#array php ajax
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Vogon Ajax Loop Interface
I wasn't being followed by as many people who might care at the time I wrote this in 2020, so here's a quick refresher on how the Ajax Loop Interface works.
An ajax controller is built that includes the backend ALI class. This class accepts an array, an initialization model that generates and array to be stored in $_SESSION (useful for file scans) or an SQL statement that can be run to generate an array.
As another property, it accepts an additional model that is designed to do whatever action is needed on a single member of this array.
This controller will then switch modes based on the current state of the process defined by the GET parameters set in the ajax request. If nothing is provided, it's an initialization state, if provided with a count and offset, we need to run the model for the given member of the array.
If the count and offset are provided but the array is currently missing (such as when resuming a process that errored out or timed out), the controller can re-run the initialization step to rebuild the array, and then instruct the frontend client to make the request again.
The frontend view then, is a javascript object that manages the requests and displays the messages provided by the various models, as well as a convenient progress bar.
For context of how quick this makes it to set up these jobs, here's the full text of the audio import controller
<?php
if(empty($_GET['dir'])){ $_GET['dir'] = ''; }
load_class('ajax_loop_interface');
$ali = new ajax_loop_interface([ 'mode' => 'session_array', 'init_model' => 'audio_import_init', 'init_data' => [ 'dir' => $_GET['dir'] ], 'model' => 'audio_import', 'ext' => 'audio', 'var_name' => 'f' ]);
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to check Email and username availability live using jquery/ajax, PHP and PDO

In this tutorial, We will learn how to How to check Email and username availability live using jQuery/ajax and PHP-PDO.
Click : https://phpgurukul.com/how-to-check-email-and-username-availability-live-using-jquery-ajax-php-and-pdo/
File Structure for this tutorials
index.php (Main File)
config.php (Database Connection file)
check_availability.php (Used to check the Email and User availability)
Create a database with name demos. In demos database, create a table with name email_availabilty Sample structure of table email_availabilty
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `email_availabilty` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`username` varchar(255) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
2. Create a database connection file
config.php
<?php
//DB Connection
define(‘DB_HOST’,’localhost’);
define(‘DB_USER’,’root’);
define(‘DB_PASS’,’’);
define(‘DB_NAME’,’demos’);
// Establish database connection.
try
{
$dbh = new PDO(“mysql:host=”.DB_HOST.”;dbname=”.DB_NAME,DB_USER, DB_PASS,array(PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_INIT_COMMAND => “SET NAMES ‘utf8’”));
}
catch (PDOException $e)
{
exit(“Error: “ . $e->getMessage());
}
3. Now Create an HTML form index.php
<?php
include_once(“config.php”);
?>
<table>
<tr>
<th width=”24%” height=”46" scope=”row”>Email Id :</th>
<td width=”71%” ><input type=”email” name=”email” id=”emailid” onBlur=”checkemailAvailability()” value=”” class=”form-control” required /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th width=”24%” scope=”row”></th>
<td > <span id=”email-availability-status”></span> </td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th height=”42" scope=”row”>User Name</th>
<td><input type=”text” name=”username” id=”username” value=”” onBlur=”checkusernameAvailability()” class=”form-control” required /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th width=”24%” scope=”row”></th>
<td > <span id=”username-availability-status”></span> </td>
</tr>
</table>
4. Jquery/ajax script where you pass variable to check_availability.php page. put this in index.php inside head.
<script>
function checkemailAvailability() {
$(“#loaderIcon”).show();
jQuery.ajax({
url: “check_availability.php”,
data:’emailid=’+$(“#emailid”).val(),
type: “POST”,
success:function(data){
$(“#email-availability-status”).html(data);
$(“#loaderIcon”).hide();
},
error:function (){}
});
}
function checkusernameAvailability() {
$(“#loaderIcon”).show();
jQuery.ajax({
url: “check_availability.php”,
data:’username=’+$(“#username”).val(),
type: “POST”,
success:function(data){
$(“#username-availability-status”).html(data);
$(“#loaderIcon”).hide();
},
error:function (){}
});
}
</script>
5.check_availability.php page in this page you will check the availability of email or email.
<?php
require_once(“config.php”);
//code check email
if(!empty($_POST[“emailid”])) {
$uemail=$_POST[“emailid”];
$sql =”SELECT email FROM email_availabilty WHERE email=:email”;
$query= $dbh -> prepare($sql);
$query-> bindParam(‘:email’, $uemail, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$query-> execute();
$results = $query -> fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_OBJ);
if($query -> rowCount() > 0)
echo “<span style=’color:red’> Email Already Exit .</span>”;
else
echo “<span style=’color:green’> Email Available.</span>”;
}
// End code check email
//Code check user name
if(!empty($_POST[“username”])) {
$username=$_POST[“username”];
$sql =”SELECT username FROM email_availabilty WHERE username=:username”;
$query= $dbh -> prepare($sql);
$query-> bindParam(‘:username’, $username, PDO::PARAM_STR);
$query-> execute();
$results = $query -> fetchAll(PDO::FETCH_OBJ);
if($query -> rowCount() > 0)
echo “<span style=’color:red’> Username already exit .</span>”;
else
echo “<span style=’color:green’> Username Available.</span>”;
}
// End code check username
?>
PHP Gurukul
Welcome to PHPGurukul. We are a web development team striving our best to provide you with an unusual experience with PHP. Some technologies never fade, and PHP is one of them. From the time it has been introduced, the demand for PHP Projects and PHP developers is growing since 1994. We are here to make your PHP journey more exciting and useful.
Website : https://phpgurukul.com
1 note
·
View note
Text
Getting Started with PHP: A Beginner's Guide to Your First "Hello World" Program

Introduction
PHP tutorial for beginners and professionals provides in-depth knowledge of PHP scripting language. Our PHP tutorial will help you to learn PHP scripting language easily.
This PHP tutorial covers all the topics of PHP such as introduction, control statements, functions, array, string, file handling, form handling, regular expression, date and time, object-oriented programming in PHP, math, PHP MySQL, PHP with Ajax, PHP with jQuery and PHP with XML.
What is PHP
PHP is an open-source, interpreted, and object-oriented scripting language that can be executed at the server side. PHP is well suited for web development. Therefore, it is used to develop web applications (an application that executes on the server and generates the dynamic page.).
PHP was created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994 but appeared in the market in 1995. PHP 7.0 is the latest version of PHP, which was released on 28 November. Some important points need to be noticed about PHP are as follows:
PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor.
PHP is an interpreted language, i.e., there is no need for compilation.
PHP can be embedded into HTML.
PHP is an object-oriented language.
PHP is an open-source scripting language.
PHP is simple and easy to learn language.

Why use PHP
PHP is a server-side scripting language, which is used to design dynamic web applications with MySQL database.
It handles dynamic content, database as well as session tracking for the website.
You can create sessions in PHP.
It can access cookies variables and also set cookies.
Using PHP language, you can control the user's to access some pages of your website.
It helps to encrypt the data and apply validation.
PHP supports several protocols such as HTTP, POP3, SNMP, LDAP, IMAP, and many more.
PHP Features

Install PHP
To install PHP, we will suggest you to install AMP (Apache, MySQL, PHP) software stack. It is available for all operating systems. There are many AMP options available in the market that are given below:
WAMP for Windows
LAMP for Linux
MAMP for Mac
SAMP for Solaris
FAMP for FreeBSD
XAMPP (Cross, Apache, MySQL, PHP, Perl) for Cross Platform: It includes some other components too such as FileZilla, OpenSSL, Webalizer, Mercury Mail, etc.
How to install XAMPP server on windows
We will learn how to install the XAMPP server on windows platform step by step. Follow the below steps and install the XAMPP server on your system.
Step 1: Click on the above link provided to download the XAMPP server according to your window requirement.
Step 2: After downloading XAMPP, double click on the downloaded file and allow XAMPP to make changes in your system. A window will pop-up, where you have to click on the Next button.
Step 3: Here, select the components, which you want to install and click Next.

