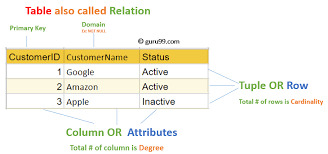
#SQL Server table structure
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Checking for the Existence of a Column in a SQL Server Table
To check if a column exists in a SQL Server table, you can use the INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS system view, which provides information about all columns in all tables in a database. Here’s a SQL query that checks if a specific column exists in a specific table: IF EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_NAME = 'YourTableName' AND COLUMN_NAME = 'YourColumnName' ) BEGIN PRINT…
View On WordPress
#check column SQL#INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS#SQL Server column existence#SQL Server table structure#validate SQL column
0 notes
Text
Structured Query Language (SQL): A Comprehensive Guide
Structured Query Language, popularly called SQL (reported "ess-que-ell" or sometimes "sequel"), is the same old language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. Developed in the early 1970s by using IBM researchers Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce, SQL has when you consider that end up the dominant language for database structures round the world.
Structured query language commands with examples
Today, certainly every important relational database control system (RDBMS)—such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and SQLite—uses SQL as its core question language.
What is SQL?
SQL is a website-specific language used to:
Retrieve facts from a database.
Insert, replace, and delete statistics.
Create and modify database structures (tables, indexes, perspectives).
Manage get entry to permissions and security.
Perform data analytics and reporting.
In easy phrases, SQL permits customers to speak with databases to shop and retrieve structured information.
Key Characteristics of SQL
Declarative Language: SQL focuses on what to do, now not the way to do it. For instance, whilst you write SELECT * FROM users, you don’t need to inform SQL the way to fetch the facts—it figures that out.
Standardized: SQL has been standardized through agencies like ANSI and ISO, with maximum database structures enforcing the core language and including their very own extensions.
Relational Model-Based: SQL is designed to work with tables (also called members of the family) in which records is organized in rows and columns.
Core Components of SQL
SQL may be damaged down into numerous predominant categories of instructions, each with unique functions.
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to outline or modify the shape of database gadgets like tables, schemas, indexes, and so forth.
Common DDL commands:
CREATE: To create a brand new table or database.
ALTER: To modify an present table (add or put off columns).
DROP: To delete a table or database.
TRUNCATE: To delete all rows from a table but preserve its shape.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE TABLE personnel (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
call VARCHAR(one hundred),
income DECIMAL(10,2)
);
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used for statistics operations which include inserting, updating, or deleting information.
Common DML commands:
SELECT: Retrieve data from one or more tables.
INSERT: Add new records.
UPDATE: Modify existing statistics.
DELETE: Remove information.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
INSERT INTO employees (id, name, earnings)
VALUES (1, 'Alice Johnson', 75000.00);
three. Data Query Language (DQL)
Some specialists separate SELECT from DML and treat it as its very own category: DQL.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT name, income FROM personnel WHERE profits > 60000;
This command retrieves names and salaries of employees earning more than 60,000.
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL instructions cope with permissions and access manage.
Common DCL instructions:
GRANT: Give get right of entry to to users.
REVOKE: Remove access.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON personnel TO john_doe;
five. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands manage transactions to ensure data integrity.
Common TCL instructions:
BEGIN: Start a transaction.
COMMIT: Save changes.
ROLLBACK:��Undo changes.
SAVEPOINT: Set a savepoint inside a transaction.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
BEGIN;
UPDATE personnel SET earnings = income * 1.10;
COMMIT;
SQL Clauses and Syntax Elements
WHERE: Filters rows.
ORDER BY: Sorts effects.
GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a assets.
HAVING: Filters companies.
JOIN: Combines rows from or greater tables.
Example with JOIN:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT personnel.Name, departments.Name
FROM personnel
JOIN departments ON personnel.Dept_id = departments.Identity;
Types of Joins in SQL
INNER JOIN: Returns statistics with matching values in each tables.
LEFT JOIN: Returns all statistics from the left table, and matched statistics from the right.
RIGHT JOIN: Opposite of LEFT JOIN.
FULL JOIN: Returns all records while there is a in shape in either desk.
SELF JOIN: Joins a table to itself.
Subqueries and Nested Queries
A subquery is a query inside any other query.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
SELECT name FROM employees
WHERE earnings > (SELECT AVG(earnings) FROM personnel);
This reveals employees who earn above common earnings.
Functions in SQL
SQL includes built-in features for acting calculations and formatting:
Aggregate Functions: SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), MIN()
String Functions: UPPER(), LOWER(), CONCAT()
Date Functions: NOW(), CURDATE(), DATEADD()
Conversion Functions: CAST(), CONVERT()
Indexes in SQL
An index is used to hurry up searches.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON employees(call);
Indexes help improve the performance of queries concerning massive information.
Views in SQL
A view is a digital desk created through a question.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
CREATE VIEW high_earners AS
SELECT call, salary FROM employees WHERE earnings > 80000;
Views are beneficial for:
Security (disguise positive columns)
Simplifying complex queries
Reusability
Normalization in SQL
Normalization is the system of organizing facts to reduce redundancy. It entails breaking a database into multiple related tables and defining overseas keys to link them.
1NF: No repeating groups.
2NF: No partial dependency.
3NF: No transitive dependency.
SQL in Real-World Applications
Web Development: Most web apps use SQL to manipulate customers, periods, orders, and content.
Data Analysis: SQL is extensively used in information analytics systems like Power BI, Tableau, and even Excel (thru Power Query).
Finance and Banking: SQL handles transaction logs, audit trails, and reporting systems.
Healthcare: Managing patient statistics, remedy records, and billing.
Retail: Inventory systems, sales analysis, and consumer statistics.
Government and Research: For storing and querying massive datasets.
Popular SQL Database Systems
MySQL: Open-supply and extensively used in internet apps.
PostgreSQL: Advanced capabilities and standards compliance.
Oracle DB: Commercial, especially scalable, agency-degree.
SQL Server: Microsoft’s relational database.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database used in cellular and desktop apps.
Limitations of SQL
SQL can be verbose and complicated for positive operations.
Not perfect for unstructured information (NoSQL databases like MongoDB are better acceptable).
Vendor-unique extensions can reduce portability.
Java Programming Language Tutorial
Dot Net Programming Language
C ++ Online Compliers
C Language Compliers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Prevent

Preventing injection requires keeping data separate from commands and queries:
The preferred option is to use a safe API, which avoids using the interpreter entirely, provides a parameterized interface, or migrates to Object Relational Mapping Tools (ORMs). Note: Even when parameterized, stored procedures can still introduce SQL injection if PL/SQL or T-SQL concatenates queries and data or executes hostile data with EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or exec().
