#how to create numpy full array
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
25 Udemy Paid Courses for Free with Certification (Only for Limited Time)

2023 Complete SQL Bootcamp from Zero to Hero in SQL
Become an expert in SQL by learning through concept & Hands-on coding :)
What you'll learn
Use SQL to query a database Be comfortable putting SQL on their resume Replicate real-world situations and query reports Use SQL to perform data analysis Learn to perform GROUP BY statements Model real-world data and generate reports using SQL Learn Oracle SQL by Professionally Designed Content Step by Step! Solve any SQL-related Problems by Yourself Creating Analytical Solutions! Write, Read and Analyze Any SQL Queries Easily and Learn How to Play with Data! Become a Job-Ready SQL Developer by Learning All the Skills You will Need! Write complex SQL statements to query the database and gain critical insight on data Transition from the Very Basics to a Point Where You can Effortlessly Work with Large SQL Queries Learn Advanced Querying Techniques Understand the difference between the INNER JOIN, LEFT/RIGHT OUTER JOIN, and FULL OUTER JOIN Complete SQL statements that use aggregate functions Using joins, return columns from multiple tables in the same query
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Python Programming Complete Beginners Course Bootcamp 2023
2023 Complete Python Bootcamp || Python Beginners to advanced || Python Master Class || Mega Course
What you'll learn
Basics in Python programming Control structures, Containers, Functions & Modules OOPS in Python How python is used in the Space Sciences Working with lists in python Working with strings in python Application of Python in Mars Rovers sent by NASA
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn PHP and MySQL for Web Application and Web Development
Unlock the Power of PHP and MySQL: Level Up Your Web Development Skills Today
What you'll learn
Use of PHP Function Use of PHP Variables Use of MySql Use of Database
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
T-Shirt Design for Beginner to Advanced with Adobe Photoshop
Unleash Your Creativity: Master T-Shirt Design from Beginner to Advanced with Adobe Photoshop
What you'll learn
Function of Adobe Photoshop Tools of Adobe Photoshop T-Shirt Design Fundamentals T-Shirt Design Projects
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Complete Data Science BootCamp
Learn about Data Science, Machine Learning and Deep Learning and build 5 different projects.
What you'll learn
Learn about Libraries like Pandas and Numpy which are heavily used in Data Science. Build Impactful visualizations and charts using Matplotlib and Seaborn. Learn about Machine Learning LifeCycle and different ML algorithms and their implementation in sklearn. Learn about Deep Learning and Neural Networks with TensorFlow and Keras Build 5 complete projects based on the concepts covered in the course.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Essentials User Experience Design Adobe XD UI UX Design
Learn UI Design, User Interface, User Experience design, UX design & Web Design
What you'll learn
How to become a UX designer Become a UI designer Full website design All the techniques used by UX professionals
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Build a Custom E-Commerce Site in React + JavaScript Basics
Build a Fully Customized E-Commerce Site with Product Categories, Shopping Cart, and Checkout Page in React.
What you'll learn
Introduction to the Document Object Model (DOM) The Foundations of JavaScript JavaScript Arithmetic Operations Working with Arrays, Functions, and Loops in JavaScript JavaScript Variables, Events, and Objects JavaScript Hands-On - Build a Photo Gallery and Background Color Changer Foundations of React How to Scaffold an Existing React Project Introduction to JSON Server Styling an E-Commerce Store in React and Building out the Shop Categories Introduction to Fetch API and React Router The concept of "Context" in React Building a Search Feature in React Validating Forms in React
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Complete Bootstrap & React Bootcamp with Hands-On Projects
Learn to Build Responsive, Interactive Web Apps using Bootstrap and React.
What you'll learn
Learn the Bootstrap Grid System Learn to work with Bootstrap Three Column Layouts Learn to Build Bootstrap Navigation Components Learn to Style Images using Bootstrap Build Advanced, Responsive Menus using Bootstrap Build Stunning Layouts using Bootstrap Themes Learn the Foundations of React Work with JSX, and Functional Components in React Build a Calculator in React Learn the React State Hook Debug React Projects Learn to Style React Components Build a Single and Multi-Player Connect-4 Clone with AI Learn React Lifecycle Events Learn React Conditional Rendering Build a Fully Custom E-Commerce Site in React Learn the Foundations of JSON Server Work with React Router
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Build an Amazon Affiliate E-Commerce Store from Scratch
Earn Passive Income by Building an Amazon Affiliate E-Commerce Store using WordPress, WooCommerce, WooZone, & Elementor
What you'll learn
Registering a Domain Name & Setting up Hosting Installing WordPress CMS on Your Hosting Account Navigating the WordPress Interface The Advantages of WordPress Securing a WordPress Installation with an SSL Certificate Installing Custom Themes for WordPress Installing WooCommerce, Elementor, & WooZone Plugins Creating an Amazon Affiliate Account Importing Products from Amazon to an E-Commerce Store using WooZone Plugin Building a Customized Shop with Menu's, Headers, Branding, & Sidebars Building WordPress Pages, such as Blogs, About Pages, and Contact Us Forms Customizing Product Pages on a WordPress Power E-Commerce Site Generating Traffic and Sales for Your Newly Published Amazon Affiliate Store
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
The Complete Beginner Course to Optimizing ChatGPT for Work
Learn how to make the most of ChatGPT's capabilities in efficiently aiding you with your tasks.
What you'll learn
Learn how to harness ChatGPT's functionalities to efficiently assist you in various tasks, maximizing productivity and effectiveness. Delve into the captivating fusion of product development and SEO, discovering effective strategies to identify challenges, create innovative tools, and expertly Understand how ChatGPT is a technological leap, akin to the impact of iconic tools like Photoshop and Excel, and how it can revolutionize work methodologies thr Showcase your learning by creating a transformative project, optimizing your approach to work by identifying tasks that can be streamlined with artificial intel
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
AWS, JavaScript, React | Deploy Web Apps on the Cloud
Cloud Computing | Linux Foundations | LAMP Stack | DBMS | Apache | NGINX | AWS IAM | Amazon EC2 | JavaScript | React
What you'll learn
Foundations of Cloud Computing on AWS and Linode Cloud Computing Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) Deploying and Configuring a Virtual Instance on Linode and AWS Secure Remote Administration for Virtual Instances using SSH Working with SSH Key Pair Authentication The Foundations of Linux (Maintenance, Directory Commands, User Accounts, Filesystem) The Foundations of Web Servers (NGINX vs Apache) Foundations of Databases (SQL vs NoSQL), Database Transaction Standards (ACID vs CAP) Key Terminology for Full Stack Development and Cloud Administration Installing and Configuring LAMP Stack on Ubuntu (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) Server Security Foundations (Network vs Hosted Firewalls). Horizontal and Vertical Scaling of a virtual instance on Linode using NodeBalancers Creating Manual and Automated Server Images and Backups on Linode Understanding the Cloud Computing Phenomenon as Applicable to AWS The Characteristics of Cloud Computing as Applicable to AWS Cloud Deployment Models (Private, Community, Hybrid, VPC) Foundations of AWS (Registration, Global vs Regional Services, Billing Alerts, MFA) AWS Identity and Access Management (Mechanics, Users, Groups, Policies, Roles) Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) - (AMIs, EC2 Users, Deployment, Elastic IP, Security Groups, Remote Admin) Foundations of the Document Object Model (DOM) Manipulating the DOM Foundations of JavaScript Coding (Variables, Objects, Functions, Loops, Arrays, Events) Foundations of ReactJS (Code Pen, JSX, Components, Props, Events, State Hook, Debugging) Intermediate React (Passing Props, Destrcuting, Styling, Key Property, AI, Conditional Rendering, Deployment) Building a Fully Customized E-Commerce Site in React Intermediate React Concepts (JSON Server, Fetch API, React Router, Styled Components, Refactoring, UseContext Hook, UseReducer, Form Validation)
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Run Multiple Sites on a Cloud Server: AWS & Digital Ocean
Server Deployment | Apache Configuration | MySQL | PHP | Virtual Hosts | NS Records | DNS | AWS Foundations | EC2
What you'll learn
A solid understanding of the fundamentals of remote server deployment and configuration, including network configuration and security. The ability to install and configure the LAMP stack, including the Apache web server, MySQL database server, and PHP scripting language. Expertise in hosting multiple domains on one virtual server, including setting up virtual hosts and managing domain names. Proficiency in virtual host file configuration, including creating and configuring virtual host files and understanding various directives and parameters. Mastery in DNS zone file configuration, including creating and managing DNS zone files and understanding various record types and their uses. A thorough understanding of AWS foundations, including the AWS global infrastructure, key AWS services, and features. A deep understanding of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) foundations, including creating and managing instances, configuring security groups, and networking. The ability to troubleshoot common issues related to remote server deployment, LAMP stack installation and configuration, virtual host file configuration, and D An understanding of best practices for remote server deployment and configuration, including security considerations and optimization for performance. Practical experience in working with remote servers and cloud-based solutions through hands-on labs and exercises. The ability to apply the knowledge gained from the course to real-world scenarios and challenges faced in the field of web hosting and cloud computing. A competitive edge in the job market, with the ability to pursue career opportunities in web hosting and cloud computing.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Cloud-Powered Web App Development with AWS and PHP
AWS Foundations | IAM | Amazon EC2 | Load Balancing | Auto-Scaling Groups | Route 53 | PHP | MySQL | App Deployment
What you'll learn
Understanding of cloud computing and Amazon Web Services (AWS) Proficiency in creating and configuring AWS accounts and environments Knowledge of AWS pricing and billing models Mastery of Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies and permissions Ability to launch and configure Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances Familiarity with security groups, key pairs, and Elastic IP addresses Competency in using AWS storage services, such as Elastic Block Store (EBS) and Simple Storage Service (S3) Expertise in creating and using Elastic Load Balancers (ELB) and Auto Scaling Groups (ASG) for load balancing and scaling web applications Knowledge of DNS management using Route 53 Proficiency in PHP programming language fundamentals Ability to interact with databases using PHP and execute SQL queries Understanding of PHP security best practices, including SQL injection prevention and user authentication Ability to design and implement a database schema for a web application Mastery of PHP scripting to interact with a database and implement user authentication using sessions and cookies Competency in creating a simple blog interface using HTML and CSS and protecting the blog content using PHP authentication. Students will gain practical experience in creating and deploying a member-only blog with user authentication using PHP and MySQL on AWS.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
CSS, Bootstrap, JavaScript And PHP Stack Complete Course
CSS, Bootstrap And JavaScript And PHP Complete Frontend and Backend Course
What you'll learn
Introduction to Frontend and Backend technologies Introduction to CSS, Bootstrap And JavaScript concepts, PHP Programming Language Practically Getting Started With CSS Styles, CSS 2D Transform, CSS 3D Transform Bootstrap Crash course with bootstrap concepts Bootstrap Grid system,Forms, Badges And Alerts Getting Started With Javascript Variables,Values and Data Types, Operators and Operands Write JavaScript scripts and Gain knowledge in regard to general javaScript programming concepts PHP Section Introduction to PHP, Various Operator types , PHP Arrays, PHP Conditional statements Getting Started with PHP Function Statements And PHP Decision Making PHP 7 concepts PHP CSPRNG And PHP Scalar Declaration
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn HTML - For Beginners
Lean how to create web pages using HTML
What you'll learn
How to Code in HTML Structure of an HTML Page Text Formatting in HTML Embedding Videos Creating Links Anchor Tags Tables & Nested Tables Building Forms Embedding Iframes Inserting Images
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn Bootstrap - For Beginners
Learn to create mobile-responsive web pages using Bootstrap
What you'll learn
Bootstrap Page Structure Bootstrap Grid System Bootstrap Layouts Bootstrap Typography Styling Images Bootstrap Tables, Buttons, Badges, & Progress Bars Bootstrap Pagination Bootstrap Panels Bootstrap Menus & Navigation Bars Bootstrap Carousel & Modals Bootstrap Scrollspy Bootstrap Themes
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
JavaScript, Bootstrap, & PHP - Certification for Beginners
A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners interested in learning JavaScript, Bootstrap, & PHP
What you'll learn
Master Client-Side and Server-Side Interactivity using JavaScript, Bootstrap, & PHP Learn to create mobile responsive webpages using Bootstrap Learn to create client and server-side validated input forms Learn to interact with a MySQL Database using PHP
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Linode: Build and Deploy Responsive Websites on the Cloud
Cloud Computing | IaaS | Linux Foundations | Apache + DBMS | LAMP Stack | Server Security | Backups | HTML | CSS
What you'll learn
Understand the fundamental concepts and benefits of Cloud Computing and its service models. Learn how to create, configure, and manage virtual servers in the cloud using Linode. Understand the basic concepts of Linux operating system, including file system structure, command-line interface, and basic Linux commands. Learn how to manage users and permissions, configure network settings, and use package managers in Linux. Learn about the basic concepts of web servers, including Apache and Nginx, and databases such as MySQL and MariaDB. Learn how to install and configure web servers and databases on Linux servers. Learn how to install and configure LAMP stack to set up a web server and database for hosting dynamic websites and web applications. Understand server security concepts such as firewalls, access control, and SSL certificates. Learn how to secure servers using firewalls, manage user access, and configure SSL certificates for secure communication. Learn how to scale servers to handle increasing traffic and load. Learn about load balancing, clustering, and auto-scaling techniques. Learn how to create and manage server images. Understand the basic structure and syntax of HTML, including tags, attributes, and elements. Understand how to apply CSS styles to HTML elements, create layouts, and use CSS frameworks.
