#how to prevent coronavirus
Text
Opinion Here’s how to get free Paxlovid as many times as you need it
When the public health emergency around covid-19 ended, vaccines and treatments became commercial products, meaning companies could charge for them as they do other pharmaceuticals. Paxlovid, the highly effective antiviral pill that can prevent covid from becoming severe, now has a list price of nearly $1,400 for a five-day treatment course.
Thanks to an innovative agreement between the Biden administration and the drug’s manufacturer, Pfizer, Americans can still access the medication free or at very low cost through a program called Paxcess. The problem is that too few people — including pharmacists — are aware of it.
I learned of Paxcess only after readers wrote that pharmacies were charging them hundreds of dollars — or even the full list price — to fill their Paxlovid prescription. This shouldn’t be happening. A representative from Pfizer, which runs the program, explained to me that patients on Medicare and Medicaid or who are uninsured should get free Paxlovid. They need to sign up by going to paxlovid.iassist.com or by calling 877-219-7225. “We wanted to make enrollment as easy and as quick as possible,” the representative said.
Indeed, the process is straightforward. I clicked through the web form myself, and there are only three sets of information required. Patients first enter their name, date of birth and address. They then input their prescriber’s name and address and select their insurance type.
All this should take less than five minutes and can be done at home or at the pharmacy. A physician or pharmacist can fill it out on behalf of the patient, too. Importantly, this form does not ask for medical history, proof of a positive coronavirus test, income verification, citizenship status or other potentially sensitive and time-consuming information.
But there is one key requirement people need to be aware of: Patients must have a prescription for Paxlovid to start the enrollment process. It is not possible to pre-enroll. (Though, in a sense, people on Medicare or Medicaid are already pre-enrolled.)
Once the questionnaire is complete, the website generates a voucher within seconds. People can print it or email it themselves, and then they can exchange it for a free course of Paxlovid at most pharmacies.
Pfizer’s representative tells me that more than 57,000 pharmacies are contracted to participate in this program, including major chain drugstores such as CVS and Walgreens and large retail chains such as Walmart, Kroger and Costco. For those unable to go in person, a mail-order option is available, too.
The program works a little differently for patients with commercial insurance. Some insurance plans already cover Paxlovid without a co-pay. Anyone who is told there will be a charge should sign up for Paxcess, which would further bring down their co-pay and might even cover the entire cost.
Several readers have attested that Paxcess’s process was fast and seamless. I was also glad to learn that there is basically no limit to the number of times someone could use it. A person who contracts the coronavirus three times in a year could access Paxlovid free or at low cost each time.
Unfortunately, readers informed me of one major glitch: Though the Paxcess voucher is honored when presented, some pharmacies are not offering the program proactively. As a result, many patients are still being charged high co-pays even if they could have gotten the medication at no cost.
This is incredibly frustrating. However, after interviewing multiple people involved in the process, including representatives of major pharmacy chains and Biden administration officials, I believe everyone is sincere in trying to make things right. As we saw in the early days of the coronavirus vaccine rollout, it’s hard to get a new program off the ground. Policies that look good on paper run into multiple barriers during implementation.
Those involved are actively identifying and addressing these problems. For instance, a Walgreens representative explained to me that in addition to educating pharmacists and pharmacy techs about the program, the company learned it also had to make system changes to account for a different workflow. Normally, when pharmacists process a prescription, they inform patients of the co-pay and dispense the medication. But with Paxlovid, the system needs to stop them if there is a co-pay, so they can prompt patients to sign up for Paxcess.
Here is where patients and consumers must take a proactive role. That might not feel fair; after all, if someone is ill, people expect that the system will work to help them. But that’s not our reality. While pharmacies work to fix their system glitches, patients need to be their own best advocates. That means signing up for Paxcess as soon as they receive a Paxlovid prescription and helping spread the word so that others can get the antiviral at little or no cost, too.
{source}
24K notes
·
View notes
Text

Article | Paywall Free
"The Food and Drug Administration approved new mRNA coronavirus vaccines Thursday [August 22, 2024], clearing the way for shots manufactured by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna to start hitting pharmacy shelves and doctor’s offices within a week.
Health officials encourage annual vaccination against the coronavirus, similar to yearly flu shots. Everyone 6 months and older should receive a new vaccine, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends.
The FDA has yet to approve an updated vaccine from Novavax, which uses a more conventional vaccine development method but has faced financial challenges.
Our scientific understanding of coronavirus vaccines has evolved since they debuted in late 2020. Here’s what to know about the new vaccines.
Why are there new vaccines?
The coronavirus keeps evolving to overcome our immune defenses, and the shield offered by vaccines weakens over time. That’s why federal health officials want people to get an annual updated coronavirus vaccine designed to target the latest variants. They approve them for release in late summer or early fall to coincide with flu shots that Americans are already used to getting.
The underlying vaccine technology and manufacturing process are the same, but components change to account for how the virus morphs. The new vaccines target the KP.2 variant because most recent covid cases are caused by that strain or closely related ones...
Do the vaccines prevent infection?
You probably know by now that vaccinated people can still get covid. But the shots do offer some protection against infection, just not the kind of protection you get from highly effective vaccines for other diseases such as measles.
The 2023-2024 vaccine provided 54 percent increased protection against symptomatic covid infections, according to a CDC study of people who tested for the coronavirus at pharmacies during the first four months after that year’s shot was released...
A nasal vaccine could be better at stopping infections outright by increasing immunity where they take hold, and one is being studied in a trial sponsored by the National Institutes of Health.
If you really want to dodge covid, don’t rely on the vaccine alone and take other precautions such as masking or avoiding crowds...
Do the vaccines help prevent transmission?
You may remember from early coverage of coronavirus vaccines that it was unclear whether shots would reduce transmission. Now, scientists say the answer is yes — even if you’re actively shedding virus.
That’s because the vaccine creates antibodies that reduce the amount of virus entering your cells, limiting how much the virus can replicate and make you even sicker. When vaccination prevents symptoms such as coughing and sneezing, people expel fewer respiratory droplets carrying the virus. When it reduces the viral load in an infected person, people become less contagious.
That’s why Peter Hotez, a physician and co-director of the Texas Children’s Hospital Center for Vaccine Development, said he feels more comfortable in a crowded medical conference, where attendees are probably up to date on their vaccines, than in a crowded airport.
“By having so many vaccinated people, it’s decreasing the number of days you are shedding virus if you get a breakthrough infection, and it decreases the amount of virus you are shedding,” Hotez said.
Do vaccines prevent long covid?
While the threat of acute serious respiratory covid disease has faded, developing the lingering symptoms of “long covid” remains a concern for people who have had even mild cases. The CDC says vaccination is the “best available tool” to reduce the risk of long covid in children and adults. The exact mechanism is unclear, but experts theorize that vaccines help by reducing the severity of illness, which is a major risk factor for long covid.
When is the best time to get a new coronavirus vaccine?
It depends on your circumstances, including risk factors for severe disease, when you were last infected or vaccinated, and plans for the months ahead. It’s best to talk these issues through with a doctor.
If you are at high risk and have not recently been vaccinated or infected, you may want to get a shot as soon as possible while cases remain high. The summer wave has shown signs of peaking, but cases can still be elevated and take weeks to return to low levels. It’s hard to predict when a winter wave will begin....
Where do I find vaccines?
CVS said its expects to start administering them within days, and Walgreens said that it would start scheduling appointments to receive shots after Sept. 6 and that customers can walk in before then.
Availability at doctor’s offices might take longer. Finding shots for infants and toddlers could be more difficult because many pharmacies do not administer them and not every pediatrician’s office will stock them given low demand and limited storage space.
This year’s updated coronavirus vaccines are supposed to have a longer shelf life, which eases the financial pressures of stocking them.
The CDC plans to relaunch its vaccine locator when the new vaccines are widely available, and similar services are offered by Moderna and Pfizer."
