#Network load balancer
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Every Growing Business Needs a Reliable Network Load Balancer Today?
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring the smooth and efficient delivery of services is critical for business success. As online platforms grow and user traffic surges, businesses require a robust infrastructure that can handle such demands. This is where a network load balancer plays a vital role. It acts as the backbone of application performance, distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload and ensure seamless access. Whether you're managing an e-commerce site, SaaS product, or enterprise-level service, adopting a network load balancer can significantly enhance reliability, uptime, and scalability—key factors that determine your competitive edge in the digital age.
Handle High Traffic Demands with Ease
Managing high volumes of user traffic is a challenge that every growing business must address. Without proper distribution, sudden traffic spikes can cripple your servers, resulting in crashes and service disruptions. A network load balancer ensures that traffic is evenly and intelligently distributed among available resources, preventing any single server from becoming a point of failure. This enables your infrastructure to adapt dynamically to demand changes, whether during a flash sale, product launch, or viral moment. By leveraging a network load balancer, businesses gain the ability to support growth confidently and deliver reliable digital experiences under any traffic condition.
Improve Uptime Through Smart Load Balancing
Downtime can damage a company’s reputation, reduce revenue, and impact user trust. With a network load balancer, uptime becomes less of a gamble and more of a guarantee. These systems monitor server health in real time and reroute traffic away from any nodes that are underperforming or down. This proactive distribution helps avoid service interruptions and ensures continuous availability. As a result, critical applications remain accessible to users, even during server failures or maintenance. By investing in a network load balancer, businesses create a foundation for high availability, which is essential for customer satisfaction and long-term operational success.
Ensure Seamless App Performance for Users
End users expect instant and consistent performance from apps and websites. Delays or glitches can lead to user frustration and abandonment. A network load balancer helps ensure applications run smoothly by optimizing how traffic is allocated to backend servers. It reduces latency, minimizes server overloads, and maintains balanced performance under varying loads. By dynamically adjusting traffic flows, a network load balancer prevents performance bottlenecks that commonly occur during peak usage times. Whether users are accessing content, submitting forms, or completing transactions, the consistent backend support provided by a network load balancer guarantees a seamless and responsive user experience.
A Network Load Balancer Boosts Service Reliability
Service reliability is essential for any business delivering digital solutions. A network load balancer enhances this reliability by acting as a strategic traffic manager that ensures your system resources are used efficiently and effectively. It detects faulty servers and automatically routes traffic to healthy ones without user interruption. This smart decision-making process keeps services running even under pressure, reducing the risk of downtime and improving system resilience. From banking applications to healthcare platforms, any service that demands real-time availability can benefit from the robust reliability offered by a network load balancer, reinforcing trust and satisfaction among end users.
Scale Business Operations Without Bottlenecks
As a business grows, its infrastructure must scale to support increased demands. Without proper distribution of network traffic, this growth can lead to performance issues and bottlenecks. A network load balancer allows companies to scale operations efficiently by automatically balancing workloads across multiple servers or cloud instances. This means new resources can be added seamlessly without affecting performance. By providing the flexibility to scale horizontally, a network load balancer empowers businesses to expand offerings, serve more users, and innovate faster—all without worrying about crashing systems or degraded user experiences. It’s a critical tool for future-proofing your IT architecture.
Protect Against Unexpected Server Failures
Server failures can strike without warning, but a network load balancer acts as a safeguard against such unpredictable events. It continuously monitors the health of servers and instantly redirects traffic to other functional servers when an issue is detected. This automatic rerouting ensures your users experience uninterrupted access to your services, even when certain parts of the system fail. Rather than relying on manual intervention, a network load balancer enables a self-healing infrastructure that minimizes downtime and protects business continuity. For industries that demand constant uptime, such as finance or e-commerce, this level of protection is not just helpful—it's essential.
Enhance User Experience with Faster Response Times
Speed plays a major role in user satisfaction. Studies show that users abandon websites or apps that load slowly. A network load balancer contributes significantly to faster response times by distributing user requests to the server with the lowest load or closest proximity. This reduces wait times and ensures users get the content or service they need quickly. Load balancing also prevents delays caused by server congestion. The result is a responsive and pleasant user experience across all devices and platforms. For businesses that rely on digital engagement, investing in a network load balancer means investing in customer retention and brand loyalty.
Conclusion
In an era where digital performance is a key business differentiator, a network load balancer is not a luxury—it's a necessity. It empowers organizations to handle high traffic volumes, maximize uptime, improve reliability, and scale operations without fear of failure. More importantly, it ensures that end users consistently enjoy a smooth and fast experience, regardless of backend complexities. Whether you're launching a startup or expanding an enterprise network, integrating a network load balancer into your infrastructure is a smart, forward-thinking move that strengthens both technical resilience and business growth in an increasingly connected world.
0 notes
Text
How Network Load Balancers Enhance Application Availability and Performance?
A network load balancer is a critical component in modern IT infrastructure, ensuring high application availability and optimal performance. By intelligently distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, it prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed, thereby reducing the risk of downtime. This load distribution enhances the responsiveness of applications, providing users with a seamless experience. Additionally, features like SSL offloading and content caching further accelerate application delivery by offloading resource-intensive tasks from backend servers. Edgenexus Limited offers advanced network load balancer solutions that integrate these capabilities, enabling businesses to maintain resilient and high-performing applications. By implementing such solutions, organizations can ensure continuous service availability and meet the growing demands of their user base.
Enhancing Application Availability through Intelligent Traffic Distribution
Network Load Balancers (NLBs) play a pivotal role in enhancing application availability by distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers. This distribution prevents any single server from becoming a bottleneck, ensuring that applications remain accessible even during high traffic periods. By balancing the load, NLBs minimize the risk of server overloads and potential downtime, thereby maintaining consistent application performance. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions exemplify this capability, providing businesses with robust tools to manage traffic efficiently and uphold high availability standards.
Optimizing Application Performance with Low-Latency Traffic Routing
One of the key advantages of NLBs is their ability to route traffic with minimal latency. By operating at the connection level (Layer 4), they efficiently direct data packets to the appropriate servers, reducing delays and enhancing user experience. This low-latency routing is crucial for applications that require real-time data processing and swift response times. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions are engineered to handle high-throughput demands, ensuring that applications perform optimally even under varying load conditions.
Achieving Scalability with Seamless Addition of Servers to Handle Growing Traffic
As businesses experience growth, the volume of incoming traffic often increases, necessitating scalable solutions. NLBs facilitate this scalability by allowing the seamless addition of servers to the network. This elasticity ensures that applications can handle increased loads without compromising performance. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions support dynamic scaling, enabling businesses to adapt to changing traffic patterns and maintain optimal application performance during peak times.