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
PHP & MySQL - Certification Course for Beginners
Learn to Build Database Driven Web Applications using PHP & MySQL
What you'll learn
PHP Variables, Syntax, Variable Scope, Keywords Echo vs. Print and Data Output PHP Strings, Constants, Operators PHP Conditional Statements PHP Elseif, Switch, Statements PHP Loops - While, For PHP Functions PHP Arrays, Multidimensional Arrays, Sorting Arrays Working with Forms - Post vs. Get PHP Server Side - Form Validation Creating MySQL Databases Database Administration with PhpMyAdmin Administering Database Users, and Defining User Roles SQL Statements - Select, Where, And, Or, Insert, Get Last ID MySQL Prepared Statements and Multiple Record Insertion PHP Isset MySQL - Updating Records
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Linode: Deploy Scalable React Web Apps on the Cloud
Cloud Computing | IaaS | Server Configuration | Linux Foundations | Database Servers | LAMP Stack | Server Security
What you'll learn
Introduction to Cloud Computing Cloud Computing Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) Cloud Server Deployment and Configuration (TFA, SSH) Linux Foundations (File System, Commands, User Accounts) Web Server Foundations (NGINX vs Apache, SQL vs NoSQL, Key Terms) LAMP Stack Installation and Configuration (Linux, Apache, MariaDB, PHP) Server Security (Software & Hardware Firewall Configuration) Server Scaling (Vertical vs Horizontal Scaling, IP Swaps, Load Balancers) React Foundations (Setup) Building a Calculator in React (Code Pen, JSX, Components, Props, Events, State Hook) Building a Connect-4 Clone in React (Passing Arguments, Styling, Callbacks, Key Property) Building an E-Commerce Site in React (JSON Server, Fetch API, Refactoring)
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Internet and Web Development Fundamentals
Learn how the Internet Works and Setup a Testing & Production Web Server
What you'll learn
How the Internet Works Internet Protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP) The Web Development Process Planning a Web Application Types of Web Hosting (Shared, Dedicated, VPS, Cloud) Domain Name Registration and Administration Nameserver Configuration Deploying a Testing Server using WAMP & MAMP Deploying a Production Server on Linode, Digital Ocean, or AWS Executing Server Commands through a Command Console Server Configuration on Ubuntu Remote Desktop Connection and VNC SSH Server Authentication FTP Client Installation FTP Uploading
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Linode: Web Server and Database Foundations
Cloud Computing | Instance Deployment and Config | Apache | NGINX | Database Management Systems (DBMS)
What you'll learn
Introduction to Cloud Computing (Cloud Service Models) Navigating the Linode Cloud Interface Remote Administration using PuTTY, Terminal, SSH Foundations of Web Servers (Apache vs. NGINX) SQL vs NoSQL Databases Database Transaction Standards (ACID vs. CAP Theorem) Key Terms relevant to Cloud Computing, Web Servers, and Database Systems
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Java Training Complete Course 2022
Learn Java Programming language with Java Complete Training Course 2022 for Beginners
What you'll learn
You will learn how to write a complete Java program that takes user input, processes and outputs the results You will learn OOPS concepts in Java You will learn java concepts such as console output, Java Variables and Data Types, Java Operators And more You will be able to use Java for Selenium in testing and development
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Learn To Create AI Assistant (JARVIS) With Python
How To Create AI Assistant (JARVIS) With Python Like the One from Marvel's Iron Man Movie
What you'll learn
how to create an personalized artificial intelligence assistant how to create JARVIS AI how to create ai assistant
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
Keyword Research, Free Backlinks, Improve SEO -Long Tail Pro
LongTailPro is the keyword research service we at Coursenvy use for ALL our clients! In this course, find SEO keywords,
What you'll learn
Learn everything Long Tail Pro has to offer from A to Z! Optimize keywords in your page/post titles, meta descriptions, social media bios, article content, and more! Create content that caters to the NEW Search Engine Algorithms and find endless keywords to rank for in ALL the search engines! Learn how to use ALL of the top-rated Keyword Research software online! Master analyzing your COMPETITIONS Keywords! Get High-Quality Backlinks that will ACTUALLY Help your Page Rank!
Enroll Now 👇👇👇👇👇👇👇 https://www.book-somahar.com/2023/10/25-udemy-paid-courses-for-free-with.html
#udemy#free course#paid course for free#design#development#ux ui#xd#figma#web development#python#javascript#php#java#cloud
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Python for Data Science: The Only Guide You Need to Get Started in 2025
Data is the lifeblood of modern business, powering decisions in healthcare, finance, marketing, sports, and more. And at the core of it all lies a powerful and beginner-friendly programming language — Python.
Whether you’re an aspiring data scientist, analyst, or tech enthusiast, learning Python for data science is one of the smartest career moves you can make in 2025.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
Why Python is the preferred language for data science
The libraries and tools you must master
A beginner-friendly roadmap
How to get started with a free full course on YouTube
Why Python is the #1 Language for Data Science
Python has earned its reputation as the go-to language for data science and here's why:
1. Easy to Learn, Easy to Use
Python’s syntax is clean, simple, and intuitive. You can focus on solving problems rather than struggling with the language itself.
2. Rich Ecosystem of Libraries
Python offers thousands of specialized libraries for data analysis, machine learning, and visualization.
3. Community and Resources
With a vibrant global community, you’ll never run out of tutorials, forums, or project ideas to help you grow.
4. Integration with Tools & Platforms
From Jupyter notebooks to cloud platforms like AWS and Google Colab, Python works seamlessly everywhere.
What You Can Do with Python in Data Science
Let’s look at real tasks you can perform using Python: TaskPython ToolsData cleaning & manipulationPandas, NumPyData visualizationMatplotlib, Seaborn, PlotlyMachine learningScikit-learn, XGBoostDeep learningTensorFlow, PyTorchStatistical analysisStatsmodels, SciPyBig data integrationPySpark, Dask
Python lets you go from raw data to actionable insight — all within a single ecosystem.
A Beginner's Roadmap to Learn Python for Data Science
If you're starting from scratch, follow this step-by-step learning path:
✅ Step 1: Learn Python Basics
Variables, data types, loops, conditionals
Functions, file handling, error handling
✅ Step 2: Explore NumPy
Arrays, broadcasting, numerical computations
✅ Step 3: Master Pandas
DataFrames, filtering, grouping, merging datasets
✅ Step 4: Visualize with Matplotlib & Seaborn
Create charts, plots, and visual dashboards
✅ Step 5: Intro to Machine Learning
Use Scikit-learn for classification, regression, clustering
✅ Step 6: Work on Real Projects
Apply your knowledge to real-world datasets (Kaggle, UCI, etc.)
Who Should Learn Python for Data Science?
Python is incredibly beginner-friendly and widely used, making it ideal for:
Students looking to future-proof their careers
Working professionals planning a transition to data
Analysts who want to automate and scale insights
Researchers working with data-driven models
Developers diving into AI, ML, or automation
How Long Does It Take to Learn?
You can grasp Python fundamentals in 2–3 weeks with consistent daily practice. To become proficient in data science using Python, expect to spend 3–6 months, depending on your pace and project experience.
The good news? You don’t need to do it alone.
🎓 Learn Python for Data Science – Full Free Course on YouTube
We’ve put together a FREE, beginner-friendly YouTube course that covers everything you need to start your data science journey using Python.
📘 What You’ll Learn:
Python programming basics
NumPy and Pandas for data handling
Matplotlib for visualization
Scikit-learn for machine learning
Real-life datasets and projects
Step-by-step explanations
📺 Watch the full course now → 👉 Python for Data Science Full Course
You’ll walk away with job-ready skills and project experience — at zero cost.
🧭 Final Thoughts
Python isn’t just a programming language — it’s your gateway to the future.
By learning Python for data science, you unlock opportunities across industries, roles, and technologies. The demand is high, the tools are ready, and the learning path is clearer than ever.
Don’t let analysis paralysis hold you back.
Click here to start learning now → https://youtu.be/6rYVt_2q_BM
#PythonForDataScience #LearnPython #FreeCourse #DataScience2025 #MachineLearning #NumPy #Pandas #DataAnalysis #AI #ScikitLearn #UpskillNow
1 note
·
View note
Text
What is Artificial Intelligence with Data Science?
Introduction:
The decision to invest capital in artificial intelligence and data science has produced a pivotal industry of innovation for various fields. An application consists of something related to the automation of complex tasks or the generation of novel predictions. While that certainly could be an answer, really, what does it mean, and how does one go about building a career in this transformative field?
Understanding the Concepts
It is an array of technologies made to build intelligence, such as those capable of performing tasks that require human intelligence. In computer science, the conventional areas of AI consist of machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. On the other hand, data science is an art, or possibly a science, of drawing valuable insights from raw or semi-raw data through statistics, data mining, and predictive analytics.
When the two disciplines merge, they create a dynamic information environment where intelligent systems are developed on data-driven decisions. AI learns and improves with time from data, while data science comes in as the skeleton and architectural plan to define this data in an efficient manner. This gives rise to systems that analyze customer behavior, customize user experience, streamline operations, and even produce content through generative AI.
Why Is This Integration Important?
The fusion of data science and AI provides powerful tools.
Predictive Analytics: AI models trained using historical data can forecast trends.
Automation: Automating repetitive and complex business processes could and should save time and resources.
Decision Support: Businesses make faster and more accurate decisions from real-time data.
Personalization: E-commerce, health, education, and entertainment platforms receive
customized experiences.
This hybrid is no longer optional for the technical companies' essential needs. That's why professionals trained in both fields are currently in high demand.
Where to Start Learning?
Structured programs like 1stepGrow's Artificial Intelligence with Data Science Course can be your gateway to entering the field or enhancing the skills you already possess.
1stepGrow is a leading ed-tech platform committed to offering career-focused training in in-demand technologies. Their Advanced Data Science Course blends theoretical knowledge with practical in-company applications, which makes it an excellent choice for beginners and professionals alike.
What Does the Course Include?
The AI with Data Science Course from 1stepGrow is meant to provide a complete course for all those beginning on this path. One can expect:
Data Science Basics: Statistics and techniques for data wrangling and data visualization.
Machine Learning Algorithms: Supervised and unsupervised modeling for predictive and classification tasks.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Working with complicated data such, as images and speech.
Generative AI Full Course: Build models such as GPT and GANs for text, image, and audio creation.
Capstone Projects: Solve industry-relevant problems using real-world datasets.
Job-Ready Skills: Resume building, interview preparation, and placement.
The course is very practically oriented and works on tools such as Python, TensorFlow, Pandas, NumPy, and others. Mentors assist the learners throughout the journey, with peers to collaborate with and continuous support on offer.
Who Should Enroll?
This program is ideal for:
Students and recent graduates from computer science, mathematics, or engineering backgrounds. Working professionals aiming to switch to a tech career.
Business analysts and developers looking to upskill.
Entrepreneurs and product managers are interested in integrating AI into their solutions.
The Future of AI and Data Science
With the increasing importance of data generation and the developing pace of intelligent technologies at a drastic rate, the careers in this industry are burgeoning. It is endless-the application: designing an algorithm for a self-driving car or analyzing healthcare data for better outcomes.
