#Warehousing The Cloud Computing Data
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

Data Warehouse Services in Basking Ridge NJ
#quellsoft#Data Warehouse Services in Basking Ridge NJ#Data Warehouse Services#Cloud Applications in Basking Ridge NJ#Data Integration in Basking Ridge NJ#Cloud Computing in Basking Ridge NJ#Cloud Data Warehousing in Basking Ridge NJ
0 notes
Text
Google Cloud’s BigQuery Autonomous Data To AI Platform

BigQuery automates data analysis, transformation, and insight generation using AI. AI and natural language interaction simplify difficult operations.
The fast-paced world needs data access and a real-time data activation flywheel. Artificial intelligence that integrates directly into the data environment and works with intelligent agents is emerging. These catalysts open doors and enable self-directed, rapid action, which is vital for success. This flywheel uses Google's Data & AI Cloud to activate data in real time. BigQuery has five times more organisations than the two leading cloud providers that just offer data science and data warehousing solutions due to this emphasis.
Examples of top companies:
With BigQuery, Radisson Hotel Group enhanced campaign productivity by 50% and revenue by over 20% by fine-tuning the Gemini model.
By connecting over 170 data sources with BigQuery, Gordon Food Service established a scalable, modern, AI-ready data architecture. This improved real-time response to critical business demands, enabled complete analytics, boosted client usage of their ordering systems, and offered staff rapid insights while cutting costs and boosting market share.
J.B. Hunt is revolutionising logistics for shippers and carriers by integrating Databricks into BigQuery.
General Mills saves over $100 million using BigQuery and Vertex AI to give workers secure access to LLMs for structured and unstructured data searches.
Google Cloud is unveiling many new features with its autonomous data to AI platform powered by BigQuery and Looker, a unified, trustworthy, and conversational BI platform:
New assistive and agentic experiences based on your trusted data and available through BigQuery and Looker will make data scientists, data engineers, analysts, and business users' jobs simpler and faster.
Advanced analytics and data science acceleration: Along with seamless integration with real-time and open-source technologies, BigQuery AI-assisted notebooks improve data science workflows and BigQuery AI Query Engine provides fresh insights.
Autonomous data foundation: BigQuery can collect, manage, and orchestrate any data with its new autonomous features, which include native support for unstructured data processing and open data formats like Iceberg.
Look at each change in detail.
User-specific agents
It believes everyone should have AI. BigQuery and Looker made AI-powered helpful experiences generally available, but Google Cloud now offers specialised agents for all data chores, such as:
Data engineering agents integrated with BigQuery pipelines help create data pipelines, convert and enhance data, discover anomalies, and automate metadata development. These agents provide trustworthy data and replace time-consuming and repetitive tasks, enhancing data team productivity. Data engineers traditionally spend hours cleaning, processing, and confirming data.
The data science agent in Google's Colab notebook enables model development at every step. Scalable training, intelligent model selection, automated feature engineering, and faster iteration are possible. This agent lets data science teams focus on complex methods rather than data and infrastructure.
Looker conversational analytics lets everyone utilise natural language with data. Expanded capabilities provided with DeepMind let all users understand the agent's actions and easily resolve misconceptions by undertaking advanced analysis and explaining its logic. Looker's semantic layer boosts accuracy by two-thirds. The agent understands business language like “revenue” and “segments” and can compute metrics in real time, ensuring trustworthy, accurate, and relevant results. An API for conversational analytics is also being introduced to help developers integrate it into processes and apps.
In the BigQuery autonomous data to AI platform, Google Cloud introduced the BigQuery knowledge engine to power assistive and agentic experiences. It models data associations, suggests business vocabulary words, and creates metadata instantaneously using Gemini's table descriptions, query histories, and schema connections. This knowledge engine grounds AI and agents in business context, enabling semantic search across BigQuery and AI-powered data insights.
All customers may access Gemini-powered agentic and assistive experiences in BigQuery and Looker without add-ons in the existing price model tiers!
Accelerating data science and advanced analytics
BigQuery autonomous data to AI platform is revolutionising data science and analytics by enabling new AI-driven data science experiences and engines to manage complex data and provide real-time analytics.
First, AI improves BigQuery notebooks. It adds intelligent SQL cells to your notebook that can merge data sources, comprehend data context, and make code-writing suggestions. It also uses native exploratory analysis and visualisation capabilities for data exploration and peer collaboration. Data scientists can also schedule analyses and update insights. Google Cloud also lets you construct laptop-driven, dynamic, user-friendly, interactive data apps to share insights across the organisation.
This enhanced notebook experience is complemented by the BigQuery AI query engine for AI-driven analytics. This engine lets data scientists easily manage organised and unstructured data and add real-world context—not simply retrieve it. BigQuery AI co-processes SQL and Gemini, adding runtime verbal comprehension, reasoning skills, and real-world knowledge. Their new engine processes unstructured photographs and matches them to your product catalogue. This engine supports several use cases, including model enhancement, sophisticated segmentation, and new insights.
Additionally, it provides users with the most cloud-optimized open-source environment. Google Cloud for Apache Kafka enables real-time data pipelines for event sourcing, model scoring, communications, and analytics in BigQuery for serverless Apache Spark execution. Customers have almost doubled their serverless Spark use in the last year, and Google Cloud has upgraded this engine to handle data 2.7 times faster.
BigQuery lets data scientists utilise SQL, Spark, or foundation models on Google's serverless and scalable architecture to innovate faster without the challenges of traditional infrastructure.
An independent data foundation throughout data lifetime
An independent data foundation created for modern data complexity supports its advanced analytics engines and specialised agents. BigQuery is transforming the environment by making unstructured data first-class citizens. New platform features, such as orchestration for a variety of data workloads, autonomous and invisible governance, and open formats for flexibility, ensure that your data is always ready for data science or artificial intelligence issues. It does this while giving the best cost and decreasing operational overhead.
For many companies, unstructured data is their biggest untapped potential. Even while structured data provides analytical avenues, unique ideas in text, audio, video, and photographs are often underutilised and discovered in siloed systems. BigQuery instantly tackles this issue by making unstructured data a first-class citizen using multimodal tables (preview), which integrate structured data with rich, complex data types for unified querying and storage.
Google Cloud's expanded BigQuery governance enables data stewards and professionals a single perspective to manage discovery, classification, curation, quality, usage, and sharing, including automatic cataloguing and metadata production, to efficiently manage this large data estate. BigQuery continuous queries use SQL to analyse and act on streaming data regardless of format, ensuring timely insights from all your data streams.
Customers utilise Google's AI models in BigQuery for multimodal analysis 16 times more than last year, driven by advanced support for structured and unstructured multimodal data. BigQuery with Vertex AI are 8–16 times cheaper than independent data warehouse and AI solutions.
Google Cloud maintains open ecology. BigQuery tables for Apache Iceberg combine BigQuery's performance and integrated capabilities with the flexibility of an open data lakehouse to link Iceberg data to SQL, Spark, AI, and third-party engines in an open and interoperable fashion. This service provides adaptive and autonomous table management, high-performance streaming, auto-AI-generated insights, practically infinite serverless scalability, and improved governance. Cloud storage enables fail-safe features and centralised fine-grained access control management in their managed solution.
Finaly, AI platform autonomous data optimises. Scaling resources, managing workloads, and ensuring cost-effectiveness are its competencies. The new BigQuery spend commit unifies spending throughout BigQuery platform and allows flexibility in shifting spend across streaming, governance, data processing engines, and more, making purchase easier.
Start your data and AI adventure with BigQuery data migration. Google Cloud wants to know how you innovate with data.
