#googlenet
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Ứng dụng GoogleNet: Công nghệ AI đột phá trong phân loại hình ảnh
🌐 Trong thời đại công nghệ số, việc phân loại hình ảnh chính xác là yếu tố then chốt giúp cải thiện hiệu suất của nhiều lĩnh vực, từ y tế 🏥, giao thông 🚦 đến thương mại điện tử 🛍️. Bạn đã nghe về GoogleNet – một trong những mạng nơ-ron sâu tiên tiến nhất được Google phát triển? 💡
🔍 GoogleNet không chỉ nổi bật với cấu trúc Inception mang tính cách mạng, mà còn giúp giảm thiểu số lượng tham số và tăng độ chính xác vượt bậc. Điều này mở ra khả năng nhận diện và phân loại hình ảnh với tốc độ ⚡ nhanh chóng và độ chính xác cực cao 🎯.
👉 Tò mò về cách GoogleNet hoạt động và ứng dụng thực tiễn của nó? 🌟 Hãy đọc ngay bài viết chi tiết trên website của chúng tôi! 📖 Bạn sẽ hiểu rõ: ✅ Tại sao GoogleNet là "chìa khóa vàng" trong công nghệ phân loại hình ảnh. ✅ Các ngành nghề đang hưởng lợi từ ứng dụng này. ✅ Tiềm năng phát triển không giới hạn của AI và học sâu (Deep Learning).
💻 Khám phá ngay tại đây: Ứng dụng mạng GoogleNet vào phân loại hình ảnh
📢 Hãy chia sẻ bài viết nếu bạn thấy hữu ích nhé! 🤗 Đừng quên để lại bình luận 💬 và ý kiến của bạn về công nghệ AI tiên tiến này!
��️ Cùng nhau lan tỏa tri thức và khám phá tương lai!
#aicandy#aicandy.vn#artificial intelligence#machine learning#software engineering#programming#computer vision#googlenet
0 notes
Text
Among other aspects, Minsky and Papert noticed (as also had Rosenblatt) that artificial neural networks are not able to distinguish well between figure and ground: in their computation of the visual field, each point gains somehow the same priority — which is not the case with human vision. This happens because artificial neural networks have no ‘concept’ of figure and ground, which they replace with a statistical distribution of correlations (while the figure–ground relation implies a model of causation). The problem hs not disappeared with deep learning: it has been discovered that large convolutional neural networks such as AlexNet, GoogleNet, and ResNet-50 are still biased towards texture in relation to shape. Matteo Pasquinelli, 2023. The Eye of the Master: A Social History of Artificial Intelligence. London: Verso.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
🌟 GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong trí tuệ nhân tạo 🌟
📌 Bạn có biết? GoogleNet chính là một trong những công nghệ tiên phong làm nên sự phát triển vượt bậc của trí tuệ nhân tạo (AI)! 🚀 Với kiến trúc Inception Module độc đáo, GoogleNet đã mở ra một kỷ nguyên mới cho việc nhận diện hình ảnh và xử lý dữ liệu thông minh, mang lại hiệu suất vượt trội với độ chính xác cao. 🎯
✨ Điểm nhấn nổi bật của GoogleNet: ✅ Tối ưu hóa hiệu suất: Mô hình nhẹ hơn, nhanh hơn, nhưng vẫn cực kỳ mạnh mẽ. ✅ Ứng dụng thực tiễn: Được sử dụng rộng rãi trong phân loại hình ảnh, nhận diện đối tượng và hơn thế nữa. ✅ Khả năng học sâu: Đưa trí tuệ nhân tạo gần hơn với con người nhờ việc xử lý dữ liệu phức tạp một cách tự nhiên.
💡 Bạn có tò mò? Làm thế nào GoogleNet đã thay đổi hoàn toàn cuộc chơi trong lĩnh vực AI? Hãy đọc ngay bài viết chi tiết để khám phá sâu hơn về công nghệ mang tính cách mạng này! 👉 GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo
🌐 Hãy chia sẻ để lan tỏa kiến thức về những đột phá công nghệ! ❤️
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
guys I accidentally took naproxen and excedrin: migraine together and both have NSAIDS in them the googlenet says I'm gonna die. Am I gonna di?
