#IPAddressing
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
youtube
0 notes
Text
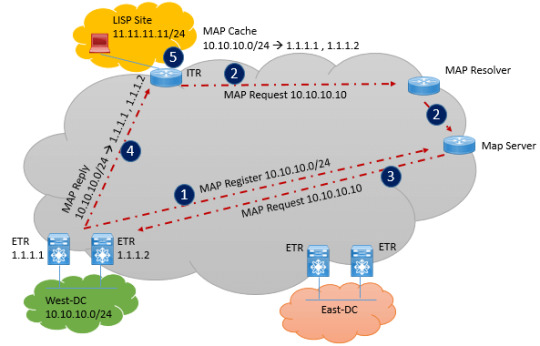
Become an Identity Services Engine expert with our #ISE courses. Master network access control, authentication, and policy enforcement. Empower your organization's security posture with precise control. https://www.dclessons.com/lisp-control-data-plane-fundamentals
#lisp#locatoridseparationprotocol#overlaynetworking#sdaccess#branchnetwork#dataplane#controlplane#mapregistration#maprequest#mapresolver#mapserver#dns#ipaddressing#networkdesign#networkautomation#networksecurity
0 notes
Text
Every device online has one—but most people have no idea what it actually does. This 60-second breakdown makes it super simple. Tap in to level up your tech knowledge!
#IPAddress#InternetBasics#TechExplained#CyberSecurity#Networking101#TechTips#DigitalLiteracy#LearnTech#BeginnerTech#IPv4#IPv6#HowTheInternetWorks#TechReel#InfoReel
0 notes
Link
#DNSconfiguration#DNSmanagement#DNSrequest#DNSsettings#DNStroubleshooting#domainmapping#dynamicIP#emailserver#IPaddress#PTRrecord#PTRupdate#reverseDNS#reverseDNSlookup#reverselookup#SMTPrelay#staticIP#Tier2support#Tier3support#Verizon#Verizonbusinessaccount#Verizonbusinesssupport#VerizonFios#Verizonnetwork#Verizonsupport#Verizontechnicalsupport
0 notes
Text
Understanding IPv4 - A Crucial Step for Network Efficiency | ComSky
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) is the cornerstone of modern networking, providing a unique identification system for devices on the internet. ComSky emphasizes the importance of IPv4 for seamless communication across the globe, ensuring data is routed effectively and securely. Despite the gradual shift to IPv6, IPv4 continues to dominate in network setups, offering compatibility with most systems.
With 32-bit addressing, IPv4 supports approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses, which has been sufficient for decades. However, due to the exponential growth of devices connected to the internet, this address space is nearing exhaustion. ComSky offers solutions to manage and optimize IPv4 usage, including address allocation, subnetting, and transition strategies to IPv6 where necessary.
Stay informed about the evolving landscape of networking and ensure your network infrastructure is both robust and future-proof with IPv4 expertise from ComSky. Visit us to know more about IPv4.
0 notes
Text
What Is Amazon Virtual Private Cloud VPC? Benefits, Features

What is Amazon VPC?
AWS resources can be launched in a logically isolated virtual network that you specify using the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) service. You are in total control of your virtual networking environment, including choosing your own range of IP addresses, setting up subnets, and configuring network gateways and route tables. The majority of the resources in your VPC are compatible with both IPv4 and IPv6, which helps to provide safe and convenient access to resources and apps.
Customizing the network setup of your VPC is simple using Amazon VPC, one of AWS’s core services. For your web servers with internet connection, you can set up a subnet that is visible to the public. Additionally, it enables you to locate your backend systems like databases or application servers in a subnet that faces the private sector and is not connected to the internet. Several security layers, such as network access control lists and security groups, can be used with Amazon VPC to assist manage access to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances within each subnet.
Benefits of Amazon VPC
Increase security
Within your virtual network, secure and keep an eye on connections, filter traffic, and limit instance access.
Save time
Reduce the amount of time you spend configuring, maintaining, and verifying your virtual network.
Manage and control your environment
Create subnets, configure route tables, and select your own IP address range to personalize your virtual network.
How it works
You have complete control over your virtual networking environment with Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), including connectivity, security, and resource placement. Set up your VPC in the AWS service panel to get started. Add resources like Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) instances and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) after that. Lastly, specify how your VPCs interact with one another across AWS Regions, Availability Zones, and accounts.