Ensuring High Availability with Automatic Failover to Healthy Servers
High availability is a critical requirement for modern applications. NLBs contribute to this by continuously monitoring the health of registered servers and automatically rerouting traffic away from any servers that are detected as unhealthy. This automatic failover mechanism ensures uninterrupted application access, even in the event of server failures. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions incorporate robust health-checking and failover features, providing businesses with reliable tools to maintain continuous application availability.
Enhancing Security by Preserving Client IP Addresses for Backend Processing
Security is a paramount concern for businesses managing sensitive data. NLBs enhance security by preserving the original client IP addresses when forwarding requests to backend servers. This feature allows backend applications to perform security checks based on the client's IP information, facilitating accurate threat analysis and response. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions support this functionality, providing businesses with enhanced security measures to protect against malicious activities.
Supporting SSL Offloading to Reduce Server Load and Improve Efficiency
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption is essential for protecting data transmitted over the internet. NLBs support SSL offloading, a process where the load balancer handles the SSL encryption and decryption tasks, freeing backend servers from this resource-intensive process. This offloading reduces the computational burden on servers, allowing them to allocate resources to application-specific tasks, thereby improving overall system efficiency. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions offer robust SSL offloading capabilities, enhancing both security and performance.
Facilitating Global Server Load Balancing for Multi-Region Application Deployment
For applications deployed across multiple regions, global server load balancing (GSLB) ensures that users are directed to the optimal server based on their geographic location and server health status. This capability enhances user experience by reducing latency and improving access speeds. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions support GSLB, enabling businesses to deliver consistent and efficient application performance to users worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, network load balancers are essential tools for enhancing application availability and performance. By intelligently distributing traffic, optimizing routing, and supporting scalable and secure configurations, NLBs ensure that applications can meet the demands of modern users. Edgenexus Limited's network load balancer solutions exemplify these capabilities, providing businesses with reliable and efficient tools to manage their application delivery needs effectively. Implementing such solutions enables organizations to maintain high-performance applications that are both available and secure, thereby supporting business growth and customer satisfaction.
0 notes
Text
Network Load Balancers vs. Application Load Balancers: Key Differences
Network Load Balancers (NLBs) and Application Load Balancers (ALBs) differ in functionality, operational layers, and use cases. NLBs operate at the transport layer (OSI Layer 4) and manage TCP/UDP traffic. They excel in low-latency, high-throughput environments like real-time applications or financial systems. ALBs work at the application layer (OSI Layer 7), handling HTTP/HTTPS traffic. They offer advanced features such as content-based routing, SSL termination, and user authentication, making them ideal for web applications and API services.
While NLBs focus on speed and efficiency, ALBs provide fine-grained control over traffic based on application-level data. Choosing between them depends on factors like performance needs, protocol support, and application complexity, with many setups benefit ing from a combination of both.
Introduction to Load Balancing
Load balancing is a crucial component in the infrastructure of web services and applications. It efficiently distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, ensuring high availability and reliability. There are two common types of load balancers used in modern networks: Network Load Balancers (NLBs) and Application Load Balancers (ALBs). Understanding the key differences between these two can help businesses choose the most appropriate solution for their specific needs.
What is a Network Load Balancer (NLB)?
A Network Load Balancer operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model. It handles the distribution of traffic based on IP addresses, TCP/UDP ports, and protocols. NLBs are designed to manage high-volume traffic and can efficiently route network requests to backend servers without modifying the data. Their primary advantage lies in their ability to handle large amounts of traffic with low latency and high throughput.
What is an Application Load Balancer (ALB)?
In contrast, an Application Load Balancer operates at the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. It is responsible for routing traffic based on the content of the request, such as the URL path, HTTP headers, cookies, and even query strings. This level of traffic inspection allows ALBs to direct requests to the appropriate backend server based on specific application logic. ALBs are ideal for handling complex, content-driven applications and microservices architectures.
Performance and Scalability: NLB vs. ALB
When comparing performance, NLBs are optimized for handling high-throughput, low-latency traffic. They are often deployed in situations where fast, simple traffic routing is required, such as for gaming servers, real-time communications, and other low-latency applications. On the other hand, ALBs are more suited for applications that require advanced routing capabilities, such as web applications that rely on different URLs for distinct functionalities. While both load balancers are scalable, NLBs can handle a higher volume of traffic with minimal overhead, making them a better choice for raw performance.
Security Features: NLB vs. ALB
Both NLBs and ALBs offer security features, but they differ in their implementation and capabilities. NLBs typically provide basic security by supporting SSL/TLS encryption for data in transit. However, the primary focus is on traffic distribution rather than deep inspection. ALBs, however, come with more advanced security capabilities, such as the ability to inspect HTTP headers, cookies, and other web application parameters. ALBs integrate seamlessly with Web Application Firewalls (WAF), offering enhanced protection against web vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Additionally, ALBs support fine-grained access control, enabling administrators to define detailed security policies based on application content.
Cost Considerations: NLB vs. ALB
The cost structure of NLBs and ALBs differsbased on their functionality and complexity. Network Load Balancers are generally more cost-effective for simpler use cases, particularly when high performance and low latency are prioritized over deep application inspection. Since NLBs handle traffic at Layer 4, they require fewer resources and are less complex to operate, thus lowering operational costs. ALBs, however, tend to be more expensive due to the advanced features they provide. The extra capabilities, such as application-layer routing and deep packet inspection, require more computing resources and can drive up the cost, making ALBs a better option for businesses that need more control over application-level traffic.
Use Cases: When to Choose NLB or ALB
The choice between a Network Load Balancer and an Application Load Balancer depends largely on the application’s needs and the type of traffic being managed. If the primary goal is to handle high-volume, low-latency traffic with minimal processing, a Network Load Balancer is the ideal choice. This is especially true for services such as streaming platforms, VoIP services, and other real-time applications. On the other hand, if your application requires content-based routing, user authentication, or deep inspection of traffic at the HTTP level, an Application Load Balancer is the better option. ALBs are perfect for dynamic web applications, microservices, and APIs, where different requests need to be routed to different servers based on application-level criteria.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Network Load Balancers (NLBs) and Application Load Balancers (ALBs) are essential components in optimizing network traffic and ensuring high availability. NLBs are perfect for applications requiring high throughput and low latency, particularly in real-time services, while ALBs excel in scenarios where more complex routing decisions are needed at the application layer. Choosing the right load balancer depends on your specific use case, performance requirements, and budget.
0 notes
Text
The Impact of Network Load Balancers on Latency and Response Times
The Impact of Network Load Balancers on Latency and Response Times" explores how network load balancers (NLBs) influence the performance of web applications by managing traffic distribution across multiple servers. NLBs are designed to route incoming requests to the optimal server based on factors like server health, traffic load, and geographic location. While their primary function is to improve scalability and availability, they can also impact latency and response times. Proper configuration of an NLB can minimize delays by efficiently directing traffic to the fastest or least-loaded server, improving overall user experience. This article discusses the balance between load balancing efficiency and performance, offering insights into how to fine-tune NLBs to reduce latency and maintain optimal response times in high-traffic environments.