Step 4: Choose a folder where you want to install the XAMPP in your system and click Next
Step 5: Click Next and move ahead
Step 6: XAMPP is ready to install, so click on the Next button and install the XAMPP.
Step 7: A finish window will display after successful installation. Click on the Finish button
Step 8: Choose your preferred language
Step 9: XAMPP is ready to use. Start the Apache server and MySQL and run the php program on the localhost.
Step 10: If no error is shown, then XAMPP is running successfully

How to run PHP code in XAMPP
Generally, a PHP file contains HTML tags and some PHP scripting code. It is very easy to create a simple PHP example. To do so, create a file and write HTML tags + PHP code and save this file with .php extension.
All PHP code goes between the php tag. It starts with <?php and ends with ?>. The syntax of PHP tag is given below:
<?php
//your code here
?>
How to run PHP programs in XAMPP PHP is a popular backend programming language. PHP programs can be written on any editor, such as - Notepad, Notepad++, Dreamweaver, etc. These programs save with .php extension, i.e., filename.php inside the htdocs folder.
For example - p1.php.
As I'm using window, and my XAMPP server is installed in D drive. So, the path for the htdocs directory will be "D:\xampp\htdocs".
Step 1: Create a simple PHP program like hello world.
<?php
echo "Hello World!";
?>
Step 2: Save the file with hello.php name in the htdocs folder, which resides inside the xampp folder.
Step 3: Run the XAMPP server and start the Apache and MySQL.
Step4: Now, open the web browser and type localhost http://localhost/hello.php on your browser window.
Step 5: The output for the above hello.php program will be shown as the screenshot below

Most of the time, PHP programs run as a web server module. However, PHP can also be run on CLI (Command Line Interface).
Credits – Shweta Patil (Backend)
MetricsViews Pvt. Ltd.
MetricsViews specializes in building a solid DevOps strategy with cloud-native including AWS, GCP, Azure, Salesforce, and many more. We excel in microservice adoption, CI/CD, Orchestration, and Provisioning of Infrastructure - with Smart DevOps tools like Terraform, and CloudFormation on the cloud.
www.metricsviews.com
0 notes
Text
Senior PHP Developer
Job title: Senior PHP Developer Company: Codewinglet Pvt Ltd Job description: Key Skills Php Education - B.C.A, B.Sc, B.Tech/B.E, M.C.A, M.Sc Job Description Key Responsibilities: A minimum of 2+ years of hands-on experience in PHP & the CodeIgniter Framework is mandatory. Demonstrated mastery of PHP, MySQL, CodeIgniter MVC framework, jQuery, JavaScript, AJAX, REST API, and an array of other relevant technologies. A profound understanding of software design patterns and adeptness with MVC frameworks are essential. Proficiency in database optimization techniques to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Adherence to the highest Coding Standards, leveraging Design Patterns, and embracing Best Practices. Ability to provide guidance, foster collaboration, and lead fellow team members to success. Familiarity with version control tools (e.g., Git, GitHub, etc) and adeptness in agile development methodologies. Exposure to international projects is a distinct advantage, showcasing your adaptability and cultural fluency. Qualifications: Bachelor's degree in Computer Science or a related field. Excellent problem-solving skills and attention to detail. Strong communication and collaboration skills to fortify a productive and harmonious work environment. A robust grasp of relational databases, tools, and PHP frameworks. Codewinglet Private Limited presents an exclusive opportunity to align your skills and aspirations with a forward-thinking organization that values innovation, professionalism, and collaborative prowess. Application Process: Eager to embark on a journey of innovation and impact? Kindly forward your updated CV, using the subject line Application for Codeigniter Developer - . Join hands with us to engineer remarkable web solutions that redefine possibilities. - Role - Industry Type IT-Hardware & Networking / IT-Software / Software Services - Number of Vacancy 2 - Gender - Job Country India Expected salary: Rs.300000 - 500000 per year Location: Surat, Gujarat Job date: Thu, 31 Aug 2023 07:58:29 GMT Apply for the job now! Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Mastering PHP: The Ultimate Guide to PHP Online Courses
In today's fast-evolving digital era, web development continues to play a vital role in shaping online experiences. One of the most trusted and widely-used server-side scripting languages in this domain is PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor). Whether you are a beginner aiming to break into web development or a seasoned programmer looking to expand your skills, enrolling in a PHP online course is a smart and strategic move.
What is PHP?
PHP is a powerful scripting language specifically designed for web development. It is open-source, easy to learn, and integrates seamlessly with HTML, databases like MySQL, and content management systems such as WordPress. PHP runs on almost all operating systems including Linux, Windows, and macOS, making it incredibly versatile.
Since its creation in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf, PHP has evolved dramatically. Today, it powers over 75% of websites on the internet, including big names like Facebook, Wikipedia, and WordPress. Its simplicity and wide applicability make it a must-know language for aspiring web developers.
Why Learn PHP Online?
1. Flexibility and Convenience
One of the biggest advantages of choosing an online PHP course is the flexibility it offers. Whether you're a college student, a working professional, or a freelance developer, you can learn PHP at your own pace, anytime and anywhere.
2. Cost-Effective Learning
Online courses are typically more affordable than in-person classes. Many platforms even offer free PHP tutorials or low-cost courses that deliver high-quality content.
3. Access to Quality Resources
Most online PHP courses provide a wealth of resources, including video lectures, downloadable content, quizzes, code editors, and forums. These materials make it easier to grasp complex concepts and practice coding in real-time.
4. Certification and Career Growth
Many PHP online courses offer certificates upon completion. These certificates can enhance your resume and make you stand out in the job market. With PHP skills, you can pursue roles such as Web Developer, Full-Stack Developer, Backend Developer, or Software Engineer.
Key Topics Covered in a PHP Online Course
A comprehensive PHP course typically includes the following modules:
1. Introduction to PHP
What is PHP?
Installation and setup (XAMPP, WAMP)
Syntax and basic structure
Embedding PHP in HTML
2. PHP Variables and Data Types
Strings, integers, floats, booleans
Arrays (indexed and associative)
Constants
Type casting
3. Control Structures
Conditional statements (if, else, switch)
Looping structures (for, while, do-while, foreach)
4. Functions and Scope
Creating and calling functions
Function parameters and return values
Variable scope (local, global, static)
5. Forms and User Input
Handling GET and POST methods
Form validation
Superglobals like $_GET, $_POST, $_REQUEST, $_SERVER
6. Working with Databases
Connecting PHP with MySQL
CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete)
Using PDO and MySQLi
Prepared statements for security
7. Error Handling
Types of errors (syntax, runtime, logical)
Try-catch blocks
Custom error handlers
8. Sessions and Cookies
Creating and managing sessions
Setting and reading cookies
Session security best practices
9. File Handling in PHP
Reading and writing files
Uploading files via forms
File permissions
10. Object-Oriented Programming in PHP
Classes and objects
Constructors and destructors
Inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism
Interfaces and traits
11. PHP and Web Security
Input validation and sanitization
Preventing SQL injection and XSS
HTTPS and secure sessions
12. Advanced PHP Topics
PHP with AJAX
REST APIs in PHP
MVC Frameworks like Laravel and CodeIgniter
Composer and dependency management
Popular Platforms Offering PHP Online Courses
Here are some of the best platforms where you can learn PHP online:
1. Udemy
Udemy offers a wide range of PHP courses for all levels. Courses like “PHP for Beginners” and “Object-Oriented PHP & MVC” are among the top-rated, featuring lifetime access and a certificate upon completion.
2. Coursera
Partnering with universities and colleges, Coursera offers structured PHP programs. You can audit most courses for free or pay to receive a certification. A good example is the Web Applications for Everybody course from the University of Michigan.
3. edX
edX features PHP-related content through universities like Harvard and MIT. Though primarily focused on computer science and web development, several PHP courses are included under broader programming paths.
4. LinkedIn Learning
LinkedIn Learning provides bite-sized PHP lessons with project-based learning. A subscription gives access to multiple courses, helpful if you're pursuing more than just PHP.
5. FreeCodeCamp and W3Schools
Both platforms are excellent for beginners who want to explore PHP basics for free. W3Schools, in particular, is well-known for its hands-on “Try It Yourself” editor.
Who Should Take a PHP Online Course?
1. Beginners in Web Development
If you're new to coding and want to start with a language that's widely used and beginner-friendly, PHP is a great option.
2. Students and Computer Science Graduates
Learning PHP alongside HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can give you a competitive edge when applying for internships or junior developer roles.
3. Freelancers and Entrepreneurs
If you're planning to build your own website or work on client projects, PHP enables you to create dynamic, database-driven websites quickly.
4. Working Professionals
Developers who want to expand their backend skills or transition into full-stack development will benefit significantly from PHP expertise.
Career Opportunities After Learning PHP
Once you complete a PHP online course, several doors open for your professional growth:
Web Developer: Design and build dynamic websites.
Backend Developer: Manage server-side logic and database interactions.
Full-Stack Developer: Handle both frontend and backend tasks.
WordPress Developer: Customize and develop plugins/themes using PHP.
Freelance Developer: Build and manage websites for clients.
According to recent job market statistics, PHP developers earn an average salary of $60,000–$90,000 annually, depending on experience, location, and industry.
Tips for Success in an Online PHP Course
Set Clear Goals: Decide whether you’re learning for a job, freelance projects, or personal growth.
Practice Regularly: The best way to learn coding is by doing it. Practice through exercises and mini-projects.
Join Online Communities: Platforms like Stack Overflow, Reddit, and GitHub can help you learn collaboratively.
Work on Real Projects: Apply what you learn by building real-world applications—this boosts your confidence and portfolio.
Keep Up With Updates: PHP continues to evolve (e.g., PHP 8.x versions), so staying updated ensures your skills remain relevant.
Conclusion
PHP remains a cornerstone of modern web development, and mastering it through an online course is an effective, convenient, and affordable way to jumpstart or advance your programming journey. With comprehensive learning resources, expert instructors, and real-world projects, PHP online courses provide everything you need to build robust, scalable, and dynamic websites.
Whether you're starting from scratch or adding PHP to your skillset, now is the perfect time to enroll and harness the power of this essential language.
#php online course#PHP Training in Chandigarh#Python Training in Chandigarh#CCNA Training in Chandigarh#MERN Stack Training in Chandigarh
0 notes
Text
Array no PHP Criando e iterando
Array no PHP Criando e iterando
Array no PHP Criando e iterando
Array no PHP é uma estrutura que relaciona valores e chaves, é uma lista de valores armazenados na memória.
Um array em PHP é equivalente ao conceito de vetor normalmente ensinado nas faculdades. Outro conceito que se asemelha é o conceito de matriz, equivale a um array multidimensional (um array composto de outros array’s). (more…)
View On WordPress
#array#array php#array php 7#array php a xml#array php add first#array php add item#array php ajax#array php foreach#array php functions#array php insert#array php to javascript#array_push php#PHP#programação
0 notes
Text
Php training course
PHP Course Overview
PHP is a widely-used general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for Web development and can be embedded into HTML.
PHP can generate the dynamic page content
PHP can create, open, read, write, and close files on the server
PHP can collect form data
PHP can send and receive cookies
PHP can add, delete, modify data in your database
PHP can restrict users to access some pages on your website
PHP can encrypt data
With PHP you are not limited to output HTML. You can output images, PDF files, and even Flash movies. You can also output any text, such as XHTML and XML.
PHP Training Course Prerequisite
HTML
CSS
Javascript
Objectives of the Course
PHP runs on different platforms (Windows, Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, etc.)
PHP is compatible with almost all servers used today (Apache, IIS, etc.)
PHP has support for a wide range of databases
PHP is free. Download it from the official PHP resource: www.php.net
PHP is easy to learn and runs efficiently on the server-side
PHP Training Course Duration
45 Working days, daily 1.30 hours
PHP Training Course Overview
An Introduction to PHP
History of PHP
Versions and Differences between them
Practicality
Power
Installation and configuring Apache and PHP
PHP Basics
Default Syntax
Styles of PHP Tags
Comments in PHP
Output functions in PHP
Datatypes in PHP
Configuration Settings
Error Types
Variables in PHP
Variable Declarations
Variable Scope
PHP’s Superglobal Variables
Variable Variables
Constants in PHP
Magic Constants
Standard Pre-defined Constants
Core Pre-defined Languages
User-defined Constants
Control Structures
Execution Control Statements
Conditional Statements
Looping Statements with Real-time Examples
Functions
Creating Functions
Passing Arguments by Value and Reference
Recursive Functions
Arrays
What is an Array?
How to create an Array
Traversing Arrays
Array Functions
Include Functions
Include, Include_once
Require, Require_once
Regular Expressions
Validating text boxes,emails,phone number,etc
Creating custom regular expressions
Object-Oriented Programming in PHP
Classes, Objects, Fields, Properties, _set(), Constants, Methods
Encapsulation
Inheritance and types
Polymorphism
Constructor and Destructor
Static Class Members, Instance of Keyword, Helper Functions
Object Cloning and Copy
Reflections
PHP with MySQL
What is MySQL
Integration with MySQL
MySQL functions
Gmail Data Grid options
SQL Injection
Uploading and downloading images in Database
Registration and Login forms with validations
Pegging, Sorting,…..
Strings and Regular Expressions
Declarations styles of String Variables
Heredoc style
String Functions
Regular Expression Syntax(POSIX)
PHP’s Regular Expression Functions(POSIX Extended)
Working with the Files and Operating System
File Functions
Open, Create and Delete files
Create Directories and Manipulate them
Information about Hard Disk
Directory Functions
Calculating File, Directory and Disk Sizes
Error and Exception Handling
Error Logging
Configuration Directives
PHP’s Exception Class
Throw New Exception
Custom Exceptions
Date and Time Functions
Authentication
HTTP Authentication
PHP Authentication
Authentication Methodologies
Cookies
Why Cookies
Types of Cookies
How to Create and Access Cookies
Sessions
Session Variables
Creating and Destroying a Session
Retrieving and Setting the Session ID
Encoding and Decoding Session Data
Auto-Login
Recently Viewed Document Index
Web Services
Why Web Services
RSS Syntax
SOAP
How to Access Web Services
XML Integration
What is XML
Create an XML file from PHP with Database records
Reading Information from XML File
MySQL Concepts
Introduction
Storage Engines
Functions
Operators
Constraints
DDL commands
DML Commands
DCL Command
TCL Commands
Views
Joins
Cursors
Indexing
Stored Procedures
Mysql with PHP Programming
Mysql with Sqlserver(Optional)
SPECIAL DELIVERY
Protocols
HTTP Headers and types
Sending Mails using PHP
Email with Attachment
File Uploading and Downloading using Headers
Implementing Chating Applications using PHP
and Ajax
SMS Gateways and sending SMS to Mobiles
Payments gateways and How to Integrate them
With Complete
MVC Architecture
DRUPAL
JOOMLA
Word Press
AJAX
CSS
JQUERY (Introduction and few plugins only)
1 note
·
View note
Link
PHP Regular Expressions with examples, php file, php session, php date, php array, php form, functions, time, xml, ajax, php mysql, regex, string, oop, addslashes(), addcslashes() etc.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Getting Web Hosting Services That Meet All Your Business Needs

