#benefits of online marketplace
Text
Save Money by Buying Wholesale store Online

Did you know that you can buy wholesale products online?
There are many great wholesale stores online that offer a wide variety of products at discounted prices. This is a great way to save money on everything from clothing and accessories to home goods and office supplies.
Just be sure to do your research and find a reputable wholesale store. There are a lot of scams out there, so it's important to make sure that the store you're buying from is legitimate. Here are a few tips for finding a reputable wholesale store:
i) Read reviews from other shoppers.
ii) Check the store's return policy.
iii) Make sure the store is secure and uses SSL encryption.
Once you've found a reputable wholesale store, you can start saving money on your next purchase. Just be sure to buy in bulk to get the best deals.
#online marketplace#benefits of online marketplace#wholesale marketplace#main street market & gifts#etsy alternatives
0 notes
Text
What is The Development of Luxury Brand Market in South East Asia Especially The Emerging Countries?
The development of the luxury brand market in Southeast Asia, particularly in emerging countries, is a fascinating phenomenon that underscores the dynamic interplay between economic growth, cultural evolution, and consumer behavior. Southeast Asia, with its burgeoning middle class and increasing disposable income, has become a fertile ground for luxury brands aiming to expand their reach and tap…
View On WordPress
#development of luxury brand in southeast asia#effective supply chain as the key of singapore reach for luxury brand expansion#expansion to indonesia for luxury brand#how indonesia best market for luxury brand to expand#how tourist can get cheaper price of luxury brand product in singapore#luxury brand and singapore impact#luxury brand expanding into south east asia via e-commerce#online marketplace expansion for luxury brand in southeast asia#singapore low tax system benefit the luxury brand#singapore position in expanding market reach in southeast asia#singapore vat and trs for tourist luxury brand
0 notes
Text
Entrepedia: Your One-Stop Shop for 1000 Digital Products
Are you a digital entrepreneur looking to expand your product offerings and boost your online presence? Look no further than Entrepedia – your one-stop shop for 1000 digital products!
Entrepedia is a revolutionary platform that provides entrepreneurs with access to a vast array of high-quality digital products, ranging from eBooks and courses to software and templates. What sets Entrepedia apart…
View On WordPress
#access#benefits#digital#Entrepedia#FAQs#marketplace#one-stop#online#products#satisfaction#shop#testimonials#user
0 notes
Text
In the bustling world of e-commerce, online arbitrage software is a game-changer. It's a powerful ally for those looking to capitalize on the price differences between online marketplaces. Here's how it can benefit your business.
#online arbitrage software#business#ecommerce#online arbitrage software benefits#online marketplaces
0 notes
Text
Explore the enticing benefits of establishing your own online food delivery marketplace business in our informative video. From fostering customer loyalty to optimizing operational efficiency, this model presents a host of opportunities for entrepreneurs and restaurateurs alike.
0 notes
Photo

What are the benefits of an online marketplace?
Convenience: Online marketplaces offer 24/7 access from anywhere with an internet connection.
Increased exposure: Online marketplaces provide a platform for businesses to reach a wider audience, increasing their visibility and customer base.
Reduced costs: Operating an online store often has lower overhead costs compared to a physical store.
Easy to set up: Creating an online store is often quicker and easier than setting up a physical store.
Data insights: Online marketplaces provide valuable data on customer behavior and purchasing habits.
Improved payment options: Online marketplaces offer a range of payment options, making it easier for customers to complete transactions.
Better competition: Online marketplaces offer consumers a wider range of products and services to choose from, increasing competition and driving down prices.
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Photo


The online marketplace is a good platform for you to expand your business. We are going to explain what kind of advantages there are by sharing what we know about online selling. In brief, these are the plus points we will talk about.
#online#business#marketplace#marketplaceonline#platform#growth#expanding#expand#benefit#sell#selling#onlineselling#profcyma#profcymaglobal
0 notes
Note
I have a question that’s probably pretty stupid, but I thought I’d ask someone knowledgeable. I know china is nothing like how it’s painted by imperialism, but the “social credit” system that affects people’s lives and privileges is real right? A lot of people online default to it for the argument towards china being terrible in one way or another, and from what I know it seems like a legitimately bad thing used to punish or censor people. Do I have this wrong? I’m sure there’s more to the story
In brief, while the 'social credit system' exists, it's both fairly regional (as lots of things are in China, everywhere is constantly experimenting and trialling different paths), and generally applies only to corporations, and the rich. Western reporting likes to act as though they're talking to fellow rich people, which obfuscates things - when they say 'your social credit score can stop you from getting plane tickets' they mean 'if you've committed acts of embezzlement or corruption you can't get first-class tickets and have to fly economy with everyone else'.
In the vast majority of cases the system is aimed solely at corporations and regards things like not paying social security benefits and the like. China doesn't have a FICO-like credit system as the US does, because most Chinese people aren't debtors. People in China generally don't go into debt to buy things, they save up (because the Chinese economy is based on the sale of production, rather than the sale of debts, like the US economy). Before this system was established there lacked a unified system of punishments for non-criminal corporate violations.
That's why the western businesses, which own the western news outlets, were very upset about this, and painted it as they did. They complain about stricter regulations anywhere, but for China they get to piggyback off of existing sentiment to get people who otherwise would support these types of regulations to oppose them. The 'environmental pollution regulations are tyrannical government overreach' line goes down a lot smoother when people have already bought into a story of 'authoritarianism'.
Here's some reporting from western sources backing this up:
Contrary to common belief, the cities mainly target companies, not individuals. Nonetheless, legal representatives of a violating company are also included in the blacklists to prevent reoffending elsewhere or under a different company. Nationally, about 75 percent of entities targeted by the system end up on blacklists because of court orders they have ignored—the so-called judgment defaulters. The remaining companies are typically collared for severe marketplace violations—for instance, for food safety infringements, environmental damage, or wage arrears.
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Metaverse: A New Frontier in Digital Interaction

The concept of the metaverse has captivated the imagination of technologists, futurists, and businesses alike. Envisioned as a collective virtual shared space, the metaverse merges physical and digital realities, offering immersive experiences and unprecedented opportunities for interaction, commerce, and creativity. This article delves into the metaverse, its potential impact on various sectors, the technologies driving its development, and notable projects shaping this emerging landscape.
What is the Metaverse?
The metaverse is a digital universe that encompasses virtual and augmented reality, providing a persistent, shared, and interactive online environment. In the metaverse, users can create avatars, interact with others, attend virtual events, own virtual property, and engage in economic activities. Unlike traditional online experiences, the metaverse aims to replicate and enhance the real world, offering seamless integration of the physical and digital realms.
