#html5 audio
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Insertar Audio y Video en tus Páginas Web con HTML5: Guía Completa
En este artículo, exploraremos cómo incorporar audio y video en tus páginas web de forma sencilla y efectiva utilizando HTML5. Aprenderás a utilizar las etiquetas <audio> y <video>, los formatos de archivo compatibles, y cómo garantizar la compatibilidad con navegadores antiguos. Además, te proporcionaremos ejemplos prácticos de código y consejos para optimizar tus contenidos multimedia para un…
#alicante#audio#compatibilidad con navegadores#comunidad valenciana#conversión de audio#conversión de video#Costa Blanca#etiqueta audio#etiqueta source#etiqueta video#eventos en Valencia#formato MP3#formato MP4#formato OGG#formato WAV#formato WebM#html5#multimedia#navegadores antiguos#SEO local#turismo en Alicante#video#web design
0 notes
Text
HTML Tutorial: A Quick Overview
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) forms the backbone of web development, enabling the structure and presentation of content on the web. It’s a markup language that defines elements like headings, paragraphs, links, images, lists, and more, providing a standardized way to format and display information in browsers.
HTML uses tags, enclosed in angle brackets, to represent different types of content. Each tag typically comes in pairs, an opening tag and a closing tag, to wrap and describe the content in between. HTML is fundamental for building web pages, allowing developers to create structured documents with defined sections and multimedia elements.
One of HTML’s key features is its ability to create links, connecting different parts of the web. This hyperlinking capability is what makes HTML unique, forming the web as we know it today. Additionally, HTML supports embedding multimedia like images, videos, and audio, which brings pages to life.
As web standards evolve, HTML has grown, too, with the latest version being HTML5. This version introduced new elements that provide semantic meaning to the structure of web documents, ensuring that content is more accessible and well-organized.
fro more:https://quipoin.com/tutorial/HTML-tutorial
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazon DCV 2024.0 Supports Ubuntu 24.04 LTS With Security

NICE DCV is a different entity now. Along with improvements and bug fixes, NICE DCV is now known as Amazon DCV with the 2024.0 release.
The DCV protocol that powers Amazon Web Services(AWS) managed services like Amazon AppStream 2.0 and Amazon WorkSpaces is now regularly referred to by its new moniker.
What’s new with version 2024.0?
A number of improvements and updates are included in Amazon DCV 2024.0 for better usability, security, and performance. The most recent Ubuntu 24.04 LTS is now supported by the 2024.0 release, which also offers extended long-term support to ease system maintenance and the most recent security patches. Wayland support is incorporated into the DCV client on Ubuntu 24.04, which improves application isolation and graphical rendering efficiency. Furthermore, DCV 2024.0 now activates the QUIC UDP protocol by default, providing clients with optimal streaming performance. Additionally, when a remote user connects, the update adds the option to wipe the Linux host screen, blocking local access and interaction with the distant session.
What is Amazon DCV?
Customers may securely provide remote desktops and application streaming from any cloud or data center to any device, over a variety of network conditions, with Amazon DCV, a high-performance remote display protocol. Customers can run graphic-intensive programs remotely on EC2 instances and stream their user interface to less complex client PCs, doing away with the requirement for pricey dedicated workstations, thanks to Amazon DCV and Amazon EC2. Customers use Amazon DCV for their remote visualization needs across a wide spectrum of HPC workloads. Moreover, well-known services like Amazon Appstream 2.0, AWS Nimble Studio, and AWS RoboMaker use the Amazon DCV streaming protocol.
Advantages
Elevated Efficiency
You don’t have to pick between responsiveness and visual quality when using Amazon DCV. With no loss of image accuracy, it can respond to your apps almost instantly thanks to the bandwidth-adaptive streaming protocol.
Reduced Costs
Customers may run graphics-intensive apps remotely and avoid spending a lot of money on dedicated workstations or moving big volumes of data from the cloud to client PCs thanks to a very responsive streaming experience. It also allows several sessions to share a single GPU on Linux servers, which further reduces server infrastructure expenses for clients.
Adaptable Implementations
Service providers have access to a reliable and adaptable protocol for streaming apps that supports both on-premises and cloud usage thanks to browser-based access and cross-OS interoperability.
Entire Security
To protect customer data privacy, it sends pixels rather than geometry. To further guarantee the security of client data, it uses TLS protocol to secure end-user inputs as well as pixels.
Features
In addition to native clients for Windows, Linux, and MacOS and an HTML5 client for web browser access, it supports remote environments running both Windows and Linux. Multiple displays, 4K resolution, USB devices, multi-channel audio, smart cards, stylus/touch capabilities, and file redirection are all supported by native clients.
The lifecycle of it session may be easily created and managed programmatically across a fleet of servers with the help of DCV Session Manager. Developers can create personalized Amazon DCV web browser client applications with the help of the Amazon DCV web client SDK.
How to Install DCV on Amazon EC2?
Implement:
Sign up for an AWS account and activate it.
