#IAM framework
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Elevating Security: Exploring the Comprehensive Services Provided by IDM Technologies, Your Premier Identity and Access Management Service Provider in India
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring secure access to organizational resources have become paramount. Identity and Access Management (IAM) serves as the linchpin in achieving these objectives, offering a comprehensive suite of services to fortify the cybersecurity posture of businesses. As your trusted Identity and Access Management Service Provider in India, IDM Technologies takes the lead in unraveling the array of services that contribute to a robust IAM framework.
Understanding the Core Services Provided by IDM Technologies:
1. Authentication Services:
At the heart of IAM lies authentication, the process of verifying the identity of users. IDM Technologies specializes in implementing cutting-edge authentication services, including multi-factor authentication, biometrics, and adaptive authentication. This ensures a secure and seamless user verification process.
2. Authorization Services:
Once users are authenticated, IDM Technologies provides robust authorization services. This involves defining access control policies and assigning permissions based on roles and responsibilities within the organization. The goal is to ensure that individuals have the appropriate level of access to resources.
3. Single Sign-On (SSO) Solutions:
SSO is a cornerstone of IAM, allowing users to log in once and access multiple systems seamlessly. IDM Technologies implements SSO solutions, reducing the need for users to remember multiple credentials, enhancing user experience, and minimizing the risk of password-related security issues.
4. User Lifecycle Management:
IDM Technologies facilitates efficient user lifecycle management, covering the entire span from onboarding to offboarding. This includes user provisioning to grant access upon joining the organization and deprovisioning to promptly revoke access when individuals leave.
5. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
RBAC is a fundamental principle in IAM, and IDM Technologies tailors RBAC frameworks to align with the organizational structure and hierarchy. This ensures that access permissions are assigned based on predefined roles, streamlining access control.
6. Identity Governance Services:
Identity governance involves establishing policies and processes to manage identities effectively. IDM Technologies assists organizations in implementing robust identity governance strategies, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards.
7. Access Management Services:
IAM includes access management, a pivotal service in controlling access to data, applications, and systems. IDM Technologies provides businesses with robust access management solutions, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
8. Federated Identity Services:
Federation enables secure communication and authentication between different systems. IDM Technologies, as a leading Identity and Access Management Service Provider in India, implements federated identity services to facilitate seamless and secure interactions across diverse platforms.
9. Password Management Services:
IDM Technologies addresses the critical aspect of password management, implementing services that enhance password security, enforce password policies, and mitigate the risk of unauthorized access through compromised credentials.
Why Choose IDM Technologies as Your Identity and Access Management Service Provider in India:
1. Expertise in IAM Solutions:
IDM Technologies brings a wealth of expertise in IAM, understanding the intricacies of managing digital identities and access control in diverse organizational environments.
2. Customized Solutions for Indian Businesses:
Recognizing the unique challenges and regulatory considerations in India, IDM Technologies offers IAM solutions specifically tailored to the needs of businesses in the region.
3. Robust Security Measures:
Security is a top priority, and IDM Technologies prioritizes the implementation of robust security measures, encryption protocols, and compliance checks to safeguard sensitive data.
4. Seamless Integration:
IDM Technologies ensures seamless integration of IAM solutions with existing IT infrastructure, minimizing disruptions and optimizing the overall user experience.
Conclusion: Empowering Digital Security with IDM Technologies
In conclusion, IAM is not just a singular service but a comprehensive suite of solutions provided by IDM Technologies, your premier Identity and Access Management Service Provider in India. By choosing IDM Technologies, businesses unlock the potential for a seamless, secure, and customized IAM framework. Trust IDM Technologies to be your partner in navigating the complexities of identity and access management, fortifying your organization’s cybersecurity defenses in the dynamic digital landscape.
#IAM framework#IAM#cybersecurity#IDM Technologies#Digital Security with IDM Technologies#Identity and Access Management
0 notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I think this part of my loathing of seeing this article passed around "i am tw, iam staying in the closet" bc it is a diary entry that was explicitly not supposed to be advice or a rubric. She origanilly aays its just 1 narrative to take in then when it gets past around she says hey this was me venting i didnt intend for anyone to read this.
I think this is the major interest in this piece. A view into the interiority of a tw whos been closeted for 20 yrs and her personal xp growin up then being a closeted tw in a University WGS dept. Some ppl might call this a fetishistic interest in the interiority of this tw, oh how they love poking around in the frankenstein monsters guts, poking his brain to see what horrid mismatched limb will jump.
I think the main reason @autolenaphilia interacted with this is bc this article was passed around by a bunch of transmisogynist who are adpting and pulling together the transmisogyny of jeniffer and her recounting of cismanhating that exists in primarily cisfeminist spaces and by extension radical and queer spaces. Jennifer does not bring up cafab transness or transmasculinity once in this article yet it is cited as inspiration for truther framework.
I do think the way that jennifer talks about not wanting to acquiesce is kinda built on a faulty conjecture which is that if she transitioned she would be able to talk about femininity in these spaces... at one point she says this probably wouldnt be true(mb just for her) but then goes back to the original argumentation on many occasions. This argumentation taken to conlusion posits that it is easier to discourse or even exist in those spaces as a tw than as a cis man that u will be more include and less ridiculed. At the time of this article she had never actually tried out this proposition, so she never got to see how this prop is at least in all the copius amounts of personal and anecdotal xp i have false. But this prop is useful for ppl who want push tw have it easier and that men are reviled for being men. Enter prager xcuse me truthers.
I also hate internalized oppression framework, imo it is an idpol tool used to shift blame from the brainwashed oppressed to som aspirational that oppressive ideology comes naturally to. Is she promoting transmisogynistic ideas? Yah, shes not bad for this but it is why its useful to truthers, and part of why it hurts to read as a tw.
@autogyne-redacted i do think its hard to see point 1, 2, and 5 of y shes not trnsn nd say these arent related to passibility. Repercussion are often contingent with passablity. Movin towards phys transn being dysphoria inducing is connected with what expectations of feminity u hav and how u line up with them(i also xp this). And the gap thing is imo her wishing she could be passable w ease and recognizing she cant so settling and saying its not worth it to try.
I think lena is apply a broader scope of trans xp to jennifers xp i dnt think this is even necessarily harmful and i dnt think shes even saying jen is wrong for it shes saying her words are easy to coopt that they are capering to these tmras which they are however unitentionally. U could also take things ive said in the past and warp them into tmra shit. I fortunately didnt write these things in a medium article. She is handling in other ways and this is wut conv therapy wants... thats what it seems they go for a lot again doesnt mean jen is bad nd lena doest say shes wrong for this. The only thing lena says is she doesnt want this for herself thats not restricting jens autonomy. And that the article and responses made her sick. They made me feel bad too. This isnt necessarily a moral judgement. It could be but idk.
All this is a dissection. I hate it. I wish her vent diary post wasnt being aired, analyzed, and discoursed. Im doing it right now ffs! It makes me want to leave the internet. I hope ppl stop talkn bout it...but they wont bc the corpse of this diary can be a useful weapon against tw so itll keep gettn used.
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tech Advice 1:
If you're a student or a fresher in computer science, sign up for AWS free tier (free for 1 year) and learn about the different services - Lambda, DynamoDB, EC2, RDS, S3, Cognito, IAM.