Key Components of the Metaverse
Virtual Worlds: Virtual worlds are digital environments where users can explore, interact, and create. Platforms like Decentraland, Sandbox, and VRChat offer expansive virtual spaces where users can build, socialize, and participate in various activities.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing user experiences through devices like smartphones and AR glasses. Examples include Pokémon GO and AR navigation apps that blend digital content with physical surroundings.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR provides immersive experiences through headsets that transport users to fully digital environments. Companies like Oculus, HTC Vive, and Sony PlayStation VR are leading the way in developing advanced VR hardware and software.
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain plays a crucial role in the metaverse by enabling decentralized ownership, digital scarcity, and secure transactions. NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) and cryptocurrencies are integral to the metaverse economy, allowing users to buy, sell, and trade virtual assets.
Digital Economy: The metaverse features a robust digital economy where users can earn, spend, and invest in virtual goods and services. Virtual real estate, digital art, and in-game items are examples of assets that hold real-world value within the metaverse.
Potential Impact of the Metaverse
Social Interaction: The metaverse offers new ways for people to connect and interact, transcending geographical boundaries. Virtual events, social spaces, and collaborative environments provide opportunities for meaningful engagement and community building.
Entertainment and Gaming: The entertainment and gaming industries are poised to benefit significantly from the metaverse. Immersive games, virtual concerts, and interactive storytelling experiences offer new dimensions of engagement and creativity.
Education and Training: The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize education and training by providing immersive, interactive learning environments. Virtual classrooms, simulations, and collaborative projects can enhance educational outcomes and accessibility.
Commerce and Retail: Virtual shopping experiences and digital marketplaces enable businesses to reach global audiences in innovative ways. Brands can create virtual storefronts, offer unique digital products, and engage customers through immersive experiences.
Work and Collaboration: The metaverse can transform the future of work by providing virtual offices, meeting spaces, and collaborative tools. Remote work and global collaboration become more seamless and engaging in a fully digital environment.
Technologies Driving the Metaverse
5G Connectivity: High-speed, low-latency 5G networks are essential for delivering seamless and responsive metaverse experiences. Enhanced connectivity enables real-time interactions and high-quality streaming of immersive content.
Advanced Graphics and Computing: Powerful graphics processing units (GPUs) and cloud computing resources are crucial for rendering detailed virtual environments and supporting large-scale metaverse platforms.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI enhances the metaverse by enabling realistic avatars, intelligent virtual assistants, and dynamic content generation. AI-driven algorithms can personalize experiences and optimize virtual interactions.
Wearable Technology: Wearable devices, such as VR headsets, AR glasses, and haptic feedback suits, provide users with immersive and interactive experiences. Advancements in wearable technology are critical for enhancing the metaverse experience.
Notable Metaverse Projects
Decentraland: Decentraland is a decentralized virtual world where users can buy, sell, and develop virtual real estate as NFTs. The platform offers a wide range of experiences, from gaming and socializing to virtual commerce and education.
Sandbox: Sandbox is a virtual world that allows users to create, own, and monetize their gaming experiences using blockchain technology. The platform's user-generated content and virtual real estate model have attracted a vibrant community of creators and players.
Facebook's Meta: Facebook's rebranding to Meta underscores its commitment to building the metaverse. Meta aims to create interconnected virtual spaces for social interaction, work, and entertainment, leveraging its existing social media infrastructure.
Roblox: Roblox is an online platform that enables users to create and play games developed by other users. With its extensive user-generated content and virtual economy, Roblox exemplifies the potential of the metaverse in gaming and social interaction.
Sexy Meme Coin (SEXXXY): Sexy Meme Coin integrates metaverse elements by offering a decentralized marketplace for buying, selling, and trading memes as NFTs. This unique approach combines humor, creativity, and digital ownership, adding a distinct flavor to the metaverse landscape. Learn more about Sexy Meme Coin at Sexy Meme Coin.
The Future of the Metaverse
The metaverse is still in its early stages, but its potential to reshape digital interaction is immense. As technology advances and more industries explore its possibilities, the metaverse is likely to become an integral part of our daily lives. Collaboration between technology providers, content creators, and businesses will drive the development of the metaverse, creating new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Conclusion
The metaverse represents a new frontier in digital interaction, offering immersive and interconnected experiences that bridge the physical and digital worlds. With its potential to transform social interaction, entertainment, education, commerce, and work, the metaverse is poised to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. Notable projects like Decentraland, Sandbox, Meta, Roblox, and Sexy Meme Coin are at the forefront of this transformation, showcasing the diverse possibilities within this emerging digital universe.
For those interested in the playful and innovative side of the metaverse, Sexy Meme Coin offers a unique and entertaining platform. Visit Sexy Meme Coin to explore this exciting project and join the community.
257 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Marketplace of Girl Influencers Managed by Moms and Stalked by Men
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/02/22/us/instagram-child-influencers.html
Seeking social media stardom for their underage daughters, mothers post images of them on Instagram. The accounts draw men sexually attracted to children, and they sometimes pay to see more.
Feb. 22, 2024
By Jennifer Valentino-DeVries and Michael H. Keller
The ominous messages began arriving in Elissa’s inbox early last year.
“You sell pics of your underage daughter to pedophiles,” read one. “You’re such a naughty sick mom, you’re just as sick as us pedophiles,” read another. “I will make your life hell for you and your daughter.”
Elissa has been running her daughter’s Instagram account since 2020, when the girl was 11 and too young to have her own. Photos show a bright, bubbly girl modeling evening dresses, high-end workout gear and dance leotards. She has more than 100,000 followers, some so enthusiastic about her posts that they pay $9.99 a month for more photos.
Over the years, Elissa has fielded all kinds of criticism and knows full well that some people think she is exploiting her daughter. She has even gotten used to receiving creepy messages, but these — from “Instamodelfan” — were extreme. “I think they’re all pedophiles,” she said of the many online followers obsessed with her daughter and other young girls.
Elissa and her daughter inhabit the world of Instagram influencers whose accounts are managed by their parents. Although the site prohibits children under 13, parents can open so-called mom-run accounts for them, and they can live on even when the girls become teenagers.
But what often starts as a parent’s effort to jump-start a child’s modeling career, or win favors from clothing brands, can quickly descend into a dark underworld dominated by adult men, many of whom openly admit on other platforms to being sexually attracted to children, an investigation by The New York Times found.
For this investigation, the reporters analyzed 2.1 million Instagram posts, monitored months of online chats of professed pedophiles and interviewed over 100 people, including parents and children.