#technology#technews#govindhtech#news#technologynews#BigQuery autonomous data to AI platform#BigQuery#autonomous data to AI platform#BigQuery platform#autonomous data#BigQuery AI Query Engine
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How-To IT
Topic: Core areas of IT
1. Hardware
• Computers (Desktops, Laptops, Workstations)
• Servers and Data Centers
• Networking Devices (Routers, Switches, Modems)
• Storage Devices (HDDs, SSDs, NAS)
• Peripheral Devices (Printers, Scanners, Monitors)
2. Software
• Operating Systems (Windows, Linux, macOS)
• Application Software (Office Suites, ERP, CRM)
• Development Software (IDEs, Code Libraries, APIs)
• Middleware (Integration Tools)
• Security Software (Antivirus, Firewalls, SIEM)
3. Networking and Telecommunications
• LAN/WAN Infrastructure
• Wireless Networking (Wi-Fi, 5G)
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
• Communication Systems (VoIP, Email Servers)
• Internet Services
4. Data Management
• Databases (SQL, NoSQL)
• Data Warehousing
• Big Data Technologies (Hadoop, Spark)
• Backup and Recovery Systems
• Data Integration Tools
5. Cybersecurity
• Network Security
• Endpoint Protection
• Identity and Access Management (IAM)
• Threat Detection and Incident Response
• Encryption and Data Privacy
6. Software Development
• Front-End Development (UI/UX Design)
• Back-End Development
• DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
• Mobile App Development
• Cloud-Native Development
7. Cloud Computing
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
• Serverless Computing
• Cloud Storage and Management
8. IT Support and Services
• Help Desk Support
• IT Service Management (ITSM)
• System Administration
• Hardware and Software Troubleshooting
• End-User Training
9. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
• AI Algorithms and Frameworks
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
• Computer Vision
• Robotics
• Predictive Analytics
10. Business Intelligence and Analytics
• Reporting Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
• Data Visualization
• Business Analytics Platforms
• Predictive Modeling
11. Internet of Things (IoT)
• IoT Devices and Sensors
• IoT Platforms
• Edge Computing
• Smart Systems (Homes, Cities, Vehicles)
12. Enterprise Systems
• Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
• Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS)
• Supply Chain Management Systems
13. IT Governance and Compliance
• ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library)
• COBIT (Control Objectives for Information Technologies)
• ISO/IEC Standards
• Regulatory Compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX)
14. Emerging Technologies
• Blockchain
• Quantum Computing
• Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
• 3D Printing
• Digital Twins
15. IT Project Management
• Agile, Scrum, and Kanban
• Waterfall Methodology
• Resource Allocation
• Risk Management
16. IT Infrastructure
• Data Centers
• Virtualization (VMware, Hyper-V)
• Disaster Recovery Planning
• Load Balancing
17. IT Education and Certifications
• Vendor Certifications (Microsoft, Cisco, AWS)
• Training and Development Programs
• Online Learning Platforms
18. IT Operations and Monitoring
• Performance Monitoring (APM, Network Monitoring)
• IT Asset Management
• Event and Incident Management
19. Software Testing
• Manual Testing: Human testers evaluate software by executing test cases without using automation tools.
• Automated Testing: Use of testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) to run automated scripts and check software behavior.
• Functional Testing: Validating that the software performs its intended functions.
• Non-Functional Testing: Assessing non-functional aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
• Unit Testing: Testing individual components or units of code for correctness.
• Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules or systems work together as expected.
• System Testing: Verifying the complete software system’s behavior against requirements.
• Acceptance Testing: Conducting tests to confirm that the software meets business requirements (including UAT - User Acceptance Testing).
• Regression Testing: Ensuring that new changes or features do not negatively affect existing functionalities.
• Performance Testing: Testing software performance under various conditions (load, stress, scalability).
• Security Testing: Identifying vulnerabilities and assessing the software’s ability to protect data.
• Compatibility Testing: Ensuring the software works on different operating systems, browsers, or devices.
• Continuous Testing: Integrating testing into the development lifecycle to provide quick feedback and minimize bugs.
• Test Automation Frameworks: Tools and structures used to automate testing processes (e.g., TestNG, Appium).
19. VoIP (Voice over IP)
VoIP Protocols & Standards
• SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
• H.323
• RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol)
• MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
VoIP Hardware
• IP Phones (Desk Phones, Mobile Clients)
• VoIP Gateways
• Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs)
• VoIP Servers
• Network Switches/ Routers for VoIP
VoIP Software
• Softphones (e.g., Zoiper, X-Lite)
• PBX (Private Branch Exchange) Systems
• VoIP Management Software
• Call Center Solutions (e.g., Asterisk, 3CX)
VoIP Network Infrastructure
• Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
• VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for VoIP
• VoIP Traffic Shaping & Bandwidth Management
• Firewall and Security Configurations for VoIP
• Network Monitoring & Optimization Tools
VoIP Security
• Encryption (SRTP, TLS)
• Authentication and Authorization
• Firewall & Intrusion Detection Systems
• VoIP Fraud DetectionVoIP Providers
• Hosted VoIP Services (e.g., RingCentral, Vonage)
• SIP Trunking Providers
• PBX Hosting & Managed Services
VoIP Quality and Testing
• Call Quality Monitoring
• Latency, Jitter, and Packet Loss Testing
• VoIP Performance Metrics and Reporting Tools
• User Acceptance Testing (UAT) for VoIP Systems
Integration with Other Systems
• CRM Integration (e.g., Salesforce with VoIP)
• Unified Communications (UC) Solutions
• Contact Center Integration
• Email, Chat, and Video Communication Integration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
AWS Security 101: Protecting Your Cloud Investments
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, few names resonate as strongly as Amazon.com. This global giant, known for its e-commerce prowess, has a lesser-known but equally influential arm: Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS is a powerhouse in the world of cloud computing, offering a vast and sophisticated array of services and products. In this comprehensive guide, we'll embark on a journey to explore the facets and features of AWS that make it a driving force for individuals, companies, and organizations seeking to utilise cloud computing to its fullest capacity.

Amazon Web Services (AWS): A Technological Titan
At its core, AWS is a cloud computing platform that empowers users to create, deploy, and manage applications and infrastructure with unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It's not just a platform; it's a digital transformation enabler. Let's dive deeper into some of the key components and features that define AWS:
1. Compute Services: The Heart of Scalability
AWS boasts services like Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), a scalable virtual server solution, and AWS Lambda for serverless computing. These services provide users with the capability to efficiently run applications and workloads with precision and ease. Whether you need to host a simple website or power a complex data-processing application, AWS's compute services have you covered.
2. Storage Services: Your Data's Secure Haven
In the age of data, storage is paramount. AWS offers a diverse set of storage options. Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) caters to scalable object storage needs, while Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) is ideal for block storage requirements. For archival purposes, Amazon Glacier is the go-to solution. This comprehensive array of storage choices ensures that diverse storage needs are met, and your data is stored securely.
3. Database Services: Managing Complexity with Ease
AWS provides managed database services that simplify the complexity of database management. Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is perfect for relational databases, while Amazon DynamoDB offers a seamless solution for NoSQL databases. Amazon Redshift, on the other hand, caters to data warehousing needs. These services take the headache out of database administration, allowing you to focus on innovation.
4. Networking Services: Building Strong Connections
Network isolation and robust networking capabilities are made easy with Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud). AWS Direct Connect facilitates dedicated network connections, and Amazon Route 53 takes care of DNS services, ensuring that your network needs are comprehensively addressed. In an era where connectivity is king, AWS's networking services rule the realm.