Understanding the Role of Network Load Balancers in Network Traffic Management
Network load balancers are crucial in distributing network traffic across multiple servers to ensure optimal resource usage and prevent overload on any single server. They are designed to improve the performance, reliability, and scalability of applications and services. By effectively managing how traffic is distributed, load balancers reduce latency and ensure that response times remain consistently fast, even during periods of high demand. In this section, we’ll explore the fundamental function of network load balancers and how they contribute to better network performance.
How Load Balancers Affect Latency in Distributed Networks
Latency is the delay between a user’s request and the server’s response. Network load balancers play a vital role in minimizing this delay by intelligently routing requests to the most appropriate server based on various criteria, such as server health, location, or current load. This helps reduce the distance data travels and avoids unnecessary delays, improving the overall user experience. In this section, we will delve into how different types of load balancing algorithms impact latency and ensure fast data transmission.
Load Balancer Algorithms: Choosing the Right One to Minimize Response Times
The efficiency of a network load balancer heavily depends on the algorithm used to distribute traffic. Popular algorithms include round-robin, least connections, and weighted load balancing, each with its advantages in terms of response time optimization. By directing traffic based on real-time server performance, these algorithms ensure that no single server becomes overwhelmed, which helps to reduce server response time and latency. This section will examine how choosing the right algorithm can drastically improve response times in high-traffic networks.
The Role of Geographical Load Balancing in Reducing Latency
Geographical load balancing involves directing user requests to the closest data center or server region to reduce the physical distance between the user and the server. This results in lower latency, as data doesn't have to travel across vast distances. For global applications, geographical load balancing is essential to ensure a seamless user experience regardless of location. This section will explore how geographical considerations and the use of content delivery networks (CDNs) can impact latency and response time in large-scale networks.
How Load Balancers Improve Server Availability and Performance Under Heavy Traffic
During peak traffic periods, network load balancers ensure that incoming traffic is distributed evenly across multiple servers, preventing any server from becoming a bottleneck. By maintaining high availability and distributing traffic evenly, load balancers contribute to reduced congestion and latency. This ensures that each server maintains optimal performance, leading to faster response times even under heavy load. In this section, we’ll examine how load balancers handle high traffic volumes and maintain server performance during demand surges.
The Impact of Load Balancer Configuration on Overall Network Efficiency
Proper load balancer configuration is key to optimizing network performance. Misconfigured load balancers can result in suboptimal traffic distribution, which may lead to increased latency and slower response times. Factors such as session persistence, SSL termination, and health checks can significantly influence how effectively a load balancer operates. This section will discuss the various configuration options that impact latency and response times and provide guidance on how to fine-tune load balancers for maximum efficiency.
The Future of Network Load Balancers: Enhancing Latency and Response Times with AI and Automation
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing the way load balancers handle network traffic. AI-powered load balancers can predict traffic patterns, automatically adjust traffic distribution, and dynamically allocate resources to reduce latency. By continuously learning from network behavior, these intelligent systems can optimize response times in real time. This section will explore the future of load balancing technology, focusing on the role of AI and automation in minimizing latency and enhancing overall network efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, network load balancers play a critical role in managing traffic and improving latency and response times across distributed networks. By using efficient load balancing algorithms, geographic distribution strategies, and advanced configuration settings, organizations can significantly reduce latency and ensure fast response times, even during periods of high traffic. The growing integration of AI and automation will further enhance the ability of load balancers to predict and adjust to network demands, making them an indispensable tool for maintaining optimal performance. As networks become increasingly complex.
0 notes
Text
Troubleshooting Common Network Load Balancer Issues
Troubleshooting Common Network Load Balancer Issues focuses on identifying and resolving frequent problems that affect the performance and reliability of network load balancers (NLBs). Common issues include incorrect load balancing algorithms, misconfigured security groups or firewall settings, and improper health check configurations, which can cause traffic distribution errors or downtime. Addressing issues such as SSL/TLS handshake failures, DNS resolution problems, or server unavailability is also key to ensuring optimal operation. The blog will guide users through diagnosing these problems, using tools like logs, performance monitoring, and error messages, as well as providing solutions such as recalibrating configurations, optimizing server resources, or updating software. A proactive approach to NLB management can significantly enhance service uptime and user experience.
What is a Network Load Balancer?
A Network Load Balancer (NLB) is a crucial component in modern network architectures. It operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model, distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure the reliability, scalability, and performance of web applications. Unlike traditional load balancers that handle HTTP or HTTPS traffic, an NLB efficiently manages non-HTTP protocols such as TCP, UDP, and TLS. This makes it ideal for applications requiring high availability and low latency, such as gaming servers, financial applications, and IoT services.
How Does a Network Load Balancer Work?
Network Load Balancers utilize algorithms like Round Robin, Least Connections, and IP Hash to distribute traffic. When a client sends a request, the NLB evaluates the incoming data packet and routes it to an appropriate backend server based on the selected algorithm. This process ensures that no single server gets overwhelmed by traffic. Furthermore, NLBs monitor the health of backend servers and automatically reroute traffic away from servers that are down, ensuring minimal service disruption. By balancing the traffic load, NLBs improve response times and prevent bottlenecks in high-demand environments.
Benefits of Using a Network Load Balancer
The use of a Network Load Balancer comes with numerous advantages. First and foremost, it ensures high availability by rerouting traffic to healthy servers, reducing the impact of server failures. Load balancing also enhances scalability, allowing businesses to add or remove servers based on demand without interrupting service. Another major benefit is improved performance, as NLBs reduce response times by efficiently distributing workloads. Additionally, NLBs often support SSL termination, offloading SSL decryption from backend servers, which frees up resources for application processing.
Key Features of a Network Load Balancer
A Network Load Balancer is equipped with a variety of features that make it a versatile solution for complex infrastructures. Some key features include TLS termination, which secures the traffic between clients and the load balancer, sticky sessions, where the load balancer keeps track of a user’s session, ensuring all requests are routed to the same backend server, and auto-scaling capabilities that allow the system to automatically adjust resources based on traffic spikes. DDoS protection is another critical feature that helps shield backend servers from malicious attacks, providing an added layer of security.
Network Load Balancer vs. Application Load Balancer: What’s the Difference?
The primary difference between a Network Load Balancer (NLB) and an Application Load Balancer (ALB) lies in the layer of the OSI model at which they operate. An NLB works at Layer 4 (Transport Layer), making it more suitable for non-HTTP traffic and protocols like TCP, UDP, and TLS. On the other hand, an ALB operates at Layer 7 (Application Layer), handling HTTP/HTTPS traffic and providing advanced features such as content-based routing, host-based routing, and SSL offloading. While both load balancers share the goal of improving performance and availability, choosing between them depends on the specific needs of your application and traffic type.