-via The Washington Post, August 22, 2024
#covid#long covid#vaccines#vaccination#covid vaccine#covid19#public health#united states#good news#hope
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Not long ago, heart attacks were primarily a problem faced by the elderly. Heart attacks are rare in people under the age of 40. Now 1 in 5 heart attack patients are under the age of 40. Many people in their 30s and 40s are at increased risk of life-threatening heart disease and sudden heart attacks. It is important to understand the cause of heart attacks in young adults. When sudden death occurs in adolescents and young adults, it is sometimes caused by undiagnosed heart disease, such as genetic heart disease. An undiagnosed heart problem can cause sudden death in a young person during physical exertion. However, sometimes sudden cardiac death can occur without exertion. Coronavirus, now the leading cause of heart problems, can directly affect and damage the muscle tissue of the heart, as can other viral infections, including some strains of influenza. The heart can be damaged and indirectly inflamed by the reaction of the body's own immune system. Dr.Nitthiyan MD, DNB Interventional Cardiologist, KG Hospital, Coimbatore, explains heart attack at a young age: how to avoid it, common risk factors, how coronavirus causes heart problems, and how to prevent it.
#kghospital#best cadiology#it is sometimes caused by undiagnosed heart disease#now the leading cause of heart problems#DNB Interventional Cardiologist#KG Hospital#Coimbatore#explains heart attack at a young age: how to avoid it#common risk factors#how coronavirus causes heart problems#and how to prevent it.#kgh#worldheartday#heartattack#kghospitalcoimbatore#loadingdose#healthlife#cardiologist#உலகஇருதயதினம்#இதயநோய்#ம���ரடைப்பு#கோவையின்இதயத்துடிப்புகேஜிமருத்துவமனை#Youtube
1 note
·
View note
Text
Coronavirus - Symptoms of COVID-19 and How to Prevent It
Coronavirus – Symptoms of COVID-19 and How to Prevent It
Is Coronavirus Is A Type of virus
A coronavirus is a type of virus that causes various illnesses, from respiratory infections to pneumonia. Known as COVID-19, this virus is airborne, making it easy to spread from person to person. The symptoms of COVID-19 are similar to those of the common cold, but they are more serious and can lead to pneumonia if not treated early.
COVID-19 is a new type of…
View On WordPress
#Can Covid-19 Be Preventable With Vaccines#Coronavirus - Symptoms of COVID-19 and How to Prevent It#COVID-19 is a new type of coronavirus#Is Coronavirus Is A Type of virus#Is COVID-19 Spread through Airborne Spread#It is harder to detect with rapid tests#Symptoms Of COVID-19#Types Of Airborne Spread Covid-19
0 notes
Text
Virus Corona
Covid-19 | Gejala | Penyebab | Diagnosis | Cara Mengobati | Cara Mencegah | Saran
Covid-19 atau dipanggil juga virus corona (Corona Virus Disease 2019) merupakan sejenis penyakit menular yang disebabkan oleh virus SARS-CoV-2. Virus ini merupakan salah satu virus yang menyerang sistem pernapasan pada manusia. Virus corona ini juga bisa menyebabkan gangguan ringan pada sistem pernapasan manusia,…

View On WordPress
#advice about covid-19#cara mencegah covid-19#cara mengobati virus covid-19#cause of covid-19#corona virus#corona virus disease19#coronavirus case#covid-19#Covid-19 diagnosis#Covid-19 symptoms#diagnosis covid-19#gejala covid-19#good trend#google health#Health#health sciences#how to prevent covid-19#how to treat covid-19#kesehatan#korban covid-19#lockdown#medical therapy#penyebab covid-19#physical distancing#sarscov2#self isolation#varian#variant#variant virus#virologi
0 notes
Text
You might be forgiven for thinking it’s been a very quiet few months for the Covid-19 pandemic. Besides the rollout of new boosters, the coronavirus has largely slipped out of the headlines. But the virus is on the move. Viral levels in wastewater are similar to what they were during the first two waves of the pandemic. Recent coverage of the so-called Pirola variant, which is acknowledged to have “an alarming number of mutations,” led with the headline “Yes, There’s a New Covid Variant. No, You Shouldn’t Panic.”
Even if you haven’t heard much about the new strain of the coronavirus, being told not to panic might induce déjà vu. In late 2021, as the Omicron variant was making its way to the United States, Anthony Fauci told the public that it was “nothing to panic about” and that “we should not be freaking out.” Ashish Jha, the Biden administration’s former Covid czar, also cautioned against undue alarm over Omicron BA.1, claiming that there was “absolutely no reason to panic.” This is a telling claim, given what was to follow—the six weeks of the Omicron BA.1 wave led to hundreds of thousands of deaths in a matter of weeks, a mortality event unprecedented in the history of the republic.
Indeed, experts have been offering the public advice about how to feel about Covid-19 since January 2020, when New York Times columnist Farhad Manjoo opined, “Panic will hurt us far more than it’ll help.” That same week, Zeke Emanuel—a former health adviser to the Obama administration, latterly an adviser to the Biden administration—said Americans should “stop panicking and being hysterical.… We are having a little too much [sic] histrionics about this.”
This concern about public panic has been a leitmotif of the Covid-19 pandemic, even earning itself a name (“elite panic”) among some scholars. But if there’s one thing we’ve learned, three and a half years into the current crisis, it’s that—contrary to what the movies taught us—pandemics don’t automatically spawn terror-stricken stampedes in the streets. Media and public health coverage have a strong hand in shaping public response and can—under the wrong circumstances—promote indifference, incaution, and even apathy. A very visible example of this was the sharp drop in the number of people masking after the CDC revised its guidelines in 2021, recommending that masking was not necessary for the vaccinated (from 90 percent in May to 53 percent in September).
As that example suggests, emphasizing the message “don’t panic” puts the cart before the horse unless tangible measures are being taken to prevent panic-worthy outcomes. And indeed, these repeated assurances against panic have arguably also preempted a more vigorous and urgent public health response—as well as perversely increasing public acceptance of the risks posed by coronavirus infection and the unchecked transmission of the virus. This “moral calm”—a sort of manufactured consent—impedes risk mitigation by promoting the underestimation of a threat. Soothing public messaging during disasters can often lead to an increased death toll: Tragically, false reassurance contributed to mortality in both the attacks on the World Trade Center and the sinking of the Titanic.
But at a deeper level, this emphasis on public sentiment has contributed to confusion about the meaning of the term “pandemic.” A pandemic is an epidemiological term, and the meaning is quite specific—pandemics are global and unpredictable in their trajectory; endemic diseases are local and predictable. Despite the end of the Public Health Emergency in May, Covid-19 remains a pandemic, by definition. Yet some experts and public figures have uncritically advanced the idea that if the public appears to be tired, bored, or noncompliant with public health measures, then the pandemic must be over.
But pandemics are impervious to ratings; they cannot be canceled or publicly shamed. History is replete with examples of pandemics that blazed for decades, sometimes smoldering for years before flaring up again into catastrophe. The Black Death (1346–1353 AD), the Antonine Plague (165–180 AD), and the Plague of Justinian (541–549 AD), pandemics all, lacked the quick resolution of the 1918 influenza pandemic. A pandemic cannot tell when the news cycle has moved on.
Yet this misperception—that pandemics can be ended by human fiat—has had remarkable staying power during the current crisis. In November 2021, the former Obama administration official Juliette Kayyem claimed that the pandemic response needed to be ended politically, with Americans getting “nudged into the recovery phase” by officials. It is fortunate that Kayyem’s words were not heeded—the Omicron wave arrived in the US just weeks after her article ran—but her basic premise has informed Biden’s pandemic policy ever since.
Perhaps even less responsibly, the physician Steven Phillips has called for “new courageous ‘accept exposure’ policies”—asserting that incautious behavior by Americans would be the true signal of the end of the pandemic. In an essay for Time this January, Phillips wrote: “Here’s my proposed definition: the country will not fully emerge from the Covid-19 pandemic until most people in our diverse nation accept the risk and consequences of exposure to a ubiquitous SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19.”