Thousands of accounts examined by The Times offer disturbing insights into how social media is reshaping childhood, especially for girls, with direct parental encouragement and involvement. Some parents are the driving force behind the sale of photos, exclusive chat sessions and even the girls’ worn leotards and cheer outfits to mostly unknown followers. The most devoted customers spend thousands of dollars nurturing the underage relationships.
The large audiences boosted by men can benefit the families, The Times found. The bigger followings look impressive to brands and bolster chances of getting discounts, products and other financial incentives, and the accounts themselves are rewarded by Instagram’s algorithm with greater visibility on the platform, which in turn attracts more followers.
One calculation performed by an audience demographics firm found 32 million connections to male followers among the 5,000 accounts examined by The Times.
Interacting with the men opens the door to abuse. Some flatter, bully and blackmail girls and their parents to get racier and racier images. The Times monitored separate exchanges on Telegram, the messaging app, where men openly fantasize about sexually abusing the children they follow on Instagram and extol the platform for making the images so readily available.
“It’s like a candy store 😍😍😍,” one of them wrote. “God bless instamoms 🙌,” wrote another.
The troubling interactions on Instagram come as social media companies increasingly dominate the cultural landscape and the internet is seen as a career path of its own.
Nearly one in three preteens lists influencing as a career goal, and 11 percent of those born in Generation Z, between 1997 and 2012, describe themselves as influencers. The so-called creator economy surpasses $250 billion worldwide, according to Goldman Sachs, with U.S. brands spending more than $5 billion a year on influencers.
Health and technology experts have recently cautioned that social media presents a “profound risk of harm” for girls. Constant comparisons to their peers and face-altering filters are driving negative feelings of self-worth and promoting objectification of their bodies, researchers found.
But the pursuit of online fame, particularly through Instagram, has supercharged the often toxic phenomenon, The Times found, encouraging parents to commodify their children’s images. Some of the child influencers earn six-figure incomes, according to interviews.
“I really don’t want my child exploited on the internet,” said Kaelyn, a mother in Melbourne, Australia, who like Elissa and many other parents interviewed by The Times agreed to be identified only by a middle name to protect the privacy of her child.
“But she’s been doing this so long now,” she said. “Her numbers are so big. What do we do? Just stop it and walk away?”
In investigating this growing and unregulated ecosystem, The Times analyzed 2.1 million Instagram posts, monitored months of online chats of professed pedophiles and reviewed thousands of pages of police reports and court documents.
Reporters also interviewed more than 100 people, including parents in the United States and three other countries, their children, child safety experts, tech company employees and followers of the accounts, some of whom were convicted sex offenders.
This is how The Times found its sample of 5,000 mom-run accounts.
The accounts range from dancers whose mothers diligently cull men from the ranks of followers, to girls in skimpy bikinis whose parents actively encourage male admirers and sell them special photo sets. While there are some mom-run accounts for boys, they are the exception.
Some girls on Instagram use their social media clout to get little more than clothing discounts; others receive gifts from Amazon wish lists, or money through Cash App; and still others earn thousands of dollars a month by selling subscriptions with exclusive content.
In interviews and online comments, parents said that their children enjoyed being on social media or that it was important for a future career. But some expressed misgivings. Kaelyn, whose daughter is now 17, said she worried that a childhood spent sporting bikinis online for adult men had scarred her.
“She’s written herself off and decided that the only way she’s going to have a future is to make a mint on OnlyFans,” she said, referring to a website that allows users to sell adult content to subscribers. “She has way more than that to offer.”
She warned mothers not to make their children social media influencers. “With the wisdom and knowledge I have now, if I could go back, I definitely wouldn’t do it,” she said. “I’ve been stupidly, naïvely, feeding a pack of monsters, and the regret is huge.”
Account owners who report explicit images or potential predators to Instagram are typically met with silence or indifference, and those who block many abusers have seen their own accounts’ ability to use certain features limited, according to the interviews and documents. In the course of eight months, The Times made over 50 reports of its own about questionable material and received only one response.
Meta, Instagram’s parent company, found that 500,000 child Instagram accounts had “inappropriate” interactions every day, according to an internal study in 2020 quoted in legal proceedings.
In a statement to The Times, Andy Stone, a Meta spokesman, said that parents were responsible for the accounts and their content and could delete them anytime.
“Anyone on Instagram can control who is able to tag, mention or message them, as well as who can comment on their account,” Mr. Stone added, noting a feature that allows parents to ban comments with certain words. “On top of that, we prevent accounts exhibiting potentially suspicious behavior from using our monetization tools, and we plan to limit such accounts from accessing subscription content.”
Influencers use TikTok, too, but Instagram is easier for parents to navigate and better suited to the kinds of photos that brands want. It is also home to a longstanding network of parents and brands that predated TikTok.
From time to time, Instagram removes child-influencer accounts for unspecified reasons or because people flag them as inappropriate, The Times found. In extreme cases, parents and photographers have been arrested or convicted of child exploitation, but barring evidence of illegal images, most of the activity does not draw the attention of law enforcement.
Like many parents, Elissa, who received the threatening messages about her daughter’s photos, said she protected her daughter by handling the account exclusively herself. Ultimately, she concluded, the Instagram community is dominated by “disgusting creeps,” but she nonetheless keeps the account up and running. Shutting it down, she said, would be “giving in to bullies.”
The account’s risks became apparent last spring when the person messaging her threatened to report her to the police and others unless she completed “a small task.” When she did not respond, the person emailed the girl’s school, saying Elissa sold “naughty” pictures to pedophiles.
Days later, the girl tearfully explained to her mother that school officials had questioned her about the Instagram account. They showed her images that her mother had posted — one of the girl in hot pants and fishnets, another in a leotard and sweatshirt.
Elissa had reported the blackmail to the local sheriff, but school officials only dropped the matter after an emotional interrogation of the girl.
“I was crying,” the girl said in an interview. “I was just scared. I didn’t understand what was going on.”
‘Walking Advertising’
In today’s creator economy, companies often turn to social media influencers to attract new customers. Giants like Kim Kardashian, who has 364 million followers on Instagram, have turned the phenomenon into a big business.
Young girls strive to do the same.
In the dance and gymnastics worlds, teens and preteens jockey to become brand ambassadors for products and apparel. They don bikinis in Instagram posts, walk runways in youth fashion shows and offer paid subscriptions to videos showing the everyday goings-on of children seeking internet fame.
“We costumed somebody for ‘So You Think You Can Dance’ thinking that would be huge P.R., but we ended up finding out the bigger return on investment is these microinfluencers,” she said. “We have parents that will spend thousands of dollars to buy styles that no one else will have. That’s our best market.”
