#HighTemperatureBolts
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Guide on Bolts: Manufacturing Process, Grades, Specifications, and Materials
Designed to securely join two or more components, bolts offer high tensile strength, durability, and reliability under varying loads and environmental conditions. Unlike simple nails or screws, bolts typically work in combination with nuts and washers, providing a strong clamping force that maintains structural integrity even under vibration, stress, and extreme temperatures.
From massive infrastructure projects like bridges and skyscrapers to critical machinery in aerospace, automotive, marine, oil & gas, and manufacturing industries, bolts ensure safety and performance across countless applications. They are available in a wide range of sizes, materials, grades, and specifications to meet the unique requirements of each industry. Understanding the different types of bolts, their manufacturing process, material grades, and specifications is crucial for selecting the right fastener for any application.
Bolt Manufacturing Process: Step-by-Step Overview
The bolt manufacturing process involves multiple stages, ensuring high-quality fasteners for diverse applications:
Raw Material Selection: The process begins by selecting raw materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, brass, titanium, Inconel, and Monel based on application needs.
Cutting: The raw material is cut into precise lengths (blanks) which are then processed into bolts.
Heading: Undergoes cold or hot forging to form the bolt head.
Thread Rolling: Threads are formed through thread rolling, enhancing the bolt's strength and precision without removing material.
Heat Treatment: Bolts are heat-treated to achieve desired mechanical properties like tensile strength, hardness, and durability.
Surface Treatment: Coatings such as zinc plating, galvanization, black oxide, or anodizing are applied for corrosion resistance.
Inspection and Testing: Each bolt undergoes strict quality checks for dimensional accuracy, strength, and surface finish.
Packaging and Dispatch: Bolts are packaged and shipped to clients worldwide.
Bolt Weight Chart: Quick Reference
A bolt weight chart helps determine the weight based on dimensions and material type, crucial for logistics and structural calculations.
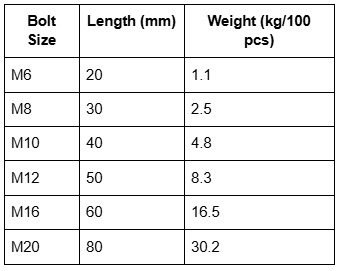
Note: Weight varies depending on material density.
High-Temperature Bolt Materials: Top Choices
For high-temperature applications, selecting the correct bolt material is crucial to ensure both safety and optimal performance.
Inconel Alloys (600, 625, 718): Superior strength and oxidation resistance.
Hastelloy: Outstanding corrosion and high-temperature resistance.
Stainless Steel (310, 321, 347): Designed to withstand high-temperature oxidation and minimize creep deformation.
Nickel Alloys: Deliver exceptional stability against thermal expansion and corrosion across a wide temperature range.
Titanium Alloys: Lightweight with excellent strength and heat resistance.
Bolt Grades: Classification and Applications
Understanding bolt grades is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and achieving optimal performance in various applications:
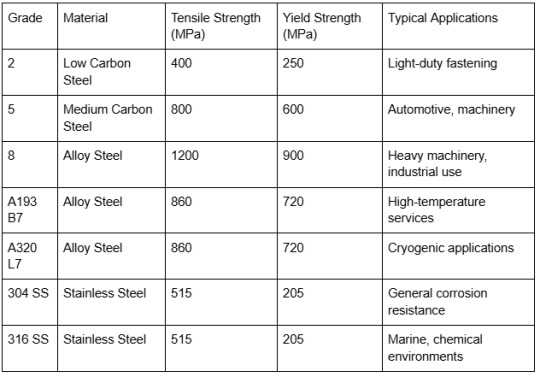
Grade 5: Produced from medium carbon steel and subjected to heat treatment, widely used in automotive, machinery, and equipment manufacturing due to its improved strength and durability.
Grade 8: Constructed from alloy steel and heat-treated, designed for heavy-duty industrial and high-stress environments.
ASTM A193 B7: An alloy steel grade engineered for high-temperature service, ideal for use in pressure vessels and piping systems.
ASTM A320 L7: Alloy steel designed for low-temperature services.
Stainless Steel Grades (304, 316, 410, 17-4PH): Superior corrosion resistance for marine and chemical industries.
Bolt Specifications: Industry Standards
Bolt specifications detail the size, material type, mechanical properties, and protective coatings needed for specific applications. Leading international standards include:
ASTM Standards: A193, A307, A325, A490.
ISO Standards: ISO 898-1.
DIN Standards: DIN 931, DIN 933.
SAE Standards: SAE J429.
Specifications generally cover:
Bolt dimensions (diameter, length, thread pitch)
Material and grade
Mechanical properties (tensile strength, yield strength, hardness)
Coating and surface finish
Bolt Grades Chart: Complete Data Table
Bolt Material Grades: Selection Criteria
Selecting the correct bolt material grade ensures performance, safety, and longevity. Consider:
Environmental factors (corrosion, temperature)
Load-bearing requirements (tensile/yield strength)
Compliance with industry standards
Cost-effectiveness
Common Bolt Material Grades:
Carbon Steel: Cost-effective for general applications.
Stainless Steel (304, 316, 410): Provides outstanding corrosion resistance, with 316 offering enhanced performance in chloride-rich environments.
Alloy Steel: Superior strength and durability.
Exotic Alloys (Inconel, Hastelloy, Monel): For extreme environments and specialty industries.
Bolts Manufacturing Industry Overview
The global bolts manufacturing industry serves numerous sectors, including construction, automotive, oil & gas, aerospace, and infrastructure development. Key growth drivers include:
Rising demand for high-performance, corrosion-resistant fasteners.
Technological advancements in CNC machining, forging, and additive manufacturing.
Expanding infrastructure projects in emerging economies.
Strict adherence to ISO, ASTM, and ASME standards ensures consistent quality, safety, and compatibility across applications.
Leading manufacturers invest significantly in R&D to develop innovative, high-strength, corrosion-resistant, and lightweight bolt solutions.
Conclusion
Bolts are indispensable fasteners that come in a variety of grades, materials, and specifications. Understanding the bolt manufacturing process, bolt weight chart, high-temperature bolt materials, bolt grades, bolt specifications, and bolt material grades ensures that engineers and procurement managers make informed choices for maximum safety, performance, and cost efficiency. The bolts manufacturing industry continues to evolve with technological advancements, offering cutting-edge solutions for every industrial need.
FAQs
Q1. What are the most commonly used bolt materials?
A1. Due to their combination of affordability, strength, and durability, carbon steel and stainless steel are the most widely used materials for bolt manufacturing.
Q2. Which materials are ideal for high-temperature bolts?
A2. Inconel, Hastelloy, certain stainless steel grades (310, 321), and titanium alloys are best suited for high-temperature environments.
Q3. What does bolt grade signify?
A3. Bolt grade indicates the mechanical characteristics like tensile strength, yield strength, and hardness, helping to select the right fastener for specific applications.
Q4. How can I calculate bolt weight?
A4. Bolt weight is calculated based on its dimensions and material density. Bolt weight charts provide quick reference values.
Q5. Why is heat treatment crucial in bolt manufacturing?
A5. Heat treatment enhances bolt strength, hardness, and durability, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
#Bolts#Fasteners#BoltManufacturing#BoltGrades#BoltSpecifications#BoltMaterials#HighTemperatureBolts#IndustrialFasteners#EngineeringFasteners#Ananka#Anankafasteners#Linkedin#manufacturer#supplier
0 notes