#Shin Takasuga
Text
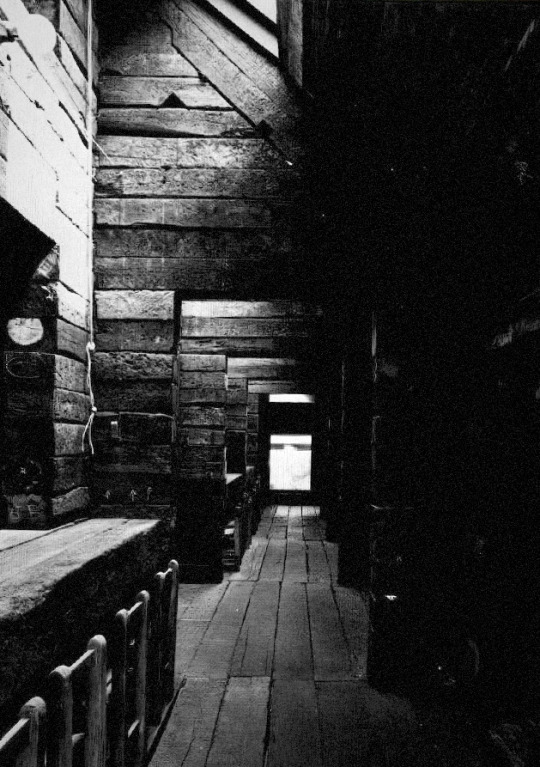
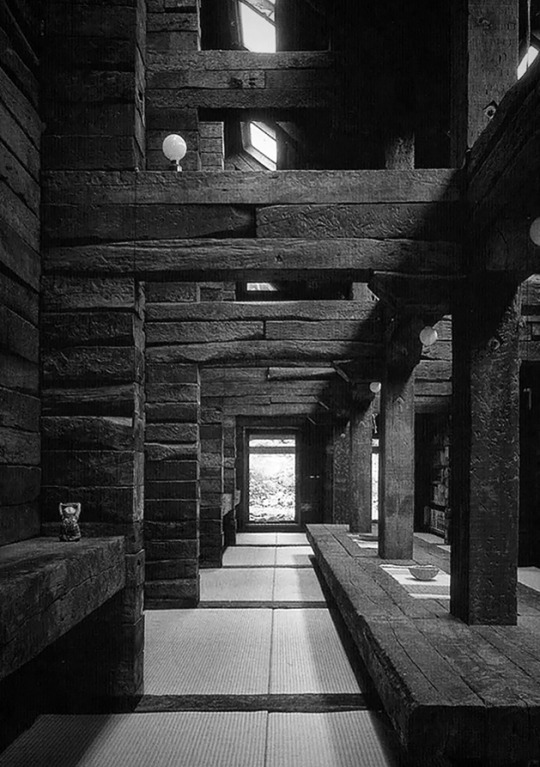
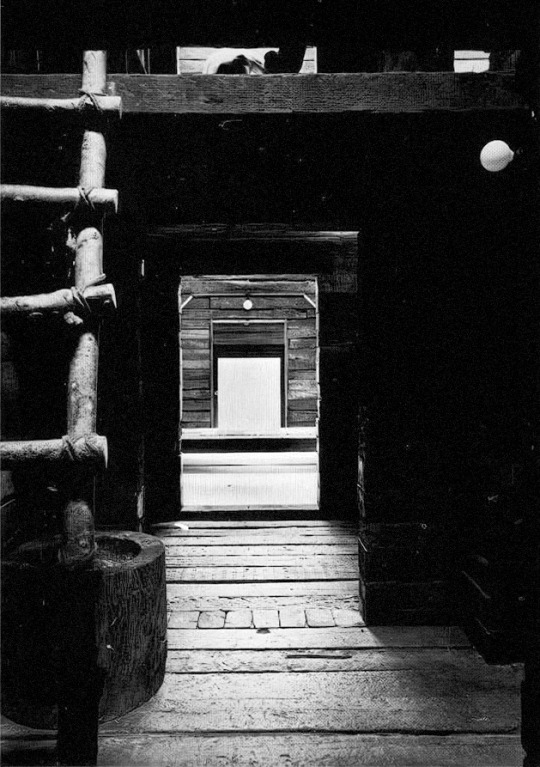
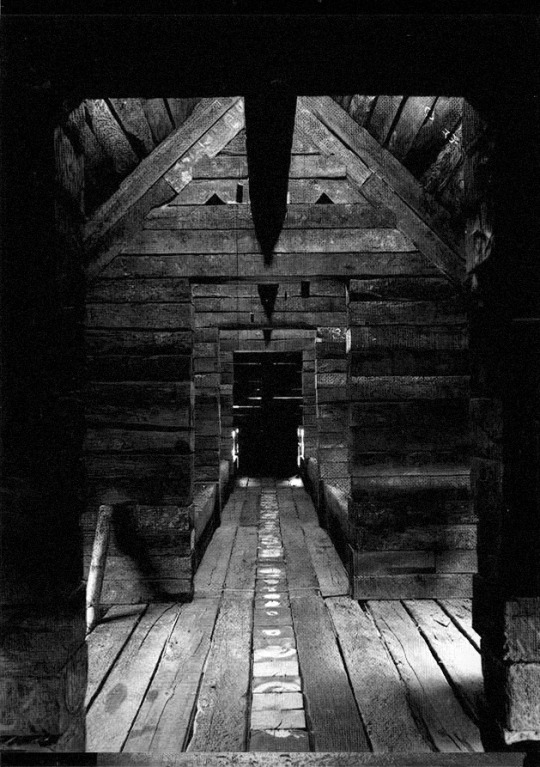
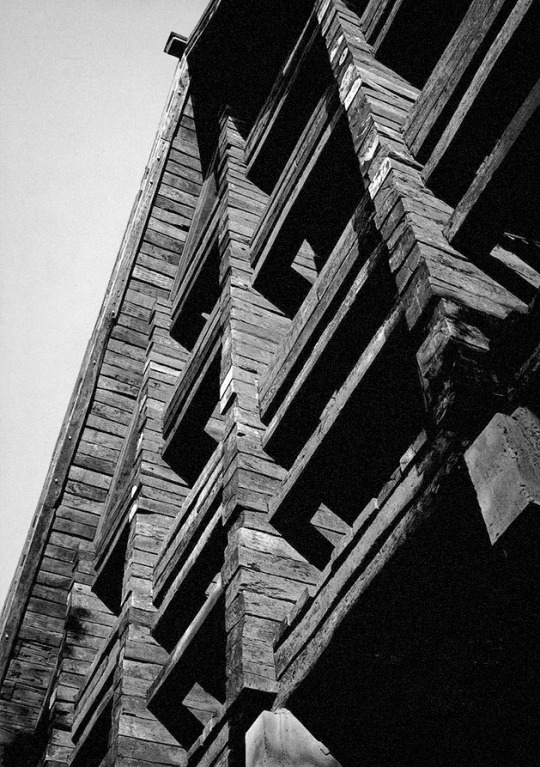