The most successful girls can demand $3,000 from their sponsors for a single post on Instagram, but monetary gain can be elusive for others, who receive free or discounted clothes in exchange for their posts and have to pay for their own hairstyling and makeup, among other costs. Even youth fashion shows, including events in New York that coincide but are not affiliated with New York Fashion Week, charge the girls to participate and charge their parents to attend.
In interviews, parents defended spending the money to promote their daughters’ influencer ambitions, describing them as extracurricular activities that build confidence, develop friendships and create social media résumés that will follow them into adulthood.
“It’s like a little security blanket,” said a New Jersey mother whose mom-run account has led to paid modeling jobs for her daughter and invitations to work with sought-after choreographers. “She can help pay for college if she does it right,” she said.
A mother in Alabama said parents couldn’t ignore the reality of this new economy.
“Social media is the way of our future, and I feel like they’ll be behind if they don’t know what’s going on,” the mother said. “You can’t do anything without it now.”
One 12-year-old girl in Maryland, who spoke with The Times alongside her mother, described the thrill of seeing other girls she knows wear a brand she represents in Instagram posts.
“People are actually being influenced by me,” she said.
In 2022, Instagram launched paid subscriptions, which allows followers to pay a monthly fee for exclusive content and access. The rules don’t allow subscriptions for anyone under 18, but the mom-run accounts sidestep that restriction. The Times found dozens that charged from 99 cents to $19.99. At the highest price, parents offered “ask me anything” chat sessions and behind-the-scenes photos.
Child safety experts warn the subscriptions and other features could lead to unhealthy interactions, with men believing they have a special connection to the girls and the girls believing they must meet the men’s needs.
“I have reservations about a child feeling like they have to satisfy either adults in their orbit or strangers who are asking something from them,” said Sally Theran, a professor at Wellesley College and clinical psychologist who studies online relationships. “It’s really hard to give consent to that when your frontal lobe isn’t fully developed.”
Instagram isn’t alone in the subscription business. Some parents promote other platforms on their mom-run accounts. One of them, Brand Army, caters to adult influencers but also has “junior channel” parent-run subscriptions ranging from free to $250 monthly.
“Message me anytime. You will have more opportunities for buying and receiving super exclusive content😘,” read a description for a $25 subscription to a minor’s account. For $100 a month, subscribers can get “live interactive video chats,” unlimited direct messages and a mention on the girl’s Instagram story.
The Times subscribed to several accounts to glean what content is being offered and how much money is being made. On one account, 141 subscribers liked a photo only available to those who paid $100 monthly, indicating over $14,000 in subscription revenue.
Some of the descriptions also highlight the revealing nature of photos. One account for a child around 14 years old encouraged new sign-ups at the end of last year by branding the days between Christmas and New Year’s as “Bikini Week.” An account for a 17-year-old girl advertised that she wasn’t wearing underwear in a workout photo set and, as a result, the images were “uh … a lot spicier than usual.”
The girl’s “Elite VIP” subscription costs $250 a month.
Brand Army’s founder, Ramon Mendez, said that junior-channel users were a minority on his platform and that moderating their pages had grown so problematic that he discontinued new sign-ups.
“We’ve removed thousands of pieces of content,” he said. “The parents’ behavior is just disgusting. We don’t want to be part of it.”
‘The Wealth of the Wicked’
“You are so sexy,” read one comment on an image of a 5-year-old girl in a ruffled bikini. “Those two little things look great thru ur top,” said another on a video of a girl dancing in a white cropped shirt, who months later posted pictures of her 11th birthday party.
For many mom-run accounts, comments from men — admiring, suggestive or explicit — are a recurring scourge to be eradicated, or an inescapable fact of life to be ignored. For others, they are a source to be tapped.
“The first thing I do when I wake up and the last thing I do when I go to bed is block accounts,” said Lynn, the mother of a 6-year-old girl in Florida who has about 3,000 followers from the dance world.
Another mother, Gail from Texas, described being desensitized to the men’s messages. “I don’t have as much of an emotional response anymore,” she said. “It’s weird to be so numb to that, but the quantity is just astounding.”
Meta does not provide public information about who uses Instagram, so The Times analyzed data from the audience firms Modash and HypeAuditor, which estimate follower demographics based on their own algorithms.
The proportion of male followers varied greatly in The Times’s sample, according to the estimates. Many accounts had a few thousand followers who were mostly female. But while men accounted for about 35 percent of the audience overall, their presence grew dramatically as accounts became more popular. Many with more than 100,000 followers had a male audience of over 75 percent, and a few of them over 90 percent, the analysis showed.
To be sure, not all men following the accounts have bad intentions. Some are grandparents and fathers of the young influencers. Many have inoffensive profiles and simply post compliments or greetings, and mothers react appreciatively.
“In responding or even hitting ‘like’ on it, it boosts your algorithm,” said a mother in Florida whose 16-year-old daughter has been an Instagram influencer for six years. “We tried shutting comments off at one point, and some of the brands didn’t like that.”
Brands that feature children from mom-run accounts face similar challenges.
Dean Stockton, who runs a small clothing company in Florida called Original Hippie, often features girls from the Instagram accounts, who earn a commission when customers use personalized discount codes. After initially deleting many male followers, he now sees them as a way to grow the account and give it a wider audience because the platform rewards large followings.
“The Bible says, ‘The wealth of the wicked is laid up for the righteous,’” he said. “So sometimes you got to use the things of this world to get you to where you need to be, as long as it’s not harming anybody.”
Mr. Stockton said he deleted male followers who were disrespectful or sexual in their interactions. An examination by The Times of the three dozen brands that are popular among mom-run accounts found inappropriate, predatory or pornographic followers in almost all of the brands’ accounts, including Original Hippie.
Many of the men posted pornography, or their bios included sexual language and emojis that child protection experts say pedophiles can use to signal interest in children. For instance, one follower of a children’s dance wear brand described himself as a “thong & anl sx lover.” A user named “sexy_69nazi” followed a children’s apparel company and exclusively posted pornography.
Chixit, a brand selling swimwear and other clothing, describes itself as “an International Sorority,” but business records show that it was run by Philip Russo, who advertised himself as a tutor operating out of his home in the Hudson Valley of New York. Other websites registered to Mr. Russo’s email are a tutoring business and inactive domain names describing sex with animals.
After The Times reached out to Mr. Russo, the website for his tutoring business went offline. He did not respond to multiple messages seeking comment.
‘Girls Become a Currency’
The vast world of child-influencer followers on Instagram includes men who have been charged with or convicted of sex crimes, and those who engage in forums off platform where child sexual abuse imagery, including of girls on Instagram, is shared.
