#Smart Factory
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Siemens' electronic works facility in Amberg, Germany
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
유비센스, 차량 제조업체들의 유연성 및 효율성 최적화 위한 스마트 팩토리 어셈블리 출시
유비센스, 차량 제조업체들의 유연성 및 효율성 최적화 위한 스마트 팩토리 어셈블리 출시
대표적인 기업 내 지능형 위치추적 솔루션 업체인 유비센스 그룹(Ubisense Group plc, http://ubisense.net/login)이 각 작업 라인의 운영상의 어려움을 해결하고 제조 복잡성의 비용 증가를 억제함으로써 전세계 차량 제조업체들을 지원해줄 스마트 팩토리 어셈블리(Smart Factory Assembly, http://goo.gl/1ayfki)를 출시했다.
스마트 팩토리 어셈블리는 차량 제조업체들이 고정된 워크스테이션으로부터 벗어나, 하이믹스(high-mix), 대량생산(high-volume) 조립 라인의 복잡성을 관리하는 데 필요한 가상화를 이용할 수 있도록 지원한다. 이러한 수��의 유연성으로 인해, 제조업자들은 현저한 비용 절감과 보장된 생산성 증대, 품질 개선 등은 물론,…
View On WordPress
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2018, 스마트공장 사례집 촬영, 시흥 마팔하이테코
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Creating a Smart Factory for a Leading Packaging Company
Developing Building Automation Applications using IoT for a Commercial Building
Big Data Storage and Analysis in Hadoop for a Retail Solutions Provider
Data Analytics and Reporting Solution for a leading Healthcare Provider
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Digital Problem Solving in Factories: Is the ROI Worth the Transition?
Everyone’s talking about digitalization in factories, but what does that actually mean when it comes to solving real problems on the shop floor? One of the biggest—and most impactful—changes is the shift from paper-based problem solving to digital, automated systems. But let’s be honest: change is hard. Transitioning from forms, binders, and spreadsheets to a structured faster problem solving software can feel overwhelming.
So… is it really worth the time, cost, and cultural change? In this blog, we’ll break down exactly why moving from paper to digital isn't just a trend—it's a logical and high-ROI move that enhances speed, quality, compliance, and visibility across the entire factory.
What’s Wrong with Traditional Problem Solving?
Despite decades of use, traditional problem-solving methods in factories are cracking under modern demands. Manufacturers still rely on paper forms, Excel logs, and siloed discussions to document, track, and solve problems. But these methods were designed for a slower, less complex world.
Today’s factories move faster, produce more variants, and face tighter compliance and quality requirements. Everyone is pushing for change because traditional tools don’t support speed, accountability, or real-time decision-making. Let’s look at why these methods fall short:
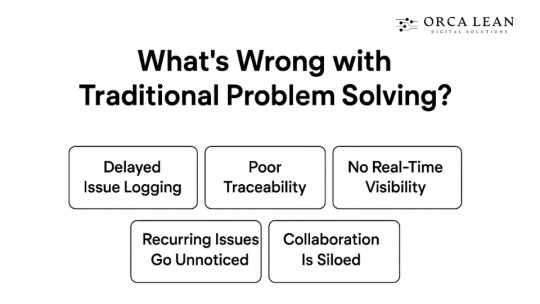
Let’s break down what’s going wrong:
1. Delayed Issue Logging - By the time an operator fills a paper form or logs a defect on Excel, the problem has already spread. Manual entries introduce delays and human error, which slows everything down.
2. Poor Traceability - Once you start hunting for a paper report from last month, you’ve already lost the battle. Traditional systems lack transparency into who reported what, when, and what action was taken.
3. No Real-Time Visibility - Supervisors and managers only see problems when someone brings them up in a meeting—by then, it’s often too late. Without live tracking, problems escalate silently.
4. Recurring Issues Go Unnoticed - When issues are solved in isolation, without centralized tracking, teams end up fixing the same problem again and again.
5. Collaboration Is Siloed - Operators write it down. Supervisors report it. Engineering looks into it later. This delay between departments kills response time.
Explore how digital transformation directly improves quality outcomes in our detailed guide: Impact of Digital Transformation on Quality Management
What Digital Problem Solving Actually Changes?
Digital problem solving is not about simply replacing paper with screens. It’s a shift in how factories identify, escalate, analyze, and eliminate issues. Traditional methods are reactive and fragmented. Digital tools are proactive, centralized, and insight-driven. This transition helps manufacturers move from “firefighting mode” to a culture of continuous improvement.
Here’s what changes when you adopt the right manufacturing software for problem solving:
A. Speed