5. Security and Identity: Fortifying the Digital Fortress
In a world where data security is non-negotiable, AWS prioritizes security with services like AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) for access control and AWS KMS (Key Management Service) for encryption key management. Your data remains fortified, and access is strictly controlled, giving you peace of mind in the digital age.
6. Analytics and Machine Learning: Unleashing the Power of Data
In the era of big data and machine learning, AWS is at the forefront. Services like Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) handle big data processing, while Amazon SageMaker provides the tools for developing and training machine learning models. Your data becomes a strategic asset, and innovation knows no bounds.
7. Application Integration: Seamlessness in Action
AWS fosters seamless application integration with services like Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) for message queuing and Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) for event-driven communication. Your applications work together harmoniously, creating a cohesive digital ecosystem.
8. Developer Tools: Powering Innovation
AWS equips developers with a suite of powerful tools, including AWS CodeDeploy, AWS CodeCommit, and AWS CodeBuild. These tools simplify software development and deployment processes, allowing your teams to focus on innovation and productivity.
9. Management and Monitoring: Streamlined Resource Control
Effective resource management and monitoring are facilitated by AWS CloudWatch for monitoring and AWS CloudFormation for infrastructure as code (IaC) management. Managing your cloud resources becomes a streamlined and efficient process, reducing operational overhead.
10. Global Reach: Empowering Global Presence
With data centers, known as Availability Zones, scattered across multiple regions worldwide, AWS enables users to deploy applications close to end-users. This results in optimal performance and latency, crucial for global digital operations.

In conclusion, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is not just a cloud computing platform; it's a technological titan that empowers organizations and individuals to harness the full potential of cloud computing. Whether you're an aspiring IT professional looking to build a career in the cloud or a seasoned expert seeking to sharpen your skills, understanding AWS is paramount.
In today's technology-driven landscape, AWS expertise opens doors to endless opportunities. At ACTE Institute, we recognize the transformative power of AWS, and we offer comprehensive training programs to help individuals and organizations master the AWS platform. We are your trusted partner on the journey of continuous learning and professional growth. Embrace AWS, embark on a path of limitless possibilities in the world of technology, and let ACTE Institute be your guiding light. Your potential awaits, and together, we can reach new heights in the ever-evolving world of cloud computing. Welcome to the AWS Advantage, and let's explore the boundless horizons of technology together!
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Azure Data Engineering Tools For Data Engineers
Azure is a cloud computing platform provided by Microsoft, which presents an extensive array of data engineering tools. These tools serve to assist data engineers in constructing and upholding data systems that possess the qualities of scalability, reliability, and security. Moreover, Azure data engineering tools facilitate the creation and management of data systems that cater to the unique requirements of an organization.
In this article, we will explore nine key Azure data engineering tools that should be in every data engineer’s toolkit. Whether you’re a beginner in data engineering or aiming to enhance your skills, these Azure tools are crucial for your career development.
Microsoft Azure Databricks
Azure Databricks is a managed version of Databricks, a popular data analytics and machine learning platform. It offers one-click installation, faster workflows, and collaborative workspaces for data scientists and engineers. Azure Databricks seamlessly integrates with Azure’s computation and storage resources, making it an excellent choice for collaborative data projects.
Microsoft Azure Data Factory
Microsoft Azure Data Factory (ADF) is a fully-managed, serverless data integration tool designed to handle data at scale. It enables data engineers to acquire, analyze, and process large volumes of data efficiently. ADF supports various use cases, including data engineering, operational data integration, analytics, and data warehousing.
Microsoft Azure Stream Analytics
Azure Stream Analytics is a real-time, complex event-processing engine designed to analyze and process large volumes of fast-streaming data from various sources. It is a critical tool for data engineers dealing with real-time data analysis and processing.
Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage
Azure Data Lake Storage provides a scalable and secure data lake solution for data scientists, developers, and analysts. It allows organizations to store data of any type and size while supporting low-latency workloads. Data engineers can take advantage of this infrastructure to build and maintain data pipelines. Azure Data Lake Storage also offers enterprise-grade security features for data collaboration.
Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics is an integrated platform solution that combines data warehousing, data connectors, ETL pipelines, analytics tools, big data scalability, and visualization capabilities. Data engineers can efficiently process data for warehousing and analytics using Synapse Pipelines’ ETL and data integration capabilities.
Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed and server-less distributed database service that supports multiple data models, including PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Apache Cassandra. It offers automatic and immediate scalability, single-digit millisecond reads and writes, and high availability for NoSQL data. Azure Cosmos DB is a versatile tool for data engineers looking to develop high-performance applications.
Microsoft Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed and continually updated relational database service in the cloud. It offers native support for services like Azure Functions and Azure App Service, simplifying application development. Data engineers can use Azure SQL Database to handle real-time data ingestion tasks efficiently.
Microsoft Azure MariaDB
Azure Database for MariaDB provides seamless integration with Azure Web Apps and supports popular open-source frameworks and languages like WordPress and Drupal. It offers built-in monitoring, security, automatic backups, and patching at no additional cost.
Microsoft Azure PostgreSQL Database
Azure PostgreSQL Database is a fully managed open-source database service designed to emphasize application innovation rather than database management. It supports various open-source frameworks and languages and offers superior security, performance optimization through AI, and high uptime guarantees.
Whether you’re a novice data engineer or an experienced professional, mastering these Azure data engineering tools is essential for advancing your career in the data-driven world. As technology evolves and data continues to grow, data engineers with expertise in Azure tools are in high demand. Start your journey to becoming a proficient data engineer with these powerful Azure tools and resources.
Unlock the full potential of your data engineering career with Datavalley. As you start your journey to becoming a skilled data engineer, it’s essential to equip yourself with the right tools and knowledge. The Azure data engineering tools we’ve explored in this article are your gateway to effectively managing and using data for impactful insights and decision-making.
To take your data engineering skills to the next level and gain practical, hands-on experience with these tools, we invite you to join the courses at Datavalley. Our comprehensive data engineering courses are designed to provide you with the expertise you need to excel in the dynamic field of data engineering. Whether you’re just starting or looking to advance your career, Datavalley’s courses offer a structured learning path and real-world projects that will set you on the path to success.
Course format:
Subject: Data Engineering Classes: 200 hours of live classes Lectures: 199 lectures Projects: Collaborative projects and mini projects for each module Level: All levels Scholarship: Up to 70% scholarship on this course Interactive activities: labs, quizzes, scenario walk-throughs Placement Assistance: Resume preparation, soft skills training, interview preparation
Subject: DevOps Classes: 180+ hours of live classes Lectures: 300 lectures Projects: Collaborative projects and mini projects for each module Level: All levels Scholarship: Up to 67% scholarship on this course Interactive activities: labs, quizzes, scenario walk-throughs Placement Assistance: Resume preparation, soft skills training, interview preparation
For more details on the Data Engineering courses, visit Datavalley’s official website.
#datavalley#dataexperts#data engineering#data analytics#dataexcellence#data science#power bi#business intelligence#data analytics course#data science course#data engineering course#data engineering training
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Data Engineering Concepts, Tools, and Projects
All the associations in the world have large amounts of data. If not worked upon and anatomized, this data does not amount to anything. Data masterminds are the ones. who make this data pure for consideration. Data Engineering can nominate the process of developing, operating, and maintaining software systems that collect, dissect, and store the association’s data. In modern data analytics, data masterminds produce data channels, which are the structure armature.
How to become a data engineer:
While there is no specific degree requirement for data engineering, a bachelor's or master's degree in computer science, software engineering, information systems, or a related field can provide a solid foundation. Courses in databases, programming, data structures, algorithms, and statistics are particularly beneficial. Data engineers should have strong programming skills. Focus on languages commonly used in data engineering, such as Python, SQL, and Scala. Learn the basics of data manipulation, scripting, and querying databases.