1115. Shin Takasuga /// Railway Sleeper House (Seitogakusha) /// Miyake Island, Tokyo, Japan /// 1975-80
OfHouses presents: Japanese Fields OfHouses, part III.
(Photos: © Shinkenchiku-sha, Urs Meister. Source: ‘Shinkenchiku’ 08/1980; ‘Tec21’ 197/2001; 'Arquitectura COAM' 358/2009.)
—
This project will be published in our upcoming book: ’Japanese Fields | OfHouses.’
#Fields3#Shin Takasuga#japan#70s#ofhouses#oldforgottenhouses#www.ofhouses.com#thecollectionofhouses#japanesefieldsofhouses
599 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Shin Takasuga, Railway Sleeper House, Island of Miyake, Japan 1970
24 notes
·
View notes
Photo

For Reference:
Railway Sleeper House by Shiin Takasuga
My building design also includes the idea of roof becoming wall, however curved. This is good construction reference.
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Shin Takasuga, Railway Sleeper House, Miyakejima, 1980
0 notes
Photo
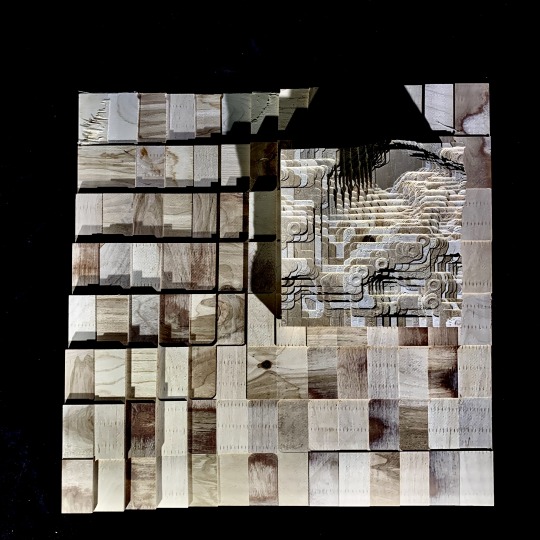








