#Variable Volume Pipette
Text
Customized Pipetting - Harnessing the Power of Variable Volume Micropipettes
In the realm of laboratory work, precision is paramount. Whether you're measuring out reagents for a delicate experiment or transferring samples for analysis, having the right tools can make all the difference. Micropipettes are essential instruments for precise liquid handling, and among them, variable volume micropipettes stand out for their versatility and adaptability. In this blog post, we'll explore how variable volume micropipettes empower researchers to customize their pipetting tasks, revolutionizing the way experiments are conducted in laboratories worldwide.

Understanding Micropipettes: Variable vs. Fixed Volume
Micropipettes are handheld devices used to accurately measure and transfer small volumes of liquid. While fixed volume micropipettes dispense a set volume of liquid with each use, variable volume micropipettes offer the flexibility to adjust the volume within a specified range. This adjustability allows researchers to customize their pipetting tasks according to the specific requirements of their experiments.
The Power of Variable Volume Micropipettes
Variable volume micropipettes offer several advantages over fixed volume micropipettes:
Versatility: Variable volume micropipettes can accommodate a wide range of volumes, allowing researchers to handle a variety of liquid samples with a single instrument.
Precision: The ability to adjust the volume ensures precise dispensing, minimizing errors and improving the reproducibility of experimental results.
Customization: Variable volume micropipettes empower researchers to tailor their pipetting tasks to meet the unique needs of their experiments, whether it's performing serial dilutions, setting up PCR reactions, or preparing samples for analysis.
Applications of Variable Volume Micropipettes
Variable volume micropipettes find applications across various laboratory disciplines, including molecular biology, biochemistry, microbiology, and more. They are used for tasks such as sample preparation, reagent dispensing, cell culture work, and enzyme assays, among others. Their versatility and precision make them indispensable tools for researchers working in diverse fields.
Choosing the Right Pipette for Your Lab
When selecting micropipettes for your lab, consider factors such as accuracy, precision, ergonomics, and ease of use. Variable volume micropipettes offer researchers the flexibility and control needed to customize their pipetting tasks, making them an essential addition to any laboratory.
Conclusion
Variable volume micropipettes represent a significant advancement in laboratory technology, allowing researchers to customize their pipetting tasks with precision and ease. By harnessing the power of variable volume micropipettes, researchers can tailor their experiments to meet specific requirements, leading to more accurate and reliable results. With customized pipetting, researchers can unlock new possibilities and push the boundaries of scientific discovery.
#variable volume micropipettes#fixed volume micropipettes#variable volume pipette#pipette lab equipment
0 notes
Text
Volume Range=2-20-mu-l; Increment=0-5-mu-l; Test Volume=20-mu-l-lt-hr-gt-10-mu-l-lt-hr-gt-2-mu-l; Accuracy error=0-90-lt-hr-gt-1-20-lt-hr-gt-3-00; Precision error=0-40-lt-hr-gt-1-00-lt-hr-gt-2-00; Shop online at Labtron.cc.

1 note
·
View note
Text
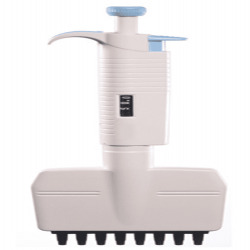
Variable Volume Multi Channel Fully Autoclavable Pipette
Variable Volume Multi-Channel Fully autoclavable pipettes Material: Polycarbonate Volume settings can be clearly read through the digital display Effortless pipetting accessibility with a rotatable dispensing head
#Pipette and Pipettors#Variable Volume Multi Channel Fully Autoclavable Pipette#Pipettes#Lab Pipettes
0 notes
Text
Liquid Handling Solutions for ELISA and Other Immunoassays
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) and other immunoassays are essential tools in laboratories for detecting and quantifying biological molecules such as proteins, antibodies, and hormones. These assays are widely used in diagnostics, research, and pharmaceutical industries due to their sensitivity and specificity. However, for these tests to deliver accurate and reproducible results, precise liquid handling is crucial.
In this blog, we’ll explore how liquid handling instruments play a key role in ELISA and other immunoassays, and what tools can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of these assays.
Understanding the Role of Liquid Handling in ELISA and Immunoassays
ELISA and immunoassays typically involve multiple steps, such as adding reagents, washing, and detecting signals from the sample. Each of these steps requires precise dispensing of liquids to ensure proper binding and reaction between molecules. Even small inconsistencies in pipetting can lead to errors in results, compromising the reliability of the data.