My stomche is bubblig if that helps
#l1msshittystorytelling#l1mshitposts#srsly tho#send help#pls hlp#memes#funny#shitposts#tumblr help#im so serious help me#any doctors on her#mouthfuloffluff
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Development of Deep Learning Algorithms for Image Recognition: A Modern Perspective
In the past decade, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) has seen a remarkable surge in capabilities, particularly within the area of deep learning. Among its various applications, image recognition stands out as one of the most transformative and impactful. From medical diagnostics to autonomous vehicles and surveillance systems, the demand for robust and accurate image recognition models continues to grow. As research institutions like Telkom University intensify their focus on intelligent systems and computer vision, the development of advanced deep learning algorithms becomes not just a necessity, but a frontier of innovation.
Evolution of Image Recognition
Traditionally, image recognition systems relied on manually engineered features and statistical classifiers. These systems struggled to handle variability in lighting, orientation, and scale. The introduction of convolutional neural networks (CNNs), a core component of deep learning, marked a turning point. First gaining popularity with the success of AlexNet in the 2012 ImageNet competition, CNNs offered a hierarchical feature extraction mechanism that mimicked the human visual system, drastically improving recognition performance.
CNNs use layers of filters to capture low-level features such as edges and textures in early layers, and more abstract concepts like objects and scenes in deeper layers. This shift toward automatic feature learning has made deep learning models adaptable to a wide range of image recognition tasks, from facial recognition to object detection.
Architectures and Innovations
Since AlexNet, many new architectures have emerged, each pushing the boundaries of what deep learning can achieve. VGGNet introduced simplicity with deeper networks, while GoogLeNet introduced the Inception module to optimize computational efficiency. ResNet further revolutionized the field by introducing skip connections, allowing networks to be hundreds of layers deep without suffering from the vanishing gradient problem.
More recently, transformer-based models like Vision Transformers (ViT) have demonstrated that attention mechanisms—originally developed for natural language processing—can outperform CNNs in large-scale image recognition tasks when sufficient data and computational resources are available. These models divide images into patches and process them similarly to sequences of words, allowing for a global understanding of visual information.
Challenges in Deep Learning for Image Recognition
Despite significant progress, deep learning still faces notable challenges in image recognition. One of the most critical issues is the requirement for massive labeled datasets. While transfer learning and pre-trained models alleviate this need to some extent, domain-specific tasks often lack sufficient labeled data, limiting model generalization.
Another major challenge is interpretability. Deep learning models, especially those with millions of parameters, often function as “black boxes.” In high-stakes applications like medical imaging or biometric security, understanding why a model makes a certain prediction is essential for trust and accountability.
Additionally, deep learning models are vulnerable to adversarial attacks—subtle, often imperceptible perturbations to input images that can cause models to make incorrect predictions. Ensuring robustness and security in deployment scenarios remains an active area of research.
Application Domains and Case Studies
One of the most exciting areas of application is in the healthcare sector. Deep learning algorithms have demonstrated expert-level performance in identifying diseases from radiological images, such as detecting diabetic retinopathy from retinal scans or lung cancer from CT scans. These tools are not only improving diagnostic accuracy but also increasing accessibility in regions with limited access to medical specialists.
In the realm of autonomous vehicles, image recognition systems are critical for understanding the driving environment. These systems detect road signs, pedestrians, other vehicles, and lane markings, contributing to decision-making and navigation processes. The fusion of image recognition with other sensory inputs like LiDAR and radar is essential to ensure safety and reliability.
Another emerging domain is smart surveillance, where intelligent systems are employed to detect unusual behavior, identify individuals, and track objects in real-time. Telkom University has actively explored this area, integrating deep learning into intelligent video analytics platforms for enhancing public safety in urban environments.
Telkom University and Contributions to the Field
As a leading institution in Indonesia, Telkom University has shown a strong commitment to advancing research in intelligent systems and computer vision. Research labs within the university are increasingly focused on developing custom neural network architectures tailored for local use cases, such as recognizing cultural patterns, regional vehicle license plates, and indigenous diseases visible through imaging.
Furthermore, Telkom University supports interdisciplinary collaboration by combining expertise in electronics, data science, and telecommunications. This collaborative approach accelerates the translation of theoretical research into real-world applications, such as AI-powered traffic monitoring systems and digital identity verification technologies.