Use positive server-side input validation. This is not a complete defense as many applications require special characters, such as text areas or APIs for mobile applications.
For any residual dynamic queries, escape special characters using the specific escape syntax for that interpreter. (escaping technique) Note: SQL structures such as table names, column names, and so on cannot be escaped, and thus user-supplied structure names are dangerous. This is a common issue in report-writing software.
Use LIMIT and other SQL controls within queries to prevent mass disclosure of records in case of SQL injection.
bonus question: think about how query on the image above should look like? answer will be in the comment section
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
🚀 Professional Database Designer | Expert in ERD & Data Modeling 🚀
Struggling to visualize your database structure? I create clear, efficient Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) that simplify complex data and improve your system’s performance.
🔹 Tailored ERD designs for your unique business needs 🔹 Support for Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL & more 🔹 Scalable and optimized database models 🔹 Detailed documentation & expert consultation included
Let’s turn your data into a powerful asset!
👉 Hire me on PeoplePerHour now: https://www.peopleperhour.com/hourlie/professional-database-designer-erd/524486
DatabaseDesign #ERDDesign #DataModeling #DataArchitecture #DatabaseExpert #SQLDatabase #DataManagement #TechSolutions #PeoplePerHour #FreelancerLife #ITConsulting #BusinessIntelligence #DataDriven #SoftwareDevelopment #CustomDatabase #DataEngineering #DatabaseConsultant #TechFreelancer #DatabaseOptimization #DataVisualization #SystemDesign #CloudDatabase #TechSupport
0 notes
Text
How to Improve Database Performance with Smart Optimization Techniques
Database performance is critical to the efficiency and responsiveness of any data-driven application. As data volumes grow and user expectations rise, ensuring your database runs smoothly becomes a top priority. Whether you're managing an e-commerce platform, financial software, or enterprise systems, sluggish database queries can drastically hinder user experience and business productivity.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical and high-impact strategies to improve database performance, reduce latency, and increase throughput.
1. Optimize Your Queries
Poorly written queries are one of the most common causes of database performance issues. Avoid using SELECT * when you only need specific columns. Analyze query execution plans to understand how data is being retrieved and identify potential inefficiencies.
Use indexed columns in WHERE, JOIN, and ORDER BY clauses to take full advantage of the database indexing system.
2. Index Strategically
Indexes are essential for speeding up data retrieval, but too many indexes can hurt write performance and consume excessive storage. Prioritize indexing on columns used in search conditions and join operations. Regularly review and remove unused or redundant indexes.
3. Implement Connection Pooling
Connection pooling allows multiple application users to share a limited number of database connections. This reduces the overhead of opening and closing connections repeatedly, which can significantly improve performance, especially under heavy load.
4. Cache Frequently Accessed Data
Use caching layers to avoid unnecessary hits to the database. Frequently accessed and rarely changing data—such as configuration settings or product catalogs—can be stored in in-memory caches like Redis or Memcached. This reduces read latency and database load.
5. Partition Large Tables
Partitioning splits a large table into smaller, more manageable pieces without altering the logical structure. This improves performance for queries that target only a subset of the data. Choose partitioning strategies based on date, region, or other logical divisions relevant to your dataset.
6. Monitor and Tune Regularly
Database performance isn’t a one-time fix—it requires continuous monitoring and tuning. Use performance monitoring tools to track query execution times, slow queries, buffer usage, and I/O patterns. Adjust configurations and SQL statements accordingly to align with evolving workloads.
7. Offload Reads with Replication
Use read replicas to distribute query load, especially for read-heavy applications. Replication allows you to spread read operations across multiple servers, freeing up the primary database to focus on write operations and reducing overall latency.
8. Control Concurrency and Locking
Poor concurrency control can lead to lock contention and delays. Ensure your transactions are short and efficient. Use appropriate isolation levels to avoid unnecessary locking, and understand the impact of each level on performance and data integrity.
0 notes
Text
Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days
Are you looking to learn backend web development and build dynamic websites with real functionality? You’re in the right place. Welcome to the Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days — a practical, beginner-friendly guide designed to help you master the fundamentals of PHP in just one week.
PHP, or Hypertext Preprocessor, is one of the most widely used server-side scripting languages on the web. It powers everything from small blogs to large-scale websites like Facebook and WordPress. Learning PHP opens up the door to back-end development, content management systems, and full-stack programming. Whether you're a complete beginner or have some experience with HTML/CSS, this tutorial is structured to help you learn PHP step by step with real-world examples.
Why Learn PHP?
Before diving into the tutorial, let’s understand why PHP is still relevant and worth learning in 2025:
Beginner-friendly: Easy syntax and wide support.
Open-source: Free to use with strong community support.
Cross-platform: Runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and integrates with most servers.
Database integration: Works seamlessly with MySQL and other databases.
In-demand: Still heavily used in CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
If you want to build contact forms, login systems, e-commerce platforms, or data-driven applications, PHP is a great place to start.
Day-by-Day Breakdown: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days
Day 1: Introduction to PHP & Setup
Start by setting up your environment:
Install XAMPP or MAMP to create a local server.
Create your first .php file.
Learn how to embed PHP inside HTML.
Example:
<?php echo "Hello, PHP!"; ?>
What you’ll learn:
How PHP works on the server
Running PHP in your browser
Basic syntax and echo statement
Day 2: Variables, Data Types & Constants
Dive into PHP variables and data types:
$name = "John"; $age = 25; $is_student = true;
Key concepts:
Variable declaration and naming
Data types: String, Integer, Float, Boolean, Array
Constants and predefined variables ($_SERVER, $_GET, $_POST)
Day 3: Operators, Conditions & Control Flow
Learn how to make decisions in PHP:
if ($age > 18) { echo "You are an adult."; } else { echo "You are underage."; }
Topics covered:
Arithmetic, comparison, and logical operators
If-else, switch-case
Nesting conditions and best practices
Day 4: Loops and Arrays
Understand loops to perform repetitive tasks:
$fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]; foreach ($fruits as $fruit) { echo $fruit. "<br>"; }
Learn about:
for, while, do...while, and foreach loops
Arrays: indexed, associative, and multidimensional
Array functions (count(), array_push(), etc.)
Day 5: Functions & Form Handling
Start writing reusable code and learn how to process user input from forms:
function greet($name) { return "Hello, $name!"; }
Skills you gain:
Defining and calling functions
Passing parameters and returning values
Handling HTML form data with $_POST and $_GET
Form validation and basic security tips
Day 6: Working with Files & Sessions
Build applications that remember users and work with files:
session_start(); $_SESSION["username"] = "admin";
Topics included:
File handling (fopen, fwrite, fread, etc.)