You can buy any course on Udemy - NodeJs, Python, C++, Java, PhP or any language/framework you're interested in and is supported by AWS.
Be it MEAN/MERN, Python, Java or any stack you use, it's a useful skill.
(I've experience but the access to this was never provided and I didn't get to learn as much as I wanted to and it's causing me trouble with getting a job)
You can also go for GCP/Azure if that looks good to you.
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Your Journey Through the AWS Universe: From Amateur to Expert
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way businesses and individuals harness technology. At the forefront of this revolution stands Amazon Web Services (AWS), a comprehensive cloud platform offered by Amazon. AWS is a dynamic ecosystem that provides an extensive range of services, designed to meet the diverse needs of today's fast-paced world.

This guide is your key to unlocking the boundless potential of AWS. We'll embark on a journey through the AWS universe, exploring its multifaceted applications and gaining insights into why it has become an indispensable tool for organizations worldwide. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or a newcomer to cloud computing, this comprehensive resource will illuminate the path to mastering AWS and leveraging its capabilities for innovation and growth. Join us as we clarify AWS and discover how it is reshaping the way we work, innovate, and succeed in the digital age.
Navigating the AWS Universe:
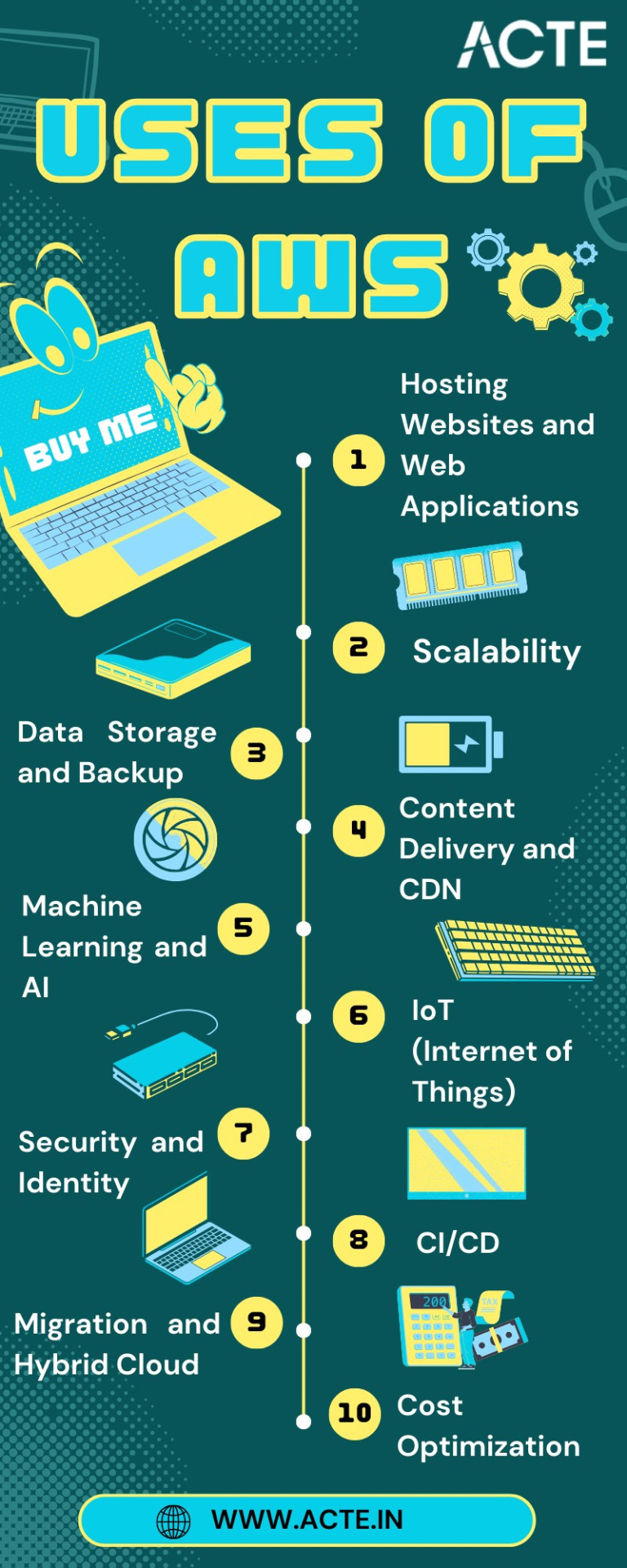
Hosting Websites and Web Applications: AWS provides a secure and scalable place for hosting websites and web applications. Services like Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3 empower businesses to deploy and manage their online presence with unwavering reliability and high performance.
Scalability: At the core of AWS lies its remarkable scalability. Organizations can seamlessly adjust their infrastructure according to the ebb and flow of workloads, ensuring optimal resource utilization in today's ever-changing business environment.
Data Storage and Backup: AWS offers a suite of robust data storage solutions, including the highly acclaimed Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS. These services cater to the diverse spectrum of data types, guaranteeing data security and perpetual availability.
Databases: AWS presents a panoply of database services such as Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, and Redshift, each tailored to meet specific data management requirements. Whether it's a relational database, a NoSQL database, or data warehousing, AWS offers a solution.
Content Delivery and CDN: Amazon CloudFront, AWS's content delivery network (CDN) service, ushers in global content distribution with minimal latency and blazing data transfer speeds. This ensures an impeccable user experience, irrespective of geographical location.
Machine Learning and AI: AWS boasts a rich repertoire of machine learning and AI services. Amazon SageMaker simplifies the development and deployment of machine learning models, while pre-built AI services cater to natural language processing, image analysis, and more.
Analytics: In the heart of AWS's offerings lies a robust analytics and business intelligence framework. Services like Amazon EMR enable the processing of vast datasets using popular frameworks like Hadoop and Spark, paving the way for data-driven decision-making.
IoT (Internet of Things): AWS IoT services provide the infrastructure for the seamless management and data processing of IoT devices, unlocking possibilities across industries.
Security and Identity: With an unwavering commitment to data security, AWS offers robust security features and identity management through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). Users wield precise control over access rights, ensuring data integrity.
DevOps and CI/CD: AWS simplifies DevOps practices with services like AWS CodePipeline and AWS CodeDeploy, automating software deployment pipelines and enhancing collaboration among development and operations teams.
Content Creation and Streaming: AWS Elemental Media Services facilitate the creation, packaging, and efficient global delivery of video content, empowering content creators to reach a global audience seamlessly.
Migration and Hybrid Cloud: For organizations seeking to migrate to the cloud or establish hybrid cloud environments, AWS provides a suite of tools and services to streamline the process, ensuring a smooth transition.
Cost Optimization: AWS's commitment to cost management and optimization is evident through tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Trusted Advisor, which empower users to monitor and control their cloud spending effectively.
In this comprehensive journey through the expansive landscape of Amazon Web Services (AWS), we've embarked on a quest to unlock the power and potential of cloud computing. AWS, standing as a colossus in the realm of cloud platforms, has emerged as a transformative force that transcends traditional boundaries.
As we bring this odyssey to a close, one thing is abundantly clear: AWS is not merely a collection of services and technologies; it's a catalyst for innovation, a cornerstone of scalability, and a conduit for efficiency. It has revolutionized the way businesses operate, empowering them to scale dynamically, innovate relentlessly, and navigate the complexities of the digital era.