Digital tools enable real-time issue logging from the shop floor—whether via tablets, kiosks, or operator dashboards. The moment a problem is entered, it’s automatically routed to the right team based on category, severity, or asset. This eliminates waiting for emails, meetings, or paper forms to reach supervisors.
B. Transparency
A digital platform provides a full audit trail. Every action taken—from issue creation to root cause analysis to final resolution—is time-stamped and visible to stakeholders. There’s no confusion over who did what or when. This transparency improves cross-functional trust and strengthens compliance tracking for ISO, IATF, and other industry audits.
Want to see how digital records outperform paper logs? Read our breakdown:Paper vs Digital Data Acquisition in Manufacturing
C. Data-Driven Insights
Digital problem-solving platforms don’t just track problems—they analyze them. They reveal repeat failures, identify top contributors by line or shift, and link problems to KPIs like scrap rate or downtime. These insights enable smarter prioritization and preventive action.
D. Team Alignment
Digital tools create shared visibility. When teams across shifts or departments see the same dashboard, handovers become seamless. Engineering, quality, and production can all contribute to the same issue without delays or duplicated work. Real-time collaboration fosters accountability and faster resolutions.
Want to explore how quality inspection helps manufacturers? Check our blog to dive into the details.
E. Centralized Knowledge Base
Instead of tribal knowledge or scattered spreadsheets, you build a growing, searchable library of past problems, tools used, actions taken, and lessons learned. This benefits new hires, supports standardization, and prevents repeated mistakes.
Digitalization in factories isn’t about bells and whistles. It’s about using software for factory workflows to enable faster, smarter, and more consistent problem solving—turning everyday issues into opportunities for growth.
But Isn’t Digitalization for Factories Difficult?
Of course it is. Change is uncomfortable—especially in factories where operators have used the same paper forms for years. But what’s often labeled as a “tech problem” is usually just a mindset shift. And mindset can be changed—with the right approach.
Start small - Don’t digitize your whole plant on day one. Begin with one production line, one shift, or one recurring issue. Prove value in a focused area, then expand. Small wins build big momentum.
Pick the right software - If your digital tool feels like it was built only for engineers, your operators will resist it. Choose faster problem solving software designed for frontline ease—tap, log, assign. No confusion. No coding. No frustration.
Make quick wins visible - People don’t rally behind technology—they rally behind results. If a defect was resolved in half the time last week, share it. Announce it on the floor. Show it on a dashboard. Let the improvement speak louder than the software.
Train, but don’t overtrain - Digitalization doesn’t require a master's degree. Short, hands-on training with real factory use cases works better than manuals. Keep it contextual, keep it relevant.
Show the story through dashboards - Dashboards turn numbers into proof. When teams see improvement live, belief follows. Metrics don’t lie.
Here’s the simple truth: your teams are already solving problems. Software just helps them do it faster, better, and visibly. That’s not disruption. That’s evolution.
Curious about how to start? Check out our 7 FAQs About Transitioning from Paper to Digital in Manufacturing to get practical answers before you take the leap.
Is the Adoption Journey Worth It?
Implementing digitalization in factory operations brings its share of doubts: “It takes too long,” “operators won’t adopt it,” “it’s too expensive.” And those concerns aren’t baseless—rollouts involve training, process tweaks, and upfront investment. But clinging to paper and spreadsheets carries hidden costs: delayed fixes, repeated defects, and firefighting modes that erode margins. Despite the challenges, the adoption journey pays dividends in efficiency, quality, and culture—making every hurdle a worthwhile investment.