Reading and writing text files
Sessions and cookies
Login system basics using session variables
Day 7: PHP & MySQL – Database Connectivity
On the final day, you’ll connect PHP to a database and build a mini CRUD app:
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "mydatabase");
Learn how to:
Connect PHP to a MySQL database
Create and execute SQL queries
Insert, read, update, and delete (CRUD operations)
Display database data in HTML tables
Bonus Tips for Mastering PHP
Practice by building mini-projects (login form, guest book, blog)
Read official documentation at php.net
Use tools like phpMyAdmin to manage databases visually
Try MVC frameworks like Laravel or CodeIgniter once you're confident with core PHP
What You’ll Be Able to Build After This PHP Tutorial
After following this 7-day PHP tutorial, you’ll be able to:
Create dynamic web pages
Handle form submissions
Work with databases
Manage sessions and users
Understand the logic behind content management systems (CMS)
This gives you the foundation to become a full-stack developer, or even specialize in backend development using PHP and MySQL.
Final Thoughts
Learning PHP doesn’t have to be difficult or time-consuming. With the Complete PHP Tutorial: Learn PHP from Scratch in 7 Days, you’re taking a focused, structured path toward web development success. You’ll learn all the core concepts through clear explanations and hands-on examples that prepare you for real-world projects.
Whether you’re a student, freelancer, or aspiring developer, PHP remains a powerful and valuable skill to add to your web development toolkit.
So open up your code editor, start typing your first <?php ... ?> block, and begin your journey to building dynamic, powerful web applications — one day at a time.

0 notes
Text
🚀 Unlock the Power of SQL TRUNCATE 🚀
Looking to quickly remove all records from a table without affecting its structure? 🤔
SQL TRUNCATE is the go-to command! It’s faster and more efficient than DELETE because it:
✅ Removes all data from a table in a snap ✅ Doesn’t log individual row deletions, improving performance ✅ Resets auto-increment counters (in some databases) ✅ Doesn't fire triggers (like DELETE does)
⚠️ Warning: You can’t roll it back once executed (unless inside a transaction).
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE student;
Perfect for situations where you need a fresh start! 🧹
Want to dive deeper into SQL TRUNCATE and see how it can optimize your workflow? Check out the full post below! 🔗👇
0 notes
Text
PHP with MySQL: Best Practices for Database Integration
PHP and MySQL have long formed the backbone of dynamic web development. Even with modern frameworks and languages emerging, this combination remains widely used for building secure, scalable, and performance-driven websites and web applications. As of 2025, PHP with MySQL continues to power millions of websites globally, making it essential for developers and businesses to follow best practices to ensure optimized performance and security.
This article explores best practices for integrating PHP with MySQL and explains how working with expert php development companies in usa can help elevate your web projects to the next level.
Understanding PHP and MySQL Integration
PHP is a server-side scripting language used to develop dynamic content and web applications, while MySQL is an open-source relational database management system that stores and manages data efficiently. Together, they allow developers to create interactive web applications that handle tasks like user authentication, data storage, and content management.
The seamless integration of PHP with MySQL enables developers to write scripts that query, retrieve, insert, and update data. However, without proper practices in place, this integration can become vulnerable to performance issues and security threats.
1. Use Modern Extensions for Database Connections
One of the foundational best practices when working with PHP and MySQL is using modern database extensions. Outdated methods have been deprecated and removed from the latest versions of PHP. Developers are encouraged to use modern extensions that support advanced features, better error handling, and more secure connections.
Modern tools provide better performance, are easier to maintain, and allow for compatibility with evolving PHP standards.
2. Prevent SQL Injection Through Prepared Statements
Security should always be a top priority when integrating PHP with MySQL. SQL injection remains one of the most common vulnerabilities. To combat this, developers must use prepared statements, which ensure that user input is not interpreted as SQL commands.
This approach significantly reduces the risk of malicious input compromising your database. Implementing this best practice creates a more secure environment and protects sensitive user data.
3. Validate and Sanitize User Inputs
Beyond protecting your database from injection attacks, all user inputs should be validated and sanitized. Validation ensures the data meets expected formats, while sanitization cleans the data to prevent malicious content.
This practice not only improves security but also enhances the accuracy of the stored data, reducing errors and improving the overall reliability of your application.
4. Design a Thoughtful Database Schema
A well-structured database is critical for long-term scalability and maintainability. When designing your MySQL database, consider the relationships between tables, the types of data being stored, and how frequently data is accessed or updated.
Use appropriate data types, define primary and foreign keys clearly, and ensure normalization where necessary to reduce data redundancy. A good schema minimizes complexity and boosts performance.
5. Optimize Queries for Speed and Efficiency
As your application grows, the volume of data can quickly increase. Optimizing SQL queries is essential for maintaining performance. Poorly written queries can lead to slow loading times and unnecessary server load.
Developers should avoid requesting more data than necessary and ensure queries are specific and well-indexed. Indexing key columns, especially those involved in searches or joins, helps the database retrieve data more quickly.
6. Handle Errors Gracefully
Handling database errors in a user-friendly and secure way is important. Error messages should never reveal database structures or sensitive server information to end-users. Instead, errors should be logged internally, and users should receive generic messages that don’t compromise security.
Implementing error handling protocols ensures smoother user experiences and provides developers with insights to debug issues effectively without exposing vulnerabilities.
7. Implement Transactions for Multi-Step Processes
When your application needs to execute multiple related database operations, using transactions ensures that all steps complete successfully or none are applied. This is particularly important for tasks like order processing or financial transfers where data integrity is essential.
Transactions help maintain consistency in your database and protect against incomplete data operations due to system crashes or unexpected failures.
8. Secure Your Database Credentials
Sensitive information such as database usernames and passwords should never be exposed within the application’s core files. Use environment variables or external configuration files stored securely outside the public directory.
This keeps credentials safe from attackers and reduces the risk of accidental leaks through version control or server misconfigurations.
9. Backup and Monitor Your Database
No matter how robust your integration is, regular backups are critical. A backup strategy ensures you can recover quickly in the event of data loss, corruption, or server failure. Automate backups and store them securely, ideally in multiple locations.
Monitoring tools can also help track database performance, detect anomalies, and alert administrators about unusual activity or degradation in performance.
10. Consider Using an ORM for Cleaner Code
Object-relational mapping (ORM) tools can simplify how developers interact with databases. Rather than writing raw SQL queries, developers can use ORM libraries to manage data through intuitive, object-oriented syntax.