According to the last industry forecasts, the demand for AI and data science professionals will continue to increase in the next ten years. Therefore, securing a solid footing by entering into an advanced data science course will assure your long-term career in this rapidly developing environment.
Final Thoughts
The combined force of data science and artificial intelligence is changing the way in which people live and work. Through trusted platforms such as 1stepGrow, being proficient in these fields opens up pleasant career opportunities where one can also make significant contributions toward shaping the digital tomorrow.
Be it building intelligent applications or applying next-gen ideas such as generative AI, the journey begins with the right course; 1stepGrow provides just that.
#advanced data science course#Data Science and Artificial Intelligence#Artificial Intelligence with Data Science Course
0 notes
Text
Level Up Data Science Skills with Python: A Full Guide
Data science is one of the most in-demand careers in the world today, and Python is its go-to language. Whether you're just starting out or looking to sharpen your skills, mastering Python can open doors to countless opportunities in data analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and beyond.
In this guide, we’ll explore how Python can take your data science abilities to the next level—covering core concepts, essential libraries, and practical tips for real-world application.
Why Python for Data Science?
Python’s popularity in data science is no accident. It’s beginner-friendly, versatile, and has a massive ecosystem of libraries and tools tailored specifically for data work. Here's why it stands out:
Clear syntax simplifies learning and ensures easier maintenance.
Community support means constant updates and rich documentation.
Powerful libraries for everything from data manipulation to visualization and machine learning.
Core Python Concepts Every Data Scientist Should Know
Establish a solid base by thoroughly understanding the basics before advancing to more complex methods:
Variables and Data Types: Get familiar with strings, integers, floats, lists, and dictionaries.
Control Flow: Master if-else conditions, for/while loops, and list comprehensions through practice.
Functions and Modules: Understand how to create reusable code by defining functions.
File Handling: Leverage built-in functions to handle reading from and writing to files.
Error Handling: Use try-except blocks to write robust programs.
Mastering these foundations ensures you can write clean, efficient code—critical for working with complex datasets.
Must-Know Python Libraries for Data Science
Once you're confident with Python basics, it’s time to explore the libraries that make data science truly powerful:
NumPy: For numerical operations and array manipulation. It forms the essential foundation for a wide range of data science libraries.
Pandas: Used for data cleaning, transformation, and analysis. DataFrames are essential for handling structured data.
Matplotlib & Seaborn: These libraries help visualize data. While Matplotlib gives you control, Seaborn makes it easier with beautiful default styles.
Scikit-learn: Perfect for building machine learning models. Features algorithms for tasks like classification, regression, clustering, and additional methods.
TensorFlow & PyTorch: For deep learning and neural networks. Choose one based on your project needs and personal preference.
Real-World Projects to Practice
Applying what you’ve learned through real-world projects is key to skill development. Here are a few ideas:
Data Cleaning Challenge: Work with messy datasets and clean them using Pandas.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): Analyze a dataset, find patterns, and visualize results.
Build a Machine Learning Model: Use Scikit-learn to create a prediction model for housing prices, customer churn, or loan approval.
Sentiment Analysis: Use natural language processing (NLP) to analyze product reviews or tweets.
Completing these projects can enhance your portfolio and attract the attention of future employers.
Tips to Accelerate Your Learning
Join online courses and bootcamps: Join Online Platforms
Follow open-source projects on GitHub: Contribute to or learn from real codebases.
Engage with the community: Join forums like Stack Overflow or Reddit’s r/datascience.
Read documentation and blogs: Keep yourself informed about new features and optimal practices.
Set goals and stay consistent: Data science is a long-term journey, not a quick race.
Python is the cornerstone of modern data science. Whether you're manipulating data, building models, or visualizing insights, Python equips you with the tools to succeed. By mastering its fundamentals and exploring its powerful libraries, you can confidently tackle real-world data challenges and elevate your career in the process. If you're looking to sharpen your skills, enrolling in a Python course in Gurgaon can be a great way to get expert guidance and hands-on experience.
DataMites Institute stands out as a top international institute providing in-depth education in data science, AI, and machine learning. We provide expert-led courses designed for both beginners and professionals aiming to boost their careers.
Python vs R - What is the Difference, Pros and Cons
youtube
#python course#python training#python institute#learnpython#python#pythoncourseingurgaon#pythoncourseinindia#Youtube
0 notes
Text
The Benefits of Learning Python: A Comprehensive Guide
Python is more than just a programming language—it’s a gateway to an array of opportunities in the tech world and beyond. Considering the kind support of Learn Python Course in Hyderabad Whatever your level of experience or reason for switching from another programming language, learning Python gets much more fun.

Known for its simplicity, versatility, and extensive ecosystem, Python has become the language of choice for developers, data scientists, and even beginners exploring programming. In this guide, we’ll delve into the numerous benefits of learning Python and why it’s worth your time and effort.
Why Python?
Python’s growing popularity is driven by its adaptability and ease of use. Let’s explore the key benefits that make Python stand out:
1. User-Friendly Syntax
Python’s syntax is simple and intuitive, resembling natural language. This makes it easier for beginners to grasp programming concepts and for experienced developers to write cleaner, more efficient code.
2. Versatility Across Industries
Python’s applications span diverse domains, including:
Web Development: Frameworks like Django and Flask simplify the creation of dynamic websites and web applications.
Data Science and Analytics: Libraries like Pandas and NumPy empower analysts to handle, manipulate, and visualize data effectively.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn make Python the backbone of AI and ML projects.
Automation and Scripting: Automate repetitive tasks and streamline workflows with Python’s scripting capabilities.
Game Development: Create interactive games using libraries like Pygame.
3. Extensive Library Support
Python boasts a rich collection of libraries and frameworks that save time and effort. Whether you’re processing data, building websites, or working on AI models, there’s likely a library to help. Enrolling in the Best Python Certification Online can help people realise Python’s full potential and gain a deeper understanding of its complexities.

4. Community and Resources
Python has one of the most active and supportive developer communities. Beginners can easily find tutorials, forums, and answers to questions on platforms like Stack Overflow, Reddit, and Python’s official documentation.
5. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Python code runs seamlessly across multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This flexibility ensures that developers can write code once and deploy it anywhere with minimal adjustments.
6. Career Opportunities
Proficiency in Python opens doors to lucrative career paths in software development, data science, AI, machine learning, web development, and more. The demand for Python developers continues to grow, making it a highly valuable skill in the job market.
7. High Productivity
Python’s simplicity allows developers to focus on solving problems rather than worrying about complex syntax or debugging errors. This boosts productivity, making Python a favorite among startups and enterprises alike.
8. Future-Proof Skill
As technology evolves, Python’s adaptability ensures its relevance across emerging fields like quantum computing, Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain. Learning Python today means investing in a skill that will remain valuable for years to come.
How to Start Learning Python
Install Python: Download it from the official Python website.
Learn the Basics: Focus on fundamental concepts like variables, loops, and functions.
Use Online Resources: Explore platforms like Codecademy, freeCodeCamp, or Coursera for structured tutorials.
Practice Projects: Build simple projects like calculators or to-do lists to reinforce your skills.
Join Communities: Engage with fellow learners and professionals to exchange ideas and gain insights.
Conclusion
Learning Python is a smart investment in your personal and professional growth. Its simplicity, wide-ranging applications, and strong community support make it an excellent choice for anyone looking to enter the tech world or enhance their skill set. Start your Python journey today and unlock endless possibilities in programming, data science, AI, and beyond!
#python course#python training#python#technology#tech#python online training#python programming#python online course#python certification#python online classes
0 notes
Text
200 FREE Courses: Web Development, Python, Programming Languages, Network and Security, Game Development, AI and Machine Learning at Eduonix

In the rapidly evolving tech landscape, acquiring new skills is essential for staying competitive. Eduonix, a leading online education platform, offers a golden opportunity for learners worldwide with 200 FREE courses across various tech domains such as Web Development, Python, Programming Languages, Network and Security, Game Development, and AI and Machine Learning. These courses empower students, professionals, and tech enthusiasts to upskill at no cost. This article dives into what these free courses offer and how they can benefit your career trajectory.
Why Choose Eduonix for Learning Tech Skills?
Eduonix is renowned for its high-quality courses, offering an array of learning resources that are not only affordable but now also free for a limited period. This makes it easier for individuals to access knowledge in Web Development, Programming Languages, and emerging fields like AI and Machine Learning.
With these 200 FREE courses, Eduonix aims to make tech education accessible to all. Whether you're a beginner looking to dive into programming or a seasoned professional aiming to sharpen your skills, these free offerings can be the stepping stones to a successful tech career.
Key Benefits of Eduonix Courses:
Free access to premium-quality content.
Detailed and up-to-date learning materials.
Courses taught by industry experts.
Flexible learning schedule with lifetime access.
A World of Free Learning: The 200 Course Offerings
Eduonix has curated an impressive list of 200 free courses covering various technology-related topics. From Web Development to Network and Security, and from Game Development to AI and Machine Learning, there is something for everyone. These courses offer comprehensive knowledge, hands-on projects, and real-world applications that cater to different learning needs.
Web Development: Building the Digital World
Web development remains one of the most sought-after skills in today’s tech world. Eduonix’s Web Development courses teach you how to build functional, visually appealing websites. Whether you’re interested in frontend technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript or backend frameworks like Node.js and Django, Eduonix covers it all.
These courses often include practical projects, enabling you to create your own websites as part of the learning process. You'll also gain skills in essential tools such as React, Angular, and Bootstrap, ensuring you stay up-to-date with industry trends.
Learn to design dynamic websites.
Master popular frameworks and libraries.
Understand how to create responsive designs.
Course Name
Difficulty
Duration
Full Stack Web Development Bootcamp
Beginner
8 weeks
React for Web Development
Intermediate
6 weeks
Mastering HTML5 and CSS3
Beginner
5 weeks
Python: The Language of Versatility
Python has established itself as a versatile and beginner-friendly programming language. Its widespread use in data science, web development, automation, and artificial intelligence makes it an essential skill. Eduonix offers a plethora of Python courses designed to cater to both newcomers and experienced programmers.
These courses delve into everything from Python basics to advanced topics such as machine learning and data visualization. By taking these free courses, you can build robust programs and explore libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib.
Learn Python from scratch.
Dive into Python libraries for data analysis.
Create powerful automation scripts.
Programming Languages: Expanding Your Coding Skills
Programming languages are the backbone of all software and applications. Eduonix’s free courses on Programming Languages provide a deep understanding of various languages such as Java, C++, JavaScript, and Go. These courses not only cover the syntax and fundamentals but also practical implementation and coding best practices.
Learn the intricacies of popular programming languages.
Build real-world applications.
Understand object-oriented programming concepts.
Language
Popular Course
Difficulty
Duration
Java
Java for Absolute Beginners
Beginner
6 weeks
C++
Mastering C++ Programming
Intermediate
8 weeks
JavaScript
JavaScript Bootcamp: Modern JavaScript from A to Z
Advanced
7 weeks
Network and Security: Safeguarding the Digital Realm
In today's interconnected world, Network and Security are vital to protecting data, systems, and users. Eduonix’s free courses on this topic equip learners with the knowledge to understand how networks function and how to secure them against cyber threats.
These courses cover topics like ethical hacking, firewall management, encryption techniques, and more. You’ll also learn the fundamentals of securing networks and protecting against vulnerabilities.
Understand how to protect digital infrastructure.
Learn ethical hacking techniques.
Master firewall configurations and network security protocols.
Game Development: Bringing Virtual Worlds to Life
If you've ever dreamt of creating your own video games, Eduonix has an array of free Game Development courses to turn your dreams into reality. From beginner-friendly tutorials on Unity and Unreal Engine to more advanced lessons on game design principles, these courses cover it all.
Build engaging 2D and 3D games.
Learn game design mechanics and player psychology.
Use game engines like Unity and Unreal Engine.
AI and Machine Learning: Pioneering the Future of Tech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. Eduonix offers specialized AI and Machine Learning courses that provide the foundational knowledge needed to start building intelligent systems.
From neural networks to deep learning algorithms, these courses focus on practical implementation using popular tools like TensorFlow, Keras, and Scikit-learn.
Understand the fundamentals of AI and ML.
Learn how to build AI-driven models.
Apply ML techniques in real-world scenarios.