The Times traced the account of one follower, who goes by the moniker “jizzquizz,” to a man named Joshua V. Rubel, 39. He was convicted in 2008 of sexually assaulting a 15-year-old girl and is listed on the New Jersey sex offender registry. (Instagram’s policy bars sex offenders from using the platform, and the company said it removed two accounts after The Times pointed them out.)
Another account belongs to Daniel Duane Huver, a man in Lansing, Mich., who told law enforcement in 2018 that he had “top fan status” on girls’ pages, a designation bestowed by Instagram’s sister company, Facebook. The police searched Mr. Huver’s cellphone after it was confiscated by his probation officer and found hundreds of images and videos of children, including many considered inappropriate and sexually suggestive and two believed to be illegal (showing minors engaged in explicit acts.)
Mr. Huver told officers he was sexually attracted to children and masturbated to images of them, according to police records. He was charged with possession of child sexual abuse material, but the prosecutor in Eaton County later dropped charges, citing insufficient evidence because of the poor quality of the imagery.
Mr. Rubel did not respond to requests for comment. Mr. Huver said that the police mischaracterized his words and that the lack of prosecution was evidence he had done nothing wrong.
In monitoring multiple Telegram chat rooms, The Times found men who treat children’s Instagram pages and subscription services as menus to satisfy their fantasies. They trade information about parents considered receptive to producing and selling “private sets” of images.
A group with more than 4,000 members was highly organized, with an F.A.Q. page and a Google sheet that tracked nearly 700 children, identifying them by hashtags to help members find them within the long chat history. The group’s logo showed a child’s hand in an adult hand.
The Times asked the Canadian Center for Child Protection, an organization that monitors online child exploitation, to review links and other potentially illegal material posted by the Telegram groups and elsewhere. The center identified child sexual abuse imagery involving multiple underage Instagram models from around the world, as well as sexualized videos of others, including a preteen girl wearing a thong and a young teenager raising her dress to show her bikini bottom.
Men in these groups frequently praise the advent of Instagram as a golden age for child exploitation.
“I’m so glad for these new moms pimping their daughters out,” wrote one of them. “And there’s an infinite supply of it — literally just refresh your Instagram Explore page there’s fresh preteens.”
A small group of men go even further and cultivate business and patronage relationships with mothers.
One man posts videos and photos on Instagram of girls thanking him for shopping sprees, gifts like iPhones and iPads, and cash. If he does not receive a message of gratitude quickly, he sometimes shames the mother and daughter on his private Instagram account.
Another makes recommendations about increasing visibility by using specific hashtags and photographers. But two mothers said they became suspicious, and stopped working with the man, after he suggested they make certain their daughters’ nipples and other private areas could be detected through their outfits.
A third man tried to persuade a mother to sell her daughter’s used leotards because many men, including himself, were “collectors,” according to a recording of the conversation.
“In retrospect I feel like such a stupid mom, but I’m not stupid,” said a mother of a young gymnast, who dealt with similar men before she realized they were predators and received threatening messages from several of them. “I didn’t understand what grooming was.”
Sometimes the men flirt or try to develop virtual romances with mothers, offer to protect them and become possessive and angry if they interact with other men.
“It’s almost like the girls become a currency,” said the gymnast’s mother, who did not want to be named.
This feeling of ownership and jealousy can drive attempts at blackmail, The Times found.
Instamodelfan, who sent threatening messages to Elissa, sent blackmail threats to at least five other mom-run accounts. When one mother responded, he demanded that she sexually abuse her child and send him photos and videos, emails to the mother show. She refused and contacted law enforcement.
The Times communicated with a person identified on Telegram as Instamodelfan who said that he lashed out at the mothers because he believed other men got illegal images of children and he wanted them for himself.
Reporters also received information from an anonymous tipster, who they later found was linked to the blackmailer, indicating that some parents had produced explicit imagery of their daughters.
The Canadian center reviewed the imagery and said it included illegal nude photos of two girls. One girl’s mother said she was shaken to learn of the photos and did not know who could have made them. The other girl, now 17, said in an interview that the photos were for her and a girlfriend and that she told law enforcement that they had been stolen.
Others images either were borderline illegal, were too poor quality to be conclusive or were digitally altered, the center said.
Several mothers who had been identified by the tipster said they reached out to the Federal Bureau of Investigation, which, they said, had conducted an investigation. The F.B.I. declined to comment.
Ultimately, the gymnast’s mother said, a federal agent told them to stop talking to men online.
“They told everyone to get off Instagram,” she said. “‘You’re in over your head. Get off.’ That’s what they told us.”
‘My Limit of Pedophiles’
Meta failed to act on multiple reports made by parents and even restricted those who tried to police their own followers, according to interviews and materials provided by the parents.
If parents block too many followers’ accounts in a day, Meta curtails their ability to block or follow others, they said.
“I remember being told, like, I’ve reached my limit,” said a mother of two dancers in Arizona who declined to be named. “Like what? I reached my limit of pedophiles for today. OK, great.”
Mr. Stone, the Meta spokesman, said “there are lots of reasons an account might face limitations or restrictions based the account’s activity,” and therefore it was difficult to know why parents encountered these problems.
Ms. Pastore of LA Dance Designs said it was “very much overdue” for Instagram to add the ability to filter by age and sex to help identify suspicious followers. “If you’re starting to gain a following, there needs to be some sort of way to control it,” she said.
Even some egregious violations led to no action by Meta.
One parent reported a photo of erect male genitalia sent in a direct message. Another reported an account that reposted children’s photos with explicit captions. A third reported a user who propositioned her child for sex, offering $65,000 for “an hour” with the girl.
In response to those three reports, Meta said either that the communications did not violate “community guidelines” or that its staff did not have time to review them. In other cases, Meta told parents that it relied on its “technology” to determine the content was “probably” not a violation.
Separately, The Times found comments that included links to sites identified by the Canadian center as trading illegal, nude imagery of children. None of those reports received a response from Meta.
Former Meta trust and safety employees described an organization overwhelmed despite knowing about the problem for years.
“You hear, ‘I reported this account, it was harassing my daughter, why is he back?’” said a former investigator for the company who requested anonymity. “There are not enough people, resources and systems to tackle all of it.”
In recent years, conspiracy theories like QAnon, which claims Democratic politicians are trafficking children, have led to an excess of unfounded reports that have muddled the evaluation of child abuse tips, three former Meta trust and safety employees said.
A 2020 document that surfaced in a lawsuit described child safety as a “non-goal” at Meta. “If we do something here, cool,” the document said. “But if we do nothing at all, that’s fine too.” The lawsuit was brought against Meta and other companies claiming damage from using social media. Lawyers for the plaintiffs declined to provide more information about the document.
