#I learned my first html coding through fiddling with my themes
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

“oh they’re not taking away chronological dashboard, well everything’s okay then” they also said in the post they’re making reblogs collapsed (like comments on twitter) so you won’t see the full conversation in a post. they also won’t get rid of tumblr live despite it being an annoying and cancerous data-miner that isn’t legal in much of the world. they won’t even let you opt out of tumblr live for more than seven days. they implemented a terrible photo viewer that mimics tiktok and makes it so you can’t zoom in on images. they took away the ability to view prev tags. they’re making it so you have to sign in with your email to view almost any thing on tumblr. they’ve already made it so you have to sign in to send asks, even on anon. they’re slowly phasing out custom blog themes.
the things that make tumblr at all usable and favored by us– the older web blog features, the anonymity– that is still being taken away. it HAS been being taken away for some time now. i am urging you people to reveiwbomb the tumblr app. force them to acknowledge that users do not like these changes.
#how idiotic it is to want to be like every other social media website#when twitter is actively shooting itself to the foot over and over and people are leaving#the charm of tumblr is the difference from the others#please listen to your userbase when we tell you this is a very bad idea#you either lose your existing userbase in favor of grabbing a couple new ones who probably won't even like it here anyway#or you keep your individuality and the existing users and perhaps draw in more users by being different#and ffs don't you dare touch the themes!#I learned my first html coding through fiddling with my themes#so many hours were put in that and I'm not talking about myself alone#look at those colorful blogs all over!#we present through our blogs what we love and do. turning them into gray or white sheets of no personality kill all of that!
98K notes
·
View notes
Text
Anonymous:
Do you have any advice on how to start an rp blog? I feel like there's so much to do and so many specific things, it looks intimidating, but I really want to get into it (and your blog seems like a safe space to ask as a baby in the matter)


Hi! Thanks you for asking and for trusting. I do admit that rping on tumblr can look daunting and there is a series of things that are considered “etiquette” that might not be obvious for newcomers. And the only way to learn is to ask, right? As I’m not sure if you would like something more specific or a step-by-step, I’m going to go through the whole process.
note: this is a repost from an ask in a more reblog-friendly format
1. Setting up the blog
You might want to make a new e-mail account for each blog you want. I recommend making a gmail/google account, so you may be able to use other services and associate them with your blog. I’ll go into more details in a minute.
Some people would rather have a personal blog and then making the RP blog as a side-blog. Or a “hub” blog and many side-blogs so they have everything centralized. The downside is that you can’t follow people with side-blogs, only the main – and some rpers are a little suspicious of personal blogs, so if you intend to go this route it might be a good idea to state somewhere in your blog that you have a RP blog.
Tip : It isn’t said too often, but I recommend saving your blog’s e-mail and password somewhere, maybe a flashdrive or even google drive. This way, if something happens you will be able to retrieve your account.
When picking the URL, for a very long time tumblr had problems tagging URLs with a hyphen ( - ). I’m not sure if it has been fixed or if there are still some issues, so I recommend only using letters and maybe numbers. Other than that, pick anything that sounds nice to you!
Themes are nice, but not entirely necessary. Not everybody has photoshop skills and all that. Some people do have commissioned themes, but if you want to try your hand at it my first stop is usually @theme-hunter or @sheathemes . They reblog many themes from many creators, so there are always many options that might suit your needs. Some creators offer very newcomer-friendly themes that you can configure a lot of things without much hassle but some might require basic HTML knowledge – a few creators have guides on how to properly set up their themes and are willing to and answer questions, so don’t be afraid to contact them! You can also send me an ask, I’m not a specialist but I can certainly help walk you through the basics.
Tip: @glenthemes have very good themes and a basic installation guide here.
When fiddling with the options, try to pick colors that have nice contrast and are easy to read. If you are bad at picking colors or have problems in finding the code for them, I recommend trying this link. There is also this one that auto-generate palettes.
Tip : If you mess with your theme, remember there is the Theme Recovery.
Tip: If you use Chrome or Firefox you can set up different profiles and associate each with a different blog, so you don’t need to log out from any of your accounts.
There are two pages that I recommend having: one is an about your muse. If they are an OC, it is always a good idea to have at least some information out there to make things easier. If they are from a canon source, not everybody is familiar with the material so it might be a good idea to state. For example, if you are going to roleplay as Altria/Arturia, it is a good idea to have a “RP blog for Saber (Altria Pendragon) from FGO/FSN “ somewhere visible. The other page that is a good idea having is a rules/guidelines page. This one can be a little intimidating, but it is usually a way to communicate important things. For example: are you comfortable writing violence? Do you have any personal triggers? There is something you absolutely won’t write? There are things you may figure out along the way and it is absolutely ok to fine-tune this session every now and then. Some people also credit source for their icons and graphics in general in their rule/guideline page.
If you are using the tumblr default themes, when you create a new page you can turn on the option to show a link to the page. If you are using a custom theme, most of the time you will have to link it manually.

Oh, and if you are planning to do a multimuse, it might be a good idea to list which muses you have. The same goes for a hub blog; list the muses and link to the pages.
Icons aren’t necessary but are considered commonplace. You can find some icons I’ve done here but there are plenty of other sources. If you want to do your own icons, keep in mind to don’t make them too big, as a courtesy to your mutuals.
Tip: Anything larger than 300 pixels will be stretched to fit the post. As of today ( 4/29/2021 ) the posts are currently 540 pixels wide. This can be useful as making banners for your blog.
Tumblr allow users to “pin” posts. This mean that they will always visible if you access your blog, even on dash/mobile. You can use this to set up a post with basic links for mobile users or something else. For example, if you are out on vacations and won’t be able to do replies, you can pin a hiatus notice and then remove the pin once you are back.
2. Introducing yourself
Time to officially join the fun! (insert a “Hi, Zuko here” joke) Don’t worry if you don’t have a fancy promo graphic or anything, most people make their initial introduction with a simple post.
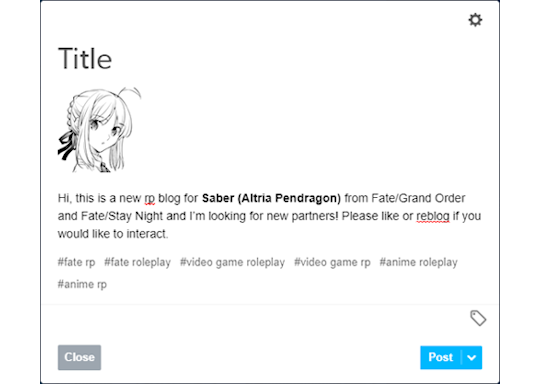
(as you can see, I’m not very good at saying ‘hi’)
Try to introduce yourself in a few lines, but make sure to state which muse you RP as. Some people also like adding their pen name/alias and establishing a brand. Follow as many people as you want that reblogged or liked your post, and tumblr is going to start recommending other blogs that are related to the tags you use normally or have any relation to the people you follow. You can put as many tags as you want, but tumblr will disregard more than 6 tags in their system. Try tags like “<fandom> rp” and “<fandom> roleplay” along with the media, such as “movie” “video game”, “anime” and so on.
It might also be a good idea to follow a few RP memes blogs. They often have options to break the ice, like one-liners that your mutual can send you.
Tip: Don’t forget to turn on the asks and the anon
3. Practical advice
Alright, now that you have a few mutuals, it is time to get to some general tips:
Tumblr can be a little “iffy”, and a great quality of life extension for RPers and navigation in general is installing the New Xkit extension. They offer a number of options to enhance your tumblr experience, but the ones I consider essential are the “editable reblogs”, “quick tags” and “blacklist”. Get it for Chrome or Firefox.
As a rule of thumb I recommend writing your RPs using Google Docs before posting or replying. By doing this you can do some spell check and if your browser crashes for any reason you can easily recover your work. You can also use Word, Open Office, or any text editor you feel like.
Because I’m a bit of a perfectionist, I also have Grammarly ( Chrome / Firefox ) installed for an extra layer of spell/grammar check. There is a subscription option, but the free one works perfectly fine.
To make things easier to locate, always tag the URL of your RP partner when doing a reply. There are other useful things you can tag, such as open starters, memes, and such.
Risking being obvious here, but when you are not interacting as your character it might be a good idea to tag as “ooc” or “out of character”.
Some people like making google docs with basic info and other useful stuff for easier access on mobile. It is a recent trend, it might be easier to edit as opposed to going through tumblr page editor and dealing with the HTML. You can find some templates here and here.
Tumblr’s activity can be unreliable, so don’t be afraid of contacting your partner to see if they have gotten your reply after a few weeks. However, some people also enjoy using the RP Thread Tracker in order to be on top of things. It might be a good idea to check it out.
Because of Tumblr shadowbanning and shenanigans, it isn’t unusual for people to have NSFW sideblogs (sometimes referred as ‘sin blogs’). If you want to write smut, it might be a good idea to consider making one.
Some people don’t like replying to asks, as Tumblr won’t let you remove the initial ask. It has become common to see people making new posts to reply to asks. This is a simple example:
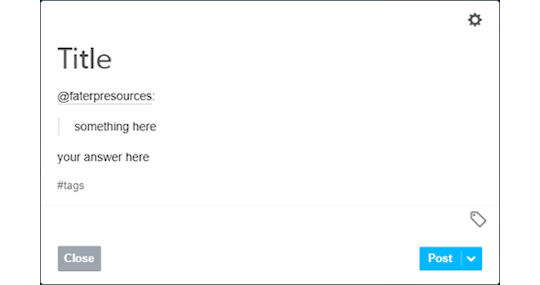
As you can see, I used the mention to have the RP partner notified then I copied and pasted their question on my post and used the quote to indicate it. You can also have fancy graphics, like a line to separate the contents, just do whatever you feel like with the formatting or keep it simple.
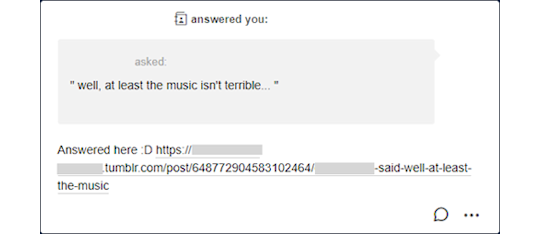
To make sure your partner got the answer, I recommend copying the link to the post and pasting on the ask and then replying it privately. An example sent to my rp blog:
4. Basic Etiquette
Ok, this is a little subjective most of the time but here are a few things that are considered universal courtesy.
Never reblog someone else’s headcanons. If you enjoy it, maybe it should politely contact the author and ask if it is ok to write something based on their original idea but you should never downright copy or lift something from another creator. It is considered rude, or even theft in some cases.
Don’t reblog threads you are not involved with. It is ok to leave a like, but never reblog. This is because Tumblr can mess up the notifications and disrupt the flow of the RP.
Don’t copy other people’s graphics. It is very rude and sometimes they commission (aka: paid) for it.
Trim your posts. What does that mean? Every time you reblog with a reply, the post tends to get longer and longer, and it can cluster your and your mutuals’ dashes. This is why the New X-Kit’s “editable reblogs” is an almost must-have tool. If for some reason you can’t install X-Kit (if you are on mobile for example), then remove the previous post or ask your partner to trim for you.
Never take control of your RP partner’s muse. This is called “godmodding” and it is heavily frowned upon. It is ok to control your muse and the possible NPCs that you inserted, but never seize someone else’s character. Likewise, it can also be very upsetting if you use what people call “meta-gaming”, applying knowledge that your muse shouldn’t know about the other. For example, let’s say your RP partner’s muse is a vampire, but they have never disclosed that information to your muse, who also doesn’t have an excuse to know that (for example, being a vampire hunter) so it can be quite jarring sometimes. When in doubt, contact your partner.
This should go without saying, but RPing sexual themes with users under the age of 18 are illegal. It doesn’t matter if the age of consent in your location is lower, once you join Tumblr you are abiding by their user guidelines and the law of the state they are located in. If you are an adult, don’t engage minors with these topics, maybe a fade to black would be a better option. If you are a minor, don’t insist or you might cause a lot of legal problems for others.
Try to tag anything triggering. Violence, gore, NSFW. Both Tumblr and the New Xkit have options to block keywords.
When picking PSDs or graphics for your blog, you should avoid templates that change the color of the skin of POCs muses and try to pick the right race/ethnicity of the muse you are going to RP as. I won’t go through a lot of details, as it is a rather lengthy subject in an already lengthy conversation but keep this in the back of your mind.
Some RPers don’t like when you reblog memes from them without sending anything. Try to always reblog from a source or to interact with the person you are reblogging from, it can be rather disheartening to be seen as a meme source rather than a RP blog. This isn’t a rule and some people don’t mind, but it is always a good idea to try to do this.
This might be more of a pet peeve of mine than proper etiquette, but it is ok to use small font. What is not ok is use small font + underscript. Some people have disabilities that might make it harder for them to read it, so it might be a good idea to refrain from using it. Maybe if you feel like doing something fancier every now and then, but I wouldn’t recommend making this a habit.
Mun and Muse are different entities. Remember that it isn’t because a muse does something (especially a villain one) that the mun condones something. Never assume anything about the mun, when in doubt talk to them.
Be mindful of your partners and treat them the way you would like to be treated.
As a rule of thumb, always talk to your RP partner. It is only fun as long both of you are enjoying it.
5. Closing Words
This got longer than I expected.
Despite all of that, don’t be too worried about not being very good at first. I assure you that you will get better with time, so don’t be afraid of experimenting as long you feel comfortable. And don’t be afraid of saying “no” if something bothers you.
My inbox is always open to questions and ideas, so feel free to contact me anytime!
I would also ask my followers: there is advice I missed/overlooked? Anything you would like someone have told you when you first started? Add your thoughts so I can update this.
Happy RPing!
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Think Like a Front-End Developer
This is an extended version of my essay “When front-end means full-stack” which was published in the wonderful Increment magazine put out by Stripe. It’s also something of an evolution of a couple other of my essays, “The Great Divide” and “Ooops, I guess we’re full-stack developers now.”
The moment I fell in love with front-end development was when I discovered the style.css file in WordPress themes. That’s where all the magic was (is!) to me. I could (can!) change a handful of lines in there and totally change the look and feel of a website. It’s an incredible game to play.
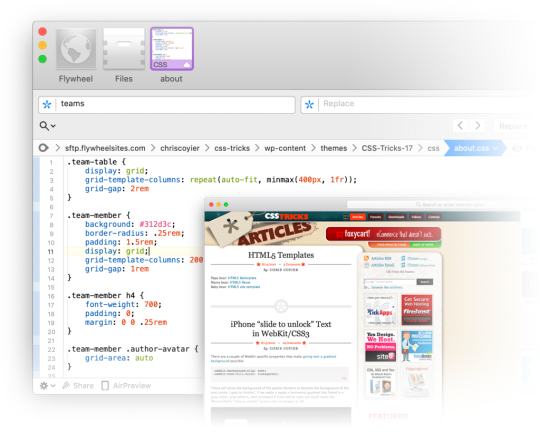
Back when I was cowboy-coding over FTP. Although I definitely wasn’t using CSS grid!
By fiddling with HTML and CSS, I can change the way you feel about a bit of writing. I can make you feel more comfortable about buying tickets to an event. I can increase the chances you share something with your friends.
That was well before anybody paid me money to be a front-end developer, but even then I felt the intoxicating mix of stimuli that the job offers. Front-end development is this expressive art form, but often constrained by things like the need to directly communicate messaging and accomplish business goals.
Front-end development is at the intersection of art and logic. A cross of business and expression. Both left and right brain. A cocktail of design and nerdery.
I love it.
Looking back at the courses I chose from middle school through college, I bounced back and forth between computer-focused classes and art-focused classes, so I suppose it’s no surprise I found a way to do both as a career.
The term “Front-End Developer” is fairly well-defined and understood. For one, it’s a job title. I’ll bet some of you literally have business cards that say it on there, or some variation like: “Front-End Designer,” “UX Developer,” or “UI Engineer.” The debate around what those mean isn’t particularly interesting to me. I find that the roles are so varied from job-to-job and company-to-company that job titles will never be enough to describe things. Getting this job is more about demonstrating you know what you’re doing more than anything else¹.
Chris Coyier Front-End Developer
The title variations are just nuance. The bigger picture is that as long as the job is building websites, front-enders are focused on the browser. Quite literally:
front-end = browsers
back-end = servers
Even as the job has changed over the decades, that distinction still largely holds.
As “browser people,” there are certain truths that come along for the ride. One is that there is a whole landscape of different browsers and, despite the best efforts of standards bodies, they still behave somewhat differently. Just today, as I write, I dealt with a bug where a date string I had from an API was in a format such that Firefox threw an error when I tried to use the .toISOString() JavaScript API on it, but was fine in Chrome. That’s just life as a front-end developer. That’s the job.
Even across that landscape of browsers, just on desktop computers, there is variance in how users use that browser. How big do they have the window open? Do they have dark mode activated on their operating system? How’s the color gamut on that monitor? What is the pixel density? How’s the bandwidth situation? Do they use a keyboard and mouse? One or the other? Neither? All those same questions apply to mobile devices too, where there is an equally if not more complicated browser landscape. And just wait until you take a hard look at HTML emails.
That’s a lot of unknowns, and the answers to developing for that unknown landscape is firmly in the hands of front-end developers.