Discounted Courses: Extending Your Learning Beyond Free Resources
While the 200 free courses are an incredible offer, Eduonix also provides discounted courses for learners who want to continue their education with more in-depth topics. These discounted courses give learners access to premium materials and certification, helping them enhance their professional profile.
Whether you're looking to dive deeper into AI, Web Development, or Game Design, Eduonix offers discounts on advanced courses for those who want to go beyond the basics.
Key Features of Discounted Courses:
Access to advanced, career-oriented content.
Premium support from instructors.
Certification upon completion.
Practical, real-world projects to showcase your skills.
How to Make the Most of Eduonix’s Free and Discounted Offerings
To make the most of these 200 FREE Courses and discounted options, it's important to choose the right courses that align with your career goals. Start by identifying which area you want to specialize in, be it Web Development, Python, or AI and Machine Learning. Utilize the flexibility of these online courses to study at your own pace, and don't hesitate to explore multiple domains to diversify your skillset.
Choose courses that match your career goals.
Take advantage of flexible learning schedules.
Explore cross-domain learning for broader skillsets.
Conclusion: Unlock Your Potential with Eduonix’s Free Courses
With 200 FREE Courses available in Web Development, Python, Programming Languages, Network and Security, Game Development, and AI and Machine Learning, Eduonix is opening doors for learners to gain invaluable skills without breaking the bank. Whether you're a beginner just starting your journey or a professional looking to upgrade your expertise, these courses provide a comprehensive learning experience. By enrolling in these free courses today, you’re setting yourself up for a brighter, more prosperous future in tech.
Don't miss this opportunity—head to Eduonix now and start learning!
0 notes
Text
Python Mastery for Data Science: Essential Tools and Techniques
Introduction
Python has emerged as a powerhouse in the world of data science. Its versatility, ease of use, and extensive libraries make it the go-to choice for data professionals. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced data scientist, mastering Python is essential for leveraging the full potential of data analysis and machine learning. In this article, we'll explore the fundamental tools and techniques in Python for data science, breaking down complex concepts into simple, easy-to-understand language.
Getting Started with Python
Before diving into data science, it's important to have a basic understanding of Python. Don't worry if you're new to programming – Python's syntax is designed to be readable and straightforward. You can start by installing Python on your computer and familiarizing yourself with basic concepts like variables, data types, and control structures.
Understanding Data Structures
In data science, manipulating and analyzing data is at the core of what you do. Python offers a variety of data structures such as lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets, which allow you to store and organize data efficiently. Understanding how to work with these data structures is crucial for performing data manipulation tasks.
Exploring Data Analysis Libraries
Python boasts powerful libraries like NumPy and Pandas, which are specifically designed for data manipulation and analysis. NumPy provides support for multi-dimensional arrays and mathematical functions, while Pandas offers data structures and tools for working with structured data. Learning how to use these libraries will greatly enhance your ability to analyze and manipulate data effectively.
Visualizing Data with Matplotlib and Seaborn
Data visualization is a key aspect of data science, as it helps you to understand patterns and trends in your data. Matplotlib and Seaborn are two popular Python libraries for creating static, interactive, and highly customizable visualizations. From simple line plots to complex heatmaps, these libraries offer a wide range of options for visualizing data in meaningful ways.
Harnessing the Power of Machine Learning
Python's extensive ecosystem includes powerful machine learning libraries such as Scikit-learn and TensorFlow. These libraries provide tools and algorithms for building predictive models, clustering data, and performing other machine learning tasks. Whether you're interested in regression, classification, or clustering, Python has you covered with its vast array of machine learning tools.
Working with Big Data
As data volumes continue to grow, the ability to work with big data becomes increasingly important. Python offers several libraries, such as PySpark and Dask, that allow you to scale your data analysis tasks to large datasets distributed across clusters of computers. By leveraging these libraries, you can analyze massive datasets efficiently and extract valuable insights from them.
Integrating Python with SQL
Many data science projects involve working with databases to extract and manipulate data. Python can be seamlessly integrated with SQL databases using libraries like SQLAlchemy and psycopg2. Whether you're querying data from a relational database or performing complex joins and aggregations, Python provides tools to streamline the process and make working with databases a breeze.
Collaborating and Sharing with Jupyter Notebooks
Jupyter Notebooks have become the de facto standard for data scientists to collaborate, document, and share their work. These interactive notebooks allow you to write and execute Python code in a web-based environment, interspersed with explanatory text and visualizations. With support for various programming languages and the ability to export notebooks to different formats, Jupyter Notebooks facilitate seamless collaboration and reproducibility in data science projects.
Continuous Learning and Community Support
Python's popularity in the data science community means that there is no shortage of resources and support available for learning and growing your skills. From online tutorials and forums to books and courses, there are numerous ways to deepen your understanding of Python for data science. Additionally, participating in data science communities and attending meetups and conferences can help you stay updated on the latest trends and developments in the field.
Conclusion
Python has cemented its place as the language of choice for data science, thanks to its simplicity, versatility, and robust ecosystem of libraries and tools. By mastering Python for data science, you can unlock endless possibilities for analyzing data, building predictive models, and extracting valuable insights. Whether you're just starting out or looking to advance your career, Python provides the essential tools and techniques you need to succeed in the dynamic field of data science.
0 notes
Text
Unleashing the Power of Python in Data Science: Key Benefits to Consider
Python has emerged as a dominant force in the field of data science, offering a multitude of advantages that can significantly enhance your data analysis and machine learning endeavors. Whether you are a novice or an experienced data scientist, learning Python can unlock a world of possibilities. In this article, we will delve into the key benefits of harnessing Python for data science, showcasing how its versatility and extensive library support can propel your data-driven projects to new heights.
Embarking on the Python learning journey becomes even more thrilling, whether you’re a complete beginner or transitioning from another programming language, especially with the valuable assistance of Python Training in Pune.

Unlocking Readability and Simplicity: Embracing Python means embracing a programming language renowned for its clean and readable syntax. With Python, you can write code that is not only efficient but also highly comprehensible, enabling you to focus more on solving complex data-related problems rather than getting entangled in convoluted programming constructs. The simplicity of Python empowers you to write elegant code that is easily understandable and maintainable by your peers.
Embracing an Extensive Ecosystem of Libraries: Python boasts an expansive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks tailored specifically for data science. At the forefront is NumPy, a powerful library that provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices. Complementing NumPy, libraries such as Pandas, Matplotlib, and SciPy offer an array of functionalities for data manipulation, analysis, visualization, and scientific computing. These libraries act as indispensable tools, accelerating your data analysis workflow and simplifying intricate data operations.
Harnessing the Power of a Supportive Community: Python's immense popularity is fueled by its vibrant community of data scientists and developers. This community-driven environment ensures that a wealth of resources, tutorials, and forums are available to facilitate your learning journey and troubleshoot challenges. Whether you seek guidance on specific data analysis techniques or wish to explore advanced machine learning algorithms, the Python community stands ready to provide assistance, fostering a collaborative and supportive atmosphere.
Empowering Machine Learning and Deep Learning: Python has become the language of choice for machine learning and deep learning projects. With libraries like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, you gain access to comprehensive toolsets for building and deploying machine learning models. These libraries offer a diverse range of algorithms and utilities for classification, regression, clustering, and neural networks. Python's simplicity and expressiveness enable you to experiment with different approaches, facilitating rapid prototyping and empowering innovation.
Enrolling in the Best Python Online Training can help people understand Python complexities and realize its full potential.
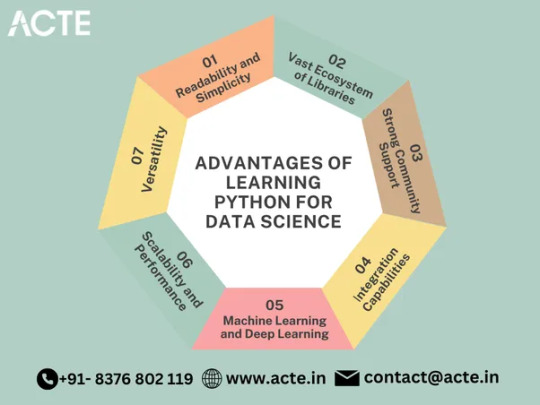
Seamless Integration Capabilities: One of Python's greatest strengths lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate with other programming languages. This feature allows data scientists to leverage existing code and libraries from languages like R, Java, or C++. By combining the best features of multiple languages, you can create a cohesive ecosystem that optimizes productivity and maximizes the potential of your data science projects.
Scaling up with Performance and Scalability: Python's performance has significantly improved over the years, making it a capable choice for handling large datasets and complex computations. Through libraries like Dask and Apache Spark, Python supports parallel processing and distributed computing, enabling you to scale your analyses efficiently. These tools empower you to process vast amounts of data seamlessly, ensuring your data science workflows remain robust and efficient.
Unleashing Versatility: Python's versatility extends beyond the realm of data science. As a general-purpose programming language, Python opens doors to diverse applications, including web development, automation, scripting, and more. By developing proficiency in Python, you gain the flexibility to explore various domains and expand your career prospects beyond the boundaries of data analysis.
Python has emerged as a powerhouse in the field of data science, offering a broad range of benefits that can elevate your data analysis and machine learning endeavors. Its readability, extensive library support, strong community, integration capabilities, performance, scalability, and versatility make it an indispensable tool for any data scientist.
By embracing Python, you unlock a world of possibilities and position yourself for success in the dynamic landscape of data science. Start your journey today and harness the true power of Python in data science.
0 notes
Text
Data Analysis Software Tools
In the era of big data, data analysis software tools have become indispensable for businesses seeking to make informed decisions and gain valuable insights from their data. These powerful tools streamline the data analysis process, allowing data analysts and professionals to explore, visualize, and interpret data with efficiency and accuracy. This article delves into the world of data analysis software tools, showcasing their versatility, features, and impact on driving data-driven success for organizations.
1. Understanding Data Analysis Software Tools:
Data analysis software tools are applications specifically designed to facilitate the process of data analysis. They cater to a wide range of users, from data analysts and scientists to business professionals and executives. These tools empower users to import, clean, manipulate, and visualize data, making the data analysis process accessible and user-friendly. To maximize your proficiency with these tools, consider enrolling in a data analytics course.
2. Popular Data Analysis Software Tools:
A variety of data analysis software tools are available in the market, catering to different user preferences and requirements. Some of the most popular and widely used tools include:
- Microsoft Excel: A familiar and widely accessible spreadsheet tool that offers basic data analysis capabilities through built-in functions and charting tools.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and visually compelling dashboards and reports. Enhance your skills with data analytics training to fully leverage its capabilities.
- Python: A versatile programming language with robust libraries, such as Pandas and NumPy, which enable data manipulation, analysis, and modeling. Consider pursuing a data analytics certification to harness the full potential of these tools for your analytical endeavors.
- R: A programming language dedicated to statistical computing and data visualization, with a rich collection of packages for advanced data analysis.
- SQL: A language for managing and querying relational databases, essential for data extraction and manipulation.
- Power BI: A business analytics tool by Microsoft that enables interactive data visualization and real-time reporting. Explore its capabilities further through a data analytics institute to master its potential.
3. Features and Capabilities:
Data analysis software tools offer a plethora of features and capabilities to cater to diverse analytical needs. These tools often provide functionalities like data import from various sources, data cleaning and transformation, data aggregation, statistical analysis, and data visualization. Some advanced tools also include machine learning algorithms, allowing for predictive modeling and prescriptive analysis. To fully leverage these tools, consider enrolling in a data analytics training course.
Moreover, data analysis software tools offer the advantage of automation, significantly reducing the manual effort required for data processing and analysis. This automation accelerates the decision-making process, enabling businesses to respond swiftly to changing market dynamics.
4. Data Visualization and Communication:
Data visualization is a critical aspect of data analysis, as it facilitates effective communication of insights to stakeholders. Data analysis software tools offer a wide array of visualization options, including bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, heat maps, and more. Interactive visualization features enable users to explore data from different angles and uncover hidden patterns.
Clear and impactful data visualizations enhance understanding and decision-making, enabling professionals to convey complex information in a visually compelling manner.
Refer this article: How much is the Data Analytics course fee in India?
5. Empowering Non-Technical Stakeholders:
Data analysis software tools have democratized data analysis, making it accessible to non-technical stakeholders. With user-friendly interfaces and intuitive drag-and-drop features, these tools empower executives, managers, and marketers to derive insights directly from data without extensive technical expertise.