This claim—that more disease risk and contagion means the end of a disease event—runs contrary to the science. Many have claimed that widespread SARS-CoV-2 infections will lead to increasingly mild disease that poses fewer concerns for an increasingly vaccinated (or previously infected) population. In fact, more disease spread means faster evolution for SARS-CoV-2, and greater risks for public health. As we (A.C. and collaborators) and others have pointed out, rapid evolution creates the risk of novel variants with unpredictable severity. It also threatens the means that we have to prevent and treat Covid-19: monoclonal antibody treatments no longer work, Paxlovid is showing signs of viral resistance, and booster strategy is complicated by viral evolution of resistance to vaccines.
But these efforts to manage and direct public feelings are not just more magical thinking; they are specifically intended to promote a return to pre-pandemic patterns of work and consumption. This motive was articulated explicitly in a McKinsey white paper from March 2022, which put forward the invented concept of “economic endemicity”—defined as occurring when “epidemiology substantially decouples from economic activity.” The “Urgency of Normal” movement similarly used an emotional message (that an “urgent return to fully normal life and schooling” is needed to “protect” children) to advocate for the near-total abandonment of disease containment measures. But in the absence of disease control measures, a rebound of economic activity can only lead to a rebound of disease. (This outcome was predicted by a team that was led by one of the authors [A.C.] in the spring of 2021.)
A pandemic is a public health crisis, not a public relations crisis. Conflating the spread of a disease with the way people feel about responding to that spread is deeply illogical—yet a great deal of the Biden administration’s management of Covid-19 has rested on this confusion. Joe Biden amplified this mistaken perspective last September when he noted that the pandemic was “over”—and then backed that claim by stating, “If you notice, no one’s wearing masks. Everybody seems to be in pretty good shape.” The presence or absence of health behaviors reveals little about a threat to health itself, of course—and a decline in mask use has been shaped, in part, by the Biden administration’s waning support for masking.
Separately, long Covid poses an ongoing threat both at an individual and a public health level. If our increasingly relaxed attitude toward public health measures and the relatively unchecked spread of the virus continue, most people will get Covid at least once a year; one in five infections leads to long Covid. Although it’s not talked about a lot, anyone can get long Covid; vaccines reduce this risk, but only modestly. This math gets really ugly.
The situation we are in today was predictable. It was predictable that the virus would rapidly evolve to evade the immune system, that natural immunity would wane quickly and unevenly in the population, that a vaccine-only strategy would not be sufficient to control widespread Covid-19 transmission through herd immunity, and that reopening too quickly would lead to a variant-driven rebound. All of these unfortunate outcomes were predicted in peer-reviewed literature in 2020–21 by a team led by one of the authors (A.C.), even though the soothing public messaging at the time called it very differently.
As should now be very clear, we cannot manifest our way to a good outcome. Concrete interventions are required—including improvements in air quality and other measures aimed at limiting spread in public buildings, more research into vaccine boosting strategy, and investments in next-generation prophylactics and treatments. Rather than damping down panic, public health messaging needs to discuss risks honestly and focus on reducing spread. Despite messages to the contrary, our situation remains unstable, because the virus continues to evolve rapidly, and vaccines alone cannot slow this evolution.
In the early months of the pandemic, many in the media drew parallels between the public’s response to Covid-19 and the well-known “stages of grief”: denial, bargaining, anger, depression, and acceptance. The current situation with Covid-19 calls for solutions, not a grieving process that should be hustled along to the final stage of acceptance.
844 notes
·
View notes
Text
Back in early 2020, the news of the strange illness causing terrible pneumonias in China saddened me, but I believed I was safe in Canada. Within weeks, there was a reckoning: thousands were dying on my doorstep, too.
Directors of an independent living residence at the start of the pandemic asked me to become the residence’s COVID-19 advisor. They had no qualified medical staff, despite supporting elderly residents. Back in those early days, anyone with a medical qualification was commandeered to help in any way they could.
Confronted with the task of providing guidance to the nonmedical staff taking care of these residents, I decided to learn everything I could about the pandemic. At that time, about 1,000 papers were being published every month detailing research into every aspect of the coronavirus. Of course, I couldn’t read all of them, but I read as many as I could and built a breadth and depth of evidenced-based knowledge about SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. I wrote up the protocols and during my tenure as COVID-19 Advisor for this residence, we kept COVID out.
As a family physician seeing COVID-19 in my practice, I came to recognize that so many of my colleagues and patients had no idea how to keep themselves safe from the coronavirus, nor were they aware of its long-term risks. I saw the need to take action and effect change, which ultimately led me to becoming an advocate for Long COVID awareness.
I started the medical education company Kojala Medical, aiming to provide evidenced-based information about medical issues in a form patients could understand and reliably trust. I wanted a credible, trustworthy site to which I could refer my patients, colleagues, friends and family. We started with a focus on COVID-19 and have now expanded to Long COVID, with the site longcovidtheanswers.com.
I first learned about Long COVID in 2020 through publicity raised by the Body Politic COVID-19 support group, then became more alarmed as I read scientific articles about the disease.
Aside from the official death toll of over 7 million from COVID-19, Long COVID has emerged from the pandemic as the single biggest disaster to afflict humanity, yet very few people who are not sick with Long COVID are aware of it, want to know about it, believe in it, or even acknowledge that it’s happening. Sadly, many in the medical profession fall within that group of non and disbelievers.
This is bizarre, especially because of the impact of the disease. One recent review estimates more than 400 million global cases of Long COVID. I am furious that not enough is being done to alleviate this suffering. The injustice of yet another neglected and marginalized chronic illness that disproportionately affects women.
So, rather than sitting around waiting for ‘someone’ or ‘body’ to do something, I decided to act.
For me, medicine is fundamentally about aiding people to get as well as possible from any sickness they have — and even more importantly, preventing people from getting sick in the first place. In both of these regards, we are failing people with Long COVID dismally.
Long COVID is not the flu, it is a multisystem debilitating infection associated chronic condition. Developing Long COVID can be disabling and life-changing. Recovery remains low — and some manifestations like heart disease, dysautonomia, and myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) may last a lifetime.
This is a terrifying situation to be in when, as a global community, we have chosen to act as though the pandemic is over and repeatedly expose ourselves to SARS-CoV-2, a grade 3 biohazard, with little to no protection.
As I read more and more research papers about Long COVID and looked at the inaction of global governments and my own profession, I feared that we were sleepwalking into a global mass disabling event unnecessarily, since we have many technologies available to prevent this.
Infection-associated chronic conditions do not have an established medical speciality, and are rarely taught in medical school. With the medical profession disengaged, people with Long COVID have been left to find answers for themselves.
My work aims to build on support groups, which have helped establish caring communities for people with Long COVID, but have also paved the way for us as scientists and medics to change the way we conduct research in a more patient-focused way. Nevertheless, they don’t entirely fulfill the need for evidence-based information about the disease in a readable format for nonmedical individuals.
I saw a huge need for a comprehensive website that would be of use to all people with Long COVID, their caregivers, the scientists researching the disease, and the multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals that would be needed to rehabilitate them. Our organization believes that Long COVID The Answers meets those requirements.
There is also a pressing need to train medical professionals so that they will acknowledge Long COVID and feel confident about diagnosing and managing it. Inspired by an interview with Dr. Ric Arsenaeau, an expert in managing complex chronic diseases, my team and I created a podcast series: so that medical providers can receive continuing professional development/educational credits from watching this series.
The podcast series features a range of experts, including people with Long COVID, doctors, scientists, educators, and medical clinicians. Some of these experts also serve on our advisory board, overlooking and participating in the project.
Our site aims to raise awareness about the dangers of continuously exposing ourselves to a perilous virus with no thought of what it will cost us and our children.
This will mobilize the people of the world to demand that their leaders properly provide safe spaces for us all to prevent us from ever getting infected in the first place.
We need to mandate our governments to access all the mitigating technologies that we have in our roster, not only vaccination. The best way of managing Long COVID is to prevent people getting infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the first place!
We need national and international indoor clean air acts – to protect us from emerging pathogens.
For people with Long COVID, awareness will bring an educated and mobilized medical profession, governmental resources, financial and sociological support, and money for research — to facilitate treatments and, hopefully, a cure.
These are the main reasons why I jump out of bed in the morning with gusto, focus, and determination, and why I’ve poured all my money and my time into educating people about Long COVID.