Web hosting has become a necessary addition to any business owner who wants to experience a high level of internet presence. With the rate of online business competition on the high, there is an increased pressure for online businesses to create a cutting edge over competitors. With several web hosting India companies coming up, it is therefore important to ensure that you get one that offers services that auger well with your business needs in order to reap maximum benefits from the venture. There are several packages offered through web hosting India companies and for this reason, it is important to know what you need before making your purchase. See it here email hosting india
Linux Web Hosting This is ranked among one of the hosting packages you can get. It has different features and catered to meet different business needs and for this reason, it is ideal to consider what suits you best. By choosing this plan, some of the features you get to enjoy include unlimited web space and monthly bandwidth. You also get other supported features such as Perl, SSI, PH4 &5, flash, GD, Curl and Cron among others. It is important to note that all these features are unlimited. There are other package details, which will also be incorporated in the Linux web hosting plan such as full support of the website, instant backups, sub domains and RAID1 Disk among others. If you are interested in this plan, it comes in 3 major plans, which include silver plan, which is charged at $ 35.44, Gold plan at $ 71 and Diamond plan at $ 133.22. Note that these are yearly rates.
Windows Hosting This is another package availed through Web hosting India. It comes with 3 plans, which include the Starter plan, which costs $ 37.67, Basic plan costing $ 73.22 and Professional plan costing $ 133.22 per year. There are several package details included here such as getting sub domains, an uptime of 99.9%, support that is free and RAID1 disk. What is more, there are also supported features in this package such as Ajax, FTP, CGI-Bin, PHP 4/5 and ASP among others. Note that you will also get some email features and control panel features, which are easy to use and designed to make your work easier.
Reseller Hosting With reseller hosting, you have the opportunity to get packages that are based on your needs. These are categorized in different mannerisms and there are certain features that determine what you are looking for. For instance, it could be based on the web space needed, the MySQL databases, FTP accounts and sub domains among others. It also comes with supported features, email settings and control panel features. To cap it all, there is also e-commerce features incorporated in this.
These are just some of the packages you can get through web hosting India. It is important to note that it gives you an endless array of packages to choose from and this is among the major reasons that it is considered ideal for business owners who are looking for diversity. What is more, it is important to note that web hosting India can also tailor the packages to meet the needs of your business.
1 note
·
View note
Photo
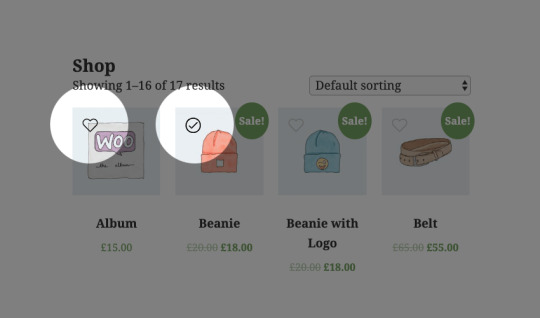
How to Create Your Own AJAX WooCommerce Wishlist Plugin
In this tutorial we will create lightweight wishlist functionality for WooCommerce using AJAX, WordPress REST API, and SVG graphics. WooCommerce doesn’t come with wishlist functionality as standard, so you’ll always need to rely on an extension to do the work for you. Unless you build it yourself for complete control..
Wish Upon a Star
Wishlist functionality will allow users to mark certain products, adding them to a list for future reference. In some eCommerce stores (such as Amazon) multiple wishlists can be created, and these can be shared with others, which makes them ideal for birthdays or weddings. In our case, the WooCommerce wishlist we’re going to create will enable customers to easily revisit products they’re considering.
Our wishlist functionality will add a heart icon to the product thumbs, which when clicked will add the product to a wishlist in a table.
Click the heart icon to add a product to the wishlist
Take a look at the demo for a proper idea of how it works.
1. Create the Plugin Structure
Let’s start by building our plugin. Create a folder with the name “wishlist” and a PHP file with the same name. Add the following snippet to the PHP file:
/* Plugin Name: Woocommerce wishlist Plugin URI: https://www.enovathemes.com Description: Ajax wishlist for WooCommerce Author: Enovathemes Version: 1.0 Author URI: http://enovathemes.com */ if ( ! defined( 'ABSPATH' ) ) { exit; // Exit if accessed directly }
We won’t go into detail about the plugin creation process, but if you are new to plugin development I highly recommend this amazing new course by Rachel McCollin:
WordPress
Introduction to WordPress Plugin Development
Rachel McCollin
Add the Plugin Functions
Let’s sketch out our plan so we know what to build:
Add wishlist toggle to products in loop and single pages using WooCommerce hooks
Create wishlist table shortcode to hold the products added to the wishlist
Create wishlist custom option in the user profile
All the plugin code will go inside the init action for the plugin, as we first need to make sure that the WooCommerce plugin is active. So right after the plugin details add the following code:
add_action('init','plugin_init'); function plugin_init(){ if (class_exists("Woocommerce")) { // Code here } }
And now let’s enqueue our plugin scripts and styles.
Add the following code to the main plugin file:
function wishlist_plugin_scripts_styles(){ wp_enqueue_style( 'wishlist-style', plugins_url('/css/style.css', __FILE__ ), array(), '1.0.0' ); wp_enqueue_script( 'wishlist-main', plugins_url('/js/main.js', __FILE__ ), array('jquery'), '', true); wp_localize_script( 'main', 'opt', array( 'ajaxUrl' => admin_url('admin-ajax.php'), 'ajaxPost' => admin_url('admin-post.php'), 'restUrl' => rest_url('wp/v2/product'), 'shopName' => sanitize_title_with_dashes(sanitize_title_with_dashes(get_bloginfo('name'))), 'inWishlist' => esc_html__("Already in wishlist","text-domain"), 'removeWishlist' => esc_html__("Remove from wishlist","text-domain"), 'buttonText' => esc_html__("Details","text-domain"), 'error' => esc_html__("Something went wrong, could not add to wishlist","text-domain"), 'noWishlist' => esc_html__("No wishlist found","text-domain"), ) ); } add_action( 'wp_enqueue_scripts', 'wishlist_plugin_scripts_styles' );
Here we enqueue the main style.css file and the main.js file for the plugin, also we pass some parameters to the main.js file to work with:
ajaxUrl – required to fetch some data from WordPress, like current User ID
ajaxPost – required to update user wishlist
restUrl – required to list the wishlist items in the wishlist table
shopName – required to add wishlist items to the session storage for non-registered or non-logged-in users
And some strings instead of hardcoding them into the js file, in case they need to be translatable.
So for now create a css, and js folder and put the corresponding files inside those folders: style.css in the css folder and main.js in the js folder.
2. Hook the Wishlist Toggle
Right inside the init action add the following code:
// Add wishlist to product add_action('woocommerce_before_shop_loop_item_title','wishlist_toggle',15); add_action('woocommerce_single_product_summary','wishlist_toggle',25); function wishlist_toggle(){ global $product; echo '<span class="wishlist-title">'.esc_attr__("Add to wishlist","text-domain").'</span><a class="wishlist-toggle" data-product="'.esc_attr($product->get_id()).'" href="#" title="'.esc_attr__("Add to wishlist","text-domain").'">'.file_get_contents(plugins_url( 'images/icon.svg', __FILE__ )).'</a>'; }
Here we add a wishlist toggle to each product in the loop and to each single product layout, using the woocommerce_before_shop_loop_item_title and woocommerce_single_product_summary hooks.
Here I want to point out the data-product attribute that contains the product ID–this is required to power the wishlist functionality. And also take a closer look at the SVG icon–this is required to power the animation.
3. Add SVG Icons
Now create an images folder in the plugin folder and put the following icon.svg in it:
<svg viewBox="0 0 471.701 471.701"> <path class="heart" d="M433.601,67.001c-24.7-24.7-57.4-38.2-92.3-38.2s-67.7,13.6-92.4,38.3l-12.9,12.9l-13.1-13.1 c-24.7-24.7-57.6-38.4-92.5-38.4c-34.8,0-67.6,13.6-92.2,38.2c-24.7,24.7-38.3,57.5-38.2,92.4c0,34.9,13.7,67.6,38.4,92.3 l187.8,187.8c2.6,2.6,6.1,4,9.5,4c3.4,0,6.9-1.3,9.5-3.9l188.2-187.5c24.7-24.7,38.3-57.5,38.3-92.4 C471.801,124.501,458.301,91.701,433.601,67.001z M414.401,232.701l-178.7,178l-178.3-178.3c-19.6-19.6-30.4-45.6-30.4-73.3 s10.7-53.7,30.3-73.2c19.5-19.5,45.5-30.3,73.1-30.3c27.7,0,53.8,10.8,73.4,30.4l22.6,22.6c5.3,5.3,13.8,5.3,19.1,0l22.4-22.4 c19.6-19.6,45.7-30.4,73.3-30.4c27.6,0,53.6,10.8,73.2,30.3c19.6,19.6,30.3,45.6,30.3,73.3 C444.801,187.101,434.001,213.101,414.401,232.701z"/> <g class="loading"> <path d="M409.6,0c-9.426,0-17.067,7.641-17.067,17.067v62.344C304.667-5.656,164.478-3.386,79.411,84.479 c-40.09,41.409-62.455,96.818-62.344,154.454c0,9.426,7.641,17.067,17.067,17.067S51.2,248.359,51.2,238.933 c0.021-103.682,84.088-187.717,187.771-187.696c52.657,0.01,102.888,22.135,138.442,60.976l-75.605,25.207 c-8.954,2.979-13.799,12.652-10.82,21.606s12.652,13.799,21.606,10.82l102.4-34.133c6.99-2.328,11.697-8.88,11.674-16.247v-102.4 C426.667,7.641,419.026,0,409.6,0z"/> <path d="M443.733,221.867c-9.426,0-17.067,7.641-17.067,17.067c-0.021,103.682-84.088,187.717-187.771,187.696 c-52.657-0.01-102.888-22.135-138.442-60.976l75.605-25.207c8.954-2.979,13.799-12.652,10.82-21.606 c-2.979-8.954-12.652-13.799-21.606-10.82l-102.4,34.133c-6.99,2.328-11.697,8.88-11.674,16.247v102.4 c0,9.426,7.641,17.067,17.067,17.067s17.067-7.641,17.067-17.067v-62.345c87.866,85.067,228.056,82.798,313.122-5.068 c40.09-41.409,62.455-96.818,62.344-154.454C460.8,229.508,453.159,221.867,443.733,221.867z"/> </g> <g class="check"> <path d="M238.933,0C106.974,0,0,106.974,0,238.933s106.974,238.933,238.933,238.933s238.933-106.974,238.933-238.933 C477.726,107.033,370.834,0.141,238.933,0z M238.933,443.733c-113.108,0-204.8-91.692-204.8-204.8s91.692-204.8,204.8-204.8 s204.8,91.692,204.8,204.8C443.611,351.991,351.991,443.611,238.933,443.733z"/> <path d="M370.046,141.534c-6.614-6.388-17.099-6.388-23.712,0v0L187.733,300.134l-56.201-56.201 c-6.548-6.78-17.353-6.967-24.132-0.419c-6.78,6.548-6.967,17.353-0.419,24.132c0.137,0.142,0.277,0.282,0.419,0.419 l68.267,68.267c6.664,6.663,17.468,6.663,24.132,0l170.667-170.667C377.014,158.886,376.826,148.082,370.046,141.534z"/> </g> </svg>
If you are new to working with SVGs I highly recommend you read these amazing tutorials on the subject:
SVG
How to Hand Code SVG
Kezz Bracey
SVG
SVG Viewport and viewBox (For Complete Beginners)
Kezz Bracey
Our SVG animation has 3 states:
Default: the heart path
Process: loading group (g tag)
End: check group (g tag)
If you now go to your shop page you will see the unstyled SVG icons piled on top of each other:
Let’s add some styling to fix this mess! Open the style.css file and paste the following code:
.wishlist-toggle { display: block; position: absolute; top: 16px; left: 16px; z-index: 5; width: 24px; height: 24px; outline: none; border:none; } .wishlist-title { display: none; } .entry-summary .wishlist-toggle { position: relative; top: 0; left: 0; display: inline-block; vertical-align: middle; margin-bottom: 8px; } .entry-summary .wishlist-title { display: inline-block; vertical-align: middle; margin-right: 8px; margin-bottom: 8px; } .wishlist-toggle:focus { outline: none; border:none; } .wishlist-toggle svg { fill:#bdbdbd; transition: all 200ms ease-out; } .wishlist-toggle:hover svg, .wishlist-toggle.active svg { fill:#000000; } .wishlist-toggle svg .loading, .wishlist-toggle svg .check { opacity: 0; } .wishlist-toggle.active svg .check { opacity: 1; } .wishlist-toggle.active svg .heart { opacity: 0; } .wishlist-toggle.loading svg .loading, .wishlist-table.loading:before { animation:loading 500ms 0ms infinite normal linear; transform-origin: center; opacity: 1; } .wishlist-toggle.loading svg .heart { opacity:0; } @keyframes loading { from {transform: rotate(0deg);} to {transform: rotate(360deg);} }
The logic here is as follows:
Initially we show the heart path of our SVG.
When the user clicks on it we will hide the heart path and show the loading path.
Once the loading finishes we will show the checkmark indicating that the product was successfully added to the wishlist.
We will toggle the loading state via JavaScript later; the loading animation is a simple transform rotate. So for now if you refresh the page (don’t forget to clear the browser cache as sometimes old styles are cached) you will see a nice heart icon with each product.
This toggle currently does nothing, so we’ll sort that out. But for now let’s keep with our plan.
4. Create Wishlist Table Shortcode
Add the following code in the init plugin action:
// Wishlist table shortcode add_shortcode('wishlist', 'wishlist'); function wishlist( $atts, $content = null ) { extract(shortcode_atts(array(), $atts)); return '<table class="wishlist-table loading"> <tr> <th><!-- Left for image --></th> <th>'.esc_html__("Name","text-domain").'</th> <th>'.esc_html__("Price","text-domain").'</th> <th>'.esc_html__("Stock","text-domain").'</th> <th><!-- Left for button --></th> </tr> </table>'; }
This is a very simple shortcode that you can add to any page, and the wishlist items will appear inside it. I won’t describe the shortcode creation process, but if you are new to this, I highly recommend reading this amazing tutorial:
Plugins
Getting Started With WordPress Shortcodes
Rohan Mehta
Make a Wishlist Page
Now from inside the WP admin create a page called “Wishlist” and put the [wishlist] shortcode inside it. Now if you go to the wishlist page you will see an empty table.
Did you notice the loading class on the table? We will remove the loading class with JavaScript later, once the wishlist items are ready to be appended to the table. But for now open the style.css and add the following code:
.wishlist-table { width:100%; position: relative; } .wishlist-table.loading:after { display: block; width: 100%; height: 100%; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; content: ""; background: #ffffff; opacity: 0.5; z-index: 5; } .wishlist-table.loading:before { display: block; width: 24px; height: 24px; position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; margin-top:-12px; margin-left:-12px; content: ""; background-image: url('../images/loading.svg'); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-size: 100%; z-index: 6; } .wishlist-table td { position: relative; } .wishlist-table a.details { padding:4px 16px; background: #000000; color: #ffffff; text-align: center; border:none !important } .wishlist-table a.wishlist-remove { display: block; width: 24px; height: 24px; position: absolute; top: 50%; left: 50%; margin-top:-12px; margin-left:-12px; background-image: url('../images/remove.svg'); background-repeat: no-repeat; background-size: 100%; z-index: 6; border:none; opacity:0; } .wishlist-table td:hover > a.wishlist-remove { opacity:1; }
Add the loading.svg image to the images folder:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" viewBox="0 0 471.701 471.701"> <path d="M409.6,0c-9.426,0-17.067,7.641-17.067,17.067v62.344C304.667-5.656,164.478-3.386,79.411,84.479 c-40.09,41.409-62.455,96.818-62.344,154.454c0,9.426,7.641,17.067,17.067,17.067S51.2,248.359,51.2,238.933 c0.021-103.682,84.088-187.717,187.771-187.696c52.657,0.01,102.888,22.135,138.442,60.976l-75.605,25.207 c-8.954,2.979-13.799,12.652-10.82,21.606s12.652,13.799,21.606,10.82l102.4-34.133c6.99-2.328,11.697-8.88,11.674-16.247v-102.4 C426.667,7.641,419.026,0,409.6,0z"/> <path d="M443.733,221.867c-9.426,0-17.067,7.641-17.067,17.067c-0.021,103.682-84.088,187.717-187.771,187.696 c-52.657-0.01-102.888-22.135-138.442-60.976l75.605-25.207c8.954-2.979,13.799-12.652,10.82-21.606 c-2.979-8.954-12.652-13.799-21.606-10.82l-102.4,34.133c-6.99,2.328-11.697,8.88-11.674,16.247v102.4 c0,9.426,7.641,17.067,17.067,17.067s17.067-7.641,17.067-17.067v-62.345c87.866,85.067,228.056,82.798,313.122-5.068 c40.09-41.409,62.455-96.818,62.344-154.454C460.8,229.508,453.159,221.867,443.733,221.867z"/> </svg>