Use cases
Launch a simple website or blog
Enforce restrictions on inbound and outbound connections to strengthen the security posture of your web application.
Host multi-tier web applications
Establish network connectivity and limitations among your databases, application servers, and web servers.
Create hybrid connections
Create and oversee a VPC network that works with both your on-premises and AWS services.
Amazon virtual private cloud pricing
Why Amazon Virtual Private Cloud?
Although setting up and utilizing an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is free, you can pay for its extra features using usage-based fees. You may modify your Amazon VPC’s control, connectivity, monitoring, and security with the help of AWS’s tools and services. Please refer to the following for precise pricing rates for these components.
There are still usage fees associated with other Amazon Web Services products, like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), which include data transfer fees. Pricing is per VPN connection-hour if you use the optional hardware virtual private network (VPN) connection to link your VPC to your corporate data center. Data transported across VPN connections will be invoiced at standard AWS Data Transfer rates, and partial hours are billed as full hours.
Amazon VPC features
Logs of Flow
To get operational insight into your network dependencies and traffic patterns, identify irregularities and stop data leaks, and troubleshoot network connectivity and configuration issues, you can keep an eye on your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) flow logs that are sent to Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) or Amazon CloudWatch. You can discover more about who started your TCP connections and the packet-level source and destination of traffic passing through intermediary layers by examining the expanded information in flow logs. To help you ful fill some compliance obligations, you can additionally archive your flow logs.
IP Address Manager (IPAM)
Planning, tracking, and monitoring IP addresses for your AWS workloads is made simpler with IPAM. IPAM eliminates the need for spreadsheet-based or in-house planning software by automating IP address assignments to your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud VPC. Additionally, it improves network observability by displaying IP utilization across several VPCs and accounts in a single operational view.
IP Addressing
Resources in your VPC can communicate with resources over the internet and with each other thanks to IP addresses. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing protocols are supported by Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). IPv4-only, dual-stack, and IPv6-only subnets can be created in a VPC, and Amazon EC2 instances can be started in these subnets. Additionally, Amazon offers you a variety of choices for giving your instances public IP addresses. You can use an IP address from the Amazon-provided IPv6 CIDRs, Elastic IPv4 addresses, or public IPv4 addresses. In addition, you have the choice to assign these instances your own IPv4 or IPv6 addresses within the Amazon VPC.
Ingress Routing
This functionality allows you to redirect all incoming and outgoing traffic to and from a virtual private gateway or internet gateway to the elastic network interface of a particular Amazon EC2 instance. Before any traffic reaches your business workloads, route it to a gateway or an Amazon EC2 instance in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Network Access Analyzer
You can confirm that your network on AWS complies with your network security and compliance requirements by using Network Access Analyzer. With the help of Network Access Analyzer, you may define your standards for network security and compliance and find unauthorized network access that doesn’t fit your needs. With the help of Network Access Analyzer, you can comprehend network access to your resources, find ways to strengthen your cloud security posture, and quickly show compliance.
Network Access Control List
An optional security feature for your VPC is a network access control list (network ACL), which functions as a firewall to regulate traffic entering and leaving one or more subnets. Network ACLs can be configured using rules that are comparable to those in your security groups.
Manager of Networks
To assist you in managing and keeping an eye on your network on AWS, Network Manager offers capabilities and tools. IP administration, network security and governance, connectivity management, and network monitoring and troubleshooting are all made simpler with Network Manager.
Analyzer of Reachability
You can examine and troubleshoot network reachability between two resources in your VPC using this static configuration analysis tool. When the source and destination resources are reachable, Reachability Analyzer generates hop-by-hop information about the virtual path between them; when they are not, it identifies the blocking factor.
Security Groups
Establish security groups to regulate incoming and outgoing traffic at the instance level, serving as a firewall for related Amazon EC2 instances. An instance can be linked to one or more security groups at the time of launch. The instance is automatically linked to the VPC’s default group if you don’t specify a group. In your VPC, each instance may be a member of a distinct group.
Mirroring of Traffic
With this capability, you can transfer network traffic to out-of-band security and monitoring appliances for deep packet inspection after copying it from an elastic network interface of Amazon EC2 instances. You may create security and compliance controls, troubleshoot problems, obtain operational insights, and identify network and security anomalies. You can directly view the network packets passing through your VPC with traffic mirroring.