Here are some steps where precise liquid handling is vital:
Sample Dispensing: Accurate measurement of the sample to ensure consistent concentration across wells.
Reagent Addition: Reagents, such as antibodies or substrates, must be added uniformly for reproducibility.
Washing: Thorough washing of wells to remove unbound material and minimize background noise.
Substrate Addition: Ensuring equal amounts of substrate to each well for uniform colorimetric or fluorescent signals.
Liquid Handling Solutions for ELISA and Immunoassays
Let’s take a look at some advanced liquid handling solutions that help labs achieve high-quality ELISA and immunoassay results.
1. Micropipettes
Micropipettes are essential tools for handling small volumes of liquid in immunoassays. Both manual and automated micropipettes are widely used for dispensing reagents and samples in ELISA. Key factors when selecting micropipettes for immunoassays include accuracy, precision, and ergonomic design.
Microlit NERO Micropipettes: Known for its ergonomic design and superior accuracy, the NERO range includes both single-channel and multi-channel micropipettes. Multi-channel options are particularly useful in ELISA, allowing multiple wells to be filled simultaneously, speeding up the process and reducing variability.
2. Electronic Dispensers
Electronic dispensers simplify repetitive pipetting tasks and reduce the chances of human error. They are useful for adding reagents in fixed or variable volumes during different stages of ELISA and immunoassays.
Microlit E-BURETTE: This E-Burette is designed to dispense precise amounts of reagents effortlessly. It eliminates user fatigue and enhances consistency, which is critical when handling large numbers of samples in immunoassays.
3. Bottle Top Dispensers
For laboratories dealing with multiple reagents in large volumes, bottle top dispensers provide an efficient solution. These dispensers allow easy, accurate, and contamination-free transfer of reagents directly from the bottle.
Microlit BEATUS: A bottle top dispenser with excellent chemical compatibility and precision, BEATUS ensures that reagents are safely and accurately dispensed, reducing the risk of cross-contamination in ELISA and immunoassays.
4. Automated Liquid Handling Systems
Automation is transforming laboratories by increasing throughput and minimizing manual intervention. Automated liquid handling systems can perform complex pipetting tasks, including sample preparation, washing, and reagent addition, with precision and speed.
While high-throughput labs benefit greatly from automation, smaller labs can still achieve consistency by using electronic pipettes and semi-automated dispensers for immunoassays.
Best Practices for Liquid Handling in ELISA and Immunoassays
To make the most of liquid handling solutions and improve the accuracy of immunoassays, labs can follow these best practices:
Regular Calibration: Ensure that pipettes and dispensers are regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
Use Multi-Channel Pipettes: Multi-channel pipettes can significantly reduce variability between wells, particularly when adding samples or reagents in ELISA plates.
Minimize Air Bubbles: When aspirating and dispensing, be mindful of air bubbles as they can cause inconsistencies in volume and affect results.
Avoid Touching the Sidewalls: During pipetting, avoid touching the sides of wells as this can lead to inaccurate volumes and cross-contamination.
Conclusion
Liquid handling plays a fundamental role in ensuring the success of ELISA and other immunoassays. By using precise and reliable tools like micropipettes, electronic dispensers, and bottle top dispensers, labs can improve the accuracy and reproducibility of their assays.
Microlit’s range of liquid handling instruments is designed to meet the high demands of immunoassays, ensuring that labs can carry out their research and diagnostics with confidence. Whether you’re running routine tests or handling critical samples, investing in high-quality liquid handling solutions will enhance the reliability of your results and streamline your workflows.
#liquid handling instruments#pipetting#liquid handling solutions#E-Burette#bottle top dispensers#electronic pipettes
0 notes
Text
Variable Volume Pipette

Labnic Variable Volume Pipette, measuring 10 to 100 μL, ensures precise pipetting and withstands autoclaving at 121 °C. It features a digital display, finger support for comfort and meets ISO 8655 standards for reliable performance.
0 notes
Text
Micropipette Guide 2024: Types, Applications and More

Micropipettes or pipettes, are instruments used to measure liquid ranging between volumes of 1-10000 µl and transfer it from one sample container to another. This is a basic liquid-handling instrument for almost all scientific laboratories.
Types of Micropipettes
There is no 1 way to classify micropipettes. It can vary in a number of ways.
1. Number of Channels
Single Channel Micropipettes
A single-channel micropipette has only 1 channel to aspirate and dispense the liquid. It means you can handle only one sample at a time.
Multi-Channel Micropipettes
Multi-channel micropipettes can handle 8, 12 or 16 samples in one go. It can attach multiple tips at the same time and you can get the work done faster especially if working in high-throughput labs.