exercise 5. part 1 - surface to solid
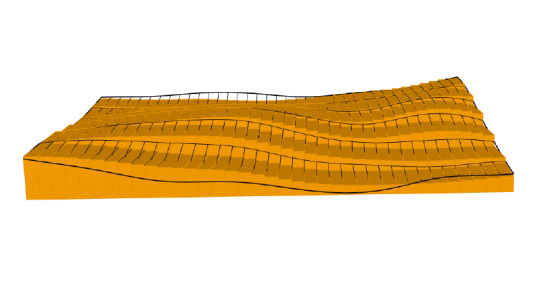
In this exercise, topographical data points were downloaded from the NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) database and translated into a digital surface. Then, this surface was put into a grasshopper definition which extruded the surface from a given plane in order to generate a solid. This solid was milled on the CNC router through a materially reductive method, in which an instruction set consisting of coordinates (generated through RhinoCAM) informed the mill’s path to cut away material from the solid block of 20″x 20″x 3″ laminated wood. This study prompts attentiveness toward the implications of relative scale throughout all stages of design and fabrication processes, both how scale functions as a generator of unknown variability and as design tool.
selection of topography - scale of earth v. scale of the product, earth’s surface is actually very flat relative to size of sphere on which it sits. This flatness reads even at the scale of a single latitude-longitude swatch of extracted data points (NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission). In order to combat this scale and define an area in the lat-long that had appropriately variable elevation, the area extracted for the surface had to be reduced to 1:100 of the original area.
adjustment of parameters of gh determined solid - once the data points had been translated into a surface using the first grasshopper (gh) definition, the baked surface that came as a result was input into the new “chunky surface” definition in order to generate the solid. At this point, various adjustments to parameters within the gh definition such as min/max count, aspect ratio, or even a surface rebuild (not within the gh definition, but rather command within rhino onto the surface) all yielded variable conditions of the base unit, or the smallest flat element within the larger topography. Object 1 has many large, rectangular units as a result of a long series of arbitrary aesthetic adjustments, which equates to lower fidelity to the variability within the original surface and a more abstracted reading. Object 2 was not subjected to any parameter changes, and therefore exhibited much smaller and more square elementary units that were able to accommodate the true topography more accurately.
translation render-to-mill - in this final step, the implications of tool capabilities and limitations were made very apparent. On object 1, the size of the milled object, though it looks much less complex and of lower variability than object 2, took much longer to mill (3 hours opposed to 30 min) due to the fact that it was 2.5x the length and width of object 2. This is of practical consideration when constructing multi-step and piece models in which material efficiency/cost and time/labor costs are of relevance. In fact, it was due to time/labor constraints that the decision was made to mill object 2 at the smaller size. This resulted in some movement of the block during the milling process, as the shear forces were strong enough to begin to dislodge the form from its constraints (small blocks visible in fig. 8). Additionally, for object 1, the angle of approach of the end mill was set to 45 degrees for the finishing portion of the job (versus 30 degrees for object 2). This angle, accompanied by the low relative depth of each unit to those surrounding compared to its surface area might have been the cause for some of the shearing forces that delaminated some of the object’s top layers (visible in fig. 9, large flat space in bottom right corner of object 1). On the other hand, the large elementary units paired well with the .5 inch end-mill, in that the corner moments, though still rounded in actuality, look very angular at the scale of the unit whole. In contrast, on object 2, due to the fact that the elementary unit was about .5″x.5″, the reading of this corner bevel resulted in a much more jagged and organic looking finish. The scalloping and sometimes fully circular moments on the final product inadvertently begin to allude to the mountainous nature from which this solid was derived, all due to a matter of relative scales.