This is the same loading SVG separated from the main icon.svg. We could use SVG sprites, but I decided to stick with a separate loading SVG.
Now, if you go to the wishlist page and refresh it you will see an empty table with loading on it. Nice, let’s move further.
5. Wishlist Custom Option in the User Profile
Our wishlist functionality will work both for logged-in users and guest users. With logged-in users we’ll store the wishlist information in the user’s metadata, and with guest users we’ll store the wishlist in the session storage.
You can also store the guest users’ wishlist in local storage, the difference being that session storage is destroyed when the user closes the tab or browser, and local storage is destroyed when the browser cache is cleared. It is up to you which option you use for guest users.
Now add the following code to the init action:
// Wishlist option in the user profile add_action( 'show_user_profile', 'wishlist_user_profile_field' ); add_action( 'edit_user_profile', 'wishlist_user_profile_field' ); function wishlist_user_profile_field( $user ) { ?> <table class="form-table wishlist-data"> <tr> <th><?php echo esc_attr__("Wishlist","text-domain"); ?></th> <td> <input type="text" name="wishlist" id="wishlist" value="<?php echo esc_attr( get_the_author_meta( 'wishlist', $user->ID ) ); ?>" class="regular-text" /> </td> </tr> </table> <?php } add_action( 'personal_options_update', 'save_wishlist_user_profile_field' ); add_action( 'edit_user_profile_update', 'save_wishlist_user_profile_field' ); function save_wishlist_user_profile_field( $user_id ) { if ( !current_user_can( 'edit_user', $user_id ) ) { return false; } update_user_meta( $user_id, 'wishlist', $_POST['wishlist'] ); }
Again, in order to remain within the scope of this tutorial, I won’t explain how to work with user metadata. If you are new to this I highly recommend reading this amazing tutorial:
WordPress
How to Work With WordPress User Metadata
Tom McFarlin
All we do here is create a text field input that will hold the wishlist items comma-separated IDs. With show_user_profile and edit_user_profile actions we add the structure of the input field, and with personal_options_update and edit_user_profile_update actions we power the save functionality.
So once the wishlist is updated it will save to the database. I you go to your profile page you will see a new text field added to it. Add whatever value you want and hit save to test if the update functionality works. With admin CSS you can hide this field if you don’t want users to see it. I will leave it as is.
6. Turn it On!
Now we are ready to power everything up!
Open the main.js file and put the following code in it:
(function($){ "use strict"; })(jQuery);
All our code will go inside this function.
Now let’s gather the required data and create some variables:
var shopName = opt.shopName+'-wishlist', inWishlist = opt.inWishlist, restUrl = opt.restUrl, wishlist = new Array, ls = sessionStorage.getItem(shopName), loggedIn = ($('body').hasClass('logged-in')) ? true : false, userData = '';
As you might remember when we enqueued our main.js script we passed some parameters to it. Here, with JavaScript, we can collect these parameters.
Next, we will create an empty wishlist array that will contains wishlist items. We will need the session storage data with our shop name (the ls variable stands for local storage), and we will need to know if the user is guest or logged-in.
Let me explain the logic here: whenever the user visits the shop page we will need to know if he or she is logged-in or is a guest-user. If the user is logged-in we will need to check if he or she has wishlist items, and if so highlight these items. If not we need to see if there are any items in the session/local storage and highlight those.
Why this is done like this? Imagine, if the user first visits the website as a guest, adds items to the wishlist, and then decides to login. If the user does not have items registered in the profile wishlist, we will need to show the ones that he or she added before login, that are stored in the session/local storage.
So let’s do that step by step:
If User is Logged-in
Fetch current user data with AJAX
If success update the wishlist
Highlight the wishlist items
Remove the session/local storage
If fail show error message in the console for the developer
if(loggedIn) { // Fetch current user data $.ajax({ type: 'POST', url: opt.ajaxUrl, data: { 'action' : 'fetch_user_data', 'dataType': 'json' }, success:function(data) { userData = JSON.parse(data); if (typeof(userData['wishlist']) != 'undefined' && userData['wishlist'] != null && userData['wishlist'] != "") { var userWishlist = userData['wishlist']; userWishlist = userWishlist.split(','); if (wishlist.length) { wishlist = wishlist.concat(userWishlist); $.ajax({ type: 'POST', url:opt.ajaxPost, data:{ action:'user_wishlist_update', user_id :userData['user_id'], wishlist :wishlist.join(','), } }); } else { wishlist = userWishlist; } wishlist = wishlist.unique(); highlightWishlist(wishlist,inWishlist); sessionStorage.removeItem(shopName); } else { if (typeof(ls) != 'undefined' && ls != null) { ls = ls.split(','); ls = ls.unique(); wishlist = ls; } $.ajax({ type: 'POST', url:opt.ajaxPost, data:{ action:'user_wishlist_update', user_id :userData['user_id'], wishlist :wishlist.join(','), } }) .done(function(response) { highlightWishlist(wishlist,inWishlist); sessionStorage.removeItem(shopName); }); } }, error: function(){ console.log('No user data returned'); } }); }
If User is Guest
Fetch wishlist from the session/local storage
else { if (typeof(ls) != 'undefined' && ls != null) { ls = ls.split(','); ls = ls.unique(); wishlist = ls; } }
As you may have noticed here we have double-AJAX and some helper functions. So first let’s create the actions of the AJAX requests, and after that I will explain our helper functions. I won’t describe in detail the AJAX functionality in WordPress, but if you are new to AJAX and WordPress, I highly recommend reading this amazing tutorial on it:
Plugins
A Primer on Ajax in the WordPress Frontend: Understanding the Process
Tom McFarlin
Our first AJAX request gets the user id and the user wishlist data from WordPress. This is done with a custom AJAX action added to the plugin code file:
// Get current user data function fetch_user_data() { if (is_user_logged_in()){ $current_user = wp_get_current_user(); $current_user_wishlist = get_user_meta( $current_user->ID, 'wishlist',true); echo json_encode(array('user_id' => $current_user->ID,'wishlist' => $current_user_wishlist)); } die(); } add_action( 'wp_ajax_fetch_user_data', 'fetch_user_data' ); add_action( 'wp_ajax_nopriv_fetch_user_data', 'fetch_user_data' );
The most important part here is the action name (fetch_user_data)–make sure it is the same for AJAX and for functions wp_ajax_fetch_user_data and wp_ajax_nopriv_fetch_user_data. Here we’re preparing JSON formatted data with user ID and user wishlist data.
Our next AJAX request updates the user wishlist if there were already wishlist items from session/local storage. Take a close look at the url option–see it is different.
The logic is the same as for the first action–the difference is that here we don’t return or echo any data, but we update the wishlist option for the current user.
function update_wishlist_ajax(){ if (isset($_POST["user_id"]) && !empty($_POST["user_id"])) { $user_id = $_POST["user_id"]; $user_obj = get_user_by('id', $user_id); if (!is_wp_error($user_obj) && is_object($user_obj)) { update_user_meta( $user_id, 'wishlist', $_POST["wishlist"]); } } die(); } add_action('admin_post_nopriv_user_wishlist_update', 'update_wishlist_ajax'); add_action('admin_post_user_wishlist_update', 'update_wishlist_ajax');
And if our user is a guest we will need to check if there are any wishlist details in the session/local storage.
Helper Functions
Before we move to the events part I want to explain our helper functions
Array.prototype.unique = function() { return this.filter(function (value, index, self) { return self.indexOf(value) === index; }); } function isInArray(value, array) {return array.indexOf(value) > -1;} function onWishlistComplete(target, title){ setTimeout(function(){ target .removeClass('loading') .addClass('active') .attr('title',title); },800); } function highlightWishlist(wishlist,title){ $('.wishlist-toggle').each(function(){ var $this = $(this); var currentProduct = $this.data('product'); currentProduct = currentProduct.toString(); if (isInArray(currentProduct,wishlist)) { $this.addClass('active').attr('title',title); } }); }
The first helper function makes the array unique, by removing duplicates, the second one checks if the given value is present in the given array. The next function executes when an item is added to the wishlist and the last one shows items that are in the wishlist.
Add Toggle
Now let’s add a click event to the wishlist toggle to power the actual functionality. On each toggle click event the animation is triggered and if the user is logged-in the wishlist update action fires with AJAX. If the user is a guest the item is added to the session/local storage.
Now if you go to the shop page, refresh the browser, and click on any wishlist toggle you will see it is working!
$('.wishlist-toggle').each(function(){ var $this = $(this); var currentProduct = $this.data('product'); currentProduct = currentProduct.toString(); if (!loggedIn && isInArray(currentProduct,wishlist)) { $this.addClass('active').attr('title',inWishlist); } $(this).on('click',function(e){ e.preventDefault(); if (!$this.hasClass('active') && !$this.hasClass('loading')) { $this.addClass('loading'); wishlist.push(currentProduct); wishlist = wishlist.unique(); if (loggedIn) { // get user ID if (userData['user_id']) { $.ajax({ type: 'POST', url:opt.ajaxPost, data:{ action:'user_wishlist_update', user_id :userData['user_id'], wishlist :wishlist.join(','), } }) .done(function(response) { onWishlistComplete($this, inWishlist); }) .fail(function(data) { alert(opt.error); }); } } else { sessionStorage.setItem(shopName, wishlist.toString()); onWishlistComplete($this, inWishlist); } } }); });
7. List Items in Wishlist Table
Now it is time to list our wishlist items in the wishlist table we created earlier.
Add the following code into main.js at the very bottom of our wrapper function:
setTimeout(function(){ if (wishlist.length) { restUrl += '?include='+wishlist.join(','); restUrl += '&per_page='+wishlist.length; $.ajax({ dataType: 'json', url:restUrl }) .done(function(response){ $('.wishlist-table').each(function(){ var $this = $(this); $.each(response,function(index,object){ $this.append('<tr data-product="'+object.id+'"><td><a class="wishlist-remove" href="#" title="'+opt.removeWishlist+'"></a>'+object.image+'</td><td>'+object.title["rendered"]+'</td><td>'+object.price+'</td><td>'+object.stock+'</td><td><a class="details" href="'+object.link+'">'+opt.buttonText+'</a></td></tr>'); }); }); }) .fail(function(response){ alert(opt.noWishlist); }) .always(function(response){ $('.wishlist-table').each(function(){ $(this).removeClass('loading'); }); }); } else { $('.wishlist-table').each(function(){ $(this).removeClass('loading'); }); } },1000);
Here we are using the WordPress REST API to get the products by ID in the wishlist array.
For each of the products we get we are adding a table row with the required data to display. We need the product image, title, stock status, button and price.
Here we have two options for the REST API:
using the WordPress REST API
using the WooCommerce REST API.
The difference here is that product data is already present in the Woocommerce REST API, but an API key is required. With the default WordPress REST API product data is absent by default, but can be added, and no API key is required. For such a simple task as a wishlist I don’t think that an API key is needed, so we will do it by extending the default WordPress REST API to return our product price, image code and the stock level.
Go to the main plugin file and at the very bottom add the following code:
// Extend REST API function rest_register_fields(){ register_rest_field('product', 'price', array( 'get_callback' => 'rest_price', 'update_callback' => null, 'schema' => null ) ); register_rest_field('product', 'stock', array( 'get_callback' => 'rest_stock', 'update_callback' => null, 'schema' => null ) ); register_rest_field('product', 'image', array( 'get_callback' => 'rest_img', 'update_callback' => null, 'schema' => null ) ); } add_action('rest_api_init','rest_register_fields'); function rest_price($object,$field_name,$request){ global $product; $id = $product->get_id(); if ($id == $object['id']) { return $product->get_price(); } } function rest_stock($object,$field_name,$request){ global $product; $id = $product->get_id(); if ($id == $object['id']) { return $product->get_stock_status(); } } function rest_img($object,$field_name,$request){ global $product; $id = $product->get_id(); if ($id == $object['id']) { return $product->get_image(); } } function maximum_api_filter($query_params) { $query_params['per_page']["maximum"]=100; return $query_params; } add_filter('rest_product_collection_params', 'maximum_api_filter');
All this does is create new fields for REST API and extends the maximum items limit per request. Again, if you are new to this subject I highly recommend reading this series.
For now, if you go to your wishlist table and refresh the page you will see the list of items that are added to your wishlist.
8. Removing Items From Wishlist
We are almost done; only the remove functionality remains. So let’s create that! Add the following code at the very bottom of the wrapper function in the main.js file
$(document).on('click', '.wishlist-remove', function(){ var $this = $(this); $this.closest('table').addClass('loading'); wishlist = []; $this.closest('table').find('tr').each(function(){ if ($(this).data('product') != $this.closest('tr').data('product')) { wishlist.push($(this).data('product')); if (loggedIn) { // get user ID if (userData['user_id']) { $.ajax({ type: 'POST', url:opt.ajaxPost, data:{ action:'user_wishlist_update', user_id :userData['user_id'], wishlist :wishlist.join(','), } }) .done(function(response) { $this.closest('table').removeClass('loading'); $this.closest('tr').remove(); }) .fail(function(data) { alert(opt.error); }); } } else { sessionStorage.setItem(shopName, wishlist.toString()); setTimeout(function(){ $this.closest('table').removeClass('loading'); $this.closest('tr').remove(); },500); } } }); });
Once the remove icon is clicked (make sure you have a remove.svg in the images folder, you can use whatever icon you want), we need to check if the user is logged-in. If so, we then remove the item ID from the wishlist using AJAX with the user_wishlist_update action. If the user is a guest we need to remove the item ID from the session/local storage.
Now go to your wishlist and refresh the page. Once you click on the remove icon your item will be removed from the wishlist.
Conclusion
That was quite a project! A simple, but comprehensive wishlist feature for your WooCommerce stores. You are free to use this plugin in any project; you can extend, modify it and make suggestions. I hope you liked it. Here is the link to the source files on GitHub. And here is the demo.
Learn More WooCommerce Theme Development
At Tuts+ we have a great collection of tutorials and courses to learn WooCommerce development. Check out these four great courses to get started!
WooCommerce
Up and Running With WooCommerce
Rachel McCollin
WordPress
Developing a WooCommerce Theme
Rachel McCollin
WordPress
Go Further With WooCommerce Themes
Rachel McCollin
WordPress
How to Make Your Theme WooCommerce Compatible
Rachel McCollin
by Karen Pogosyan via Envato Tuts+ Code https://ift.tt/2WTWfiG
1 note
·
View note
Text
jQuery Dependent DropDown List – States and Districts Using PHP-PDO