Use Cases for Network Load Balancers
Network Load Balancers are employed in a variety of use cases across different industries. They are particularly well-suited for applications requiring low latency and high throughput, such as online gaming platforms, VoIP services, and financial transaction systems. NLBs are also critical for high-performance computing environments, where distributed applications require seamless traffic distribution to optimize resource utilization. Additionally, NLBs are ideal for handling unpredictable traffic patterns, such as those seen in cloud-based services and microservices architectures, where scalability and reliability are paramount.
How to Implement a Network Load Balancer in Your Infrastructure?
Implementing a Network Load Balancer involves a few key steps. First, determine your traffic requirements and decide on the type of NLB that suits your needs (e.g., a cloud-based NLB like AWS NLB or an on-premise solution). Next, configure the backend servers, ensuring they are properly secured and optimized for performance. After setting up the NLB, integrate monitoring tools to track traffic flow, server health, and system performance. Finally, ensure failover configurations are in place, so the NLB can redirect traffic to healthy servers if any fail. This process will help maintain system uptime and ensure high availability.
Conclusion
Network Load Balancers play a pivotal role in the performance, scalability, and security of modern network infrastructures. By efficiently distributing traffic, they ensure high availability and prevent server overloads. With their ability to support various protocols and integrate seamlessly into cloud-based and on-premise environments, NLBs are indispensable for businesses looking to maintain fast, secure, and reliable services. As traffic demands increase and applications evolve, leveraging a Network Load Balancer becomes an essential strategy for maintaining optimal system performance and user experience.
0 notes
Text
youtube
Elevate your business to new heights with Cyfuture Cloud's revolutionary Load Balancer. In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, maintaining a strong online presence is paramount for businesses. Our Load Balancer is the game-changing solution you need, offering scalability, smooth performance, and unmatched dependability.
Ever worried about sudden traffic surges crashing your website? Fear not – Cyfuture Cloud's Load Balancer ensures your website stays robust by evenly distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers. This proactive approach eliminates downtime, slow loading times, and unresponsiveness, providing your clients with an impeccable user experience. Our team of experts stands ready to customize Load Balancer setups based on your unique requirements, ensuring optimal performance at all times.
https://cyfuture.cloud/load-balancer
0 notes
Video
youtube
Terraform on AWS - AWS Network Load Balancer TCP and TLS with Terraform ...
#youtube#🚀 Deploy AWS Network Load Balancer (NLB) with TCP & TLS using Terraform! In this step-by-step tutorial learn how to configure an AWS Networ
0 notes
Text
VMware Networking: 5 Concepts to Master
VMware Networking: 5 Concepts to Master #homelab #selfhosted #vmware #VMwareNetworkingEssentials #vSphereStandardVsDistributedSwitch #ManagingMultipleUplinks #UnderstandingVMwareFailovers #MasteringLoadBalancingInVirtualEnvironments #VLANTaggingInVMware
One of the challenges when getting into virtualization using VMware ESXi and vSphere with vCenter Server is understanding the many different networking concepts. There are a few foundational concepts in the VMware networking layer that you need to understand and master that will provide a basis for building your environment connected to the virtual network in your VMware environment. Table of…

View On WordPress
#configuring VMkernel ports#ensuring security with virtual switches#managing multiple uplinks#mastering load balancing in virtual environments#optimizing virtual and physical network communication#understanding VMware failovers#VLAN tagging in VMware#VMware network traffic management#VMware networking essentials#vSphere Standard vs Distributed Switch
1 note
·
View note
Text
‧₊˚ The Science Behind @luckykiwiii101's Distraction Technique *ೃ༄



Relaxing °. *࿐
Relaxation techniques are more effective when the body is at ease. A comfortable position minimizes physical distractions and prepares the body for a shift into a relaxed, meditative state, which is essential for reducing stress and activating the parasympathetic nervous system.
The Alpha State °. *࿐
Alpha Brainwaves: The alpha state refers to a brainwave frequency range (8-12 Hz) that is associated with relaxation, creativity, and heightened suggestibility. Alpha is a common state for the brain and occurs whenever a person is alert, but not actively processing information. You can increase alpha by closing your eyes or deep breathing and decrease alpha by thinking or calculating. ଳ Sub band low alpha: 8-10: inner-awareness of self, mind/body integration, balance ଳ Sub band high alpha: 10-12: centering, healing, mind/body connection
Counting and Visualization: Counting down and visualizing numbers can help quiet the mind, reduce external distractions, and induce relaxation. This repetitive task shifts attention inward and promotes alpha wave activity. It activates areas of the brain linked to visualization, like the occipital and parietal lobes. Adding another layer of mental activity, further grounding you in the internal, relaxed state.
Distraction Through Visualization °. *࿐
Distraction vs. Focus: The paradox here is that by intentionally distracting yourself with a scene or an internal activity (like playing a song mentally), you stop focusing on the external world (the "3D"). This detachment from external stimuli is key to shifting into an altered state of consciousness.
Default Mode Network (DMN): When you visualize or let your mind wander, the DMN, a network of brain regions activated during rest and self-referential thought, becomes active. This helps in decoupling from immediate sensory input and encourages a meditative or void-like state.
Letting Go: The act of distraction prevents overthinking about reaching the void, which can be counterproductive. When you're engrossed in a scene or mental song, you're no longer "trying," which facilitates a natural shift into the void.
Induce Pure Consciousness °. *࿐
Guaranteed Results: The process relies on reducing external focus and internal resistance. The void state is associated with a deeply relaxed state of consciousness, where mental barriers (ego) dissolves. This does not mean it's a deep meditative state, it's just "pure consciousness" as its name suggests.
Neuroscientific Basis °. *࿐
Relaxation Response: Inducing the alpha state triggers the relaxation response, reducing stress hormones (like cortisol) and increasing focus.
Cognitive Load Diversion: By distracting the conscious mind with visualization or mental activities, the subconscious becomes more accessible.
Hypnagogic State: The method resembles techniques used to enter the hypnagogic state, a transitional phase between wakefulness and sleep, where visualization and suggestion are potent.



#empyrealoasis#law of assumption#loa#void state#pure consciousness#master manifestor#manifest#reality shifting#shifting#shiftblr#voidblr#void#4d reality#desired reality#anti shifters dni#affirm and persist#robotic affirming#manifestation#law of manifestation
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
How a Network Load Balancer Maximizes Uptime and Performance Across Traffic Spikes?