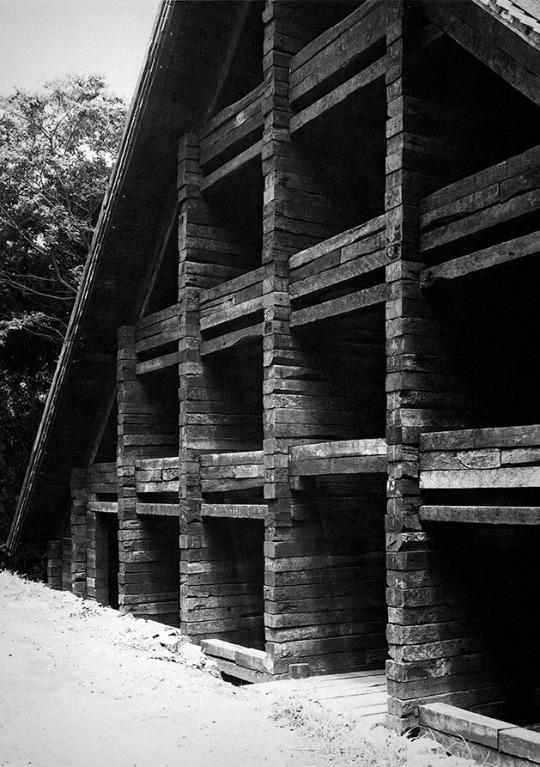
The milled objects hold some connection to the following systems example in Deplazes: Shin Takasuga’s Railway Sleeper House. “The universal utilisation of one single type of construction element for the whole structure – walls, floors, columns, roof structure, the built-in furniture too” (106) of the house allows it to read as a sort of natural extension of the forested topography of Miyake island, on which it is situated. Further blurring lines between landscape and building, “in the Railway SleeperHouse we can identify a subtractive design principle: the rooms seem to have been hacked out of a closed, cruciform stack with a rigid outer shape”. Similarly, the raw materials rely on the subtractive quality of the milling process to reveal the varied 'stacked’ surface conditions. One might even begin to reimagine the above exercise objects to some human scale, as containing qualities among its ridges and folds, where ridges begin to read as semi-hollow surfaces and platforms with habitable internal structure.
Source for Discussion:
Andrea Deplazes (ed.) “Materials - Modules: Timber, The Threads of the Net” in Constructing Architecture: Materials, Processes, Structures: A Handbook. Berlin: Birkhauser, 2005. pp. 106 -112.
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
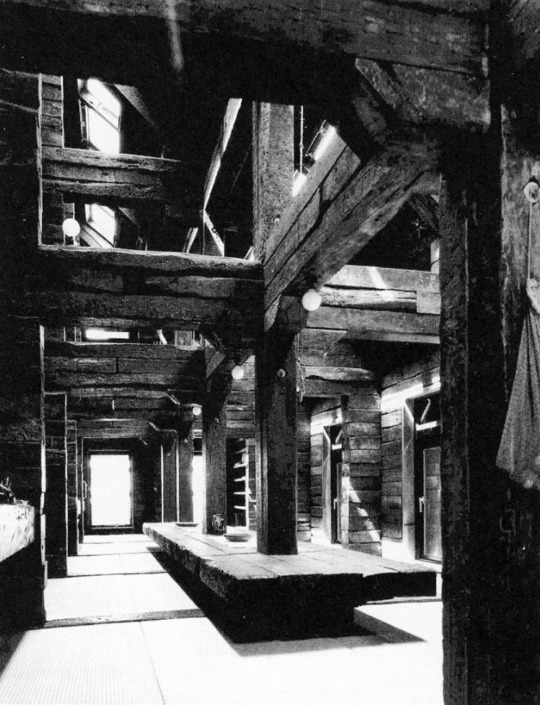
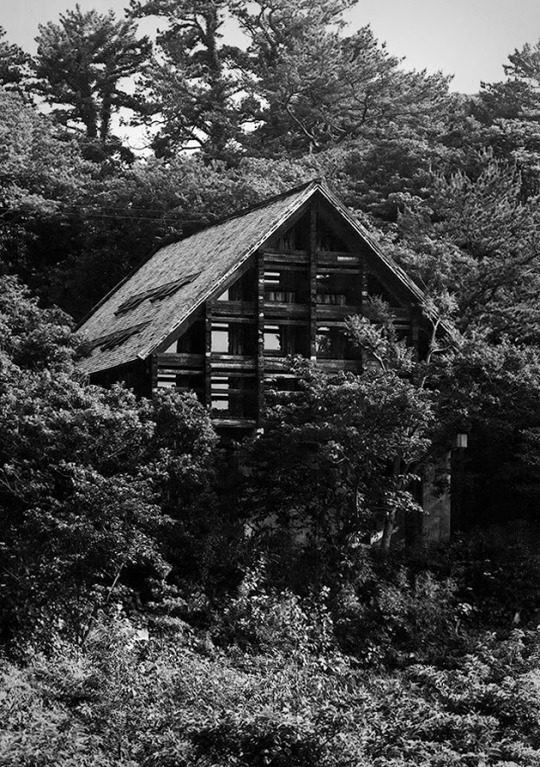
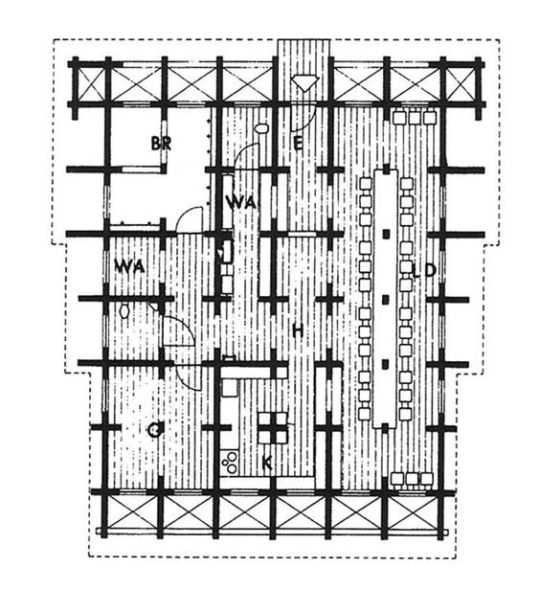
In 1970, Japanese architect Shin Takasuga designed a house in the middle of the forest on the Pacific Ocean’s island of Miyake. Students of the New Left and members of Peace movements planned the construction of a communal residential building and retreat camp which was meant to be realised within minimum budget and with almost no skills by the same inhabitants. Takasuga decided the house to be built using old wooden railways sleepers for the whole structure as well as the interior furniture and affirmed that the building did not not have to be designed, but rather generated by the stacking and crossing of railway sleepers as a structural principle.
A concrete sub-structure lies under the three-floors. The public areas, kitchen, assembly room and bathrooms, are all located on the ground floor, while a long dining hall which takes the whole building height becomes the main collective space. In the upper floors are located the sleeping rooms (all with the same surface), accessible only by ladders.
The triangular roof, covered in wooden shingles, embraces the whole building defining its exterior appearance. This main element is a reference to traditional japanese houses which were mostly identified by their imposing roofs, the first built part after the structure was erected.
The interior is characterized by the strict three-dimentional grid of structural wood made by the intersecting sleepers which appear the same in plan and section.
#gallery-0-4 { margin: auto; } #gallery-0-4 .gallery-item { float: left; margin-top: 10px; text-align: center; width: 12%; } #gallery-0-4 img { border: 2px solid #cfcfcf; } #gallery-0-4 .gallery-caption { margin-left: 0; } /* see gallery_shortcode() in wp-includes/media.php */
Railway Sleeper House on Miyake Island | Shin Takasuga In 1970, Japanese architect Shin Takasuga designed a house in the middle of the forest on the Pacific Ocean’s island of Miyake.
#budget#detail#hotel#house#japanese#landscape#material#Miyake Island#nature#old#railways#renovation#residential#roof#room#Shin Takasuga#sleepers#structure#triangular#wood