In this tutorial, we are going to learn how to change the district dropdown list option based on the selected state name using PHP-PDO.
In this example, we have two dropdowns for listing states and districts. On changing states drop-down values, the corresponding district dropdown values will be loaded dynamically using jQuery AJAX.
Click: https://phpgurukul.com/jquery-dependent-dropdown-list-states-and-districts-using-php-pdo/
File structure for this tutorial
config.php — Database connection file.
index.php — Main file having drop down
get_district.php — used to retrieve the district based on the selected state name.
MySQL Database structure for this tutorial
In this tutorial two MySQL Database table is used.
state
district
state table structure
CREATE TABLE `state` (
`StCode` int(11) NOT NULL,
`StateName` varchar(150) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
district table structure
CREATE TABLE `district` (
`DistCode` int(11) NOT NULL,
`StCode` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`DistrictName` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
Step 1: Create a database connection file (config.php)
<?php
// DB credentials.
error_reporting(0);
define(‘DB_HOST’,’localhost’);
define(‘DB_USER’,’root’);
define(‘DB_PASS’,’’);
define(‘DB_NAME’,’demos’);
// Establish database connection.
try
{
$dbh = new PDO(“mysql:host=”.DB_HOST.”;dbname=”.DB_NAME,DB_USER, DB_PASS,array(PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_INIT_COMMAND => “SET NAMES ‘utf8’”));
}
catch (PDOException $e)
{
exit(“Error: “ . $e->getMessage());
}
?>
Step2: Create a HTML form with two fields . One is for state and another one is for district.
<form name=”insert” action=”” method=”post”>
<table width=”100%” height=”117" border=”0">
<tr>
<th width=”27%” height=”63" scope=”row”>Sate :</th>
<td width=”73%”><select onChange=”getdistrict(this.value);” name=”state” id=”state” class=”form-control” >
<option value=””>Select</option>
<! — — Fetching States — ->
<?php
$sql=”SELECT * FROM state”;
$stmt=$dbh->query($sql);
$stmt->setFetchMode(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
while($row =$stmt->fetch()) {
?>
<option value=”<?php echo $row[‘StCode’];?>”><?php echo $row[‘StateName’];?></option>
<?php }?>
</select></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope=”row”>District :</th>
<td><select name=”district” id=”district-list” class=”form-control”>
<option value=””>Select</option>
</select></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
Step3: Getting States using jQuery AJAX
This script contains a function that will be called on changing state dropdown values. It will send AJAX request to a PHP page to get corresponding district dropdown options.
<script>
function getdistrict(val) {
$.ajax({
type: “POST”,
url: “get_district.php”,
data:’state_id=’+val,
success: function(data){
$(“#district-list”).html(data);
}
});
}
</script>
Step 4: Read the district table using PHP based on the selected state name.
This PHP code connects the database to retrieve district table values based on the state id passed by jQuery AJAX call.
<?php
require_once(“config.php”);
if(!empty($_POST[“state_id”]))
{
$stateid=$_POST[“state_id”];
$sql=$dbh->prepare(“SELECT * FROM district WHERE StCode=:stateid”);
$sql->execute(array(‘:stateid’ => $stateid));
?>
<option value=””>Select District</option>
<?php
while($row =$sql->fetch())
{
?>
<option value=”<?php echo $row[“DistrictName”]; ?>”><?php echo $row[“DistrictName”]; ?></option>
<?php
}
}
?>
How to run this script
1.Download the zip file
2.Extract the file and copy statedistdropdown-pdo folder
3.Paste inside root directory(for xampp xampp/htdocs, for wamp wamp/www, for lamp var/www/html)
4.Open PHPMyAdmin (http://localhost/phpmyadmin)
5.Create a database with name demos
6.Import regdb.sql file(given inside the zip package )
7.Run the script http://localhost/statedistdropdown-pdo
PHP Gurukul
Welcome to PHPGurukul. We are a web development team striving our best to provide you with an unusual experience with PHP. Some technologies never fade, and PHP is one of them. From the time it has been introduced, the demand for PHP Projects and PHP developers is growing since 1994. We are here to make your PHP journey more exciting and useful.
Website : https://phpgurukul.com
0 notes
Text
PHP Master - Best Course to Learn from ADMEC

