#Junit annotations
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Is The Purpose of JUnit In Java Application Testing?
JUnit is a widely-used testing framework in Java that plays a critical role in unit testing ensuring that individual components (typically methods) of a program work as intended. Its purpose is to automate the process of testing Java applications by enabling developers to write repeatable tests and run them efficiently.
JUnit provides annotations like @Test, @BeforeEach, @AfterEach, and assertions such as assertEquals(), assertTrue(), and assertNotNull() that make it easy to write readable and maintainable test cases. By isolating and testing individual methods or classes, JUnit helps developers detect bugs early in the development cycle, preventing costly issues later in production. It also supports test-driven development (TDD), where tests are written before the actual code, promoting better software design and reduced debugging time.
Integrated with build tools like Maven or Gradle and CI/CD platforms like Jenkins, JUnit becomes a core part of the software delivery pipeline. It enables continuous testing, automated builds, and faster deployment with higher code quality.
Overall, JUnit enhances the reliability, maintainability, and robustness of Java applications, making it an essential skill for anyone learning or working in Java development.
To master such testing tools and become job-ready, consider enrolling in a comprehensive java full stack developer course.
0 notes
Text
10 Must-Know Java Libraries for Developers
Java remains one of the most powerful and versatile programming languages in the world. Whether you are just starting your journey with Java or already a seasoned developer, mastering essential libraries can significantly improve your coding efficiency, application performance, and overall development experience. If you are considering Java as a career, knowing the right libraries can set you apart in interviews and real-world projects. In this blog we will explore 10 must-know Java libraries that every developer should have in their toolkit.

1. Apache Commons
Apache Commons is like a Swiss Army knife for Java developers. It provides reusable open-source Java software components covering everything from string manipulation to configuration management. Instead of reinventing the wheel, you can simply tap into the reliable utilities offered here.
2. Google Guava
Developed by Google engineers, Guava offers a wide range of core libraries that include collections, caching, primitives support, concurrency libraries, common annotations, string processing, and much more. If you're aiming for clean, efficient, and high-performing code, Guava is a must.
3. Jackson
Working with JSON data is unavoidable today, and Jackson is the go-to library for processing JSON in Java. It’s fast, flexible, and a breeze to integrate into projects. Whether it's parsing JSON or mapping it to Java objects, Jackson gets the job done smoothly.
4. SLF4J and Logback
Logging is a critical part of any application, and SLF4J (Simple Logging Facade for Java) combined with Logback offers a powerful logging framework. SLF4J provides a simple abstraction for various logging frameworks, and Logback is its reliable, fast, and flexible implementation.
5. Hibernate ORM
Handling database operations becomes effortless with Hibernate ORM. It maps Java classes to database tables, eliminating the need for complex JDBC code. For anyone aiming to master backend development, getting hands-on experience with Hibernate is crucial.
6. JUnit
Testing your code ensures fewer bugs and higher quality products. JUnit is the leading unit testing framework for Java developers. Writing and running repeatable tests is simple, making it an essential part of the development workflow for any serious developer.
7. Mockito
Mockito helps you create mock objects for unit tests. It’s incredibly useful when you want to test classes in isolation without dealing with external dependencies. If you're committed to writing clean and reliable code, Mockito should definitely be in your toolbox.
8. Apache Maven
Managing project dependencies manually can quickly become a nightmare. Apache Maven simplifies the build process, dependency management, and project configuration. Learning Maven is often part of the curriculum in the best Java training programs because it’s such an essential skill for developers.
9. Spring Framework
The Spring Framework is practically a requirement for modern Java developers. It supports dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and offers comprehensive infrastructure support for developing Java applications. If you’re planning to enroll in the best Java course, Spring is something you’ll definitely want to master.
10. Lombok
Lombok is a clever little library that reduces boilerplate code in Java classes by automatically generating getters, setters, constructors, and more using annotations. This means your code stays neat, clean, and easy to read.
Conclusion
Choosing Java as a career is a smart move given the constant demand for skilled developers across industries. But mastering the language alone isn't enough—you need to get comfortable with the libraries that real-world projects rely on. If you are serious about becoming a proficient developer, make sure you invest in the best Java training that covers not only core concepts but also practical usage of these critical libraries. Look for the best Java course that blends hands-on projects, mentorship, and real-world coding practices. With the right skills and the right tools in your toolkit, you'll be well on your way to building powerful, efficient, and modern Java applications—and securing a bright future in this rewarding career path.
0 notes
Text
Do you want to know what every Java developer should know? We have shortlisted some of the highly recommended concepts and components of Java language for beginners and senior programmers. These things to learn in Java may help you get the best Java developer job you deserve. Java technology has evolved and has become really huge in the last decade. There are just too many things and its almost impossible for one person to master all of them. Your knowledge about Java technology will depend completely on what you working on. In any technology say Java or some other language, it is more important and valuable to know the language fundamentals thoroughly (OOP concepts, interfaces, class, objects, threading, etc.) rather than specific frameworks or syntax. It's always easy to quickly learn new technologies when you master the fundamentals. Are you are a beginner? Looking for some help and guidance on how to get started on this language, our exclusive article on How to Learn Java and Java libraries to know is a must read for you before getting started on Java. I just updated this article in November 2016 and things are more relevant to recent Java trends. Java Interview Preparation Tips Part 0: Things You Must Know For a Java Interview Part 1: Core Java Interview Questions Part 2: JDBC Interview Questions Part 3: Collections Framework Interview Questions Part 4: Threading Interview Questions Part 5: Serialization Interview Questions Part 6: Classpath Related Questions Part 7: Java Architect Scalability Questions Java developers knowledge expectation changes based on the profile. In this post I have divided it into 3 profiles: College Graduate, Experienced Java Developer, Experienced Java Web Developer. 7 Things a College graduate must know to get a Java developer job If you are a college graduate with no job experience then as a Java developer you need to understand the following basic things. How Java Virtual Machine works? e.g. (Platform Independence, Garbage Collection, class files, etc) What are the Object-Oriented Programming Concepts Implemented in Java? Multi-threading Java Collection framework Good understanding of data types and few of "java.lang" classes like String, Math, System, etc. java.io stream concepts. Understand the concept of Swing/AWT event-based programming. Do not spend a lot of time on this but understand the best practices. Servlets and JSP concepts. 9 Things an experienced Java Developer must know to thrive If you are an experienced professional then as a Java developer you may also need to understand the following basic things in addition to the ones listed above. Understand design patterns and its usage in Java Improvements in language from major version changes (Lambda, NIO, Generics, Annotations, Enums, ...). Coding Conventions. Build tool (Ant) or Project Management Tool (Maven). Version control System like GIT/SVN/Perforce/Clearcase. Apache Commons Libraries & few other common open source libraries. Continuous Integration Tools e.g. Jenkins and Hudson. Unit testing - e.g. JUnit and TestNG Unit testing Mocking libraries like Mockito Fundamental understanding of JSON and XML Understand Business layer frameworks - like Spring Understanding dependency injection (e.g. Spring, Google Guice, and Plain Java Dependency injection) 4 Things a Java Web Developer (JEE) Developer must know If you are an experienced professional working on Web-based development then as a JEE developer you also need to understand the following basic things in addition to the ones (7+9) listed above. Understanding of MVC Frameworks - Open source web frameworks like - Spring MVC, Struts, Vaadin, etc. Understanding of Microservice based framework like Spring Boot. Important Note: A lot of Front End UI development is now shifted to JavaScript frameworks. Therefore do not focus on Java-based frameworks that focus on the user interface (e.g. JSF or related frameworks).