A network load balancer is a critical component in today’s digital infrastructure, especially for businesses that rely heavily on web applications, APIs, or cloud-based services. It ensures the seamless distribution of incoming network traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. By intelligently managing traffic, a network load balancer enhances the efficiency, reliability, and scalability of your system. In the era of 24/7 digital access and unpredictable surges in traffic, this technology is indispensable for maintaining performance. Whether for e-commerce, finance, gaming, or media platforms, a network load balancer plays a central role in maintaining service continuity.
Ensures High Availability During Peak User Demand
During times of peak demand—such as sales events, product launches, or viral content spikes—a network load balancer ensures high availability by evenly routing requests to healthy, responsive servers. It prevents bottlenecks and ensures users get uninterrupted access, regardless of how many are connected simultaneously. Without a load balancer, even the most robust infrastructure can crumble under pressure. By maintaining service availability even during high traffic, a network load balancer helps uphold user satisfaction and brand reputation. It acts as a strategic buffer that intelligently controls traffic surges to maintain a consistent user experience without slowing down or crashing systems.
Balances Traffic Loads Across Multiple Servers
A key function of a network load balancer is to distribute workloads across multiple servers, ensuring no single resource is overburdened. This improves server utilization and reduces the risk of hardware failure due to excessive strain. When configured correctly, a network load balancer continuously monitors server performance and redirects requests based on real-time capacity and responsiveness. This balancing act is vital in maintaining operational stability across the infrastructure. Whether handling millions of API calls or hundreds of database queries per second, the ability of the load balancer to evenly allocate traffic keeps applications responsive and infrastructure costs optimized.
Minimizes Downtime with Real-Time Failover Support
One of the most valuable benefits of a network load balancer is its real-time failover capability. When a server goes offline due to hardware failure, overload, or scheduled maintenance, the load balancer detects this instantly and reroutes traffic to other healthy nodes. This automated process minimizes downtime and ensures business continuity. Failover support not only protects against unexpected server failures but also allows system administrators to perform updates and maintenance without disrupting user access in high-availability systems where every second of uptime matters. Having a network load balancer with failover functionality is crucial to delivering uninterrupted service.
A Network Load Balancer Distributes Traffic Efficiently
Efficiency is at the core of what a network load balancer delivers. It evaluates incoming traffic, analyzes the state of backend servers, and makes quick routing decisions to distribute data streams where they are most efficiently handled. This not only reduces latency but also maximizes resource utilization and processing speed. By employing algorithms like round-robin, least connections, or IP-hash-based distribution, the network load balancer ensures optimized delivery paths. Efficient distribution of requests directly correlates with improved user experiences and smoother application workflows. Whether traffic is steady or erratic, the network load balancer keeps the system operating at peak efficiency.
Adapts to Traffic Spikes with Scalable Routing
A modern network load balancer can dynamically adapt to sudden traffic spikes by leveraging scalable routing techniques. When user requests surge, it quickly allocates new server resources, often within cloud environments, to handle the increase without slowing down performance. This auto-scaling behavior is essential for applications that experience fluctuating demand, such as e-commerce platforms during holiday seasons or streaming services during live events. The ability to adjust routing rules in real-time allows the load balancer to maintain high throughput and low latency even under stress. This adaptability ensures that services remain stable, responsive, and available when traffic demands fluctuate rapidly.
Enhances Application Performance During Usage Surges
Application performance can degrade rapidly under sudden user load, but a network load balancer plays a pivotal role in preventing such degradation. By offloading tasks to the least busy servers and ensuring traffic is intelligently split, it eliminates performance bottlenecks. This results in faster response times, smoother application behavior, and overall better user satisfaction. Load balancers can also integrate with performance monitoring tools to detect slowdowns and reroute requests proactively. This continuous feedback loop helps maintain consistent application quality. When usage surges occur, the network load balancer becomes the silent hero that keeps your applications running fast and efficiently.
A Network Load Balancer Improves Uptime and Reliability
Uptime and reliability are non-negotiable in mission-critical applications. A network load balancer significantly contributes to both by continuously monitoring server health and distributing requests only to available nodes. This eliminates single points of failure and allows redundant infrastructure to operate seamlessly. Load balancers often include SSL termination and TCP optimization features, further improving speed and reducing the load on backend servers. With constant real-time monitoring and traffic control, the network load balancer provides a robust safety net against outages. By improving uptime and ensuring predictable reliability, it becomes a cornerstone of any enterprise-grade IT strategy and system architecture.
Conclusion
In today’s fast-paced digital world, a network load balancer is essential for maintaining high performance, availability, and reliability of online services. Whether managing thousands of users or supporting real-time applications, load balancers ensure that servers work smarter, not harder. They reduce downtime, optimize resource usage, and offer seamless scalability to meet unpredictable user demand. Investing in a network load balancer is not just a technical upgrade—it’s a strategic move toward delivering a superior user experience and safeguarding digital infrastructure. For any business aiming to stay competitive, implementing a network load balancer is a vital step toward operational excellence.
0 notes
Text
Firewall Friday: Defending Against DDoS Attacks - How to Keep Your Network Safe
Welcome to Firewall Friday, where we dive into the world of DDoS attacks and equip you with the knowledge to safeguard your network against these digital bullies. But don’t worry, we won’t let these troublemakers ruin our Friday vibes. Instead, we’ll tackle the topic with a humorous tone, using analogies and emojis to make it easy for even the most novice readers to understand. So, put on your…

View On WordPress
#anomaly detection#cloud-based defenses#cybersecurity#DDoS attacks#firewall#intrusion prevention systems#load balancing#network security#rate limiting#traffic analysis
0 notes
Text
How Network Load Balancers Optimize Traffic for High-Performance Systems
Network Load Balancer (NLBs) are designed to manage and optimize traffic for high-performance systems by intelligently distributing client requests across multiple servers. Operating at the transport layer (Layer 4 of the OSI model), NLBs handle TCP/UDP traffic with minimal latency, making them ideal for real-time applications like online gaming, financial systems, and video conferencing. They monitor server health to avoid routing traffic to unresponsive nodes, ensuring continuous service availability. By evenly balancing workloads, NLBs prevent server overload, enhance responsiveness, and support seamless scaling during traffic spikes. With features like session persistence and advanced routing algorithms, they improve resource utilization and deliver consistent performance, making them essential for modern, high-demand IT infrastructures.
Introduction to Network Load Balancers: Key Components of High-Performance Systems
In high-performance computing environments, efficient traffic management is crucial. Network Load Balancer (NLBs) serve as a vital tool to ensure that traffic is evenly distributed across multiple servers or nodes. This distribution prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed, thus ensuring optimal performance and uptime. NLBs allow systems to handle vast amounts of data and traffic while maintaining speed, reliability, and minimal latency. The introduction of load balancing technologies has been a game-changer, particularly in modern cloud architectures and data centers.