In a world where data reigns supreme and agility is a competitive advantage, AWS has become the bedrock upon which countless industries build their success stories. Its versatility, reliability, and ever-expanding suite of services continue to shape the future of technology and business.
Yet, AWS is not a solitary journey; it's a collaborative endeavor. Institutions like ACTE Technologies play an instrumental role in empowering individuals to master the AWS course. Through comprehensive training and education, learners are not merely equipped with knowledge; they are forged into skilled professionals ready to navigate the AWS universe with confidence.
As we contemplate the future, one thing is certain: AWS is not just a destination; it's an ongoing journey. It's a journey toward greater innovation, deeper insights, and boundless possibilities. AWS has not only transformed the way we work; it's redefining the very essence of what's possible in the digital age. So, whether you're a seasoned cloud expert or a newcomer to the cloud, remember that AWS is not just a tool; it's a gateway to a future where technology knows no bounds, and success knows no limits.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
PureVPN Redefines Identity & Access Management Security
PureVPN has introduced a new built-in Password Manager, promising to change the identity & access management game. The shift helps fill a significant hole in cybersecurity dual-vector attacks on credentials and network access by combining password security and VPN protection in an encrypted environment.

According to the recent study conducted by the company (1.5 million breached records, 2023–2025), 2235 percent of high-impact attacks use weak credentials and unprotected networks in combination. Specifically vulnerable were the users with a high-risk profile, such as journalists, crypto holders, and influencers, who in most cases experienced account takeovers or lost money.
The Password Manager is a feature included in the main PureVPN app and is used in conjunction with such functions as Always-On VPN, Dark Web Monitoring, and a free Credential Leak Checker to provide comprehensive IAM security. As PureVPN notes, this built-in framework allows users not to change applications, thereby ensuring a smooth and safe identity & access management process.
The tool provides excellent IAM protocols with auto-fill, password health checks, advanced encryption, and a zero-knowledge architecture. With increasing threats to cybersecurity, the innovation of PureVPN brings a new standard of identity & access management in daily digital life.
For More Info visit: https://www.ciobulletin.com/identity-and-access-management/purevpn-identity-access-management-security
0 notes
Text
Defending the Digital Frontier: Key Skills Validated by a Cloud Security Certification
In 2025, the cloud isn't just a technology; it's the new digital frontier, powering everything from innovative startups in Shela, Gujarat, to the mission-critical operations of global enterprises. However, with unprecedented scalability and agility comes a unique and complex set of security challenges. Protecting these dynamic, distributed environments demands a specialized skillset – one that traditional cybersecurity alone often cannot fully address. This is why a cloud security certification has become the gold standard, not just for demonstrating knowledge, but for validating the precise cloud security skills essential for defending this crucial digital landscape.
For professionals looking to build a resilient cloud security career, understanding the core and emerging skills required is paramount. This guide will delve into the critical cloud security skills that are highly valued by employers, explain how a cloud security certification validates these competencies, and highlight why these credentials are indispensable for safeguarding data and applications in the cloud era.
Why Specialized Cloud Security Skills Are Paramount
The intricacies of cloud computing necessitate a distinct approach to security, setting it apart from traditional on-premise models. Here’s why possessing specialized cloud security skills is non-negotiable:
Shared Responsibility Model: Unlike on-premise where organizations control everything, the cloud operates on a shared responsibility model. Understanding this model and knowing whose responsibility it is to secure what (e.g., the cloud provider secures the infrastructure, the customer secures data and configurations) is foundational.
Dynamic and Ephemeral Resources: Cloud environments are highly agile. Virtual machines, containers, and serverless functions are spun up and down rapidly, often automated. Security needs to be integrated into this dynamic flow, requiring skills in automation, Infrastructure as Code (IaC) security, and continuous monitoring.
Distributed Nature: Cloud services are distributed across regions and availability zones. Securing this vast, interconnected network requires different network security paradigms compared to a centralized data center.
Cloud-Native Services and Tools: Each cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP) offers a unique suite of security services and tools (e.g., AWS Security Hub, Azure Sentinel, Google Security Command Center). Proficiency in these specific tools is crucial for effective cloud defense.
New Attack Vectors: Cloud environments introduce new attack surfaces, such as misconfigured S3 buckets, insecure APIs, or compromised cloud credentials. Specialized skills are needed to identify and mitigate these specific threats.
Compliance in the Cloud: Regulatory frameworks like India's DPDPA, GDPR, and HIPAA apply to cloud data. Implementing and proving compliance in a dynamic cloud environment requires specific expertise.
Core Cloud Security Skills Validated by Certifications
Leading cloud security certifications are meticulously designed to validate a comprehensive array of cloud security skills that directly address the challenges above. These include:
Identity and Access Management (IAM): This is foundational. You'll master skills in managing user identities, defining roles and permissions, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA), and ensuring the principle of least privilege across cloud resources. This includes understanding federated identity and integrating corporate directories with cloud IAM.
Network Security in the Cloud: Key skills include designing and securing Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) or Virtual Networks (VNets), configuring network segmentation, implementing security groups and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs), setting up cloud-native Web Application Firewalls (WAFs), and securing connectivity via VPNs or direct connect services.
Data Protection and Encryption: Validated skills involve implementing encryption for data at rest (e.g., using Key Management Services like AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, Google Cloud KMS) and in transit (e.g., TLS for API endpoints). Understanding data classification, data loss prevention (DLP) strategies, and secure data storage practices (e.g., secure S3 buckets) is paramount.
Logging, Monitoring, and Auditing: Proficiency in configuring cloud-native logging services (e.g., AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, Google Cloud Logging), integrating with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, analyzing security logs, and setting up alerts for suspicious activity. Skills in continuous monitoring and threat detection are validated here.
Compliance and Governance: Cloud security certifications validate your ability to understand and implement security controls that meet various regulatory frameworks (like India's DPDPA, ISO 27001, SOC 2). This includes establishing security policies, conducting audits, and ensuring adherence to industry best practices and cloud security posture management (CSPM).
Incident Response and Forensics in the Cloud: Skills in detecting, analyzing, containing, eradicating, and recovering from cloud-specific security incidents. This involves understanding cloud-native forensic tools and processes for investigating breaches in a distributed cloud environment.
Application Security in the Cloud: Validated skills include securing cloud-native applications, understanding API security, securing serverless functions (e.g., AWS Lambda, Azure Functions), and implementing container security (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes).
Cloud Risk Management: Identifying cloud-specific risks, conducting threat modeling exercises for cloud deployments, and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies.
Beyond the Core: Emerging Cloud Security Skills Validated
As cloud technology rapidly evolves, so do the required security skills. Leading cloud security certifications increasingly incorporate and validate expertise in these emerging areas:
DevSecOps Automation: The ability to integrate security into every phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC) within cloud environments. This includes skills in Infrastructure as Code (IaC) security, security automation tools (e.g., Terraform, CloudFormation), and embedding security into CI/CD pipelines.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Security: As organizations often use more than one cloud provider or integrate cloud with on-premise infrastructure, skills in securing diverse, heterogeneous cloud environments are critical.