2. Volume Adjustment
Fixed Volume Micropipettes
Here the volume a pipette can aspirate and dispense remains the same and you don’t have the option to adjust or choose between a range. They offer consistent and accurate results for repetitive pipetting.

Variable Volume Micropipettes
Variable volume pipettes give you the flexibility to choose the volume you want to pipette (within the given range). You need to set the volume manually on the dial. High-performance pipettes also come with a volume lock feature for enhanced safety and reliability.

3. Operating Mechanism
Mechanical Pipettes
These are the standard pipettes widely used in all laboratories. Mechanical micropipettes operate on a piston-driven system, where users manually set the desired volume using a dial and apply thumb pressure on the plunger to aspirate and dispense liquids.

Electronic Micropipettes
Electronic micropipettes are more expensive than mechanical ones because they have digital controls, programmability and eliminates the element of human error to a certain extent. It has an electronic display and is ideal for high-throughput labs where reproducibility is paramount.
Components of Micropipette
Plunger
The plunger is one of the main components of the micropipette. Use your thumb to press down on the plunger to aspirate and dispense the liquid.
Then, with a firmer push, sometimes called the “blow-out stop,” it ensures a thorough expulsion of any remaining liquid, guaranteeing accurate measurements—a two-step process of liquid control.
Ergonomics are a key point here since lab professionals will be pipetting repeatedly for long hours. A low-force mechanism which does not require excessive plunge force, will minimize the RSI.
Volume Adjustment Dial
By twisting the volume adjustment dial, you dictate the micropipette’s plunger movement, determining your experiment’s liquid dosage. In micropipettes with adjustable volumes, this feature offers precise measurement control, no matter how small or large the quantity is.
Tip Ejector
Keep your hands and micropipette clean by disposing of used tips promptly. Utilize the convenient tip ejector button to effortlessly remove micropipette tips, ensuring a fuss-free and contamination-free experiment environment.
Tip Cone
The tip cone, also known as the shaft, is the crucial component of a micropipette where the disposable tip is inserted. Its primary function is to ensure a snug fit for the tip, ensuring precision in measurements and preventing air leakage. Its adaptable shape accommodates various sizes and styles of tips, allowing for versatile and secure usage without concerns of detachment or disruptions.
Calibration Screw
Inside the micropipette lies a crucial component, the calibration screw. This is what makes accuracy possible. Twisting this tiny screw adjusts the liquid output, fine-tuning the micropipette’s performance. Regular checks and tweaks, as advised by the manufacturer, ensure precision in your measurements, keeping everything flowing smoothly.
Applications of Micropipettes in Laboratory
Micropipettes are used to measure any small amount of liquid samples for testing and research. They are crucial in lab settings like molecular biology and diagnostics, precisely transferring tiny liquid volumes, facilitating diverse experiments. Mastery of their principles is key to effective scientific research and analysis.
Some common applications include:
1. Molecular Biology
2. Biochemistry
3. Cell Culture
4. Microbiology
5. Analytical Chemistry
6. Clinical Diagnostics
7. Pharmaceutical Research
How does a Micropipette work?
Micropipettes operate on the principle of air displacement. They consist of a plunger connected to an internal piston, which moves to two distinct positions:
Filling Position: When the plunger is depressed to the first stop, the internal piston displaces a volume of air equal to the desired volume shown on the volume indicator dial. This creates a vacuum, drawing the liquid into the tip.
Dispensing Position: The second stop on the plunger is used solely for dispensing the contents of the tip without drawing in additional air.
How to use a micropipette?
1. Start with choosing the right micropipette and micropipette tips
Select the one that is best for your application. While pipettes are similar in the way they function, what sets them apart is the accuracy and precision of the measurement, ergonomics and general durability of the instrument.
Set the volume based on your requirement and ensure the tips match the volume of the pipettes.
2. Attach the micropipette tip to the micropipette
Don’t use excessive force here because good quality pipettes will be quick and seamless to attach to the tips and should provide a leak-proof seal.Immerse the pipette in the liquid at 90 degrees
Be mindful of your posture and keep the position upright.
Aspirate and dispense 2-3 times before actually measuring the liquid
3. Forward or Reverse Pipetting
First let’s talk about forward pipetting:To aspirate the liquid in the tip, press the plunger to the first stop. Immerse the pipette tip vertically in the liquid.
Slowly release the plunger while the tip is immersed. The liquid will be aspirated into the pipette tip.