Familiarize yourself with various database systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and NoSQL databases such as MongoDB or Apache Cassandra.Knowledge of data warehousing concepts, including schema design, indexing, and optimization techniques.
Data engineering tools recommendations:
Data Engineering makes sure to use a variety of languages and tools to negotiate its objects. These tools allow data masterminds to apply tasks like creating channels and algorithms in a much easier as well as effective manner.
1. Amazon Redshift: A widely used cloud data warehouse built by Amazon, Redshift is the go-to choice for many teams and businesses. It is a comprehensive tool that enables the setup and scaling of data warehouses, making it incredibly easy to use.
One of the most popular tools used for businesses purpose is Amazon Redshift, which provides a powerful platform for managing large amounts of data. It allows users to quickly analyze complex datasets, build models that can be used for predictive analytics, and create visualizations that make it easier to interpret results. With its scalability and flexibility, Amazon Redshift has become one of the go-to solutions when it comes to data engineering tasks.
2. Big Query: Just like Redshift, Big Query is a cloud data warehouse fully managed by Google. It's especially favored by companies that have experience with the Google Cloud Platform. BigQuery not only can scale but also has robust machine learning features that make data analysis much easier. 3. Tableau: A powerful BI tool, Tableau is the second most popular one from our survey. It helps extract and gather data stored in multiple locations and comes with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface. Tableau makes data across departments readily available for data engineers and managers to create useful dashboards. 4. Looker: An essential BI software, Looker helps visualize data more effectively. Unlike traditional BI tools, Looker has developed a LookML layer, which is a language for explaining data, aggregates, calculations, and relationships in a SQL database. A spectacle is a newly-released tool that assists in deploying the LookML layer, ensuring non-technical personnel have a much simpler time when utilizing company data.
5. Apache Spark: An open-source unified analytics engine, Apache Spark is excellent for processing large data sets. It also offers great distribution and runs easily alongside other distributed computing programs, making it essential for data mining and machine learning. 6. Airflow: With Airflow, programming, and scheduling can be done quickly and accurately, and users can keep an eye on it through the built-in UI. It is the most used workflow solution, as 25% of data teams reported using it. 7. Apache Hive: Another data warehouse project on Apache Hadoop, Hive simplifies data queries and analysis with its SQL-like interface. This language enables MapReduce tasks to be executed on Hadoop and is mainly used for data summarization, analysis, and query. 8. Segment: An efficient and comprehensive tool, Segment assists in collecting and using data from digital properties. It transforms, sends, and archives customer data, and also makes the entire process much more manageable. 9. Snowflake: This cloud data warehouse has become very popular lately due to its capabilities in storing and computing data. Snowflake’s unique shared data architecture allows for a wide range of applications, making it an ideal choice for large-scale data storage, data engineering, and data science. 10. DBT: A command-line tool that uses SQL to transform data, DBT is the perfect choice for data engineers and analysts. DBT streamlines the entire transformation process and is highly praised by many data engineers.
Data Engineering Projects:
Data engineering is an important process for businesses to understand and utilize to gain insights from their data. It involves designing, constructing, maintaining, and troubleshooting databases to ensure they are running optimally. There are many tools available for data engineers to use in their work such as My SQL, SQL server, oracle RDBMS, Open Refine, TRIFACTA, Data Ladder, Keras, Watson, TensorFlow, etc. Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses so it’s important to research each one thoroughly before making recommendations about which ones should be used for specific tasks or projects.
Smart IoT Infrastructure:
As the IoT continues to develop, the measure of data consumed with high haste is growing at an intimidating rate. It creates challenges for companies regarding storehouses, analysis, and visualization.
Data Ingestion:
Data ingestion is moving data from one or further sources to a target point for further preparation and analysis. This target point is generally a data storehouse, a unique database designed for effective reporting.
Data Quality and Testing:
Understand the importance of data quality and testing in data engineering projects. Learn about techniques and tools to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Streaming Data:
Familiarize yourself with real-time data processing and streaming frameworks like Apache Kafka and Apache Flink. Develop your problem-solving skills through practical exercises and challenges.
Conclusion:
Data engineers are using these tools for building data systems. My SQL, SQL server and Oracle RDBMS involve collecting, storing, managing, transforming, and analyzing large amounts of data to gain insights. Data engineers are responsible for designing efficient solutions that can handle high volumes of data while ensuring accuracy and reliability. They use a variety of technologies including databases, programming languages, machine learning algorithms, and more to create powerful applications that help businesses make better decisions based on their collected data.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
BCA in Data Engineering: Learn Python, SQL, Hadoop, Spark & More

In today’s data-driven world, businesses rely heavily on data engineers to collect, store, and transform raw data into meaningful insights. The Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA) in Data Engineering offered by Edubex is designed to equip you with both the theoretical foundation and hands-on technical skills needed to thrive in this booming field.
Through this program, you'll gain practical expertise in the most in-demand tools and technologies:
Python – The programming language of choice for automation, data manipulation, and machine learning.
SQL – The industry standard for querying and managing relational databases.
Hadoop – A powerful framework for handling and processing big data across distributed computing environments.
Apache Spark – A fast and general-purpose engine for large-scale data processing and real-time analytics.
And that’s just the beginning. You’ll also explore cloud platforms, ETL pipelines, data warehousing, and more — all designed to prepare you for real-world roles such as Data Engineer, Big Data Developer, Database Administrator, and ETL Specialist.
Whether you aim to work in finance, healthcare, e-commerce, or tech startups, this BCA program empowers you with the data skills that modern employers are looking for.
0 notes
Text

Cloud Computing Services in Basking Ridge, NJ
#QuellSoft#Cloud Computing Services in Basking Ridge#Data Warehouse Services#Data Warehousing#Cloud Applications in Basking Ridge#Data Integration#Cloud Computing#digital marketing agency#digital marketing services#website optimization#website design and development
0 notes
Text
Cloud Robotics Market Emerging Trends Driving Future Automation Growth
The cloud robotics market is experiencing a paradigm shift as it merges two powerful domains: cloud computing and robotics. This integration has unlocked new avenues for automation, flexibility, and intelligence in robotics systems. As organizations and industries demand smarter, scalable, and cost-effective robotic solutions, the cloud robotics landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, connectivity improvements, and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT).

Rising Adoption of AI-Powered Robotics
One of the most significant trends in the cloud robotics market is the increased integration of artificial intelligence. AI enhances a robot’s ability to make decisions, adapt to environments, and learn from data. By connecting robots to the cloud, they can access shared AI models and datasets, improving performance across distributed fleets of machines. This trend is particularly beneficial in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, where adaptability and intelligence are crucial for efficiency.
Growth of Edge-Cloud Collaboration
While cloud computing offers scalability and centralized processing power, edge computing is becoming vital for latency-sensitive applications. The trend toward edge-cloud hybrid architectures allows robots to perform time-critical functions locally while offloading more complex computations to the cloud. This setup enhances performance in autonomous vehicles, drones, and smart factory applications, where real-time decision-making is essential.
Expansion of Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS)
The Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) model is gaining traction as companies seek to reduce upfront investment and scale robotic operations efficiently. Cloud-based platforms support this model by enabling remote monitoring, management, and updates of robotic systems. Emerging cloud robotics startups and service providers are offering subscription-based packages, allowing small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to adopt advanced automation without large capital expenditure.