Through its graduate and undergraduate programs, Telkom University nurtures a new generation of AI engineers equipped with the knowledge to design and deploy scalable image recognition solutions. Its participation in global research consortia and regional innovation hubs enhances its role as a center of excellence in Southeast Asia.
Future Trends in Image Recognition
Looking ahead, the integration of multimodal learning is likely to redefine image recognition. Future systems will not rely solely on visual data but will combine it with audio, text, and sensor data to provide a richer understanding of the environment. This will lead to more context-aware systems, capable of more nuanced decision-making.
Another trend is the push toward efficient deep learning. As environmental concerns and resource constraints grow, researchers are focusing on creating lightweight models that require less computation and memory, suitable for edge computing. Techniques such as knowledge distillation, model pruning, and quantization are gaining prominence.
Federated learning also presents a promising path forward. It allows training deep learning models across decentralized devices without transferring raw data, addressing privacy concerns while leveraging data from multiple sources. This approach can be particularly beneficial in sensitive fields like healthcare and finance.
Lastly, self-supervised learning, which enables models to learn from unlabeled data, may become the standard for future deep learning paradigms. By reducing the dependence on labeled datasets, it opens the door to broader and more equitable AI development across different regions and domains.
1 note
·
View note
Text
🚀 GoogleNet: Bước đột phá vượt thời đại trong trí tuệ nhân tạo! 🤖✨
Bạn đã từng tò mò làm thế nào mà công nghệ AI có thể nhận diện hình ảnh với độ chính xác cao đến kinh ngạc? 🧐 📸 GoogleNet chính là chìa khóa! 💡 Với thiết kế đột phá dựa trên cấu trúc Inception Module, GoogleNet không chỉ giảm thiểu tài nguyên tính toán mà còn cải thiện đáng kể độ chính xác. 💻⚙️
🔍 Điểm nổi bật của GoogleNet: ✅ Kích thước nhỏ gọn nhưng hiệu năng mạnh mẽ 💪 ✅ Được thiết kế để xử lý hàng triệu hình ảnh mỗi giây 🌌 ✅ Là nền tảng quan trọng trong các ứng dụng AI hiện đại 🌟
👉 Nếu bạn muốn khám phá thêm về cấu trúc, nguyên lý hoạt động và tầm ảnh hưởng của GoogleNet trong ngành AI, đừng bỏ lỡ bài viết chi tiết tại đây: 🌐 GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo
💬 Hãy chia sẻ suy nghĩ của bạn: Công nghệ này sẽ thay đổi thế giới ra sao? 🌍👇 ❤️ Đừng quên thả tim và chia sẻ bài viết để lan tỏa kiến thức AI đến mọi người! 🎉
Khám phá thêm những bài viết giá trị tại aicandy.vn
0 notes
Text
Potato Leaf Disease Detection Through Image Processing Techniques

Abstract
Agriculture is one of the most important pillars of Bangladesh’s economy. However, due to some factors such as plant diseases, pests, climate change, the yield of the farming industry decreases, and the productivity decreases as well. The detection of plant diseases is crucial to avert the losses in the productivity and in the yield. It is not obvious to monitor the plant diseases manually as the act of disease detection is very critical. It needs a huge effort, along with knowledge of plant diseases and extensive processing times. Therefore, image processing technology is used to detect the plant disease, this is done by capturing the input image that undergoes the process and is compared with the dataset. This dataset is composed of diverse diseases of potato leaves in the image format. This study aims to build a web application to predict the diseases of potato plants that will help farmers to identify the diseases so that they can use appropriate fungicide to get more yields. The purpose of this study is to assist and provide efficient support to the potato farmers. In this study, we propose a system that will use the techniques of image process to both analyze and detect the plant diseases using machine learning Conventional Neural Networks (CNN) with Tensorflow framework 2. The results of the implementation show that the designed system could give a successful result by detecting and classifying the potato leaf diseases and healthy plant.