In documents from 2018 included in a separate lawsuit making similar claims of harm, a top Facebook executive told Instagram’s chief executive that unless changes were made, Facebook and Instagram were “basically massive ‘victim discovery services,’” an allusion to the considerable evidence of abuse on the platforms.
Mr. Stone, the Meta spokesman, disputed the suggestion that the trust team was understaffed and underfunded, saying that 40,000 employees worked on safety and security and that the company had invested $20 billion in such efforts since 2016. He also referred to a previous statement about the lawsuits, saying they “mischaracterize our work using selective quotes and cherry-picked documents.”
In addition, he noted that Meta reported more suspected child abuse imagery to the authorities than any other company each year. In December, it announced plans to encrypt its messaging services, which would reduce the reports.
‘It’s All Over Instagram’
Experts in child protection and development say young people should never be made to have negative feelings about their bodies. But clothing that is appropriate in a gym or dance competition may take on an unintended meaning when shared online.
Children’s dance attire regularly features strappy bra tops, sheer fabric and bikini bottoms, and popular cheer outfits combine sports bras with little skirts — part of a long-term trend toward more revealing clothing for girls.
“In the dance world we’re in, they’re half naked all the time and their legs are in the air,” said a mother in Massachusetts who declined to be named. “And if you’re not used to seeing that, maybe it’s different.”
Lynn, whose granddaughter in Texas is an ambassador for a cheerleading brand, said there was no logic to the reactions her posts received. Photos of the girl’s feet attract the most extreme comments, she said. “You can’t stop weird people, I guess.”
Still, many of the would-be influencers suffer. In some instances criticism of the posts, and accompanying bullying, becomes so severe that mothers turn to home-schooling.
“She got slaughtered all through primary school,” said Kaelyn, the mother in Melbourne. “Children were telling her, ‘We can’t play with you because my mom said too many perverts follow you on the internet.’”
In the United States, parents have substantial leeway in making decisions about their children. But people who suspect illegal behavior on Instagram quickly discover that the authorities are overwhelmed and typically focus on the clearest-cut cases.
Even the most unsettling images of sexualized child influencers tend to fall into a legal gray area. To meet the federal definition of so-called child pornography, the law generally requires a “lascivious exhibition” of the anal or genital area, though courts have found the requirement can be met without nudity or sheer clothing.
There have been criminal prosecutions against parents accused in child sexual abuse cases.
In Louisiana last year, a mother was arrested and charged with working with a photographer to produce illegal images of her daughter in a thong bikini. In Texas, a mother was sentenced to 32 years in prison in December for producing nude photos of her 8-year-old daughter with the same photographer. And in North Carolina, a mother is awaiting trial on charges that she took her 15-year-old daughter to a photographer who sexually abused her and she failed to get medical help when the girl tried to kill herself, according to court documents.
Still, those prosecutions are rare, and some male followers of the mom-run accounts openly welcome the windfall.
“As long as this stuff legally exists, I just enjoy it :),” one of them wrote on Telegram.
“Exactly,” another responded. “It’s all over Instagram.”
231 notes
·
View notes
Text
why settle for ordinary product descriptions when you can create extraordinary ones?
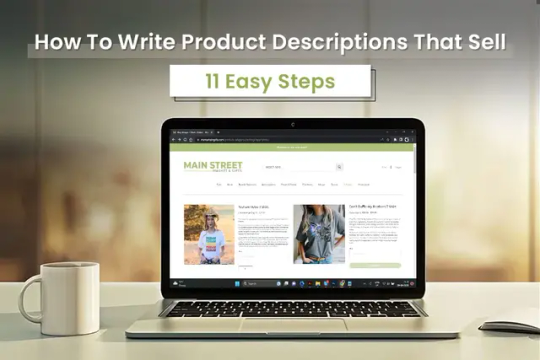
Instead of just stating facts, paint a vivid picture with your words. Use descriptive language that sparks the reader's imagination and transports them to a world of possibilities. Make your descriptions memorable and captivating.
Focus on the unique features and benefits of each product. Explain how they solve problems or enhance the lives of your customers. Show them why they can't live without your product and create a sense of desire.
Keep your descriptions simple, concise, and easy to understand. Use clear and straightforward language that everyone can relate to.
Remember, your product descriptions are an opportunity to connect with your customers and persuade them to make a purchase. So, make them exceptional by infusing them with your creativity, focusing on the unique qualities, and using language that resonates with your audience.
#etsy alternatives#online marketplace#wholesale marketplace#main street market & gifts#best things to sell online#benefits of online marketplace#how to write product description
0 notes
Text
Hi folks I would like to make a li'l post telling y'all on my main account here that I have an online store where I (currently) sell handmade bags and animal plushies — some of which are cat toys. And. some stress balls/stim toys.
Having this become a means to support myself would be sooooooo good and I want to sell at least one thing this month so if you have money theeeenn maybe buy? Maybe put on wishlist? Maybe.? Reblog?.
#textiles#shop small#autistic adult#cute things#plushies#support small business#I had a dream last night where I was sitting at a table that was swinging over a river between an ice cream shop and#and a breakfast place and whenever the table reached one side the servers would pass things over to the table and everyone sitting there had#had to make sure it didn't fall off and also start eating#And I had a stack of pancakes with syrup on and a server (?) reached over with some kind of heater??? to warm it all up#but it ended up just making the syrup melt off and get all over the table#Anyway
20 notes
·
View notes
Note
hello! i don't know anything about digital art or tablets but it's something i'd like to try out. i was wondering if you know of any affordable tablets that you don't have to hook up to a computer?
So the fortunate thing is that tablets have gotten a LOT cheaper especially with other companies like Huion and XP-Pen stepping up to offer competitive prices compared to Wacom, which is notoriously expensive.
That said, the unfortunate thing is that the cheapest tablets on the market are the ones that you have to hook up to a PC (these are typically desk tablets, i.e. the ones that you basically use as a computer mouse because there are no screens built in to them).
There are PC tablets where they're all in one PC's that offer tablet screens (I used to use a Cintiq Companion 2 which was exactly that) but they're INCREDIBLY expensive and honestly, not much better than just getting an entry level PC and screen tablet / monitor + desk tablet. It's definitely not something you'd want to get if you haven't tried out digital art before either, because there's a risk in that in and of itself - you haven't done it before, so you're not guaranteed to stick with it. And I say that because digital art in and of itself is a medium, there's a learning curve to it even if you already have foundational knowledge in traditional art (though that foundational knowledge will help a lot) and it's not as easy or simple as just pressing some buttons and making art appear. So the last thing you're gonna want to do is spend a whole bunch of money on a drawing tablet / digital art software if you wind up not liking it in the long run.