To dispense the liquid, place the tip on the inner wall of the receiving vessel at a steep angle
Slowly press the plunger to the first stop to dispense the liquid.
To empty the tip completely, press the plunger to the second stop.
Now for reverse pipetting
The reverse technique is suitable for dispensing reagents/solutions that have high viscosity or a tendency to foam easily. It is also recommended for dispensing very small volumes.To aspirate the liquid in the tip, press the plunger to the second stop and immerse the pipette tip vertically in the liquid.
Slowly release the plunger while the tip is immersed. The liquid will be aspirated into the pipette tip.
To dispense the liquid, place the tip on the inner wall of the tube at a steep angle.
Slowly press the plunger to the first stop.
Finally, eject the tip and dispose it off
Calibration of Micropipettes
Calibration is conducted through gravimetric testing, which involves weighing the amount of pure water delivered in a single operation of the pipette. The obtained mass is divided by the density of water to determine its volume. Variable volume pipettes should undergo testing at three or more points across their designated range, typically at maximum volume, 50% of maximum volume, and the lower limit of their range.
Here’s a general guide on how to calibrate a micropipette:
1. Gather MaterialsMicropipette(s) to be calibrated
Appropriate pipette tips
Distilled water or a calibration solution
Weighing balance with appropriate accuracy (usually in milligrams)
Gloves and lab coat for safety
2. Prepare the Micropipette
Ensure the micropipette is clean and free from any residue.
Attach a fresh and compatible pipette tip to the micropipette.
3. Pre-Wet the Pipette Tip (Optional)
For some micropipettes, pre-wetting the tip with the liquid being used can help ensure accuracy. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding pre-wetting.
4. Prepare the Calibration Solution
Use distilled water or a calibration solution recommended by the micropipette manufacturer.
Ensure the calibration solution is at room temperature to minimize density variations.
5. Set the Micropipette to the Desired Volume
Adjust the micropipette to the volume you want to calibrate (e.g., if calibrating a 10-100 μL micropipette, set it to 50 μL).
6. Dispense Liquid into a Weighing Boat or Container
Dispense the liquid from the micropipette into a weighing boat or a container placed on a weighing balance.
Note down the initial weight (W1) of the liquid dispensed.
7. Weigh the Dispensed Liquid
Carefully weigh the liquid dispensed using the weighing balance. Ensure the balance is calibrated and accurate.
Record the final weight (W2) of the liquid.
8. Calculate the Dispensed Volume
Subtract the initial weight (W1) from the final weight (W2) to determine the weight of the liquid dispensed (W).
Convert the weight of the liquid dispensed to volume using the density of the liquid or the known density of the calibration solution.
Calculate the actual volume dispensed using the formula:

9. Compare with Expected Volume
Compare the calculated volume dispensed with the expected volume (e.g., 50 μL for a 10-100 μL micropipette).
Calculate the percent error to assess the accuracy of the micropipette calibration:

10. Adjust if Necessary
If the percent error is within an acceptable range (typically ±2-5%), the micropipette is calibrated. Otherwise, adjustments may be needed.
Consult the micropipette’s user manual for instructions on how to adjust the volume settings. Adjust carefully and recheck the calibration until the desired accuracy is achieved.
11. Record Calibration Data
Keep a record of the calibration process, including the micropipette serial number, date of calibration, volume settings, calibration solution used, measured weights, calculated volumes, and any adjustments made.
12. Final Checks
After calibration, perform a final check to ensure the micropipette is dispensing accurately and consistently across the volume range.
When is micropipette calibration required?
Micropipette calibration is typically required in the following situations:
Initial Use
New micropipettes should be calibrated before their initial use to ensure accuracy and precision.
Scheduled Calibration
Regular calibration intervals are recommended to maintain the accuracy of micropipettes over time. The frequency of calibration depends on factors such as the frequency of use, the criticality of the measurements, and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
After Maintenance or Repair
Calibration should be performed after any maintenance or repair work on the micropipette to verify that it meets the required specifications.
Change in Operating Conditions
If there is a significant change in the operating conditions, such as temperature or altitude, recalibration may be necessary to account for these factors’ effects on the micropipette’s performance.
Compliance Requirements
Laboratories may have regulatory or quality assurance requirements that mandate regular calibration of micropipettes to ensure traceability and compliance with standards.
Where do we get the best micropipette for the lab?