Dr. Funmi Okunola is a British Family Physician who lives and works in Vancouver, Canada. She is the President and CEO of Kojala Medical, a digital medical education company behind COVID-19 The Answers and Long COVID The Answers.
#long covid#covid#mask up#pandemic#covid 19#wear a mask#sars cov 2#public health#coronavirus#still coviding#wear a respirator
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
One-Page Masterlist
안녕하세요! Hey everyone! I recently got an ask about my old masterlist, which is the same as my broken-down masterlist except it has all of my lessons on one page, rather than on multiple separate posts. Some may find this expanded version easier to navigate, so I’ll keep this up for y’all! My broken-up masterlist, of course, will still be available for those who find that more helpful :)
Hangul Lessons
Consonants
Vowels
Writing/Reading Korean Syllables
Some 받침 Rules
Diphthongs
Stroke Order
Some More 받침 Rules
Irregular Verbs
The Basics
Common Phrases
Numbers
Sino-Korean vs. Native Korean Numbers (Instagram Post)
Sentence Structure and Particles
Present-Tense Conjugations and Formal Language
Adjectives
Questions
Honorifics and Casual Language
Beginner
Negative Sentences
잘 and 못
Past Tense
Future Tense (-ㄹ / 을 것이다)
-ㄹ / 을 까요? (Shall we…? / I wonder…?)
-(으)세요 (Giving Commands / Asking Questions)
Telling Time
-고 싶다 (I want to…)
How to Say “And”
-지만 (However)
아/어/여서 (So…)
Negative Commands
Spacing (띄어쓰기)
Adverbs
ㅂ Irregular
Comparatives and Superlatives
난, 날, & 내가
Upper-Beginner
-(으)면 (If…)
아/어/여도 (Even though…/Even if…)
(으)면 되다 / 아/어/여도 되다 (I can…/You may…)
-아/어도 되다: Asking for and Giving Permission (Instagram post)
-(으)면 되다 & -(으)면 안 되다 (Instagram post)
아/어/여야 되다 and 아/어/여야 하다(Have to / Should)
Present Progressive (-고 있다)
How to Say “Or”
-아/어/여하다
All About 중
How to Use -(으)로
Before & After
-ㄴ/은 채로
Intermediate
Describing Nouns with Verbs (-는 것)
Describing Nouns with Verbs - Past & Future Tense (-ㄴ/은 / -ㄹ/을 것)
Nominalization
것 같다 (I think… / It seems…)
-러 가다 / -러 오다
-(으)려고 (In order to…)
-기로 하다 (to Decide to do Smth)
척하다 (To Pretend)
-게 되다
-군요 / -구나
아/어/여 보다 (to try…)
-은/ㄴ 적 있다 / 없다 (I have / have not)
-ㄹ/을 게요 (Future Tense)
겠다
-ㄹ/을 수 있다/없다 (I can / cannot)
-ㄹ/을 때 (When…)
-ㄴ/는다면 (If)
-(으)면서 and -(으)며
-(으)니까 (Because / So)
-아/어/여주다
-(ㄴ/는)다 (Narrative Form)
Quoting
Let’s…
Quoting continued
(으)ㄹ래요? (Wanna…?)
-죠
-대로
More Quoting - 대 & 래
잘하다 & 못하다 vs. 잘 하다 & 못 하다
-아/어 가지고
-(으)려면
-는 길에 & -는 길이다
-(으)면 vs. -ㄴ/는다면 (Instagram Post)
-았/었을 것이다
-느라고
-는 데(에)
-ㄹ/을 뻔하다
Upper-Intermediate
-ㄴ/는데
-(으)ㄴ/는지 (Whether or not)
-(이)라는…
All About 아무리
-잖아요
Expressing Surprise
-시 (Honorific)
Making Comparisons
-아/어/여지다
I might…
So that…/To the point where…
Causative Verbs
시키다
Passive Verbs (part 1)
Passive Verbs (part 2)
-ㄴ/은가 보다 & -나 보다 (I guess…)
-ㄹ/을수록
Other Meanings of 싶다
-자마자 & -는 대로(As soon as…)
-긴 하다
-치고
-김에
차라리 (Rather)
-(으)ㅁ Nominalization
-기는 무슨 & -기는 개뿔
-고 보니까
-듯(이)
버리다
-(으)면 좋겠다 & -(으)면 하다
-길 바라다
Advanced
-거든(요)
-줄 알다/모르다
-ㄹ/을 테니까 and -ㄹ/을 텐데
-았/었던
아니라 and 대신에
-ㄹ/을 리가 없다
편이다, 별로, and More
-지 그렇다 (Why don’t you…?)
-ㄹ/을 걸
-ㄹ/을 까 보다
-다면서요
-다니 part 1
-다니 part 2
뜻이다 & 말이다
-다가
-더라고(요)
-더니
Some colloquialisms: 아니시에이팅 and 뭐 이렇게
-(으)ㅁ Sentence Ending
-다 보니까
What does 따위 mean?
-ㄴ/는데도
Korean Idioms
Vocabulary
Must-Know People
Must-Know Places
Must-Know Things
Must-Know Verbs
Must-Know Adjectives
Countries
Months, Days of the Week, and More
Clothing (옷)
School (학교)
Autumn (가을)
Autumn (w/Pictures!)
More Questions
House / Apartment (집 / 아파트)
Emotions / Feelings ( 감정)
Animals (동물)
Loan / Konglish Words
Food and Drink (먹을 것과 마실 것)
Parts of the Body (몸)
Counters
Modes of Transportation (교통 수단)
Colors (색깔)
Colors (with Pictures!)
Weather (날씨)
Winter (겨울)
Music & Instruments (음악과 악기)
Baking Gingerbread Cookies
Emergency (비상)
Hygiene & Bathroom (위생 & 화장실)
Indefinite Pronouns
Work / Office (일 / 사무실)
Spring (봄)
Coronavirus Prevention (코로나바이러스 방역)
How to Wash Your Hands (손을 씻기)
Time (시간)
Korean Cuisine (한식)
Summer (여름)
Summer (여름) w/Pictures!
Graduation (졸업)
Identity (독자성)
Korean Text Slang
Similar Words
Makeup w/Pictures! (화장품)
Family (with Pictures!)
Pronouns
How to Say “Still” and “Already” in Korean
Tastes & Textures (맛과 질감)
K-Pop Audition
K-Pop Fandom Terminology
Different Ways to Say “Change”
Flower Names
What Does 원래 Mean?
What does 오히려 Mean?
College
Hanja Lessons
최
수
악
식
급
동
부 & 불
애
출
퇴
예
음
중
학
습
연
생
대
입
인
문
감
과
원
특
만
후
무
Charts
Present, Past, and Future Tense
Question Words
잘 vs. 못 and Negative Conjugations
Future Tenses
-았/었던 vs. -던 (at end of lesson)
Particles
Some 받침 Rules
Gifving Commands
Conjunctions and -아/어/여서 vs. -(으)니까
-(으)면 vs. -다/라면 and Different Ways to Say “And”
How to Say “Or” (at end of lesson)
Telling Time (at end of lesson)
Comparatives and Superlatives
잘하다 & 못하다 vs. 잘 하다 & 못 하다 (at end of lesson)
Comparing 잘하다/못하다, 잘 하다/못 하다, & 수 있다/수 없다
Irregular Verbs
Pop Quizzes
Level 1
K-Pop Breakdowns
TXT - “Cat & Dog”
Twice - “Feel Special”
Enhypen - “Fever”
2NE1 - “Go Away”
Lee Hi - “Only”
“기억을 걷는 시간 (Time Spent Walking Through Memories)”
KCM - “An Old Love Story (흑백사진)”
Taeyeon - “Can’t Control Myself”
Epik High - “Lost One”
Colde - “A Song Nobody Knows”
IU - “My Sea”
Enhypen - “Polaroid Love”
유라 (youra) - “하양 (RAL 9002)″
BTS - “Ddaeng”
Stray Kids - “For You”
Woozie - “어떤 미래 (What Kind of Future)
TXT - “Eternally”
LOONA - “Heart Attack”
Stray Kids - “Muddy Water”
LOONA - “Girl Front”
Pentagon - “Daisy”
BTS - “Sea”
Semester in SK
Nami Island (남이섬)
Things to Buy at Daiso
Shopping Phrases
Ordering Coffee
Signs in Korea
Ordering at a Restaurant
Riding the Seoul Subway
Things at the 편의점
Korean Curse Words
Etiquette in South Korea
Drinking Culture
Hanja in Real Life
Holidays in South Korea
Korean Cuisine
Concert Ticketing in South Korea
K-pop Comebacks in Korea
Summer in South Korea
What I Learned
#korean#korean language#hangul#korean grammar#korean vocab#korean vocabulary#learn korean#learning korean#langblr#Korean langblr#masterlist#apok#apopofkorean#study korean#studying korean#kpop#kpop lyrics#basic korean#beginner korean#intermediate korean#advanced korean#hanja#한국어#한글#한자#한국어 공부하기#한국어 배우기#한국어 문법#한국어 어휘#초급 한국어
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
For Sander van der Linden, misinformation is personal.