Real Impact: What You Can Expect to Improve
Digital problem-solving isn’t about theory—it’s about real, trackable results. When manufacturers shift from paper to structured, software-driven processes, they unlock tangible improvements across quality, efficiency, compliance, and culture. The ROI becomes visible not in quarters, but in weeks. Here’s what companies typically experience after implementing faster problem solving software like Solvonext:

Conclusion
You’re already solving problems—every shift, every day. But if you're still relying on paper, you're solving them slower, with less visibility and more waste. Paper systems were built for yesterday.
Today’s factories need speed, traceability, and actionable insights—and that’s exactly what digital problem-solving delivers. The return isn’t just in faster resolutions—it’s in fewer defects, stronger audits, and a culture of continuous improvement.
Solvonext helps you make that leap—without disruption. With built-in tools, real-time tracking, and frontline-ready design, it's everything your team needs to solve smarter.
Book a Demo today and explore Solvonext: your next step to operational excellence.
1 note
·
View note
Text
youtube
Sandy Munro reveals why Chinese Car companies are 5 years ahead
🚗 In this eye-opening video, legendary automotive engineer Sandy Munro breaks down why Chinese car companies are now 5 years ahead of global competitors in the EV revolution! From groundbreaking battery technology, manufacturing efficiency, and cutting-edge design, to game-changing strategies in electric vehicles, Munro exposes how brands like BYD, NIO, Xpeng, and Li Auto are dominating the future of electric cars. Discover how China's EV innovation, supply chain control, and smart factory integration are reshaping the automotive industry faster than Tesla and legacy automakers ever imagined. Don’t miss this deep dive into the global shift in EV leadership, and find out what it means for the future of electric mobility, autonomous driving, and sustainable transportation.
#Sandy Munro#smart factory#ev manufacturing#ev sales#american decline#competition#BYD#Youtube#tesla killer#elon musk#China#usa
1 note
·
View note
Text
Smart Factory Market to Hit $30.1 Billion by 2029: The Future of Manufacturing is Here

The smart factory market is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by a blend of advanced technologies, robust government support, and the rising demand for efficient, automated production processes. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets™, the smart factory market is expected to surge from $18.8 billion in 2024 to $30.1 billion by 2029, growing at an impressive CAGR of 9.8%.
This growth reflects a major shift in how industries operate, moving from traditional manufacturing to connected, intelligent, and automated ecosystems. The smart factory revolution is well underway, and industries are leading the charge.
What’s Fueling the Smart Factory Boom?
Several factors are contributing to this explosive market growth
1. Advanced Technology Adoption
The rapid implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT, AI, machine learning, and 3D printing, is transforming the industrial landscape. Manufacturers are using real-time data, automation, and smart systems to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality.
2. Strong Government Support
The government has created a favorable environment for innovation, funding R&D initiatives, and pushing for the adoption of digital manufacturing technologies across sectors. Programs such as Manufacturing USA are key enablers, accelerating the transition to smarter, more agile manufacturing processes.
3. Focus on Operational Efficiency
Increased pressure to optimize resource usage, reduce downtime, and ensure product traceability is driving companies to adopt smart factory solutions. By digitizing workflows, factories can enhance responsiveness and quality while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Key Segments Leading the Market Growth
The report highlights several crucial components and solutions that are powering the smart factory boom in the
1. Industrial Sensors
In 2023, industrial sensors captured a significant share of the market. These sensors are critical for monitoring machinery, detecting anomalies, and collecting real-time data. As factories become smarter, sensors enable predictive maintenance, process optimization, and real-time decision-making.
Driven by the Internet of Things (IoT), the adoption of smarter sensors helps manufacturers reduce waste, enhance safety, and remain competitive in an increasingly digital ecosystem.
2. Industrial 3D Printing
Industrial 3D printing is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period. This technology plays a vital role in enabling rapid prototyping, on-demand production, and customization. With strong demand from aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries, 3D printing is becoming a core component of smart manufacturing.
The benefits from a rich base of technological infrastructure and a skilled workforce make it a global leader in 3D printing adoption.
3. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
MES solutions are expected to hold a significant share of the smart factory market. MES bridges the gap between factory floor operations and enterprise systems, ensuring that data flows seamlessly and efficiently.
With real-time visibility into production activities, MES helps manufacturers manage resources, monitor performance, and make informed decisions. It’s especially valuable in industries like pharmaceuticals, automotive, and electronics, where precision and compliance are essential.
Market Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
Increased investments in AI, robotics, and IoT
Government support for digital infrastructure
Rising need for mass customization
Adoption of cloud platforms and edge computing
These trends are unlocking new possibilities, allowing manufacturers to innovate faster, reduce operational costs, and maintain global competitiveness.
Challenges
While the outlook is positive, the smart factory market faces notable hurdles
High upfront costs for advanced technologies and infrastructure
Integration challenges with legacy systems
Cybersecurity concerns due to increased connectivity
Shortage of skilled labor for operating and maintaining smart systems
Companies must address these challenges with thoughtful planning, training programs, and robust cybersecurity strategies.
Leading Market Players
The smart factory ecosystem is supported by prominent industry leaders, including
Emerson Electric Co.
General Electric
Honeywell International Inc.
Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Dwyer Instruments, LLC.
Stratasys
3D Systems Corporation
These companies are pushing the envelope by developing innovative hardware and software solutions that form the backbone of modern smart factories.
Conclusion: The Future is Automated and Intelligent
The growth of the smart factory market signals a broader transformation in the way goods are designed, produced, and delivered. From smart sensors and 3D printers to MES platforms and predictive analytics, smart factories are at the heart of the next industrial revolution.
To stay ahead, businesses must embrace these changes and invest in digital transformation. With the right strategy and technology, the future of manufacturing looks smarter, faster, and more resilient than ever.
#digital transformation#smart factory#manufacturing industry#automated production processes#monitoring machinery#thirdeye ai#ai
1 note
·
View note
Text