When purchasing a micropipette for your lab, consider key factors such as accuracy, precision, ergonomics, and ease of maintenance. Research the brands and models, compare specifications, and read user reviews to make an informed decision. Evaluate additional features like adjustable volume settings and compatibility with automation systems. Set a budget and balance costs with desired features. Check warranty coverage and customer support options for added peace of mind.
Cleaning and Maintenance of Micropipettes
1. External CleaningRemove and Clean the Tip Ejector: Begin by detaching the tip ejector and giving it a thorough wipe-down.
Wipe Down All Exposed Surfaces: Take a lint-free cloth or tissue and carefully wipe all visible parts of the micropipette, including the body, buttons, operating rod, and tip holder. Be diligent in cleaning any scuffs, marks, or accumulated debris in hard-to-reach areas.
Use a Brush for Stubborn Debris: If there are persistent stains or dirt, consider using a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub the affected areas.
Reassemble and Allow to Dry: Once the exterior surfaces are clean, reattach the tip ejector and ensure it is securely in place. Leave the pipette to air dry completely before further use.
Final Wipe with Cleaning Solution: Finish the cleaning process by wiping down the outer surfaces once more with a cleaning solution to remove any remaining residue. Allow the alcohol to evaporate fully before returning the pipette to service.
2. Internal Cleaning
Cleaning the inside of a pipette should be handled by trained personnel to avoid incorrect reassembly, which can damage the micropipette and affect its performance, leading to decreased accuracy and potential leakage.Disassemble the Micropipette: Carefully take apart the pipette, placing the upper part in a clean, dry area.
Wipe with Alcohol-Coated Wipes: Use alcohol-coated wipes to thoroughly clean the entire interior, including the body, connecting nut, tip holder, O-ring, seal, and the stainless steel surface of the piston. Ensure the piston is completely dry to prevent corrosion.
Allow Alcohol to Evaporate: Let the alcohol evaporate fully from the interior of the pipette.
Check for Lubrication Needs: Refer to the instruction manual to determine if any parts, like the piston assembly and seals, require lubrication. Follow the manual’s guidance for reassembly, ensuring proper alignment and placement of components.
Maintaining Micropipettes
When the pipette is not in use it should be stored in an upright position. The pipette should be inspected prior to use each day for any dust or contamination on outside surfaces. Special attention should be given to the tip cone. No solvent other than isopropanol should be used to clean the pipette. If the pipette is used daily, an internal parts inspection should be performed every three months.
Choosing the right micropipette for your applicationEnsure that the micropipette can accommodate the desired range of liquid volumes for your pipetting needs.
Verify if the micropipette features a universal tip cone to accommodate various types of pipette tips.
Check if the micropipette is autoclavable at the necessary temperature to ensure proper sterilization.
Check if the micropipette is UV resistant so that they can be kept inside the hood even when the UV mode is on.
Assess the ergonomic design of the micropipette for smooth and comfortable handling during use.
Confirm if the micropipette is calibrated to guarantee precise dispensing of liquids.
Evaluate the accuracy and precision of the micropipette’s readings to ensure compliance with ISO standards.
Ergonomics is a key factor in choosing a pipette because repetitive strain injury is common amongst lab personnel who pipette regularly. Low-force tip ejection and minimal plunge force are crucial.
Accumax Lab Devices specializes in manufacturing high-precision liquid handling instruments for top-tier laboratories worldwide. With a focus on innovation, it offers an advanced range of micropipettes designed to enhance user experience within real-world laboratory settings. Especially our range of FAB and FAB LF pipettes, which are specially designed for accuracy and precision with excellent ergonomics to elevate your pipetting experience like never before.
Micropipette FAQs
1. Can I use any brand of pipette tips with my micropipette?
Whether you can use any brand of pipette tips with your micropipette depends on its tip cone design. If your micropipette has a universal tip cone, it means it’s compatible with a wide range of international pipette tip brands, as long as they’re suitable for your micropipette’s volume capacity.
2. What’s the best way to sterilize my pipette before use?
To clean your micropipette before using it, first, check if it can be sterilized using an autoclave. If it can, follow the instructions in the manual to know the right temperature and duration for sterilization. Make sure to consider the type of liquid you’ll be using it for.
3. Is there a simple way to check if my micropipette is calibrated correctly?
Set it to the usual volume, then dispense water five times. Weigh what you piped out on a scale. If it matches up nicely with the ISO standard, your micropipette is good to go. If not, it’s time for a recalibration.
4. How frequently should I recalibrate my micropipette?
For regular use, it’s good to check your micropipette’s calibration every 3 to 6 months. Following the ISO 8655 standard, it’s recommended to have it calibrated annually.