Into the unknoooooowwwn. – Elsa
The most important aspect of the job? The people that use these browsers. That’s why we’re building things at all. These are the people I’m trying to impress with my mad CSS skills. These are the people I’m trying to get to buy my widget. Who all my business charts hinge upon. Who’s reaction can sway my emotions like yarn in the breeze. These users, who we put on a pedestal for good reason, have a much wider landscape than the browsers do. They speak different languages. They want different things. They are trying to solve different problems. They have different physical abilities. They have different levels of urgency. Again, helping them is firmly in the hands of front-end developers. There is very little in between the characters we type into our text editors and the users for whom we wish to serve.
Being a front-end developer puts us on the front lines between the thing we’re building and the people we’re building it for, and that’s a place some of us really enjoy being.
That’s some weighty stuff, isn’t it? I haven’t even mentioned React yet.
The “we care about the users” thing might feel a little precious. I’d think in a high functioning company, everyone would care about the users, from the CEO on down. It’s different, though. When we code a <button>, we’re quite literally putting a button into a browser window that users directly interact with. When we adjust a color, we’re adjusting exactly what our sighted users see when they see our work.
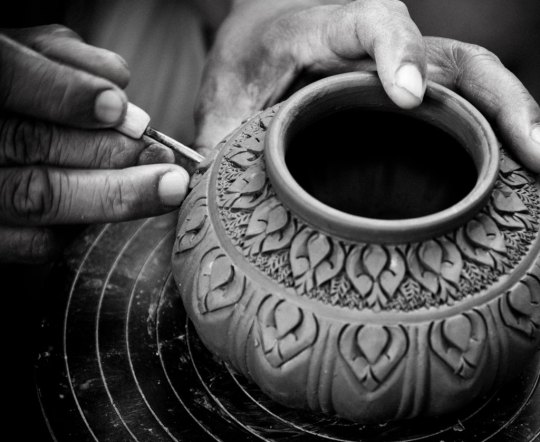

That’s not far off from a ceramic artist pulling a handle out of clay for a coffee cup. It’s applying craftsmanship to a digital experience. While a back-end developer might care deeply about the users of a site, they are, as Monica Dinculescu once told me in a conversation about this, “outsourcing that responsibility.”
We established that front-end developers are browser people. The job is making things work well in browsers. So we need to understand the languages browsers speak, namely: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript². And that’s not just me being some old school fundamentalist; it’s through a few decades of everyday front-end development work that knowing those base languages is vital to us doing a good job. Even when we don’t work directly with them (HTML might come from a template in another language, CSS might be produced from a preprocessor, JavaScript might be mostly written in the parlance of a framework), what goes the browser is ultimately HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, so that’s where debugging largely takes place and the ability of the browser is put to work.
CSS will always be my favorite and HTML feels like it needs the most love — but JavaScript is the one we really need to examine The last decade has seen JavaScript blossom from a language used for a handful of interactive effects to the predominant language used across the entire stack of web design and development. It’s possible to work on websites and writing nothing but JavaScript. A real sea change.
JavaScript is all-powerful in the browser. In a sense, it supersedes HTML and CSS, as there is nothing either of those languages can do that JavaScript cannot. HTML is parsed by the browser and turned into the DOM, which JavaScript can also entirely create and manipulate. CSS has its own model, the CSSOM, that applies styles to elements in the DOM, which JavaScript can also create and manipulate.
This isn’t quite fair though. HTML is the very first file that browsers parse before they do the rest of the work needed to build the site. That firstness is unique to HTML and a vital part of making websites fast.
In fact, if the HTML was the only file to come across the network, that should be enough to deliver the basic information and functionality of a site.
That philosophy is called Progressive Enhancement. I’m a fan, myself, but I don’t always adhere to it perfectly. For example, a <form> can be entirely functional in HTML, when it’s action attribute points to a URL where the form can be processed. Progressive Enhancement would have us build it that way. Then, when JavaScript executes, it takes over the submission and has the form submit via Ajax instead, which might be a nicer experience as the page won’t have to refresh. I like that. Taken further, any <button> outside a form is entirely useless without JavaScript, so in the spirit of Progressive Enhancement, I should wait until JavaScript executes to even put that button on the page at all (or at least reveal it). That’s the kind of thing where even those of us with the best intentions might not always toe the line perfectly. Just put the button in, Sam. Nobody is gonna die.
JavaScript’s all-powerfulness makes it an appealing target for those of us doing work on the web — particularly as JavaScript as a language has evolved to become even more powerful and ergonomic, and the frameworks that are built in JavaScript become even more-so. Back in 2015, it was already so clear that JavaScript was experiencing incredible growth in usage, Matt Mullenweg, co-founder of WordPress, gave the developer world homework: “Learn JavaScript Deeply”³. He couldn’t have been more right. Half a decade later, JavaScript has done a good job of taking over front-end development. Particularly if you look at front-end development jobs.
While the web almanac might show us that only 5% of the top-zillion sites use React compared to 85% including jQuery, those numbers are nearly flipped when looking around at front-end development job requirements.
I’m sure there are fancy economic reasons for all that, but jobs are as important and personal as it gets for people, so it very much matters.
So we’re browser people in a sea of JavaScript building things for people. If we take a look at the job at a practical day-to-day tasks level, it’s a bit like this:
Translate designs into code
Think in terms of responsive design, allowing us to design and build across the landscape of devices
Build systemically. Construct components and patterns, not one-offs.
Apply semantics to content
Consider accessibility
Worry about the performance of the site. Optimize everything. Reduce, reuse, recycle.
Just that first bullet point feels like a college degree to me. Taken together, all of those points certainly do.
This whole list is a bit abstract though, so let’s apply it to something we can look at. What if this website was our current project?

Our brains and fingers go wild!
Let’s build the layout with CSS grid.
What fonts are those? Do we need to load them in their entirety or can we subset them? What happens as they load in? This layout feels like it will really suffer from font-shifting jank.
There are some repeated patterns here. We should probably make a card design pattern. Every website needs a good card pattern.
That’s a gorgeous color scheme. Are the colors mathematically related? Should we make variables to represent them individually or can we just alter a single hue as needed? Are we going to use custom properties in our CSS? Colors are just colors though, we might not need the cascading power of them just for this. Should we just use Sass variables? Are we going to use a CSS preprocessor at all?
The source order is tricky here. We need to order things so that they make sense for a screen reader user. We should have a meeting about what the expected order of content should be, even if we’re visually moving things around a bit with CSS grid.
The photographs here are beautifully shot. But some of them match the background color of the site… can we get away with alpha-transparent PNGs here? Those are always so big. Can any next-gen formats help us? Or should we try to match the background of a JPG with the background of the site seamlessly. Who’s writing the alt text for these?
There are some icons in use here. Inline SVG, right? Certainly SVG of some kind, not icon fonts, right? Should we build a whole icon system? I guess it depends on how we’re gonna be building this thing more broadly. Do we have a build system at all?
What’s the whole front-end plan here? Can I code this thing in vanilla HTML, CSS, and JavaScript? Well, I know I can, but what are the team expectations? Client expectations? Does it need to be a React thing because it’s part of some ecosystem of stuff that is already React? Or Vue or Svelte or whatever? Is there a CMS involved?
I’m glad the designer thought of not just the “desktop” and “mobile” sizes but also tackled an in-between size. Those are always awkward. There is no interactivity information here though. What should we do when that search field is focused? What gets revealed when that hamburger is tapped? Are we doing page-level transitions here?
I could go on and on. That’s how front-end developers think, at least in my experience and in talking with my peers.
A lot of those things have been our jobs forever though. We’ve been asking and answering these questions on every website we’ve built for as long as we’ve been doing it. There are different challenges on each site, which is great and keeps this job fun, but there is a lot of repetition too.
Allow me to get around to the title of this article.
While we’ve been doing a lot of this stuff for ages, there is a whole pile of new stuff we’re starting to be expected to do, particularly if we’re talking about building the site with a modern JavaScript framework. All the modern frameworks, as much as they like to disagree about things, agree about one big thing: everything is a component. You nest and piece together components as needed. Even native JavaScript moves toward its own model of Web Components.