Lattice
You can reliably connect, keep an eye on, and protect conversations between your apps with the aid of this service. Network traffic control, access, and monitoring policies can simplify and standardize compute service connections across instances, containers, and serverless apps.
Public Access Is Blocked by VPC
This feature ensures that resources in your Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) are not accidentally exposed to the public by offering a single declarative control that makes it simple to prevent direct Internet access VPCs via the Internet Gateway or Egress-only Gateway. You can choose to ban only ingress Internet connections or both egress and ingress Internet connections in the VPC.
Read more on Govidhtech.com
#AmazonEC2#AmazonVirtualPrivateCloud#VPC#AmazonVPC#IPaddresses#EC2instances#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#Govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Proxiyum: The Future of Business Automation
Explore the transformative power of Proxiyum, the cutting-edge solution for automating your business tasks. From reducing manual work to improving accuracy, find out how Proxiyum is shaping the future of business automation and what it can do for your organization.

0 notes
Text
Come implementare Privacy Shield per non bloccare domini leciti

Perché il Piracy Shield non funziona e come sarebbe dovuto essere implementato. Nell’era digitale, la gestione della proprietà intellettuale e la lotta contro la pirateria online rappresentano sfide cruciali per i regolatori, le industrie creative e i fornitori di servizi internet. Il “Piracy Shield”, un’iniziativa dell’Autorità per le Garanzie nelle Comunicazioni (AGCOM), rappresenta un tentativo significativo di affrontare il problema della pirateria digitale in Italia. Questo strumento è stato ideato per identificare e bloccare l’accesso ai siti web che violano i diritti di proprietà intellettuale, sfruttando tecnologie di filtraggio degli “FQDN e degli indirizzi IP” (citando testualmente AGCOM). Nonostante le sue nobili intenzioni, il Piracy Shield ha suscitato non poche controversie e dibattiti riguardo la sua efficacia e le implicazioni per la libertà di espressione e il diritto alla privacy. In questo articolo tecnico-scientifico, si intende esplorare e discutere le ragioni per cui il Privacy Shield non ha raggiunto pienamente i suoi obiettivi, mettendo in luce le difficoltà tecniche, legali e etiche incontrate.

Sarà inoltre illustrato come, attraverso un approccio innovativo basato sulla configurazione di record CNAME, sia possibile distinguere tra servizi legittimi e illeciti associati allo stesso indirizzo IPv4. Questa dimostrazione pratica non solo evidenzierà le potenzialità di tali tecniche, ma anche come esse potrebbero essere integrate efficacemente in un framework rinnovato per la lotta alla pirateria, suggerendo modifiche e migliorie al sistema attuale del Piracy Shield. Le Content Delivery Network Le Content Delivery Networks (CDN) sono infrastrutture distribuite di server progettate per ottimizzare la consegna di contenuti web agli utenti finali. Le CDN migliorano la velocità e l’affidabilità di accesso ai dati riducendo la distanza fisica tra il server e l’utente, distribuendo il contenuto su diversi server posizionati in varie località geografiche. Funzionamento delle CDN Quando un utente accede a un sito web che utilizza una CDN, la richiesta di dati non viene inviata direttamente al server principale del sito, ma viene reindirizzata al server della CDN più vicino all’utente. Questo server “edge” contiene copie dei contenuti del sito, come file HTML, immagini, video e altri tipi di dati. Grazie a questa architettura, il tempo di caricamento delle pagine si riduce notevolmente, migliorando l’esperienza dell’utente e riducendo il carico sui server centrali. Mascheramento dell’IP reale Un effetto importante dell’uso delle CDN è il mascheramento dell’indirizzo IP pubblico reale del server di origine dei contenuti. Quando un servizio online adotta una CDN, gli indirizzi IP visibili al pubblico sono quelli dei server della rete CDN. Questo significa che l’IP percepito come fonte del servizio è in realtà quello della CDN, non del server originale. Questo ha implicazioni per la sicurezza, la privacy e la gestione del traffico, ma