Instead, learn JavaScript related frameworks like Angular.js or Backbone.js Fundamental understanding of Web Services and REST based service development. Good understanding of Web/Application server like Tomcat, Glassfish, WebLogic, WebSphere, Jetty, etc. Unix environment - A working knowledge of Unix environment can be beneficial as most of the Java servers are hosted on Unix based environment in production. Looking at the list of things it really feels difficult for a person to know each and everything in depth. As I already said it is more important and valuable to know the language fundamentals thoroughly and rest can be learned quickly when required. Can you think of something which is not part of this post? Please don't forget to share it with me in the comments section & I will try to include it in the list. Article Updates Article updated in April 2019 - Updated Introduction section, fixed minor text, and updated answers. Updated on November 2016 - Made changes as per latest technology trends and stacks.
0 notes
Text
Share tips for improving code quality and maintainability.
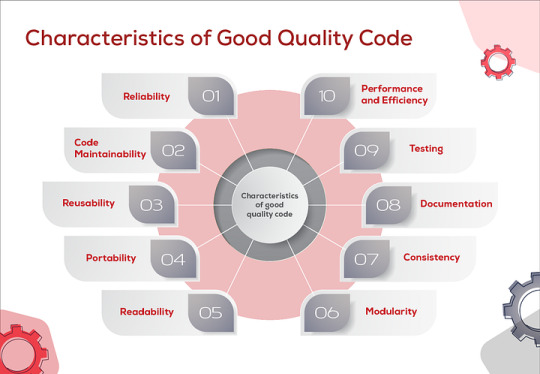
1. Follow Java Naming Conventions
Classes: Use PascalCase for class names (e.g., EmployeeDetails).
Methods/Variables: Use camelCase for method and variable names (e.g., calculateSalary).
Constants: Use uppercase letters with underscores for constants (e.g., MAX_LENGTH).
2. Use Proper Object-Oriented Principles
Encapsulation: Make fields private and provide public getters and setters to access them.
Inheritance: Reuse code via inheritance but avoid deep inheritance hierarchies that can create tightly coupled systems.
Polymorphism: Use polymorphism to extend functionalities without changing existing code.
3. Write Clean and Readable Code
Keep Methods Small: Each method should do one thing and do it well. If a method is too long or does too much, break it down into smaller methods.
Avoid Nested Loops/Conditionals: Too many nested loops or conditionals can make code hard to read. Extract logic into separate methods or use design patterns like the Strategy or State pattern.
4. Use Design Patterns
Leverage proven design patterns like Singleton, Factory, Observer, and Strategy to solve common problems in a standardized, maintainable way.
Avoid overcomplicating things; use patterns only when they add clarity and solve a specific problem.
5. Implement Proper Error Handling
Use exceptions appropriately. Don’t overuse them, and catch only the exceptions you can handle.
Ensure that exceptions are logged for better debugging and auditing.
Use custom exceptions to represent domain-specific issues, so they are easier to debug.
6. Utilize Java’s Stream API
The Stream API (introduced in Java 8) helps reduce boilerplate code when performing collection operations like filtering, mapping, and reducing.
It makes code more concise and expressive, which helps with readability and maintainability.
7. Write Unit Tests
Use JUnit and Mockito for unit testing and mocking dependencies.
Write test cases for all critical methods and components to ensure the behavior is as expected.
Use Test-Driven Development (TDD) to ensure code correctness from the start.
8. Use Dependency Injection
Prefer Dependency Injection (DI) for managing object creation and dependencies. This decouples components and makes testing easier (using tools like Spring Framework or Guice).
DI helps to make your classes more modular and improves maintainability.
9. Avoid Code Duplication
Use methods or utility classes to avoid repeating code.
If the same logic is used in multiple places, refactor it into a single reusable method.
10. Use Annotations
Use Java annotations (like @Override, @NotNull, @Entity, etc.) to improve code clarity and reduce boilerplate code.
Annotations help to enforce business logic and constraints without having to manually check them.
11. Leverage IDE Features
Use tools like IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse to automatically format code and identify potential issues.
Many IDEs have integrated tools for running tests, refactoring code, and applying coding standards, so make full use of these features.
12. Optimize for Performance Without Sacrificing Readability
Only optimize performance when necessary. Premature optimization can lead to complex code that’s difficult to maintain.
Profile your code to identify bottlenecks, but prioritize clarity and maintainability over micro-optimizations.
13. Implement Proper Logging
Use a logging framework like SLF4J with Logback or Log4j2 for logging. This provides a consistent logging mechanism across the application.
Ensure that logs are meaningful, providing information about the application’s state, errors, and flow, but avoid excessive logging that clutters output.
14. Document Your Code
Use JavaDocs to generate documentation for public methods and classes.
Document not just the what but also the why behind critical decisions in the codebase.
15. Keep Your Codebase Modular
Break your project into smaller, well-defined modules, and avoid large monolithic classes.
Use packages to group related classes, ensuring that each class or module has a single responsibility.
16. Use Static Analysis Tools
Integrate tools like Checkstyle, PMD, and SonarQube to enforce coding standards, detect bugs, and ensure code quality.
These tools help you identify code smells and areas where quality can be improved.
0 notes
Text
Top Automation Testing Frameworks for Efficient Software Development

Whether you are a seasoned developer or a newcomer, the need for tools that allow software developers to make their software high quality delivered quickly is a necessity. Automation Testing has proven to be a game changer, allowing the developers and QA teams to maintain the quality of the software, shorten time-to-market, and optimize repetitive testing processes. However, the main factor behind successful Automation Testing is selecting the appropriate test automation framework.
In this blog, we will discuss some of the most popular Test Automation frameworks, their features that make them unique and how they enhance QA process that helps in efficient Software Development. GhostQA can certainly help you in delivering seamless and efficient Automation Testing strategies if you're looking for a professional approach in implementing the ideal framework.
What is a Test Automation Framework?
A Test Automation framework means a collection of guidelines, tools, and practices that are used to automate the testing process in a simple and standardized way. This application serves as a guiding framework for scripting automation in a homogenous way which can be easily maintainable and scalable.
By adopting the right framework, the team can leverage the benefits of Automation Testing, such as increased speed, better coverage, and below human error.
Why Choosing the Right Framework Matters
The Test Automation framework is the single most important decision that will affect the effectiveness and reliability of testing efforts. Here’s why choosing the appropriate framework is important:
Ensure all technology stacks are compatible with your tech.
Makes test scripts easier to write and maintain.
Improves team collaboration and productivity.
Increases scalability for future project needs.
Decreases the overall test cost, without compromising on quality.
Top Automation Testing Frameworks
Let us look at some of the most used and efficient Automation Testing frameworks:
1. Selenium
Overview: Selenium is an open-source framework most commonly used to perform testing on web applications. It works with various browsers, platforms, and programming languages.
Features:
Functional on multiple browsers and multiple platforms.
Strong community support and regular iterations.
Best For: Web application functional and regression testing.
2. Appium
Overview: Appium is a widely used open-source framework for testing mobile applications. It is compatible with Android, iOS, and Windows apps.
Features:
Works with native, hybrid and mobile web apps.
It works with the same APIs across multiple platforms.