Open the AWS Management Console and log in.
Either download and install the relevant Amazon DCV server on your EC2 instance, or choose the proper Amazon DCV AMI from the Amazon Web Services Marketplace, then create an AMI using your application stack.
After confirming that traffic on port 8443 is permitted by your security group’s inbound rules, deploy EC2 instances with the Amazon DCV server installed.
Link:
On your device, download and install the relevant Amazon DCV native client.
Use the web client or native Amazon DCV client to connect to your distant computer at https://:8443.
Stream:
Use AmazonDCV to stream your graphics apps across several devices.
Use cases
Visualization of 3D Graphics
HPC workloads are becoming more complicated and consuming enormous volumes of data in a variety of industrial verticals, including Oil & Gas, Life Sciences, and Design & Engineering. The streaming protocol offered by Amazon DCV makes it unnecessary to send output files to client devices and offers a seamless, bandwidth-efficient remote streaming experience for HPC 3D graphics.
Application Access via a Browser
The Web Client for Amazon DCV is compatible with all HTML5 browsers and offers a mobile device-portable streaming experience. By removing the need to manage native clients without sacrificing streaming speed, the Web Client significantly lessens the operational pressure on IT departments. With the Amazon DCV Web Client SDK, you can create your own DCV Web Client.
Personalized Remote Apps
The simplicity with which it offers streaming protocol integration might be advantageous for custom remote applications and managed services. With native clients that support up to 4 monitors at 4K resolution each, Amazon DCV uses end-to-end AES-256 encryption to safeguard both pixels and end-user inputs.
Amazon DCV Pricing
Amazon Entire Cloud:
Using Amazon DCV on AWS does not incur any additional fees. Clients only have to pay for the EC2 resources they really utilize.
On-site and third-party cloud computing
Please get in touch with DCV distributors or resellers in your area here for more information about licensing and pricing for Amazon DCV.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AmazonDCV#Ubuntu24.04LTS#Ubuntu#DCV#AmazonWebServices#AmazonAppStream#EC2instances#AmazonEC2#News#TechNews#TechnologyNews#Technologytrends#technology#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
This day in history

Catch me in Miami! I'll be at Books and Books in Coral Gables on Jan 22 at 8PM.

#15yrsago Wingsuit base jumpers are human flying squirrels — video https://vimeo.com/1778399
#10yrsago RIP, Neal Barret Junior https://locusmag.com/2014/01/neal-barrett-jr-1929-2014/
#10yrsago Patent mess goes to the Supreme Court https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2014/01/supreme-court-looks-to-rein-in-top-patent-court-with-two-new-cases/
#10yrsago Requirements for DRM in HTML5 are a secret https://memex.craphound.com/2014/01/14/requirements-for-drm-in-html5-are-a-secret/
#10yrsago NSA official: mass spying has foiled one (or fewer) plots in its whole history https://www.theguardian.com/world/2014/jan/10/nsa-mass-surveillance-powers-john-inglis-npr
#5yrsago From the empty, shutdown IRS, automated processes are sending out property seizure notices, and no human can stop them https://theintercept.com/2019/01/14/irs-shutdown-federal-government-shut-down-irs-asset-seizures/
#5yrsago Google Walkout meets #MeToo in a new anti-arbitration campaign https://endforcedarbitration.medium.com/googlers-for-ending-forced-arbitration-launch-public-education-campaign-via-social-media-e46d7608cd0e
#5yrsago Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez reaches more people on Twitter than the press and establishment Democrats https://www.axios.com/2019/01/13/ocasio-cortez-dominates-twitter
#5yrsago In LA, the teachers of America’s largest school district are on strike https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2019/jan/14/la-teachers-working-class-power-labor-strikes
#1yrago Kate Beaton's "Ducks" https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/14/hark-an-oilpatch/#kate-beaton

I'm Kickstarting the audiobook for The Bezzle, the sequel to Red Team Blues, narrated by @wilwheaton! You can pre-order the audiobook and ebook, DRM free, as well as the hardcover, signed or unsigned. There's also bundles with Red Team Blues in ebook, audio or paperback.