AI/ML in Cloud Security: Understanding how Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are leveraged for advanced threat detection, anomaly analysis, and automating security operations within cloud platforms.
Serverless and Container Security: Specific expertise in securing these modern, highly scalable, and often ephemeral computing paradigms, which present unique security challenges compared to traditional virtual machines.
Cloud-Native Security Services: Deep proficiency in the rapidly expanding suite of security services offered by each major cloud provider (e.g., AWS WAF, Azure Firewall, Google Cloud Armor).
How Cloud Security Certifications Validate These Skills
A reputable cloud security certification serves as a robust validation mechanism for these essential cloud security skills through:
Rigorous Exam Blueprints: Certifications base their exams on meticulously defined blueprints that directly reflect industry-demanded skills and knowledge areas.
Performance-Based Assessments: Many advanced cloud security certification exams include hands-on labs or simulations, requiring candidates to demonstrate actual proficiency in configuring, troubleshooting, or deploying security controls in a live cloud environment. This is a critical differentiator.
Comprehensive Training Paths: Certification bodies and their authorized training partners offer structured cloud security training and cloud security courses designed to impart these skills, often including extensive lab work and real-world scenarios. EC-Council, for instance, emphasizes practical learning in their programs, such as the C|CSE (Certified Cloud Security Engineer), which includes significant lab components across multiple cloud providers.
Industry Recognition: When a cloud security certification is widely recognized, it means industry experts, employers, and recruiters trust that the certified individual possesses the validated skills to perform effectively.
Choosing the Right Cloud Security Certification to Validate Your Skills
Given the array of skills required, choosing the right cloud security certification is a strategic decision that depends on your current expertise and career aspirations. Whether you're aiming for a foundational understanding or deep specialization, there's a certification designed to validate specific competencies. For a comprehensive overview of the different credentials and their skill validations, exploring the ultimate guide to the best cloud security certifications in 2025 can provide invaluable insights, helping you to align your learning path with the most sought-after skills in the industry.
The Impact of Validated Skills on Your Cloud Security Career
Possessing validated cloud security skills through a cloud security certification has a profound impact on your career:
Increased Employability: You become a highly attractive candidate for roles where cloud security expertise is a prerequisite.
Higher Earning Potential: Employers are willing to pay a premium for certified professionals who can secure their critical cloud assets.
Ability to Tackle Complex Projects: Your validated skills enable you to confidently take on challenging cloud migration, deployment, and security projects.
Contribution to Organizational Resilience: You become a key player in defending your organization against sophisticated cloud-native threats, directly contributing to its business continuity and reputation.
Clear Career Trajectory: Certified skills provide a strong foundation for continuous learning and progression into more advanced and specialized roles within the cloud security career path.
Conclusion
In 2025, defending the digital frontier requires a specialized arsenal of cloud security skills. From mastering Identity and Access Management and network security in the cloud to understanding compliance and automating security controls, these competencies are vital for safeguarding modern digital infrastructure. A cloud security certification serves as the definitive validator of these crucial skills, proving to employers that you possess the practical abilities needed to excel. By strategically acquiring and validating these key cloud security skills, you position yourself at the forefront of a high-demand industry, ready to protect the most valuable assets in the digital age.
0 notes
Text
Cloud Security Market Emerging Trends Driving Next-Gen Protection Models
The cloud security market is undergoing rapid transformation as organizations increasingly migrate their workloads to cloud environments. With the rise of hybrid and multi-cloud deployments, the demand for robust and scalable cloud security solutions is growing. Emerging trends in cloud security reflect both technological evolution and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. These trends are reshaping how enterprises secure data, manage compliance, and maintain trust in cloud-based systems.

Zero Trust Architecture Becoming a Core Principle
One of the most significant shifts in cloud security is the adoption of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). Zero Trust eliminates the traditional notion of a trusted internal network and instead requires continuous verification of user identities and devices, regardless of their location. With cloud environments inherently distributed, ZTA is becoming essential. Enterprises are integrating identity and access management (IAM), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and micro-segmentation to strengthen their security postures.
AI and ML Enhancing Threat Detection and Response
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cloud security tools is accelerating. These technologies are being used to detect anomalies, automate threat responses, and provide real-time risk analysis. AI-driven security platforms can process massive volumes of data from cloud logs and network activities, enabling early detection of sophisticated attacks like insider threats, ransomware, or credential stuffing. Predictive analytics is also helping security teams to anticipate potential vulnerabilities and reinforce defenses proactively.
SASE and SSE Frameworks Gaining Ground
The Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Security Service Edge (SSE) frameworks are rapidly gaining traction. SASE combines network security functions such as secure web gateways (SWG), cloud access security brokers (CASB), and firewall-as-a-service (FWaaS) with wide-area networking (WAN) capabilities. SSE, a component of SASE, focuses on delivering security services through the cloud. These models offer centralized policy enforcement and visibility, crucial for organizations supporting remote and hybrid workforces.
Cloud-Native Security Tools on the Rise
As organizations build and deploy applications directly in the cloud, the need for cloud-native security is growing. These tools are designed to work seamlessly with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. Examples include cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), cloud security posture management (CSPM), and container security solutions. They allow for automated scanning, misconfiguration detection, and policy management in dynamic environments such as containers, microservices, and Kubernetes.
Shift-Left Security Practices Becoming Standard
In response to increasing DevOps adoption, Shift-Left security is emerging as a best practice. This trend involves integrating security earlier in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), ensuring that vulnerabilities are addressed during code development rather than post-deployment. Tools like automated code scanning, infrastructure as code (IaC) analysis, and security-focused CI/CD pipelines are empowering developers to embed security into their workflows without slowing innovation.
Increased Emphasis on Regulatory Compliance and Data Sovereignty
Regulatory requirements are evolving globally, and organizations must ensure compliance with data privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and upcoming regional cloud regulations. There is a growing trend toward data sovereignty, where governments require that data be stored and processed within specific geographic boundaries. This is pushing cloud providers to localize data centers and offer compliance-friendly security configurations tailored to regional laws.
Serverless and Edge Computing Security Gaining Focus
The expansion of serverless architectures and edge computing introduces new security challenges. These technologies reduce infrastructure management but also create ephemeral and distributed attack surfaces. Security solutions are evolving to monitor and protect functions triggered by events in real-time. Serverless security tools focus on identity-based access, runtime protection, and least privilege policies, while edge security emphasizes endpoint hardening, network segmentation, and data encryption at rest and in motion.
Third-Party and Supply Chain Risk Management
Cloud environments often rely on a vast ecosystem of third-party tools and APIs, which can introduce vulnerabilities. There is a growing focus on supply chain security, ensuring that software components and service providers adhere to strong security practices. Enterprises are increasingly conducting security assessments, continuous monitoring, and third-party audits to manage these risks effectively.
Conclusion
The cloud security market is evolving rapidly to keep pace with the complexity and scale of modern cloud infrastructure. Emerging trends such as Zero Trust, AI-driven security, SASE/SSE frameworks, and Shift-Left development practices reflect a broader movement toward adaptive, intelligent, and integrated security models. As cloud adoption accelerates, businesses must stay ahead by embracing these innovations and investing in comprehensive, forward-looking security strategies. The future of cloud security lies in being proactive, predictive, and resilient—ensuring trust, agility, and compliance in an increasingly digital world.