Enables scripts to be reused on multiple platforms.
Best For: The testing of apps for mobile devices.
3. TestNG
Overview: TestNG is a framework for the Java programming language inspired from JUnit. This supports a variety of different test setups and annotations.
Features:
Enables parallel execution to speed things up.
Various flexible options for test configuration
Provides extensive reporting that you can tailor to your specifications.
Best For: Integration, functional and unit testing.
4. Cypress
Overview: Cypress is an end-to-end testing framework for modern web applications.
Features:
Test execution with on-the-fly reloading.
Waits for commands and DOM updates implicitly.
Debugging tools for developers built into the platform.
Best For: UI Testing and end-to-end testing for web-based applications.
5. JUnit
Overview: JUnit is another popular framework for Java applications mainly focused on unit testing.
Features:
Makes test-driven development (TDD) easier.
Rich support for assertions and annotations.
Best for small and focused tests.
Best For: When writing unit tests for Java-based applications.
6. Katalon Studio
Overview: Katalon Studio is an end-to-end testing solution providing web, API, mobile, and desktop testing capabilities.
Features:
Built-in templates and intuitive interface
Favors manual as well as through automation testing.
Best For: Teams looking for a user-friendly, all-in-one solution.
7. Robot Framework
Overview: Robot Framework is a generic open-source test automation framework that uses a keyword-driven approach.
Features:
Easily readable test cases.
You can extend with libraries and tools.
Great for the less technical members of your team.
Best For: Acceptance test and RPA (Robotic process automation).
How Automation Testing Benefits Software Development
There are several advantages of adopting Automation Testing frameworks:
Faster Testing Cycles: Automated tests run faster than manual tests leading to a decreased testing time.
Improved Accuracy: Reduced human error leads to more accurate results
Reusability of Tests: The frameworks help in reusing the test scripts on different projects.
Increased Test Coverage: It allows the testing of huge datasets and numerous scenarios.
Cost Efficiency: Despite the initial investment, it saves a lot of time and resources in the long run.
Challenges in Automation Testing
Although Automation Testing comes with lots of advantages, there are also some challenges:
High Initial Costs: Setting up a framework will require time and resources.
Complex Tool Integration: Deciding to use the right tools and ensuring compatibility can be a struggle.
Skill Gaps: Team members might require training in order to effectively use advanced frameworks.
Maintenance Effort: Whenever the application changes, it is imperative to update the test scripts.
GhostQA: Your Trusted Partner for Automation Testing
GhostQA focuses on helping businesses with effective Automation Testing solutions. So, if you want help regarding selecting a Test Automation framework, or want us to implement solid strategies, GhostQA is your choice.
Why Choose GhostQA?
Deep knowledge of frameworks (Selenium, Appium, Cypress, etc.).
Custom solutions designed around your specific project requirements.
Proven approaches for overcoming automation dilemmas.
Professional service to guarantee that your testing workflow is smooth and trustworthy.
Best Practices for Using Automation Frameworks
Select the Right Framework: Make sure it suits your project requirements and team experience.
Plan Test Cases Strategically: Prioritize high-value and repeated tasks to be automated.
Incorporate Regular Maintenance: Refresh the scripts based on modifications in the application and the environment.
Use a Hybrid Approach: Integrate both manual and automated testing for coverage
Leverage Reporting Tools: Take advantage of detailed reports to monitor progress and find opportunities for growth.
Conclusion
It is obligatory to select the right Automation Testing framework for the best software development. Testing frameworks such as Selenium, Appium, and Katalon Studio have a variety of features that help fast-track testing tasks and improve product quality.
Joining forces with GhostQA gives you a road of expertise and solutions right for you making sure your Test Automation steps are easy and prosperous.
Start using the appropriate Automation Testing framework now to reduce your development cycles, enhance test accuracy, and build superior software. Get in touch with GhostQA to see how we can revolutionize your testing methodologies.
#quality assurance#automated testing#test automation#software testing#performance testing#automation testing#functional testing#regression testing#load testing
0 notes
Text
Selenium WebDriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework
Introduction to Selenium WebDriver, Java, and TestNG
What is Selenium WebDriver?
Selenium WebDriver is a widely used open-source automation testing tool for web applications. It allows testers to execute tests directly on browsers and supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, and C#.
Why Use Java for Selenium?
Java is the most popular language for Selenium due to its robust libraries, extensive community support, and compatibility with various tools like TestNG and Maven.
What is TestNG Framework?
TestNG (Test Next Generation) is a testing framework inspired by JUnit but offers advanced features like annotations, data-driven testing, and parallel execution, making it an ideal companion for Selenium.
Setting Up Selenium WebDriver with Java
Prerequisites for Installation
Java Installation
Ensure Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed on your system. Use the command java -version to confirm the installation.
Eclipse IDE Setup
Download and install Eclipse IDE for Java Developers. It provides a user-friendly environment for writing Selenium scripts.
Configuring Selenium WebDriver
Downloading Selenium JAR Files
Visit the Selenium website and download the WebDriver Java Client Library.
Adding JAR Files to Eclipse
Import the downloaded JAR files into your Eclipse project by navigating to Project > Build Path > Add External JARs.
Introduction to TestNG Framework
Why TestNG for Selenium?
TestNG simplifies test case management with features like grouping, prioritization, and result reporting.
Installing TestNG in Eclipse
TestNG Plugin Installation
Install the TestNG plugin via Eclipse Marketplace.
Verifying Installation
After installation, you should see the TestNG option in the Eclipse toolbar.
Writing Your First Selenium Test Script
Creating a Java Project in Eclipse
Start by creating a new Java project and adding Selenium and TestNG libraries to it.
Writing a Basic Selenium Script
Launching a Browser
Use WebDriver commands to open a browser, e.g., WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();.
Navigating to a Web Page
Navigate to a URL using the driver.get("URL"); method.
Locating Web Elements
Use locators like ID, Name, or XPath to interact with elements.
Integrating TestNG with Selenium
Writing TestNG Annotations
Annotations like @Test, @BeforeTest, and @AfterTest help structure your test cases.
Executing Test Cases with TestNG
@Test Annotation Explained
Mark methods as test cases with the @Test annotation.
Generating TestNG Reports
After execution, TestNG generates a detailed HTML report showing test results.
Advanced Features of Selenium with TestNG
Parameterization in TestNG
Using DataProvider Annotation
DataProvider allows you to pass multiple sets of data to a test case.
Passing Parameters via XML
Define test parameters in the TestNG XML file for dynamic execution.
Parallel Test Execution
Running Tests in Parallel Browsers
Configure the TestNG XML file to execute tests simultaneously on different browsers.
Handling Web Elements in Selenium
Working with Forms
Input Fields and Buttons
Automate form filling and button clicks using WebDriver commands.
Managing Dropdowns and Checkboxes
Use Select class for dropdowns and isSelected() for checkboxes.
Handling Alerts and Popups
Switch to alerts with driver.switchTo().alert(); for handling popups.
Best Practices for Selenium Testing
Designing Modular Test Scripts
Break down test scripts into reusable modules for better maintainability.
Implementing Page Object Model (POM)
Organize your code by creating separate classes for each page in your application.
Handling Synchronization Issues
Use implicit and explicit waits to handle delays in element loading.
Debugging and Troubleshooting Selenium Scripts
Common Errors in Selenium Testing
ElementNotVisibleException
Occurs when attempting to interact with hidden elements.
