Companies that invest in high-quality case packers are better positioned to meet market demands and enhance their competitive edge.
Conclusion
Case packer machines play an integral role in modern packaging operations. By improving efficiency, consistency, and safety, they help manufacturers meet the growing demands of their customers while optimizing their production processes. As technology continues to evolve, case packers will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated, further revolutionizing the packaging industry. For businesses looking to enhance their packaging capabilities, investing in a case packer machine is a strategic move toward operational excellence.
0 notes