0 notes
Text
Information Security: Building a Resilient Future Through Data Protection
In an increasingly digital world, data has become one of the most valuable assets for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Every transaction, communication, and operation involves data in some form. As the volume, complexity, and sensitivity of this data continue to grow, so does the risk associated with its misuse or compromise. This is where Information Security steps in as a critical component of modern digital infrastructure.
What is Information Security?
Information Security (InfoSec) refers to the practice of defending information—whether digital or physical—from unauthorized access, disruption, modification, or destruction. It encompasses a broad set of strategies, policies, and tools aimed at ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, commonly referred to as the CIA Triad:
Confidentiality ensures that sensitive data is only accessible to those who have the proper authorization.
Integrity maintains the accuracy and completeness of data by preventing unauthorized modification.
Availability guarantees that information and systems are accessible to authorized users when needed.
The Evolving Threat Landscape
The threat landscape in information security is constantly changing, driven by technological advancements and the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals. Some of the most common threats include:
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks: These exploit human behavior to gain unauthorized access to systems or sensitive information.
Ransomware: Malicious software that encrypts data and demands payment for its release.
Insider Threats: These occur when employees or contractors misuse their access for malicious purposes or by mistake.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): Long-term, targeted attacks often carried out by well-funded threat actors.
Zero-Day Exploits: Attacks that take advantage of unknown or unpatched vulnerabilities in software or hardware.
With these threats increasing in frequency and impact, proactive and adaptive information security strategies are more important than ever.
Key Domains of Information Security
Information security is a multi-layered field that includes several specialized areas:
1. Network Security
Protects internal networks from intrusions by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and virtual private networks (VPNs).
2. Application Security
Focuses on securing software applications by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities during the development process and through updates.
3. Endpoint Security
Secures devices such as computers, smartphones, and tablets that connect to the network.
4. Data Security
Involves encryption, masking, and secure storage to protect data both at rest and in transit.
5. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Controls who has access to what resources, and ensures proper authentication and authorization.
6. Cloud Security
As businesses increasingly move to the cloud, protecting cloud-based infrastructures, platforms, and data becomes essential.
Information Security Frameworks and Standards
To ensure consistency and compliance, many organizations adopt established frameworks and standards such as:
ISO/IEC 27001: A globally recognized standard for managing information security.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A set of guidelines for improving critical infrastructure security.
GDPR and HIPAA: Regulatory standards that enforce strict data protection rules in specific sectors and regions.
Implementing these frameworks helps organizations reduce risk, maintain compliance, and create a culture of security awareness.
The Human Factor in Information Security
Despite advances in technology, humans remain one of the weakest links in the security chain. Employees may fall victim to phishing emails, use weak passwords, or accidentally leak sensitive data. That’s why training and awareness are just as important as technical solutions.
Effective information security programs include:
Regular employee training and simulated phishing exercises
Clear security policies and procedures
Encouraging a security-first mindset across departments
Future Trends in Information Security
The future of Information Security is being shaped by new technologies and shifting work environments. Some key trends include:
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: These technologies help detect anomalies, automate threat responses, and improve predictive analytics.
Zero Trust Architecture: A security model that assumes no user or device should be trusted by default.
Decentralized Identity Management: Blockchain and similar technologies are offering new ways to verify identity securely.
Quantum Computing: While still in development, quantum computers pose both opportunities and challenges for encryption and data security.

0 notes
Text
Zero Trust Architecture: Why It’s Essential for Modern Businesses
In today’s digital-first world, traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer enough. With remote work, cloud adoption, and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, businesses must rethink how they protect their data and networks. That’s where Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) comes in.
✅ What Is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a security model that operates on the principle:
“Never trust, always verify.”
Instead of automatically trusting users or devices inside the corporate network, Zero Trust requires continuous authentication, authorization, and validation of every access request—regardless of location.
🚨 Why Traditional Security Is Failing
Old security models assume anything inside the network is safe. But in 2025:
70% of attacks originate from compromised internal accounts
Remote employees and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies expose new vulnerabilities
SaaS tools and third-party integrations expand your attack surface
A single compromised endpoint can now threaten your entire organization.
🔐 Key Components of Zero Trust Architecture
Identity & Access Management (IAM)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Least-privilege access policies
Micro-Segmentation
Breaks the network into zones to contain threats
Continuous Monitoring
Real-time analytics to detect and respond to anomalies
Device Trust
Every device must meet security standards before accessing resources
Encryption & Data Protection
Data is protected both in transit and at rest
💼 Business Benefits of Zero Trust
✅ Enhanced Security Stop lateral movement of threats and reduce attack surface.
✅ Support for Remote Work Secure access for users working from anywhere.
✅ Regulatory Compliance Helps meet GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection laws.
✅ Scalable Security Grows with your cloud infrastructure and modern work environment.
🚀 How R&B Networks Can Help
At R&B Networks, we specialize in designing and implementing Zero Trust strategies for businesses of all sizes. Our team helps:
Assess your current infrastructure
Deploy Zero Trust tools and frameworks
Train your team and monitor for threats
Don’t leave your business exposed.
🔗 Ready to Secure Your Business?
Get started with a custom Zero Trust plan today. 👉 Visit: www.randbnetworks.com
0 notes
Text
Is Your Cloud Really Secure? A CISOs Guide to Cloud Security Posture Management

Introduction: When “Cloud-First” Meets “Security-Last”
The cloud revolution has completely transformed how businesses operate—but it’s also brought with it an entirely new battleground. With the speed of cloud adoption far outpacing the speed of cloud security adaptation, many Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) are left asking a critical question: Is our cloud truly secure?
It’s not a rhetorical query. As we move towards multi-cloud and hybrid environments, traditional security tools and mindsets fall short. What worked on-prem doesn’t necessarily scale—or protect—in the cloud. This is where Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) enters the picture. CSPM is no longer optional; it’s foundational.
This blog explores what CSPM is, why it matters, and how CISOs can lead with confidence in the face of complex cloud risks.
1. What Is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a framework, set of tools, and methodology designed to continuously monitor cloud environments to detect and fix security misconfigurations and compliance issues.
CSPM does three key things:
Identifies misconfigurations (like open S3 buckets or misassigned IAM roles)
Continuously assesses risk across accounts, services, and workloads
Enforces best practices for cloud governance, compliance, and security
Think of CSPM as your real-time cloud security radar—mapping the vulnerabilities before attackers do.
2. Why Traditional Security Tools Fall Short in the Cloud
CISOs often attempt to bolt on legacy security frameworks to modern cloud setups. But cloud infrastructure is dynamic. It changes fast, scales horizontally, and spans multiple regions and service providers.
Here’s why old tools don’t work:
No perimeter: The cloud blurs the traditional boundaries. There’s no “edge” to protect.
Complex configurations: Cloud security is mostly about “how” services are set up, not just “what” services are used.
Shadow IT and sprawl: Teams can spin up instances in seconds, often without central oversight.
Lack of visibility: Multi-cloud environments make it hard to see where risks lie without specialized tools.
CSPM is designed for the cloud security era—it brings visibility, automation, and continuous improvement together in one integrated approach.
3. Common Cloud Security Misconfigurations (That You Probably Have Right Now)
Even the most secure-looking cloud environments have hidden vulnerabilities. Misconfigurations are one of the top causes of cloud breaches.