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Let's understand HTML

Cover these topics to complete your HTML journey.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used to create web pages. Here's a comprehensive list of key topics in HTML:
1. Basics of HTML
Introduction to HTML
HTML Document Structure
HTML Tags and Elements
HTML Attributes
HTML Comments
HTML Doctype
2. HTML Text Formatting
Headings (<h1> to <h6>)
Paragraphs (<p>)
Line Breaks (<br>)
Horizontal Lines (<hr>)
Bold Text (<b>, <strong>)
Italic Text (<i>, <em>)
Underlined Text (<u>)
Superscript (<sup>) and Subscript (<sub>)
3. HTML Links
Hyperlinks (<a>)
Target Attribute
Creating Email Links
4. HTML Lists
Ordered Lists (<ol>)
Unordered Lists (<ul>)
Description Lists (<dl>)
Nesting Lists
5. HTML Tables
Table (<table>)
Table Rows (<tr>)
Table Data (<td>)
Table Headings (<th>)
Table Caption (<caption>)
Merging Cells (rowspan, colspan)
Table Borders and Styling
6. HTML Forms
Form (<form>)
Input Types (<input>)
Text Fields (<input type="text">)
Password Fields (<input type="password">)
Radio Buttons (<input type="radio">)
Checkboxes (<input type="checkbox">)
Drop-down Lists (<select>)
Textarea (<textarea>)
Buttons (<button>, <input type="submit">)
Labels (<label>)
Form Action and Method Attributes
7. HTML Media
Images (<img>)
Image Maps
Audio (<audio>)
Video (<video>)
Embedding Media (<embed>)
Object Element (<object>)
Iframes (<iframe>)
8. HTML Semantic Elements
Header (<header>)
Footer (<footer>)
Article (<article>)
Section (<section>)
Aside (<aside>)
Nav (<nav>)
Main (<main>)
Figure (<figure>), Figcaption (<figcaption>)
9. HTML5 New Elements
Canvas (<canvas>)
SVG (<svg>)
Data Attributes
Output Element (<output>)
Progress (<progress>)
Meter (<meter>)
Details (<details>)
Summary (<summary>)
10. HTML Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
Canvas
Inline SVG
Path Element
11. HTML APIs
Geolocation API
Drag and Drop API
Web Storage API (localStorage and sessionStorage)
Web Workers
History API
12. HTML Entities
Character Entities
Symbol Entities
13. HTML Meta Information
Meta Tags (<meta>)
Setting Character Set (<meta charset="UTF-8">)
Responsive Web Design Meta Tag
SEO-related Meta Tags
14. HTML Best Practices
Accessibility (ARIA roles and attributes)
Semantic HTML
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) Basics
Mobile-Friendly HTML
15. HTML Integration with CSS and JavaScript
Linking CSS (<link>, <style>)
Adding JavaScript (<script>)
Inline CSS and JavaScript
External CSS and JavaScript Files
16. Advanced HTML Concepts
HTML Templates (<template>)
Custom Data Attributes (data-*)
HTML Imports (Deprecated in favor of JavaScript modules)
Web Components
These topics cover the breadth of HTML and will give you a strong foundation for web development.
Full course link for free: https://shorturl.at/igVyr
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Working on my website, and damn if there isn't a good audio player, through Wix hosting.
Luckily, I have access to the custom app creator, and with a little HTML5, JavaScript, and CSS, I should be able to cobble up an audio player that saves your place, and can have a customizable seek option.
Now how to integrate it with accounts, and CMS?
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the difference between HTML and HTML5?
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is the standard markup language used to create web pages. HTML5 is the fifth and latest version of HTML. Here are some key differences:
New Features: HTML5 introduced several new features and elements that were not available in previous versions, such as <video>, <audio>, <canvas>, <header>, <footer>, <nav>, and <article>. These elements enhance multimedia support and provide better semantic structure for web documents.
Improved Semantics: HTML5 provides better semantic markup, allowing developers to create more structured and meaningful web pages. Semantic elements like <section>, <article>, <header>, <footer>, and <nav> help in defining the structure and purpose of different parts of a web page.
Compatibility: HTML5 is designed to be backward compatible with older browsers, ensuring that web pages created with HTML5 can still be viewed and function properly on browsers that do not support HTML5 features. However, some advanced features may not be fully supported in older browsers.
Multimedia Support: HTML5 provides native support for embedding audio and video content directly into web pages using the <audio> and <video> elements, eliminating the need for third-party plugins like Adobe Flash.
Improved Forms: HTML5 introduces new input types, attributes, and validation features for forms, making it easier to create user-friendly and accessible forms without relying on JavaScript or additional libraries.
Offline Support: HTML5 includes features like the Application Cache and Web Storage, which allow web applications to work offline and store data locally on the user's device, providing a more seamless and responsive user experience.
Overall, HTML5 represents a significant advancement over previous versions of HTML, offering developers more powerful tools and capabilities for creating modern and interactive web experiences.
Read more .....
#tech#technology#computer#computer science#computer generated image#computer art#phones#old technology#computing
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
More Notes on the Computer Music Playpen
I have finished maintenance on the VST3 plugin opcodes for Csound, Csound for Android, and some other things, and am re-focusing in composition.
One thing that happened as I was cleaning up the VST3 opcodes is that I discovered a very important thing. There are computer music programs that function as VST3 plugins and that significantly exceed the quality or power what Csound has so far done on it own, just for examples that I am using or plan to use:
The Valhalla reverbs by Sean Costello -- I think these actually derive from a reverb design that Sean did in the 1990s when he and I both were attending the Woof meetings at Columbia University. Sean's reverb design was ported first to Csound orchestra code, and then to C as a built-in opcode. It's the best and most widely used reverb in Csound, but it's not as good as the Valhalla reverbs, partly because the Valhalla reverbs can do a good job of preserving stereo.