NoSuchElementException
Triggered when the WebDriver cannot locate an element.
Debugging Tools in Eclipse
Use breakpoints and the debugging perspective in Eclipse to identify issues.
Conclusion
Mastering Selenium WebDriver with Java and TestNG opens doors to efficient and robust automation testing. By understanding the basics, leveraging TestNG’s features, and adhering to best practices, you can build a powerful testing suite.
FAQs
Can I use Selenium with other programming languages?
Yes, Selenium supports multiple languages like Python, C#, Ruby, and JavaScript.
What are the limitations of Selenium WebDriver?
Selenium cannot test non-web applications, handle captchas, or manage dynamic page loads efficiently without additional tools.
How does TestNG differ from JUnit?
TestNG offers more advanced features, including parallel testing, better test configuration, and detailed reporting.
Is Selenium WebDriver suitable for mobile testing?
Not directly, but tools like Appium extend Selenium for mobile application testing.
How do I manage dependencies in a large Selenium project?
Use build tools like Maven or Gradle to manage dependencies efficiently.
0 notes
Text
Learn Full Stack Development with Spring Boot and Angular
Full stack development is a powerful skill, enabling developers to create seamless and scalable applications by integrating front-end and back-end technologies. Combining Spring Boot for back-end development with Angular for the front-end provides a robust framework for building modern web applications. This guide will walk you through learning full stack development with these two technologies.
Why Choose Spring Boot and Angular?
Spring Boot
A Java-based framework that simplifies the creation of production-ready applications.
Provides built-in configurations to reduce boilerplate code.
Offers excellent support for REST APIs and database management.
Angular
A TypeScript-based front-end framework by Google.
Enables the development of dynamic, single-page applications (SPAs).
Offers features like two-way data binding, dependency injection, and a component-based architecture.
By integrating Spring Boot and Angular, you can create full stack applications that are efficient, scalable, and maintainable.
Prerequisites
Before diving into Spring Boot and Angular, ensure you have a basic understanding of:
Java and Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts.
TypeScript and JavaScript fundamentals.
HTML, CSS, and basic front-end development.
Familiarity with RESTful APIs and database concepts.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
For Spring Boot
Install Java Development Kit (JDK).
Set up an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), such as IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse.
Add Maven or Gradle for dependency management.
Use Spring Initializr to bootstrap your Spring Boot project.
For Angular
Install Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager).
Install the Angular CLI using the command: npm install -g @angular/cli
Set up a code editor like Visual Studio Code.
Key Concepts to Master
Back-End with Spring Boot
Creating REST APIs
Use annotations like @RestController, @RequestMapping, and @PostMapping.
Implement services and controllers to handle business logic.
Database Integration
Use Spring Data JPA with Hibernate for ORM (Object-Relational Mapping).
Work with relational databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Security
Implement authentication and authorization with Spring Security.
Use JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for secure communication.
Testing
Write unit tests with JUnit and integration tests using MockMvc.
Front-End with Angular
Component-Based Architecture
Learn to create reusable components with Angular CLI.
Manage application state and communication between components.
Routing and Navigation
Use the Angular Router to create SPAs with multiple views.
HTTP Client
Communicate with back-end APIs using Angular’s HttpClientModule.
Forms and Validation
Implement reactive forms and template-driven forms.
Validate user inputs effectively.
Integrating Spring Boot and Angular
Set Up Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
Configure Spring Boot to allow requests from the Angular front-end.
Connect Front-End and Back-End
Use Angular’s HttpClient to send requests to Spring Boot endpoints.
Serve Angular from Spring Boot
Build the Angular project and place the output in the Spring Boot static directory.
Deploy the Application
Use tools like Docker to containerize the application for deployment.
Fullstack course in chennai
Fullstack development course in chennai
Fullstack training in chennai

0 notes
Text
What Skills Are Required To Use Selenium Effectively?

Introduction
Selenium is a widely used open-source tool for web browser automation and testing web applications. It provides testers and developers with a flexible and efficient platform to ensure the quality and functionality of web-based software. However, to leverage Selenium effectively, individuals need a robust set of skills. This article explores the essential technical and soft skills that empower professionals to excel with Selenium.
Understanding The Basics Of Web Technologies
Before diving into Selenium, it's crucial to have a solid grasp of fundamental web technologies. Embark on the journey to unlock the full potential of automation testing with Selenium Training in Chennai at Infycle Technologies, the leading destination for mastering automation tools. These include:
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Since Selenium interacts with web elements like buttons, forms, and links, understanding how these elements are structured and styled is essential.
DOM (Document Object Model): Familiarity with the DOM enables testers to locate and interact efficiently with elements on a webpage.
HTTP Protocols: Knowing how web browsers communicate with servers helps understand page load issues and debug network-related test failures.
Proficiency In Programming Languages
Selenium supports multiple programming languages, including Python, Java, C#, Ruby, & JavaScript. To use Selenium effectively, one must:
Choose a programming language based on project requirements and team expertise.
Master the selected language's syntax, logic, and object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts.
Understand how to write clean, maintainable, and modular code.
For example, Python is often favoured for its simplicity, while Java is widely used in enterprise environments.
Knowledge Of Selenium Frameworks
Familiarity with Selenium frameworks enhances test automation. Key frameworks include:
TestNG and JUnit (for Java): These testing frameworks allow for better organization, annotation, and test execution.
Pytest (for Python): A robust framework that simplifies test case management and reporting.
Page Object Model (POM): A design pattern used to create object repositories for web elements, improving test script readability and reusability.
XPath And CSS Selectors Mastery
Locating elements is a core functionality in Selenium. XPath and CSS selectors are powerful tools for identifying elements on a webpage. Skills in:
Writing efficient and precise XPath expressions.
Utilizing CSS selectors for faster and cleaner element identification.
Handling dynamic elements with relative XPath or custom attributes.
Version Control Systems (VCS)
Selenium scripts are often part of larger development projects. Using version control systems like Git ensures collaboration and proper version management. A Selenium tester should:
Understand Git commands for committing, branching, merging, and reverting changes.
Use platforms like GitHub or GitLab for code sharing and version tracking.
Familiarity With Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Tools
In modern software development, CI/CD tools integrate Selenium scripts into automated pipelines. Popular CI/CD tools include:
Jenkins: For scheduling and managing automated test runs.
CircleCI and Travis CI: For seamless integration of test scripts with deployment processes.
Understanding how to configure these tools and integrate Selenium tests into the pipeline is invaluable.
Debugging And Problem-Solving Skills
Test automation often involves troubleshooting. Effective debugging skills include:
Identifying and resolving broken locators, synchronization problems, and environment-specific errors.
Using browser developer tools to inspect web elements and network activity.
Logging errors and analyzing stack traces for quick fixes.
Soft Skills: Communication And Team Collaboration
Technical expertise is only part of the equation. Selenium testers often work in collaborative environments where soft skills matter. These include:
Clear Communication: Explaining test results and automation coverage to non-technical stakeholders.
Team Collaboration: Working closely with developers, product managers, and QA teams to align testing objectives with business goals.
Adaptability: Adjusting to new tools, frameworks, and methodologies as projects evolve.
Experience With Testing Methodologies
A strong foundation in testing methodologies enhances the effectiveness of Selenium testing. Key methodologies include:
Manual Testing Fundamentals: Understanding the principles of manual testing provides insights into writing meaningful automated tests.