Common culprits include:
Publicly exposed storage buckets
Overly permissive IAM policies
Unencrypted data at rest or in transit
Open management ports (SSH/RDP)
Lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Default credentials or forgotten access keys
Disabled logging or monitoring
CSPM continuously scans for these issues and provides prioritized alerts and auto-remediation.
4. The Role of a CISO in CSPM Strategy
CSPM isn’t just a tool—it’s a mindset shift, and CISOs must lead that cultural and operational change.
The CISO must:
Define cloud security baselines across business units
Select the right CSPM solutions aligned with the organization’s needs
Establish cross-functional workflows between security, DevOps, and compliance teams
Foster accountability and ensure every developer knows they share responsibility for security
Embed security into CI/CD pipelines (shift-left approach)
It’s not about being the gatekeeper. It’s about being the enabler—giving teams the freedom to innovate with guardrails.
5. CSPM in Action: Real-World Breaches That Could Have Been Avoided
Let’s not speak in hypotheticals. Here are a few examples where lack of proper posture management led to real consequences.
Capital One (2019): A misconfigured web application firewall allowed an attacker to access over 100 million customer accounts hosted in AWS.
Accenture (2021): Left multiple cloud storage buckets unprotected, leaking sensitive information about internal operations.
US Department of Defense (2023): An exposed Azure Blob led to the leakage of internal training documents—due to a single misconfiguration.
In all cases, a CSPM solution would’ve flagged the issue—before it became front-page news.
6. What to Look for in a CSPM Solution
With dozens of CSPM tools on the market, how do you choose the right one?
Key features to prioritize:
Multi-cloud support (AWS, Azure, GCP, OCI, etc.)
Real-time visibility and alerts
Auto-remediation capabilities
Compliance mapping (ISO, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, etc.)
Risk prioritization dashboards
Integration with services like SIEM, SOAR, and DevOps tools
Asset inventory and tagging
User behavior monitoring and anomaly detection
You don’t need a tool with bells and whistles. You need one that speaks your language—security.
7. Building a Strong Cloud Security Posture: Step-by-Step
Asset Discovery Map every service, region, and account. If you can’t see it, you can’t secure it.
Risk Baseline Evaluate current misconfigurations, exposure, and compliance gaps.
Define Policies Establish benchmarks for secure configurations, access control, and logging.
Remediation Playbooks Build automation for fixing issues without manual intervention.
Continuous Monitoring Track changes in real time. The cloud doesn’t wait, so your tools shouldn’t either.
Educate and Empower Teams Your teams working on routing, switching, and network security need to understand how their actions affect overall posture.
8. Integrating CSPM with Broader Cybersecurity Strategy
CSPM doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s one pillar in your overall defense architecture.
Combine it with:
SIEM for centralized log collection and threat correlation
SOAR for automated incident response
XDR to unify endpoint, application security, and network security
IAM governance to ensure least privilege access
Zero Trust to verify everything, every time
At EDSPL, we help businesses integrate these layers seamlessly through our managed and maintenance services, ensuring that posture management is part of a living, breathing cyber resilience strategy.
9. The Compliance Angle: CSPM as a Compliance Enabler
Cloud compliance is a moving target. Regulators demand proof that your cloud isn’t just configured—but configured correctly.
CSPM helps you:
Map controls to frameworks like NIST, CIS Benchmarks, SOC 2, PCI, GDPR
Generate real-time compliance reports
Maintain an audit-ready posture across systems such as compute, storage, and backup
10. Beyond Technology: The Human Side of Posture Management
Cloud security posture isn’t just about tech stacks—it’s about people and processes.
Cultural change is key. Teams must stop seeing security as “someone else’s job.”
DevSecOps must be real, not just a buzzword. Embed security in sprint planning, code review, and deployment.
Blameless retrospectives should be standard when posture gaps are found.
If your people don’t understand why posture matters, your cloud security tools won’t matter either.
11. Questions Every CISO Should Be Asking Right Now
Do we know our full cloud inventory—spanning mobility, data center switching, and compute nodes?
Are we alerted in real-time when misconfigurations happen?
Can we prove our compliance posture at any moment?
Is our cloud posture improving month-over-month?
If the answer is “no” to even one of these, CSPM needs to be on your 90-day action plan.
12. EDSPL’s Perspective: Securing the Cloud, One Posture at a Time
At EDSPL, we’ve worked with startups, mid-market leaders, and global enterprises to build bulletproof cloud environments.
Our expertise includes:
Baseline cloud audits and configuration reviews
24/7 monitoring and managed CSPM services
Custom security policy development
Remediation-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Network security, application security, and full-stack cloud protection
Our background vision is simple: empower organizations with scalable, secure, and smart digital infrastructure.
Conclusion: Posture Isn’t Optional Anymore
As a CISO, your mission is to secure the business and enable growth. Without clear visibility into your cloud environment, that mission becomes risky at best, impossible at worst.
CSPM transforms reactive defense into proactive confidence. It closes the loop between visibility, detection, and response—at cloud speed.
So, the next time someone asks, “Is our cloud secure?” — you’ll have more than a guess. You’ll have proof.
Secure Your Cloud with EDSPL Today
Call: +91-9873117177 Email: [email protected] Reach Us | Get In Touch Web: www.edspl.net
Please visit our website to know more about this blog https://edspl.net/blog/is-your-cloud-really-secure-a-ciso-s-guide-to-cloud-security-posture-management/
0 notes
Text
Why Zero Trust Security Models Are a Must in 2025

In 2025, the cybersecurity landscape has evolved dramatically, making traditional perimeter-based defenses obsolete. The rise of remote work, cloud computing, and sophisticated cyber threats necessitates a shift towards Zero Trust Security Models. This approach, emphasizing “never trust, always verify,” ensures robust protection for modern enterprises.
Understanding Zero Trust Security
The Core Principles
Zero Trust Security operates on the premise that no user or device, inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. Key principles include:
Continuous Verification: Every access request is authenticated and authorized based on multiple factors.
Least Privilege Access: Users receive only the access necessary for their roles.
Assumed Breach: The model assumes that breaches can occur, focusing on minimizing potential damage.
These principles align with the guidelines set forth by NIST SP 800–207, which provides a comprehensive framework for implementing Zero Trust architectures.
The Imperative for Zero Trust in 2025
Evolving Threat Landscape
Cyber threats have become more sophisticated, with attackers exploiting vulnerabilities in traditional security models. The increasing prevalence of remote work and cloud services expands the attack surface, making Zero Trust not just advisable but essential.
Regulatory Compliance
Governments and regulatory bodies are mandating stricter cybersecurity measures. Adopting Zero Trust helps organizations comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and others, ensuring data protection and privacy.
Technological Advancements
The integration of AI and machine learning enhances Zero Trust implementations by enabling real-time threat detection and response. These technologies facilitate dynamic policy enforcement, adapting to changing contexts without manual intervention.
Implementing Zero Trust: A Strategic Approach
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Robust IAM systems are foundational to Zero Trust, ensuring that only authenticated users can access resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO) are critical components.
Microsegmentation
Dividing the network into smaller segments limits lateral movement by attackers, containing potential breaches and protecting sensitive data.