5. How to adjust the volume of a micropipette?
To adjust the volume on your micropipette, look for the display showing numbers indicating the volume range. If you have a fixed-volume micropipette, the range is predetermined. However, if you have a variable volume micropipette, you can adjust it within the given range by using the rotational dial located at the top of the micropipette plunger. Alternatively, you can consult the manual for specific instructions on changing the volume.
6. Why is it important to avoid touching the tips of the micropipette?
When you touch the tips of a micropipette, you risk transferring oils and other substances from your fingers onto them. This can interfere with the accuracy of volume measurements and potentially contaminate your samples. To maintain precision and avoid contamination, it’s best to handle the micropipette tips only with the instrument itself.
7. What happens if I release the plunger of the micropipette too quickly?
Releasing the micropipette plunger too quickly can lead to inadequate liquid draw up and dispensing, causing potential inaccuracies in your measurements.
8. What should I do if my micropipette isn’t working right?
If your micropipette isn’t working properly, it’s time for some troubleshooting. Start by double-checking if it’s properly calibrated and if the volume setting is correct. Ensure that the pipette tips are securely attached and not damaged. If the issue persists, you might need to clean or maintain the micropipette according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If all else fails, it might be time to consult with a colleague or contact technical support for further assistance.
9. Can my micropipette handle different types of liquids?
Your micropipette is designed to handle a variety of liquids, whether they’re watery solutions, viscous substances, or even oils. As long as you’re using the appropriate tip size and technique, your micropipette can smoothly pipette different types of liquids.
This blog originally posted here: Micropipette Guide 2024: Types, Applications and More
0 notes
Text
Adjustable Variable Pipette

The Adjustable Variable Pipette is a versatile and essential tool for precise liquid handling in laboratories. Designed for accuracy and ease of use, it allows for effortless volume adjustments to accommodate various experimental needs. The ergonomic design ensures comfort during prolonged use, while its durable construction guarantees long-lasting performance. Ideal for applications ranging from molecular biology to chemistry, this pipette enhances productivity and reliability, making it a must-have for any lab seeking precision and efficiency.
0 notes
Text
Ensuring Accuracy: Pipette Calibration, Burette Calibration, and Beaker Calibration in Dubai, UAE
Maintaining the integrity of your laboratory measurements is crucial for reliable research and quality control. This is where pipette calibration, burette calibration, and beaker calibration become essential practices. Dubai, UAE, boasts a range of calibration service providers to ensure your volumetric instruments meet the highest standards.
The Importance of Calibration
Volumetric instruments like pipettes, burettes, and beakers are the workhorses of many laboratories. Over time, due to wear and tear or even minor manufacturing inconsistencies, their accuracy can drift. Regular calibration helps identify and rectify these deviations, guaranteeing the validity of your measurements.
Pipette Calibration: Pipettes are used for transferring precise volumes of liquids. Inaccurate pipetting can significantly impact your results. Calibration ensures each pipette delivers the intended volume within acceptable tolerances.
Burette Calibration: Burettes are used for dispensing variable volumes of liquids during titrations. Precise burette calibration safeguards the accuracy of your titrations, leading to reliable data.
Beaker Calibration: While not as critical for some applications, calibrating beakers ensures they accurately reflect the volume they contain. This is particularly important for preparing precise solutions.
Benefits of Regular Calibration
Enhanced Data Integrity: Accurate measurements are the foundation of reliable research and quality control. Regular calibration minimizes errors and ensures data integrity.
Compliance with Regulations: Many industries have regulations mandating regular calibration of laboratory instruments. Calibration certificates serve as proof of compliance.
Cost Savings: Inaccurate measurements can lead to wasted materials, failed experiments, and even product recalls. Calibration helps prevent these costly issues.
Finding Calibration Services in Dubai, UAE
Several reputable laboratories in Dubai, UAE, offer pipette calibration, burette calibration, and beaker calibration services. When choosing a provider, consider factors like:
Accreditation: Look for laboratories accredited by a recognized body like ENAS (Emirates National Accreditation System).
Calibration Capabilities: Ensure the provider can calibrate your specific instruments and volume ranges.
Turnaround Time: Consider the time it takes for calibration and the return of your instruments.
Cost: Calibration costs can vary depending on the complexity of the instruments and the volume ranges involved.
By partnering with a reliable calibration service provider in Dubai, UAE, you can ensure your pipettes, burettes, and beakers deliver the precise measurements your research and quality control processes demand.