This practice improves productivity, promotes code readability, and makes maintaining the application easier in the long run. While it’s not always necessary, using an ORM can be especially helpful for teams working on large or complex applications.
Why Choose Professional Help?
While these best practices can be implemented by experienced developers, working with specialized php development companies in usa ensures your web application follows industry standards from the start. These companies bring:
Deep expertise in integrating PHP and MySQL
Experience with optimizing database performance
Knowledge of the latest security practices
Proven workflows for development and deployment
Professional PHP development agencies also provide ongoing maintenance and support, helping businesses stay ahead of bugs, vulnerabilities, and performance issues.
Conclusion
PHP and MySQL remain a powerful and reliable pairing for web development in 2025. When integrated using modern techniques and best practices, they offer unmatched flexibility, speed, and scalability.
Whether you’re building a small website or a large-scale enterprise application, following these best practices ensures your PHP and MySQL stack is robust, secure, and future-ready. And if you're seeking expert assistance, consider partnering with one of the top php development companies in usa to streamline your development journey and maximize the value of your project.
0 notes
Text
Master SQL in 2025: The Only Bootcamp You’ll Ever Need

When it comes to data, one thing is clear—SQL is still king. From business intelligence to data analysis, web development to mobile apps, Structured Query Language (SQL) is everywhere. It’s the language behind the databases that run apps, websites, and software platforms across the world.
If you’re looking to gain practical skills and build a future-proof career in data, there’s one course that stands above the rest: the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL.
Let’s dive into what makes this bootcamp a must for learners at every level.
Why SQL Still Matters in 2025
In an era filled with cutting-edge tools and no-code platforms, SQL remains an essential skill for:
Data Analysts
Backend Developers
Business Intelligence Specialists
Data Scientists
Digital Marketers
Product Managers
Software Engineers
Why? Because SQL is the universal language for interacting with relational databases. Whether you're working with MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, or Microsoft SQL Server, learning SQL opens the door to querying, analyzing, and interpreting data that powers decision-making.
And let’s not forget—it’s one of the highest-paying skills on the job market today.
Who Is This Bootcamp For?
Whether you’re a complete beginner or someone looking to polish your skills, the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL is structured to take you through a progressive learning journey. You��ll go from knowing nothing about databases to confidently querying real-world datasets.
This course is perfect for:
✅ Beginners with no prior programming experience ✅ Students preparing for tech interviews ✅ Professionals shifting to data roles ✅ Freelancers and entrepreneurs ✅ Anyone who wants to work with data more effectively
What You’ll Learn: A Roadmap to SQL Mastery
Let’s take a look at some of the key skills and topics covered in this course:
🔹 SQL Fundamentals
What is SQL and why it's important
Understanding databases and tables
Creating and managing database structures
Writing basic SELECT statements
🔹 Filtering & Sorting Data
Using WHERE clauses
Logical operators (AND, OR, NOT)
ORDER BY and LIMIT for controlling output
🔹 Aggregation and Grouping
COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX
GROUP BY and HAVING
Combining aggregate functions with filters
🔹 Advanced SQL Techniques
JOINS: INNER, LEFT, RIGHT, FULL
Subqueries and nested SELECTs
Set operations (UNION, INTERSECT)
Case statements and conditional logic
🔹 Data Cleaning and Manipulation
UPDATE, DELETE, and INSERT statements
Handling NULL values
Using built-in functions for data formatting
🔹 Real-World Projects
Practical datasets to work on
Simulated business cases
Query optimization techniques
Hands-On Learning With Real Impact
Many online courses deliver knowledge. Few deliver results.
The 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL does both. The course is filled with hands-on exercises, quizzes, and real-world projects so you actually apply what you learn. You’ll use modern tools like PostgreSQL and pgAdmin to get your hands dirty with real data.
Why This Course Stands Out
There’s no shortage of SQL tutorials out there. But this bootcamp stands out for a few big reasons:
✅ Beginner-Friendly Structure
No coding experience? No problem. The course takes a gentle approach to build your confidence with simple, clear instructions.
✅ Practice-Driven Learning
Learning by doing is at the heart of this course. You’ll write real queries, not just watch someone else do it.
✅ Lifetime Access
Revisit modules anytime you want. Perfect for refreshing your memory before an interview or brushing up on a specific concept.
✅ Constant Updates
SQL evolves. This bootcamp evolves with it—keeping you in sync with current industry standards in 2025.
✅ Community and Support
You won’t be learning alone. With a thriving student community and Q&A forums, support is just a click away.
Career Opportunities After Learning SQL
Mastering SQL can open the door to a wide range of job opportunities. Here are just a few roles you’ll be prepared for:
Data Analyst: Analyze business data and generate insights
Database Administrator: Manage and optimize data infrastructure
Business Intelligence Developer: Build dashboards and reports
Full Stack Developer: Integrate SQL with web and app projects
Digital Marketer: Track user behavior and campaign performance
In fact, companies like Amazon, Google, Netflix, and Facebook all require SQL proficiency in many of their job roles.
And yes—freelancers and solopreneurs can use SQL to analyze marketing campaigns, customer feedback, sales funnels, and more.
Real Testimonials From Learners
Here’s what past students are saying about this bootcamp:
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “I had no experience with SQL before taking this course. Now I’m using it daily at my new job as a data analyst. Worth every minute!” – Sarah L.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “This course is structured so well. It’s fun, clear, and packed with challenges. I even built my own analytics dashboard!” – Jason D.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “The best SQL course I’ve found on the internet—and I’ve tried a few. I was up and running with real queries in just a few hours.” – Meera P.
How to Get Started
You don’t need to enroll in a university or pay thousands for a bootcamp. You can get started today with the 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL and build real skills that make you employable.
Just grab a laptop, follow the course roadmap, and dive into your first database. No fluff. Just real, useful skills.
Tips to Succeed in the SQL Bootcamp
Want to get the most out of your SQL journey? Keep these pro tips in mind:
Practice regularly: SQL is a muscle—use it or lose it.
Do the projects: Apply what you learn to real datasets.
Take notes: Summarize concepts in your own words.
Explore further: Try joining Kaggle or GitHub to explore open datasets.
Ask questions: Engage in course forums or communities for deeper understanding.
Your Future in Data Starts Now
SQL is more than just a skill. It’s a career-launching power tool. With this knowledge, you can transition into tech, level up in your current role, or even start your freelance data business.
And it all begins with one powerful course: 👉 2025 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL
So, what are you waiting for?