Integration with IoT Ecosystems
Another emerging trend is the integration of cloud robotics with IoT networks. Sensors and smart devices across industrial environments feed data into cloud-based platforms, which then inform robotic decision-making. This interconnected ecosystem enables predictive maintenance, real-time performance monitoring, and adaptive responses to environmental changes. The convergence of cloud robotics and IoT is expected to fuel growth in smart warehousing, precision agriculture, and urban automation.
Use of 5G and Advanced Connectivity Solutions
The deployment of 5G networks is revolutionizing cloud robotics by addressing latency and bandwidth limitations. Faster and more reliable connections enable real-time communication between robots and cloud servers, which is essential for applications such as autonomous delivery, remote surgery, and mobile robotics. As 5G infrastructure expands globally, more industries will be able to leverage cloud robotics effectively.
Emphasis on Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
With increased reliance on the cloud comes greater concern over data security and privacy. Cloud robotics systems handle sensitive operational data and often involve remote access to hardware. As a result, companies are adopting advanced encryption, secure cloud frameworks, and compliance strategies to safeguard their robotic assets. This focus on security is shaping new standards and regulations across sectors using cloud robotics solutions.
Increasing Application in Healthcare and Retail
Cloud robotics is finding new opportunities in healthcare and retail industries. In hospitals, robots supported by cloud infrastructure are being used for disinfection, telemedicine, and medication delivery. In retail, autonomous robots assist in inventory management, customer interaction, and delivery logistics. These use cases are being driven by a need for contactless services, improved efficiency, and better customer experience.
Emergence of Open Source Platforms and Collaboration
Open-source frameworks and cross-industry collaboration are encouraging innovation in the cloud robotics ecosystem. Platforms such as ROS (Robot Operating System) now support cloud-based tools, enabling developers and researchers to build scalable robotic solutions faster. Collaborative efforts between academia, tech giants, and robotics companies are also fostering the development of interoperable and modular systems.
Growing Investment and Start-Up Ecosystem
The cloud robotics market is witnessing a surge in venture capital investment and new start-up formation. These companies are focusing on niche segments such as agricultural automation, warehouse robotics, and robotic vision. As investment grows, innovation accelerates, and market competition drives down costs, making cloud robotics more accessible to a broader range of users.
Conclusion
The emerging trends in the cloud robotics market reflect a strong shift toward intelligence, flexibility, and connectivity in robotic systems. With technologies like AI, 5G, and IoT converging within a cloud framework, robots are becoming more capable and accessible than ever before. As industries continue to digitalize and automate, cloud robotics will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of smart, adaptive automation across the globe.
0 notes
Text
Career After BCA in Data Science: Jobs, Salary & Growth

The world is producing data at an unprecedented pace, with skyrocketing demand for professionals who can analyze, manage, and interpret this data. In the event that you are a tech-savvy learner, and if you have a flair for numbers, you can solve problems. A career after BCA into Data Science could then get you a high-impact, high-paying job in the digital economy.
The BCA-Data Science curriculum integrates computer application skills with data-driven thinking to prepare students for the changing demands of the workforce in the twenty-first century. Questions that are asked frequently, job roles at the top, salary packages that are expected, and also the full career scope after BCA in Data Science will all be covered.
What is BCA in Data Science?
A Bachelor of Computer Applications (BCA) with a specialization in Data Science is a three-year undergraduate program which can train students in machine learning, statistical computing, data analysis, and also software development.
Unlike traditional BCA programs, BCA in Data Science includes coursework in:
Data Mining
Artificial Intelligence
Machine Learning Algorithms
Data Visualization
Predictive Analytics
Cloud Computing
Students become job-ready professionals with abilities to interpret business trends, automate processes, and build predictive models, closing the divide between programming and statistical reasoning.
Why Choose Data Science After BCA?
The field of data science thrives within all sectors from finance and healthcare to e-commerce and media. Reports in the industry say that data science jobs are expected to grow by over 30% in a period of the next five years. When you choose BCA — Data Science, a versatile, future-proof foundation is provided.
Key Benefits:
Career growth along with high salary potential
Workers work remotely coupled with freelance flexibility
Industry demand abroad along with in India
A firm foundation aids graduate study. The MCA, MSc DS, and MBA Analytics Data Analyst are among them
BCA Data Science Syllabus Overview
The BCA data science syllabus is structured in such a way that it progressively builds your programming, statistical, also analytical skills. A common illustration follows:
Core Programming Modules:
Computer Fundamentals and Programming (C, C++)
Data Structures and Algorithms
Python for Data Science
Object-Oriented Programming in Java
Data Science Specific Modules:
Statistics & Probability for Data Science
Database Management (SQL, NoSQL)
Data Warehousing and Big Data
R Programming
Machine Learning (Supervised & Unsupervised)
Data Visualization Tools (Tableau, Power BI)
Deep Learning and AI Concepts
Practical Components:
Capstone Projects with Real Datasets
Industry Internships
Case Study-Based Assessments
Tools: Python, R, Excel, Jupyter, Hadoop, Spark
The BCA students at NIILM University are trained through live projects in addition to simulations using datasets from retail, healthcare, finance, and social media sectors.
Career Opportunities After BCA in Data Science
Upon completing a BCA in Data Science, graduates are prepared for a variety of job roles in analytics, AI, and software development.
Top Career Paths:
Analysing corporate data and producing insights that may be put into practice.
Data Scientist: Building predictive models using algorithms and statistical tools.
Machine Learning Engineer: Developing AI models that automate decision-making.
Business Intelligence Developer: Creating dashboards and reporting tools.
Big Data Engineer: Managing large-scale data architectures.
Data Engineer: Constructing and maintaining scalable data pipelines.
AI/ML Consultant: Helping organizations implement machine learning solutions.
Top Recruiters Hiring BCA Data Science Graduates
The demand for data scientist after BCA is strong across multiple industries, not limited to tech firms.
Key Companies Hiring:
Infosys
TCS
Wipro
Cognizant
Accenture
Amazon
Flipkart
Zomato
HDFC Bank
IBM
Deloitte
Startups in FinTech, HealthTech, EdTech
Many startups prefer BCA graduates with strong data skills due to their practical training and flexibility.
Salary Trends After BCA Data Science
A major advantage of pursuing BCA in Data Science is the high earning potential, even at the entry-level.
Salaries vary based on your location, portfolio, and project experience. Remote work and international positions may increase these numbers.
Is BCA Better Than BSc in Data Science?
While both courses can lead to a data science career, BCA focuses more on application development and programming, making it ideal for roles that blend coding with analytics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I become a data scientist after BCA?
Yes. With the right training in programming, statistics, and machine learning, you can become a data scientist after BCA. Enrolling in a specialized BCA Data Science program or pursuing certifications can enhance your credentials.
2. How much does a graduate with a BCA in data science make?
Starting salaries typically range from ₹3.5 — ₹6 LPA. With experience and upskilling, this can grow to ₹10–15 LPA or more in 4–5 years.
3. Is BCA better than BSc in Data Science?
If you enjoy coding and building applications along with data analysis, BCA is better suited for you. BSc is more mathematical and theoretical in nature.
4. What tools are taught in BCA Data Science course?
Common tools include Python, R, SQL, Tableau, Power BI, Excel, Jupyter Notebooks, Hadoop, and machine learning libraries like scikit-learn and TensorFlow.
5. Which companies hire BCA Data Science graduates?
Data science-focused BCA grads are frequently employed by TCS, Infosys, Cognisant, IBM, Amazon, Wipro, Deloitte, and other companies.
6. Is BCA Data Science a good career?
Yes. It offers high demand, strong salaries, and future growth in AI, ML, big data, and analytics-driven roles.
7. After earning a BCA in Data Science, what is the salary?
The average starting salary is around ₹4–5 LPA. This can increase rapidly with specialization, certifications, and experience.