I like it, this idea of components. It allows you and your team to build the abstractions that make the most sense to you and what you are building.
Your Card component does all the stuff your card needs to do. Your Form component does forms how your website needs to do forms. But it’s a new concept to old developers like me. Components in JavaScript have taken hold in a way that components on the server-side never did. I’ve worked on many a WordPress website where the best I did was break templates into somewhat arbitrary include() statements. I’ve worked on Ruby on Rails sites with partials that take a handful of local variables. Those are useful for building re-usable parts, but they are a far cry from the robust component models that JavaScript frameworks offer us today.
All this custom component creation makes me a site-level architect in a way that I didn’t use to be. Here’s an example. Of course I have a Button component. Of course I have an Icon component. I’ll use them in my Card component. My Card component lives in a Grid component that lays them out and paginates them. The whole page is actually built from components. The Header component has a SearchBar component and a UserMenu component. The Sidebar component has a Navigation component and an Ad component. The whole page is just a special combination of components, which is probably based on the URL, assuming I’m all-in on building our front-end with JavaScript. So now I’m dealing with URLs myself, and I’m essentially the architect of the entire site. [Sweats profusely]
Like I told ya, a whole pile of new responsibility.
Components that are in charge of displaying content are almost certainly not hard-coded with data in them. They are built to be templates. They are built to accept data and construct themselves based on that data. In the olden days, when we were doing this kind of templating, the data has probably already arrived on the page we’re working on. In a JavaScript-powered app, it’s more likely that that data is fetched by JavaScript. Perhaps I’ll fetch it when the component renders. In a stack I’m working with right now, the front end is in React, the API is in GraphQL and we use Apollo Client to work with data. We use a special “hook” in the React components to run the queries to fetch the data we need, and another special hook when we need to change that data. Guess who does that work? Is it some other kind of developer that specializes in this data layer work? No, it’s become the domain of the front-end developer.
Speaking of data, there is all this other data that a website often has to deal with that doesn’t come from a database or API. It’s data that is really only relevant to the website at this moment in time.
Which tab is active right now?
Is this modal dialog open or closed?
Which bar of this accordion is expanded?
Is this message bar in an error state or warning state?
How many pages are you paginated in?
How far is the user scrolled down the page?
Front-end developers have been dealing with that kind of state for a long time, but it’s exactly this kind of state that has gotten us into trouble before. A modal dialog can be open with a simple modifier class like <div class="modal is-open"> and toggling that class is easy enough with .classList.toggle(".is-open"); But that’s a purely visual treatment. How does anything else on the page know if that modal is open or not? Does it ask the DOM? In a lot of jQuery-style apps of yore, yes, it would. In a sense, the DOM became the “source of truth” for our websites. There were all sorts of problems that stemmed from this architecture, ranging from a simple naming change destroying functionality in weirdly insidious ways, to hard-to-reason-about application logic making bug fixing a difficult proposition.
Front-end developers collectively thought: what if we dealt with state in a more considered way? State management, as a concept, became a thing. JavaScript frameworks themselves built the concept right in, and third-party libraries have paved and continue to pave the way. This is another example of expanding responsibility. Who architects state management? Who enforces it and implements it? It’s not some other role, it’s front-end developers.
There is expanding responsibility in the checklist of things to do, but there is also work to be done in piecing it all together. How much of this state can be handled at the individual component level and how much needs to be higher level? How much of this data can be gotten at the individual component level and how much should be percolated from above? Design itself comes into play. How much of the styling of this component should be scoped to itself, and how much should come from more global styles?
It’s no wonder that design systems have taken off in recent years. We’re building components anyway, so thinking of them systemically is a natural fit.
Let’s look at our design again:

A bunch of new thoughts can begin!
Assuming we’re using a JavaScript framework, which one? Why?
Can we statically render this site, even if we’re building with a JavaScript framework? Or server-side render it?
Where are those recipes coming from? Can we get a GraphQL API going so we can ask for whatever we need, whenever we need it?
Maybe we should pick a CMS that has an API that will facilitate the kind of front-end building we want to do. Perhaps a headless CMS?
What are we doing for routing? Is the framework we chose opinionated or unopinionated about stuff like this?
What are the components we need? A Card, Icon, SearchForm, SiteMenu, Img… can we scaffold these out? Should we start with some kind of design framework on top of the base framework?
What’s the client state we might need? Current search term, current tab, hamburger open or not, at least.
Is there a login system for this site or not? Are logged in users shown anything different?
Is there are third-party componentry we can leverage here?
Maybe we can find one of those fancy image components that does blur-up loading and lazy loading and all that.
Those are all things that are in the domain of front-end developers these days, on top of everything that we already need to do. Executing the design, semantics, accessibility, performance… that’s all still there. You still need to be proficient in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and how the browser works. Being a front-end developer requires a haystack of skills that grows and grows. It’s the natural outcome of the web getting bigger. More people use the web and internet access grows. The economy around the web grows. The capability of browsers grows. The expectations of what is possible on the web grows. There isn’t a lot shrinking going on around here.
We’ve already reached the point where most front-end developers don’t know the whole haystack of responsibilities. There are lots of developers still doing well for themselves being rather design-focused and excelling at creative and well-implemented HTML and CSS, even as job posts looking for that dwindle.
There are systems-focused developers and even entire agencies that specialize in helping other companies build and implement design systems. There are data-focused developers that feel most at home making the data flow throughout a website and getting hot and heavy with business logic. While all of those people might have “front-end developer” on their business card, their responsibilities and even expectations of their work might be quite different. It’s all good, we’ll find ways to talk about all this in time.
In fact, how we talk about building websites has changed a lot in the last decade. Some of my early introduction to web development was through WordPress. WordPress needs a web server to run, is written in PHP, and stores it’s data in a MySQL database. As much as WordPress has evolved, all that is still exactly the same. We talk about that “stack” with an acronym: LAMP, or Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP. Note that literally everything in the entire stack consists of back-end technologies. As a front-end developer, nothing about LAMP is relevant to me.
But other stacks have come along since then. A popular stack was MEAN (Mongo, Express, Angular and Node). Notice how we’re starting to inch our way toward more front-end technologies? Angular is a JavaScript framework, so as this stack gained popularity, so too did talking about the front-end as an important part of the stack. Node and Express are both JavaScript as well, albeit the server-side variant.
The existence of Node is a huge part of this story. Node isn’t JavaScript-like, it’s quite literally JavaScript. It makes a front-end developer already skilled in JavaScript able to do server-side work without too much of a stretch.
“Serverless” is a much more modern tech buzzword, and what it’s largely talking about is running small bits of code on cloud servers. Most often, those small bits of code are in Node, and written by JavaScript developers. These days, a JavaScript-focused front-end developer might be writing their own serverless functions and essentially being their own back-end developer. They’ll think of themselves as full-stack developers, and they’ll be right.
Shawn Wang coined a term for a new stack this year: STAR or Design System, TypeScript, Apollo, and React. This is incredible to me, not just because I kind of like that stack, but because it’s a way of talking about the stack powering a website that is entirely front-end technologies. Quite a shift.
I apologize if I’ve made you feel a little anxious reading this. If you feel like you’re behind in understanding all this stuff, you aren’t alone.
In fact, I don’t think I’ve talked to a single developer who told me they felt entirely comfortable with the entire world of building websites. Everybody has weak spots or entire areas where they just don’t know the first dang thing. You not only can specialize, but specializing is a pretty good idea, and I think you will end up specializing to some degree whether you plan to or not. If you have the good fortune to plan, pick things that you like. You’ll do just fine.
The only constant in life is change.
– Heraclitus – Motivational Poster – Chris Coyier
¹ I’m a white dude, so that helps a bunch, too. ↩️ ² Browsers speak a bunch more languages. HTTP, SVG, PNG… The more you know the more you can put to work! ↩️ ³ It’s an interesting bit of irony that WordPress websites generally aren’t built with client-side JavaScript components. ↩️
The post How to Think Like a Front-End Developer appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
How to Think Like a Front-End Developer published first on https://deskbysnafu.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers
This is an extended version of my essay “When front-end means full-stack” which was published in the wonderful Increment magazine put out by Stripe. It’s also something of an evolution of a couple other of my essays, “The Great Divide” and “Ooops, I guess we’re full-stack developers now.”
The moment I fell in love with front-end development was when I discovered the style.css file in WordPress themes. That’s where all the magic was (is!) to me. I could (can!) change a handful of lines in there and totally change the look and feel of a website. It’s an incredible game to play.
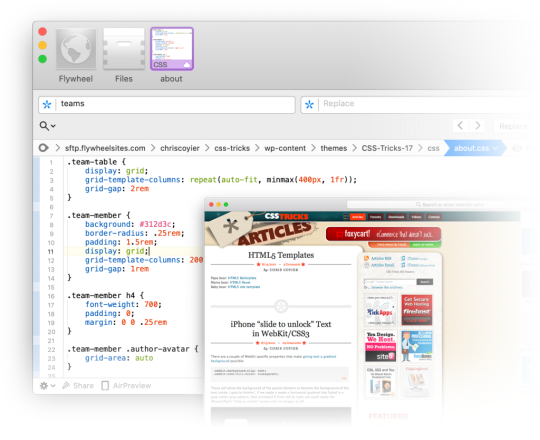
Back when I was cowboy-coding over FTP. Although I definitely wasn’t using CSS grid!
By fiddling with HTML and CSS, I can change the way you feel about a bit of writing. I can make you feel more comfortable about buying tickets to an event. I can increase the chances you share something with your friends.
That was well before anybody paid me money to be a front-end developer, but even then I felt the intoxicating mix of stimuli that the job offers. Front-end development is this expressive art form, but often constrained by things like the need to directly communicate messaging and accomplish business goals.
Front-end development is at the intersection of art and logic. A cross of business and expression. Both left and right brain. A cocktail of design and nerdery.
I love it.
Looking back at the courses I chose from middle school through college, I bounced back and forth between computer-focused classes and art-focused classes, so I suppose it’s no surprise I found a way to do both as a career.
The term “Front-End Developer” is fairly well-defined and understood. For one, it’s a job title. I’ll bet some of you literally have business cards that say it on there, or some variation like: “Front-End Designer,” “UX Developer,” or “UI Engineer.” The debate around what those mean isn’t particularly interesting to me. I find that the roles are so varied from job-to-job and company-to-company that job titles will never be enough to describe things. Getting this job is more about demonstrating you know what you’re doing more than anything else¹.
Chris Coyier Front-End Developer
The title variations are just nuance. The bigger picture is that as long as the job is building websites, front-enders are focused on the browser. Quite literally:
front-end = browsers
back-end = servers
Even as the job has changed over the decades, that distinction still largely holds.
As “browser people,” there are certain truths that come along for the ride. One is that there is a whole landscape of different browsers and, despite the best efforts of standards bodies, they still behave somewhat differently. Just today, as I write, I dealt with a bug where a date string I had from an API was in a format such that Firefox threw an error when I tried to use the .toISOString() JavaScript API on it, but was fine in Chrome. That’s just life as a front-end developer. That’s the job.
Even across that landscape of browsers, just on desktop computers, there is variance in how users use that browser. How big do they have the window open? Do they have dark mode activated on their operating system? How’s the color gamut on that monitor? What is the pixel density? How’s the bandwidth situation? Do they use a keyboard and mouse? One or the other? Neither? All those same questions apply to mobile devices too, where there is an equally if not more complicated browser landscape. And just wait until you take a hard look at HTML emails.
That’s a lot of unknowns, and the answers to developing for that unknown landscape is firmly in the hands of front-end developers.

Into the unknoooooowwwn. – Elsa
The most important aspect of the job? The people that use these browsers. That’s why we’re building things at all. These are the people I’m trying to impress with my mad CSS skills. These are the people I’m trying to get to buy my widget. Who all my business charts hinge upon. Who’s reaction can sway my emotions like yarn in the breeze. These users, who we put on a pedestal for good reason, have a much wider landscape than the browsers do. They speak different languages. They want different things. They are trying to solve different problems. They have different physical abilities. They have different levels of urgency. Again, helping them is firmly in the hands of front-end developers. There is very little in between the characters we type into our text editors and the users for whom we wish to serve.
Being a front-end developer puts us on the front lines between the thing we’re building and the people we’re building it for, and that’s a place some of us really enjoy being.
That’s some weighty stuff, isn’t it? I haven’t even mentioned React yet.
The “we care about the users” thing might feel a little precious. I’d think in a high functioning company, everyone would care about the users, from the CEO on down. It’s different, though. When we code a <button>, we’re quite literally putting a button into a browser window that users directly interact with. When we adjust a color, we’re adjusting exactly what our sighted users see when they see our work.