Agile and DevOps Practices: Familiarity with iterative development models ensures test automation aligns with rapid development cycles.
Test Strategies: Creating test plans, prioritizing cases, and managing test environments.
Database And API Knowledge
Web applications often interact with databases and APIs. Enhance your journey toward a successful career in software development with Infycle Technologies, the Best Software Training Institute in Chennai. Selenium testers should:
Understand basic SQL queries to verify back-end data.
Use API testing tools like Postman or REST-assured for end-to-end testing scenarios.
Cloud Testing Platforms
Cloud-based platforms like BrowserStack and Sauce Labs allow for cross-browser and cross-platform testing. Skills required include:
Configuring tests to run on different browser and OS combinations.
Using platform-specific features for debugging and reporting.
Keeping Up With Updates And Trends
Selenium evolves continuously, and staying updated is vital. This includes:
Learning new features introduced in Selenium WebDriver.
Understanding emerging technologies like Selenium Grid 4 for distributed testing.
Exploring alternatives or complementary tools like Cypress and Playwright.
Conclusion
Mastering Selenium requires technical expertise, problem-solving capabilities, and collaborative skills. By building a strong foundation in programming, web technologies, and testing frameworks while staying adaptable to new trends, professionals can harness the full potential of Selenium for robust test automation. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced tester, developing these skills will ensure that you remain competitive in the ever-evolving field of software testing.
0 notes
Text
Unlock Your Career Potential with Selenium Automation Testing in Mohali
In the rapidly evolving world of software development, automation testing has become a critical component of ensuring product quality and efficiency. Among the various tools available, Selenium stands out as one of the most popular and effective frameworks for web application testing. If you’re looking to enhance your skills in automation testing, Mohali is home to some of the best training institutes, including Mohali Career Point (MCP).
Why Choose Selenium for Automation Testing?
Selenium is an open-source automation testing tool widely used in the IT industry. Its advantages include:
Cost-Effective: Being open-source, Selenium has no licensing fees, making it an economical choice for organizations of all sizes.
Versatile and Efficient: Selenium supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Python, and Ruby. It also works seamlessly across various operating systems and web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
Robust Community Support: With a large and active community, developers can easily find resources, plugins, and tools to extend Selenium’s functionality.
Flexibility: Selenium can be integrated with other testing frameworks like TestNG and JUnit, providing greater flexibility in test case management.
Comprehensive Selenium Training at MCP in Mohali
At Mohali Career Point, we offer a structured Selenium training program that caters to beginners and advanced users alike. Our course is divided into six comprehensive modules, covering everything from the basics to advanced automation concepts.
Course Modules Overview
Selenium Introduction: Understand what Selenium is, its components, and how it compares to other tools like QTP.
Selenium IDE and RC: Learn how to install and use Selenium IDE for creating and running test cases.
Core Java Introduction and OOPs Concepts: Gain foundational knowledge in Java programming, which is essential for using Selenium effectively.
Selenium WebDriver and Selenium Grid: Dive deep into WebDriver features, browser navigation, element identification, and cross-browser testing.
TestNG and Testing Frameworks: Explore TestNG for managing your tests efficiently, including annotations, data providers, and report generation.
Database Testing — Java Data Base Connectivity: Learn how to connect your test cases to databases and execute queries using JDBC.
Real-Time Project Training
What sets our training apart is the emphasis on practical experience. Our live project training module is designed to give you hands-on experience, allowing you to apply what you’ve learned in a real-world setting. This practical knowledge is invaluable and can significantly enhance your employability.
Why Choose MCP for Selenium Training in Mohali?
Expert Trainers: Our trainers are seasoned professionals with extensive experience in automation testing. They provide in-depth knowledge and practical insights to help you excel.
Tailored Learning: We cater to individual learning paces, ensuring that every student fully grasps the concepts before moving forward.
Career Support: MCP is committed to your success. We offer career counseling and job placement assistance to help you secure high-paying positions in the IT industry.
Diverse Course Offerings: In addition to Selenium, MCP offers various courses in advanced Java, Python, and database management, allowing you to broaden your skill set.
Join MCP Today!
If you’re looking to kickstart a successful career in automation testing, look no further than Mohali Career Point. Our comprehensive Selenium training program will equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to thrive in the competitive IT landscape.
Contact Us Today!
📧 Email: [email protected] 📞 Phone: +91 7696 2050 51 / +91 7906 6891 91 📍 Address: SC-130 Top Floor, Phase 7, Mohali, 160059
Embrace the future of software testing. Choose MCP for your Selenium training in Mohali and take the first step towards a rewarding career in automation testing!
0 notes
Text
Reliance Infrastructure Announces Major Expansion Plans

Reliance Infrastructure, part of the Anil Ambani-led Reliance Group, has unveiled its plans for a major expansion in key sectors, including power, roads, and urban infrastructure. The company aims to strengthen its position in the growing Indian infrastructure market by investing in sustainable energy projects, upgrading transportation networks, and enhancing urban development. With these strategic moves, Reliance Infrastructure is set to capitalize on the rising demand for infrastructure services across the country, positioning itself as a leader in the sector.
Read more about-
Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework: A Complete Guide

In today’s fast-paced digital world, automated testing has become a critical component in ensuring software quality and speed of development. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, understanding how to use Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework can greatly enhance your software testing capabilities. This combination not only helps you automate testing for web applications but also makes the testing process more efficient and less prone to human error.
In this blog, we will dive into the details of Selenium Webdriver, why it is paired with Java, and how using TestNG as a testing framework creates a powerful testing toolset for web automation.
What is Selenium Webdriver?
Selenium Webdriver is an open-source tool designed for automating web application testing. Its primary function is to enable you to simulate user actions on a browser, from clicking buttons and filling out forms to navigating through pages. It supports multiple browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari, making it a versatile tool for cross-browser testing.
Using Selenium Webdriver with Java offers a unique advantage because Java is widely adopted, easy to learn, and highly scalable. The pairing of these two tools allows developers and testers to write concise and reusable test scripts that are maintainable across different environments.
Why Choose Selenium with Java?
Selenium Webdriver can be used with multiple programming languages like Python, C#, Ruby, and Java. But Selenium Webdriver with Java is particularly popular for a few reasons:
Extensive Libraries: Java has a rich set of libraries that simplify coding and interaction with browsers.
Large Community Support: Since Java is one of the most widely used programming languages, there’s ample community support to help troubleshoot any issues you encounter.
Integration with Tools: Java integrates easily with tools like Maven, Jenkins, and other CI/CD pipelines, making it perfect for test automation in agile environments.
Understanding TestNG: The Power of Test Organization
TestNG is a testing framework inspired by JUnit and NUnit but with more powerful features. It allows you to organize your test cases effectively, manage the execution of those tests, and generate detailed reports on the results.
Combining Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework provides a robust environment where you can easily manage and scale your test cases. Some key benefits of using TestNG are:
Annotations: TestNG uses annotations like @Test, @BeforeTest, and @AfterTest to manage the execution flow of tests.
Parallel Execution: You can run tests in parallel, which reduces the overall test execution time.
Grouping: It allows you to group your test cases and execute specific groups, depending on the testing scenario.
Detailed Reports: TestNG automatically generates detailed reports after the test execution, highlighting passed, failed, and skipped tests.