As a child in the Netherlands, the University of Cambridge social psychologist discovered that almost all of his mother’s family had been executed by the Nazis during the Second World War. He became absorbed by the question of how so many people came to support the ideas of someone like Adolf Hitler, and how they might be taught to resist such influence.
While studying psychology at graduate school in the mid-2010s, van der Linden came across the work of American researcher William McGuire. In the 1960s, stories of brainwashed prisoners-of-war during the Korean War had captured the zeitgeist, and McGuire developed a theory of how such indoctrination might be prevented. He wondered whether exposing soldiers to a weaker form of propaganda might have equipped them to fight off a full attack once they’d been captured. In the same way that army drills prepared them for combat, a pre-exposure to an attack on their beliefs could have prepared them against mind control. It would work, McGuire argued, as a cognitive immunizing agent against propaganda—a vaccine against brainwashing.
Traditional vaccines protect us by feeding us a weaker dose of pathogen, enabling our bodies’ immune defenses to take note of its appearance so we’re better equipped to fight the real thing when we encounter it. A psychological vaccine works much the same way: Give the brain a weakened hit of a misinformation-shaped virus, and the next time it encounters it in fully-fledged form, its “mental antibodies” remember it and can launch a defense.
Van der Linden wanted to build on McGuire’s theories and test the idea of psychological inoculation in the real world. His first study looked at how to combat climate change misinformation. At the time, a bogus petition was circulating on Facebook claiming there wasn’t enough scientific evidence to conclude that global warming was human-made, and boasting the signatures of 30,000 American scientists (on closer inspection, fake signatories included Geri Halliwell and the cast of M*A*S*H).
Van der Linden and his team took a group of participants and warned them that there were politically motivated actors trying to deceive them—the phony petition in this case. Then they gave them a detailed takedown of the claims of the petition; they pointed out, for example, Geri Halliwell’s appearance on the list. When the participants were later exposed to the petition, van der Linden and his group found that people knew not to believe it.
The approach hinges on the idea that by the time we’ve been exposed to misinformation, it’s too late for debunking and fact-checking to have any meaningful effect, so you have to prepare people in advance—what van der Linden calls “prebunking.” An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
When he published the findings in 2016, van der Linden hadn’t anticipated that his work would be landing in the era of Donald Trump’s election, fake news, and post-truth; attention on his research from the media and governments exploded. Everyone wanted to know, how do you scale this up?
Van der Linden worked with game developers to create an online choose-your-own-adventure game called Bad News, where players can try their hand at writing and spreading misinformation. Much like a broadly protective vaccine, if you show people the tactics used to spread fake news, it fortifies their inbuilt bullshit detectors.
But social media companies were still hesitant to get on board; correcting misinformation and being the arbiters of truth is not part of their core business model. Then people in China started getting sick with a mysterious flulike illness.
The coronavirus pandemic propelled the threat of misinformation to dizzying new heights. Van der Linden began working with the British government and bodies like the World Health Organization and the United Nations to create a more streamlined version of the game specifically revolving around Covid, which they called GoViral! They created more versions, including one for the 2020 US presidential election, and another to prevent extremist recruitment in the Middle East. Slowly, Silicon Valley came around.
A collaboration with Google has resulted in a campaign on YouTube in which the platform plays clips in the ad section before the video starts, warning viewers about misinformation tropes like scapegoating and false dichotomies and drawing examples from Family Guy and Star Wars. A study with 20,000 participants found that people who viewed the ads were better able to spot manipulation tactics; the feature is now being rolled out to hundreds of millions of people in Europe.
Van der Linden understands that working with social media companies, who have historically been reluctant to censor disinformation, is a double-edged sword. But, at the same time, they’re the de facto guardians of the online flow of information, he says, “and so if we’re going to scale the solution, we need their cooperation.” (A downside is that they often work in unpredictable ways. Elon Musk fired the entire team who was working on pre-bunking at Twitter when he became CEO, for instance.)
This year, van der Linden wrote a book on his research, titled Foolproof: Why We Fall for Misinformation and How to Build Immunity. Ultimately, he hopes this isn’t a tool that stays under the thumb of third-party companies; his dream is for people to inoculate one another. It could go like this: You see a false narrative gaining traction on social media, you then warn your parents or your neighbor about it, and they’ll be pre-bunked when they encounter it. “This should be a tool that’s for the people, by the people,” van der Linden says.
441 notes
·
View notes
Text
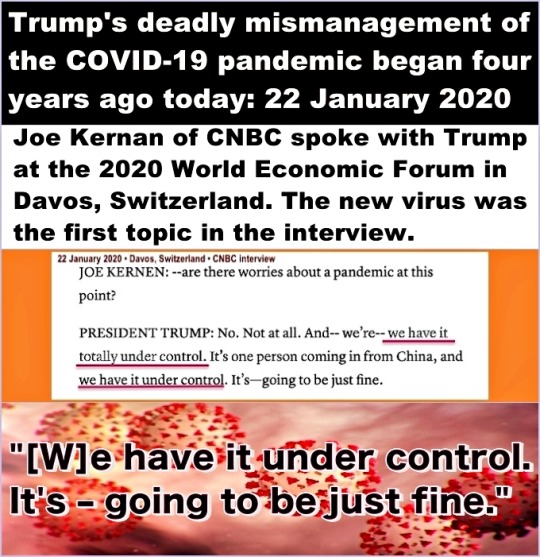
Just so nobody can say this is out of context, here's a vid of the entire interview.
The Obama administration successfully contained the Ebola outbreak in the United States. The death toll for Ebola in the US was under a dozen. So before leaving office, the Obama National Security Council created a 69-page handbook on how to deal with a pandemic. Trump and his flunkies ignored it with disastrous results.
Trump team failed to follow NSC’s pandemic playbook
The US death toll from COVID-19 is in seven digits. Other industrialized countries with advanced technological infrastructure such as Canada, Taiwan, Germany, and New Zealand had lower fatality rates per capita.
Trump largely ignored the virus until well into March when it had a chance to spread across the US.
The missing six weeks: how Trump failed the biggest test of his life
The president was aware of the danger from the coronavirus – but a lack of leadership has created an emergency of epic proportions
The Trump administration, at best, was in denial; at worst, it sabotaged the pandemic response.
youtube
Trump White House made 'deliberate efforts' to undermine Covid response, report says
Trump zombies who claim the economy was marvelous under Trump conveniently forget about everything that happened after February of 2020. Trump's early bungling of the pandemic plunged the economy into recession. The COVID supply chain problems and the economic stimulus required to prevent a depression led to the spurt in inflation which is finally receding.
People who are nostalgic about taking hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin, drinking bleach, and sticking UV lights up their butts must be excited about the opportunity to vote for Trump again.
#donald trump#botched pandemic response#covid-19#coronavirus#public health#anniversary of trump's awful covid-19 response#gross incompetence of the trump administration#the trump recession#trump tanked the economy#trump is a loser#vote blue no matter who#election 2020#election 2024
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
From BioClandestine on Telegram
If Trump wins 2024, he will halt all funding for Ukraine, negotiate an end to conflict with Putin, thus preventing WW3.