That’s not far off from a ceramic artist pulling a handle out of clay for a coffee cup. It’s applying craftsmanship to a digital experience. While a back-end developer might care deeply about the users of a site, they are, as Monica Dinculescu once told me in a conversation about this, “outsourcing that responsibility.”
We established that front-end developers are browser people. The job is making things work well in browsers. So we need to understand the languages browsers speak, namely: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript². And that’s not just me being some old school fundamentalist; it’s through a few decades of everyday front-end development work that knowing those base languages is vital to us doing a good job. Even when we don’t work directly with them (HTML might come from a template in another language, CSS might be produced from a preprocessor, JavaScript might be mostly written in the parlance of a framework), what goes the browser is ultimately HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, so that’s where debugging largely takes place and the ability of the browser is put to work.
CSS will always be my favorite and HTML feels like it needs the most love — but JavaScript is the one we really need to examine The last decade has seen JavaScript blossom from a language used for a handful of interactive effects to the predominant language used across the entire stack of web design and development. It’s possible to work on websites and writing nothing but JavaScript. A real sea change.
JavaScript is all-powerful in the browser. In a sense, it supersedes HTML and CSS, as there is nothing either of those languages can do that JavaScript cannot. HTML is parsed by the browser and turned into the DOM, which JavaScript can also entirely create and manipulate. CSS has its own model, the CSSOM, that applies styles to elements in the DOM, which JavaScript can also create and manipulate.
This isn’t quite fair though. HTML is the very first file that browsers parse before they do the rest of the work needed to build the site. That firstness is unique to HTML and a vital part of making websites fast.
In fact, if the HTML was the only file to come across the network, that should be enough to deliver the basic information and functionality of a site.
That philosophy is called Progressive Enhancement. I’m a fan, myself, but I don’t always adhere to it perfectly. For example, a <form> can be entirely functional in HTML, when it’s action attribute points to a URL where the form can be processed. Progressive Enhancement would have us build it that way. Then, when JavaScript executes, it takes over the submission and has the form submit via Ajax instead, which might be a nicer experience as the page won’t have to refresh. I like that. Taken further, any <button> outside a form is entirely useless without JavaScript, so in the spirit of Progressive Enhancement, I should wait until JavaScript executes to even put that button on the page at all (or at least reveal it). That’s the kind of thing where even those of us with the best intentions might not always toe the line perfectly. Just put the button in, Sam. Nobody is gonna die.
JavaScript’s all-powerfulness makes it an appealing target for those of us doing work on the web — particularly as JavaScript as a language has evolved to become even more powerful and ergonomic, and the frameworks that are built in JavaScript become even more-so. Back in 2015, it was already so clear that JavaScript was experiencing incredible growth in usage, Matt Mullenweg, the founding developer of WordPress, gave the developer world homework: “Learn JavaScript Deeply”³. He couldn’t have been more right. Half a decade later, JavaScript has done a good job of taking over front-end development. Particularly if you look at front-end development jobs.
While the web almanac might show us that only 5% of the top-zillion sites use React compared to 85% including jQuery, those numbers are nearly flipped when looking around at front-end development job requirements.
I’m sure there are fancy economic reasons for all that, but jobs are as important and personal as it gets for people, so it very much matters.
So we’re browser people in a sea of JavaScript building things for people. If we take a look at the job at a practical day-to-day tasks level, it’s a bit like this:
Translate designs into code
Think in terms of responsive design, allowing us to design and build across the landscape of devices
Build systemically. Construct components and patterns, not one-offs.
Apply semantics to content
Consider accessibility
Worry about the performance of the site. Optimize everything. Reduce, reuse, recycle.
Just that first bullet point feels like a college degree to me. Taken together, all of those points certainly do.
This whole list is a bit abstract though, so let’s apply it to something we can look at. What if this website was our current project?

Our brains and fingers go wild!
Let’s build the layout with CSS grid.
What fonts are those? Do we need to load them in their entirety or can we subset them? What happens as they load in? This layout feels like it will really suffer from font-shifting jank.
There are some repeated patterns here. We should probably make a card design pattern. Every website needs a good card pattern.
That’s a gorgeous color scheme. Are the colors mathematically related? Should we make variables to represent them individually or can we just alter a single hue as needed? Are we going to use custom properties in our CSS? Colors are just colors though, we might not need the cascading power of them just for this. Should we just use Sass variables? Are we going to use a CSS preprocessor at all?
The source order is tricky here. We need to order things so that they make sense for a screen reader user. We should have a meeting about what the expected order of content should be, even if we’re visually moving things around a bit with CSS grid.
The photographs here are beautifully shot. But some of them match the background color of the site… can we get away with alpha-transparent PNGs here? Those are always so big. Can any next-gen formats help us? Or should we try to match the background of a JPG with the background of the site seamlessly. Who’s writing the alt text for these?
There are some icons in use here. Inline SVG, right? Certainly SVG of some kind, not icon fonts, right? Should we build a whole icon system? I guess it depends on how we’re gonna be building this thing more broadly. Do we have a build system at all?
What’s the whole front-end plan here? Can I code this thing in vanilla HTML, CSS, and JavaScript? Well, I know I can, but what are the team expectations? Client expectations? Does it need to be a React thing because it’s part of some ecosystem of stuff that is already React? Or Vue or Svelte or whatever? Is there a CMS involved?
I’m glad the designer thought of not just the “desktop” and “mobile” sizes but also tackled an in-between size. Those are always awkward. There is no interactivity information here though. What should we do when that search field is focused? What gets revealed when that hamburger is tapped? Are we doing page-level transitions here?
I could go on and on. That’s how front-end developers think, at least in my experience and in talking with my peers.
A lot of those things have been our jobs forever though. We’ve been asking and answering these questions on every website we’ve built for as long as we’ve been doing it. There are different challenges on each site, which is great and keeps this job fun, but there is a lot of repetition too.
Allow me to get around to the title of this article.
While we’ve been doing a lot of this stuff for ages, there is a whole pile of new stuff we’re starting to be expected to do, particularly if we’re talking about building the site with a modern JavaScript framework. All the modern frameworks, as much as they like to disagree about things, agree about one big thing: everything is a component. You nest and piece together components as needed. Even native JavaScript moves toward its own model of Web Components.

I like it, this idea of components. It allows you and your team to build the abstractions that make the most sense to you and what you are building.
Your Card component does all the stuff your card needs to do. Your Form component does forms how your website needs to do forms. But it’s a new concept to old developers like me. Components in JavaScript have taken hold in a way that components on the server-side never did. I’ve worked on many a WordPress website where the best I did was break templates into somewhat arbitrary include() statements. I’ve worked on Ruby on Rails sites with partials that take a handful of local variables. Those are useful for building re-usable parts, but they are a far cry from the robust component models that JavaScript frameworks offer us today.
All this custom component creation makes me a site-level architect in a way that I didn’t use to be. Here’s an example. Of course I have a Button component. Of course I have an Icon component. I’ll use them in my Card component. My Card component lives in a Grid component that lays them out and paginates them. The whole page is actually built from components. The Header component has a SearchBar component and a UserMenu component. The Sidebar component has a Navigation component and an Ad component. The whole page is just a special combination of components, which is probably based on the URL, assuming I’m all-in on building our front-end with JavaScript. So now I’m dealing with URLs myself, and I’m essentially the architect of the entire site. [Sweats profusely]
Like I told ya, a whole pile of new responsibility.
Components that are in charge of displaying content are almost certainly not hard-coded with data in them. They are built to be templates. They are built to accept data and construct themselves based on that data. In the olden days, when we were doing this kind of templating, the data has probably already arrived on the page we’re working on. In a JavaScript-powered app, it’s more likely that that data is fetched by JavaScript. Perhaps I’ll fetch it when the component renders. In a stack I’m working with right now, the front end is in React, the API is in GraphQL and we use Apollo Client to work with data. We use a special “hook” in the React components to run the queries to fetch the data we need, and another special hook when we need to change that data. Guess who does that work? Is it some other kind of developer that specializes in this data layer work? No, it’s become the domain of the front-end developer.
Speaking of data, there is all this other data that a website often has to deal with that doesn’t come from a database or API. It’s data that is really only relevant to the website at this moment in time.
Which tab is active right now?
Is this modal dialog open or closed?
Which bar of this accordion is expanded?
Is this message bar in an error state or warning state?
How many pages are you paginated in?
How far is the user scrolled down the page?
Front-end developers have been dealing with that kind of state for a long time, but it’s exactly this kind of state that has gotten us into trouble before. A modal dialog can be open with a simple modifier class like <div class="modal is-open"> and toggling that class is easy enough with .classList.toggle(".is-open"); But that’s a purely visual treatment. How does anything else on the page know if that modal is open or not? Does it ask the DOM? In a lot of jQuery-style apps of yore, yes, it would. In a sense, the DOM became the “source of truth” for our websites. There were all sorts of problems that stemmed from this architecture, ranging from a simple naming change destroying functionality in weirdly insidious ways, to hard-to-reason-about application logic making bug fixing a difficult proposition.
Front-end developers collectively thought: what if we dealt with state in a more considered way? State management, as a concept, became a thing. JavaScript frameworks themselves built the concept right in, and third-party libraries have paved and continue to pave the way. This is another example of expanding responsibility. Who architects state management? Who enforces it and implements it? It’s not some other role, it’s front-end developers.
There is expanding responsibility in the checklist of things to do, but there is also work to be done in piecing it all together. How much of this state can be handled at the individual component level and how much needs to be higher level? How much of this data can be gotten at the individual component level and how much should be percolated from above? Design itself comes into play. How much of the styling of this component should be scoped to itself, and how much should come from more global styles?
It’s no wonder that design systems have taken off in recent years. We’re building components anyway, so thinking of them systemically is a natural fit.
Let’s look at our design again:

A bunch of new thoughts can begin!
Assuming we’re using a JavaScript framework, which one? Why?
Can we statically render this site, even if we’re building with a JavaScript framework? Or server-side render it?
Where are those recipes coming from? Can we get a GraphQL API going so we can ask for whatever we need, whenever we need it?
Maybe we should pick a CMS that has an API that will facilitate the kind of front-end building we want to do. Perhaps a headless CMS?
What are we doing for routing? Is the framework we chose opinionated or unopinionated about stuff like this?
What are the components we need? A Card, Icon, SearchForm, SiteMenu, Img… can we scaffold these out? Should we start with some kind of design framework on top of the base framework?
What’s the client state we might need? Current search term, current tab, hamburger open or not, at least.
Is there a login system for this site or not? Are logged in users shown anything different?
Is there are third-party componentry we can leverage here?
Maybe we can find one of those fancy image components that does blur-up loading and lazy loading and all that.
Those are all things that are in the domain of front-end developers these days, on top of everything that we already need to do. Executing the design, semantics, accessibility, performance… that’s all still there. You still need to be proficient in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and how the browser works. Being a front-end developer requires a haystack of skills that grows and grows. It’s the natural outcome of the web getting bigger. More people use the web and internet access grows. The economy around the web grows. The capability of browsers grows. The expectations of what is possible on the web grows. There isn’t a lot shrinking going on around here.
We’ve already reached the point where most front-end developers don’t know the whole haystack of responsibilities. There are lots of developers still doing well for themselves being rather design-focused and excelling at creative and well-implemented HTML and CSS, even as job posts looking for that dwindle.
There are systems-focused developers and even entire agencies that specialize in helping other companies build and implement design systems. There are data-focused developers that feel most at home making the data flow throughout a website and getting hot and heavy with business logic. While all of those people might have “front-end developer” on their business card, their responsibilities and even expectations of their work might be quite different. It’s all good, we’ll find ways to talk about all this in time.
In fact, how we talk about building websites has changed a lot in the last decade. Some of my early introduction to web development was through WordPress. WordPress needs a web server to run, is written in PHP, and stores it’s data in a MySQL database. As much as WordPress has evolved, all that is still exactly the same. We talk about that “stack” with an acronym: LAMP, or Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP. Note that literally everything in the entire stack consists of back-end technologies. As a front-end developer, nothing about LAMP is relevant to me.
But other stacks have come along since then. A popular stack was MEAN (Mongo, Express, Angular and Node). Notice how we’re starting to inch our way toward more front-end technologies? Angular is a JavaScript framework, so as this stack gained popularity, so too did talking about the front-end as an important part of the stack. Node and Express are both JavaScript as well, albeit the server-side variant.
The existence of Node is a huge part of this story. Node isn’t JavaScript-like, it’s quite literally JavaScript. It makes a front-end developer already skilled in JavaScript able to do server-side work without too much of a stretch.
“Serverless” is a much more modern tech buzzword, and what it’s largely talking about is running small bits of code on cloud servers. Most often, those small bits of code are in Node, and written by JavaScript developers. These days, a JavaScript-focused front-end developer might be writing their own serverless functions and essentially being their own back-end developer. They’ll think of themselves as full-stack developers, and they’ll be right.
Shawn Wang coined a term for a new stack this year: STAR or Design System, TypeScript, Apollo, and React. This is incredible to me, not just because I kind of like that stack, but because it’s a way of talking about the stack powering a website that is entirely front-end technologies. Quite a shift.
I apologize if I’ve made you feel a little anxious reading this. If you feel like you’re behind in understanding all this stuff, you aren’t alone.
In fact, I don’t think I’ve talked to a single developer who told me they felt entirely comfortable with the entire world of building websites. Everybody has weak spots or entire areas where they just don’t know the first dang thing. You not only can specialize, but specializing is a pretty good idea, and I think you will end up specializing to some degree whether you plan to or not. If you have the good fortune to plan, pick things that you like. You’ll do just fine.
The only constant in life is change.
– Heraclitus – Motivational Poster – Chris Coyier
¹ I’m a white dude, so that helps a bunch, too. ↩️ ² Browsers speak a bunch more languages. HTTP, SVG, PNG… The more you know the more you can put to work! ↩️ ³ It’s an interesting bit of irony that WordPress websites generally aren’t built with client-side JavaScript components. ↩️
The post The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
😉SiliconWebX | 🌐CSS-Tricks
0 notes
Text
I added a CodeMentor badge to my website
That was a LOT more work than I'd like to admit. Seriously, it took me several hours. And I'll explain why. But first, let's see the result:

Sweet, isn't it? Now, let me walk you through the process of creating it.
First of all, I needed a CodeWars icon in font format. Why is that, you ask? Well, that's how the theme I'm using on my website works. Each of the badges is a link, which has the icon inserted into it from a custom font. I tried using an image, but it wouldn't work. It would just break the layout, and the highlighting didn't work either (note how the icons subtly change color when they are hovered over).
Iconoclastic
So, where do I get a font that includes a CodeWars icon? The website isn't nearly as popular as Google, Github, or Facebook, so obviously, no icon was included in the theme. But looking at how the theme implemented the icons, I found an interesting lead: the font it was using was called "Fontello". The Fontello website explained that it isn't really a fixed font set (like FontAwesome), but rather, a custom font generator, that lets you upload your own icons and turn them into a webfont. Neat!
Okay, so I now I knew how I could make a font with that icon in it, but where do I get the icon? The Fontello website only accepts SVG files. But the site favicon is an ICO file. SVG is a vector file format, but ICO is a pixel-based format. Not helpful. Thankfully, I had the idea to check out the “badge” feature on Codewars. Actually, that’s where I started this whole journey – I wanted to add a badge to my website, but I didn’t like any of the formats they provided, because they wouldn’t look clean in my theme.
If you go to your user profile and add "/badges" to the end of the URL, you’ll see a collection of badges that you can add to your website. And those happen to be in SVG format, AND they include the CodeWars logo!

Don’t badger me, bro!
Alright, but the problem is, it's not just the logo. There's a bunch of other stuff that I can't use! How do I get rid of that?
Well, that's when I remembered that SVG files are just plain text files, like HTML. In fact, SVG has a very similar syntax to HTML, and you can actually inspect SVG files using Chrome's web inspector, which helpfully even highlights the corresponding elements in the image.

From here, I could see that the icon was just a single <path> element. Good. I could download this file, and remove all the other extraneous stuff, and then I'd only be left with the logo itself. So far so good. But the logo is still in a square box, and being created from only a single path, I could not easily remove that. That's when I had to dive deeper. Time to learn us some SVG!
Okay, okay, I'm only kidding. Well... sort of. After looking up the Paths Tutorial on MDN, I quickly gave up on the idea of just editing this by hand, even with Atom's awesome SVG previewer. I needed a graphical editor. A quick Google search led me to MacSVG, which is both free AND gives you full control over the source code, while still providing helpful tools to arrange things graphically.
I'll spare you a bunch of extremely detailed and complicated fiddling with this editor. Safe to say I spent about an hour or two just whipping the outer shape of the logo into a circle. In the process, I actually learned quite a bit about how SVG paths work, and the practical difference between Bezier curves and elliptical arcs. But eventually, I had my round Codewars logo, and I had it in SVG format!

So, next, I uploaded this file to Fontello, downloaded my new font, and added it to my website theme. I'll spare you the details of another half hour or so of annoying fiddling, but in the end, it worked. Well, sorta. After reloading the site (which looked fine in the preview) in Chrome, all the other badges had disappeared, and only the CodeWars badge remained. But when I loaded the site in Safari, it looked fine, just as expected. I supposed I’ll try to fix this eventually, but after all that work, I needed a little break.
0 notes
Note
Do you have any advice on how to start an rp blog? I feel like there's so much to do and so many specific things, it looks intimidating, but I really want to get into it (and your blog seems like a safe space to ask as a baby in the matter)

Hi! Thanks you for asking and for trusting. I do admit that rping on tumblr can look daunting and there is a series of things that are considered “etiquette” that might not be obvious for newcomers. And the only way to learn is to ask, right? As I’m not sure if you would like something more specific or a step-by-step, I’m going to go through the whole process with pictures.
1. Setting up the blog
You might want to make a new e-mail account for each blog you want. I recommend making a gmail/google account, so you may be able to use other services and associate them with your blog. I’ll go into more details in a minute.
Some people would rather have a personal blog and then making the RP blog as a side-blog. Or a “hub” blog and many side-blogs so they have everything centralized. The downside is that you can’t follow people with side-blogs, only the main – and some rpers are a little suspicious of personal blogs, so if you intend to go this route it might be a good idea to state somewhere in your blog that you have a RP blog.
Tip : It isn’t said too often, but I recommend saving your blog’s e-mail and password somewhere, maybe a flashdrive or even google drive. This way, if something happens you will be able to retrieve your account.
When picking the URL, for a very long time tumblr had problems tagging URLs with a hyphen ( - ). I’m not sure if it has been fixed or if there are still some issues, so I recommend only using letters and maybe numbers. Other than that, pick anything that sounds nice to you!
Themes are nice, but not entirely necessary. Not everybody has photoshop skills and all that. Some people do have commissioned themes, but if you want to try your hand at it my first stop is usually @theme-hunter or @sheathemes . They reblog many themes from many creators, so there are always many options that might suit your needs. Some creators offer very newcomer-friendly themes that you can configure a lot of things without much hassle but some might require basic HTML knowledge – a few creators have guides on how to properly set up their themes and are willing to and answer questions, so don’t be afraid to contact them! You can also send me an ask, I’m not a specialist but I can certainly help walk you through the basics.
Tip: @glenthemes have very good themes and a basic installation guide here.
When fiddling with the options, try to pick colors that have nice contrast and are easy to read. If you are bad at picking colors or have problems in finding the code for them, I recommend trying this link. There is also this one that auto-generate palettes.
Tip : If you mess with your theme, remember there is the Theme Recovery.
Tip: If you use Chrome or Firefox you can set up different profiles and associate each with a different blog, so you don’t need to log out from any of your accounts.
There are two pages that I recommend having: one is an about your muse. If they are an OC, it is always a good idea to have at least some information out there to make things easier. If they are from a canon source, not everybody is familiar with the material so it might be a good idea to state. For example, if you are going to roleplay as Altria/Arturia, it is a good idea to have a “RP blog for Saber (Altria Pendragon) from FGO/FSN “ somewhere visible. The other page that is a good idea having is a rules/guidelines page. This one can be a little intimidating, but it is usually a way to communicate important things. For example: are you comfortable writing violence? Do you have any personal triggers? There is something you absolutely won’t write? There are things you may figure out along the way and it is absolutely ok to fine-tune this session every now and then. Some people also credit source for their icons and graphics in general in their rules/guidelines page.
If you are using the tumblr default themes, when you create a new page you can turn on the option to show a link to the page. If you are using a custom theme, most of the time you will have to link it manually.

Oh, and if you are planning to do a multimuse, it might be a good idea to list which muses you have. The same goes for a hub blog; list the muses and link to the pages.
Icons aren’t necessary but are considered commonplace. You can find some icons I’ve done here but there are plenty of other sources. If you want to do your own icons, keep in mind to don’t make them too big, as a courtesy to your mutuals.
Tip: Anything larger than 300 pixels will be stretched to fit the post. As of today ( 4/29/2021) the posts are currently 540 pixels wide. This can be useful as making banners for your blog.
Tumblr allow users to “pin” posts. This mean that they will always visible if you access your blog, even on dash/mobile. You can use this to set up a post with basic links for mobile users or something else. For example, if you are out on vacations and won’t be able to do replies, you can pin a hiatus notice and then remove the pin once you are back.
2. Introducing yourself
Time to officially join the fun! (insert a “Hi, Zuko here” joke) Don’t worry if you don’t have a fancy promo graphic or anything, most people make their initial introduction with a simple post.

(as you can see, I’m not very good at saying ‘hi’)
Try to introduce yourself in a few lines, but make sure to state which muse you RP as. Some people also like adding their pen name/alias and establishing a brand. Follow as many people as you want that reblogged or liked your post, and tumblr is going to start recommending other blogs that are related to the tags you use normally or have any relation to the people you follow. You can put as many tags as you want, but tumblr will disregard more than 6 tags in their system. Try tags like “<fandom> rp” and “<fandom> roleplay” along with the media, such as “movie” “video game”, “anime” and so on.
It might also be a good idea to follow a few RP memes blogs. They often have options to break the ice, like one-liners that your mutual can send you.
Tip: Don’t forget to turn on the asks and the anon
3. Practical advice
Alright, now that you have a few mutuals, it is time to get to some general tips:
Tumblr can be a little “iffy”, and a great quality of life extension for RPers and navigation in general is installing the New Xkit extension. They offer a number of options to enhance your tumblr experience, but the ones I consider essential are the “editable reblogs”, “quick tags” and “blacklist”. Get it for Chrome or Firefox. Update (12/25/2021): There is another option called Xkit Rewritten that recently added the option to trim reblogs. Get it for Chrome or Firefox.
As a rule of thumb I recommend writing your RPs using Google Docs before posting or replying. By doing this you can do some spell check and if your browser crashes for any reason you can easily recover your work. You can also use Word, Open Office, or any text editor you feel like.
Because I’m a bit of a perfectionist, I also have Grammarly ( Chrome / Firefox ) installed for an extra layer of spell/grammar check. There is a subscription option, but the free one works perfectly fine.
To make things easier to locate, always tag the URL of your RP partner when doing a reply. There are other useful things you can tag, such as open starters, memes, and such.
Risking being obvious here, but when you are not interacting as your character it might be a good idea to tag as “ooc” or “out of character”.
Some people like making google docs with basic info and other useful stuff for easier access on mobile. It is a recent trend, it might be easier to edit as opposed to going through tumblr page editor and dealing with the HTML. You can find some templates here and here. Some people use a site called carrd instead.
Tumblr’s activity can be unreliable, so don’t be afraid of contacting your partner to see if they have gotten your reply after a few weeks. However, some people also enjoy using the RP Thread Tracker in order to be on top of things. It might be a good idea to check it out.
Because of Tumblr shadowbanning and shenanigans, it isn’t unusual for people to have NSFW sideblogs (sometimes referred as sin blogs). If you want to write smut, it might be a good idea to consider making one. Update (12/25/2021): tumblr now is hiding a few selected tags on the ios app, meaning that certain posts with the NSFW tag won’t appear at all. You can read about this here.
Some people don’t like replying to asks, as Tumblr won’t let you remove the initial ask. It has become common to see people making new posts to reply to asks. This is a simple example:

As you can see, I used the mention to have the RP partner notified then I copied and pasted their question on my post and used the quote to indicate it. You can also have fancy graphics, like a line to separate the contents, just do whatever you feel like with the formatting or keep it simple.
To make sure your partner got the answer, I recommend copying the link to the post and pasting on the ask and then replying it privately. An example sent to my rp blog:

4. Basic Etiquette
Ok, this is a little subjective most of the time but here are a few things that are considered universal courtesy.
Never reblog someone else’s headcanons. If you enjoy it, maybe it should politely contact the author and ask if it is ok to write something based on their original idea but you should never downright copy or lift something from another creator. It is considered rude, or even theft in some cases.
Don’t reblog threads you are not involved with. It is ok to leave a like, but never reblog. This is because Tumblr can mess up the notifications and disrupt the flow of the RP.
Don’t copy other people’s graphics. It is very rude and sometimes they commission (aka: paid) for it.
Trim your posts. What does that mean? Every time you reblog with a reply, the post tends to get longer and longer, and it can cluster your and your mutuals’ dashes. This is why the New X-Kit’s “editable reblogs” is an almost must-have tool. If for some reason you can’t install X-Kit (if you are on mobile for example), then remove the previous post or ask your partner to trim for you.
Never take control of your RP partner’s muse. This is called “godmodding” and it is heavily frowned upon. It is ok to control your muse and the possible NPCs that you inserted, but never seize someone else’s character. Likewise, it can also be very upsetting if you use what people call “meta-gaming”, applying knowledge that your muse shouldn’t know about the other. For example, let’s say your RP partner’s muse is a vampire, but they have never disclosed that information to your muse, who also doesn’t have an excuse to know that (for example, being a vampire hunter) so it can be quite jarring sometimes. When in doubt, contact your partner.
This should go without saying, but RPing sexual themes with users under the age of 18 are illegal. It doesn’t matter if the age of consent in your location is lower, once you join Tumblr you are abiding by their user guidelines and the law of the state they are located in. If you are an adult, don’t engage minors with these topics, maybe a fade to black would be a better option. If you are a minor, don’t insist or you might cause a lot of legal problems for others.
Try to tag anything triggering. Violence, gore, NSFW. Both Tumblr and the New Xkit have options to block keywords.
When picking PSDs or graphics for your blog, you should avoid templates that change the color of the skin of POCs muses and try to pick the right race/ethnicity of the muse you are going to RP as. I won’t go through a lot of details, as it is a rather lengthy subject in an already lengthy conversation but keep this in the back of your mind.
Some RPers don’t like when you reblog memes from them without sending anything. Try to always reblog from a source or to interact with the person you are reblogging from, it can be rather disheartening to be seen as a meme source rather than a RP blog. This isn’t a rule and some people don’t mind, but it is always a good idea to try to do this.
This might be more of a pet peeve of mine than proper etiquette, but it is ok to use small font. What is not ok is use small font + underscript. Some people have disabilities that might make it harder for them to read it, so it might be a good idea to refrain from using it. Maybe if you feel like doing something fancier every now and then, but I wouldn’t recommend making this a habit.
Mun and Muse are different entities. Remember that it isn’t because a muse does something (especially a villain one) that the mun condones something. Never assume anything about the mun, when in doubt talk to them.
Be mindful of your partners and treat them the way you would like to be treated.
As a rule of thumb, always talk to your RP partner. It is only fun as long both of you are enjoying it.
5. Closing Words
This got longer than I expected.
Despite all of that, don’t be too worried about not being very good at first. I assure you that you will get better with time, so don’t be afraid of experimenting as long you feel comfortable. And don’t be afraid of saying “no” if something bothers you.
My inbox is always open to questions and ideas, so feel free to contact me anytime!
I would also ask my followers: there is advice I missed/overlooked? Anything you would like someone have told you when you first started? Add your thoughts so I can update this.
Happy RPing!
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers
This is an extended version of my essay “When front-end means full-stack” which was published in the wonderful Increment magazine put out by Stripe. It’s also something of an evolution of a couple other of my essays, “The Great Divide” and “Ooops, I guess we’re full-stack developers now.”
The moment I fell in love with front-end development was when I discovered the style.css file in WordPress themes. That’s where all the magic was (is!) to me. I could (can!) change a handful of lines in there and totally change the look and feel of a website. It’s an incredible game to play.

Back when I was cowboy-coding over FTP. Although I definitely wasn’t using CSS grid!
By fiddling with HTML and CSS, I can change the way you feel about a bit of writing. I can make you feel more comfortable about buying tickets to an event. I can increase the chances you share something with your friends.
That was well before anybody paid me money to be a front-end developer, but even then I felt the intoxicating mix of stimuli that the job offers. Front-end development is this expressive art form, but often constrained by things like the need to directly communicate messaging and accomplish business goals.
Front-end development is at the intersection of art and logic. A cross of business and expression. Both left and right brain. A cocktail of design and nerdery.
I love it.

Looking back at the courses I chose from middle school through college, I bounced back and forth between computer-focused classes and art-focused classes, so I suppose it’s no surprise I found a way to do both as a career.
The term “Front-End Developer” is fairly well-defined and understood. For one, it’s a job title. I’ll bet some of you literally have business cards that say it on there, or some variation like: “Front-End Designer,” “UX Developer,” or “UI Engineer.” The debate around what those mean isn’t particularly interesting to me. I find that the roles are so varied from job-to-job and company-to-company that job titles will never be enough to describe things. Getting this job is more about demonstrating you know what you’re doing more than anything else¹.
Chris Coyier Front-End Developer
The title variations are just nuance. The bigger picture is that as long as the job is building websites, front-enders are focused on the browser. Quite literally:
front-end = browsers
back-end = servers
Even as the job has changed over the decades, that distinction still largely holds.
As “browser people,” there are certain truths that come along for the ride. One is that there is a whole landscape of different browsers and, despite the best efforts of standards bodies, they still behave somewhat differently. Just today, as I write, I dealt with a bug where a date string I had from an API was in a format such that Firefox threw an error when I tried to use the .toISOString() JavaScript API on it, but was fine in Chrome. That’s just life as a front-end developer. That’s the job.
Even across that landscape of browsers, just on desktop computers, there is variance in how users use that browser. How big do they have the window open? Do they have dark mode activated on their operating system? How’s the color gamut on that monitor? What is the pixel density? How’s the bandwidth situation? Do they use a keyboard and mouse? One or the other? Neither? All those same questions apply to mobile devices too, where there is an equally if not more complicated browser landscape. And just wait until you take a hard look at HTML emails.
That’s a lot of unknowns, and the answers to developing for that unknown landscape is firmly in the hands of front-end developers.

Into the unknoooooowwwn. – Elsa
The most important aspect of the job? The people that use these browsers. That’s why we’re building things at all. These are the people I’m trying to impress with my mad CSS skills. These are the people I’m trying to get to buy my widget. Who all my business charts hinge upon. Who’s reaction can sway my emotions like yarn in the breeze. These users, who we put on a pedestal for good reason, have a much wider landscape than the browsers do. They speak different languages. They want different things. They are trying to solve different problems. They have different physical abilities. They have different levels of urgency. Again, helping them is firmly in the hands of front-end developers. There is very little in between the characters we type into our text editors and the users for whom we wish to serve.
Being a front-end developer puts us on the front lines between the thing we’re building and the people we’re building it for, and that’s a place some of us really enjoy being.
That’s some weighty stuff, isn’t it? I haven’t even mentioned React yet.
The “we care about the users” thing might feel a little precious. I’d think in a high functioning company, everyone would care about the users, from the CEO on down. It’s different, though. When we code a <button>, we’re quite literally putting a button into a browser window that users directly interact with. When we adjust a color, we’re adjusting exactly what our sighted users see when they see our work.

That’s not far off from a ceramic artist pulling a handle out of clay for a coffee cup. It’s applying craftsmanship to a digital experience. While a back-end developer might care deeply about the users of a site, they are, as Monica Dinculescu once told me in a conversation about this, “outsourcing that responsibility.”
We established that front-end developers are browser people. The job is making things work well in browsers. So we need to understand the languages browsers speak, namely: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript². And that’s not just me being some old school fundamentalist; it’s through a few decades of everyday front-end development work that knowing those base languages is vital to us doing a good job. Even when we don’t work directly with them (HTML might come from a template in another language, CSS might be produced from a preprocessor, JavaScript might be mostly written in the parlance of a framework), what goes the browser is ultimately HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, so that’s where debugging largely takes place and the ability of the browser is put to work.
CSS will always be my favorite and HTML feels like it needs the most love — but JavaScript is the one we really need to examine The last decade has seen JavaScript blossom from a language used for a handful of interactive effects to the predominant language used across the entire stack of web design and development. It’s possible to work on websites and writing nothing but JavaScript. A real sea change.
JavaScript is all-powerful in the browser. In a sense, it supersedes HTML and CSS, as there is nothing either of those languages can do that JavaScript cannot. HTML is parsed by the browser and turned into the DOM, which JavaScript can also entirely create and manipulate. CSS has its own model, the CSSOM, that applies styles to elements in the DOM, which JavaScript can also create and manipulate.
This isn’t quite fair though. HTML is the very first file that browsers parse before they do the rest of the work needed to build the site. That firstness is unique to HTML and a vital part of making websites fast.
In fact, if the HTML was the only file to come across the network, that should be enough to deliver the basic information and functionality of a site.
That philosophy is called Progressive Enhancement. I’m a fan, myself, but I don’t always adhere to it perfectly. For example, a <form> can be entirely functional in HTML, when it’s action attribute points to a URL where the form can be processed. Progressive Enhancement would have us build it that way. Then, when JavaScript executes, it takes over the submission and has the form submit via Ajax instead, which might be a nicer experience as the page won’t have to refresh. I like that. Taken further, any <button> outside a form is entirely useless without JavaScript, so in the spirit of Progressive Enhancement, I should wait until JavaScript executes to even put that button on the page at all (or at least reveal it). That’s the kind of thing where even those of us with the best intentions might not always toe the line perfectly. Just put the button in, Sam. Nobody is gonna die.
JavaScript’s all-powerfulness makes it an appealing target for those of us doing work on the web — particularly as JavaScript as a language has evolved to become even more powerful and ergonomic, and the frameworks that are built in JavaScript become even more-so. Back in 2015, it was already so clear that JavaScript was experiencing incredible growth in usage, Matt Mullenweg, co-founder of WordPress, gave the developer world homework: “Learn JavaScript Deeply”³. He couldn’t have been more right. Half a decade later, JavaScript has done a good job of taking over front-end development. Particularly if you look at front-end development jobs.
While the web almanac might show us that only 5% of the top-zillion sites use React compared to 85% including jQuery, those numbers are nearly flipped when looking around at front-end development job requirements.
I’m sure there are fancy economic reasons for all that, but jobs are as important and personal as it gets for people, so it very much matters.
So we’re browser people in a sea of JavaScript building things for people. If we take a look at the job at a practical day-to-day tasks level, it’s a bit like this:
Translate designs into code
Think in terms of responsive design, allowing us to design and build across the landscape of devices
Build systemically. Construct components and patterns, not one-offs.
Apply semantics to content
Consider accessibility
Worry about the performance of the site. Optimize everything. Reduce, reuse, recycle.
Just that first bullet point feels like a college degree to me. Taken together, all of those points certainly do.
This whole list is a bit abstract though, so let’s apply it to something we can look at. What if this website was our current project?

Our brains and fingers go wild!
Let’s build the layout with CSS grid.
What fonts are those? Do we need to load them in their entirety or can we subset them? What happens as they load in? This layout feels like it will really suffer from font-shifting jank.
There are some repeated patterns here. We should probably make a card design pattern. Every website needs a good card pattern.
That’s a gorgeous color scheme. Are the colors mathematically related? Should we make variables to represent them individually or can we just alter a single hue as needed? Are we going to use custom properties in our CSS? Colors are just colors though, we might not need the cascading power of them just for this. Should we just use Sass variables? Are we going to use a CSS preprocessor at all?
The source order is tricky here. We need to order things so that they make sense for a screen reader user. We should have a meeting about what the expected order of content should be, even if we’re visually moving things around a bit with CSS grid.
The photographs here are beautifully shot. But some of them match the background color of the site… can we get away with alpha-transparent PNGs here? Those are always so big. Can any next-gen formats help us? Or should we try to match the background of a JPG with the background of the site seamlessly. Who’s writing the alt text for these?
There are some icons in use here. Inline SVG, right? Certainly SVG of some kind, not icon fonts, right? Should we build a whole icon system? I guess it depends on how we’re gonna be building this thing more broadly. Do we have a build system at all?
What’s the whole front-end plan here? Can I code this thing in vanilla HTML, CSS, and JavaScript? Well, I know I can, but what are the team expectations? Client expectations? Does it need to be a React thing because it’s part of some ecosystem of stuff that is already React? Or Vue or Svelte or whatever? Is there a CMS involved?
I’m glad the designer thought of not just the “desktop” and “mobile” sizes but also tackled an in-between size. Those are always awkward. There is no interactivity information here though. What should we do when that search field is focused? What gets revealed when that hamburger is tapped? Are we doing page-level transitions here?
I could go on and on. That’s how front-end developers think, at least in my experience and in talking with my peers.
A lot of those things have been our jobs forever though. We’ve been asking and answering these questions on every website we’ve built for as long as we’ve been doing it. There are different challenges on each site, which is great and keeps this job fun, but there is a lot of repetition too.
Allow me to get around to the title of this article.
While we’ve been doing a lot of this stuff for ages, there is a whole pile of new stuff we’re starting to be expected to do, particularly if we’re talking about building the site with a modern JavaScript framework. All the modern frameworks, as much as they like to disagree about things, agree about one big thing: everything is a component. You nest and piece together components as needed. Even native JavaScript moves toward its own model of Web Components.