Cardinal -- This is a fairly complete port of the VCV Rack "virtual Eurorack" patchable modular synthesiser not only to a VST3 plugin, but also to a WebAssembly module. This is exactly like sticking a very good Eurorack synthesizer right into Csound.
plugdata -- This is most of Pure Data, but with a slightly different and somewhat smoother user interface, as a VST3 plugin.
I also discovered that some popular digital audio workstations (DAWs), the workhorses of the popular music production industry, can embed algorithmic composition code written in a scripting language. For example, Reaper can host scripts written in Lua or Python, both of which are entirely capable of sophisticated algorithmic composition, and both of which have Csound APIs. And of course any of these DAWs can host Csound in the form of a Cabbage plugin.
All of this raises for me the question: What's the playpen? What's the most productive environment for me to compose in? Is it a DAW that now embeds my algorithms and my Csound instruments, or is it just code?
Right now the answer is not simply code, but specifically HTML5 code. And here is my experience and my reasons for not jumping to a DAW.
I don't want my pieces to break. I want my pieces to run in 20 years (assuming I am still around) just as they run today. Both HTML5 and Csound are "versionless" in the sense that they intend, and mostly succeed, in preserving complete backwards compatibility. There are Csound pieces from before 1990 that run just fine today -- that's over 33 years. But DAWs, so far, don't have such a good record in this department. I think many people find they have to keep porting older pieces to keep then running in newer software.
I'm always using a lot of resources, a lot of software, a lot of libraries. The HTML5 environment just makes this a great deal easier. Any piece of software that either is written in JavaScript or WebAssembly, or provides a JavaScript interface, can be used in a piece with a little but of JavaScript glue code. That includes Csound itself, my algorithmic composition software CsoundAC, the live coding system Strudel, and now Cardinal.
The Web browser itself contains a fantastic panoply of software, notably WebGL and WebAudio, so it's very easy to do visual music in the HTML5 environment.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Modern Website Development Technologies: Best Comprehensive Guide
HTML5, the fifth and latest version of Hyper Text Markup Language, remains the backbone of web development. It provides the structural foundation for web content, allowing developers to define the structure of a webpage with elements like headings, paragraphs, links, and images. HTML5 has introduced new elements and attributes that enhance multimedia capabilities, making it very easier to embed videos, audio, and interactive content.

2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is HTML5 and its uses?
HTML5 is the latest version of HTML, which is the standard markup language for creating web pages. HTML5 was released in 2014 and has since become the most widely used version of HTML. HTML5 includes many new features and improvements over previous versions of HTML.
New Features in HTML5
Here are some of the new features in HTML5:
Semantic elements: HTML5 includes new semantic elements such as <header>, <footer>, <nav>, and <article>. These elements provide more meaning to the content of a web page, making it easier for search engines to index and understand the content.
Multimedia support: HTML5 includes built-in support for multimedia elements such as <video> and <audio>. This makes it easier to embed videos and audio files into web pages without requiring third-party plugins such as Adobe Flash.
Form validation: HTML5 includes new form validation features that allow developers to validate user input without requiring JavaScript. This makes it easier to create forms that are more user-friendly and accessible.
Canvas: HTML5 includes a new element called <canvas>, which allows developers to create dynamic graphics and animations using JavaScript.
Uses of HTML5
HTML5 is used for creating a wide range of web applications and websites. Here are some examples:
Responsive web design: HTML5 provides many features that make it easier to create responsive web designs that work well on different devices such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones.
Mobile apps: HTML5 can be used to create mobile apps that run on different platforms such as iOS, Android, and Windows Phone. This is done using frameworks such as Apache Cordova or PhoneGap.
Games: HTML5 can be used to create games that run in a web browser without requiring any plugins. This is done using frameworks such as Phaser or PixiJS.
Web applications: HTML5 can be used to create web applications that run entirely in a web browser without requiring any server-side processing. This is done using frameworks such as AngularJS or React.
Here are some resources that can help you learn HTML:
W3Schools: W3Schools is a popular online learning platform that offers free HTML tutorials. Their tutorials are designed for beginners and cover everything from the basics to advanced topics .
MDN Web Docs: MDN Web Docs is another great resource for learning HTML. They offer comprehensive HTML tutorials that cover everything from the basics to advanced topics .
e-Tuitions: e-Tuitions offers online classes for HTML coding. You can visit their website at e-Tuitions to book a free demo class.
Codecademy: Codecademy is an online learning platform that offers interactive HTML courses. Their courses are designed for beginners and cover everything from the basics to advanced topics .
In conclusion, HTML5 is the latest version of HTML and includes many new features and improvements over previous versions. It is widely used for creating web applications and websites, including responsive designs, mobile apps, games, and web applications.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
So the history is a little bit more complex, in the way that his history is generally are.