How Load Balancers Improve System Scalability and Redundancy
One of the major benefits of NLBs is their ability to scale systems seamlessly. As web traffic grows, it’s essential to scale infrastructure horizontally by adding more servers. Load balancers efficiently allocate traffic to these servers, which enhances scalability. In terms of redundancy, NLBs can detect failing servers and reroute traffic to healthy ones, ensuring uninterrupted service. This ability ensures that even during peak traffic periods or in the event of a failure, the system remains operational, offering fault tolerance and robustness to the system.
Traffic Distribution Algorithms in Load Balancers
Network load balancer use different algorithms to distribute incoming traffic based on specific criteria. Common strategies include round-robin, least connections, and IP hash. The round-robin method sends requests sequentially to each available server. The least connections approach prioritizes servers with the fewest active connections. The IP hash method, on the other hand, assigns traffic based on the source IP address. These algorithms are essential for achieving a balanced load across servers, thus optimizing resource utilization and improving system performance.
Performance Optimization: Minimizing Latency and Maximizing Throughput
One of the main objectives of using NLBs is minimizing latency and maximizing throughput, especially for applications requiring real-time processing. By distributing traffic effectively, NLBs ensure that requests are handled by the most available and capable server, preventing slowdowns. Load balancers can detect server load and health status, routing traffic dynamically to reduce bottlenecks. High-throughput systems, such as video streaming platforms or online gaming servers, benefit from optimized network traffic, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted experiences for end users.
NLBs and their Role in Cloud-Based Systems
With the rise of cloud computing, the role of NLBs has become increasingly important. Cloud service providers, like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, rely heavily on NLBs to manage traffic in distributed cloud environments. These cloud-based load balancers can operate at various layers of the OSI model, with support for both Layer 4 (TCP/UDP) and Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) traffic. By utilizing cloud-native network load balancer services, businesses can ensure that their cloud infrastructure is optimized for performance, scalability, and high availability, with automatic adjustments based on traffic demands.
Security Considerations: Protecting Systems with Load Balancers
While load balancers excel at managing traffic, they also play a significant role in enhancing security. By acting as intermediaries between clients and servers, NLBs can help protect backend systems from DDoS attacks, unauthorized access, and malicious traffic. Security features such as SSL/TLS offloading can also be handled by the load balancer, freeing up server resources for other critical tasks. Additionally, load balancers can use Web Application Firewalls (WAF) to inspect incoming traffic, blocking harmful requests before they reach the server. This layer of protection is crucial for maintaining system integrity and safeguarding sensitive data.
The Future of Network Load Balancing: Evolving Technologies and Trends
As technology evolves, so do the capabilities of NLBs. Future advancements in load balancing may incorporate machine learning algorithms to predict traffic patterns and optimize distribution automatically. This predictive capability would allow NLBs to make more informed decisions about traffic routing, further enhancing system performance. Additionally, the rise of 5G and edge computing is set to revolutionize how load balancing operates. With edge servers placed closer to end users, NLBs will be crucial in distributing traffic efficiently between the central cloud and distributed edge locations, reducing latency and improving overall performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, network load balancers are indispensable in optimizing traffic flow for high-performance systems. Their ability to scale, ensure redundancy, and minimize latency makes them crucial for modern web applications, cloud environments, and data-intensive services. By distributing traffic efficiently, they ensure that systems remain reliable, responsive, and capable of handling large-scale traffic volumes without compromising performance. With the continuous evolution of networking technologies, NLBs will undoubtedly play an even more prominent role in shaping the future of high-performance, secure, and scalable systems.
0 notes
Text
Comparing Network Load Balancers From AWS, Azure, And Google Cloud
Comparing Network Load Balancers from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud explores the key features, benefits, and differences between the network load balancing services offered by the three major cloud providers. This guide provides an in-depth comparison of AWS Elastic Load Balancing, Azure Load Balancer, and Google Cloud's Network Load Balancer, focusing on factors such as scalability, reliability, ease of configuration, and pricing. It also looks at performance capabilities, including how each service handles high traffic volumes, fault tolerance, and geographic distribution. By comparing these solutions, readers will gain insight into which load balancer is best suited for their specific needs, whether it's for small businesses or large enterprise-level applications, helping them make informed decisions when choosing a cloud provider for their infrastructure.
Overview of Network Load Balancers in Cloud Platforms
In the modern cloud ecosystem, efficient load balancing is crucial for ensuring high availability, performance, and scalability of applications. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer robust network load balancing solutions, each with unique features. This section explores the fundamentals of network load balancers across these platforms, providing insight into their capabilities and use cases. Understanding the core functionalities will help businesses choose the right solution based on specific needs.
AWS Network Load Balancer: Features and Benefits
AWS offers the Network Load Balancer (NLB), designed for ultra-low latency and high-throughput scenarios. With its ability to handle millions of requests per second while maintaining high availability, NLB is ideal for applications requiring both speed and reliability. This section will delve into its key features, such as support for TCP, TLS, and UDP protocols, as well as integration with other AWS services, like Auto Scaling and EC2 instances. The performance metrics and security features that make NLB a popular choice for enterprises will also be discussed.
Azure Load Balancer: Scalability and Flexibility
Microsoft Azure provides the Azure Load Balancer, a highly available and scalable solution suitable for cloud-native and hybrid architectures. This section explores its capabilities in providing Layer 4 load balancing for both inbound and outbound traffic. We'll compare the Standard and Basic tiers, evaluating their benefits in terms of performance, global distribution, and integration with Azure Virtual Machines and Availability Zones. The ability to handle millions of concurrent connections with low latency makes Azure Load Balancer an excellent choice for highly dynamic environments.
Google Cloud Load Balancer: Advanced Routing and Traffic Management
The Google Cloud Load Balancer stands out for its advanced traffic management capabilities. Supporting global distribution and intelligent routing, this solution enables users to optimize application performance across multiple regions. This section will focus on its key features, such as URL map-based routing, SSL offloading, and global backend service support. With an emphasis on intelligent traffic distribution and real-time load balancing, Google Cloud Load Balancer ensures that applications run smoothly, regardless of geographic location or traffic spikes.
Comparing Performance: Latency, Throughput, and Scalability
When it comes to network load balancing, performance metrics like latency, throughput, and scalability play a pivotal role in selecting the right platform. This section compares the performance of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud’s load balancers, highlighting their strengths in different scenarios. AWS NLB excels in handling high-throughput applications with minimal latency, while Azure Load Balancer ensures efficient distribution of traffic within virtual networks. Google Cloud Load Balancer, with its global architecture, is designed to manage traffic at scale across regions, ensuring minimal latency even for globally distributed applications.