By enabling data-driven decision-making across all levels of an organization, data analysis software tools foster a data-centric culture and drive innovation.
6. Integration with Big Data and Cloud Computing:
As the volume of data continues to grow exponentially, data analysis software tools have evolved to accommodate big data analytics. Many tools offer integration with big data platforms and cloud computing services, enabling efficient processing and analysis of large datasets.
Cloud-based data analysis solutions also provide scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to adapt their analytical capabilities to changing data requirements.
7. Future Trends and Innovations:
The field of data analysis software tools is continually evolving, with ongoing advancements and innovations. Machine learning capabilities within these tools are expanding, enabling users to leverage sophisticated algorithms for predictive and prescriptive analytics.
Additionally, data analysis software tools are embracing automation and natural language processing, simplifying the data analysis process even further.
Conclusion:
Data analysis software tools are a driving force behind the data-driven revolution, empowering businesses and professionals to extract valuable insights from data with ease and precision. From Microsoft Excel's accessibility to Tableau's powerful visualization capabilities and Python's versatility, these tools cater to a diverse range of analytical needs.
By democratizing data analysis and enhancing data visualization and communication, data analysis software tools bridge the gap between technical and non-technical stakeholders, enabling informed decision-making at all levels of an organization.
As these tools continue to evolve and incorporate cutting-edge technologies, the future of data analysis looks promising. With automation, machine learning, and cloud integration, data analysis software tools are poised to play an even more significant role in driving data-driven success and innovation for businesses worldwide. Embrace the power of data analysis software tools, and unlock the full potential of your data to thrive in the data-centric world of tomorrow.
0 notes
Text
Why Learning Python is a Game Changer for Your Career: A Deep Dive into the Best Training Options in Chandigarh
In the fast-paced world of technology, programming languages continue to evolve, offering endless possibilities and career opportunities. Among the numerous programming languages available, Python has emerged as one of the most popular and versatile choices. Whether you're an aspiring software developer, data scientist, automation engineer, or just a curious learner, Python is the perfect starting point to delve into the world of programming.
But what makes Python so special? Why are students and professionals alike racing to master this language? And most importantly, where can you receive the best training to harness its full potential—especially if you're in Chandigarh? Let’s explore all these questions in detail and understand why Python Training could be your gateway to a successful tech career.
The Power of Python in the Tech Ecosystem
Python is not just another programming language—it's a gateway to innovation. With its easy-to-understand syntax, extensive libraries, and active community, Python makes coding accessible even for beginners. From web development and automation to artificial intelligence and data analytics, Python serves as the backbone for numerous modern applications.
Some key advantages of Python include:
Simplicity and Readability: Python's clean syntax resembles English, making it an ideal language for beginners.
Versatile Application: It supports a wide array of domains—web development (Django, Flask), data science (Pandas, NumPy), machine learning (TensorFlow, scikit-learn), and automation (Selenium, PyAutoGUI).
Strong Community Support: Python has one of the most active global communities, meaning help is always just a click away.
High Demand in Job Market: Companies such as Google, Netflix, and NASA use Python extensively, creating a strong demand for skilled professionals.
Python for Beginners and Professionals
Whether you're a college student aiming to enhance your resume, a working professional looking to upskill, or an entrepreneur wanting to automate tasks, Python is for you. One of Python’s biggest advantages is its adaptability. It scales well across different levels of expertise.
Beginners: Learn programming concepts such as loops, functions, variables, and data structures with ease.
Intermediate Learners: Start exploring web frameworks and build real-world projects.
Advanced Users: Dive into machine learning, data visualization, and backend development.
With continuous updates and evolving libraries, Python ensures that learners remain at the cutting edge of technology.
Why Take a Structured Python Training Course?
While learning through online resources or tutorials might be tempting, a structured training program offers several unmatched advantages:
Comprehensive Curriculum: Covers all the core and advanced topics systematically.
Hands-On Projects: Helps in applying theoretical knowledge to real-world problems.
Mentorship and Guidance: Personalized feedback and support to improve your learning curve.
Career-Oriented Training: Focus on job preparation with mock interviews, resume building, and placement assistance.
Certifications: Adds credibility to your skillset, increasing your chances of getting hired.
Choosing the right training institute plays a crucial role in how efficiently and effectively you learn Python.
What Makes Chandigarh an Ideal Place to Learn Python?
Chandigarh, with its growing IT sector and educational infrastructure, has become a hotspot for tech education. The city hosts a number of reputed institutes, making it easier for students and professionals to find quality courses. The blend of affordability, experienced trainers, and a vibrant learning atmosphere makes Chandigarh a preferred location for tech training.
Moreover, the city is home to several startups and IT firms that offer ample internship and job opportunities for Python developers. This means you can gain practical experience while studying, enhancing your resume and confidence.
Where to Get the Best Python Training in Chandigarh?
If you're looking to master Python and unlock new career opportunities, CBITSS Technologies stands out as one of the most trusted training providers. Known for its industry-relevant curriculum and hands-on teaching approach, CBITSS offers a robust Python Training program that caters to beginners and advanced learners alike.
The program includes:
In-depth training modules from basics to advanced concepts.
Real-time project work that mirrors industry challenges.
Certified trainers with real-world experience.
Interactive classroom sessions and flexible timing.
Support for internship and placement opportunities.
With a solid reputation and high student satisfaction rates, CBITSS continues to be a top choice for those seeking the Best Python Training in Chandigarh.
Real-Life Applications of Python That You’ll Learn
The course is not just theoretical. Students are trained to build projects that solve actual problems. Some of the domains you'll explore during your Python training include:
Web Development: Learn to build dynamic websites using Django and Flask.
Data Science: Understand how to manipulate data using libraries like Pandas and visualize it using Matplotlib.
Machine Learning: Dive into predictive analytics using Scikit-learn and TensorFlow.
Scripting and Automation: Automate repetitive tasks like sending emails or web scraping.
App Development: Explore GUI development using Tkinter.
These practical applications make your learning relevant and increase your confidence to work in real-world scenarios.
What You’ll Gain from Python Training at CBITSS
Career Boost: Increase your chances of landing high-paying jobs in tech.
Portfolio Building: Showcase the projects you’ve built during the training.
Problem-Solving Skills: Learn to write efficient, clean, and bug-free code.
Industry Insight: Understand how Python is used in startups and MNCs.
Moreover, CBITSS assists you with career planning by offering interview preparation, resume reviews, and placement drives.
What Students Say
Here are some experiences shared by past learners:
“The training at CBITSS helped me understand Python from scratch. The trainers were highly experienced and always ready to help. I especially loved the hands-on projects.” — Anjali Sharma
“As a working professional, I needed a course that could fit my schedule. CBITSS offered flexible timings and weekend batches, which made it easier for me to balance work and learning.” — Rajiv Mehta
“After completing the course, I got placed as a Python developer at a local startup. The placement team really helped me prepare for the interviews.” — Mohit Arora
Final Thoughts
Python is more than just a language—it's a skill that can transform your career. Whether you’re stepping into the tech world or looking to specialize in a high-demand area, Python provides a solid foundation.
Enrolling in a professional Python Training program will ensure you're not just learning theory but also applying your knowledge in meaningful ways. And when it comes to the Best Python Training in Chandigarh, CBITSS Technologies emerges as a reliable and effective choice.
Start your journey today and become part of the ever-growing community of Python developers shaping the future of technology.
0 notes
Text
youtube
Python Numpy Tutorials
#numpy tutorials#numpy for beginners#numpy arrays#what is array in numpy#numpy full array#how to create numpy full array#what is numpy full array#how to use numpy full array#uses of numpy full array#how to define the shape of numpy array#python for beginners#python full course#numpy full course#numpy python playlist#numpy playlist#complete python numpy tutorials#numpy full array function#python array#python numpy library#how to create arrays in python numpy#Youtube
0 notes
Text
NumPy
The crown jewel of NumPy is the ndarray. The ndarray is a homogeneous n-dimensional array object. What does that mean? 🤨
A Python List or a Pandas DataFrame can contain a mix of strings, numbers, or objects (i.e., a mix of different types). Homogenous means all the data have to have the same data type, for example all floating-point numbers.
And n-dimensional means that we can work with everything from a single column (1-dimensional) to the matrix (2-dimensional) to a bunch of matrices stacked on top of each other (n-dimensional).
To import NumPy: import numpy as np
To make a 1-D Array (Vector): my_array = np.array([1.1, 9.2, 8.1, 4.7])
To get the shape (rows, columns): my_array.shape
To access a particular value by the index: my_array[2]
To get how many dimensions there are: my_array.ndim
To make a 2D Array (matrix):
array_2d = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 9],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])
To get the shape (columns, rows): array_2d.shape
To get a particular 1D vector: mystery_array[2, 1, :]
Use .arange()to createa a vector a with values ranging from 10 to 29: a = np.arange(10, 30)
The last 3 values in the array: a[-3:]
An interval between two values: a[3:6]
All the values except the first 12: a[12:]
Every second value; a[::2]
To reverse an array: f = np.flip(a) OR a[::-1]
To get the indices of the non-zero elements in an array: nz_indices = np.nonzero(b)
To generate a random 3x3x3 array:
from numpy.random import random
z = random((3,3,3))
z
or use the full path to call it.
z = np.random.random((3,3,3)) # without an import statement
print(z.shape)
z
or
random_array = np.random.rand(3, 3, 3)
print(random_array)
To create a vector of size 9 from 0 to 100 with values evenly spaced: x = np.linspace(0,100, num=9)
To create an array called noise and display it as an image:
noise = np.random.random((128,128,3))
print(noise.shape)
plt.imshow(noise)

To display a random picture of a raccoon:
img = misc.face()
plt.imshow(img)
1 note
·
View note
Text
From Coding to Innovation: How Python Fuels Technology Careers
Introduction
Python has emerged as a powerhouse in the programming world, offering versatile applications across various domains. Mastering Python opens up an array of career opportunities, enabling professionals to tackle complex challenges and drive innovation in today's technology-driven landscape. Let's delve into the diverse job prospects that await Python learners. Considering the kind support of Learn Python Course in Pune, Whatever your level of experience or reason for switching from another programming language, learning Python gets much more fun.

Exploring Career Opportunities After Learning Python
1. Software Development Maven
Python is widely used in software development for its simplicity and readability. As a Python developer, you can create scalable applications, build robust APIs, and automate workflows. Whether you're developing mobile apps, web applications, or enterprise software solutions, Python's extensive libraries and frameworks like Django and Flask provide a solid foundation for building cutting-edge software.
2. Data Science Enthusiast
Python's dominance in data science stems from its powerful libraries such as Pandas, NumPy, and SciPy. Data scientists leverage Python for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning model development. With Python, you can extract insights from vast datasets, build predictive models, and visualize data to drive data-driven decision-making across industries.
3. Cloud Computing Specialist
Python's versatility extends to cloud computing, where it is used for infrastructure automation, orchestration, and management. Cloud engineers proficient in Python can deploy and manage cloud resources, configure infrastructure as code using tools like Terraform and Ansible, and optimize cloud environments for scalability and cost-efficiency.
Enrolling in the Best Python Certification Online can help people realise Python’s full potential and gain a deeper understanding of its complexities.

4. AI and Machine Learning Architect
Python is the preferred language for AI and machine learning due to its rich ecosystem of libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras. AI engineers and machine learning specialists use Python to develop and deploy advanced algorithms for natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics. Python's flexibility enables practitioners to experiment with different models and algorithms to solve complex problems.
5. Cybersecurity Expert
In cybersecurity, Python is indispensable for tasks like penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, and threat detection. Python's extensive libraries and scripting capabilities enable cybersecurity professionals to automate security operations, analyze network traffic, and respond swiftly to cyber threats. With Python, you can build security tools, conduct forensic investigations, and fortify defenses against evolving cyber threats.
6. DevOps Champion
Python plays a crucial role in DevOps practices by enabling automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. DevOps engineers proficient in Python can streamline software development workflows, manage infrastructure through code, and ensure seamless collaboration between development and operations teams. Python's scripting capabilities make it ideal for automating routine tasks and optimizing DevOps processes for faster and more reliable software releases.