può anche complicare alcune operazioni di controllo e filtraggio del contenuto. Implicazioni per il filtraggio di contenuti Se un’autorità come AGCOM implementa misure per bloccare l’accesso a contenuti ritenuti illegali (come quelli piratati) mediante il filtraggio degli indirizzi IP attraverso strumenti come il Piracy Shield, si potrebbero verificare problemi significativi. Poiché un singolo indirizzo IP di una CDN può essere utilizzato per trasmettere i contenuti di numerosi servizi diversi, il blocco di quell’IP potrebbe avere l’effetto collaterale di interrompere l’accesso a servizi legittimi e non solo a quelli illegali. Questo scenario potrebbe portare a interruzioni di servizio per utenti che non sono coinvolti nella fruizione di contenuti piratati. Facciamo chiarezza con un esempio pratico Per comprendere meglio come funziona la navigazione su internet e l’interazione con una Content Delivery Network (CDN), prendiamo come esempio il processo di collegamento a un sito web, come “www.libero.it”. Questo esempio ci permetterà di osservare come, durante la navigazione, il nome di dominio inizialmente richiesto possa in realtà essere servito da un dominio completamente diverso, come “d31d9gezsyt1z8.cloudfront.net”, che appartiene a una CDN. DNS Query Il processo inizia quando l’utente digita “www.libero.it” nel browser. Il browser deve risolvere questo nome di dominio in un indirizzo IP per poter stabilire una connessione. Questo avviene tramite una richiesta DNS (Domain Name System). Il browser consulta i server DNS configurati (tipicamente forniti dal provider di servizi internet o specificati manualmente dall’utente) per ottenere l’indirizzo IP associato al nome di dominio. (Si vede evidenziata la richiesta) Ricezione della risposta DNS I server DNS eseguono la ricerca e, una volta trovato l’indirizzo IP, lo restituiscono al browser. Se il dominio è ospitato su una CDN, l’IP restituito sarà quello di uno dei server edge della CDN più vicino all’utente, non l’IP del server originale di “libero.it”. (Si vede evidenziata la risposta Apertura della connessione (Handshake) Con l’indirizzo IP in mano, il browser inizia un handshake TCP con il server al fine di stabilire una connessione affidabile. Questo include la sincronizzazione dei numeri di sequenza per garantire che i pacchetti di dati vengano inviati e ricevuti in ordine. Durante l’handhsake il client invia un segmento SYN , il server risponde con un SYN + ACK , il client termina l’handshake con un ACK. (Si vede in figura nella riga evidenziata l’inizio dell’handshake verso la CDN di libero).
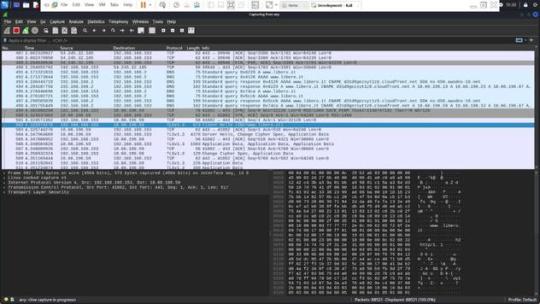
Negoziazione TLS (Transport Layer Security) Dopo aver stabilito una connessione TCP, il browser inizia una negoziazione TLS per assicurare che la comunicazione sia sicura e criptata. Questo processo inizia con l’invio del “ClientHello”, che include la versione di TLS supportata, i metodi di cifratura proposti, e altri dettagli necessari per la sicurezza.

Il server risponde con un “ServerHello”, che conferma i dettagli della crittografia che sarà utilizzata, seleziona un metodo di cifratura tra quelli proposti dal client e prosegue con l’invio dei certificati, la verifica della chiave, e la conferma finale di inizio della cifratu Comunicazione sicura Una volta completata la negoziazione TLS, tutte le trasmissioni successive tra il browser e il server sono completamente criptate. Il browser può ora richiedere le risorse web da “www.libero.it”, che in realtà potrebbero essere servite dal dominio della CDN, come “d31d9gezsyt1z8.cloudfront.net”. Questo esempio mostra come, nella pratica, un sito che l’utente intende visitare possa essere effettivamente distribuito attraverso una rete CDN, rendendo il nome del dominio CDN visibile nelle comunicazioni di rete, anche se l’utente potrebbe non essere immediatamente consapevole di tale fatto. Considerazioni Questa architettura farà in modo che www.libero.it avrà una serie di IP associati all’ASN di cloudfront che vengono usati per far funzionare la CDN. Questi IP saranno associati non solo a www.libero.it ma anche a molti altri FQDN (Altre web app) che usano la CDN. Ricordiamo che questi servizi vengono distinti fra loro grazie ai record CNAME che puntano a FQDN univoci come questo: d31d9gezsyt1z8.cloudfront.net.