Continuous Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of user behavior and network activity allows for the detection of anomalies and swift incident response.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Zero Trust Adoption
Microsoft’s Secure Future Initiative
Microsoft’s initiative exemplifies the effective implementation of Zero Trust principles. By integrating Zero Trust into its security framework, Microsoft has enhanced its ability to protect against internal and external threats.
Surespan’s Transformation
Surespan, a UK-based manufacturer, transitioned to a Zero Trust model to secure its global operations. This shift improved performance, reduced costs, and enhanced collaboration across international teams.
The Role of The Security Outlook
The Security Outlook has been instrumental in highlighting the importance of Zero Trust Security Models. Through in-depth analyses and expert insights, the publication educates organizations on best practices and emerging trends in cybersecurity.
By featuring case studies and expert opinions, The Security Outlook provides valuable resources for businesses aiming to strengthen their security posture.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve, adopting a Zero Trust Security Model is no longer optional — it’s a necessity. Organizations must embrace this paradigm shift to protect their assets, comply with regulations, and maintain customer trust.
The Security Outlook remains a vital resource for staying informed about the latest developments in Zero Trust and broader cybersecurity strategies.
0 notes
Text
Unifying Business Functions Through Intelligent Tech Stack Design
The Power of a Cohesive Enterprise Technology Stack
In the modern business environment, efficiency and adaptability go hand in hand. To keep pace with dynamic markets and shifting customer expectations, enterprises must leverage tech stacks that are both comprehensive and flexible. An intelligently designed technology stack creates synergy across diverse departments, transforming isolated workflows into a synchronized system of operations.
When different business functions—such as marketing, logistics, finance, and customer service—are connected through integrated software platforms, the organization benefits from greater visibility and shared intelligence. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and cloud-based data lakes are just a few of the tools that form the foundation of these smart tech environments. The result is more informed decision-making, enhanced responsiveness, and cost savings across the board.
Tailoring Tools Without Losing Alignment
Although consistency is key, no two departments operate exactly the same. Sales teams need access to real-time customer insights, while HR may prioritize compliance tools and employee engagement platforms. A successful enterprise tech stack respects these variations while maintaining a unified architecture that connects all tools and datasets.
This balance is achieved through scalable platforms that offer customizable modules and seamless third-party integrations. Middleware and APIs allow each department to personalize its tools without breaking the larger framework. As a result, every team works with software that suits its daily tasks while contributing to a larger ecosystem that supports the company’s mission and strategy.
Improving Workflow Through Cross-Functional Automation
Automation is one of the most valuable benefits of a unified tech stack. By integrating systems, businesses can eliminate repetitive tasks and reduce the risk of manual errors. Workflow automation not only boosts productivity but also ensures consistency in business processes across departments.
For example, an automated billing system can pull information from a CRM after a sale closes, generate an invoice through the ERP, and update the accounting software instantly. These seamless handoffs improve turnaround time and reduce administrative burden. Automation also frees employees to focus on high-value activities like strategy, customer engagement, and innovation.
Building for Growth and Future Readiness
A tech stack should not only serve present needs but also support future expansion. Whether scaling up operations, entering new markets, or embracing new technologies, businesses require infrastructure that evolves with them. Cloud-native tools and modular software are essential for this kind of forward compatibility.
By choosing platforms that offer on-demand scalability, businesses can expand their tech capabilities without overhauling their systems. Additionally, companies that invest in platforms with machine learning or predictive analytics features can stay ahead of trends and proactively address challenges before they escalate. This future readiness builds a resilient digital foundation that supports long-term growth.
Strengthening Security While Enhancing Accessibility
Security is another non-negotiable factor in enterprise tech design. With data flowing between departments and across platforms, every component of the stack must uphold strict security protocols. This includes encrypted communication, role-based access control, and regular vulnerability assessments.
At the same time, access to the right information at the right time is crucial for productivity. Identity and access management (IAM) solutions help balance security with ease of use, ensuring that employees get what they need without compromising sensitive data. Smart tech stacks support both agility and accountability, giving IT teams the tools to monitor systems without becoming a bottleneck.
By aligning tools, teams, and technology under a single digital umbrella, enterprises can operate with greater efficiency, flexibility, and resilience. Leveraging enterprise tech stacks across diverse operations means building smarter—not just bigger. It’s about creating an environment where systems speak the same language, departments collaborate more naturally, and growth becomes a built-in feature of the business model.
0 notes
Text
Privileged Access Management Market Size, Share, Analysis, Forecast, and Growth Trends to 2032: Trends Shaping the Future of Access Security
Privileged Access Management Market was valued at USD 2.69 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 17.42 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 23.13% from 2024-2032.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) Market is rapidly gaining traction as organizations worldwide recognize the critical need to secure sensitive credentials and reduce insider threats. The increasing frequency of cyberattacks and data breaches has put PAM solutions at the forefront of cybersecurity strategies, especially in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government across the USA and Europe. Businesses are investing heavily in PAM to ensure strict access controls and maintain compliance with stringent regulations.
Privileged Access Management Market in the US: Trends, Growth Drivers, and Future Outlook
U.S. Market was valued at USD 0.72 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 4.57 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 22.81% from 2024-2032.
Privileged Access Management Market continues to evolve with advancements in cloud adoption, AI, and zero-trust architectures. Enterprises are adopting PAM not just for protection but also to improve operational efficiency by automating credential management and monitoring privileged activities in real-time. This market growth is particularly prominent in the USA and Europe, where digital transformation and regulatory pressures drive demand for comprehensive access governance.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/6666
Market Keyplayers:
Fortinet (FortiPAM, FortiAuthenticator)
BeyondTrust (Password Safe, Privilege Management for Windows & Mac)
CyberArk (Privileged Access Manager, Endpoint Privilege Manager)
Broadcom (Symantec PAM, Symantec PAM Gateway)
Imprivata (OneSign, Privileged Access Management)
Optiv Security (Privileged Access Management Services, Identity & Access Management Solutions)
Okta (Okta Privileged Access, Okta Identity Governance)
IBM (Security Verify Privilege Vault, Security Identity Governance & Intelligence)
Micro Focus (OpenText) (NetIQ Privileged Account Manager, NetIQ Identity Governance)
ManageEngine (Zoho) (PAM360, Password Manager Pro)
HashiCorp (Vault, Boundary)
One Identity (Safeguard for Privileged Sessions, Safeguard for Privileged Passwords)
ARCON (Privileged Access Management, Session Monitoring & Recording)
Netwrix (Privileged Access Management, Auditor for Active Directory)
Delinea (Secret Server, Privilege Manager)
Wallix (Bastion, AdminBastion)
Saviynt (Saviynt for Privileged Access, Identity Governance Cloud)
Senhasegura (PAM Core, DevOps Secret Manager)
KronTech (Single Connect, Dynamic Password Controller)
miniOrange (PAM Solution, Identity Broker)
EmpowerID (Privileged Access Manager, Identity Governance Platform)
StrongDM (Infrastructure Access Platform, Admin UI)
CyberSolve (PAM Advisory, Identity & Access Consulting Services)
Opal Security (Access Review Automation, Just-in-Time Access)
Foxpass (PAM Solution, LDAP-as-a-Service)
Secureden (PAM Software, Remote Access Management)
RevBits (Privileged Access Management, Endpoint Security)
Silverfort (Unified Identity Protection, Secure Access for PAM)
Market Analysis
The PAM market is shaped by the rising sophistication of cyber threats and the increasing complexity of IT environments. Organizations are challenged to protect critical infrastructure and data from unauthorized privileged access. Enhanced regulatory frameworks in the USA and Europe, including GDPR and CCPA, compel businesses to implement stringent access controls. Cloud migration and hybrid IT infrastructures further push the need for dynamic PAM solutions that offer scalability, ease of deployment, and real-time threat detection.