Security Features: Protecting Your Network Traffic
Security is a critical concern when managing network traffic, and each cloud provider offers different features to safeguard applications. AWS NLB integrates with AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) and offers encryption for secure connections. Azure Load Balancer provides features such as DDoS Protection and integration with Azure Security Center to detect and mitigate threats. Google Cloud Load Balancer leverages Google’s security infrastructure, offering SSL/TLS offloading and protection against common attacks. This section examines the security features of each solution and compares their effectiveness in protecting applications from vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
Cost Comparison: Pricing Models and Value for Money
Understanding the pricing models for network load balancers is essential for businesses to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of each solution. This section compares the pricing structures of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud load balancers, focusing on factors like data processing fees, number of requests, and resource allocation. AWS typically charges based on the number of Load Balancer Capacity Units (LCUs), Azure uses a per-usage model with additional charges for outbound traffic, and Google Cloud charges based on traffic volume and the type of resources used. The analysis will help readers determine which platform offers the best value for their specific use case.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the best network load balancer for your cloud infrastructure depends on several factors, including performance requirements, scalability, security needs, and cost considerations. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud each offer robust solutions tailored to different environments and use cases. AWS Network Load Balancer is ideal for high-throughput, low-latency applications, while Azure Load Balancer excels in hybrid cloud deployments and virtual network management. Google Cloud Load Balancer stands out for its global reach and intelligent traffic routing. By evaluating these aspects.
0 notes
Text
Best Practices for Implementing Network Load Balancers
Implementing requires careful planning and adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your application and network requirements to determine the appropriate load balancing strategy. Choose a load balancing algorithm that aligns with your traffic distribution needs, whether it's round-robin, least connections, or weighted round-robin.Next, deploy redundant load balancers for high availability and fault tolerance. Configure health checks to monitor backend server status and automatically remove or add servers based on their health. Additionally, optimize security by implementing SSL termination and enforcing access control policies. Regularly monitor and tune your load balancers to accommodate changing traffic patterns and scale as needed. Following these best practices will help maximize the effectiveness of your network load balancers and ensure seamless application delivery
Overview of Network Load Balancers
Explore the fundamental concepts of network load balancer (NLBs) in modern IT infrastructure. Learn how NLBs efficiently distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources to optimize performance and reliability.
Benefits of Network Load Balancers
Discover the key benefits of using network load balancers. Explore how NLBs improve application availability, scalability, and responsiveness by intelligently distributing traffic and managing server loads.
Network Load Balancer Deployment Strategies
Discuss different deployment strategies for network load balancers. Explore options such as hardware-based vs. software-based NLBs, on-premises vs. cloud-based deployments, and considerations for scalability and high availability.
Load Balancing Algorithms
Examine popular load balancing algorithms used in network load balancers. Discuss algorithms such as round-robin, least connections, and IP hash, and understand how they influence traffic distribution and server selection.
Security Considerations with Network Load Balancers
Address security considerations associated with network load balancers. Explore features such as SSL termination, DDoS protection, and access control mechanisms that enhance security posture when using NLBs.
Monitoring and Performance Optimization
Learn about monitoring tools and techniques for network load balancers. Explore performance optimization strategies, including health checks, metrics monitoring, and scaling policies to ensure efficient traffic management.
Integration with Cloud Services and Container Orchestration
Discuss the integration of network load balancers with cloud services and container orchestration platforms. Explore how NLBs interact with AWS Elastic Load Balancing (ELB), Kubernetes Ingress controllers, and service mesh technologies like Istio for managing microservices traffic.
Conclusion
Implementing requires adherence to best practices to ensure optimal performance and reliability in your IT infrastructure. By following established guidelines for load balancer sizing, health monitoring, and configuration of routing policies, organizations can achieve high availability and scalability. It's essential to prioritize security measures such as SSL termination, encryption, and access control to protect against cyber threats. Regular monitoring and performance optimization are key to identifying and addressing potential issues proactively. Additionally, leveraging automation and orchestration tools can streamline load balancer deployment and management processes. By adopting these best practices, businesses can maximize the benefits of improving application delivery and user experience while maintaining robustness and resilience in their network architecture.
0 notes
Text
Part of fortune in the degrees
Part of Fortune in the degrees is like the hidden spice mix in your astrological fortune. The degree can flavor your Part of Fortune with deeper nuance, karmic energy, and even timing.
0° – The Origin Point
Fresh start energy! Your joy comes from pioneering something totally new. You’re here to plant seeds that grow into empires. This is “first on the scene” vibes—trailblazer status.
1° – The Initiator
Action = alignment. You’re someone who taps into fortune when you just begin. Taking the first step (even if you’re not ready) opens the door for magic.
2° – The Sensual Stabilizer
Joy comes from grounded pleasures. Your fortune is tied to patience, beauty, and appreciating the realness of life. Think soft power and quiet luxury.
3° – The Curious Connector
Success shows up when you’re thinking, talking, moving, or exchanging ideas. Your mind is a magnet, and your network = gold.
4° – The Soul Rooter
Your fortune is buried deep—in emotions, memories, ancestry, or the past. When you feel safe and emotionally full, life blesses you.
5° – The Performer
You’re meant to shine. Creative self-expression, fun, or dramatic flair are your keys to joy. When you’re playing or performing, everything clicks.
6° – The Healer Hustler
Service brings success. Whether you’re organizing chaos, helping others, or mastering routines, this degree thrives in the little details that build big blessings.
7° – The Lover
Love, aesthetics, and harmony bring fortune. This is a “soft life” degree—where grace, diplomacy, and connection unlock golden paths.
8° – The Alchemist
Deep transformations = fortune. You’re here to transmute pain into power. This is intense but magnetic—your glow-up is probably legendary.
9° – The Seeker
Adventure calls! Joy comes from travel, study, or expanding your worldview. If you’re bored, you’re blocking blessings. Keep moving.
10° – The Architect
Success comes from structure. You build it, brick by brick. You’re playing the long game—and winning. This degree is all about legacy.
11° – The Visionary
You’re ahead of your time. Your ideas are wild in the best way, and when you trust your weird, you win. Your fortune lies in the future you’re helping build.
12° – The Dreamer
Mystical, intuitive, and creatively charged—this degree feels its way to fortune. If it feels right in your soul, the universe will handle the rest.
13° – The Rebel
Unpredictable magic. You don’t follow the rules—you invent them. Fortune strikes when you embrace chaos and follow your electric instincts.
14° – The Messenger
You’re the cosmic translator. Whether it’s through writing, speaking, or vibes, your voice brings value. Say the thing that needs to be said.
15° – The Magnetic Middle
This is peak attraction energy. You draw in fortune by simply being. Balance, charm, and centered confidence = unstoppable glow.
16° – The Analyst
Your mind is your superpower. You thrive on patterns, logic, and discernment. Fortune favors your sharp eye and strategic brain.
17° – The Soul Climber
You’re here to rise—and you will. This degree blends ambition with intuition. When you align your path with your purpose, blessings rain in.