0 notes
Text
0 notes
Text
Lab Equipment
1. Beakers and Flasks: Foundations of Measurement
Beakers and flasks are iconic symbols of laboratory Equipment work, serving as vessels for holding, mixing, and measuring liquids. Beakers come in various sizes, typically marked with volume gradations for accurate measurement. They are versatile, allowing scientists to perform tasks such as stirring, heating, and pouring. Flasks, on the other hand, often have narrower necks and are used for more precise measurements and reactions where evaporation needs to be minimised. Together, these basic containers form the backbone of liquid handling in labs worldwide.
2. Microscopes: Unlocking the Microcosm
Microscopes are indispensable lab equipment tools for exploring the microscopic world. They enable scientists to magnify objects hundreds or even thousands of times, revealing details that are invisible to the naked eye. From examining cells and microorganisms to analyzing materials at the nanoscale, microscopes play a crucial role in fields such as biology, medicine, materials science, and beyond. With advancements like electron microscopy and confocal microscopy, researchers can delve even deeper into the intricacies of the microcosm.
3. Centrifuges: Separating Powerhouses
Centrifuges harness the principles of centrifugal force to separate substances based on their density. By spinning samples at high speeds, centrifuges cause heavier particles to settle at the bottom while lighter components rise to the top. This process is invaluable for tasks such as isolating DNA, purifying proteins, and separating blood components in medical diagnostics. Modern centrifuges offer a range of capabilities, including variable speed settings, temperature control, and specialized rotors for specific applications.
4. Spectrophotometers: Shedding Light on Chemical Analysis
lab equipment Spectrophotometers are instrumental in quantifying the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a substance across different wavelengths. This information is used to determine the concentration of analytes in solutions, making spectrophotometry a cornerstone technique in fields like biochemistry, environmental science, and pharmaceuticals. UV-visible spectrophotometers are commonly used for measuring organic compounds, while infrared and atomic absorption spectrophotometers cater to different analytical needs.
5. Incubators and Ovens: Cultivating Conditions
lab equipment and ovens provide controlled environments for cultivating cells, growing cultures, and conducting experiments that require specific temperature and humidity conditions. Incubators are crucial for cell culture work, microbiology research, and molecular biology techniques like PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Ovens, on the other hand, are used for sterilization, drying, and heat treatments in applications ranging from sample preparation to materials testing.
6. Pipettes and Dispensers: Precise Liquid Handling
Pipettes and dispensers are precision instruments used for transferring precise volumes of liquids. Manual pipettes are operated by hand and are available in various formats, including micropipettes for small volumes and multichannel pipettes for high-throughput applications. Automated pipetting systems offer increased efficiency and reproducibility, making them ideal for tasks like serial dilutions, liquid handling in high-throughput screening, and molecular biology workflows.
7. Analytical Balances: Weighing with Precision
Analytical balances provide accurate measurements of mass, essential for tasks like preparing solutions, dosing reagents, and determining the purity of substances. These balances offer high precision, often capable of measuring weights down to the microgram or even nanogram level. They are equipped with features such as draft shields to minimize environmental interference and calibration routines to ensure accuracy.
lab equipment, the workhorses of any laboratory. Beakers, test tubes, and flasks, made from durable glass, are used for mixing, storing, and heating various substances. Pipettes, with their precise markings, ensure accurate measurements of even the smallest volumes. And who can forget the ubiquitous Bunsen burner, providing heat for countless experiments?
Delving deeper:
As we move beyond the basics, we encounter a world of specialized equipment. Microscopes, with their powerful lenses, unveil the unseen world of cells and microorganisms. Centrifuges separate mixtures based on density, while spectrometers analyze the composition of materials. Each piece of equipment is designed for a specific purpose, contributing to the scientific process in its own unique way.
The cutting edge:
Modern science is constantly evolving, and so is the equipment that supports it. Advanced tools like 3D printers and gene sequencers are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. These sophisticated instruments allow scientists to create complex structures, analyze DNA, and unlock the secrets of life itself.
Beyond the tools:
But lab equipment is more than just tools. They are partners in discovery, silent witnesses to countless experiments and breakthroughs. They represent the dedication and ingenuity of scientists, engineers, and technicians who design, build, and use these instruments to push the frontiers of knowledge.