7. Entrepreneurial Innovator
Python empowers entrepreneurs to innovate and disrupt industries by leveraging its versatility and scalability. Whether you're launching a tech startup, developing software products, or creating data-driven solutions, Python provides the tools and frameworks necessary to transform ideas into successful ventures. Python's broad applicability across domains allows entrepreneurs to build scalable solutions, reach new markets, and drive business growth in a competitive landscape.
Conclusion
Python's widespread adoption and robust ecosystem make it a valuable skill for professionals aspiring to excel in today's digital economy. Whether you're passionate about software development, data science, cloud computing, AI, cybersecurity, DevOps, or entrepreneurship, Python offers a versatile platform to explore diverse career paths and make a significant impact. Embrace the opportunities that Python brings and embark on a rewarding career journey filled with innovation, growth, and professional fulfillment.
#python course#python#python training#python programming#python online classes#python online course#python online training
0 notes
Text
My Programming Journey: Understanding Music Genres with Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence is used everyday, by regular people and businesses, creating such a positive impact in all kinds of industries and fields that it makes me think that AI is only here to stay and grow, and help society grow with it. AI has evolved considerably in the last decade, currently being able to do things that seem taken out of a Sci-Fi movie, like driving cars, recognizing faces and words (written and spoken), and music genres.
While Music is definitely not the most profitable application of Machine Learning, it has benefited tremendously from Deep Learning and other ML applications. The potential AI possess in the music industry includes automating services and discovering insights and patterns to classify and/or recommend music.
We can be witnesses to this potential when we go to our preferred music streaming service (such as Spotify or Apple Music) and, based on the songs we listen to or the ones we’ve previously saved, we are given playlists of similar songs that we might also like.
Machine Learning’s ability of recognition isn’t just limited to faces or words, but it can also recognize instruments used in music. Music source separation is also a thing, where a song is taken and its original signals are separated from a mixture audio signal. We can also call this Feature Extraction and it is popularly used nowadays to aid throughout the cycle of music from composition and recording to production. All of this is doable thanks to a subfield of Music Machine Learning: Music Information Retrieval (MIR). MIR is needed for almost all applications related to Music Machine Learning. We’ll dive a bit deeper on this subfield.
Music Information Retrieval
Music Information Retrieval (MIR) is an interdisciplinary field of Computer Science, Musicology, Statistics, Signal Processing, among others; the information within music is not as simple as it looks like. MIR is used to categorize, manipulate and even create music. This is done by audio analysis, which includes pitch detection, instrument identification and extraction of harmonic, rhythmic and/or melodic information. Plain information can be easily comprehended (such as tempo (beats per minute), melody, timbre, etc.) and easily calculated through different genres. However, many music concepts considered by humans can’t be perfectly modeled to this day, given there are many factors outside music that play a role in its perception.
Getting Started
I wanted to try something more of a challenge for this post, so I am attempting to Visualize and Classify audio data using the famous GTZAN Dataset to perform an in depth analysis of sound and understand what features we can visualize/extract from this kind of data. This dataset consists of: · A collection of 10 genres with 100 audio (WAV) files each, each having a length of 30 seconds. This collection is stored in a folder called “genres_original”. · A visual representation for each audio file stored in a folder called “images_original”. The audio files were converted to Mel Spectrograms (later explained) to make them able to be classified through neural networks, which take in image representation. · 2 CVS files that contain features of the audio files. One file has a mean and variance computed over multiple features for each song (full length of 30 seconds). The second CVS file contains the same songs but split before into 3 seconds, multiplying the data times 10. For this project, I am yet again coding in Visual Studio Code. On my last project I used the Command Line from Anaconda (which is basically the same one from Windows with the python environment set up), however, for this project I need to visualize audio data and these representations can’t be done in CLI, so I will be running my code from Jupyter Lab, from Anaconda Navigator. Jupyter Lab is a web-based interactive development environment for Jupyter notebooks (documents that combine live runnable code with narrative text, equations, images and other interactive visualizations). If you haven’t installed Anaconda Navigator already, you can find the installation steps on my previous blog post. I would quickly like to mention that Tumblr has a limit of 10 images per post, and this is a lengthy project so I’ll paste the code here instead of uploading code screenshots, and only post the images of the outputs. The libraries we will be using are:
> pandas: a data analysis and manipulation library.
> numpy: to work with arrays.
> seaborn: to visualize statistical data based on matplolib.
> matplotlib.pyplot: a collection of functions to create static, animated and interactive visualizations.
> Sklearn: provides various tools for model fitting, data preprocessing, model selection and evaluation, among others.
· naive_bayes
· linear_model
· neighbors
· tree
· ensemble
· svm
· neural_network
· metrics
· preprocessing
· decomposition
· model_selection
· feature_selection
> librosa: for music and audio analysis to create MIR systems.
· display
> IPython: interactive Python
· display import Audio
> os: module to provide functions for interacting with the operating system.
> xgboost: gradient boosting library
· XGBClassifier, XGBRFClassifier
· plot_tree, plot_importance
> tensorflow:
· Keras
· Sequential and layers
Exploring Audio Data
Sounds are pressure waves, which can be represented by numbers over a time period. We first need to understand our audio data to see how it looks. Let’s begin with importing the libraries and loading the data:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
import librosa
import librosa.display
import IPython.display as ipd
from IPython.display import Audio
import os
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier, LogisticRegression
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from xgboost import XGBClassifier, XGBRFClassifier
from xgboost import plot_tree, plot_importance
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score, roc_auc_score, roc_curve
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import *
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# Loading the data
general_path = 'C:/Users/807930/Documents/Spring 2021/Emerging Trends in Technology/MusicGenre/input/gtzan-database-music-genre-classification/Data'
Now let’s load one of the files (I chose Hit Me Baby One More Time by Britney Spears):
print(list(os.listdir(f'{general_path}/genres_original/')))
#Importing 1 file to explore how our Audio Data looks.
y, sr = librosa.load(f'{general_path}/genres_original/pop/pop.00019.wav')
#Playing the audio
ipd.display(ipd.Audio(y, rate=sr, autoplay=True))
print('Sound (Sequence of vibrations):', y, '\n')
print('Sound shape:', np.shape(y), '\n')
print('Sample Rate (KHz):', sr, '\n')
# Verify length of the audio
print('Check Length of Audio:', 661794/22050)
We took the song and using the load function from the librosa library, we got an array of the audio time series (sound) and the sample rate of sound. The length of the audio is 30 seconds. Now we can trim our audio to remove the silence between songs and use the librosa.display.waveplot function to plot the audio file into a waveform. > Waveform: The waveform of an audio signal is the shape of its graph as a function of time.
# Trim silence before and after the actual audio
audio_file, _ = librosa.effects.trim(y)
print('Audio File:', audio_file, '\n')
print('Audio File Shape:', np.shape(audio_file))
#Sound Waves 2D Representation
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
librosa.display.waveplot(y = audio_file, sr = sr, color = "b");
plt.title("Sound Waves in Pop 19", fontsize = 25);
After having represented the audio visually, we will plot a Fourier Transform (D) from the frequencies and amplitudes of the audio data. > Fourier Transform: A mathematical function that maps the frequency and phase content of local sections of a signal as it changes over time. This means that it takes a time-based pattern (in this case, a waveform) and retrieves the complex valued function of frequency, as a sine wave. The signal is converted into individual spectral components and provides frequency information about the signal.
#Default Fast Fourier Transforms (FFT)
n_fft = 2048 # window size
hop_length = 512 # number audio of frames between STFT columns
# Short-time Fourier transform (STFT)
D = np.abs(librosa.stft(audio_file, n_fft = n_fft, hop_length = hop_length))
print('Shape of time-frequency of the Audio File:', np.shape(D))
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
plt.plot(D);
plt.title("Fourier Transform in Pop 19", fontsize = 25);
The Fourier Transform only gives us information about the frequency values and now we need a visual representation of the frequencies of the audio signal so we can calculate more audio features for our system. To do this we will plot the previous Fourier Transform (D) into a Spectrogram (DB). > Spectrogram: A visual representation of the spectrum of frequencies of a signal as it varies with time.
DB = librosa.amplitude_to_db(D, ref = np.max)
# Creating the Spectrogram
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
librosa.display.specshow(DB, sr = sr, hop_length = hop_length, x_axis = 'time', y_axis = 'log'
cmap = 'cool')
plt.colorbar();
plt.title("Pop 19 Spectrogram", fontsize = 25);
The output:
Audio Features
Now that we know what the audio data looks like to python, we can proceed to extract the Audio Features. The features we will need to extract, based on the provided CSV, are: · Harmonics · Percussion · Zero Crossing Rate · Tempo · Spectral Centroid · Spectral Rollof · Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients · Chroma Frequencies Let’s start with the Harmonics and Percussive components:
# Decompose the Harmonics and Percussive components and show Representation
y_harm, y_perc = librosa.effects.hpss(audio_file)
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
plt.plot(y_harm, color = 'g');
plt.plot(y_perc, color = 'm');
plt.title("Harmonics and Percussive components", fontsize = 25);
Using the librosa.effects.hpss function, we are able to separate the harmonics and percussive elements from the audio source and plot it into a visual representation.
Now we can retrieve the Zero Crossing Rate, using the librosa.zero_crossings function.
> Zero Crossing Rate: The rate of sign-changes (the number of times the signal changes value) of the audio signal during the frame.
#Total number of zero crossings
zero_crossings = librosa.zero_crossings(audio_file, pad=False)
print(sum(zero_crossings))
The Tempo (Beats per Minute) can be retrieved using the librosa.beat.beat_track function.
# Retrieving the Tempo in Pop 19
tempo, _ = librosa.beat.beat_track(y, sr = sr)
print('Tempo:', tempo , '\n')
The next feature extracted is the Spectral Centroids. > Spectral Centroid: a measure used in digital signal processing to characterize a spectrum. It determines the frequency area around which most of the signal energy concentrates.
# Calculate the Spectral Centroids
spectral_centroids = librosa.feature.spectral_centroid(audio_file, sr=sr)[0]
print('Centroids:', spectral_centroids, '\n')
print('Shape of Spectral Centroids:', spectral_centroids.shape, '\n')
# Computing the time variable for visualization
frames = range(len(spectral_centroids))
# Converts frame counts to time (seconds)
t = librosa.frames_to_time(frames)
print('Frames:', frames, '\n')
print('Time:', t)
Now that we have the shape of the spectral centroids as an array and the time variable (from frame counts), we need to create a function that normalizes the data. Normalization is a technique used to adjust the volume of audio files to a standard level which allows the file to be processed clearly. Once it’s normalized we proceed to retrieve the Spectral Rolloff.
> Spectral Rolloff: the frequency under which the cutoff of the total energy of the spectrum is contained, used to distinguish between sounds. The measure of the shape of the signal.
# Function that normalizes the Sound Data
def normalize(x, axis=0):
return sklearn.preprocessing.minmax_scale(x, axis=axis)
# Spectral RollOff Vector
spectral_rolloff = librosa.feature.spectral_rolloff(audio_file, sr=sr)[0]
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
librosa.display.waveplot(audio_file, sr=sr, alpha=0.4, color = '#A300F9');
plt.plot(t, normalize(spectral_rolloff), color='#FFB100');
Using the audio file, we can continue to get the Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients, which are a set of 20 features. In Music Information Retrieval, it’s often used to describe timbre. We will employ the librosa.feature.mfcc function.
mfccs = librosa.feature.mfcc(audio_file, sr=sr)
print('Mel-Frequency Ceptral Coefficient shape:', mfccs.shape)
#Displaying the Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients:
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
librosa.display.specshow(mfccs, sr=sr, x_axis='time', cmap = 'cool');
The MFCC shape is (20, 1,293), which means that the librosa.feature.mfcc function computed 20 coefficients over 1,293 frames.
mfccs = sklearn.preprocessing.scale(mfccs, axis=1)
print('Mean:', mfccs.mean(), '\n')
print('Var:', mfccs.var())
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 6))
librosa.display.specshow(mfccs, sr=sr, x_axis='time', cmap = 'cool');
Now we retrieve the Chroma Frequencies, using librosa.feature.chroma_stft. > Chroma Frequencies (or Features): are a powerful tool for analyzing music by categorizing pitches. These features capture harmonic and melodic characteristics of music.