0 notes
Text
The 30 questions
Tagged by @juststuffsimightneed~
Thanks for tagging me <33333
1)Nicknames : Mary
2)Gender : Female
3)Star sign: Gemini
4)Height: 5′6
5)Time: 7:45 PM
6)Birthday: 10th June
7)Favorite bands: Every YG group! KARD, Spyair, EXO, girls’ generation, NCT, little mix, fifth harmony
8)Favorite solo artists: Every solo artist from YG, IU, Jay park, Jessie, Eric nam
9)Song stuck in my head: Shin megami tensei’s op lol
10)Last movie I’ve watched:
11)Last show I’ve watched: Queen for seven days T____T
12)When did I create this blog: 2013
13)What do I post: GINTAMA with a pinch of other animes lool
14)Last thing I googled: Shin Megami Tensei
15)Do you have any other blogs: Yeah, @gintsuweek
16)Do you ever get asks: rarely... plz pay attention to me T__T
17)Why did you choose your url: Favourite vocaloid, favourite number, the initial of my name.
18)Followers: 733
19)Following: 889 (um...)
20)Favorite color: All shades of blueee
21)Average hours of sleep: 6-9
22)Lucky number : 2
23)Instruments : I don’t play anything
24)What am I wearing: kameez and tights
25)How many blankets do I need to sleep with: 1 in summer, 5 in winter
26)Dream job: Maybe a medical professor or a neurosurgeon.
27)Dream trip: Korea, Japan , or canada
28)Favorite song: Changes all the time
29)Nationality: Pakistani
30)Song I’m listening to: nothing
Tagging: @takasuga, @ykchahine, @akelyokikagu, @gin-tsu <3333
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lecture: Tech
What kind of tree, how it will weather and what environment is it in.
Filigree construction:
Non load bearing timber,
Properties of timber:
Thermal:
0.13 W/mK for soft wood
0.20 W/mK for hard wood
Strength:
parallel with the grain it can provide tensional and compression properties
Types of products,
Layered, Particleboards, fibreboards.
How to reuse materials,
i.e wood chipping can be used for wall insulation
Ballon Frame construction
Kapp Skill Maritime Museum
steel structural frame,
thin clad timber
Ekko Installation, Denmark (2012)
concrete ‘shoes’ to keep timber dry
Parametric wood architecture,
woven wooden architecture (textile influence)
Shin Takasuga ‘railway sleeper house’
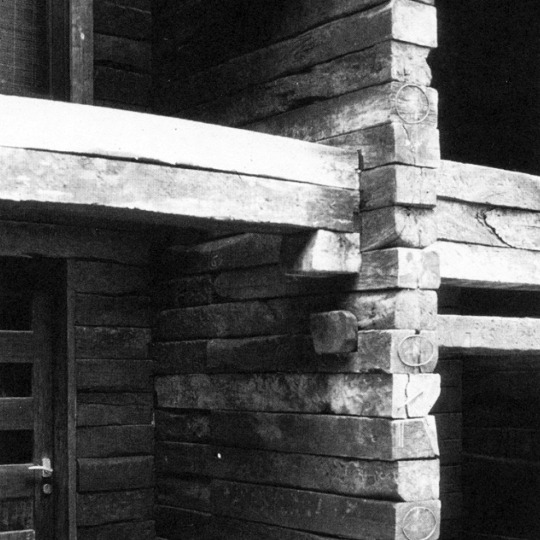
lock and key log joints
Timber Foundations:
excavation drawings for underground areas
Pad, strip, raft, and pile foundations,
rats are rarely used as pile foundations are cheaper, smaller and lighter.
(look at lecture slides how section is annotated)
timber section, a rectangle with a cross inside.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Timber lecture
Timber is rich and organic – poetry in design
Resort in Thailand Soneva Kiri Resort
three different type of roof
work with nature timber in angle etc.
Types of timber determine how it weathers, its aesthetic qualities
Timber in city need to be specific? What relationship does mentality have with the building and site?
Always consider where materials come from.
Solid and filigree construction
some trees can be fast growing
tree is less harmful to the earth
you can laser cutting timber into a geometry shapes.
Everything have time line – architecture need to think the life use of the materials when choosing materials. Everything/ materials need to be replace.
Timber
Densities depending on the species of the trees and moisture content.
Different tree growing different rang – all wood will get testing before using in the construction.
Depend where it grows, you will get different type of tree.
Properties of timber: - Timber does have a thermal property.
How you cut timber is also important – when cutting wood, it start to bend but there is a technique to make timber straight.
Specify the timber.
Timber from sawmill, conveying the chips, fibrous pulp on forming…
Solid timber