Open the door to endless opportunities and unlock the world of data.
0 notes
Text
SQL injection

we will recall SQLi types once again because examples speak louder than explanations!
In-band SQL Injection
This technique is considered the most common and straightforward type of SQL injection attack. In this technique, the attacker uses the same communication channel for both the injection and the retrieval of data. There are two primary types of in-band SQL injection:
Error-Based SQL Injection: The attacker manipulates the SQL query to produce error messages from the database. These error messages often contain information about the database structure, which can be used to exploit the database further. Example: SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND 1=CONVERT(int, (SELECT @@version)). If the database version is returned in the error message, it reveals information about the database.
Union-Based SQL Injection: The attacker uses the UNION SQL operator to combine the results of two or more SELECT statements into a single result, thereby retrieving data from other tables. Example: SELECT name, email FROM users WHERE id = 1 UNION ALL SELECT username, password FROM admin.
Inferential (Blind) SQL Injection
Inferential SQL injection does not transfer data directly through the web application, making exploiting it more challenging. Instead, the attacker sends payloads and observes the application’s behaviour and response times to infer information about the database. There are two primary types of inferential SQL injection:
Boolean-Based Blind SQL Injection: The attacker sends an SQL query to the database, forcing the application to return a different result based on a true or false condition. By analysing the application’s response, the attacker can infer whether the payload was true or false. Example: SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND 1=1 (true condition) versus SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1 AND 1=2 (false condition). The attacker can infer the result if the page content or behaviour changes based on the condition.
Time-Based Blind SQL Injection: The attacker sends an SQL query to the database, which delays the response for a specified time if the condition is true. By measuring the response time, the attacker can infer whether the condition is true or false. Example: SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1; IF (1=1) WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:05'--. If the response is delayed by 5 seconds, the attacker can infer that the condition was true.
Out-of-band SQL Injection
Out-of-band SQL injection is used when the attacker cannot use the same channel to launch the attack and gather results or when the server responses are unstable. This technique relies on the database server making an out-of-band request (e.g., HTTP or DNS) to send the query result to the attacker. HTTP is normally used in out-of-band SQL injection to send the query result to the attacker's server. We will discuss it in detail in this room.
Each type of SQL injection technique has its advantages and challenges.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Power BI Training 2025 – Learn Data Analytics from Scratch | Naresh i Technologies"
🌐 Introduction: Why Power BI Matters in 2025
With data now being a central asset for every industry—from retail to healthcare—tools that simplify data analysis and visualization are essential. Power BI by Microsoft has emerged as one of the top tools in this space. It’s more than just charts—Power BI transforms data into decisions.
Whether you’re a beginner, a working professional, or planning a career transition into data analytics, this guide offers a practical roadmap to becoming proficient in Power BI.
📅 Want to join our latest Power BI training batch? Check all new batches and register here

🔍 What is Power BI?
Power BI is a cloud-based business intelligence platform by Microsoft that helps you visualize data, build interactive dashboards, and generate actionable insights. It's known for being user-friendly, scalable, and deeply integrated with Microsoft services like Excel, Azure, and SQL Server.
🧠 Key Features of Power BI
📊 Custom dashboards & reports
🔄 Real-time data streaming
🔍 AI-powered insights
🔌 Connects to 100+ data sources
🔐 Enterprise-grade security
These features make Power BI a top choice for companies looking to turn data into decisions—fast.
🧩 Types of Power BI Tools Explained
Power BI Tool What It Does Ideal For Power BI Desktop Free tool for creating and designing reports Analysts, developers Power BI Service (Pro) Online collaboration & sharing reports Teams, SMEs Power BI Premium Dedicated cloud capacity & advanced AI features Enterprises Power BI Mobile View dashboards on-the-go Managers, execs Power BI Embedded Embed visuals in your apps or web apps Software developers Power BI Report Server On-premise deployment for sensitive data Government, finance sectors
🧭 How to Learn Power BI in 2025 (Beginner to Advanced Path)
Here's a practical learning roadmap:
✅ Step 1: Start with Basics
Understand the UI and connect to Excel or CSV files.
Learn what datasets, reports, and dashboards are.
✅ Step 2: Learn Data Cleaning (Power Query)
Transform messy data into clean, structured tables.
✅ Step 3: Master DAX (Data Analysis Expressions)
Create measures, calculated columns, KPIs, and time intelligence functions.
✅ Step 4: Build Projects
Work on real-life dashboards (Sales, HR, Finance, Marketing).
✅ Step 5: Publish & Share Reports
Use Power BI Service to collaborate and distribute your insights.
✅ Step 6: Get Certified
Earn Microsoft’s PL-300: Power BI Data Analyst Associate certification to boost your credibility.
🎓 Explore our Power BI Training Programs & Enroll Today
Power BI Career Path in 2025:
As more companies prioritize data to guide their decisions, professionals who can interpret and visualize that data are in high demand. Power BI, Microsoft’s business analytics tool, has quickly become a preferred skill for analysts, developers, and business teams across the world.
But what does a career in Power BI actually look like?
Let’s break it down.
🛤️ A Realistic Power BI Career Progression
🔹 1. Data Analyst (Beginner Level)
If you're just starting out, you’ll likely begin as a data analyst using Power BI to create basic dashboards, import data from Excel, and build reports for stakeholders.
Tools to learn: Power BI Desktop, Excel, Power Query
Skills needed: Data cleaning, basic visualization, storytelling with charts
Typical salary: ₹3–5 LPA (India) | $60,000–75,000 (US)
🔹 2. Power BI Developer (Mid Level)
With 1–2 years of experience, you’ll be developing complex dashboards and working with large datasets. Here, DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) becomes essential.
Tools to learn: DAX, SQL, Power BI Service, Azure Data Sources
Responsibilities: Data modeling, report optimization, data refresh automation
Typical salary: ₹6–12 LPA (India) | $80,000–100,000 (US)
🔹 3. Business Intelligence Consultant / Sr. Analyst
At this stage, you’ll work on enterprise-scale BI projects, helping organizations plan, deploy, and manage full BI solutions using Power BI alongside cloud platforms like Azure.
Additional skills: Azure Synapse, Dataflows, Row-Level Security (RLS), Power BI Gateway
Salary range: ₹12–20+ LPA (India) | $100,000–130,000+ (US)
🛠 Must-Know Tools & Skills Alongside Power BI
Skill/Tool Why It’s Useful Excel Easily integrates and helps with modeling SQL Useful for custom queries and joining data Power Query Data cleaning and transformation DAX Metrics, logic, and analytics Azure Synapse or SQL Server Common Power BI data sources Python/R For statistical or advanced data science workflows
📌 Conclusion: Why Start Power BI Now?