The reason Biden and the Deep State cannot negotiate with Putin, is because Putin wants their heads for crimes against humanity, namely for manufacturing C19.
This is not speculation on my part. Russian MIL literally listed Joe Biden, Hillary Clinton, Barack Obama, and George Soros, as being the main ideologists behind the plot to manufacture coronavirus strains in Ukraine, with US DoD funding, and there is an open source paper trail to back it up. You can debate on whether or not you believe them, but the reality is, Putin wants the “Western Elites” and Xi agrees with him.
It’s not hyperbolic to say that this is life or death for the Deep State actors. If Trump wins and negotiates a settlement with Putin, Russian MIL have already been demanding for activation of Articles V and VI of the Biological Weapons Treaty, which would result in a Security Council investigation and international military tribunals. That’s what Russian MIL have been demanding at the UN for nearly 2 years now. And that’s just the biological stuff, not even accounting for the whole 2014 coup, shelling the Donbas, funding and supporting Ukraine in 2022, Nord Stream, etc.
What do you think Trump is going to say? No? Trump wants to prosecute the exact same people for crimes against humanity! Putin is literally demanding that all of Trump’s enemies trying to imprison him, must be prosecuted by military tribunal… How could Trump say no to that?! He’d be killing multiple birds with one stone. And Trump’s DOJ wouldn’t have to do the prosecuting. It would be a coalition of military judges from different countries around the world. It would be far more legitimate and no way could the Dems cry “partisanship”. It’s international law.
Y’all might think it’s crazy, but this is the trajectory we are headed on if Trump wins, which is why the Biden regime are going to do everything in their power to prevent Trump from winning. If they fail, they will be treated as international war criminals, and will face the ultimate penalty.
Extinction Level Event (for the deep state, for globalism, for all their synvophants in levels of government and the MSM).
Let’s say Russia and China are lying, and the US did not manufacture C19.
Then why would Fauci, Collins, and the US government, put so much effort into covering up the lab origins?
Why are the US and their allies the only ones NOT interested in who caused a global pandemic?
Why did government health agencies and Big Tech censor scientists and journalists who pointed out its lab origins? If someone else created this virus, why are the US government so invested in covering up who is responsible? Over a million Americans died, shouldn’t they be tirelessly trying to find out who killed all those people?
Who benefited from the pandemic? American Pharmaceutical companies, that began the vaccine development BEFORE the pandemic. Who funds the MSM and Deep State politicians? Big Pharma.
If Russia and China are lying, why is it that the US veto every request at the UN Security Council for a joint investigation into the origins of C19?
There are two options. Elements within the US are responsible, or, a different entity is responsible and the US government went out of their way to cover it up.
The paper trail confirms it’s the former, but either way, heads must roll.
#truth#common sense#msm is the enemy#globalist playbook#BioClandestine#donald trump#big pharma#putin#vaccine#deep state
114 notes
·
View notes
Text
I'll Be There for You - Platonic Smosh x Reader

Summary: 2020 starts great for reader before covid enters the chat and flips her world upside down. Her friends at Smosh are there to support her through one of the hardest times of her life.
Word Count: 2.5K
CW: covid, quarantine, parent death, panic attack
AN: Was listening to a Smosh Mouth episode and they brought up filming during quarantine and it randomly inspired this story. I lost my own dad during covid and Smosh was absolutely one of my escapes during that time so this story may just be me processing that haha
No romantic relationships for reader in this, just lots of supportive friends.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
From the moment you hear about this new virus, you’re nervous about it. The news stations are trying to keep everything positive, spin it like this is no big deal. But what you see on social media is telling a different story.
You’re not so much worried for yourself as you are for your family. They’re all the way across the country on the east coast while you’re in Los Angeles. And many of your family members have lung issues. While you don’t know much about this coronavirus, it seems to be most harmful to people’s lungs, leaving you to worry.
It seems crazy to be taking a trip right now, but the threat doesn’t seem to be too bad. Travel is still permitted, and so your group goes ahead with your trip to Australia. You’ve been looking forward to this for months, and try so hard to not allow your anxieties overshadow your excitement.
It’s a solid group on the trip: Shayne, Courtney, Ian, Damien, Sarah, and Matt Raub. All of you are trying to ignore the increasingly worrisome news and keep things light. You attend two different expos, doing live shows as well as meet and greets with fans. Those bookend the trip, with lots of different activities in the middle, including visits to a couple zoos to learn about local wildlife.
You hold koalas and snakes, laugh with your friends, and for a little while, you forget all about the bad things that are happening.
But you can’t hide from it forever. Despite everyone joking about the virus, you can’t help but be afraid. Every day of the trip, more news is revealed, and things look more and more grim.
Towards the end of the trip you do a couple planned meet and greets at Sydney’s Madame Tussauds. You’re on the verge of a panic attack the whole time, feeling like every person you talk to could be carrying this unpredictable virus.
Ian picks up on this and pulls you aside during a break.
“You okay?” he asks, concern etched on his face.
“I can’t shake this feeling, like we’re all going to get infected and then bring it back home, and every time a new person comes in the room it’s like another chance for germs to spread. What happens if we get sick? We don’t know anything about this virus, or what it can do to people, and there’s more and more cases everyday-” your rambling cuts off as you gasp for a breath. The panic attack is officially setting in, the room spinning around you as it gets harder to breathe.
You hear Ian say something, but the ringing in your ears prevents you from understanding him. A moment later Sarah is standing in front of you, catching your eye and encouraging you to breathe with her. After a minute of matching her breaths, you’ve calmed down and gotten through the worst of the panic attack.
Sarah leads you to the couch, sitting next to you, close enough to be a grounding presence but far enough that you don’t feel closed in. Ian walks over, crouching in front of you and handing you a water bottle.
“Sorry about that,” you finally say.
“Don’t you dare apologize,” Sarah says. “Your feelings are completely valid.”
Ian nods before saying, “I know we’re all making jokes about this, but I think everyone’s just covering up how scared they are. I’m definitely scared. You’re right to say that there’s so much we don’t know. I’d say don’t worry about all that, but that’s stupid because you’re gonna worry anyway.”
You laugh at that, feeling much better now knowing that you’re not alone. Ian smiles and places a comforting hand on your knee and you reach out to hold Sarah’s hand as well. The three of you sit for a moment and then Shayne walks in the room saying, “Time to start up again.”
He looks at you guys, sees the redness in your eyes and notices the way the others are comforting you and asks, “Everything okay?”
“Yea, I’m good now,” you answer. “We’ll be right out.”
Shayne nods and walks away. You go to stand but before you can get up Ian says, “You don’t have to go back out there if you’re not comfortable. We can do the rest without you if you need some space.”
“I’ll be fine, but thank you,” you reply. He smiles and gives your leg one last squeeze before standing and giving you a hand up. It’s a nice moment, one where you’re reminded about how wonderful it is to work for Ian. He’s a kind boss, but also like a big brother to you, and you appreciate having him in your life.
The rest of the time in Australia goes smoothly, and then it’s time to fly home. Sarah and Ian stick by you throughout the long day of travel. You don’t ask them to, but you can tell they’re worried that you’ll get anxious in such a crowded space. Somehow that makes it easier, and you’re able to spend the day joking with your friends rather than panicking.
You’re exhausted when you get home, saying a rushed goodbye to your friends and heading home.
And then the isolation begins. The world practically shuts down completely as soon as you get back to the states. You go from constantly being around people, to being completely alone. It’s fine at first, you’re exhausted from traveling and this gives you a good excuse to be lazy for a few days.
You spend a lot of time on the phone with your family, begging them to stay inside the house and stay safe. And they seem to listen, only going out twice for supplies. But apparently that’s all it takes.
Just over a week after the Australia trip your mom gets sick. It’s obvious right away that it’s covid. For one thing, your mom has worked with children for decades. Her immune system is impeccable, you’ve never seen her get a cold or the flu before. For her to be sick is odd, plus she has all the symptoms, so it’s a no brainer.
And then a few days later, your dad is sick as well. You knew it was inevitable, that once the virus was in the house he was going to get it as well, but hearing it for sure makes your blood run cold.