Setting Up Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG
Step 1: Download and Install Java
Before you begin, you’ll need to install the Java Development Kit (JDK). Ensure you have the correct version installed and set up the Java environment variables.
Step 2: Install Selenium Webdriver
Next, download Selenium Webdriver from the official Selenium website. Selenium provides a Java Client Library that you’ll need to add to your project.
Step 3: Install TestNG
TestNG is a third-party library, and you can add it to your project through Maven or manually download the JAR files. If you're using Maven, simply add the TestNG dependency to your pom.xml file.
Step 4: Writing Your First Test
Once everything is set up, you can create your first test. Below is a simple example of how to use Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework.
java
Copy code
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class SeleniumTest {
WebDriver driver;
@BeforeTest
public void setup() {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "path/to/chromedriver");
driver = new ChromeDriver();
}
@Test
public void openGoogle() {
driver.get("https://www.google.com");
System.out.println("Google page opened");
}
@AfterTest
public void teardown() {
driver.quit();
}
}
In this example, the @BeforeTest annotation ensures that the ChromeDriver is set up before running the test. The @Test method opens Google and prints a confirmation message, while the @AfterTest method closes the browser once the test is complete.
Key Advantages of Using Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG
Cross-browser Testing: Selenium Webdriver allows you to test on multiple browsers, ensuring your web application performs consistently across platforms.
Scalability: The combination of Java and TestNG allows you to create modular, scalable tests that can be executed in parallel.
CI/CD Integration: Using TestNG with Selenium Webdriver ensures smooth integration into CI/CD pipelines, enabling continuous testing.
Extensive Documentation: Both Selenium and Java have extensive documentation, making it easier for developers to find solutions and get started quickly.
Free AI Tools for Testing Automation
In the modern age of technology, you can also take advantage of free AI tools that assist in test automation. Many AI-powered testing platforms help reduce the time it takes to write test cases by suggesting test scripts, predicting potential failure points, and automating repetitive tasks. Tools like Mabl and Testim use AI to enhance traditional testing strategies, giving developers an edge when managing complex test suites. You can integrate these tools with Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework to further streamline your automation testing process.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Synchronization Issues: Sometimes, the web elements may take time to load, and Selenium might not wait long enough before interacting with them. The solution is to use WebDriverWait for explicit waits. Example: java Copy code WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 10);
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id("element_id")));
Handling Multiple Windows: While testing, you might encounter scenarios where a new window or tab opens. Selenium allows you to switch between multiple windows using the switchTo() method. Example: java Copy code String mainWindow = driver.getWindowHandle();
for (String handle : driver.getWindowHandles()) {
driver.switchTo().window(handle);
}
Dynamic Elements: Some web elements have dynamic IDs or names that change every time the page is reloaded. In such cases, it’s best to use CSS selectors or XPath. Example: java Copy code WebElement dynamicElement = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[contains(@id, 'dynamic')]"));
Conclusion
Mastering Selenium Webdriver with Java & TestNG Testing Framework is essential for anyone looking to excel in the field of automated web testing. The combination of these tools allows you to create efficient, reusable, and scalable test scripts that ensure your web applications are bug-free and performant. Whether you’re testing a small-scale project or managing a large automation suite, the flexibility and power of these tools make them invaluable.
By integrating AI tools into your automation pipeline, you can take your testing strategies to the next level, reducing manual intervention and making the testing process faster and more reliable.
In summary, leveraging Selenium Webdriver with Java along with the robust features of TestNG sets you up for success in the automation world. If you’re looking to enhance your testing knowledge or explore more advanced concepts, start building your test suites today! Happy testing!
0 notes
Text
The Best Java Libraries and Frameworks for Beginners
Java remains one of the most widely used programming languages, prized for its versatility, portability, and robust performance.
As a beginner, familiarizing yourself with Java's vast ecosystem of libraries and frameworks can significantly enhance your coding efficiency and project development.
Here are some of the best Java libraries and frameworks for beginners to help you get started on the right track.
1. Spring Framework
The Spring Framework is a powerful, feature-rich framework that simplifies enterprise Java development. It provides comprehensive infrastructure support for developing Java applications.
For beginners, Spring Boot is an excellent starting point within the Spring ecosystem. Spring Boot simplifies the setup and development of new Spring applications by providing defaults for code and configuration, helping you focus more on writing business logic rather than boilerplate code.
Key Features:
Simplifies dependency management
Built-in support for microservices
Extensive documentation and community support
2. Apache Commons
Apache Commons is a collection of reusable Java components that provide utility functions for various purposes, from I/O operations to collections. As a beginner, Apache Commons can help you avoid reinventing the wheel for common tasks and focus on solving unique problems.
Key Libraries:
Commons Lang: Extends the Java standard library with additional utilities for string manipulation, concurrency, and more.
Commons IO: Simplifies file I/O operations.
Commons Collections: Enhances the standard Java Collections framework.
3. JUnit
JUnit is the most widely used testing framework in the Java ecosystem. Writing tests is an integral part of software development, and JUnit makes it easy to write and run repeatable tests. As a beginner, learning JUnit will instill good testing practices early in your programming career.
Key Features:
Annotations for defining test methods
Assertions for testing expected results
Test runners to execute tests
4. Maven
Maven is a build automation and dependency management tool that simplifies the project build process. It manages project dependencies and builds lifecycle, making it easier to manage complex projects. For beginners, Maven's convention-over-configuration approach helps streamline project setup.
Key Features:
Simplifies dependency management
Standardizes project structures
Integrates with various IDEs and CI/CD tools
5. Hibernate
Hibernate is an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database interactions in Java applications. It allows you to map Java objects to database tables and vice versa, abstracting the underlying database operations.
For beginners, Hibernate eliminates the need to write complex SQL queries, making database programming more accessible.
Key Features:
Simplifies CRUD operations
Supports advanced query capabilities
Handles database connections and transactions
6. Google Guava
Google Guava is a set of core libraries that provide essential utilities for Java projects. It includes utilities for collections, caching, primitives support, concurrency, common annotations, string processing, and more. Guava's utilities can enhance productivity by providing ready-to-use implementations for common tasks.
Key Features:
Advanced collection utilities
Caching utilities
Functional programming support
Conclusion
Choosing the ideal libraries and frameworks is essential for effective Java development.
As a beginner, starting with Spring Framework, Apache Commons, JUnit, Maven, Hibernate, and Google Guava will provide you with a solid foundation and significantly boost your productivity.
These tools simplify common programming tasks and instill best practices that benefit your Java training journey. By leveraging these powerful resources, you'll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of Java projects with confidence and efficiency.
0 notes
Text
The Top Selenium Frameworks for Effective Automated Testing
Selenium is a leading tool for web application automation, but to fully leverage its capabilities, it's essential to pair it with a suitable testing framework. This guide delves into some of the best Selenium frameworks, each offering unique features and benefits to help streamline your testing process.

Why a Testing Framework Matters
A robust testing framework is the backbone of any automated testing strategy. Embracing Selenium's capabilities becomes even more accessible and impactful with Selenium Training in Pune. It provides structure for writing, managing, and executing test cases, enhancing productivity, improving test coverage, and ensuring reliable results. Here, we explore several top-tier frameworks that integrate seamlessly with Selenium.
TestNG: Versatile and Robust
Overview
Inspired by JUnit and NUnit, TestNG is designed to handle various test categories, including unit, functional, end-to-end, and integration tests. Its powerful features cater to complex testing needs.