To start with your head, Internet Explorer, or Netscape. There were other browsers which Netscape was based on, but generally speaking once things had settled down it was Internet explorer or Netscape..
Opera was around, but generally nobody really used it and it was pretending to be Netscape.
Netscape Navigator wanted to do everything. It wanted to be your web browser and your email client.
Which these days is a whole bunch of so what?
But back in the days when computers were running on single digits of megabytes, it was considered very bloated and slow.
Internet explorer three for example was actually a lot faster and slimmed down.
Then in the early 2000s, because Netscape becomes so bloated, a new browser came out. It was called Phoenix.
Phoenix was very fast and use less memory. It was still based on Netscape’s code which intern was based on mosaic.
They also got into trouble with somebody else who claimed that the Phoenix name was interfering with their trademark, so they renamed it to Firebird. And more or less the exact same thing happened again so they called it Firefox.
Which is a type of red panda.
Overtime Firefox has become more bloated, but at the same time RAM and storage has expanded and plateaued.
Now, there was also the KDE based web browser Konqueror, which is a little bit of dark humour – first comes navigator, then explorer, and then conqueror…
Apple looked at the KDE open source browser, and did what they always do.
Namely, they grabbed the code renamed it to Safari, which is fully in keeping with the dark humour origins of its original name, and then pretended that they invented it. Sorry – “innovated it“.
However, because Apple had the money to poor development into the project, and because it was open source, the fork which was renamed to Web kit turned out to be a lot better than Internet Explorer or mosaic/Netscape based code.
So Google picked it up for it again into the chromium project, developed chrome and went from there.
Because the chromium browser project was pretty much able to do anything – HTML5 video, audio, supporting flash, advanced CSS, supporting DRM, plug-ins, and crucially, able to re a text without it looking junk as all get out…
… And it could also run Java and JavaScript very fast…
… A lot of the other browser project stopped trying to write their own code and just went with chromium. There was even a text editor called Atom built on the chromium project. Which is great if you don’t mind opening up a text editor that immediately eats 1/4 of your RAM.
But because everybody immediately moved to chromium because it had chrome and Apple funding the development of the base project, we ended up with the homogenised ecosystem.
Including Microsoft Edge, which is a really good browser apart from the normal Microsoft bullshit.
Firefox on the other hand, stuck to its own code base, which has got sections that are prehistoric. For example they used to be a well-known bug that Firefox had no intention of fixing – if you turned on certain graphics settings that were very useful in computer games, it would blur every webpage that Firefox opened.
And Firefox has overtime loaded itself down massively, plumping itself up to the point where it is now no longer the fast nimble web browser that it was supposed to be to replace Netscape.
Unfortunately, even chromium based browsers that are nominally open source are also memory hogs. And because chrome likes to assert dominance over the base code (which is still partially an Apple project) they keep messing around and sticking in things like this new manifest concept which is pretty much dead in the water but that’s not going to stop them, to prevent you using plug-ins to prevent adverts.
Because while Google was a search engine, they made their money from supplying Google ads which were far less horrifying and intrusive and a better user experience.
Which they immediately threw away as soon as they had market dominance.
So now the world is full of basically three types of browser:
Chromium based stuff which is possibly morally and technologically dodgy because it’s still being developed by an evil corporation which is obsessed with preventing people avoiding advertising.
Firefox, which is not good, it’s just less evil. The Firefox foundation is nominally a nonprofit however you will notice that they do like to slip in paid content into new installs, that you then have to dig around to turn off. And eventually they will indeed start explaining that they can’t support certain plug-ins because their biggest donators have a vested interest in not allowing and blocking.
And finally weird twiddly little projects that you’ve never heard of. These tend to be permanently in beta, and most often get to the point where the one or two people dealing with them just give up. Or they are based on an outdated paradigm, like everything should be piped through the command line and displayed as a plain text file.
Which at this point is starting to sound slightly attractive.
So what’s a girl to do?
Use multiple browsers. Go and turn on all of the security, and run DNS blockers and firewalls, and VPNs.
Stop reading webpages directly. Pipe them all through a local read later service, or Firefox pocket to strip out everything but the main article (which doesn’t always work).
Pick up all of your website reading through an RSS reader, and then open up the webpages in an RSS client that removes all of the adverts and re-passes the page as plain text.
If you are slightly horrified by the amount of effort that I’ve just described, congratulations you are a normal human being. You are basically doomed because the bar for entry is now so high that you have to spend months, or years learning the technology to open up a webpage without having your soul sucked out.
If you have strong opinions on which services should be used and which webpages should be blacklisted because they aren’t VPN compliant, hey welcome to the club! You are a terrible awful nerd, just like me.