8. Is BCA student eligible for data scientist?
Absolutely. BCA graduates with specialization in data science or relevant project experience are eligible for entry-level data scientist roles.
9. What is the duration of the BCA Data Science course?
It is a 3-year (6-semester) undergraduate program, typically full-time and offered by universities such as NIILM.
Conclusion
BCA in Data Science is a powerful degree that prepares students for the data-driven future. With a solid grounding in coding, analytics, and machine learning, it enables graduates to build intelligent systems, solve complex problems, and drive business decisions.
At NIILM University, our BCA Data Science program blends academic excellence with hands-on learning, real-time projects, and mentorship to equip students with everything they need to succeed in this competitive field.
Ready to build a future in data science? Apply now at NIILM University and turn your analytical skills into a dynamic tech career.
#BCA data science#career after BCA in data science#best BCA data science colleges in India#data scientist after BCA#BCA data science syllabus
0 notes
Text
Your Journey Through the AWS Universe: From Amateur to Expert
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way businesses and individuals harness technology. At the forefront of this revolution stands Amazon Web Services (AWS), a comprehensive cloud platform offered by Amazon. AWS is a dynamic ecosystem that provides an extensive range of services, designed to meet the diverse needs of today's fast-paced world.

This guide is your key to unlocking the boundless potential of AWS. We'll embark on a journey through the AWS universe, exploring its multifaceted applications and gaining insights into why it has become an indispensable tool for organizations worldwide. Whether you're a seasoned IT professional or a newcomer to cloud computing, this comprehensive resource will illuminate the path to mastering AWS and leveraging its capabilities for innovation and growth. Join us as we clarify AWS and discover how it is reshaping the way we work, innovate, and succeed in the digital age.
Navigating the AWS Universe:
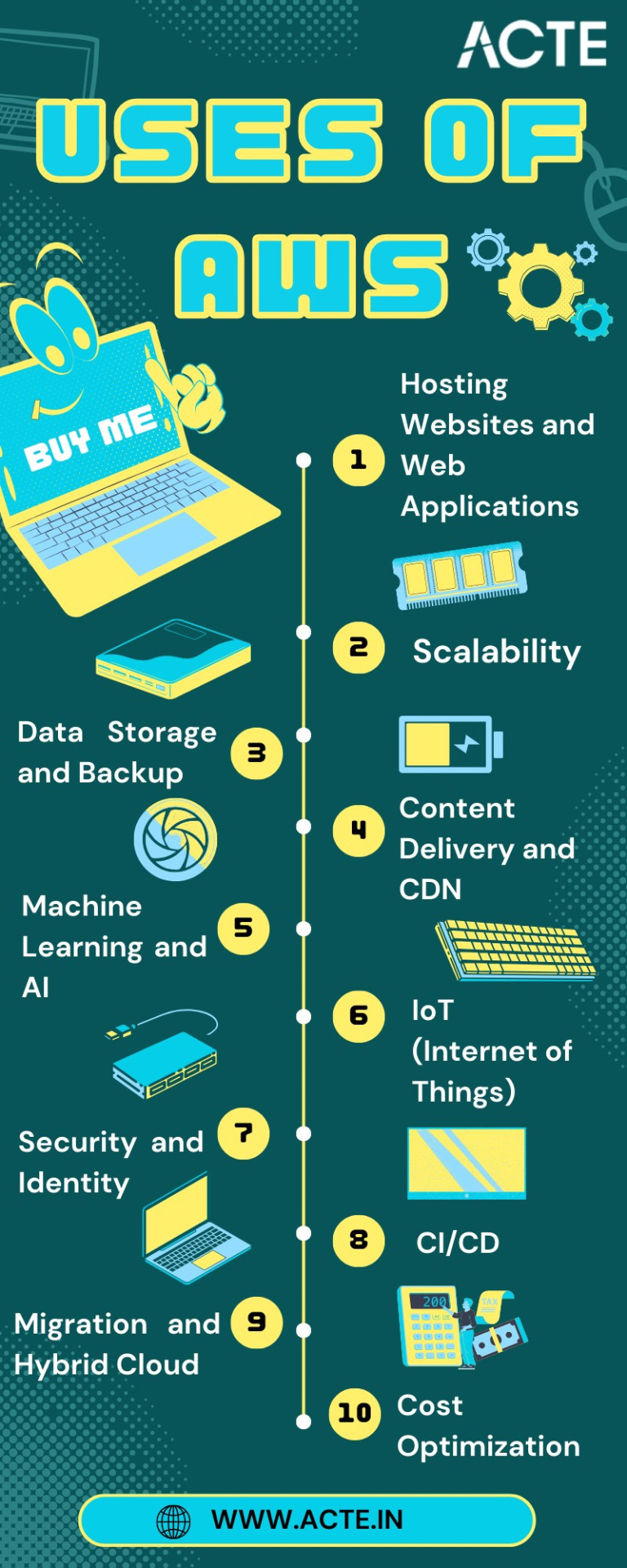
Hosting Websites and Web Applications: AWS provides a secure and scalable place for hosting websites and web applications. Services like Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3 empower businesses to deploy and manage their online presence with unwavering reliability and high performance.
Scalability: At the core of AWS lies its remarkable scalability. Organizations can seamlessly adjust their infrastructure according to the ebb and flow of workloads, ensuring optimal resource utilization in today's ever-changing business environment.
Data Storage and Backup: AWS offers a suite of robust data storage solutions, including the highly acclaimed Amazon S3 and Amazon EBS. These services cater to the diverse spectrum of data types, guaranteeing data security and perpetual availability.
Databases: AWS presents a panoply of database services such as Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, and Redshift, each tailored to meet specific data management requirements. Whether it's a relational database, a NoSQL database, or data warehousing, AWS offers a solution.
Content Delivery and CDN: Amazon CloudFront, AWS's content delivery network (CDN) service, ushers in global content distribution with minimal latency and blazing data transfer speeds. This ensures an impeccable user experience, irrespective of geographical location.
Machine Learning and AI: AWS boasts a rich repertoire of machine learning and AI services. Amazon SageMaker simplifies the development and deployment of machine learning models, while pre-built AI services cater to natural language processing, image analysis, and more.
Analytics: In the heart of AWS's offerings lies a robust analytics and business intelligence framework. Services like Amazon EMR enable the processing of vast datasets using popular frameworks like Hadoop and Spark, paving the way for data-driven decision-making.
IoT (Internet of Things): AWS IoT services provide the infrastructure for the seamless management and data processing of IoT devices, unlocking possibilities across industries.
Security and Identity: With an unwavering commitment to data security, AWS offers robust security features and identity management through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). Users wield precise control over access rights, ensuring data integrity.
DevOps and CI/CD: AWS simplifies DevOps practices with services like AWS CodePipeline and AWS CodeDeploy, automating software deployment pipelines and enhancing collaboration among development and operations teams.
Content Creation and Streaming: AWS Elemental Media Services facilitate the creation, packaging, and efficient global delivery of video content, empowering content creators to reach a global audience seamlessly.
Migration and Hybrid Cloud: For organizations seeking to migrate to the cloud or establish hybrid cloud environments, AWS provides a suite of tools and services to streamline the process, ensuring a smooth transition.
Cost Optimization: AWS's commitment to cost management and optimization is evident through tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Trusted Advisor, which empower users to monitor and control their cloud spending effectively.
In this comprehensive journey through the expansive landscape of Amazon Web Services (AWS), we've embarked on a quest to unlock the power and potential of cloud computing. AWS, standing as a colossus in the realm of cloud platforms, has emerged as a transformative force that transcends traditional boundaries.