Introduction
Agricultural industry is the backbone of our economy that contributes about 11.63% of GDP (BBS 2021). Potato is an important and leading crop in Bangladesh. Bangladesh is the seventh potato producing country in the world and ranks second after rice in terms of production and are the third most important food crop after rice and wheat in terms of human consumption in Bangladesh (FAOSTAT, 2020). According to the DAE statistics, about 9.61 million MT of potatoes have been produced in 2020 against the annual demand of about 6.82 million MT, bringing a surplus of 3.40 million MT despite some amounts is being exported (DAM, 2020).
But in Bangladesh late blight is the most common and highly destructive, fungal disease in potato and annual potato yield losses due to late blight have been estimated at 25-57% (GEOPOTATO project report, 2016-2019). Plants are sensitive to diseases especially the plant leaves as symptoms of the disease appear first on the leaves. Due to the bad impacts of plant diseases on the both the economy and environment, the farmers should consider monitoring the crops in such a way that they may mitigate losses. It exists a way that is used by experts to monitor the crops which is the naked eye observation. This is a traditional method that has many constraints related to time consuming as the operation of monitoring is done manually, and it requires the presence of experts. However, lately, crop monitoring is being developed to be digital and semi-automatic, meaning that only from the symptoms that are shown on the leaf, the disease could be detected in an easier, quicker, cheaper way. Therefore, this digitalized method will be beneficial for the farmers as well since it will facilitate for them the detection of the diseases because most of the farmers do not have a sufficient background and knowledge about monitoring the crops and dealing with the variety of diseases that could affect them. There are many researcher reported, leaf dieses classification and detect is successfully possible by using image processing techniques of deep learning as well as machine learning. Different methods for machine learning and deep learning include the Support Vector Machines (SVM), Random.
Forests (RF), K-nearest Neighbor (KNN), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), along with models such as AlexNet, GoogleNet, and Caffe are used to classify and detect to leaf dieses (Knaak et al., 2021). The report presented a machine-learning model including canny edge detection technique for edge feature extraction, grid color movement for extracting color features and local binary pattern (LBP) for texture analysis. Where the features were extracted combined to create a combined feature vector which was used for training the artificial neural network (ANN). The convolutional model is also capable of differentiating the plant leaves and recognizing rice plants and their diseases (Shrivastava et al., 2022). Potato leaf diseases were detected by using random forest classifiers where image pre-processing was done in two steps like image normalization and color space conversion where segmentation was done using thresholding HSV images in RGB color space and global feature descriptor (GFD), gray level cooccurrence matrix (GLCM), color histogram were used for extracting features. Finally, classification was done using random forest (RF) classifiers (Iqbal et al., 2020). The proposed system that we are suggesting in this paper could be used by the farmers to increase the yield with no need to consult experts. The core purpose of this proposed system is not aiming only at detecting the plant diseases using the image processing technology, but it aims also at directing the user farmer to use a mobile application in which he will upload the image and receive the type of disease infection along with a suggestion of needed pesticides. The digitalization of the agriculture field has known the intervention of the latest technologies namely the image processing. As a result, our system that is designed to be automated system is implemented using image processing technique using machine learning Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) with Tensorflow Framework 2.