Power BI is more than just a skill—it’s a career accelerator. Whether you're entering data analytics, trying to land a job abroad, or upskilling in your current role, Power BI is your go-to tool in 2025.
🎉 Ready to learn Power BI and land your next role? View all our upcoming batches and enroll now
🎓 Naresh i Technologies – One Destination for All In-Demand Courses
Naresh i Technologies doesn’t just offer Power BI—they provide a full spectrum of career-building IT courses, both online and in-classroom, guided by real-time professionals.
Whether you're interested in Power BI, cloud computing, software testing, or core development, Naresh has you covered.
🟢 Popular Courses at Naresh i Technologies:
✅ DevOps with Multi-Cloud Training in KPHB – Learn CI/CD, AWS, Azure, and real-world deployment.
✅ Full Stack Software Testing Training – Covers manual, automation (Selenium), API testing & more.
✅ Core Java Training in KPHB – Master Java OOPs, multithreading, JDBC, and more for strong backend foundations.
💬 Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is Power BI better than Tableau? Depends on your needs—Power BI is better for Microsoft ecosystem integration and affordability. Tableau is strong in flexibility and advanced visuals.
Q2. Can I learn Power BI in one month? Yes, if you dedicate consistent daily time, you can cover the basics and build a simple project within 30 days.
Q3. Is Power BI coding-based? Not
#PowerBITraining#LearnPowerBI#PowerBI2025#DataAnalyticsTraining#NareshTechnologies#BusinessIntelligence#DAX#PowerQuery#MicrosoftPowerBI#DataVisualization#BItools#KPHBTraining#ITCoursesHyderabad
0 notes
Text
The 10 most important data science tools you need to know
In today’s data-driven economy, the demand for skilled data scientists is soaring. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, organizations are investing heavily in data to drive smarter decisions. If you’re aspiring to build a successful career in this field, having hands-on knowledge of essential tools is non-negotiable. For those seeking the best data science training in Hyderabad, understanding and mastering the tools listed below is a solid place to start.
1. Python
Python is the most popular programming language in data science due to its simplicity, readability, and rich ecosystem.Statistical analysis, machine learning, and data manipulation are made possible with Python libraries like Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-Learn, and Matplotlib.
2. R Programming
Known for its powerful statistical capabilities, R is a favorite among statisticians and researchers. It excels in data visualization with packages like ggplot2 and Shiny.
3. SQL
SQL is essential for working with structured data. It enables you to extract, filter, and aggregate data from relational databases quickly and efficiently.
4. Tableau
Tableau is a leading data visualization tool that helps convert complex datasets into interactive dashboards and reports, making data accessible to decision-makers.
5. Power BI
Microsoft’s Power BI is gaining popularity for business analytics. Enhanced productivity is achieved through seamless integration with Excel and other Microsoft services.
6. Apache Hadoop
Hadoop is crucial for managing large datasets distributed across multiple servers. Big data projects benefit from its storage and processing capabilities.
7. Apache Spark
By offering in-memory data processing, Spark complements Hadoop and is ideal for real-time analytics and big data applications.
8. Jupyter Notebook
An essential tool for data scientists, Jupyter allows for interactive coding, visualizations, and documentation in one place—perfect for collaborative projects and presentations.
9. Excel
Excel remains relevant for quick data analysis, pivot tables, and data cleaning. It’s often the first tool analysts use before diving into more complex platforms.
10. TensorFlow
Developed by Google, TensorFlow is a powerful open-source framework used for building and training deep learning models.
Conclusion
For your business to remain competitive, you need to stay up-to-date with the field of data science. If you're serious about learning from experts and gaining real-world experience, consider enrolling with SSSIT Computer Education—your gateway to a rewarding data science career.
#best data science training in hyderabad#best data science training in kukatpally#best data science training in KPHB#Best data science training institute in Hyderabad
0 notes
Text
How to Choose a Database Management System: The Best Tools and Software for 2025
Data is at the core of every modern business. Whether it’s customer information, financial records, or product inventories, managing data efficiently is crucial for smooth operations and decision-making. A database management system (DBMS) helps businesses store, organize, and retrieve data securely and efficiently.
However, with so many database management tools and software available, choosing the right one can be challenging. Businesses need to consider factors like scalability, security, performance, and cost before making a decision.
This article explores how to choose the best database management system (DBMS) for your needs and highlights some of the top tools available in 2025.
1. What is a Database Management System (DBMS)?
A database management system (DBMS) is software that enables users to create, retrieve, update, and manage data efficiently. It acts as an interface between the database and users, ensuring data is stored securely and can be accessed when needed.
Key Functions of a DBMS
Data Storage — Organizes large volumes of structured and unstructured data.
Data Retrieval — Allows users and applications to access specific information quickly.
Data Security — Protects sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Data Integrity — Ensures accuracy and consistency in stored data.
Multi-User Access — Supports multiple users accessing and modifying data simultaneously.
Businesses of all sizes — from startups to enterprises — need a well-structured database to manage operations efficiently.
2. How to Choose a Database Management System?
Selecting the right database management tools and software requires careful consideration. The ideal DBMS should align with your business needs, performance expectations, and budget.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a DBMS
Scalability
Can the database handle growing amounts of data as your business expands? Cloud-based and distributed database solutions offer better scalability than traditional on-premise databases.
Performance
Look for a DBMS that ensures fast query processing and efficient indexing. Performance is crucial for applications handling real-time data processing, such as e-commerce or financial platforms.
Security Features
Data security is critical, especially for businesses handling sensitive information. The DBMS should offer encryption, access control, and regular backups to prevent data breaches.
Compatibility and Integration
Your DBMS should integrate seamlessly with existing software, including ERP systems, business intelligence tools, and cloud applications.
Cost and Licensing
Some database management systems are open-source and free, while others require licensing fees or subscription models. Factor in hosting, maintenance, and upgrade costs before making a choice.
Ease of Use and Administration
If your team lacks database expertise, choose a DBMS with a user-friendly interface and automated management features.
3. Best Database Management Tools and Software in 2025
The database landscape is diverse, with options ranging from relational databases (SQL) to NoSQL and cloud-based solutions. Below are some of the best database management tools and software in 2025.
A) Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) (SQL-Based)
Relational databases store data in structured tables, making them ideal for applications that require consistency and complex queries.
1. MySQL
One of the most popular open-source relational databases.
Best for web applications, e-commerce, and content management systems.
Supports high availability and replication.