Smart Factory-Digitalisierung | Nevolvis
Der Einsatz digitaler Technologie kann die Arbeitsweise von Fabriken verändern und Einnahmen generieren. Und wenn Sie Technologie in Ihrer Fertigungseinheit implementieren, wird daraus eine Smart Factory Digitalisierung. Möchten Sie wissen, wie Sie Ihre Fertigungseinheit in eine Smart Factory umwandeln können? Nehmen Sie jetzt Kontakt mit uns auf.
1 note
·
View note
Link

Factory automation leads to the generation of valuable data around processes and allows IoT systems to improve operations smartly and sustainably. This clears that IoT, i.e. Internet of Things holds a great scope in factory automation and provides an unbeatable application to enhance operations, ultimately providing better results.
1 note
·
View note
Link

Industrial automation and IoT are ushering a new era of smart connected factories and industries, enabled by disruptive technological advancements in M2M communications, embedded computing, cloud enablement, mobility, and analytics. We understand the key aspects of a truly connected industry, right from sensors to analytics and beyond. Our industrial practice focuses not only on industrial product lifecycle from ‘concept to production’ support, but also on making the industries smarter through our connected digital solutions expertise.
1 note
·
View note
Link
OSG announces Project OSG 4.0 and the construction of the NEO Shinshiro Factory for smart manufacturing.
#OSG Corporation#osgtools#NEO Shinshiro Factory#smart factory#smart manufacturing#Project OSG 4.0#OSG 4.0
1 note
·
View note
Link
The term Industry 4.0 was introduced by the German Government to describe the fourth industrial revolution. It integrates manufacturing with modern technologies such as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data and Cloud Computing to make “Smart Factory” or “Smart Manufacturing”. It merges real and virtual worlds based on Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) and Cyber-Physical Production Systems (CPPS).
#Smart Manufacturing semiconductor#Smart Manufacturing semiconductor service#Smart Manufacturing semiconductor solutions#Smart Manufacturing#Smart Factory#Cyber Physical Systems#Cyber Physical Production Systems
1 note
·
View note
Photo

2018, 스마트공장 사례집 촬영, 양산 코렌스
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 (https://www.indovisionglobal.com/industry4.0/) and the fast ascent of robotization is leading the consistently changing landscape of manufacturing intelligence (https://www.indovisionglobal.com/industry4-0/) processes of Sisteplant India (https://www.indovisionglobal.com/industry4-0/). Makers are given the test of redesigning and digitizing their frameworks as methods for introducing life span in their organizations. Inability to do as such dangers them falling behind their client’s developing requests. Digitisation, robotization and information gathering are the key standards of Industry 4.0 that makers must adjust themselves to. Thusly, makers can enhance efficiencies while streamlining costs and keeping up a quality client encounter. As a main provider and producer of basic part arrangements,smart factory (https://www.indovisionglobal.com/industry4-0/),Sisteplant,Sisteplant) India (https://www.indovisionglobal.com/industry4-0/) Essentra Components are one of the numerous makers simply beginning on their Industry 4.0 voyage.
www.indovisionglobal.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
FACTS4WORKERS networking workshop at Mensch und Computer 2015
More than 750 participants from Germany, Austria, and Switzerland came together for four days to share their ideas, knowledge and experiences at the Mensch und Computer 2015 (MuC15). MuC15 is the largest annual German-speaking conference for Human-Computer/Machine-Interaction which this year took place at Stuttgart University from Sep 6 to Sep 9.
The FACTS4WORKERS project had the opportunity to organize a one-day Workshop on the topic "Smart Factories" at MuC15. We dedicated this workshop to the discussion of theories, models, technologies, demonstrators, case studies, and practical experiences on worker-centric information systems for collaboration in factories of the future.
The reactions on our call for papers was very positive and at the end we accepted 16 submissions for presentation at the workshop. The workshop took place at 8/9 and was facilitated by Alexander Richter from the University of Zurich and Alexander Stocker from Virtual Vehicle. It was organized in three sessions:
Session 1 started with an introduction giving about 30 curious workshop-participants the opportunity to brainstorm one important aspect of Smart Factories, which was then documented on a flip-chart. In the ‘main event’ of session 1 four 20 minute presentations provided valuable insights into the Smart Factory projects AMBIWISE (from DE), ASSIST40 (from AT), and SO-PC-PRO (a FP7 Factory of the Future project) sharing many commonalities with FACTS4WORKERS and into a fascinating demonstrator of a ‘control station of the future’.
A System Architecture for Knowledge Exchange in the Industrial Domain (Fabian Quint, Jörn Kreutel, Frieder Loch, Magnus Volkmer, Peter Pollmanns)
Multimodale Interaktion in der Produktionsstätte der Zukunft (Hermann Fürntratt, Ferdinand Fuhrmann)
Mobiles Wissensmanagement in der Industrie 4.0 (Peter Brandl, Helmut Aschbacher, Sabine Hösch) ◾ Driven Improvement of Processes in Smart Factories (Udo Kannengiesser, Matthias Neubauer, Chiara Di Francescomarino, Mauro Dragoni, Chiara Ghidini, Richard Heininger)