Website is developed using front end programming languages as well back end programming languages. Front end is acknowledged by everyone as they can see it. But back-end is only visible to the developer. The basic language that plays a vital role in serving the server side is PHP i.e. Hypertext Preprocessor. You can consider it as a lifeline of website's backend. It is safe, secure, fast and above all a platform independent language which makes it the most desirable one for the programmers. To master such a language which is advisable to get PHP training form the best PHP training institute in delhi such as ADMEC Multimedia Institute which offers PHP Master which the best course to learn from this institute.
Lets see,
The Qualities of PHP Attracts the Developers :-
It is simple
Easy to learn
Platform independent
Provides better security
Flexible
Free - Open course available
Makes complex programs easy
Supports major protocols such as POP3, IMAP etc
It is very forgiving language as it is loosely typed
It is C based
Integrates with large number of databases
I am sure they are enough to tempt you to explore about the course. You will actually release that why is this institute best to learn about this vital programming language.
Name of Course : PHP Master Course
Duration : 2 Months
Mode of Training : Online as well as Classroom mode
Pre-requisites : Proper knowledge of HTML and CSS. Also, better to have advanced understanding of PHP.
Learning this involves knowledge about two i.e. PHP and MySQL. Where MySQL is the Relational Database Management System where we store all the data of the website.
It involves 5 parts :
Part 1 - Core PHP
Here you will get the complete guidance of :
o What is PHP and MySQL
o Indepth understanding of PHP
o Its syntax and variables
o Arrays
o Functions
o String handling
o Different types of PHP
o How to work with cookies and sessions
o Working different file systems
Part 2 - Integration with MySQL
In this session you will get to know about :
o Introduction to MySQL
o How to install MySQL
o Connection MySQL with Hypertext Preprocessor file
o Performing database queries
o Connecting database with web forms
o Organizing database
o How and why to troubleshoot MySQL
Part 3 - Advanced guidance about PHP
This section involves :
o Introduction to OO PHP i.e. Object Oriented Hypertext Preprocessor
o Exception and error handling will be explained here
o Configuring it
o Debugging Different styles
o Improving site with the help of log sites.
Part 4 - Establishing Connections
Here you will get to know :
o How to send E-mails
o Its integration with JavaScript
o As well as integrating it with Ajax
Part 5 - Frameworks
This section explains :
o Planning structure for coding
o Implementation of CRUD
o Tts Framework - Codeignitor
After all this a proper test and project will be allotted to you. To see till what level have you understood the details of this language.
To know about the course in better manner go through the detailed brochure at PHP Master Course page which you can even download.
Conclusion :
Reading this blog must have excited you to learn this amazing software that to from the best PHP training center. What are you waiting for? Take a step forward towards your prosperous career. For any query feel free to contact them on +91 9811 - 818 - 122 and +91 9911 - 782 - 350.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Php json decode unicode