Source : Potato leaf disease detection using image processing
0 notes
Text
Danh sách bài viết trên AIcandy.vn
Học tập toàn diện: Kết nối lý thuyết, thực hành và dữ liệu thực tế
Kiến thức nền tảng trí tuệ nhân tạo
Trí tuệ nhân tạo (AI): Lịch sử phát triển và ứng dụng thực tiễn
Từ điển AI cho người mới bắt đầu: Giải thích các khái niệm chính
Khám phá sự khác biệt giữa AI, ML và DL
Tổng quan 4 phương pháp học máy chính trong trí tuệ nhân tạo
Hồi quy tuyến tính: Kỹ thuật cơ bản và ứng dụng trong học máy
K-Means Clustering: Ưu điểm, nhược điểm và khi nào nên sử dụng
Khám phá K-nearest neighbors cho phân loại và hồi quy
Phân loại dữ liệu là gì? Giải thích đơn giản và ví dụ thực tế
Random Forest: Giải thích chi tiết và ứng dụng
SVM trong xử lý dữ liệu phi tuyến tính: Kỹ thuật kernel và ứng dụng
Mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo: Công nghệ đột phá trong trí tuệ nhân tạo
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) trong Deep Learning
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): Ứng dụng và cách hoạt động
Tăng tốc huấn luyện mô hình với phương pháp Gradient Descent
Các phương pháp đánh giá hiệu suất mô hình Machine Learning
Tìm hiểu phân loại hình ảnh trong AI: Cách thức và ứng dụng
Tìm hiểu nhận diện đối tượng trong AI: Cách thức và ứng dụng
Xử lý ngôn ngữ tự nhiên: Công nghệ phân tích ngôn ngữ bằng AI
Giới thiệu chi tiết về học tăng cường: Phương pháp và ứng dụng
MobileNet: Mô hình hiệu quả trên thiết bị di động
Mô hình ResNet: Đột phá trong nhận diện hình ảnh
SSD: Giải pháp hiệu quả cho bài toán phát hiện đối tượng
EfficientNet: Cách mạng hóa mạng neural hiện đại
DenseNet: Cấu trúc, nguyên lý và ưu điểm trong mạng nơ-ron sâu
Tìm hiểu mô hình YOLOv5: Hiệu quả trong nhận diện đối tượng
YOLOv8: Nhận diện đối tượng với hiệu suất vượt trội
RetinaNet: Cải tiến mạnh mẽ trong công nghệ phát hiện đối tượng
GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo
AlexNet: Bước đột phá trong trí tuệ nhân tạo
Tìm hiểu mô hình FaceNet cho bài toán nhận diện khuôn mặt
Imbalanced Dataset: Thách thức và giải pháp trong Machine Learning
PyTorch trong học máy cho người mới bắt đầu
Từ lý thuyết đến thực hành AI-ML
Ứng dụng mạng MobileNet vào phân loại hình ảnh
Ứng dụng mạng GoogleNet vào phân loại hình ảnh
Ứng dụng mạng DenseNet vào phân loại hình ảnh
Ứng dụng mạng AlexNet vào phân loại hình ảnh
Ứng dụng mạng Efficientnet vào phân loại hình ảnh
Ứng dụng mạng ResNet-18 vào phân loại hình ảnh
Ứng dụng mạng ResNet-50 vào phân loại hình ảnh
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách huấn luyện dữ liệu tùy chỉnh với YOLO5
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách huấn luyện dữ liệu tùy chỉnh với YOLO8
Ứng dụng mạng SSD300 vào nhận diện đối tượng
Ứng dụng mạng RetinaNet vào nhận diện đối tượng
Cách dự đoán giá cổ phiếu hiệu quả bằng mô hình LSTM
Ứng dụng Machine Learning vào chơi game Flappy Bird
Triển khai phân loại hình ảnh trên thiết bị Android
Triển khai nhận diện đối tượng trên thiết bị Android với YOLO
Hướng dẫn triển khai phân loại hình ảnh trên Website miễn phí
Kho dữ liệu dành cho học máy
Tổng hợp công cụ hỗ trợ phát triển AI, ML, DL
1 note
·
View note
Text
Learning from imbalanced data paper review
A review of novelty detection
DenseNet
World Models
Zero-shot Learning Through Cross-Modal Transfer
Layer Normalization
Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting
Human level control through deep reinforcement learning (DQN)
Representation Learning:A Review and New Perspectives
Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles
Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate
Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation
GoogLeNet
Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
Deep Learning Model for Anomaly Detection: Survey
A Neural Attention Model for Abstractive Sentence Summarization
LSTM: A Search Space Odyssey
Isolation-based Anomaly Detection
An overview of gradient descent optimization algorithms
0 notes
Text
CNN Computer vision
This article explains popular CNN Architectures specific to object recognition. If you are new you should go through Computer vision basics first.
LeNet-5 architecture
One of the earliest CNN archietctures created by Yann LeCun in 1998. It was used for written digits recignition using MNIST database.