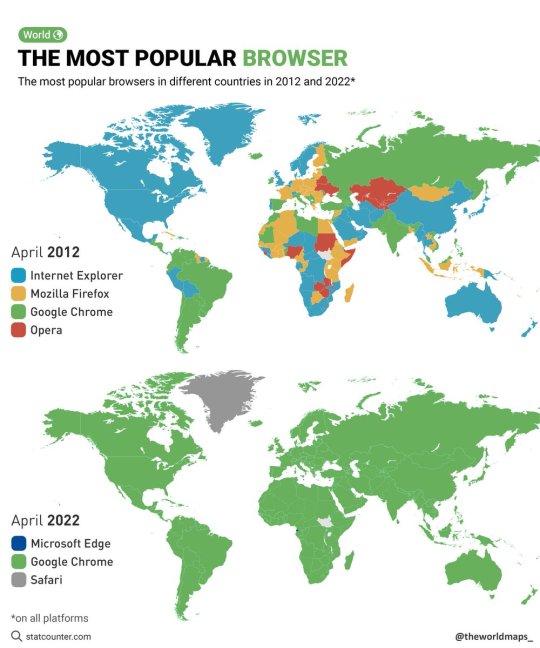
The most popular browsers in different countries in 2012 and 2022.
by @theworldmaps_
163K notes
·
View notes
Text
HTML Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners in 2025

If you’re just starting your journey in web development, one of the first technologies you’ll encounter is HTML—the foundational language for creating web pages. Whether you're preparing for your first job interview or an internship opportunity, being confident in HTML interview questions and answers can set you apart from other candidates.
In this blog, “HTML Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners in 2025,” we’ve compiled the most relevant, updated, and beginner-friendly HTML questions that hiring managers are likely to ask this year. These questions are designed to not only test your basic understanding but also help you think critically about how HTML is used in real-world scenarios.
Why HTML Knowledge Is Crucial in 2025
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) remains the backbone of every website on the internet. Even with advancements in frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue, the core of all web development still starts with HTML. That’s why interviewers consistently assess your understanding of HTML—especially if you’re applying for roles like:
Front-End Developer
Web Designer
UI Developer
Full-Stack Developer (Entry-Level)
In 2025, as more companies move towards web-first experiences, HTML knowledge remains a must-have skill.
HTML Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners
Here’s a curated list of beginner-friendly HTML questions with simple yet effective answers to help you ace your interview.
1. What is HTML?
Answer: HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It is the standard markup language used to create web pages. HTML uses a set of elements (called tags) to define the structure and content of a webpage.
2. What are HTML tags and elements?
Answer: HTML tags are used to mark the beginning and end of an element. Example: <p> is an opening tag, and </p> is a closing tag. An HTML element includes the opening tag, content, and closing tag. Example: <p>This is a paragraph.</p>
3. What is the difference between HTML and HTML5?
Answer: HTML5 is the latest version of HTML. It introduces new tags (<article>, <section>, <video>, <audio>, etc.), supports audio/video embedding, and improves semantic structure and browser compatibility.
4. What is the role of the <head> and <body> tags in HTML?
Answer:
contains meta information about the document (title, links, scripts).
contains the visible content that displays in the browser window.
5. What is a semantic tag in HTML5?
Answer: Semantic tags describe the meaning of the content inside them. Examples include <header>, <footer>, <article>, <nav>, and <section>. They improve code readability and SEO.
6. What is the difference between <div> and <span>?
Answer:
is a block-level element used to group larger sections of content.
is an inline element used to group small chunks of content inside other elements.
7. What is the purpose of the alt attribute in the <img> tag?
Answer: The alt (alternative text) attribute provides a text description of the image, which is helpful for screen readers and when the image cannot be displayed.
8. How do you create a hyperlink in HTML?
Answer: Use the <a> tag. Example:
<a href="https://example.com">Visit Example</a>
9. How can you insert a list in HTML?
Answer: There are two types:
Ordered list () – for numbered items
Unordered list () – for bullet points
Example:
<ul> <li>HTML</li> <li>CSS</li> <li>JavaScript</li> </ul>
10. What is the use of the <form> tag in HTML?
Answer: The <form> tag is used to collect user input. Inside a form, you can use input fields, buttons, checkboxes, and other elements to capture data and send it to a server.
11. How do you add a comment in HTML?
Answer: HTML comments are written like this:
<!-- This is a comment -->
12. Can you nest one HTML element inside another?
Answer: Yes, HTML elements can be nested. Proper nesting is essential for the correct rendering of a page. Example:
<p>This is <strong>important</strong> text.</p>
13. What are empty elements in HTML?
Answer: Empty elements do not have closing tags. Example: <br>, <img>, <input>, <hr>
14. What is the purpose of the doctype declaration?
Answer: The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration tells the browser which version of HTML is being used and helps render the page correctly.
15. What are meta tags?
Answer: Meta tags provide metadata about the webpage, such as character encoding, viewport settings, keywords, and descriptions. They go inside the <head> section.
Example:
<meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="description" content="Learn HTML interview questions for beginners.">
Final Thoughts
HTML is not just about writing tags—it's about structuring content properly so browsers and users can understand it. By mastering the questions in this blog, "HTML Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners in 2025," you'll gain the confidence to answer any foundational HTML question thrown your way.