2. PostgreSQL
Advanced open-source RDBMS with powerful performance and security features.
Great for handling complex queries and large-scale data applications.
Supports JSON and NoSQL-like functionality.
3. Microsoft SQL Server
A high-performance RDBMS designed for enterprises.
Integrates with Microsoft Azure and business intelligence tools.
Strong security features like Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
4. Oracle Database
Best for large enterprises that need high availability and reliability.
Features AI-powered automation and in-memory data processing.
High licensing costs but offers advanced analytics and security.
B) NoSQL Database Management Systems
NoSQL databases are designed for handling unstructured and semi-structured data, making them ideal for real-time applications, big data, and cloud-based services.
5. MongoDB
A document-based NoSQL database used for flexible data storage.
Ideal for content management systems, mobile applications, and IoT.
Supports horizontal scaling and distributed storage.
6. Cassandra
Best for handling large-scale distributed data across multiple servers.
Used by major tech companies like Netflix and Facebook.
Offers fault tolerance and high availability.
7. Firebase
A cloud-based NoSQL database by Google, built for mobile and web apps.
Offers real-time data synchronization and offline access.
Best suited for startups and small businesses.
C) Cloud-Based Database Management Systems
Cloud databases provide scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency, making them an excellent choice for businesses that want managed database solutions.
8. Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
A fully managed cloud database service by AWS.
Supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and more.
Automated backups, scaling, and security management.
9. Google Cloud Firestore
A NoSQL document-based database optimized for real-time applications.
Integrates well with Google Cloud services.
Serverless, making it easy to scale applications.
10. Microsoft Azure SQL Database
A cloud-based RDBMS designed for high availability and disaster recovery.
AI-powered performance tuning and security monitoring.
Supports automatic scaling based on workload.
4. Key Trends in Database Management for 2025
As businesses generate more data than ever, database technologies are evolving. Here are some trends shaping the future of database management tools and software in 2025.
AI and Automation in Database Management
AI-powered databases like Oracle Autonomous Database are improving performance, security, and self-healing capabilities without human intervention.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Databases
Businesses are increasingly using multi-cloud and hybrid database solutions to avoid vendor lock-in and improve redundancy.
Edge Computing and Distributed Databases
With the rise of IoT and edge computing, distributed databases like Apache Cassandra are becoming more popular for handling real-time data processing at scale.
Graph Databases for Advanced Analytics
Graph databases like Neo4j are being used for applications requiring deep data relationships, such as fraud detection and recommendation engines.
Choosing the right database system depends on your business needs, application type, and data management requirements. If your business requires structured data storage and complex queries, a relational database like MySQL or PostgreSQL is ideal.
For real-time applications, big data, and scalability, a NoSQL solution like MongoDB or Firebase may be the best choice. For businesses looking for fully managed, scalable solutions, cloud databases like Amazon RDS or Microsoft Azure SQL Database provide automated security and maintenance.
0 notes
Text
DBMS Tutorial Explained: Concepts, Types, and Applications

In today’s digital world, data is everywhere — from social media posts and financial records to healthcare systems and e-commerce websites. But have you ever wondered how all that data is stored, organized, and managed? That’s where DBMS — or Database Management System — comes into play.
Whether you’re a student, software developer, aspiring data analyst, or just someone curious about how information is handled behind the scenes, this DBMS tutorial is your one-stop guide. We’ll explore the fundamental concepts, various types of DBMS, and real-world applications to help you understand how modern databases function.
What is a DBMS?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that enables users to store, retrieve, manipulate, and manage data efficiently. Think of it as an interface between the user and the database. Rather than interacting directly with raw data, users and applications communicate with the database through the DBMS.
For example, when you check your bank account balance through an app, it’s the DBMS that processes your request, fetches the relevant data, and sends it back to your screen — all in milliseconds.
Why Learn DBMS?
Understanding DBMS is crucial because:
It’s foundational to software development: Every application that deals with data — from mobile apps to enterprise systems — relies on some form of database.
It improves data accuracy and security: DBMS helps in organizing data logically while controlling access and maintaining integrity.
It’s highly relevant for careers in tech: Knowledge of DBMS is essential for roles in backend development, data analysis, database administration, and more.
Core Concepts of DBMS
Let’s break down some of the fundamental concepts that every beginner should understand when starting with DBMS.
1. Database
A database is an organized collection of related data. Instead of storing information in random files, a database stores data in structured formats like tables, making retrieval efficient and logical.
2. Data Models
Data models define how data is logically structured. The most common models include:
Hierarchical Model
Network Model
Relational Model
Object-Oriented Model
Among these, the Relational Model (used in systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle) is the most popular today.
3. Schemas and Tables
A schema defines the structure of a database — like a blueprint. It includes definitions of tables, columns, data types, and relationships between tables.
4. SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is the standard language used to communicate with relational DBMS. It allows users to perform operations like:
SELECT: Retrieve data
INSERT: Add new data
UPDATE: Modify existing data
DELETE: Remove data
5. Normalization
Normalization is the process of organizing data to reduce redundancy and improve integrity. It involves dividing a database into two or more related tables and defining relationships between them.
6. Transactions
A transaction is a sequence of operations performed as a single logical unit. Transactions in DBMS follow ACID properties — Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability — ensuring reliable data processing even during failures.
Types of DBMS
DBMS can be categorized into several types based on how data is stored and accessed:
1. Hierarchical DBMS
Organizes data in a tree-like structure.
Each parent can have multiple children, but each child has only one parent.
Example: IBM’s IMS.
2. Network DBMS
Data is represented as records connected through links.
More flexible than hierarchical model; a child can have multiple parents.
Example: Integrated Data Store (IDS).
3. Relational DBMS (RDBMS)
Data is stored in tables (relations) with rows and columns.
Uses SQL for data manipulation.
Most widely used type today.
Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server.
4. Object-Oriented DBMS (OODBMS)
Data is stored in the form of objects, similar to object-oriented programming.
Supports complex data types and relationships.
Example: db4o, ObjectDB.
5. NoSQL DBMS
Designed for handling unstructured or semi-structured data.
Ideal for big data applications.
Types include document, key-value, column-family, and graph databases.
Examples: MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, Neo4j.
Applications of DBMS
DBMS is used across nearly every industry. Here are some common applications:
1. Banking and Finance
Customer information, transaction records, and loan histories are stored and accessed through DBMS.
Ensures accuracy and fast processing.
2. Healthcare
Manages patient records, billing, prescriptions, and lab reports.
Enhances data privacy and improves coordination among departments.
3. E-commerce
Handles product catalogs, user accounts, order histories, and payment information.