PHP JSON DECODE UNICODE GENERATOR
PHP JSON DECODE UNICODE UPDATE
Specifies a bitmask (JSON_BIGINT_AS_STRING, Object will be converted into an associative array. Json_decode( string, assoc, depth, options) Parameter Values Parameter PHP Examples PHP Examples PHP Compiler PHP Quiz PHP Exercises PHP Certificate PHP - AJAX AJAX Intro AJAX PHP AJAX Database AJAX XML AJAX Live Search AJAX Poll PHP XML PHP XML Parsers PHP SimpleXML Parser PHP SimpleXML - Get PHP XML Expat PHP XML DOM
PHP JSON DECODE UNICODE UPDATE
MySQL Database MySQL Database MySQL Connect MySQL Create DB MySQL Create Table MySQL Insert Data MySQL Get Last ID MySQL Insert Multiple MySQL Prepared MySQL Select Data MySQL Where MySQL Order By MySQL Delete Data MySQL Update Data MySQL Limit Data PHP OOP PHP What is OOP PHP Classes/Objects PHP Constructor PHP Destructor PHP Access Modifiers PHP Inheritance PHP Constants PHP Abstract Classes PHP Interfaces PHP Traits PHP Static Methods PHP Static Properties PHP Namespaces PHP Iterables PHP Advanced PHP Date and Time PHP Include PHP File Handling PHP File Open/Read PHP File Create/Write PHP File Upload PHP Cookies PHP Sessions PHP Filters PHP Filters Advanced PHP Callback Functions PHP JSON PHP Exceptions PHP Forms PHP Form Handling PHP Form Validation PHP Form Required PHP Form URL/E-mail PHP Form Complete Store the expression in a $json2 variable and echo it.Superglobals $GLOBALS $_SERVER $_REQUEST $_POST $_GET PHP RegEx Use the decoded JSON object as the first parameter to the json_encode() function and the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT option as the second parameter. Then, use the json_decode() function on the variable $json1. Create a variable $json1 and store a raw JSON object in it. We will take the JSON object and decode it using the json_decode() function and then will encode it with the json_encode() function along with the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT option.įor example, set the Content-Type to application/json as we did in the method above. We will prettify a JSON object in the following example. We also use the header() function like in the second method to notify the browser about the JSON format. We can use the json_encode() function with the json_decode() function and the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT as the parameters to prettify the JSON string in PHP. Use the json_encode() and json_decode() Functions to Prettify the JSON String in PHP Header('Content-Type: application/json') Įcho json_encode($age, JSON_PRETTY_PRINT) As a result, we will get a prettified version of JSON data in each new line.Įxample Code: $age = array("Marcus"=>23, "Mason"=>19, "Jadon"=>20) In the next line, use the json_encode() function with the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT option on the array as we did in the first method. We can use the json_encode() function as in the first method.įor example, write the header() function and set the Content-Type to application/json. We will use the same associative array for the demonstration. We can use the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT option as in the first method to prettify the string. We can use the header() function to set the Content-Type to application/json to notify the browser type. Use the application/json and JSON_PRETTY_PRINT Options to Prettify the JSON String in PHP $json_pretty = json_encode($age, JSON_PRETTY_PRINT) Then, echo the variable enclosing it with the HTML tag.Įxample Code: $age = array("Marcus"=>23, "Mason"=>19, "Jadon"=>20) Next, use the json_encode() function on the $age variable and write the option JSON_PRETTY_PRINT as the second parameter and store the expression in $json_pretty variable. Write the keys Marcus, Mason, and Jadon and the values 23, 19, and 20.
PHP JSON DECODE UNICODE GENERATOR
QR Code Generator in PHP with Source Code 2021 | freeload | PHP Projects with Source Code 2021įor example, create an associative array in the variable $age. The tag preserves the line break after each key-value pair in the string. We will prettify an associative array in the example below. However, we can use the HTML tags to indent the strings to the new line. It will add some spaces between the characters and makes the string looks better. We can specify the string to be prettified and then the option in the json_encode() function. The json_encode() function has a option JSON_PRETTY_PRINT which prettifies the JSON string. We can encode indexed array, associative array, and objects to the JSON format. We can use the json_encode() function to convert a value to a JSON format. Use the HTML Tag and the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT Option to Prettify the JSON String in PHP This article will introduce different methods to prettify the raw JSON string in PHP.
Use the json_encode() and json_decode() Functions to Prettify the JSON String in PHP.
Use the application/json and JSON_PRETTY_PRINT Options to Prettify the JSON String in PHP.
Use the HTML Tag and the JSON_PRETTY_PRINT Option to Prettify the JSON String in PHP.