Here’s how to make the most of this guide:
Practice writing each tag and structure by hand Build small projects to test your understanding Review real-world examples of semantic HTML Stay updated with HTML5 best practices
Ready for the Interview?
Whether you're preparing for an internship, a junior developer role, or even freelance web design work, these HTML interview questions and answers for beginners are your starting point. Learn them, understand them, and practice explaining them clearly—that’s the key to acing your next interview in 2025.
#HTML interview Question#HTML interview Question for beginners#Interview question for freshers#python for beginners
0 notes
Text
What Is Cross-Browser Testing? A Complete Guide for Seamless Web Experiences

In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, users access websites from a wide array of devices, operating systems, and browsers. From Chrome and Firefox to Safari and Edge—each browser interprets your website code slightly differently. This is where Cross Browser Testing becomes essential.
This blog dives deep into what cross browser testing is, why it matters, what features it covers, and how to do it effectively—ensuring your website delivers a consistent, bug-free experience across all platforms.
What is Cross Browser Testing?
Cross Browser Testing is a type of non-functional testing that verifies whether a web application functions and appears correctly across different web browsers, browser versions, and devices.
It helps developers and QA engineers ensure that:
The UI renders consistently
Core functionalities work correctly
There are no browser-specific bugs or issues
Cross browser testing is not just about aesthetics—it’s about ensuring usability, performance, and accessibility for all users, regardless of how they access your website.
Why is Cross Browser Testing Important?
If you’re only testing your website on Chrome, you’re missing the bigger picture.
Here’s why cross browser testing is crucial:
1. Diverse User Base
Your users might be on Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Edge, or Opera, and using different devices like desktops, tablets, or smartphones. Testing across these ensures everyone has a uniform experience.
2. Browser Rendering Engines Differ
Browsers like Chrome (Blink), Safari (WebKit), and Firefox (Gecko) interpret HTML, CSS, and JavaScript differently. Even a small deviation in rendering can lead to layout breakages or functionality issues.
3. Prevent Loss of Traffic and Conversions
A buggy checkout page on Safari or broken navigation on Firefox can significantly hurt conversion rates and user trust.
4. SEO and Accessibility
Search engines value user experience. Broken layouts or slow load times on certain browsers can negatively affect SEO performance and bounce rates.
What Features are Analyzed in a Cross Browser Test?
Here are the key features and areas evaluated during cross browser testing:
✅ 1. Layout and Design Consistency
CSS rendering
Font sizes, spacing, padding
Media queries and responsiveness
Grid and flex layouts
✅ 2. JavaScript Functionality
Form validation
Dynamic content rendering (DOM updates)
Event handling
Navigation toggles
✅ 3. HTML5 and CSS3 Compatibility
Audio/video elements
Animations
Flexbox, grid, shadows, gradients
✅ 4. Third-Party Integrations
Plugins (chatbots, tracking tools)
Embedded maps or videos
Social sharing buttons
✅ 5. Performance and Speed
Load times across browsers
JavaScript execution speed
Rendering behavior
✅ 6. Security and Cookie Behavior
HTTPS redirection
Local storage and session cookies handling
How is Cross Browser Testing Done?
Cross browser testing can be performed manually or via automation tools. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Define Your Browser Coverage
Choose browsers based on:
Your website’s Google Analytics browser report
Global browser usage statistics
Market demographics (e.g., Safari for iOS users)
Example Browser Matrix:

Read also: How Playwright Enhances Cross-Browser Testing Efficiency
Step 2: Set Up Your Test Environment
You can use:
Real Devices: For high accuracy
Emulators/Simulators: Quick tests for layout
Cloud Testing Platforms like:
BrowserStack
Sauce Labs
LambdaTest
CrossBrowserTesting.com
Step 3: Run Tests (Manual or Automated)
🔹 Manual Testing
Test scenarios using real devices and browsers, inspecting UI and performing tasks manually.
🔹 Automated Testing
Use frameworks like:
Selenium
Playwright
Cypress
TestCafe
Automation helps:
Reduce testing time
Run tests in parallel
Integrate with CI/CD pipelines
Step 4: Log and Fix Issues
Document browser-specific bugs, prioritize them, and retest after fixes.
Step 5: Continuous Cross Browser Testing
Use CI tools (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI) to schedule tests automatically on every build or code change.
Best Practices for Cross Browser Testing
✅ Always test on real user data (Google Analytics insights)
✅ Prioritize critical user flows first
✅ Automate repetitive tests, but don’t skip manual exploratory testing
✅ Regularly update browser versions in your testing matrix
✅ Perform regression testing after any major frontend update
Conclusion
Cross Browser Testing is not optional—it’s a necessity in today’s fragmented web ecosystem. Ensuring that your application works flawlessly across all major browsers not only boosts user experience and trust but also strengthens your brand’s credibility
As a leading Web application testing company, at Testrig Technologies, we specialize in comprehensive Cross Browser Testing Services that guarantee flawless digital experiences on any browser, device, or OS. Whether you're launching a new site or scaling an existing one, our QA experts are here to help.