# Increase or decrease hop_length to change how granular you want your data to be
hop_length = 5000
# Chromogram
chromagram = librosa.feature.chroma_stft(audio_file, sr=sr, hop_length=hop_length)
print('Chromogram shape:', chromagram.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6))
librosa.display.specshow(chromagram, x_axis='time', y_axis='chroma', hop_length=hop_length, cmap='coolwarm');
The output:
Exploratory Data Analysis
Now that we have a visual understanding of what an audio file looks like, and we’ve explored a good set of features, we can perform EDA, or Exploratory Data Analysis. This is all about getting to know the data and data profiling, summarizing the dataset through descriptive statistics. We can do this by getting a description of the data, using the describe() function or head() function. The describe() function will give us a description of all the dataset rows, and the head() function will give us the written data. We will perform EDA on the csv file, which contains all of the features previously analyzed above, and use the head() function:
# Loading the CSV file
data = pd.read_csv(f'{general_path}/features_30_sec.csv')
data.head()
Now we can create the correlation matrix of the data found in the csv file, using the feature means (average). We do this to summarize our data and pass it into a Correlation Heatmap.
# Computing the Correlation Matrix
spike_cols = [col for col in data.columns if 'mean' in col]
corr = data[spike_cols].corr()
The corr() function finds a pairwise correlation of all columns, excluding non-numeric and null values.
Now we can plot the heatmap:
# Generate a mask for the upper triangle
mask = np.triu(np.ones_like(corr, dtype=np.bool))
# Set up the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 11));
# Generate a custom diverging colormap
cmap = sns.diverging_palette(0, 25, as_cmap=True, s = 90, l = 45, n = 5)
# Draw the heatmap with the mask and correct aspect ratio
sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, cmap=cmap, vmax=.3, center=0,
square=True, linewidths=.5, cbar_kws={"shrink": .5}
plt.title('Correlation Heatmap (for the MEAN variables)', fontsize = 25)
plt.xticks(fontsize = 10)
plt.yticks(fontsize = 10);
Now we will take the data and, extracting the label(genre) and the tempo, we will draw a Box Plot. Box Plots visually show the distribution of numerical data through displaying percentiles and averages.
# Setting the axis for the box plot
x = data[["label", "tempo"]]
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 9));
sns.boxplot(x = "label", y = "tempo", data = x, palette = 'husl');
plt.title('Tempo(BPM) Boxplot for Genres', fontsize = 25)
plt.xticks(fontsize = 14)
plt.yticks(fontsize = 10);
plt.xlabel("Genre", fontsize = 15)
plt.ylabel("BPM", fontsize = 15)
Now we will draw a Scatter Diagram. To do this, we need to visualize possible groups of genres:
# To visualize possible groups of genres
data = data.iloc[0:, 1:]
y = data['label']
X = data.loc[:, data.columns != 'label']
We use data.iloc to get rows and columns at integer locations, and data.loc to get rows and columns with particular labels, excluding the label column. The next step is to normalize our data:
# Normalization
cols = X.columns
min_max_scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
np_scaled = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(X)
X = pd.DataFrame(np_scaled, columns = cols)
Using the preprocessing library, we rescale each feature to a given range. Then we add a fit to data and transform (fit_transform).
We can proceed with a Principal Component Analysis:
# Principal Component Analysis
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
principalComponents = pca.fit_transform(X)
principalDf = pd.DataFrame(data = principalComponents, columns = ['principal component 1', 'principal component 2'])
# concatenate with target label
finalDf = pd.concat([principalDf, y], axis = 1)
PCA is used to reduce dimensionality in data. The fit learns some quantities from the data. Before the fit transform, the data shape was [1000, 58], meaning there’s 1000 rows with 58 columns (in the CSV file there’s 60 columns but two of these are string values, so it leaves with 58 numeric columns).
Once we use the PCA function, and set the components number to 2 we reduce the dimension of our project from 58 to 2. We have found the optimal stretch and rotation in our 58-dimension space to see the layout in two dimensions.
After reducing the dimensional space, we lose some variance(information).
pca.explained_variance_ratio_
By using this attribute we get the explained variance ratio, which we sum to get the percentage. In this case the variance explained is 46.53% .
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 9))
sns.scatterplot(x = "principal component 1", y = "principal component 2", data = finalDf, hue = "label", alpha = 0.7,
s = 100);
plt.title('PCA on Genres', fontsize = 25)
plt.xticks(fontsize = 14)
plt.yticks(fontsize = 10);
plt.xlabel("Principal Component 1", fontsize = 15)
plt.ylabel("Principal Component 2", fontsize = 15)
plt.savefig("PCA Scattert.jpg")
The output:
Genre Classification
Now we know what our data looks like, the features it has and have analyzed the principal component on all genres. All we have left to do is to build a classifier model that will predict any new audio data input its genre. We will use the CSV with 10 times the data for this.
# Load the data
data = pd.read_csv(f'{general_path}/features_3_sec.csv')
data = data.iloc[0:, 1:]
data.head()
Once again visualizing and normalizing the data.
y = data['label'] # genre variable.
X = data.loc[:, data.columns != 'label'] #select all columns but not the labels
# Normalization
cols = X.columns
min_max_scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
np_scaled = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(X)
# new data frame with the new scaled data.
X = pd.DataFrame(np_scaled, columns = cols)
Now we have to split the data for training. Like I did in my previous post, the proportions are (70:30). 70% of the data will be used for training and 30% of the data will be used for testing.
# Split the data for training
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
I tested 7 algorithms but I decided to go with K Nearest-Neighbors because I had previously used it.
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=19)
knn.fit(X_train, y_train)
preds = knn.predict(X_test)
print('Accuracy', ':', round(accuracy_score(y_test, preds), 5), '\n')
# Confusion Matrix
confusion_matr = confusion_matrix(y_test, preds) #normalize = 'true'
plt.figure(figsize = (16, 9))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matr, cmap="Blues", annot=True,
xticklabels = ["blues", "classical", "country", "disco", "hiphop", "jazz", "metal", "pop", "reggae", "rock"],
yticklabels=["blues", "classical", "country", "disco", "hiphop", "jazz", "metal", "pop", "reggae", "rock"]);
The output:
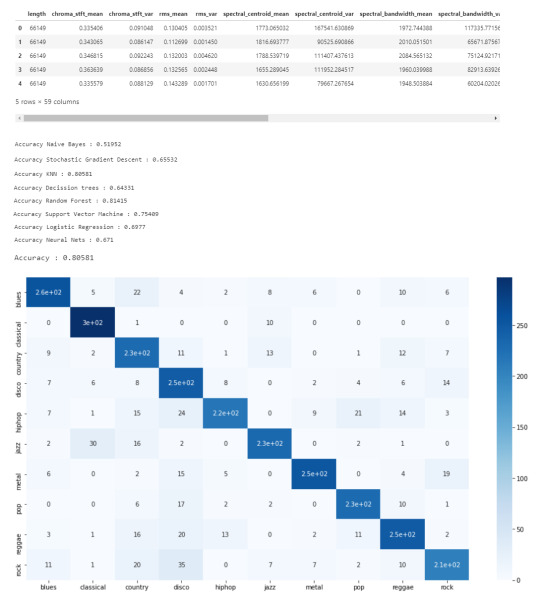
youtube
References
· https://medium.com/@james_52456/machine-learning-and-the-future-of-music-an-era-of-ml-artists-9be5ef27b83e
· https://www.kaggle.com/andradaolteanu/work-w-audio-data-visualise-classify-recommend/
· https://www.kaggle.com/dapy15/music-genre-classification/notebook
· https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-start-implementing-machine-learning-to-music-4bd2edccce1f
· https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Music_information_retrieval
· https://pandas.pydata.org
· https://scikit-learn.org/
· https://seaborn.pydata.org
· https://matplotlib.org
· https://librosa.org/doc/main/index.html
· https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost
· https://docs.python.org/3/library/os.html
· https://www.tensorflow.org/
· https://www.hindawi.com/journals/sp/2021/1651560/
0 notes
Text
python numpy
original source : https://github.com/joeyajames/Python/blob/master/Numpy/Python%20Numpy%20Intro.ipynb
Python Numpy Intro
An introduction to the Python Numpy numerical python library. The core data structure behind Numpy is the n-dimensional Numpy Array. It is 3x to 10x faster and more memory efficient than Python's lists because, similar to Java arrays, it uses contiguous blocks of memory, and all elements are the same data type so there is no type checking at runtime. The Numpy library also includes many built-in code-saving mathematical functions that can be performed on an entire array or any slice of an array with a single line of code (ie. no for loops). Numpy n-dimensional arrays are also sometimes referred to as nd-arrays.
Install Numpy using pip: pip install numpy The convention for importing numpy is import numpy as np.
import numpy as np
Creating a Numpy Array
There are MANY ways to instantiate a numpy array. I covered the most common ones below. Docs here cover more constructors.
Pass in a list to the array() constructor
Use the arange function, similar to the range function but used for Numpy arrays. Uses arguments, (start, stop+1, step).
Use linspace to create an array of n equally spaced values. Uses arguments (start, stop, number of items).
Create an array empty, full of ones or zeros, or full of any fill value. Uses argument (shape) in the form of a tuple.
You can pass in dtype as an optional argument for any of these. This is especially useful if you want to limit memory usage for a very large array of small integers because int8 and int16 use much less space than the default int32.
In [96]:
a = np.array([1,3,5,7,9,11]) print(a) a = np.arange(1, 12, 2) # (start, stop, step) print(a) a = np.linspace(5, 8, 13) # (start, stop, number of items) print(a) a = np.zeros((4, 2)) print(a) a = np.ones((2, 3), dtype=np.int16) print(a) a = np.full((6,), 88) print(a) a = np.fromstring('25 30 35 40', dtype=np.int, sep=' ') print(a) a = np.array([[1,3,5],[7,9,11]]) print(a) b = np.zeros_like(a) # _like gives you a new array in the same shape as the argument. print(b)
[ 1 3 5 7 9 11] [ 1 3 5 7 9 11] [5. 5.25 5.5 5.75 6. 6.25 6.5 6.75 7. 7.25 7.5 7.75 8. ] [[0. 0.] [0. 0.] [0. 0.] [0. 0.]] [[1 1 1] [1 1 1]] [88 88 88 88 88 88] [25 30 35 40] [[ 1 3 5] [ 7 9 11]] [[0 0 0] [0 0 0]]
Numpy Array Attributes
Get size (number of items), shape (dimensions), itemsize(bytes of memory for each item), and dtype (numpy data type). See how many bytes of memory space the whole array uses from the product of size and itemsize. See complete list of attributes and methods.
In [97]:
print(a.size) print(a.shape) print(a.ndim) print(a.itemsize) print(a.dtype) print(a.nbytes) # same as a.size * a.itemsize
6 (2, 3) 2 4 int32 24
Indexing and Slicing
Use square brackets to get any item of an array by index. Multi-dimensional arrays can use multiple square brackets.
There are three arguments for slicing arrays, all are optional: [start:stop:step]. If start is left blank it defaults to 0. If stop is left blank it defaults to the end of the array. Step defaults to 1.
In [98]:
print(a) print(a[1]) print(a[0][2]) print(b[2:4]) print(a[:1]) print(a[1:3:2]) print(a[:, 1:2]) # all elements on dimension 0, only element 1 on dimension 1
[[ 1 3 5] [ 7 9 11]] [ 7 9 11] 5 [] [[1 3 5]] [[ 7 9 11]] [[3] [9]]
Reshape, Swap Axes, Flatten
See full list of array manipulation routines.
In [99]:
c = np.arange(-9, -3,).reshape(2,3) print(c) c = c.swapaxes(0,1) print(c) c = c.flatten() print(c)
[[-9 -8 -7] [-6 -5 -4]] [[-9 -6] [-8 -5] [-7 -4]] [-9 -6 -8 -5 -7 -4]
Use dtype to Save Space
Default data types (int32 and float64) are memory hogs. If you don't need the higher precision you can save a lot of memory space and improve speed of operations by using smaller data types. For large data sets this makes a big difference.
In [100]:
d = np.arange(0,100) print(d.dtype, type(d[1])) print(d.nbytes) d = np.arange(0,100, dtype='int8') print(d.dtype, type(d[1])) print(d.nbytes)
int32 <class 'numpy.int32'> 400 int8 <class 'numpy.int8'> 100
UpCasting, Rounding, Print Formatting
Data type of all Items is upcast to the most precise element.