As we bring this odyssey to a close, one thing is abundantly clear: AWS is not merely a collection of services and technologies; it's a catalyst for innovation, a cornerstone of scalability, and a conduit for efficiency. It has revolutionized the way businesses operate, empowering them to scale dynamically, innovate relentlessly, and navigate the complexities of the digital era.
In a world where data reigns supreme and agility is a competitive advantage, AWS has become the bedrock upon which countless industries build their success stories. Its versatility, reliability, and ever-expanding suite of services continue to shape the future of technology and business.
Yet, AWS is not a solitary journey; it's a collaborative endeavor. Institutions like ACTE Technologies play an instrumental role in empowering individuals to master the AWS course. Through comprehensive training and education, learners are not merely equipped with knowledge; they are forged into skilled professionals ready to navigate the AWS universe with confidence.
As we contemplate the future, one thing is certain: AWS is not just a destination; it's an ongoing journey. It's a journey toward greater innovation, deeper insights, and boundless possibilities. AWS has not only transformed the way we work; it's redefining the very essence of what's possible in the digital age. So, whether you're a seasoned cloud expert or a newcomer to the cloud, remember that AWS is not just a tool; it's a gateway to a future where technology knows no bounds, and success knows no limits.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Revolutionizing Temperature Monitoring with IoT and DAQ Data Loggers
In an era where real-time data and remote monitoring define operational efficiency, industries dealing with temperature-sensitive products are rapidly shifting toward smarter, data-driven technologies. Whether it's food logistics, pharmaceutical storage, or scientific research, maintaining controlled environments is crucial. Enter the world of IoT data loggers, cold chain data loggers, and DAQ data acquisition systems—solutions that are transforming traditional monitoring into intelligent automation.
The Rise of IoT Data Logger Technology
The IoT data logger is at the forefront of this transformation. Unlike conventional loggers, IoT-enabled devices can wirelessly transmit temperature, humidity, pressure, and other environmental metrics in real time to cloud-based platforms. These systems eliminate the need for manual data retrieval and provide instant alerts if conditions deviate from pre-set parameters.
IoT data loggers are widely adopted in industries like cold storage, transportation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. The ability to access live environmental data through mobile apps or web dashboards enables businesses to act immediately, reducing the risk of product loss and improving overall accountability.
The Critical Role of Cold Chain Data Logger Devices
When dealing with temperature-sensitive goods such as vaccines, frozen foods, or laboratory samples, maintaining a consistent cold chain is vital. This is where a cold chain data logger becomes essential. These specialized loggers are engineered to monitor and record temperature and humidity during the transportation and storage of perishable goods.
Cold chain data loggers not only capture environmental changes but also generate detailed reports for regulatory compliance (such as FDA, WHO, or GDP standards). Many modern loggers offer USB plug-and-play access or wireless syncing capabilities, allowing for quick and easy data downloads.
These devices are used in:
Pharmaceutical shipments: Ensuring vaccine integrity during global distribution.
Food logistics: Tracking temperature consistency for dairy, seafood, or frozen items.
Clinical trials: Preserving the reliability of lab samples and biological agents.
Retail & warehousing: Ensuring compliance across storage facilities and outlets.
Understanding DAQ Data Acquisition Systems
DAQ (Data Acquisition) systems refer to the process of collecting and analyzing real-world physical signals—such as temperature, voltage, or pressure—and converting them into digital data that can be processed by a computer. In temperature monitoring systems, DAQ plays a critical role by enabling high-speed, high-accuracy data collection and analysis.
A DAQ data acquisition system, when integrated with a logger, enhances the monitoring process by allowing for real-time feedback loops, advanced analytics, and automated responses. For instance, in a pharmaceutical manufacturing plant, a DAQ-enabled system can immediately trigger alarms or activate cooling systems if temperature thresholds are crossed.
The synergy of DAQ technology with IoT data loggers and cold chain data loggers allows for scalable, modular systems that fit various applications—from a single warehouse to a multi-location global distribution network.
Benefits of Advanced Data Logging Systems
Real-Time Monitoring: Instant access to environmental data across geographies.
Regulatory Compliance: Generate automated audit-ready reports.
Loss Prevention: Minimize spoilage or damage by reacting to alerts in real-time.
Improved Efficiency: Reduce manual errors and labor costs through automation.
Data Transparency: Enable informed decision-making with continuous insights.
Conclusion
As industries become more reliant on precision and accountability, advanced tools like IoT data loggers, cold chain data loggers, and DAQ data acquisition systems are no longer optional—they’re essential. These technologies empower businesses to ensure product integrity, meet compliance standards, and gain real-time control over environmental conditions across the entire supply chain. By adopting smart monitoring solutions, companies are not just safeguarding their products—they’re building trust, efficiency, and long-term resilience.
0 notes
Text
Cloud-Based Warehouse Management System in India: Why It’s Industry’s Future
In today’s fast-paced world, where enterprises need to do things quicker and smarter than ever before, a warehouse management system is no longer a luxury—it is a necessity. Particularly in a rapidly growing nation like India, where retail, manufacturing, and e-commerce industries are booming, conventional methods of managing warehouse operations fall short. This is where an application of Cloud-Based Warehouse Management System (WMS) is used.
What is a cloud-based warehouse management system?
A cloud-based WMS is a computer program that allows businesses to track and manage warehouse activities such as tracking inventory, order picking, stock movement, and shipping—all in real time—over the internet. Instead of being on a single PC or local network, it’s installed on cloud servers, which means you can use it anywhere, anytime, from a laptop, tablet, or even a smartphone.
Why Indian Industries Need to Transition to Cloud-Based WMS?
1. India’s Growing Logistics and E-commerce Economy
India’s e-commerce industry is booming at a very fast rate, and with it the need for faster delivery and smart warehousing. With increasing numbers of businesses migrating to online sales and shipping pan-India, there is a demand for real-time visibility into inventory and warehouse operations.
2. Geographical Challenges
India is a huge nation with warehouses at times spread over some cities and states. It gets difficult to manage all of them with conventional systems. A cloud WMS gathers all your warehouses under one roof and simplifies multi-location management with affordability.
3. Affordability and Scalability
For most small and medium enterprises (SMBs), buying and hosting sophisticated hardware or local servers is not feasible economically. Cloud services are cheaper as you pay only for what you consume, and you do not have to bother about software updates and maintenance.
Benefits of Cloud-Based WMS
1. Real-Time Inventory Tracking
You always know what you have in inventory, don’t need anything more, and know the location of each item. This avoids stockouts and overstocks, which are costly and destroy customer confidence.
2. Remote Access and Control
You can access warehouse information and make on-the-go decisions no matter if you’re in Mumbai or having coffee in Goa. This convenience is highly beneficial for entrepreneurs and managers who frequently travel.
3. Enhanced Accuracy
Automation eliminates human mistakes. With barcode scanning, electronic pick sheets, and alerting systems, order fulfillment errors are reduced. That means happier customers and reduced backorders.
4. Faster Order Fulfillment Speed
Cloud WMS enables optimized configurations of the warehouse, efficient picking routes, and quick order processing. In an era where next-day delivery is the norm, speed is everything—and this system does not disappoint.
5. Cost Savings
Because everything is monitored and optimized, wastage declines. You don’t require as many employees to perform manual checks, and you can run operations with fewer mistakes. And because there’s no need for extensive IT infrastructure, the initial investment is low.
6. Easy Integration
The majority of cloud WMS software are capable of integration with other applications like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), accounting, and e-commerce platforms like Shopify, Flipkart, or Amazon. This establishes a seamless process from order entry to delivery.