I like it, this idea of components. It allows you and your team to build the abstractions that make the most sense to you and what you are building.
Your Card component does all the stuff your card needs to do. Your Form component does forms how your website needs to do forms. But it’s a new concept to old developers like me. Components in JavaScript have taken hold in a way that components on the server-side never did. I’ve worked on many a WordPress website where the best I did was break templates into somewhat arbitrary include() statements. I’ve worked on Ruby on Rails sites with partials that take a handful of local variables. Those are useful for building re-usable parts, but they are a far cry from the robust component models that JavaScript frameworks offer us today.
All this custom component creation makes me a site-level architect in a way that I didn’t use to be. Here’s an example. Of course I have a Button component. Of course I have an Icon component. I’ll use them in my Card component. My Card component lives in a Grid component that lays them out and paginates them. The whole page is actually built from components. The Header component has a SearchBar component and a UserMenu component. The Sidebar component has a Navigation component and an Ad component. The whole page is just a special combination of components, which is probably based on the URL, assuming I’m all-in on building our front-end with JavaScript. So now I’m dealing with URLs myself, and I’m essentially the architect of the entire site. [Sweats profusely]
Like I told ya, a whole pile of new responsibility.
Components that are in charge of displaying content are almost certainly not hard-coded with data in them. They are built to be templates. They are built to accept data and construct themselves based on that data. In the olden days, when we were doing this kind of templating, the data has probably already arrived on the page we’re working on. In a JavaScript-powered app, it’s more likely that that data is fetched by JavaScript. Perhaps I’ll fetch it when the component renders. In a stack I’m working with right now, the front end is in React, the API is in GraphQL and we use Apollo Client to work with data. We use a special “hook” in the React components to run the queries to fetch the data we need, and another special hook when we need to change that data. Guess who does that work? Is it some other kind of developer that specializes in this data layer work? No, it’s become the domain of the front-end developer.
Speaking of data, there is all this other data that a website often has to deal with that doesn’t come from a database or API. It’s data that is really only relevant to the website at this moment in time.
Which tab is active right now?
Is this modal dialog open or closed?
Which bar of this accordion is expanded?
Is this message bar in an error state or warning state?
How many pages are you paginated in?
How far is the user scrolled down the page?
Front-end developers have been dealing with that kind of state for a long time, but it’s exactly this kind of state that has gotten us into trouble before. A modal dialog can be open with a simple modifier class like <div class="modal is-open"> and toggling that class is easy enough with .classList.toggle(".is-open"); But that’s a purely visual treatment. How does anything else on the page know if that modal is open or not? Does it ask the DOM? In a lot of jQuery-style apps of yore, yes, it would. In a sense, the DOM became the “source of truth” for our websites. There were all sorts of problems that stemmed from this architecture, ranging from a simple naming change destroying functionality in weirdly insidious ways, to hard-to-reason-about application logic making bug fixing a difficult proposition.
Front-end developers collectively thought: what if we dealt with state in a more considered way? State management, as a concept, became a thing. JavaScript frameworks themselves built the concept right in, and third-party libraries have paved and continue to pave the way. This is another example of expanding responsibility. Who architects state management? Who enforces it and implements it? It’s not some other role, it’s front-end developers.
There is expanding responsibility in the checklist of things to do, but there is also work to be done in piecing it all together. How much of this state can be handled at the individual component level and how much needs to be higher level? How much of this data can be gotten at the individual component level and how much should be percolated from above? Design itself comes into play. How much of the styling of this component should be scoped to itself, and how much should come from more global styles?
It’s no wonder that design systems have taken off in recent years. We’re building components anyway, so thinking of them systemically is a natural fit.
Let’s look at our design again:

A bunch of new thoughts can begin!
Assuming we’re using a JavaScript framework, which one? Why?
Can we statically render this site, even if we’re building with a JavaScript framework? Or server-side render it?
Where are those recipes coming from? Can we get a GraphQL API going so we can ask for whatever we need, whenever we need it?
Maybe we should pick a CMS that has an API that will facilitate the kind of front-end building we want to do. Perhaps a headless CMS?
What are we doing for routing? Is the framework we chose opinionated or unopinionated about stuff like this?
What are the components we need? A Card, Icon, SearchForm, SiteMenu, Img… can we scaffold these out? Should we start with some kind of design framework on top of the base framework?
What’s the client state we might need? Current search term, current tab, hamburger open or not, at least.
Is there a login system for this site or not? Are logged in users shown anything different?
Is there are third-party componentry we can leverage here?
Maybe we can find one of those fancy image components that does blur-up loading and lazy loading and all that.
Those are all things that are in the domain of front-end developers these days, on top of everything that we already need to do. Executing the design, semantics, accessibility, performance… that’s all still there. You still need to be proficient in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and how the browser works. Being a front-end developer requires a haystack of skills that grows and grows. It’s the natural outcome of the web getting bigger. More people use the web and internet access grows. The economy around the web grows. The capability of browsers grows. The expectations of what is possible on the web grows. There isn’t a lot shrinking going on around here.
We’ve already reached the point where most front-end developers don’t know the whole haystack of responsibilities. There are lots of developers still doing well for themselves being rather design-focused and excelling at creative and well-implemented HTML and CSS, even as job posts looking for that dwindle.
There are systems-focused developers and even entire agencies that specialize in helping other companies build and implement design systems. There are data-focused developers that feel most at home making the data flow throughout a website and getting hot and heavy with business logic. While all of those people might have “front-end developer” on their business card, their responsibilities and even expectations of their work might be quite different. It’s all good, we’ll find ways to talk about all this in time.
In fact, how we talk about building websites has changed a lot in the last decade. Some of my early introduction to web development was through WordPress. WordPress needs a web server to run, is written in PHP, and stores it’s data in a MySQL database. As much as WordPress has evolved, all that is still exactly the same. We talk about that “stack” with an acronym: LAMP, or Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP. Note that literally everything in the entire stack consists of back-end technologies. As a front-end developer, nothing about LAMP is relevant to me.
But other stacks have come along since then. A popular stack was MEAN (Mongo, Express, Angular and Node). Notice how we’re starting to inch our way toward more front-end technologies? Angular is a JavaScript framework, so as this stack gained popularity, so too did talking about the front-end as an important part of the stack. Node and Express are both JavaScript as well, albeit the server-side variant.
The existence of Node is a huge part of this story. Node isn’t JavaScript-like, it’s quite literally JavaScript. It makes a front-end developer already skilled in JavaScript able to do server-side work without too much of a stretch.
“Serverless” is a much more modern tech buzzword, and what it’s largely talking about is running small bits of code on cloud servers. Most often, those small bits of code are in Node, and written by JavaScript developers. These days, a JavaScript-focused front-end developer might be writing their own serverless functions and essentially being their own back-end developer. They’ll think of themselves as full-stack developers, and they’ll be right.
Shawn Wang coined a term for a new stack this year: STAR or Design System, TypeScript, Apollo, and React. This is incredible to me, not just because I kind of like that stack, but because it’s a way of talking about the stack powering a website that is entirely front-end technologies. Quite a shift.
I apologize if I’ve made you feel a little anxious reading this. If you feel like you’re behind in understanding all this stuff, you aren’t alone.
In fact, I don’t think I’ve talked to a single developer who told me they felt entirely comfortable with the entire world of building websites. Everybody has weak spots or entire areas where they just don’t know the first dang thing. You not only can specialize, but specializing is a pretty good idea, and I think you will end up specializing to some degree whether you plan to or not. If you have the good fortune to plan, pick things that you like. You’ll do just fine.
The only constant in life is change.
– Heraclitus – Motivational Poster – Chris Coyier
¹ I’m a white dude, so that helps a bunch, too. ↩️ ² Browsers speak a bunch more languages. HTTP, SVG, PNG… The more you know the more you can put to work! ↩️ ³ It’s an interesting bit of irony that WordPress websites generally aren’t built with client-side JavaScript components. ↩️
The post The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers published first on https://deskbysnafu.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers
This is an extended version of my essay “When front-end means full-stack” which was published in the wonderful Increment magazine put out by Stripe. It’s also something of an evolution of a couple other of my essays, “The Great Divide” and “Ooops, I guess we’re full-stack developers now.”
The moment I fell in love with front-end development was when I discovered the style.css file in WordPress themes. That’s where all the magic was (is!) to me. I could (can!) change a handful of lines in there and totally change the look and feel of a website. It’s an incredible game to play.

Back when I was cowboy-coding over FTP. Although I definitely wasn’t using CSS grid!
By fiddling with HTML and CSS, I can change the way you feel about a bit of writing. I can make you feel more comfortable about buying tickets to an event. I can increase the chances you share something with your friends.
That was well before anybody paid me money to be a front-end developer, but even then I felt the intoxicating mix of stimuli that the job offers. Front-end development is this expressive art form, but often constrained by things like the need to directly communicate messaging and accomplish business goals.
Front-end development is at the intersection of art and logic. A cross of business and expression. Both left and right brain. A cocktail of design and nerdery.
I love it.

Looking back at the courses I chose from middle school through college, I bounced back and forth between computer-focused classes and art-focused classes, so I suppose it’s no surprise I found a way to do both as a career.
The term “Front-End Developer” is fairly well-defined and understood. For one, it’s a job title. I’ll bet some of you literally have business cards that say it on there, or some variation like: “Front-End Designer,” “UX Developer,” or “UI Engineer.” The debate around what those mean isn’t particularly interesting to me. I find that the roles are so varied from job-to-job and company-to-company that job titles will never be enough to describe things. Getting this job is more about demonstrating you know what you’re doing more than anything else¹.
Chris Coyier Front-End Developer
The title variations are just nuance. The bigger picture is that as long as the job is building websites, front-enders are focused on the browser. Quite literally:
front-end = browsers
back-end = servers
Even as the job has changed over the decades, that distinction still largely holds.
As “browser people,” there are certain truths that come along for the ride. One is that there is a whole landscape of different browsers and, despite the best efforts of standards bodies, they still behave somewhat differently. Just today, as I write, I dealt with a bug where a date string I had from an API was in a format such that Firefox threw an error when I tried to use the .toISOString() JavaScript API on it, but was fine in Chrome. That’s just life as a front-end developer. That’s the job.
Even across that landscape of browsers, just on desktop computers, there is variance in how users use that browser. How big do they have the window open? Do they have dark mode activated on their operating system? How’s the color gamut on that monitor? What is the pixel density? How’s the bandwidth situation? Do they use a keyboard and mouse? One or the other? Neither? All those same questions apply to mobile devices too, where there is an equally if not more complicated browser landscape. And just wait until you take a hard look at HTML emails.
That’s a lot of unknowns, and the answers to developing for that unknown landscape is firmly in the hands of front-end developers.

Into the unknoooooowwwn. – Elsa
The most important aspect of the job? The people that use these browsers. That’s why we’re building things at all. These are the people I’m trying to impress with my mad CSS skills. These are the people I’m trying to get to buy my widget. Who all my business charts hinge upon. Who’s reaction can sway my emotions like yarn in the breeze. These users, who we put on a pedestal for good reason, have a much wider landscape than the browsers do. They speak different languages. They want different things. They are trying to solve different problems. They have different physical abilities. They have different levels of urgency. Again, helping them is firmly in the hands of front-end developers. There is very little in between the characters we type into our text editors and the users for whom we wish to serve.
Being a front-end developer puts us on the front lines between the thing we’re building and the people we’re building it for, and that’s a place some of us really enjoy being.
That’s some weighty stuff, isn’t it? I haven’t even mentioned React yet.
The “we care about the users” thing might feel a little precious. I’d think in a high functioning company, everyone would care about the users, from the CEO on down. It’s different, though. When we code a <button>, we’re quite literally putting a button into a browser window that users directly interact with. When we adjust a color, we’re adjusting exactly what our sighted users see when they see our work.