Market Trends
Growing adoption of cloud-native PAM solutions
Integration with Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems
Rise of AI-powered behavioral analytics for anomaly detection
Increased focus on Zero Trust security frameworks
Automation of credential lifecycle management
Expansion of PAM solutions into DevOps environments
Enhanced compliance and audit capabilities
Market Scope
The Privileged Access Management Market scope is broadening as organizations seek comprehensive, scalable solutions to secure critical access points across complex ecosystems.
Dynamic access controls for cloud and on-premises environments
Real-time monitoring and alerting of privileged activities
Automated password vaulting and rotation
Context-based access policies and multi-factor authentication
Integration with enterprise security platforms
Support for hybrid and multi-cloud architectures
Customizable workflows for privileged session management
Forecast Outlook
The PAM Market is poised for robust growth driven by the escalating need for cybersecurity resilience and regulatory compliance. Innovations in AI and machine learning will enhance PAM capabilities, enabling predictive threat detection and automated response. The USA and Europe will continue to lead in market adoption, with organizations increasingly prioritizing privileged access security as a critical component of their overall cybersecurity framework. Market players are expected to focus on delivering integrated, user-friendly solutions that adapt to evolving IT landscapes and threat vectors.
Access Complete Report:https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/privileged-access-management-market-6666
Conclusion
As cyber threats become more sophisticated and regulatory landscapes tighten, the Privileged Access Management Market is emerging as an indispensable pillar of modern cybersecurity. Organizations across the USA and Europe are embracing PAM not only as a security necessity but as a strategic enabler to safeguard critical assets while boosting operational efficiency.
Related Reports:
Discover leading graph database solutions driving growth across the US
Explore the growth trends in the U.S. Identity and Access Management market
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
0 notes
Text
Appit Software Cyber Security Cloud Services: Defend, Detect, Protect
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, frequent, and damaging. Enterprises of all sizes must prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard their data, infrastructure, and reputation. Appit Software Cyber Security Cloud Services are designed to provide a robust, scalable, and proactive defense strategy that protects your organization around the clock.
With a layered security approach, real-time threat detection, and next-gen tools, we empower businesses to defend against attacks, detect anomalies swiftly, and protect critical assets with precision.
Why Choose Appit for Cloud Cybersecurity Services?
At Appit Software, we bring a comprehensive and strategic approach to cybersecurity. Our team of certified security experts leverages cloud-native tools, AI, and automation to mitigate risks before they become threats. We secure your digital transformation with enterprise-grade solutions tailored to your industry, compliance requirements, and business goals.
Key advantages of partnering with Appit:
Cloud-First, Security-Always Architecture
Proactive Threat Detection and Incident Response
AI-Driven Security Analytics
Compliance Readiness and Governance
End-to-End Managed Security Services
Comprehensive Threat Protection Across Your Cloud Ecosystem
Appit offers multi-layered protection across all major cloud platforms including AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. We ensure your workloads, applications, and data remain secure—no matter where they reside.
Our cloud security services include:
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Zero Trust Security Frameworks
Encryption and Key Management
With Appit, you gain visibility, control, and continuous monitoring of your cloud environments to stay ahead of every cyber threat.
Real-Time Threat Detection and Response
A fast response is critical to minimizing damage during a cyber incident. Appit provides Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions powered by AI and behavioral analytics.
We offer:
24/7 Security Operations Center (SOC) Monitoring
Threat Hunting and Automated Detection
Anomaly and Behavior-Based Alerting
Machine Learning for Threat Correlation
Incident Response Playbooks and Containment
Our detection engines are constantly updated to adapt to emerging threats, ensuring immediate response and rapid containment.
Next-Gen Firewall and Network Security
Networks are often the first line of defense—and the first target. Appit fortifies your network perimeter and internal traffic with advanced security controls:
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
Intrusion Detection & Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Micro-Segmentation for East-West Traffic Protection
DNS Filtering and Web Gateways
VPN and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
We secure your network architecture while maintaining high performance, reducing attack surface and eliminating vulnerabilities.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) with Zero Trust
Controlling who accesses your data is just as important as defending it. Appit implements granular IAM policies and Zero Trust security to ensure users only access what they need—nothing more.
Our IAM services include:
Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Identity Federation and Lifecycle Management
Continuous Access Evaluation
With Zero Trust, every user and device must verify before accessing your environment, ensuring maximum protection against internal and external threats.
Data Protection, Backup, and Disaster Recovery
Your data is your most valuable asset—and Appit ensures it’s never compromised or lost. We provide end-to-end data security with encryption, policy enforcement, and reliable backup strategies.
Our services include:
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
At-Rest and In-Transit Encryption
Secure Data Archiving and Retention Policies
Automated Cloud Backups
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
In the event of a breach or outage, we help your organization bounce back quickly, with minimal disruption.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Navigating the regulatory landscape can be overwhelming. Appit simplifies compliance through automated tools, frameworks, and expert guidance.
We support:
GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, ISO 27001, SOC 2, NIST, and more
Risk Assessments and Gap Analysis
Audit-Ready Reporting and Evidence Collection
Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Third-Party Vendor Risk Management
Our goal is to make compliance seamless and sustainable, reducing both risk and overhead.
Security Awareness and Training Programs
Human error is one of the biggest cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Appit helps you build a security-first culture through ongoing education and simulation-based training:
Phishing Simulations
Security Awareness Workshops
Role-Based Cyber Hygiene Training
Executive Security Briefings
Incident Reporting Protocols
Empowered users become your first line of defense, reducing insider threats and unintentional breaches.
Managed Security Services (MSS) for Peace of Mind
Appit provides fully managed cybersecurity services, so your team can focus on innovation while we handle protection. Our MSS include:
24x7x365 SOC Operations
Vulnerability Scanning and Patch Management
SIEM Management and Threat Intelligence
Regular Security Audits and Reports
Strategic Advisory and Security Roadmaps
We act as an extension of your IT team, delivering continuous protection, compliance, and confidence.
Cybersecurity Solutions for Every Industry
Appit tailors cybersecurity strategies to meet the unique challenges of each industry:
Healthcare – HIPAA-compliant data security and secure EHR systems
Finance – High-frequency threat detection, AML compliance, and secure APIs
Retail & eCommerce – PCI-DSS compliance and secure transaction environments
Manufacturing – OT security and industrial system protection
Public Sector – Secure citizen data handling and FedRAMP compliance
We ensure your industry-specific risks are fully accounted for and proactively managed.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is no longer optional—it’s foundational to business success. Appit Software Cyber Security Cloud Services are designed to defend your enterprise against evolving threats, detect malicious activity in real time, and protect your assets with advanced, cloud-native tools.
0 notes