In [101]:
e = np.array([(1.566666,2,3), (4,5,6)]) print(e.dtype) e = e.round(4) print(e) np.set_printoptions(precision=2, suppress=True) # show 2 decimal places, suppress scientific notation print(e)
float64 [[1.57 2. 3. ] [4. 5. 6. ]] [[1.57 2. 3. ] [4. 5. 6. ]]
Numpy Data Types Available
uint is unsigned int, for positive numbers.
In [102]:
import pprint as pp pp.pprint(np.sctypes)
{'complex': [<class 'numpy.complex64'>, <class 'numpy.complex128'>], 'float': [<class 'numpy.float16'>, <class 'numpy.float32'>, <class 'numpy.float64'>], 'int': [<class 'numpy.int8'>, <class 'numpy.int16'>, <class 'numpy.int32'>, <class 'numpy.int32'>, <class 'numpy.int64'>], 'others': [<class 'bool'>, <class 'object'>, <class 'bytes'>, <class 'str'>, <class 'numpy.void'>], 'uint': [<class 'numpy.uint8'>, <class 'numpy.uint16'>, <class 'numpy.uint32'>, <class 'numpy.uint32'>, <class 'numpy.uint64'>]}
Reading and Writing to Files
Can use loadtxt, or genfromtxt to load data to load an entire file into an array at once. Genfromtxt is more fault tolerant. Use savetxt to write an array to file.
In [103]:
f = np.loadtxt('data.txt', skiprows=1, delimiter=',', dtype=np.int32) print(f) print(f.dtype) np.savetxt('data2.txt', f, delimiter=';', fmt='%d', header='a;b;c;d;e;f;g;h;i;j', comments='')
[[9 3 8 7 6 1 0 4 2 5] [1 7 4 9 2 6 8 3 5 0] [4 8 3 9 5 7 2 6 0 1] [1 7 4 2 5 9 6 8 0 3] [0 7 5 2 8 6 3 4 1 9] [5 9 1 4 7 0 3 6 8 2]] int32
In [111]:
g = np.genfromtxt('data.txt', skip_header=1, delimiter=',', dtype=np.int32) print(g)
[[9 3 8 7 6 1 0 4 2 5] [1 7 4 9 2 6 8 3 5 0] [4 8 3 9 5 7 2 6 0 1] [1 7 4 2 5 9 6 8 0 3] [0 7 5 2 8 6 3 4 1 9] [5 9 1 4 7 0 3 6 8 2]]
Mathematical Functions
Numpy has an extensive list of math and scientific functions. The best part is that you don't have to iterate. You can apply an operation to the entire array or a slice of an array at once.
In [105]:
print(g > 4) print(g ** 2 - 1)
[[ True False True True True False False False False True] [False True False True False True True False True False] [False True False True True True False True False False] [False True False False True True True True False False] [False True True False True True False False False True] [ True True False False True False False True True False]] [[80 8 63 48 35 0 -1 15 3 24] [ 0 48 15 80 3 35 63 8 24 -1] [15 63 8 80 24 48 3 35 -1 0] [ 0 48 15 3 24 80 35 63 -1 8] [-1 48 24 3 63 35 8 15 0 80] [24 80 0 15 48 -1 8 35 63 3]]
In [106]:
print(g.min()) print(g.max()) print(g.sum()) print(g.mean()) print(g.var()) # variance print(g.std()) # standard deviation print(g.sum(axis=1)) print(g.min(axis=0)) print(g.argmin()) # index of min element print(g.argmax()) # index of max element print(g.argsort()) # returns array of indices that would put the array in sorted order
0 9 270 4.5 8.25 2.8722813232690143 [45 45 45 45 45 45] [0 3 1 2 2 0 0 3 0 0] 6 0 [[6 5 8 1 7 9 4 3 2 0] [9 0 4 7 2 8 5 1 6 3] [8 9 6 2 0 4 7 5 1 3] [8 0 3 9 2 4 6 1 7 5] [0 8 3 6 7 2 5 1 4 9] [5 2 9 6 3 0 7 4 8 1]]
Column Operations
Apply functions only to specific columns by slicing, or create a new array from the columns you want, then work on them. But Beware that creating a new pointer to the same data can screw up your data if you're not careful.
In [113]:
print(g[:, 2:3]) print(g[:, 2:3].max()) col3 = g[:, 3:4] # not a copy, just a pointer to a slice of g print(col3.std()) col3 *= 100 # Beware: this is applied to g data print(g)
[[8] [4] [3] [4] [5] [1]] 8 298.607881119482 [[ 9 3 8 70000 6 1 0 4 2 5] [ 1 7 4 90000 2 6 8 3 5 0] [ 4 8 3 90000 5 7 2 6 0 1] [ 1 7 4 20000 5 9 6 8 0 3] [ 0 7 5 20000 8 6 3 4 1 9] [ 5 9 1 40000 7 0 3 6 8 2]]
Numpy Random Functions
¶
In [ ]:
np.set_printoptions(precision=5, suppress=True) # show 5 decimal places, suppress scientific notation h = np.random.random(6) print(h) h = np.random.randint(10, 99, 8) # (low, high inclusive, size) print(h) np.random.shuffle(h) # in-place shuffle print(h) print(np.random.choice(h)) h.sort() # in-place sort print(h)
0 notes
Text
Pandas Github

Pandas Challenge Github
Pandas Github
Github Pandas Tutorial
Panda Vpn Pro
Pandas Github Issues
Pandas Github License
Up to date remote data access for pandas, works for multiple versions of pandas.

< Data Indexing and Selection | Contents | Handling Missing Data >
Since Python 3.4, pathlib has been included in the Python standard library. Path objects provide a simple and delightful way to interact with the file system. The pandas-path package enables the Path API for pandas through a custom accessor.path.Getting just the filenames from a series of full file paths is as simple as myfiles.path.name. Dask uses existing Python APIs and data structures to make it easy to switch between NumPy, pandas, scikit-learn to their Dask-powered equivalents. You don't have to completely rewrite your code or retrain to scale up. A REST API based on Flask for serving Pandas Dataframes to Grafana. This way, a native Python application can be used to directly supply data to Grafana both easily and powerfully. It was inspired by and is compatible with the simple json datasource. Pandas is a fast, powerful, flexible and easy to use open source data analysis and manipulation tool, built on top of the Python programming language. Install pandas now!
One of the essential pieces of NumPy is the ability to perform quick element-wise operations, both with basic arithmetic (addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.) and with more sophisticated operations (trigonometric functions, exponential and logarithmic functions, etc.).Pandas inherits much of this functionality from NumPy, and the ufuncs that we introduced in Computation on NumPy Arrays: Universal Functions are key to this.

Pandas includes a couple useful twists, however: for unary operations like negation and trigonometric functions, these ufuncs will preserve index and column labels in the output, and for binary operations such as addition and multiplication, Pandas will automatically align indices when passing the objects to the ufunc.This means that keeping the context of data and combining data from different sources–both potentially error-prone tasks with raw NumPy arrays–become essentially foolproof ones with Pandas.We will additionally see that there are well-defined operations between one-dimensional Series structures and two-dimensional DataFrame structures.
Ufuncs: Index Preservation¶
Because Pandas is designed to work with NumPy, any NumPy ufunc will work on Pandas Series and DataFrame objects.Let's start by defining a simple Series and DataFrame on which to demonstrate this:
If we apply a NumPy ufunc on either of these objects, the result will be another Pandas object with the indices preserved:
ABCD0-1.0000007.071068e-011.000000-1.000000e+001-0.7071071.224647e-160.707107-7.071068e-012-0.7071071.000000e+00-0.7071071.224647e-16
Any of the ufuncs discussed in Computation on NumPy Arrays: Universal Functions can be used in a similar manner.
UFuncs: Index Alignment¶
Pandas Challenge Github
For binary operations on two Series or DataFrame objects, Pandas will align indices in the process of performing the operation.This is very convenient when working with incomplete data, as we'll see in some of the examples that follow.
Index alignment in Series¶
As an example, suppose we are combining two different data sources, and find only the top three US states by area and the top three US states by population:
Let's see what happens when we divide these to compute the population density:
The resulting array contains the union of indices of the two input arrays, which could be determined using standard Python set arithmetic on these indices:
Pandas Github
Any item for which one or the other does not have an entry is marked with NaN, or 'Not a Number,' which is how Pandas marks missing data (see further discussion of missing data in Handling Missing Data).This index matching is implemented this way for any of Python's built-in arithmetic expressions; any missing values are filled in with NaN by default:
If using NaN values is not the desired behavior, the fill value can be modified using appropriate object methods in place of the operators.For example, calling A.add(B) is equivalent to calling A + B, but allows optional explicit specification of the fill value for any elements in A or B that might be missing:
Index alignment in DataFrame¶
A similar type of alignment takes place for both columns and indices when performing operations on DataFrames:
Notice that indices are aligned correctly irrespective of their order in the two objects, and indices in the result are sorted.As was the case with Series, we can use the associated object's arithmetic method and pass any desired fill_value to be used in place of missing entries.Here we'll fill with the mean of all values in A (computed by first stacking the rows of A):
The following table lists Python operators and their equivalent Pandas object methods:
Python OperatorPandas Method(s)+add()-sub(), subtract()*mul(), multiply()/truediv(), div(), divide()//floordiv()%mod()**pow()
Ufuncs: Operations Between DataFrame and Series¶
When performing operations between a DataFrame and a Series, the index and column alignment is similarly maintained.Operations between a DataFrame and a Series are similar to operations between a two-dimensional and one-dimensional NumPy array.Consider one common operation, where we find the difference of a two-dimensional array and one of its rows:
According to NumPy's broadcasting rules (see Computation on Arrays: Broadcasting), subtraction between a two-dimensional array and one of its rows is applied row-wise.
In Pandas, the convention similarly operates row-wise by default:
If you would instead like to operate column-wise, you can use the object methods mentioned earlier, while specifying the axis keyword:
Note that these DataFrame/Series operations, like the operations discussed above, will automatically align indices between the two elements:
This preservation and alignment of indices and columns means that operations on data in Pandas will always maintain the data context, which prevents the types of silly errors that might come up when working with heterogeneous and/or misaligned data in raw NumPy arrays.
< Data Indexing and Selection | Contents | Handling Missing Data >
Display pandas dataframes clearly and interactively in a web app using Flask.
Web apps are a great way to show your data to a larger audience. Simple tables can be a good place to start. Imagine we want to list all the details of local surfers, split by gender. This translates to a couple of pandas dataframes to display, such as the dataframe females below.
Transforming dataframes into html tables
Using the pandas function to_html we can transform a pandas dataframe into a html table. All tables have the class dataframe by default. We can add on more classes using the classes parameter. For example, writing
results in a html table with the classes dataframe female as shown below.
Prepare the file structure for flask app
The simple_tables directory will contains all the scripts, css and html needed for the web app to run. The script site_tables.py will sit in this directory, and from here we will run the app and populate the app’s pages. Any html templates must be stored in the templates directory. Any css sheets must be within the static directory.
Below is the file structure I have used for this surfing example.
Create a flask app that pulls the dataframes
We can create a page on our web app called tables. Every time this page loads, we pull the data, filter and format to get two dataframes, females and males.
The dataframes are then transformed into html tables with classes dataframe female and dataframe male respectively. These html tables are sent as a list to the template view.html, which is stored in the templates directory. We also send a list of titles to use as a heading for each table.
Running the app using debug=True allows the app to auto-update every time the code gets edited.
Define the html template using jinja2

The html template view.html pulls css from the style sheet style.css in the static directory. We will check out the css in the next section.
Next, the jinja2 language allows us to loop through the html table list tables. Using loop.index provides the index of the loop. This starts from 1 so we need to convert between python list indices and those for jinja2 loops. Then we can pull out the correct title for each table.
For each table in the list, the table title is shown, and then the table itself. safe tells jinja2 to show this parameter as a html object.
Style the tables with css
We can use the following styling to make the tables a bit more pretty. The classes male and female have been defined with different header colours. This enables us to highlight different groups of tabled data from the initial site_tables.py script.
Github Pandas Tutorial
Some nice touches include using tr:nth-child(odd) and tr:nth-child(even) to have alternate row colours. Also tr:hover gives an interactive feel to the tables.
View the web app
Panda Vpn Pro
Running the script site_tables.py from bash will serve the web app on your local host. Your web page should look like the one below.
Pandas Github Issues
Feedback
Pandas Github License
Always feel free to get in touch with other solutions, general thoughts or questions.

0 notes