Key Features
Parallel Execution: TestNG allows for parallel test runs, significantly reducing the time needed to execute extensive test suites.
Comprehensive Reports: It generates detailed, customizable reports that provide insights into test executions.
Annotations: Offers a rich set of annotations like @Test, @BeforeMethod, and @AfterMethod, aiding in efficient test management.
Data-Driven Testing: Facilitates data-driven tests with the @DataProvider annotation, enabling the same test to run with different data sets.
Benefits
TestNG's flexibility and comprehensive feature set make it ideal for complex scenarios. Its ability to run parallel tests and generate detailed reports saves time and enhances test analysis.
JUnit: Simplicity and Effectiveness
Overview
JUnit is a widely used testing framework for Java applications, renowned for its simplicity and ease of use.
Key Features
User-Friendly: JUnit’s straightforward approach simplifies writing and executing tests.
Annotations: Provides essential annotations like @Test, @Before, and @After, aiding in test case management.
Integration: Seamlessly integrates with various development tools and CI/CD pipelines. To unlock the full potential of Selenium and master the art of web automation, consider enrolling in the Top Selenium Online Training.

Benefits
JUnit's simplicity makes it perfect for small to medium-sized projects. Its ease of integration and straightforward testing approach can speed up development and ensure quality.
Cucumber: BDD for Better Collaboration
Overview
Cucumber facilitates Behavior Driven Development (BDD), allowing test cases to be written in plain English using the Gherkin language, making them accessible to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Key Features
Plain Language Syntax: Uses Gherkin to make test cases readable by anyone on the project, including business analysts and non-technical team members.
BDD Focus: Encourages collaboration between developers, QA, and business stakeholders, ensuring comprehensive application testing.
Multi-Language Support: Supports various programming languages, including Java, Ruby, and Kotlin.
Benefits
Cucumber’s BDD approach ensures clear communication among all stakeholders, fostering better collaboration and reducing misunderstandings. Its versatility and plain language syntax make it easy to adopt.
Robot Framework: Simplifying Testing with Keywords
Overview
Robot Framework is a generic, open-source automation framework using keyword-driven testing. Known for its easy-to-read syntax and extensive library support, it's highly accessible.
Key Features
Keyword-Driven: Uses keywords to define test cases, simplifying the process of writing and reading tests.
Library Support: Supports numerous libraries, including SeleniumLibrary, for using Selenium WebDriver.
Language-Independent: Its modular architecture supports various tools and libraries.
Benefits
Robot Framework’s keyword-driven approach makes test case creation straightforward, accessible to testers with varying technical expertise. Its extensive library support and modular architecture enhance its versatility.
Conclusion
Choosing the right framework for Selenium testing hinges on your specific project requirements and team capabilities. TestNG offers flexibility and detailed reporting for complex scenarios. JUnit’s simplicity and ease of use are ideal for smaller projects. Cucumber’s BDD approach promotes collaboration between technical and non-technical team members. Robot Framework’s keyword-driven testing simplifies test creation, making it accessible and versatile.
Understanding the strengths and unique features of each framework will help you select the one that best fits your needs, ensuring efficient and effective Selenium testing. Whether you're handling a small project or a large, intricate system, there’s a Selenium framework tailored to help you achieve your testing goals.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Selenium: Key Points to Learn
Selenium is a powerful tool for automating web applications for testing purposes, but it can also be used for web scraping and automating repetitive web-based tasks. For those keen to excel in Selenium, enrolling in a Selenium course in Pune can be highly advantageous. Such a program provides a unique opportunity to acquire comprehensive knowledge and practical skills crucial for mastering Selenium. To effectively learn and use Selenium, here are the key points to focus on:

1. Understanding Selenium and Its Components
Selenium WebDriver: The core component that drives the browser.
Selenium IDE: A browser extension for record-and-playback of interactions.
Selenium Grid: A tool to run tests on different machines and browsers in parallel.
2. Setting Up the Environment
Install WebDriver: Download the WebDriver for the browser you intend to automate (e.g., ChromeDriver for Google Chrome).
Configure IDE: If using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Eclipse, IntelliJ, or VSCode, ensure it's set up with necessary plugins.
3. Programming Languages
Language Support: Selenium supports multiple programming languages including Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and JavaScript.
Learning Basics: Have a good grasp of the basics of the programming language you'll use with Selenium.
4. Basic Selenium Commands
Navigation: Learn how to navigate to URLs and interact with browser history.
Locators: Master different locators (ID, Name, Class Name, Tag Name, CSS Selector, XPath) to find elements on a web page.
Actions: Perform actions like click, sendKeys (for typing), and others like drag and drop.

5. Advanced Interactions
Waits: Implement implicit and explicit waits to handle dynamic web content.
Frames and Windows: Handle frames, windows, and alerts effectively.
Keyboard and Mouse Events: Use Actions class for complex user interactions like double-click, right-click, and hover.
6. Page Object Model (POM)
Design Pattern: Use POM to create an object repository for web elements, enhancing test maintenance and reducing code duplication.
Implementation: Structure your project to include page classes and test classes.
7. Test Framework Integration
JUnit/TestNG: Integrate Selenium with testing frameworks like JUnit or TestNG for better test structure, reporting, and annotations.
Assertions: Use assertions to validate test outcomes.
8. Handling Web Elements
Dynamic Elements: Learn strategies to interact with elements that change dynamically.
Dropdowns, Checkboxes, and Radio Buttons: Work with common form elements effectively.
9. Error Handling and Debugging
Exception Handling: Implement try-catch blocks to handle exceptions.
Logs and Reports: Utilize logging frameworks and create detailed test reports. Enrolling in a top-rated Selenium course online can unleash the full power of Selenium, offering individuals a deeper understanding of its intricacies.
10. Selenium Grid
Parallel Execution: Set up Selenium Grid to run tests across multiple environments simultaneously.
Configuration: Understand hub and node configuration and how to set up and tear down the Grid.
11. Best Practices
Clean Code: Write readable, maintainable, and reusable code.
Modular Approach: Break tests into smaller, manageable units.
Continuous Integration: Integrate Selenium tests with CI/CD pipelines using tools like Jenkins.
12. Community and Resources
Documentation: Regularly consult the official Selenium documentation.
Community Forums: Engage with the Selenium community through forums, Stack Overflow, and GitHub.
Tutorials and Courses: Leverage online tutorials, courses, and webinars for continuous learning.
Conclusion
Learning Selenium is a journey that involves understanding its core components, setting up the environment, mastering basic and advanced commands, implementing design patterns like POM, integrating with test frameworks, and following best practices. By focusing on these key areas, you can become proficient in automating web testing and other web-related tasks using Selenium. Happy testing!
0 notes
Text
Mastering Selenium: A Comprehensive Resource for Effective Web Automation Testing
In the wide spectrum of web development, prime importance is accorded to quality assurance as it guarantees the smooth functioning of applications across various platforms and browsers. Selenium steps into this scene as a significant player with its suite of tools designed for automating web browsers. For professionals in QA and development, becoming proficient in Selenium equates to excelling in maintaining sturdy web applications. Selenium offers a diverse and complete set of tools, particularly useful for tasks like UI testing and regression, although it requires mindful study to be approached correctly. To transition from a Selenium beginner to a maestro, you can consider enrolling in a Selenium Course in Bangalore which provides an in-depth comprehension of crucial Selenium features and practices for a range of web automation tasks.