0 notes
Text
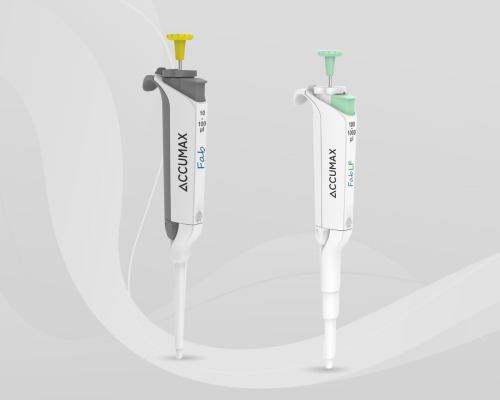
Microlit Ergonomic Pipettes - Precision Lab Equipment
Explore Microlit's comprehensive selection of ergonomic pipettes, including single-channel and variable fixed-volume micropipettes. Our state-of-the-art technology ensures unparalleled precision and convenience for liquid handling in laboratory settings. Order your ergonomic pipettes for precise lab work today!
#ergonomic pipettes#variable volume micropipettes#microlit micropipette#fixed volume micropipettes#micropipette holder
0 notes
Text
No. of Channels: 8; Volume Range: 50-300 mu-l; Increment: 5 mu/l; Test Volume: 300 mu/l-lt-hr-gt-150-mu-l-lt-hr-gt-50-mu-l; Accuracy error: 0-70 lt-hr-gt-1-00-lt-hr-gt-1-50; Shop online at Labtron.cc.

1 note
·
View note
Text

Variable Volume Multi Channel Pipette
Variable Volume Multi-Channel Pipette Autoclavable at 121 °C Material: Polycarbonate Volume settings can be clearly read through the digital display. For more visit www.labmate.com.
0 notes
Text
What type of electronic pipette do you recommend?
Electronic pipettes, also known as motorized pipettes, have become indispensable tools in laboratories worldwide due to their precision, accuracy, and ease of use. They are particularly beneficial for tasks that require repetitive pipetting, such as serial dilutions, sample preparation, and ELISA assays. When selecting an electronic pipette, several factors must be considered to ensure it meets your specific laboratory needs.
Types of Electronic Pipettes
There are three primary types of electronic pipettes:
Single-channel pipettes: These are suitable for pipetting a single volume at a time. They are ideal for general laboratory tasks as liquid handling instruments and are available in a wide range of volume capacities.
Multi-channel pipettes: These pipettes allow you to pipette multiple samples simultaneously, significantly improving efficiency and reducing the risk of errors. Multi-channel pipettes are commonly used for tasks such as PCR, cell culture, and protein assays.
Variable volume pipettes: These pipettes allow you to adjust the volume being pipetted within a specific range. They are versatile and can be used for various applications.
Key Factors to Consider
When choosing an electronic pipette, consider the following factors:
Volume range: Determine the specific volume range you need for your applications. Ensure the pipette's volume range covers your requirements.
Accuracy and precision: Electronic pipettes are known for their accuracy and precision. However, it's essential to check the pipette's specifications to ensure it meets your laboratory automation standards.
Ergonomics: A comfortable and ergonomic pipette design can help prevent repetitive strain injuries and improve overall user experience. Look for pipettes with features like adjustable finger rests and lightweight construction.
Ease of use: Electronic pipettes are generally user-friendly, but some models may have more advanced features or require additional training. Consider your laboratory's experience level and choose a pipette that is easy to operate.
Battery life: If you plan to use the pipette in the field or in areas without easy access to power outlets, battery life is a crucial factor. Look for pipettes with long-lasting batteries or rechargeable options.
Calibration: Regular calibration is essential to ensure the accuracy of your pipettes. Some electronic pipettes have built-in calibration features or can be easily calibrated using external devices.
Brand reputation: Choose a reputable brand that is known for producing high-quality electronic pipettes. Look for brands with a track record of reliability and customer satisfaction.
Recommendations
While the best electronic pipette for your laboratory depends on your specific needs, here are some popular and reputable brands to consider:
Gilson: Gilson is a well-known manufacturer of pipettes, offering a wide range of single-channel, multi-channel, and variable volume models.
Eppendorf: Eppendorf is another leading brand in the pipette industry, known for its precision and reliability.
Rainin: Rainin offers a variety of electronic pipettes with innovative features and ergonomic designs.
Thermo Fisher Scientific: Thermo Fisher Scientific is a large scientific equipment company that also manufactures high-quality electronic pipettes.
BioRad: BioRad offers a range of electronic pipettes suitable for various laboratory applications.
By carefully considering these factors and evaluating the available options, you can select the electronic pipette that best suits your laboratory's needs and ensures accurate and efficient pipetting.
#electronic pipette#electronic pipettes#liquid handling instruments#best electronic pipette#pipettes#pipetting
0 notes