Session 2 included eleven three minute talks on various topics relevant for Smart Factories, including useable assistance systems, PLM/PDM systems, knowledge sharing in Web 2.0 communities, secure and safe networks of smart machines, maintenance process documentation with smart glasses, OSLC and linked engineering data, competency management, federated recommender systems, interactive engineering labs, job-based usability testing and information integration. After these twelve initial talks, all participants had the opportunity to experience the presented research and conduct fruitful discussions in an open poster and demo area.
Gestaltung gebrauchstauglicher Assistenzsysteme für Industrie 4.0 (Michael Wächter, Angelika C. Bullinger)
Visual PLM - Integrating 3D data in PLM (Reiner Schlenker, Patrick Müller, Giacomo d’Antonio)
Zehn Jahre Wissensaustausch und Communities in References+ (Johannes Müller, Jaren Krchnavi, Christina Moser, Anita Weihermann-Kollar, Heiko Jahr, Nils Hennig, Morten Torchalla, Martin Amacher, Rubén André Lorenzo)
Sichere Vernetzung von Geräten in Smart Factories mit MQTT (Martin Maritsch, Christian Kittl, Thomas Ebner)
Using Smart Glasses to Document Maintenance Processes (Fabian Quint, Frieder Loch)
Smart Engineering for Smart Factories: How OSLC Could Enable Plug & Play Tool Integration (Christian Kaiser, Beate Herbst)
Kompetenzvernetzung für Wertschöpfungschampions (Steffen Kinkel, Ralph Lichtner, Brita Schemmann, Andreas P. Schmidt, Sebastian Behrendt, Michael Koch, Christine Kunzmann, Alexander Richter)
Unified Information Access for Knowledge Workers via a Federated Recommender System (Heimo Gursch, Hermann Ziak, Roman Kern)
Kollaborative Systemkonzipierung im interaktiven Entwicklungslabor (Roman Dumitrescu, Christian Tschirner, Alexander A. Albers, Lukas Bretz)
Job-Based Usability Testing to Enhance Tool-Prototyping (Stefan Rössler, Manfred Rosenberger, Markus Pirker, Daniela Gadanji, Andrea Denger, Alexander Stocker)
Informationsvernetzungstechnologien im Bereich Automotive Engineering (Michael Spitzer, Markus Zoier, Bernd Fachbach)

Session 3 was an interactive session which gave four groups of workshop participants the opportunity to actively work on four dedicated Smart Factory Challenges. These four challenges, (1) digital assistance systems, (2) motivation and incentive systems for content creation, (3) information integration across the product lifecycle, and (4) prototype evaluation through data analytics have been developed by clustering all Smart Factory aspects provided by the participants at the start of the first session.

The workshop has provided innumerable fruitful discussions and fully met the expectancy of both, the workshop providers, and the workshop organizers Alexander Stocker, Andrea Denger, Martin Wifling, Johannes Fritz, Christian Kaiser (all Virtual Vehicle), Christian Kittl (evolaris), and Alexander Richter (University of Zurich). It is therefore planned to continue this success and to submit another Smart Factory workshop proposal to the Mensch und Computer 2016, which will be held in Aachen.
1 note
·
View note
Link
Personalized Production: The Brilliant Factory Will Match the Right Parts With the Right Tools, says GE Manufacturing Maven Christine Furstoss
1 note
·
View note