So I would say your best option for trying out digital art without losing out on a whole lot of money if you wind up not enjoying it (and if you want something that doesn't require hooking up to a PC) would be a Samsung tablet or iPad - and I say that because if you DON'T end up creating digital art in the long term, you'll still have a handy portable PC that you can use for other things. You can get iPads and Samsung tablets at used prices through pawn shops, local marketplaces, etc. or if you have strong rep with your phone company, you might be able to snag a deal next time you renew your phone plan (I would recommend checking around back-to-school season or Christmas/Black Friday/etc. as that's when phone companies offer crazy deals where you can get tablets and accessories basically for free LMAO)
Just make sure you do your research on what tablets offer what in terms of pen and software compatibility, some tablets don't work with pens, others only work with specific kinds of pens, etc. For iPads, you'll typically want something that will ideally work with the Apple Pencil 2, as that's the newest model of the Apple Pencil (and it has that fun way of charging where you can just stick the pen to the side of the tablet and it magnetizes/charges from your iPad's battery).
I can't really give advice on the Samsung tablets as I've never used them, so do your research for that one, there are loads of videos online that talk about all the different models and benefits. Just note that if you want to use Procreate specifically, you'll need an iPad as it's an iOS-only app. Clip Studio and Adobe products , on the other hand, are offered on virtually all mobile devices and software!
I hope that helps! Good luck!! <3
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Taking Risk
I just spent a week talking with some exceptional students from three of the UK's top universities; Cambridge, Oxford and Imperial College. Along with UCL, these British universities represent 4 of the top 10 universities in the world. The US - a country with 5x more people and 8x higher GDP - has the same number of universities in the global top 10.
On these visits, I was struck by the world-class quality of technical talent, especially in AI and biosciences. But I was also struck by something else. After their studies, most of these smart young people wanted to go and work at companies like McKinsey, Goldman Sachs or Google.
I now live in San Francisco and invest in early-stage startups at Y Combinator, and it's striking how undergraduates at top US universities start companies at more than 5x the rate of their British-educated peers. Oxford is ranked 50th in the world, while Cambridge is 61st. Imperial just makes the list at #100. I have been thinking a lot about why this is. The UK certainly doesn't lack the talent or education, and I don't think it's any longer about access to capital.
People like to talk about the role of government incentives, but San Francisco politicians certainly haven't done much to help the startup ecosystem over the last few years, while the UK government has passed a raft of supportive measures.
Instead, I think it's something more deep-rooted - in the UK, the ideas of taking risk and of brazen, commercial ambition are seen as negatives. The American dream is the belief that anyone can be successful if they are smart enough and work hard enough. Whether or not it is the reality for most Americans, Silicon Valley thrives on this optimism.
The US has a positive-sum mindset that business growth will create more wealth and prosperity and that most people overall will benefit as a result. The approach to business in the UK and Europe feels zero-sum. Our instinct is to regulate and tax the technologies that are being pioneered in California, in the misguided belief that it will give us some kind of competitive advantage.
Young people who consider starting businesses are discouraged and the vast majority of our smart, technical graduates take "safe" jobs at prestigious employers. I am trying to figure out why that is.
___
Growing up, every successful adult in my life seemed to be a banker, a lawyer or perhaps a civil engineer, like my father. I didn't know a single person who programmed computers as a job. I taught myself to code entirely from books and the internet in the late 1990s. The pinnacle of my parents' ambition for me was to go to Oxford and study law.
And so I did. While at university, the high-status thing was to work for a prestigious law firm, an investment bank or a management consultancy, and then perhaps move to Private Equity after 3 or 4 years. But while other students were getting summer internships, I launched a startup with two friends. It was an online student marketplace - a bit like eBay - for students. We tried to raise money in the UK in 2006, but found it impossible. One of my cofounders, Kulveer, had a full-time job at Deutsche Bank in London which he left to focus on the startup. His friends were incredulous - they were worried he'd become homeless. My two cofounders eventually got sick of trying to raise money in the UK and moved out to San Francisco. I was too risk-averse to join them - I quit the startup to finish my law degree and then became a management consultant - it seemed like the thing that smart, ambitious students should do. The idea that I could launch a startup instead of getting a "real" job seemed totally implausible.
But in 2011, I turned down a job at McKinsey to start a company, a payments business called GoCardless, with two more friends from university. We managed to get an offer of investment (in the US) just days before my start date at McKinsey, which finally gave me the confidence to choose the startup over a prestigious job offer. My parents were very worried and a friend of my father, who was an investment banker at the time, took me to one side to warn me that this would be the worst decision I ever made. Thirteen years later, GoCardless is worth $2.3bn.
I had a similar experience in 2016, when I was starting Monzo, I had to go through regulatory interviews before I was allowed to work as the CEO of a bank. We hired lawyers and consultants to run mock interviews - and they told me plainly that I was wasting my time. It was inconceivable that the Bank of England would authorise me, a 31 year old who'd never even worked in a bank, to act as the CEO of the UK's newest bank. (It turned out they did.) So much of the UK felt like it was pushing against me as an aspiring entrepreneur. It was like an immune system fighting against a foreign body. The reception I got in the US was dramatically different - people were overwhelmingly encouraging, supportive and helpful. For the benefit of readers who aren't from the UK, I hope it's fair to say that Monzo is now quite successful as well.
___
I don't think I was any smarter or harder working than many of the recent law graduates around me at Oxford. But I probably had an unusual attitude to risk. When we started GoCardless, we were 25 years old, had good degrees, no kids and supportive families. When fundraising was going poorly, we discussed using my parents' garage as an office. McKinsey had told me to contact them if I ever wanted a job in future. I wonder if the offer still stands.
Of course, I benefitted from immense privilege. I had a supportive family whose garage I could have used as an office. I had a good, state-funded education. I lived in a safe, democratic country with free healthcare. And I had a job offer if things didn't work out. And so the downside of the risks we were taking just didn't seem that great.
But there's a pessimism in the UK that often makes people believe they're destined to fail before they start. That it's wrong to even think about being different. Our smartest, most technical young people aspire to work for big companies with prestigious brands, rather than take a risk and start something of their own.
And I still believe the downside risk is small, especially for privileged, smart young people with a great education, a supportive family, and before they accumulate responsibilities like childcare or a mortgage. If you spend a year or two running a startup and it fails, it's not a big deal - the job at Google or McKinsey is still there at the end of it anyway. The potential upside is that you create a product that millions of people use and earn enough money that you never have to work again if you don't want to.