Ensures real-time data updates and personalization.
4. Education
Maintains student information, attendance, grades, and scheduling.
Helps in online learning platforms and academic administration.
5. Telecommunications
Manages user profiles, billing systems, and call records.
Supports large-scale data processing and service reliability.
Final Thoughts
In this DBMS tutorial, we’ve broken down what a Database Management System is, why it’s important, and how it works. Understanding DBMS concepts like relational models, SQL, and normalization gives you the foundation to build and manage efficient, scalable databases.
As data continues to grow in volume and importance, the demand for professionals who understand database systems is also rising. Whether you're learning DBMS for academic purposes, career development, or project needs, mastering these fundamentals is the first step toward becoming data-savvy in today’s digital world.
Stay tuned for more tutorials, including hands-on SQL queries, advanced DBMS topics, and database design best practices!
0 notes
Text
How a Full Stack Developer Course Prepares You for Real-World Projects
The tech world is evolving rapidly—and so are the roles within it. One role that continues to grow in demand is that of a full-stack developer. These professionals are the backbone of modern web and software development. But what exactly does it take to become one? Enrolling in a full-stack developer course can be a game-changer, especially if you're someone who enjoys both the creative and logical sides of building digital solutions.
In this article, we'll explore the top 7 skills you’ll master in a full-stack developer course—skills that not only make you job-ready but also turn you into a valuable tech asset.
1. Front-End Development
Let’s face it: first impressions matter. The front-end is what users see and interact with. You’ll dive deep into the languages and frameworks that make websites beautiful and functional.
You’ll learn:
HTML5 and CSS3 for content and layout structuring.
JavaScript and DOM manipulation for interactivity.
Frameworks like React.js, Angular, or Vue.js for scalable user interfaces.
Responsive design using Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS.
You’ll go from building static web pages to creating dynamic, responsive user experiences that work across all devices.
2. Back-End Development
Once the front-end looks good, the back-end makes it work. You’ll learn to build and manage server-side applications that drive the logic, data, and security behind the interface.
Key skills include:
Server-side languages like Node.js, Python (Django/Flask), or Java (Spring Boot).
Building RESTful APIs and handling HTTP requests.
Managing user authentication, data validation, and error handling.
This is where you start to appreciate how things work behind the scenes—from processing a login request to fetching product data from a database.
3. Database Management
Data is the lifeblood of any application. A full-stack developer must know how to store, retrieve, and manipulate data effectively.
Courses will teach you:
Working with SQL databases like MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Understanding NoSQL options like MongoDB.
Designing and optimising data models.
Writing CRUD operations and joining tables.
By mastering databases, you’ll be able to support both small applications and large-scale enterprise systems.
4. Version Control with Git and GitHub
If you’ve ever made a change and broken your code (we’ve all been there!), version control will be your best friend. It helps you track and manage code changes efficiently.
You’ll learn:
Using Git commands to track, commit, and revert changes.
Collaborating on projects using GitHub.
Branching and merging strategies for team-based development.
These skills are not just useful—they’re essential in any collaborative coding environment.
5. Deployment and DevOps Basics
Building an app is only half the battle. Knowing how to deploy it is what makes your work accessible to the world.
Expect to cover:
Hosting apps using Heroku, Netlify, or Vercel.
Basics of CI/CD pipelines.
Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure.
Using Docker for containerisation.
Deployment transforms your local project into a living, breathing product on the internet.
6. Problem Solving and Debugging
This is the unspoken art of development. Debugging makes you patient, sharp, and detail-orientated. It’s the difference between a good developer and a great one.
You’ll master
Using browser developer tools.
Analysing error logs and debugging back-end issues.
Writing clean, testable code.
Applying logical thinking to fix bugs and optimise performance.
These problem-solving skills become second nature with practice—and they’re highly valued in the real world.
7. Project Management and Soft Skills
A good full-stack developer isn’t just a coder—they’re a communicator and a team player. Most courses now incorporate soft skills and project-based learning to mimic real work environments.
Expect to develop:
Time management and task prioritisation.
Working in agile environments (Scrum, Kanban).
Collaboration skills through group projects.
Creating portfolio-ready applications with documentation.
By the end of your course, you won’t just have skills—you’ll have confidence and real-world project experience.
Why These Skills Matter
The top 7 skills you’ll master in a full-stack developer course are a balanced mix of hard and soft skills. Together, they prepare you for a versatile role in startups, tech giants, freelance work, or your own entrepreneurial ventures.
Here’s why they’re so powerful:
You can work on both front-end and back-end—making you highly employable.
You’ll gain independence and control over full product development.
You’ll be able to communicate better across departments—design, QA, DevOps, and business.
Conclusion
Choosing to become a full-stack developer is like signing up for a journey of continuous learning. The right course gives you structured learning, industry-relevant projects, and hands-on experience.
Whether you're switching careers, enhancing your skill set, or building your first startup, these top 7 skills you’ll master in a Full Stack Developer course will set you on the right path.
So—are you ready to become a tech all-rounder?
0 notes
Text
Why Learn SQL for Data Management in 2025?

Managing information efficiently has become an utmost priority in the present data-driven world. SQL, the Structured Query Language, is one of the most essential skills required by any database personnel. If you are aiming toward a career in software development, web development, or data science, learning SQL should definitely be in your to-do list in 2025.
TCCI Computer Coaching Institute offers practical hands-on training in SQL, for students, IT professionals, and anyone who wants to know how databases work.
💡Benefits of Learning SQL:
Fast Data Retrieval – Query any data from huge databases effectively.
All Major DBMS Compatibility– MySQL, PostgreSQL, MS SQL Server, and Oracle.
Database Creation And Management– Design tables, manage records, and organize data.
Analysis Integration– Mix with Python, Excel, and BI tools.
Whether you choose programming, analytics, or back-end development, SQL is key and paramount in certification.
🎯Career Scope After SQL
Database Developer
Data Analyst
Software Engineer
Backend Developer
SQL knowledge will add weight to your CV and get you into many high-paying jobs in technology.
📚SQL at the TCCI Computer Coaching Institute
Our SQL course is beginner friendly and provides a range of real-world database projects with full explanations of concepts and guidance from our experts. We prepare you for employment and further pathways in data science, programming, and software development.
Location: Bopal & Iskon-Ambli Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Visit Our Website: http://tccicomputercoaching.com/
#best computer courses near me#Programming Classes near Shela & Shilaj Ahmedabad#software training institute in bopal Ahmedabad#SQL Training Course in Bopal Ahmedabad#TCCI - Tririd Computer Coaching Institute
0 notes