He already has a couple of lung issues, and you can’t help but feel like this isn’t going to go well. You hate that you’re stuck on opposite coasts and can’t do anything to help. You call them as much as possible, wanting to stay positive and hearing their voices always helps.
But then your dad gets worse and ends up in the hospital. You finally tell your Smosh friends what is going on. You’d kept it quiet at first, but they picked up that something is wrong.
You try to continue on like normal, assuring your friends that you’re fine, but they don’t accept that. While they never overstep, you’re often surprised with kind texts or things appearing on your doorstep.
It’s a particularly bad day. Your dad has just been placed on a ventilator. You get the news while in a zoom meeting, and everyone can tell that something has happened.
“You okay, Y/N?” Courtney asks.
You shake your head no and think about what to answer. You could be vague, just say it’s an update about your father and leave it at that. But these are people that care about you, that want to support you.
“My dad just got put on a ventilator,” you reply.
“My god, Y/N, I’m so sorry. Did they say anything else?” Shayne says.
“Apparently the doctors said it’s a preventative measure. Supposed to let his lungs heal. But we’ve all seen the statistics. Most covid patients don’t come off the vent.”
“If you need to go you can,” Ian says. “Don’t feel like you need to stay on this call.”
“No, that’s okay. I’d rather keep working. Either that or sit in silence in my apartment,” you answer with a shrewd laugh.
“Alright, well if you need to leave at any time please feel free. No explanation needed, we’ll understand,” Ian says.
The meeting resumes and you sit quietly while they plan the upcoming Smosh Games schedule. You don’t have any input, and it’s pretty clear you’re not really listening, but you’re comforted by the sound of your friends' voices.
The zoom call finishes, and you’re left alone with your thoughts. You’re not sure how much time passes, but the sun has moved to shine through a new window as husk begins so it must be a while.
You’re startled back to reality by a text on your phone. Your heart races, fearing it’s you mom with even worse news. You breathe a sigh of relief when you see it’s from Spencer, his message saying, “Check out your front door.”
Doing as he’d instructed, you see a bag that had been delivered. It’s takeout from chilis, enough food for multiple meals, all your favorites.
This is just what you needed. Your appetite hasn't been great, but smelling the familiar food has your stomach growling. After sending him a thank you message you dig in.
Now full of comfort food, you manage to do your normal nightly routine of cleaning up the apartment and taking a shower. You go to bed feeling scared, but supported.
Three days later, you get the news you’d been dreading. Your moms calls in the morning, saying the doctors think he won’t make it through the day. It’s a Sunday, and you have nothing to distract you. People text, but you leave them unanswered.
It’s a beautiful day in Los Angeles, and you do the only thing you’re allowed to do: take a walk.
Losing track of time, you wander through neighborhoods, making sure to keep distance from other people out walking. It pains you to see happy families, people who are making the most out of this pandemic. People whose lives aren’t being drastically changed forever.
You get back home in the early afternoon. Soon after, your mom calls. You almost ignore it, knowing what she’s going to say but wanting to delay the inevitable. But you know you can’t do that.
It’s a short conversation, your mother unable to say too much between the tears.
You hang up feeling numb. It grows dark outside and finally you text Ian, asking for the next day off.
His response is immediate, expressing his condolences and telling you to take at least the week off. You ask him to send a message to the others, not wanting to have to do it yourself.
You wrap yourself into a cocoon of blankets, lay in bed, and cry over the loss.
The next few days you find that you’re exhausted, with random bursts of high energy. You use the energy to respond to your friends' messages, thanking them for reaching out and telling them you’re okay.
You speak on the phone with Damien for a while a couple days after it happens. While all of your friends are supportive, he’s the only one who’s been through this before. He truly understands what it’s like to lose a father. His experience, his words, everything he has to offer is incredibly comforting to you. And when he says he’ll always be there to listen, you know he’s telling the truth and not just saying what he thinks is the “right thing”.
And then that Thursday, just a couple days after your dads death, the vlog of your time in Australia is released.
You get the notification that it’s been posted as you always do, and instead of being excited that a new video is up, it sends you into a breakdown. You’re crying, gasping for breath, and you need someone there with you.
For the first time since all of this began you cannot be alone. People have been offering to stop by and because it’s been over two weeks since any of you have been around others it’s technically safe. But you always refused, assuring them that you’re fine.
Now, however, you need people around you. Through tears you find your phone and immediately call Courtney, asking if she and Shayne could come over. She says yes without hesitation and stays on the call while the two of them make their way to your place.
Needing the comfort of your room you say, “Front door is open. I’ll be in my bedroom when you get here.”
“Just a couple more minutes,” Courtney replies as you climb under the covers.
“Okay,” you murmur to let her know you heard her.
As promised she and Shayne enter a few minutes later. Without hesitation Courtney climbs into bed with you, wrapping you up in your arms. You melt into the embrace, sobs ripping through your body.
When you’ve finally cried yourself out, you pull away and notice Shayne’s no longer in the room. A moment later he walks back in, carrying water, tissues, and your favorite cookies. You smile weakly at him and pat the bed, inviting him to join you and Courtney.
He sits next to you, and you’re effectively sandwiched between the two of them. It’s comforting to be surrounded by two of your best friends. You’d always been close with them, and we’re happy that nothing changed when they started dating.
They’re two people who will always have your back, no matter what. They stay with you until the next morning, Shayne leaving temporarily to pick up anything he and Courtney need for the night.
You hadn’t realized how much you needed to be around people, but it’s clear how much it helps to actually see people and talk to them without a screen.
Finally, you start accepting people’s invitations to hang out. You make good use of your apartment complex’s patio area so that you can hang out while still social distancing. You don’t often talk about your dad or how you’re doing, but rather about other mundane things. It feels good to talk to friends about something even somewhat normal.
The other cast members take turns filling in for videos that you’re supposed to appear in. You’d tried going back to business as usual, but found that you couldn’t be as lighthearted and funny as you usually were. Rather than try to fake it, you’d switched to a more behind the scenes role for the time being.
In May and June, fans start to notice that you aren’t appearing in any videos. Many theories float around, and you decide you’re ready to make the news about your dad public, instead of letting the rumors continue to spread.
You make a post about your father on Instagram, a picture of the two of you with a caption explaining the loss. Support floods in, from friends, family, and fans alike.
Though it’s the hardest thing you’ve ever experienced, it’s so nice to know you have such wonderful people who will always have your back.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AN: Thanks so much for reading! I'm working on two stories for Whumptober, One Spencer x reader and the other Damien x reader!
#smosh x reader#smosh fanfiction#spencer agnew x reader#shayne topp x reader#courtney miller x reader#ian hecox x reader#sarah whittle x reader#damien haas x reader
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mucosal adenovirus vaccine boosting elicits IgA and durably prevents XBB.1.16 infection in nonhuman primates | Nature Immunology - September 3, 2024
A mucosal route of vaccination could prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) replication at the site of infection and limit transmission.
We compared protection against heterologous XBB.1.16 challenge in nonhuman primates (NHPs) ~5 months following intramuscular boosting with bivalent mRNA encoding WA1 and BA.5 spike proteins or mucosal boosting with a WA1–BA.5 bivalent chimpanzee adenoviral-vectored vaccine delivered by intranasal or aerosol device. NHPs boosted by either mucosal route had minimal virus replication in the nose and lungs, respectively. By contrast, protection by intramuscular mRNA was limited to the lower airways. The mucosally delivered vaccine elicited durable airway IgG and IgA responses and, unlike the intramuscular mRNA vaccine, induced spike-specific B cells in the lungs. IgG, IgA and T cell responses correlated with protection in the lungs, whereas mucosal IgA alone correlated with upper airway protection. This study highlights differential mucosal and serum correlates of protection and how mucosal vaccines can durably prevent infection against SARS-CoV-2.
#covid#mucosal immunity#nasal vaccines#research#study#data#nasal vaccine#vaccines#good news#immunology#nature journal
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
(archive)
For Sander Van der Linden, misinformation is personal.