18° – The Intense Transformer
Like 8°, but with more fire. This degree is intense, karmic, and power-packed. Your fortune may come through radical change—or rising from the ashes.
19° – The Channel
You’re tuned in. This degree has psychic undertones and creative genius. Dreams, visions, or gut instincts often lead you to your blessings.
20° – The Master Builder
You’re here to create something real. This degree carries serious manifestation power. With time, effort, and vision—you will make it happen.
21° – The Muse
Creative, charming, and maybe a little flirty—this degree lives for inspiration and play. Fortune shows up when you’re vibing, not forcing.
22° – The Wise One
This is a “master number” degree—loaded with karmic depth. You’ve been here before, and your fortune often comes from helping or guiding others.
23° – The Charmer
You have it. This degree brings social grace, storytelling power, and a magnetic vibe. You’re luckiest when you’re being authentically YOU.
24° – The Grounded Mystic
Spiritual + practical = unstoppable. You’re in tune with both realms, and your fortune comes when you integrate them. This is “divine timing” energy.
25° – The Phoenix
Massive transformation potential. This degree can feel intense at times, but it leads to deep healing and empowerment. You’re the comeback king/queen.
26° – The Dream Doer
You can manifest the ethereal. Ideas, visions, or creative bursts? You make them real. The dream becomes the empire with this degree.
27° – The Revolutionary
Break the mold. Your fortune lies in doing things your way—even if no one gets it at first. Trailblazer energy with a bold twist.
28° – The Old Soul
You’ve done the work in lifetimes past, and now you’re here to refine and complete. Success comes when you trust your deep wisdom and wrap up cycles with grace.
29° – The Anointed One (Anaretic Degree)
You’re here to master this energy—and fast. High highs, intense tests, but major rewards. This is “last level of the game” energy—go big or go cosmic.
#astro notes#astrology#birth chart#astro observations#astro community#astrology observations#astrology community#astrology degrees#astro#astroblr#astrology content#astrology insights#part of fortune
710 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi @netflix and @warnerbrostv! I'd like to talk about the show Supernatural and how its history and legacy can provide some insight on why you should reconsider your decision to end Dead Boy Detectives after one singular season.
Supernatural is undoubtedly one of the most successful television fantasy franchises, but many don't know that it was nearly cancelled after season 2. Thankfully (and luckily) for the network they didn't go through with cancelling the show and by season 4 it was regularly breaking viewership records. A show that was nearly cut short in its prime - much like Dead Boy Detectives - became one of the largest and most recognizable fandoms across social media platforms between the years of 2010 and 2014. The show was so wildly popular that a confession scene between two of its leading characters (Dean and Cas) is STILL used today in a meme format to circulate everything from fandom news to world politics and current events. You can't go to a single comic-con without running into something relating to Supernatural, and ever since its conclusion there has been an opening in the market for a show to take its place.
I can say with absolute certainty that, given the proper time to flourish, Dead Boy Detectives would be the show to fill the spot Supernatural has left behind. It has loads of charm alongside a sensational balance of action, whimsy, heartwrenching character development, and horror. Furthermore it is objectively better with representation than Supernatural was, which is always something embraced in fandom spaces (which are diverse and filled to the brim with queer, neurodivergent, and/or a wide range of people of color).
I also think it's fair to remind you that one of your most popular "Nerd" shows, Stranger Things, is coming to an end after a 10-year-run, leaving behind yet another gap to fill, but this time on your very own platform.
It isn't too late to reconsider the cancellation of Dead Boy Detectives. The fanbase is dedicated and hungry for more, and we know you are currently sitting on finished season 2 scripts, making it impossible for the writers to take this story anywhere else for quite some time. The scripts are there, the cast, crew, and writers love what they do and want to make more... there's simply no reason to not give Dead Boy Detectives the chance it deserves - this time with an entire fandom that wants nothing more than to consume this show, market the hell out of it, and buy merch relating to it (another win for you).
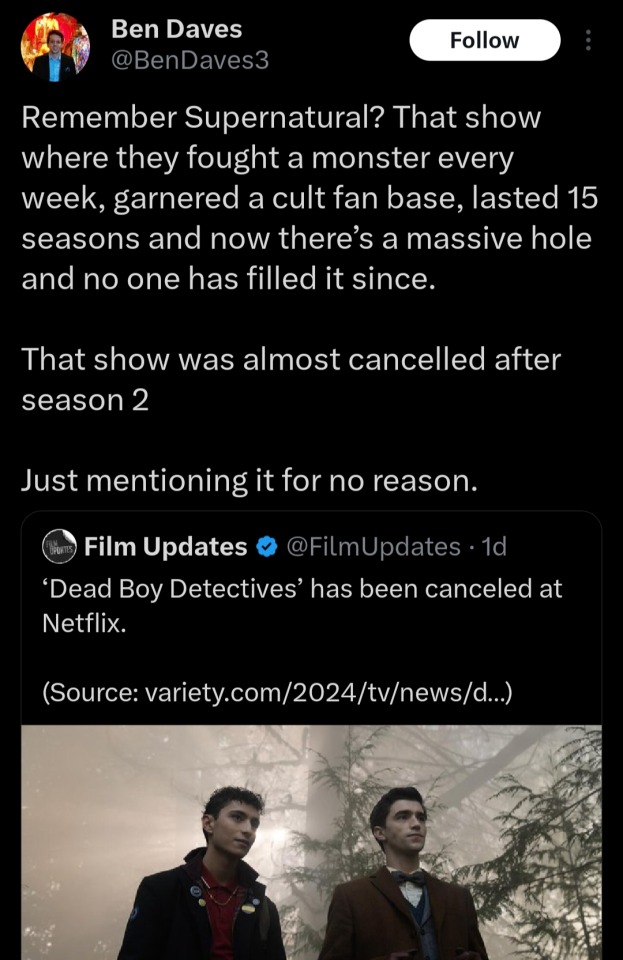
(Source x)
Oh and did I mention that Steve Yockey was a co-producer on Supernatural as well? You know, that wildly popular show I just told you about that lasted 15 seasons. You are sitting on a golden goose; Steve Yockey and Beth Schwartz, among the other talented writers, cast, and crew, know what they're doing.
Give this show its time and market it well and you will have a hit on your hands. Frankly just based on the steady, continual fandom growth since Dead Boy Detectives' release in April and the vocal outrage over its cancellation just in the last 24 hours, I'd argue you already have a hit on your hands that rivals several shows you currently have on your platform.
Dead Boy Detectives has one of the most active fandoms of the year - do the right thing by them and bring Dead Boy Detectives back. It isn't too late!
#dead boy detectives#dbda#renew dead boy detectives#revive dead boy detectives#save dead boy detectives#the dead boy detectives#dead boy detective agency#the dead boy detective agency#dead boy detectives netflix#dbda netflix#supernatural
369 notes
·
View notes