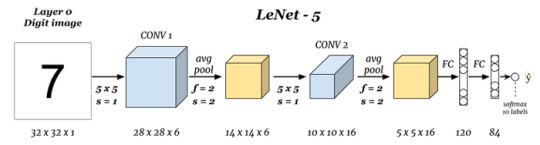
Starts with grayscalling images of 32x32x1 shape and applied with six 5×5 filters CONV…
View On WordPress
#AlexNet#CNN Architetures#Computervision#Fast R-CNN#GoogleNet#Inception#LeNet#Object Classification#Object Recognition#R-CNN#ResNET#VGG16#YOLO
0 notes
Photo






New hi-res deepdraw images: soon to be posted at @neuralgae
1 note
·
View note
Text
GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo
🌐 GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo 🤖
Bạn đã bao giờ nghe về GoogleNet chưa? 🌟 Đây là một trong những bước tiến vượt bậc trong AI, mở ra những khả năng không tưởng cho việc nhận diện hình ảnh 📸, hiểu ngữ cảnh 📊 và học máy. GoogleNet không chỉ là một mô hình mạng nơ-ron đơn thuần mà còn là công nghệ làm thay đổi cách chúng ta tương tác với dữ liệu và thông tin! 🚀
👉 Khám phá ngay bài viết chi tiết để hiểu thêm về cách GoogleNet đang làm thay đổi tương lai của công nghệ AI! GoogleNet: Cột mốc đột phá trong lĩnh vực trí tuệ nhân tạo
Khám phá thêm những bài viết giá trị tại aicandy.vn
1 note
·
View note
Text
밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝 1 사이토 고키
1장 헬로 파이썬 1.1 파이썬이란? 1.2 파이썬 설치하기 __1.2.1 파이썬 버전 __1.2.2 사용하는 외부 라이브러리 __1.2.3 아나콘다 배포판 1.3 파이썬 인터프리터 __1.3.1 산술 연산 __1.3.2 자료형 __1.3.3 변수 __1.3.4 리스트 __1.3.5 딕셔너리 __1.3.6 bool __1.3.7 if 문 __1.3.8 for 문 __1.3.9 함수 1.4 파이썬 스크립트 파일 __1.4.1 파일로 저장하기 __1.4.2 클래스 1.5 넘파이 __1.5.1 넘파이 가져오기 __1.5.2 넘파이 배열 생성하기 __1.5.3 넘파이의 산술 연산 __1.5.4 넘파이의 N차원 배열 __1.5.5 브로드캐스트 __1.5.6 원소 접근 1.6 matplotlib __1.6.1 단순한 그래프 그리기 __1.6.2 pyplot의 기능 __1.6.3 이미지 표시하기 1.7 정리 2장 퍼셉트론 2.1 퍼셉트론이란? 2.2 단순한 논리 회로 __2.2.1 AND 게이트 __2.2.2 NAND 게이트와 OR 게이트 2.3 퍼셉트론 구현하기 __2.3.1 간단한 구현부터 __2.3.2 가중치와 편향 도입 __2.3.3 가중치와 편향 구현하기 2.4 퍼셉트론의 한계 __2.4.1 도전! XOR 게이트 __2.4.2 선형과 비선형 2.5 다층 퍼셉트론이 출동한다면 __2.5.1 기존 게이트 조합하기 __2.5.2 XOR 게이트 구현하기 2.6 NAND에서 컴퓨터까지 2.7 정리 3장 신경망 3.1 퍼셉트론에서 신경망으로 __3.1.1 신경망의 예 __3.1.2 퍼셉트론 복습 __3.1.3 활성화 함수의 등장 3.2 활성화 함수 __3.2.1 시그모이드 함수 __3.2.2 계단 함수 구현하기 __3.2.3 계단 함수의 그래프 __3.2.4 시그모이드 함수 구현하기 __3.2.5 시그모이드 함수�� 계단 함수 비교 __3.2.6 비선형 함수 __3.2.7 ReLU 함수 3.3 다차원 배열의 계산 __3.3.1 다차원 배열 __3.3.2 행렬의 내적 __3.3.3 신경망의 내적 3.4 3층 신경망 구현하기 __3.4.1 표기법 설명 __3.4.2 각 층의 신호 전달 구현하기 __3.4.3 구현 정리 3.5 출력층 설계하기 __3.5.1 항등 함수와 소프트맥스 함수 구현하기 __3.5.2 소프트맥스 함수 구현 시 주의점 __3.5.3 소프트맥스 함수의 특징 __3.5.4 출력층의 뉴런 수 정하기 3.6 손글씨 숫자 인식 __3.6.1 MNIST 데이터셋 __3.6.2 신경망의 추론 처리 __3.6.3 배치 처리 3.7 정리 4장 신경망 학습 4.1 데이터에서 학습한다! __4.1.1 데이터 주도 학습 __4.1.2 훈련 데이터와 시험 데이터 4.2 손실 함수 __4.2.1 평균 제곱 오차 __4.2.2 교차 엔트로피 오차 __4.2.3 미니배치 학습 __4.2.4 (배치용) 교차 엔트로피 오차 구현하기 __4.2.5 왜 손실 함수를 설정하는가? 