Glulam for the surface is laminate the timber, plywood, veneer etc.
Plywood
Veneer plywood – finishing wood
Fibreboards are a huge used
Timber platform building during the construction:
Latest form of timber construction appeared in Central Europe and Scandinavia.
With construct the timber building need to think about how many people will get involved in this construction because everything and everyone are cost money.
Shaping deficit of new technology – this move form solid materials because it cheaper and quicker to construct the building.
How can you use the waste materials to do something else? Waste materials can be used for the insulation
Scaffolding is very important for construction.
Cardboard model – if you going to use timber for your building, you need to use card and show how timber going to construct together (do card model and timber model).
Timber can play with the way to layout the panel e.g. vertical or horizontal way.
Need to think how each wood panel going to joint together (very specific)
Concrete and timber are working well together for the combination.
Kasp skill maritime – recycled materials and sun shade.
- Everything is recycling materials
- They try to be different from other practice
- Sculpture element and emphasis on the joint.
EKKO installation by Thilo Frank
Weaving joint method
Woven wood- supreme court building in New Zealand
One of the tower is using timber, might be good to look at how it constructs.
Parametric wood architecture
Building a small furniture
Need to use model to work out the density etc.
Design is all about making decision.
Timber frame Hose Model
Conversion of a truck in a Japanese shrine
they check each timber individually and mark the area they want to use.
They spread the tree to find the best part of the tree to use.
Get the most use out of the tree.
Modern Japanese in 1980- in parse of shadow (Japanese timber structure book)
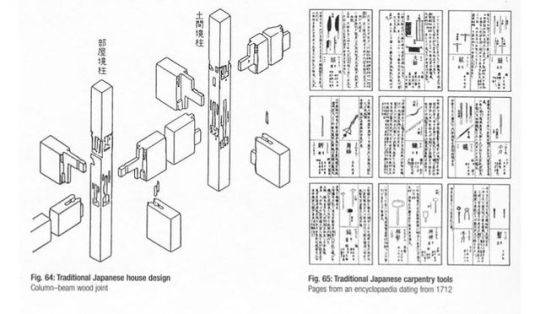
Shin Takasuga - Each panel is pin together to allow the movement, it one single type of element, every element is built form timber. Foundation is made from concrete.
Diagram to show the detail of how wood joint together
Timber can have a quality like a stone? Specific special quality.
Most architecture use Basic Geography data – geography, geology, infrastructure etc.
When showing the site in plan – used thin red line to high light the site in plan drawing.
GPS meaning Global positioning systems
Safety and security are very important.
Staircase
Eadweard Muybridge, Human and animal
Rise and going usually equal dimension – usually the standard rise for the stair is 200mm and the going is depending on you.
Hand drill is 90mm height.
Planningportal.gov.uk (building regulation)
Timber staircase – there is a many trick about timber stair. Start with simple way and later can development but still need to proof why?
Log construction
Frame construction
Erecting a Penal construction element
Platform frame construction element stacked.
Building kit
Custom prefabrication
Wood is taking over the world – with architects parsing its sustainability, quality, and speed of construction.
Tate Modern staircase
1 note
·
View note
Text
Architectural technology 2-ARCT 1070 Shaun’s lecture part 3 –TIMBER
- how to design details, cad, annotation is key
-timber is rich and organic
-keep away from moisture
-revealing the structure aesthetically, lattice structure
-work with the angles
-how everything works between the building and the occupants of the building
-the type of tree and relationship of the material and the relationship between the site.
-simple standard detailing needs to be professional
FOR NEXT WEEK THURSDAY
-in CAD with eaves over hang a section pitched roof
-proof what you understood by adding notes in the drawing
-staircase,ramp,wall,window something outside, and foundations
Filigree construction:
-concrete and steel –lattice –efficient material.
-cross laminated material –less harmful to the environment
make decisions
where wood comes from?
- Certain trees are specifically made for construction
- The pore structure of wood
- The structure of trees
- Different types of trees: heartwood trees, ripe wood trees, sapwood trees.
- Tensile forces
- Conductivity
- Compression forces
- Stresses and strains
- Grain
- What specific cuts through the wood?
- When you cut wood, it starts to distort.
- There’s hardly any waste from using wood.
- Glulam laminated timber-table tops etc.
- Plywood
- Veneer plywood –thin finish
- Multi ply boards
- Wood based plywood
- Chipboard
- Fibre board –insulating
- Flake board
- Oriental strand board
- MDF
- Timber platform frame
- Scandinavia famous for wood
- 1.Fundamental manual skill, 2. Complimentary layers in platform frame construction, 3 Shaping deficits of new technologies, 4 the search of an adequate structure and form, 5 CAD-CAM-ROBOTING
- cardboard model on scale of structure, model each individual element and show how one thing hits another thing, and begin to annotate it and do it according to how it would be constructed on site.
- Look at construction details on websites.
- Clarity is key!!!!!
- Kaap skil Marotome Museum by Mecanoo –vernacular architecture
- The joints
- Secret fixings
- Timber can’t be in contact with wet ground
- flat sheets you could heat bended
-�� parametric wood
- design is all about making in decisions
- fabric constructions look in other
- weaving wood in New Zealand supreme court
- flat elements take more load
- small elements take less load
Japanese work with timber buildings
-mark each end of the plumb line
-bamboo
-understanding how it dries
-in praise of shadow –talks about Japanese construction of timber
-Shin Takasuga: ‘Railway sleeper house’, house formerly belonging to the Seitogakushi School
-designing it to its context –moving ground allows certain movement between the fixings
- detailing of keys and locks, sleepers
-foundations site boundary with thick red line
-basic geography data using digital data
-survey the site and setting out the building foot print
-GPS –global positioning system are used to setting out
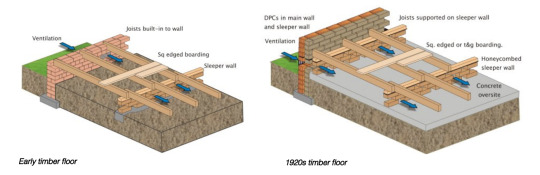
-sleeper wall and wall joist
-damp proof course
- add more information
-scaffolding
-temporary steps
Foundations:
-Pad, strip Raft and Pile Foundation?
-Pad foundation- discrete /for ground that isn’t stable
-Strip footing –linear
-Raft foundation- planar
-timber rectangle and cross (in section)
-damp proof course
-damp proof membrane (because its underground)
-trench on an angle (because it’s a basement)
-French drain
-sitting water is the most dangerous thing
-superstructure-the extension of the building above ground
-substructure -the extension of the building above below
-contiguous bored piles carving out the plan of the building
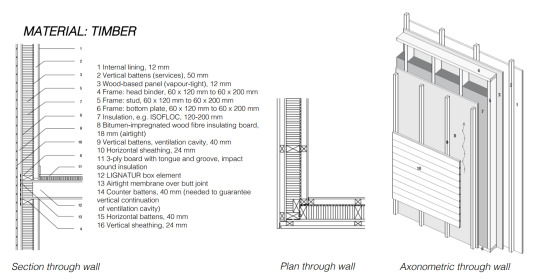
-plan though wall, section through wall, axonometric through wall
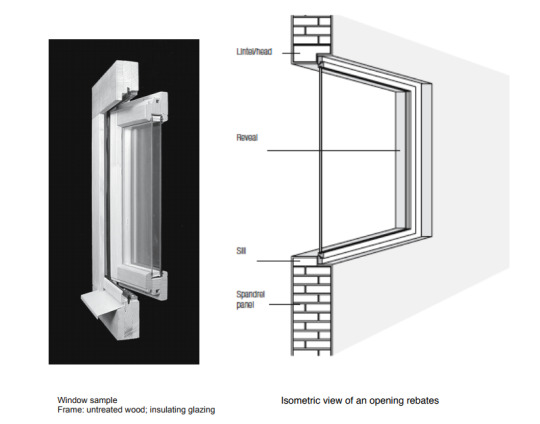
-windows act as a threshold between spaces! very important specifically what your viewing outside
-door ironmongery
-door types
-single leaf hinged door, double leaf hinged door, double door
-floor can have different dynamics
-ventilation sleeper walls
-cold bridge
-staircase -rise max 200,300 could be going
-rhythm of staircases
-in a construction drawing you would number each step
-standard staircase and then do the ambitious one
-Platform frame construction elements axonometric
-C&C cutting
- www.planningportal.gov.uk building regulations
- CF MOLLER ARCHITECTS ,wood scrapper in Stockholm
- If you dip wood in salt you can turn it into stone structure?
- De Rijke staircase at Tate Modern
(NEED TO START TO DO SECTIONS)
1 note
·
View note
Text
25/01/2018 Timber Lecture Notes