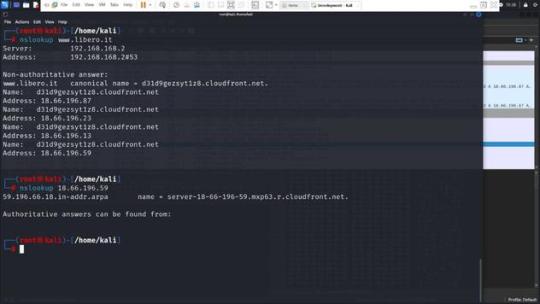
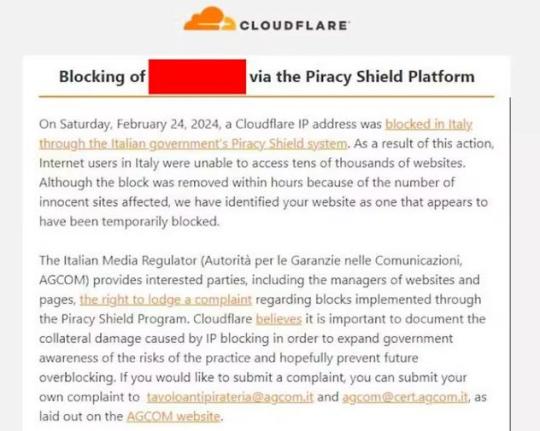
Dimostrazione del problema Con l’esempio precedente abbiamo quindi dimostrato che quando un servizio è integrato ad una CDN la corrispondenza servizio – IP non è più della cardinalità 1:1 , ma bensì N:1. Quindi se viene filtrato un indirizzo IP, N servizi vengono oscurati, pur non essendo tutti illegali. Lo abbiamo visto con l’esempio precedente in cui libero viene deliberatamente associato a diversi IP, condivisi con altri servizi della CDN cloudFront. Infatti una delle CDN che ha lamentato proprio questo problema è la nota Cloudflare che ha emesso un comunicato ad alcuni suoi clienti, esortandoli all’invio di una lettera di richiamo alla stessa AGCOM chiedendo di annullare l’ingiusto provvedimento.
Non si può quindi pensare di bloccare il traffico IP semplicemente filtrando un indirizzo IPv4/IPv6. Come si potrebbe procedere Per affrontare efficacemente le sfide poste dal filtraggio di contenuti attraverso indirizzi IP in un ambiente dove sono ampiamente utilizzate le Content Delivery Networks (CDN), è essenziale adottare metodi più sofisticati che prendano in considerazione le peculiarità tecniche delle CDN stesse. Una strategia più mirata e meno suscettibile di causare danni collaterali può essere implementata analizzando in dettaglio le proprietà di rete associate agli indirizzi IP, in particolare l’Autonomous System Number (ASN). Analisi dell’ASN Prima di procedere al blocco di un indirizzo IP sospettato di veicolare contenuti piratati, è cruciale determinare a quale sistema autonomo appartiene quel determinato IP. Se l’IP è associato all’ASN di una CDN nota, questo indica che potrebbe essere utilizzato per servire una moltitudine di clienti e servizi, molti dei quali legittimi. Il blocco diretto di tali IP potrebbe quindi interrompere l’accesso a servizi legittimi, causando interruzioni non necessarie e potenzialmente estese. Blocco basato su FQDN della CDN Invece di bloccare indiscriminatamente gli indirizzi IP, si dovrebbe valutare l’opzione di filtrare specifici Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDN) direttamente legati a contenuti illeciti. Un metodo più mirato consiste nell’analizzare i record CNAME, che collegano un FQDN a un altro dominio, spesso usato per identificare contenuti specifici all’interno di una CDN. Il sistema attuale del Piracy Shield già applica il blocco agli FQDN e agli indirizzi IP, ma non estende questo trattamento ai FQDN univoci usati dalle CDN. Ad esempio, bloccando il dominio pubblico www.libero.it ed i suoi indirizzi IP, si impedisce anche l’accesso agli IP come 18.66.196.87, 18.66.196.23, 18.66.196.13 e 18.66.196.59. Tali indirizzi, associati a una CDN, vengono utilizzati anche da