That’s not far off from a ceramic artist pulling a handle out of clay for a coffee cup. It’s applying craftsmanship to a digital experience. While a back-end developer might care deeply about the users of a site, they are, as Monica Dinculescu once told me in a conversation about this, “outsourcing that responsibility.”
We established that front-end developers are browser people. The job is making things work well in browsers. So we need to understand the languages browsers speak, namely: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript². And that’s not just me being some old school fundamentalist; it’s through a few decades of everyday front-end development work that knowing those base languages is vital to us doing a good job. Even when we don’t work directly with them (HTML might come from a template in another language, CSS might be produced from a preprocessor, JavaScript might be mostly written in the parlance of a framework), what goes the browser is ultimately HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, so that’s where debugging largely takes place and the ability of the browser is put to work.
CSS will always be my favorite and HTML feels like it needs the most love — but JavaScript is the one we really need to examine The last decade has seen JavaScript blossom from a language used for a handful of interactive effects to the predominant language used across the entire stack of web design and development. It’s possible to work on websites and writing nothing but JavaScript. A real sea change.
JavaScript is all-powerful in the browser. In a sense, it supersedes HTML and CSS, as there is nothing either of those languages can do that JavaScript cannot. HTML is parsed by the browser and turned into the DOM, which JavaScript can also entirely create and manipulate. CSS has its own model, the CSSOM, that applies styles to elements in the DOM, which JavaScript can also create and manipulate.
This isn’t quite fair though. HTML is the very first file that browsers parse before they do the rest of the work needed to build the site. That firstness is unique to HTML and a vital part of making websites fast.
In fact, if the HTML was the only file to come across the network, that should be enough to deliver the basic information and functionality of a site.
That philosophy is called Progressive Enhancement. I’m a fan, myself, but I don’t always adhere to it perfectly. For example, a <form> can be entirely functional in HTML, when it’s action attribute points to a URL where the form can be processed. Progressive Enhancement would have us build it that way. Then, when JavaScript executes, it takes over the submission and has the form submit via Ajax instead, which might be a nicer experience as the page won’t have to refresh. I like that. Taken further, any <button> outside a form is entirely useless without JavaScript, so in the spirit of Progressive Enhancement, I should wait until JavaScript executes to even put that button on the page at all (or at least reveal it). That’s the kind of thing where even those of us with the best intentions might not always toe the line perfectly. Just put the button in, Sam. Nobody is gonna die.
JavaScript’s all-powerfulness makes it an appealing target for those of us doing work on the web — particularly as JavaScript as a language has evolved to become even more powerful and ergonomic, and the frameworks that are built in JavaScript become even more-so. Back in 2015, it was already so clear that JavaScript was experiencing incredible growth in usage, Matt Mullenweg, the founding developer of WordPress, gave the developer world homework: “Learn JavaScript Deeply”³. He couldn’t have been more right. Half a decade later, JavaScript has done a good job of taking over front-end development. Particularly if you look at front-end development jobs.
While the web almanac might show us that only 5% of the top-zillion sites use React compared to 85% including jQuery, those numbers are nearly flipped when looking around at front-end development job requirements.
I’m sure there are fancy economic reasons for all that, but jobs are as important and personal as it gets for people, so it very much matters.
So we’re browser people in a sea of JavaScript building things for people. If we take a look at the job at a practical day-to-day tasks level, it’s a bit like this:
Translate designs into code
Think in terms of responsive design, allowing us to design and build across the landscape of devices
Build systemically. Construct components and patterns, not one-offs.
Apply semantics to content
Consider accessibility
Worry about the performance of the site. Optimize everything. Reduce, reuse, recycle.
Just that first bullet point feels like a college degree to me. Taken together, all of those points certainly do.
This whole list is a bit abstract though, so let’s apply it to something we can look at. What if this website was our current project?

Our brains and fingers go wild!
Let’s build the layout with CSS grid.
What fonts are those? Do we need to load them in their entirety or can we subset them? What happens as they load in? This layout feels like it will really suffer from font-shifting jank.
There are some repeated patterns here. We should probably make a card design pattern. Every website needs a good card pattern.
That’s a gorgeous color scheme. Are the colors mathematically related? Should we make variables to represent them individually or can we just alter a single hue as needed? Are we going to use custom properties in our CSS? Colors are just colors though, we might not need the cascading power of them just for this. Should we just use Sass variables? Are we going to use a CSS preprocessor at all?
The source order is tricky here. We need to order things so that they make sense for a screen reader user. We should have a meeting about what the expected order of content should be, even if we’re visually moving things around a bit with CSS grid.
The photographs here are beautifully shot. But some of them match the background color of the site… can we get away with alpha-transparent PNGs here? Those are always so big. Can any next-gen formats help us? Or should we try to match the background of a JPG with the background of the site seamlessly. Who’s writing the alt text for these?
There are some icons in use here. Inline SVG, right? Certainly SVG of some kind, not icon fonts, right? Should we build a whole icon system? I guess it depends on how we’re gonna be building this thing more broadly. Do we have a build system at all?
What’s the whole front-end plan here? Can I code this thing in vanilla HTML, CSS, and JavaScript? Well, I know I can, but what are the team expectations? Client expectations? Does it need to be a React thing because it’s part of some ecosystem of stuff that is already React? Or Vue or Svelte or whatever? Is there a CMS involved?
I’m glad the designer thought of not just the “desktop” and “mobile” sizes but also tackled an in-between size. Those are always awkward. There is no interactivity information here though. What should we do when that search field is focused? What gets revealed when that hamburger is tapped? Are we doing page-level transitions here?
I could go on and on. That’s how front-end developers think, at least in my experience and in talking with my peers.
A lot of those things have been our jobs forever though. We’ve been asking and answering these questions on every website we’ve built for as long as we’ve been doing it. There are different challenges on each site, which is great and keeps this job fun, but there is a lot of repetition too.
Allow me to get around to the title of this article.
While we’ve been doing a lot of this stuff for ages, there is a whole pile of new stuff we’re starting to be expected to do, particularly if we’re talking about building the site with a modern JavaScript framework. All the modern frameworks, as much as they like to disagree about things, agree about one big thing: everything is a component. You nest and piece together components as needed. Even native JavaScript moves toward its own model of Web Components.

I like it, this idea of components. It allows you and your team to build the abstractions that make the most sense to you and what you are building.
Your Card component does all the stuff your card needs to do. Your Form component does forms how your website needs to do forms. But it’s a new concept to old developers like me. Components in JavaScript have taken hold in a way that components on the server-side never did. I’ve worked on many a WordPress website where the best I did was break templates into somewhat arbitrary include() statements. I’ve worked on Ruby on Rails sites with partials that take a handful of local variables. Those are useful for building re-usable parts, but they are a far cry from the robust component models that JavaScript frameworks offer us today.
All this custom component creation makes me a site-level architect in a way that I didn’t use to be. Here’s an example. Of course I have a Button component. Of course I have an Icon component. I’ll use them in my Card component. My Card component lives in a Grid component that lays them out and paginates them. The whole page is actually built from components. The Header component has a SearchBar component and a UserMenu component. The Sidebar component has a Navigation component and an Ad component. The whole page is just a special combination of components, which is probably based on the URL, assuming I’m all-in on building our front-end with JavaScript. So now I’m dealing with URLs myself, and I’m essentially the architect of the entire site. [Sweats profusely]
Like I told ya, a whole pile of new responsibility.
Components that are in charge of displaying content are almost certainly not hard-coded with data in them. They are built to be templates. They are built to accept data and construct themselves based on that data. In the olden days, when we were doing this kind of templating, the data has probably already arrived on the page we’re working on. In a JavaScript-powered app, it’s more likely that that data is fetched by JavaScript. Perhaps I’ll fetch it when the component renders. In a stack I’m working with right now, the front end is in React, the API is in GraphQL and we use Apollo Client to work with data. We use a special “hook” in the React components to run the queries to fetch the data we need, and another special hook when we need to change that data. Guess who does that work? Is it some other kind of developer that specializes in this data layer work? No, it’s become the domain of the front-end developer.
Speaking of data, there is all this other data that a website often has to deal with that doesn’t come from a database or API. It’s data that is really only relevant to the website at this moment in time.
Which tab is active right now?
Is this modal dialog open or closed?
Which bar of this accordion is expanded?
Is this message bar in an error state or warning state?
How many pages are you paginated in?
How far is the user scrolled down the page?
Front-end developers have been dealing with that kind of state for a long time, but it’s exactly this kind of state that has gotten us into trouble before. A modal dialog can be open with a simple modifier class like <div class="modal is-open"> and toggling that class is easy enough with .classList.toggle(".is-open"); But that’s a purely visual treatment. How does anything else on the page know if that modal is open or not? Does it ask the DOM? In a lot of jQuery-style apps of yore, yes, it would. In a sense, the DOM became the “source of truth” for our websites. There were all sorts of problems that stemmed from this architecture, ranging from a simple naming change destroying functionality in weirdly insidious ways, to hard-to-reason-about application logic making bug fixing a difficult proposition.
Front-end developers collectively thought: what if we dealt with state in a more considered way? State management, as a concept, became a thing. JavaScript frameworks themselves built the concept right in, and third-party libraries have paved and continue to pave the way. This is another example of expanding responsibility. Who architects state management? Who enforces it and implements it? It’s not some other role, it’s front-end developers.
There is expanding responsibility in the checklist of things to do, but there is also work to be done in piecing it all together. How much of this state can be handled at the individual component level and how much needs to be higher level? How much of this data can be gotten at the individual component level and how much should be percolated from above? Design itself comes into play. How much of the styling of this component should be scoped to itself, and how much should come from more global styles?
It’s no wonder that design systems have taken off in recent years. We’re building components anyway, so thinking of them systemically is a natural fit.
Let’s look at our design again:

A bunch of new thoughts can begin!
Assuming we’re using a JavaScript framework, which one? Why?
Can we statically render this site, even if we’re building with a JavaScript framework? Or server-side render it?
Where are those recipes coming from? Can we get a GraphQL API going so we can ask for whatever we need, whenever we need it?
Maybe we should pick a CMS that has an API that will facilitate the kind of front-end building we want to do. Perhaps a headless CMS?
What are we doing for routing? Is the framework we chose opinionated or unopinionated about stuff like this?
What are the components we need? A Card, Icon, SearchForm, SiteMenu, Img… can we scaffold these out? Should we start with some kind of design framework on top of the base framework?
What’s the client state we might need? Current search term, current tab, hamburger open or not, at least.
Is there a login system for this site or not? Are logged in users shown anything different?
Is there are third-party componentry we can leverage here?
Maybe we can find one of those fancy image components that does blur-up loading and lazy loading and all that.
Those are all things that are in the domain of front-end developers these days, on top of everything that we already need to do. Executing the design, semantics, accessibility, performance… that’s all still there. You still need to be proficient in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and how the browser works. Being a front-end developer requires a haystack of skills that grows and grows. It’s the natural outcome of the web getting bigger. More people use the web and internet access grows. The economy around the web grows. The capability of browsers grows. The expectations of what is possible on the web grows. There isn’t a lot shrinking going on around here.
We’ve already reached the point where most front-end developers don’t know the whole haystack of responsibilities. There are lots of developers still doing well for themselves being rather design-focused and excelling at creative and well-implemented HTML and CSS, even as job posts looking for that dwindle.
There are systems-focused developers and even entire agencies that specialize in helping other companies build and implement design systems. There are data-focused developers that feel most at home making the data flow throughout a website and getting hot and heavy with business logic. While all of those people might have “front-end developer” on their business card, their responsibilities and even expectations of their work might be quite different. It’s all good, we’ll find ways to talk about all this in time.
In fact, how we talk about building websites has changed a lot in the last decade. Some of my early introduction to web development was through WordPress. WordPress needs a web server to run, is written in PHP, and stores it’s data in a MySQL database. As much as WordPress has evolved, all that is still exactly the same. We talk about that “stack” with an acronym: LAMP, or Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP. Note that literally everything in the entire stack consists of back-end technologies. As a front-end developer, nothing about LAMP is relevant to me.
But other stacks have come along since then. A popular stack was MEAN (Mongo, Express, Angular and Node). Notice how we’re starting to inch our way toward more front-end technologies? Angular is a JavaScript framework, so as this stack gained popularity, so too did talking about the front-end as an important part of the stack. Node and Express are both JavaScript as well, albeit the server-side variant.
The existence of Node is a huge part of this story. Node isn’t JavaScript-like, it’s quite literally JavaScript. It makes a front-end developer already skilled in JavaScript able to do server-side work without too much of a stretch.
“Serverless” is a much more modern tech buzzword, and what it’s largely talking about is running small bits of code on cloud servers. Most often, those small bits of code are in Node, and written by JavaScript developers. These days, a JavaScript-focused front-end developer might be writing their own serverless functions and essentially being their own back-end developer. They’ll think of themselves as full-stack developers, and they’ll be right.
Shawn Wang coined a term for a new stack this year: STAR or Design System, TypeScript, Apollo, and React. This is incredible to me, not just because I kind of like that stack, but because it’s a way of talking about the stack powering a website that is entirely front-end technologies. Quite a shift.
I apologize if I’ve made you feel a little anxious reading this. If you feel like you’re behind in understanding all this stuff, you aren’t alone.
In fact, I don’t think I’ve talked to a single developer who told me they felt entirely comfortable with the entire world of building websites. Everybody has weak spots or entire areas where they just don’t know the first dang thing. You not only can specialize, but specializing is a pretty good idea, and I think you will end up specializing to some degree whether you plan to or not. If you have the good fortune to plan, pick things that you like. You’ll do just fine.
The only constant in life is change.
– Heraclitus – Motivational Poster – Chris Coyier
¹ I’m a white dude, so that helps a bunch, too. ↩️ ² Browsers speak a bunch more languages. HTTP, SVG, PNG… The more you know the more you can put to work! ↩️ ³ It’s an interesting bit of irony that WordPress websites generally aren’t built with client-side JavaScript components. ↩️
The post The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers appeared first on CSS-Tricks.
You can support CSS-Tricks by being an MVP Supporter.
The Widening Responsibility for Front-End Developers published first on https://deskbysnafu.tumblr.com/
0 notes