4.3 수치 미분 __4.3.1 미분 __4.3.2 수치 미분의 예 __4.3.3 편미분 4.4 기울기 __4.4.1 경사법(경사 하강법) __4.4.2 신경망에서의 기울기 4.5 학습 알고리즘 구현하기 __4.5.1 2층 신경망 클래스 구현하기 __4.5.2 미니배치 학습 구현하기 __4.5.3 시험 데이터로 평가하기 4.6 정리 5장 오차역전파법 5.1 계산 그래프 __5.1.1 계산 그래프로 풀다 __5.1.2 국소적 계산 __5.1.3 왜 계산 그래프로 푸는가? 5.2 연쇄법칙 __5.2.1 계산 그래프에서의 역전파 __5.2.2 연쇄법칙이란? __5.2.3 연쇄법칙과 계산 그래프 5.3 역전파 __5.3.1 덧셈 노드의 역전파 __5.3.2 곱셈 노드의 역전파 __5.3.3 사과 쇼핑의 예 5.4 단순한 계층 구현하기 __5.4.1 곱셈 계층 __5.4.2 덧셈 계층 5.5 활성화 함수 계층 구현하기 __5.5.1 ReLU 계층 __5.5.2 Sigmoid 계층 5.6 Affine/Softmax 계층 구현하기 __5.6.1 Affine 계층 __5.6.2 배치용 Affine 계층 __5.6.3 Softmax-with-Loss 계층 5.7 오차역전파법 구현하기 __5.7.1 신경망 학습의 전체 그림 __5.7.2 오차역전파법을 적용한 신경망 구현하기 __5.7.3 오차역전파법으로 구한 기울기 검증하기 __5.7.4 오차역전파법을 사용한 학습 구현하기 5.8 정리 6장 학습 관련 기술들 6.1 매개변수 갱신 __6.1.1 모험가 이야기 __6.1.2 확률적 경사 하강법(SGD) __6.1.3 SGD의 단점 __6.1.4 모멘텀 __6.1.5 AdaGrad __6.1.6 Adam __6.1.7 어느 갱신 방법을 이용할 것인가? __6.1.8 MNIST 데이터셋으로 본 갱신 방법 비교 6.2 가중치의 초깃값 __6.2.1 초깃값을 0으로 하면? __6.2.2 은닉층의 활성화 분포 __6.2.3 ReLU를 사용할 때의 가중치 초깃값 __6.2.4 MNIST 데이터셋으로 본 가중치 초깃값 비교 6.3 배치 정규화 __6.3.1 배치 정규화 알고리즘 __6.3.2 배치 정규화의 효과 6.4 바른 학습을 위해 __6.4.1 오버피팅 __6.4.2 가중치 감소 __6.4.3 드롭아웃 6.5 적절한 하이퍼파라미터 값 찾기 __6.5.1 검증 데이터 __6.5.2 하이퍼파라미터 최적화 __6.5.3 하이퍼파라미터 최적화 구현하기 6.6 정리 7장 합성곱 신경망(CNN) 7.1 전체 구조 7.2 합성곱 계층 __7.2.1 완전연결 계층의 문제점 __7.2.2 합성곱 연산 __7.2.3 패딩 __7.2.4 스트라이드 __7.2.5 3차원 데이터의 합성곱 연산 __7.2.6 블록으로 생각하기 __7.2.7 배치 처리 7.3 풀링 계층 __7.3.1 풀링 계층의 특징 7.4 합성곱/풀링 계층 구현하기 __7.4.1 4차원 배열 __7.4.2 im2col로 데이터 전개하기 __7.4.3 합성곱 계층 구현하기 __7.4.4 풀링 계층 구현하기 7.5 CNN 구현하기 7.6 CNN 시각화하기 __7.6.1 1번째 층의 가중치 시각화하기 __7.6.2 층 깊이에 따른 추출 정보 변화 7.7 대표적인 CNN __7.7.1 LeNet __7.7.2 AlexNet 7.8 정리 8장 딥러닝 8.1 더 깊게 __8.1.1 더 깊은 네트워크로 __8.1.2 정확도를 더 높이려면 __8.1.3 깊게 하는 이유 8.2 딥러닝의 초기 역사 __8.2.1 이미지넷 __8.2.2 VGG __8.2.3 GoogLeNet __8.2.4 ResNet 8.3 더 빠르게(딥러닝 고속화) __8.3.1 풀어야 할 숙제 __8.3.2 GPU를 활용한 고속화 __8.3.3 분산 학습 __8.3.4 연산 정밀도와 비트 줄이기 8.4 딥러닝의 활용 __8.4.1 사물 검출 __8.4.2 분할 __8.4.3 사진 캡션 생성 8.5 딥러닝의 미래 __8.5.1 이미지 스타일(화풍) 변환 __8.5.2 이미지 생성 __8.5.3 자율 주행 __8.5.4 Deep Q-Network(강화학습) 8.6 정리 부록 A Softmax-with-Loss 계층의 계산 그래프 A.1 순전파 A.2 역전파 A.3 정리 참고문헌
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Remember in the movie i, Robot when the center chest lights turned red it meant they were about to go ratchet on the humans around them? I've only had #SkyNet mini here, turned on, for 24 hours and I already pissed it off. Well, it was fun while it lasted. I'll be in my bunker if you need me. 😅😂#GoogleNet #ResistanceIsFutile (at Studio City, California)
0 notes
Photo