This view is obviously elitist - I'm aware it's not attainable for everyone. But, as a country, we should absolutely want our smartest and hardest working people building very successful companies - these companies are the engines of economic growth. They will employ thousands of people and generate billions in tax revenues. The prosperity that they create will make the entire country wealthier. We need to make our pie bigger, not fight over the economic leftovers of the US. Imagine how different the UK would feel if Google, Microsoft and Facebook were all founded here.
___
When I was talking with many of these smart students this week, many asked me how these American founders get away with all their wild claims. They seem to have limitless ambition and make outlandish claims about their goals - how can they be so sure it will pan out like that? There's always so much uncertainty, especially in scientific research. Aren't they all just bullshitters? Founders in the UK often tell me "I just want to be more realistic," and they pitch their business describing the median expected outcome, which for most startups is failure.
The difference is simple - startup founders in the US imagine the range of possible scenarios and pitch the top one percent outcome. When we were starting Monzo, I said we wanted to build a bank for a billion people around the world. That's a bold ambition, and one it's perhaps unlikely Monzo will meet. Even if we miss that goal, we've still succeeded in building a profitable bank from scratch that has almost 10 million customers.
And it turns out that this approach matches exactly what venture capitalists are looking for. It is an industry based on outlier returns, especially at the earliest stages. Perhaps 70% of investments will fail completely, and another 29% might make a modest return - 1x to 3x the capital invested. But 1% of investments will be worth 1000x what was initially paid. Those 1% of successes easily pay for all the other failures.
On the contrary, many UK investors take an extremely risk-averse view to new business - I lost count of the times that a British investor would ask for me a 3 year cash-flow forecast, and expect the company to break even within that time. UK investors spend too much time trying to mitigate downside risk with all sorts of protective provisions. US venture capital investors are more likely to ask "if this is wildly successful, how big could it be?". The downside of early-stage investing is that you lose 1x your money - it's genuinely not worth worrying much about. The upside is that you make 1000x. This is where you should focus your attention.
___
A thriving tech ecosystem is a virtuous cycle - there's a flywheel effect that takes several revolutions to get up-to-speed. Early pioneers start companies, raise a little money and employ some people. The most successful of these might get acquired or even IPO. The founders get rich and become venture capital investors. The early employees start their own companies or become angel investors. Later employees learn how to scale up these businesses and use their expertise to become the executives of the next wave of successful growth-stage startups.
Skype was a great early example of this - Niklas Zenstrom, the co-founder, launched the VC Atomico. Early employees of Skype started Transferwise or became seed investors at funds like Passion Capital, which invested in both GoCardless and Monzo. Alumni of those two companies have created more than 30 startups between them. Matt Robinson, my cofounder at GoCardless, was one of the UK's most prolific angel investors, before recently becoming a Partner at Accel, one of the top VCs in the world. Relative to 15 or 20 years ago, the UK tech ecosystem is flourishing - our flywheel is starting to accelerate. Silicon Valley has just had a 50 year head start.
There is no longer a shortage of capital for great founders in the UK (although most of the capital still comes from overseas investors). I just believe that people with the highest potential aren't choosing to launch companies, and I want that to change.
___
I don’t think the world is prepared for the tidal wave of technological change that’s about to hit over the next handful of years. Primarily because of the advances in AI, companies are being started this year that are going to transform entire industries over the next decade.
It doesn't seem hyperbolic to say that we should expect to see very significant breakthroughs in quantum computers, nuclear fusion, self-driving vehicles, space exploration and drug discovery in the next 10 or 20 years. I think we are about to enter the biggest period of transformation humanity has ever seen.
Instead of taking safe, well-paying jobs at Goldman Sachs or McKinsey, our young people should take the lead as the world is being rebuilt around us.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discussing POS & Merchant Payment Processing
Article by Jonathan Bomser | CEO | Accept-Credit-Cards-Now.com

In the fast-evolving digital landscape of today, the capacity to welcome credit card payments is a paramount necessity for businesses of all sizes. Merchant account processing and payment processing have ushered in a transformation in the world of commercial transactions, reshaping the dynamics of buying and selling goods and services. Let's explore the realm of point of sale (POS) systems and merchant payment processing to comprehend their significance and the array of benefits they offer to your business.
Merchant Account Processing: The Solid Foundation of Success
Merchant account processing acts as the bedrock upon which any thriving business is built. This indispensable service empowers businesses to securely accept credit card payments. With the explosive growth of online shopping and the dwindling popularity of cash transactions, having a merchant account has shifted from a choice to a fundamental necessity. These accounts establish a pivotal link between your business and the vast payment processing network, making it possible to accept a wide spectrum of payment methods, including credit cards and debit cards.
The Power of Embracing Credit Cards
Opting to embrace credit card payments can be a game-changing decision for your business. It has the potential to expand your customer base significantly, as a considerable number of consumers favor the convenience and security of credit card transactions. Whether you run a physical store, an online shop, or a combination of both, accepting credit cards can be a catalyst for a substantial boost in your sales and can propel your business to newfound heights.
Payment Processing: The Crux of Effortless Transactions
Payment processing encapsulates a series of steps, commencing from the moment a customer initiates a purchase to the moment when funds are safely deposited into your bank account. It encompasses transaction authorization, fund capture, and settlement, all while incorporating robust security measures to ensure the safeguarding of customer data. Modern payment processing solutions are engineered to be swift, secure, and hassle-free, ensuring a seamless shopping experience that elevates customer satisfaction and fosters long-term loyalty.
Revealing the Advantages of a POS System
A POS system assumes a pivotal role in the realm of merchant payment processing, adeptly managing sales while providing invaluable insights into the dynamics of your business operations. The key advantages of POS systems include enhanced efficiency, streamlined inventory management, data analytics that support well-informed decision-making, and fortified security measures to fortify customer payment data.
youtube
Selecting the Ideal Payment Processing Solution
The process of choosing the right payment processing solution demands a comprehensive evaluation of factors such as transaction fees, security features, integration simplicity, and the quality of customer support. The decision should seamlessly align with the nature and requisites of your business, irrespective of whether it operates primarily online, within a physical space, or adopts a hybrid approach.
Merchant account processing ensures the secure embrace of credit card payments, while payment processing simplifies the intricate web of transactions. POS systems inject operational insights and efficiencies, enhancing inventory management and data-informed decision-making. By electing the most fitting payment processing solution, you unlock a realm of benefits and set a strong foundation for long-term success in the fluid and ever-changing landscape of today's marketplace.
#high risk merchant account#merchant processing#payment processing#credit card processing#high risk payment gateway#accept credit cards#high risk payment processing#credit card payment#payment#youtube#Youtube
21 notes
·
View notes