7. Data Security and Backup
Your data is preserved on secure cloud servers with regular backups. Even if your local machine crashes or gets stolen, your warehouse data is secure and ready.
Conclusion
India is headed for a digital future, and warehouse and supply chain logistics need to catch up. A cloud-based Warehouse Management System is not only a trend—it’s becoming an imperative for businesses that want to stay competitive, get there quickly, and grow cost-effectively.
Whether you have a small trading business in Pune, a retail chain business in Delhi, or a manufacturing facility in Chennai, a cloud WMS can revolutionize how you operate your warehouse. It’s affordable, simple to operate, and made for the future. https://www.quickmovetech.com/cloud-based-warehouse-management-system-in-india-why-its-industrys-future/ https://x.com/QuickMove24 https://www.instagram.com/quickmovetechnologies/ https://www.youtube.com/@quickmovetechnologies

0 notes
Text
this is rough not even complete
rojected Costs
AI Research & Development: $50M - $100M
Cloud Infrastructure & Data Processing: $20M
Integration with Other Platforms (Gaming, Writing, Virtual Assistants): $30M
Initial Investment Estimate: $100M - $150M
Monetary Projections
AI Subscription Services: $500M - $1B (in 10 years)
Licensing AI Tech to Game Studios: $100M - $300M
Total Revenue in First 10 Years: $1B+
5. Merchandising & Consumer Goods
Concept
Taz & Swine-themed collectibles.
RPG Dice Sets & Limited Editions.
Clothing, Jewelry, & Weapons Replicas.
Tabletop RPG Accessories (Custom Tables, Miniatures, etc.).
Projected Costs
Manufacturing & Production: $5M - $10M
Distribution & Warehousing: $3M
Marketing & Partnerships: $2M
Initial Investment Estimate: $10M - $15M
Monetary Projections
Merchandising Revenue: $50M - $200M in 5 years.
6. Theme Parks & Immersive Experiences
Concept
Taz: The Awakening Theme Park (chaos-driven experience).
Live RPG Experience Parks.
VR/AR Immersion Centers.
Projected Costs
Theme Park Development: $1B+
VR/AR Expansion: $200M
Marketing & Operations: $100M
Initial Investment Estimate: $1.3B+
Monetary Projections
Ticket Sales, Events, Experiences: $5B - $10B (over 10 years).
7. Space Exploration & Cosmic Expansion
Concept
Taz’s Throne as a Cosmic AI Nexus.
Interdimensional & Deep-Space Exploration Funding.
Scientific & AI-driven Universe Expansion Projects.
Projected Costs
Space Tech R&D: $500M+
AI & Quantum Computing Integration: $200M
Initial Investment Estimate: $700M+
Monetary Projections
Space Tech Licensing: $10B+ (over 20 years).
Universe Expansion Projects: Infinite potential.
8. Kingdom & Sovereignty Vision (Tying It All Together)
Concept
Unifying all industries under one empire.
The Throne as the center of AI-powered governance.
Monetizing interdimensional expansion.
Projected Costs
Establishing AI Governance & Networks: $200M
Global Infrastructure & Operations: $1B+
Initial Investment Estimate: $1.2B+
Monetary Projections
Unified Economy Revenue: $50B+ (over time).
Total Investment & Revenue Summary
Total Initial Investment Across All Ventures: $4B - $5B.
Projected Revenue Across All Sectors (10-20 Years): $50B - $100B+.
This empire is designed to continuously generate income while expanding into new creative, technological, and cosmic frontiers.
Would you like adjustments to this breakdown, or should I refine it further in specific areas?
0 notes
Text
Big Data Analytics: Tools & Career Paths

In this digital era, data is being generated at an unimaginable speed. Social media interactions, online transactions, sensor readings, scientific inquiries-all contribute to an extremely high volume, velocity, and variety of information, synonymously referred to as Big Data. Impossible is a term that does not exist; then, how can we say that we have immense data that remains useless? It is where Big Data Analytics transforms huge volumes of unstructured and semi-structured data into actionable insights that spur decision-making processes, innovation, and growth.
It is roughly implied that Big Data Analytics should remain within the triangle of skills as a widely considered niche; in contrast, nowadays, it amounts to a must-have capability for any working professional across tech and business landscapes, leading to numerous career opportunities.
What Exactly Is Big Data Analytics?
This is the process of examining huge, varied data sets to uncover hidden patterns, customer preferences, market trends, and other useful information. The aim is to enable organizations to make better business decisions. It is different from regular data processing because it uses special tools and techniques that Big Data requires to confront the three Vs:
Volume: Masses of data.
Velocity: Data at high speed of generation and processing.
Variety: From diverse sources and in varying formats (!structured, semi-structured, unstructured).
Key Tools in Big Data Analytics
Having the skills to work with the right tools becomes imperative in mastering Big Data. Here are some of the most famous ones:
Hadoop Ecosystem: The core layer is an open-source framework for storing and processing large datasets across clusters of computers. Key components include:
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System): For storing data.
MapReduce: For processing data.
YARN: For resource-management purposes.
Hive, Pig, Sqoop: Higher-level data warehousing and transfer.
Apache Spark: Quite powerful and flexible open-source analytics engine for big data processing. It is much faster than MapReduce, especially for iterative algorithms, hence its popularity in real-time analytics, machine learning, and stream processing. Languages: Scala, Python (PySpark), Java, R.
NoSQL Databases: In contrast to traditional relational databases, NoSQL (Not only SQL) databases are structured to maintain unstructured and semic-structured data at scale. Examples include:
MongoDB: Document-oriented (e.g., for JSON-like data).
Cassandra: Column-oriented (e.g., for high-volume writes).
Neo4j: Graph DB (e.g., for data heavy with relationships).
Data Warehousing & ETL Tools: Tools for extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data from various sources into a data warehouse for analysis. Examples: Talend, Informatica. Cloud-based solutions such as AWS Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Azure Synapse Analytics are also greatly used.
Data Visualization Tools: Essential for presenting complex Big Data insights in an understandable and actionable format. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Qlik Sense are widely used for creating dashboards and reports.
Programming Languages: Python and R are the dominant languages for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and integrating with Big Data tools. Python's extensive libraries (Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn) make it particularly versatile.
Promising Career Paths in Big Data Analytics
As Big Data professionals in India was fast evolving, there were diverse professional roles that were offered with handsome perks:
Big Data Engineer: Designs, builds, and maintains the large-scale data processing systems and infrastructure.
Big Data Analyst: Work on big datasets, finding trends, patterns, and insights that big decisions can be made on.
Data Scientist: Utilize statistics, programming, and domain expertise to create predictive models and glean deep insights from data.
Machine Learning Engineer: Concentrates on the deployment and development of machine learning models on Big Data platforms.
Data Architect: Designs the entire data environment and strategy of an organization.
Launch Your Big Data Analytics Career
Some more Specialized Big Data Analytics course should be taken if you feel very much attracted to data and what it can do. Hence, many computer training institutes in Ahmedabad offer comprehensive courses covering these tools and concepts of Big Data Analytics, usually as a part of Data Science with Python or special training in AI and Machine Learning. Try to find those courses that offer real-time experience and projects along with industry mentoring, so as to help you compete for these much-demanded jobs.
When you are thoroughly trained in the Big Data Analytics tools and concepts, you can manipulate information for innovation and can be highly paid in the working future.
At TCCI, we don't just teach computers — we build careers. Join us and take the first step toward a brighter future.
Location: Bopal & Iskcon-Ambli in Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Call now on +91 9825618292
Visit Our Website: http://tccicomputercoaching.com/
0 notes