altri servizi che sarebbero ingiustamente bloccati. Soluzione proposta Quando viene rilevato che un servizio usa una CDN, la strategia corretta sarebbe quella di bloccare esclusivamente gli FQDN specifici alla CDN, come d31d9gezsyt1z8.cloudfront.net e www.libero.it, senza intervenire sugli indirizzi IP. In questo modo gli altri servizi che usano la CDN non saranno bloccati. Conclusioni Adottando queste pratiche migliorate, AGCOM e altre autorità simili potrebbero ottimizzare le loro strategie di enforcement senza suscitare controversie legate a interruzioni di servizio ingiustificate o a violazioni dei diritti alla privacy e alla libertà di espressione. Questo equilibrio tra l’efficacia del blocco e il rispetto per i diritti degli utenti è essenziale per mantenere la fiducia nel regolamento digitale e nella protezione della proprietà intellettuale nel contesto globale e interconnesso di oggi Read the full article
#AgCom#CDNcloudFront#contentdeliverynetwork#dnsquery#filtering#FQDN#indirizziIP#ipaddress#PrivacyShield
0 notes
Text
What is Proxy Extension?
1 note
·
View note
Text
0 notes
Video
youtube
What is IP address and how to find it | Tech Questions
0 notes
Text
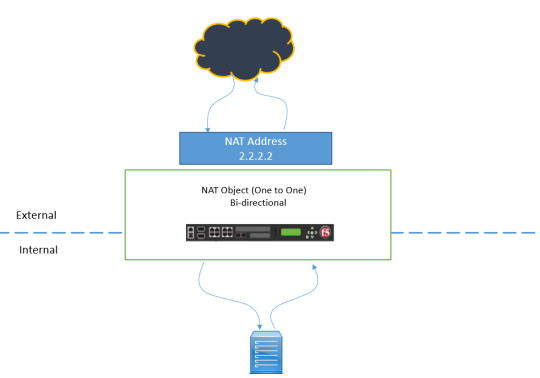
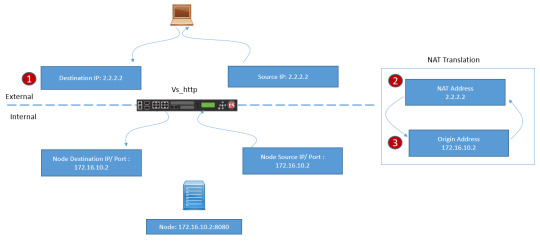
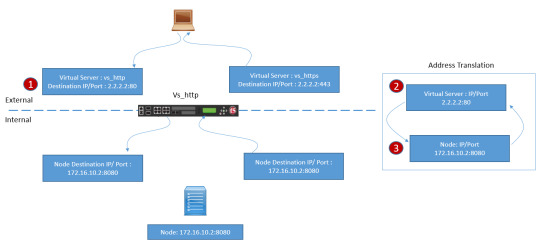
Are you ready to unravel the mysteries of Network Address Translation (NAT) and Source NAT (SNAT)? DC Lessons offers a comprehensive course designed for IT professionals, network administrators, and anyone intrigued by the world of network address manipulation. https://www.dclessons.com/nat-snat-concepts
#NAT#StaticNAT#Networking#ITTraining#DClessons#Cisco#NetworkSecurity#IPaddress#ITConcepts#RoutingAndSwitching#TechEducation#NetworkEngineering#NetworkTopology#ITCertification#CCNA
0 notes
Text
How can I find the IP address of a device connected to my Netgear router?

Have you ever wanted to learn more about IP addresses? In this article, we'll discuss what an IP address is, and how to find the IP address of a device connected to your Netgear router.
What Is An IP Address?
An IP address is a unique numerical identifier assigned to each device connected to the internet protocol for communication. It allows devices to communicate with each other and find each other on the network. Every device has a different IP address, and they are usually assigned by your ISP (internet service provider). You can think of an IP address like a phone number for your computer - it's how other devices on the internet know how to find and connect to it. You can find the IP address of any device connected to your router by logging into your router's web interface and looking at the list of connected devices. The IP address will be listed next to each device.