0 notes
Text
Array no PHP Aprenda como criar e iterar
Array no PHP Aprenda como criar e iterar
Array no PHP Aprenda como criar e iterar com foreach e while
Array no PHP aprenda como criar e iterar, pois array é uma estrutura que relaciona valores e chaves, é uma lista de valores armazenados na memória.
Um array em PHP é equivalente ao conceito de vetor normalmente ensinado nas faculdades. Outro conceito que se asemelha é o conceito de matriz, equivale a um array multidimensional (um array…
View On WordPress
#array#array php#array php 7#array php add first#array php add item#array php ajax#array php foreach#array php functions#array php insert#array php to javascript#array_push php#PHP#programação
0 notes
Text
Php get file path

Php get file path update#
Php get file path full#
Reads a file and writes it to the output bufferĪlias of stream_set_write_buffer(). Returns information about a file or symbolic link Returns an array of filenames / directories matching a specified patternĬhecks whether a file was uploaded via HTTP POSTĬhanges the group ownership of a symbolic linkĬhanges the user ownership of a symbolic link Truncates an open file to a specified length Returns the current position in an open file Parses input from an open file according to a specified format Reads from the current position in a file - until EOF, and writes the resultįormats a line as CSV and writes it to an open file Matches a filename or string against a specified pattern Returns the last modification time of a file Returns a line from an open file - strippedĬhecks whether or not a file or directory exists Returns a single character from an open fileĭeprecated from PHP 7.3. Returns the total size of a filesystem or diskĬhecks if the "end-of-file" (EOF) has been reached for an open file Returns the free space of a filesystem or disk Returns the directory name component of a path PHP Examples PHP Examples PHP Compiler PHP Quiz PHP Exercises PHP Certificate PHP - AJAX AJAX Intro AJAX PHP AJAX Database AJAX XML AJAX Live Search AJAX Poll The latter also contains the filename extension.
Php get file path full#
PHP XML PHP XML Parsers PHP SimpleXML Parser PHP SimpleXML - Get PHP XML Expat PHP XML DOM It’s easy to get the filename and directory name components of a full path name with PHP using the dirname(), basename() and pathinfo() functions. fputcsv () Formats a line as CSV and writes it to an open file. fpassthru () Reads from the current position in a file - until EOF, and writes the result to the output buffer.
Php get file path update#
MySQL Database MySQL Database MySQL Connect MySQL Create DB MySQL Create Table MySQL Insert Data MySQL Get Last ID MySQL Insert Multiple MySQL Prepared MySQL Select Data MySQL Where MySQL Order By MySQL Delete Data MySQL Update Data MySQL Limit Data fnmatch () Matches a filename or string against a specified pattern. PHP OOP PHP What is OOP PHP Classes/Objects PHP Constructor PHP Destructor PHP Access Modifiers PHP Inheritance PHP Constants PHP Abstract Classes PHP Interfaces PHP Traits PHP Static Methods PHP Static Properties PHP Namespaces PHP Iterables PHP Advanced PHP Date and Time PHP Include PHP File Handling PHP File Open/Read PHP File Create/Write PHP File Upload PHP Cookies PHP Sessions PHP Filters PHP Filters Advanced PHP Callback Functions PHP JSON PHP Exceptions PHP Forms PHP Form Handling PHP Form Validation PHP Form Required PHP Form URL/E-mail PHP Form Complete Superglobals $GLOBALS $_SERVER $_REQUEST $_POST $_GET PHP RegEx

0 notes
Text
How to Use Yajra Datatables in Laravel 9 Application

User data display is a fundamental necessity for web development. This tutorial's main goal is to show you how to use Yajra Datatables, a third-party package, to generate Datatables in Laravel. This Laravel datatables tutorial demonstrates how to construct yajra datatables in Laravel while also teaching us the necessary techniques. We will work to eliminate any ambiguity that may have surrounded your creation of the Laravel datatables example. We'll look at a laravel datatables AJAX example and a laravel Bootstrap datatable simultaneously. Consider a scenario where you are presented with thousands of records and must manually search through each one to find the information you need. Doesn't seem easy, does it? To manage the data dynamically in the table, Datatables provides easy search, pagination, ordering, and sorting functions, in my opinion making our task less dreary. A plug-in driven by jQuery, also known as the Javascript library, is called DataTables. It is a remarkably adaptable tool that adds all of these subtle and cutting-edge features to any static HTML table. It was created on the principles of progressive and dynamic augmentation.
Features
- Pagination - Instant search - Multi-column ordering - Use almost any data source - Easily theme-able - Wide variety of extensions - Mobile friendly Even though we will only be using a few functionalities, such as search, sort, and pagination, we will attempt to integrate these elements with aesthetically pleasing HTML tables that are robust from a UI/UX standpoint.
Table of Contents
- Install Laravel App - Install Yajra Datatables - Set Up Model and Migrations - Insert Dummy Data - Create Controller - Define Route - Create View
Install Laravel App
In general, deploying a new Laravel application is the main emphasis of our initial step. Install the sacred canon by executing the artisan command listed below. composer create-project laravel/laravel laravel-yajra-datatables --prefer-dist cd laravel-yajra-datatables
Install Yajra Datatable Package
Yajra Datatables Library is a jQuery DataTables API for Laravel 4|5|6|7, and I wonder whether you've heard of it. By taking into account the Eloquent ORM, Fluent Query Builder, or Collection, this plugin manages the server-side operations of the DataTables jQuery plugin through the AJAX option. The following command should theoretically assist you in installing the Yajra DataTable plugin in Laravel. composer require yajra/laravel-datatables-oracle Expand the basic functions of the package, such as the datatable service provider in the providers section and the alias inside the config/app.php file. ..... ..... 'providers' => 'aliases' => ..... ..... Continue by running the vendor publish command; this step is optional. php artisan vendor:publish --provider="YajraDataTablesDataTablesServiceProvider"
Set Up Model and Migrations
Run a command to generate a model, which contains the database table's schema. php artisan make:model Student -m Add the following code to the file database/migrations/timestamp create students table.php. public function up() { Schema::create('students', function (Blueprint $table) { $table->id(); $table->string('name'); $table->string('email')->unique(); $table->string('username'); $table->string('phone'); $table->string('dob'); $table->timestamps(); }); } Open the Student.php file in app/Models and add the schema to the $fillable array. Read the full article
#howtouseyajradatatablesinlaravel9#laravel9datatablesajaxexample#laravel9datatablesexample#laravel9installyajradatatables#laravel9yajradatatablesexample#laravel9yajradatatablesserversiteserverside
0 notes