Plunging into Web Technologies
To master Selenium automation, a thorough understanding of web technologies is fundamental. HTML lays the structure, CSS embellishes it, and JavaScript instills dynamics into a stagnant webpage. Mastery over these three is crucial for seamlessly pinpointing and altering web elements with Selenium. This knowledge shapes both, your perception of web applications and your ability to programmatically control them.
The Language of Selenium – Choose What You Prefer
Selenium's beauty lies in its multilingual capabilities; it converses in the language you find easiest. Be it the object-oriented style of Java, Python’s clear syntax, C#'s sturdiness, or JavaScript's widespread application, you pick your preference. Familiarity with language semantics, syntax, control structures, and exception handling equips you with the tools to script your test cases effectively.
Selenium WebDriver: Navigating Your Test Suite
The Selenium WebDriver goes beyond being a mere tool; it acts as the command center of your automated testing environment. Although setting it up is easy, learning to exploit its full potential demands time and perseverance. It involves understanding how web browsers respond to your instructions, how the WebDriver interacts with browser engines, and how you can execute tasks ranging from simple clicks to more intricate parallel executions.
Locating Strategies: Directing WebDriver
The complex web of elements necessitates a sharp sense of navigation. A diverse set of tools is at your disposal—IDs, classes, names, XPath expressions, and CSS selectors. Each locator caters to a distinct need, and the key to a consistent test is selecting the appropriate one. Striking a balance between accuracy and efficiency is crucial for writing locators resilient to minor UI alterations.
Capitalizing on Test Frameworks: Structuring Your Tests
Frameworks like JUnit, TestNG, and others not only organize test execution but provide context. Assertions validate the expected behavior of our applications, annotations designate the roles of various methods, while reports provide a detailed account of the tests’ successes and failures. The adoption of a framework isn't solely about utilizing tools; it's about crafting a quality assurance narrative for your application.

Controlling the Flight of Time: Managing Synchronization
Races, including web testing, can spring unexpected winners, highlighting race conditions. Synchronization isn’t merely about pausing; it's about orchestrating harmonious interactions. Whether it is using explicit waits for specific conditions or implicit waits that set a baseline patience for the WebDriver, executing scripts smoothly without unnecessary delays requires fine balancing.
The Page Object Model: Organizing Test Blueprints
Envision navigating a labyrinth as intricate as a webpage. The Page Object Model doesn’t merely delineate a route; it generates a comprehensive labyrinth map. By encompassing page elements and interactions within classes, the POM ensures test maintainability and scalability. Further, it separates the test logic from the UI specifics, transforming maintenance from a feared overhaul into a scripted dance.
Test Automation Philosophies: Standardizing Reliable Coding
Scripting test codes mirrors an art form, calling for clean, reusable, and modular code. It requires meaningful naming conventions reflecting their actions and error handling that communicates effectively. The objective isn't limited to automation but extends to establishing an ecosystem where each test script functions like a well-positioned cog in a well-engineered machine, comprehensible, and lasting.
The CI Connection: Maintaining Constant Quality
Incorporating Selenium into CI pipelines using Jenkins or Azure DevOps signifies a cultural shift rather than automation. It embraces a practice where every commit is scrutinized, preventing any regression or bug from going unnoticed. It's about early identification of issues in the development process, reinforcing confidence in deployment.
Beyond Automation: The Art of Exploratory Testing
While Selenium excels in functional testing, exploratory testing thrives in the realm of creativity. Here, human intuition and ingeniousness come into play, discerning nuanced use-cases and user experience issues that algorithms struggle to identify. Automation and exploratory testing function in unison, enriching and informing each other.
Lifelong Learning: Achieving Mastery in Selenium
Becoming a Selenium maestro isn't an overnight feat; it unveils through constant learning and practice. It extends beyond tool familiarity to a deep understanding of its relationship with software development practices, design patterns, and human-computer interaction. It establishes a symbiotic relationship where each advancement in web technology opens a new window for testing, and in return, Selenium guides these technologies towards maturity.
To acquire extensive expertise in using Selenium WebDriver for diverse web automation tasks, contemplate enrolling in Selenium Online Training, which provides community support and job placement assistance.
Conclusion
Emerging as a Selenium expert symbolizes a journey—a fusion of technological comprehension, programming skills, tool mastery, and adherence to best practices. It's about laying foundations, structuring, and incessant innovation to pace with web application development. With concentration, diligence, and a zest for exploration, the ultimate aim of gaining proficiency in Selenium automation testing will stand not just as a testament to your abilities, but a beacon of quality in the software development community.
Take the next step to become a Selenium master, harness power, and shape web application quality into its epitome. And most importantly, remember that just like any craft, it is the commitment to refining the details that breeds excellence.
0 notes
Text
Top 10 Java Libraries and Frameworks Every Developer Should Know

Top 10 Java Libraries and Frameworks Every Developer Should Know
1. Spring Framework
Comprehensive ecosystem for enterprise Java development — Dependency injection — MVC architecture — Microservices support
2. Hibernate
Object-relational mapping (ORM) library — Simplifies database interactions — Supports multiple databases — Reduces boilerplate database code
3. Apache Maven
Project management and build automation tool — Dependency management — Standardized project structure — Easy integration with CI/CD pipelines
4. JUnit
—
Unit testing framework — Supports test-driven development — Annotations for test configuration — Wide IDE integration
5. Apache Spark — Big data processing framework — Distributed computing — Machine learning capabilities — Real-time data streaming
6. Mockito — Mocking framework for unit tests — Allows creation of test doubles — Verifies method interactions — Simplifies complex testing scenarios
7. Lombok — Reduces boilerplate code — Automatic getter/setter generation — @Data, @Builder annotations — Improves code readability
8. Jackson — JSON processing library — Object serialization/deserialization — High-performance JSON parsing — Supports complex object mappings
9. Log4j — Logging framework — Configurable logging levels — Performance optimization — Multiple output destinations
10. Guava — Google’s core libraries — Utility classes — Functional programming support — Improved collections and caching
WEBSITE: https://www.ficusoft.in/core-java-training-in-chennai/
0 notes
Text
Key points to learn the Spring Framework
key points to learn the Spring Framework:
Java Basics: Ensure solid understanding of Java fundamentals.
Spring Basics: Read official Spring documentation for an overview.
Core Concepts: Learn Inversion of Control (IoC) and Dependency Injection (DI).
Spring Boot: Explore Spring Boot for quick setup and configuration.
Dependency Injection: Understand IoC containers, XML, and annotation-based configurations.
Spring MVC: Grasp Model-View-Controller architecture for web applications.
Data Access: Explore data access using JDBC, ORM (like Hibernate), and Spring Data.
Security: Learn Spring Security for authentication and authorization.
RESTful Web Services: Build RESTful APIs using Spring MVC or WebFlux.
Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP): Understand AOP for handling cross-cutting concerns.
Testing: Write unit and integration tests using tools like JUnit.
Real-World Projects: Apply knowledge through practical projects.
Community Engagement: Join Spring community discussions and forums.
Advanced Topics: Explore Spring Cloud, Spring Batch, and other advanced features.
Continuous Learning: Stay updated with the latest releases and features.
#magistersign#Java#SpringFramework#Programming#Coding#SoftwareDevelopment#JavaDevelopment#WebDevelopment#SpringBoot#DependencyInjection#SpringMVC#DataAccess
0 notes