How to Find the IP Address Of A Device Connected To Your Router?
When it comes to finding the IP address of a device connected to your router, there are several methods you can use. Here is a list of them: Through the Router's Web Interface The easiest way to find the IP address of a device connected to your router is through the router's web interface. To identify the IP address of a device connected to your router: - Access the login page for your router. For NETGEAR routers, refer to the instructions on "How do I log in to my NETGEAR home router?" Note: If you do not have a NETGEAR router, consult your specific model's user manual or support page. - Locate the section of the router's web interface that displays connected devices. - On NETGEAR routers, navigate to the "Attached Devices" page under the "BASIC" tab. Note: The menu label may vary on other models and be called "Device Manager" or similar. - Each connected device will display information such as the device name and IP address. For further assistance, refer to your router's support page or contact NETGEAR Support. Using a Command Prompt (Windows) If you're using Windows, you can find your IP address by opening a command prompt and typing "ipconfig". Your IP address will be displayed next to the "IPv4 Address" field. Using Network Settings (MacOS/iOS) If you want to find the IP address of a device connected to your router, you can do so using the network settings on your Mac or iOS device. - Access System Preferences and select the Network option. - Select the location that corresponds to your current network setup (if you need help determining which one it is, look at the network icon in the menu bar). - Click on Advanced and then select the TCP/IP tab. - The IP address will be listed next to "Router". Using a Network Scanner A third way to find the IP address of a device connected to your router is by using a network scanner. Network scanners are software tools that scan your network and provide information about connected devices, including IP addresses. There are many different network scanners available, both paid and free. Some popular options include Fing and Advanced IP Scanner. Note: It's worth noting that some devices may have a dynamic IP address which can change over time.In conclusion, finding the IP address of a device connected to your router is a straightforward process that can be accomplished using various methods. Whether you choose to use the router's web interface, command prompt or terminal, or a network scanner, you should be able to quickly identify the IP address of the device you are trying to locate. Knowing the IP address of a device connected to your router can be helpful in a variety of situations, such as troubleshooting network issues or configuring security settings. With this knowledge, you can easily manage and maintain your home network.Reference form: https://mynetgearrouterlogin.com/find-the-ip-address-of-connected-device/ Read the full article
#mynetgearrouterlogin#IPaddress#router#network#deviceIP#networkmanagement#homenetwork#networktroubleshooting#IPconfig#networkscanner#netgear
0 notes
Text
Alpha Infolab: Your Trusted ARIN Qualified Facilitator

Alpha Infolab, a leading provider of digital solutions, is proud to announce its recent recognition as an ARIN Qualified Facilitator. This achievement underscores our commitment to providing top-tier services to our clients and our expertise in the field of Internet number resources. Don't miss out on the opportunity to streamline your Internet number resources transfer process. Contact us today to learn more about our services!
The American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) is a non-profit corporation that manages the distribution of Internet number resources, including IPv4, IPv6, and Autonomous System Number (ASN) resources. The ARIN Qualified Facilitator Program is designed to assist organizations in acquiring or transferring these valuable resources.
As an ARIN Qualified Facilitator, we have undergone a rigorous review process by ARIN's experienced staff and have demonstrated our ability to streamline the transfer process with ARIN Registration Services. This status allows us to better serve organizations looking to obtain or transfer IPv4 address space or ASNs.
The ARIN Qualified Facilitator Program is particularly beneficial for organizations unsure of how to obtain needed IPv4 address space, those with unused IPv4 address space who wish to transfer it, and organizations needing guidance to navigate the complex resource transfer process.
At Alpha Infolab, we are committed to providing our clients with the best possible service. Our recognition as an ARIN Qualified Facilitator is a testament to our dedication and expertise in the field. We look forward to continuing to serve our clients with the highest level of service and professionalism.
Ready to streamline your Internet number resources transfer process? Don't wait any longer! Contact Alpha Infolab, your trusted ARIN Qualified Facilitator, today! Visit our website or contact us to learn more about our services and start your journey to more efficient Internet number resources management.
0 notes
Text

Connection-Oriented vs Connectionless Service . . . . for more information https://bit.ly/43LQtAQ check the above link
#macaddress#ipaddress#cdma#gsm#connectionorientedservice#connectionlessservice#internet#internetworking#networking#intranet#topologies#javatpoint
0 notes