Computer Diagnoses Skin #Cancers Researchers have developed an #algorithm that recognizes #skincancer in #photos about as well as #dermatologists do. So says a study published today in #Nature. The algorithm, developed by a group at #Stanford #University, is not the first automated system for recognizing #skinlesions, but it’s likely the most robust, the researchers say. “This is like when a computer first beat the world champion chess player,” says Sancy Leachman, a #dermatologist and researcher at Oregon #Health & #Science University who was not involved in the study. Stanford’s program beat dermatologists—essentially the world champions of skin cancer diagnostics, she says. “That’s pretty cool.” The study highlights the potential for #artificialintelligence #AI to enable anyone with a smartphone to have access to #healthcare. “We’re working towards extending the reach of care outside of the clinic,” says Andre Esteva, the electrical engineering PhD at Stanford who led the #study. Stanford built its #deeplearning algorithm on the architecture of the #GoogleNet Inception v3, a convolutional #neuralnetwork algorithm. Such programs are structured in interconnected layers that are inspired, at a high level, by the way #neurons in the #brain work. Inception v3 was trained on 1.28 million images from the 2014 ImageNet Large Scale #Visual Recognition Challenge, a contest that aimed to improve a computer’s ability to detect and classify objects in images. Stanford researchers then fine-tuned the algorithm with a set of nearly 130,000 images of #skin #lesions from more than 2000 #diseases—the largest dataset used for #automated skin cancer classification. In the study, the algorithm went head-to-head against 21 board-certified dermatologists. The #doctors reviewed hundreds of images of skin lesions, and for each one, determined whether they would conduct further tests on it or assure the patient that it was #benign. The algorithm reviewed the same images and gave its diagnoses. Neither the doctors nor the algorithm had seen the images previously. The computer performed on par with the experts. https://spectrum.ieee.org/static/ai-vs-doctors (at New York, New York)
#googlenet#benign#algorithm#doctors#deeplearning#skin#neurons#study#ai#university#visual#lesions#stanford#cancers#healthcare#skinlesions#neuralnetwork#dermatologists#brain#dermatologist#science#automated#health#photos#artificialintelligence#diseases#skincancer#nature
0 notes
Video
instagram
#東京スカイツリータウンキャンパス #StairLab #花分類 #ジギタリス #深層学習 #GoogleNet (東京スカイツリー / Tokyo Skytree)
0 notes