As a child in the Netherlands, the University of Cambridge social psychologist discovered that almost all of his mother’s family had been executed by the Nazis during the Second World War. He became absorbed by the question of how so many people came to support the ideas of someone like Adolf Hitler, and how they might be taught to resist such influence.
While studying psychology at graduate school in the mid-2010s, van der Linden came across the work of American researcher William McGuire. In the 1960s, stories of brainwashed prisoners-of-war during the Korean War had captured the zeitgeist, and McGuire developed a theory of how such indoctrination might be prevented. He wondered whether exposing soldiers to a weaker form of propaganda might have equipped them to fight off a full attack once they’d been captured. In the same way that army drills prepared them for combat, a pre-exposure to an attack on their beliefs could have prepared them against mind control. It would work, McGuire argued, as a cognitive immunizing agent against propaganda—a vaccine against brainwashing.
Traditional vaccines protect us by feeding us a weaker dose of pathogen, enabling our bodies’ immune defenses to take note of its appearance so we’re better equipped to fight the real thing when we encounter it. A psychological vaccine works much the same way: Give the brain a weakened hit of a misinformation-shaped virus, and the next time it encounters it in fully-fledged form, its “mental antibodies” remember it and can launch a defense.
Van der Linden wanted to build on McGuire’s theories and test the idea of psychological inoculation in the real world. His first study looked at how to combat climate change misinformation. At the time, a bogus petition was circulating on Facebook claiming there wasn’t enough scientific evidence to conclude that global warming was human-made, and boasting the signatures of 30,000 American scientists (on closer inspection, fake signatories included Geri Halliwell and the cast of M*A*S*H).
Van der Linden and his team took a group of participants and warned them that there were politically motivated actors trying to deceive them—the phony petition in this case. Then they gave them a detailed takedown of the claims of the petition; they pointed out, for example, Geri Halliwell’s appearance on the list. When the participants were later exposed to the petition, van der Linden and his group found that people knew not to believe it.
The approach hinges on the idea that by the time we’ve been exposed to misinformation, it’s too late for debunking and fact-checking to have any meaningful effect, so you have to prepare people in advance—what van der Linden calls “prebunking.” An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
When he published the findings in 2016, van der Linden hadn’t anticipated that his work would be landing in the era of Donald Trump’s election, fake news, and post-truth; attention on his research from the media and governments exploded. Everyone wanted to know, how do you scale this up?
Van der Linden worked with game developers to create an online choose-your-own-adventure game called Bad News, where players can try their hand at writing and spreading misinformation. Much like a broadly protective vaccine, if you show people the tactics used to spread fake news, it fortifies their inbuilt bullshit detectors.
But social media companies were still hesitant to get on board; correcting misinformation and being the arbiters of truth is not part of their core business model. Then people in China started getting sick with a mysterious flulike illness.
The coronavirus pandemic propelled the threat of misinformation to dizzying new heights. Van der Linden began working with the British government and bodies like the World Health Organization and the United Nations to create a more streamlined version of the game specifically revolving around Covid, which they called GoViral! They created more versions, including one for the 2020 US presidential election, and another to prevent extremist recruitment in the Middle East. Slowly, Silicon Valley came around.
A collaboration with Google has resulted in a campaign on YouTube in which the platform plays clips in the ad section before the video starts, warning viewers about misinformation tropes like scapegoating and false dichotomies and drawing examples from Family Guy and Star Wars. A study with 20,000 participants found that people who viewed the ads were better able to spot manipulation tactics; the feature is now being rolled out to hundreds of millions of people in Europe.
Van der Linden understands that working with social media companies, who have historically been reluctant to censor disinformation, is a double-edged sword. But, at the same time, they’re the de facto guardians of the online flow of information, he says, “and so if we’re going to scale the solution, we need their cooperation.” (A downside is that they often work in unpredictable ways. Elon Musk fired the entire team who was working on pre-bunking at Twitter when he became CEO, for instance.)
This year, van der Linden wrote a book on his research, titled Foolproof: Why We Fall for Misinformation and How to Build Immunity. Ultimately, he hopes this isn’t a tool that stays under the thumb of third-party companies; his dream is for people to inoculate one another. It could go like this: You see a false narrative gaining traction on social media, you then warn your parents or your neighbor about it, and they’ll be pre-bunked when they encounter it. “This should be a tool that’s for the people, by the people,” van der Linden says.
–
Everyone needs to play this game.
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
COVID-19 is a leading cause of death in children and young people in the US - Published Jan 31, 2023
A new study led by researchers at the University of Oxford’s Department of Computer Science has found that, between 2021 and 2022, COVID-19 was a leading cause of death in children and young people in the United States, ranking eighth overall. The results demonstrate that pharmaceutical and public health interventions should continue to be applied to limit the spread of the coronavirus and protect again severe disease in this age group.
COVID-19 was the underlying cause of death for more than 940,000 people in the US, including over 1,300 deaths among children and young people aged 0–19 years. Until now, it had been unclear how the burden of deaths from COVID-19 compared with other leading causes of deaths in this age group.
The researchers investigated this using data from US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention databases for the period 1 August 2021 to 31 July 2022.
Get the full article and a link to the study at our covid archive:
#covid#wear a respirator#coronavirus#sars cov 2#mask up#public health#wear a mask#pandemic#covid 19#still coviding#covid deaths#covid in children#covidー19#covid pandemic#covid is airborne#covid isn't over
172 notes
·
View notes
Text
Vocabulary, Hanja, & Charts Masterlist
Click here for the masterlist of all my lessons!
Vocabulary
Must-Know People
Must-Know Places
Must-Know Things
Must-Know Verbs
Must-Know Adjectives
Countries
Months, Days of the Week, and More
Clothing (옷)
School (학교)
Autumn (가을)
Autumn (w/Pictures!)
More Questions
House / Apartment (집 / 아파트)
Emotions / Feelings ( 감정)
Animals (동물)
Loan / Konglish Words
Food and Drink (먹을 것과 마실 것)
Parts of the Body (몸)
Counters
Modes of Transportation (교통 수단)
Colors (색깔)
Colors (with Pictures!)
Weather (날씨)
Winter (겨울)
Music & Instruments (음악과 악기)
Baking Gingerbread Cookies
Emergency (비상)
Hygiene & Bathroom (위생 & 화장실)
Indefinite Pronouns
Work / Office (일 / 사무실)
Spring (봄)
Coronavirus Prevention (코로나바이러스 방역)
How to Wash Your Hands (손을 씻기)
Time (시간)
Korean Cuisine (한식)
Summer (여름)
Summer (여름) w/Pictures!
Graduation (졸업)
Identity (독자성)
Korean Text Slang
Similar Words
Makeup w/Pictures! (화장품)
Family (with Pictures!)
Pronouns
How to Say “Still” and “Already” in Korean
Tastes & Textures (맛과 질감)
K-Pop Audition
K-Pop Fandom Terminology
Different Ways to Say “Change”
Flower Names
What Does 원래 Mean?
What does 오히려 Mean?
College
Hanja Lessons
최
수
악
식
급
동
부 & 불
애
출
퇴
예
음
중
학
습
연
생
대
입
인
문
감
과
원
특
만
후
무
Charts
Present, Past, and Future Tense
Question Words
잘 vs. 못 and Negative Conjugations
Future Tenses
-았/었던 vs. -던 (at end of lesson)
Particles
Some 받침 Rules
Gifving Commands
Conjunctions and -아/어/여서 vs. -(으)니까
-(으)면 vs. -다/라면 and Different Ways to Say “And”
How to Say “Or” (at end of lesson)
Telling Time (at end of lesson)
Comparatives and Superlatives
잘하다 & 못하다 vs. 잘 하다 & 못 하다 (at end of lesson)
Comparing 잘하다/못하다, 잘 하다/못 하다, & 수 있다/수 없다
Irregular Verbs
#korean#korean language#korean vocab#korean vocabulary#hanja#langblr#korean langblr#learn korean#learning korean#study korean#studying korean#korean lesson#korean resource#한국어#한국어 어휘#한자#한글#한국어 공부하기#한국어 배우기#한국어 레슨
317 notes
·
View notes