Timber
· Friedrich Keisler – Elastic Architecture
· Warm Material – Cross Laminated Timber, layered timber – a lot stronger. Thermal 0.13W/Mk soft wood. 0.2 for Hard wood. Drying can produce distortion – shrinkage.


· Different parts of the tree have different forces exposed on it. Strength – Grain, parallel can carry a lot more weight than perpendicular. Different cuts will get different radial paths

· Locally sourced? Primary structure – hard woods, secondary can be soft woods.
· Potentially talk to a specialist.
· Porosity varies, so drying times vary.
· Consider renewable – Epping forest’s history and sustainability.
· Rounded wood reduces the burn time
· Waste chips from timber can be used as insulation
· Pulp can become fibre boards

· Particle Boards – can be used for temporary structures.


· Timber models, you can relate the rhythm to the movement of people through the space. Carpentry – Jointing and framing techniques. A stud – used for walls, not usually load bearing. Just used in construction.

· Glass with timber cladding. Pinned together with steel, inserted inside the timber for discretion - galvanised steel so it doesn’t rust.

· Reveal the timber within the structure – Primary structure and then add in secondary structure.

· Store trees in the pond for 3 years to prevent cracking

· Distressed nature of the natural over time seen as a beautiful thing – In Praise of Shadows – Ask Henry C for his copy of the book. Roof larger tiles on the bottom then smaller on top – weathering. Change parts incrementally as they fail. Railway Sleeper House, Shin Takasuga – Jointing, micro details.


· FOUNDATION
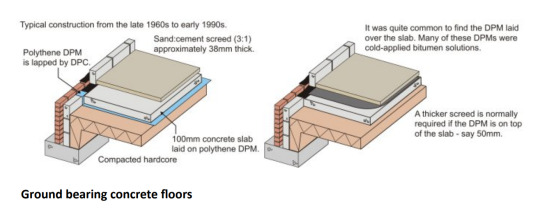
· Site preparation, GPS tracking, peoples main route to the building, general temp and light of the site. Soil must be angled to prevent it from falling in. Unstable ground – you need appropriate foundation. Lorry size, and routes that need to be taken. NEVER HAVE A TIMBER FOUNDATION – Concrete or masonry foundation – Timber will decay and so must come out of the ground. Consider drainage coming out from the wall.


· Superstructure – The extension of the building above ground
· Substructure – The extension of the building below ground
· WALL
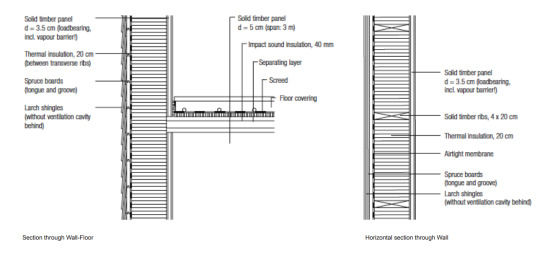
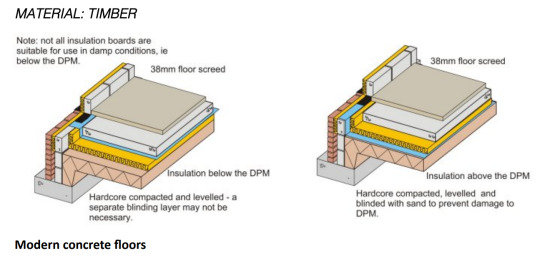
· Timber frame construction with studs, axo diagram can reveal whether its thermal or decorative. Cutaway revealing the decisions. [X] means it’s a smooth saw. Linear elements need horizontal elements to support them. Underfloor heating, insulation takes place below.
· Connection to the outside – Timber frame windows. Horizontal windows working with the landscape. Thresholds, breaking down, picture frame. How the frame can become a piece of the architecture.
· Floor can be an inhabitable space, design for a purpose.
0 notes
Photo
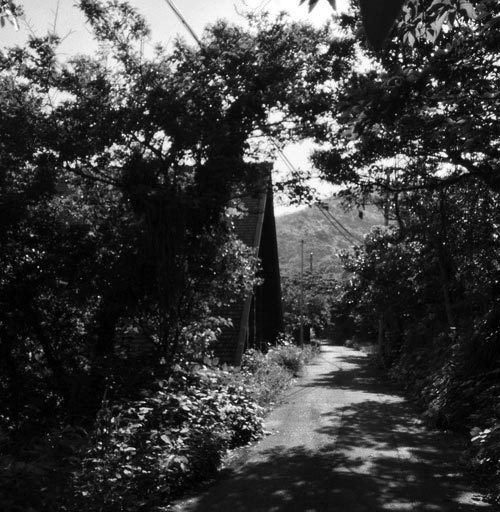










Shin Takasuga
1970, Railway Sleeper House
original post by SOCKS
http://socks-studio.com/2016/03/06/inhabiting-a-three-dimensional-grid-the-railway-sleeper-house-by-shin-takasuga/
48 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Inspiration: Shin Takasuga, Railway Sleeper House, Miyake Island, 1970's.
303 notes
·
View notes