0 notes
Text
O risco de beber água da chuva – DW – 24/05/2025
News https://portal.esgagenda.com/o-risco-de-beber-agua-da-chuva-dw-24-05-2025/
O risco de beber água da chuva – DW – 24/05/2025

A água da chuva se tornou uma fonte alternativa de água potável devido à escassez causada pelas mudanças climáticas e ao crescimento populacional. No entanto, os Centros de Controle e Prevenção de Doenças (CDC) não recomendam o uso dessa água para beber, cozinhar ou tomar banho sem tratamento prévio e enfatizam que a análise dela é importante já que pode detectar contaminantes.
E foi justamente isso que um grupo de pesquisadores da Universidade Estadual de Campinas (Unicamp) fez. Eles coletaram amostras de água da chuva entre agosto de 2019 e setembro de 2021 em três cidades paulistas: Campinas, Brotas e a capital São Paulo. Eles descobriram que essa água pode ser uma fonte de contaminação por agrotóxicos.
Segundo a pesquisa, cujo resultado foi divulgado na revista científica Chemosphere no final de abril, 14 tipos de agrotóxicos foram identificados nessas amostras.
“Nós já sabíamos que uma quantidade de agrotóxico é encontrada nas águas dos rios, mas na água da chuva foi a primeira vez que foi estudado no Brasil. Isso mostra que essas partículas de agrotóxicos estão presentes no ar”, explica Cassiana Montagner, pesquisadora do Instituto de Química da Unicamp, coordenadora do Laboratório de Química Ambiental.
Os agrotóxicos podem chegar aos rios de várias maneiras, como através do escoamento superficial da água da chuva que carrega os produtos químicos, do manejo inadequado do solo ou do vazamento ou derramamentos acidentais.
Os agrotóxicos encontrados
O herbicida atrazina, usado em larga escala pelo agronegócio no país, foi detectado em todas as amostras de água da chuva coletadas nas três cidades que integram o estudo e o fungicida carbendazim, que tem seu uso proibido no Brasil, foi encontrado em 88% do material coletado. Em Brotas ele foi o agrotóxico encontrado em maior quantidade. O herbicida tebuthiuron foi detectado pela primeira vez em água de chuva, estando presente em 75% das amostras.
Agrotóxicos: banidos na Europa, mas livres no Brasil
To play this audio please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 audio
Em 2022, a Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (Anvisa) proibiu o uso do carbendazim, dando o prazo de doze meses para que os agricultores se adequassem à nova regra. A substância pode causar mutações genéticas, diminuir a fertilidade e prejudicar o feto.
As concentrações dos agrotóxicos encontradas nas amostras não ultrapassaram os limites permitidos para a água potável no Brasil. Porém, algumas das substâncias detectadas não têm padrões de segurança estabelecidos, ou seja, não há indicadores de concentração segura.
Além disso, segundo os pesquisadores, a exposição crônica mesmo a baixas doses dessas substâncias pode causar danos à saúde humana a longo prazo. “Ninguém bebe ou tem contato com essa água da chuva todos os dias, então o risco não é direto. Mas esse estudo acende um alerta. Por exemplo, alguns desses produtos têm relação com doenças crônicas como infertilidade, doenças neurológicas, respiratórias e podem causar câncer”, acrescenta Montagner.
Presentes na atmosfera
Com relação ao reuso, a pesquisadora afirma que não há problemas em usar essa água da chuva para lavar os quintais, por exemplo.
Outro ponto importante, segundo o estudo, é que ao encontrar essas partículas de agrotóxicos na água da chuva, isso mostra que essas substâncias estão presentes na atmosfera, ou seja, também pode estar presente no ar que respiramos.
A pesquisa apontou também que Campinas foi a cidade que apresentou a maior concentração de agrotóxicos, com 701 microgramas por metro quadrado. O município tem quase metade do território ocupado por lavouras – o maior território de plantio entre as cidades analisadas no estudo.
Em Brotas, onde os plantios ocupam 30% da cidade, ficou em segundo lugar com a média de 680 microgramas por metro quadrado. Já em São Paulo, que possui apenas 7% do seu território agrícola, os índices chegaram a 223.
Como os agrotóxicos vão parar na água da chuva
Parte dos agrotóxicos aplicados nas lavouras se dissipa na atmosfera e pequenas partículas podem se condensar nas gotículas de água que formam a chuva. Com a precipitação, o produto retorna ao solo e pode alcançar locais mais distantes das plantações. Isso acontece porque fatores como vento, temperatura e umidade influenciam na sua distribuição.
O que ocorre com os agrotóxicos é semelhante ao que ocorre com a chuva ácida. Esse tipo de chuva é caracterizado pelos níveis elevados de ácidos sulfúrico e nítrico, formados pela reação de dióxido de enxofre (SO₂) e óxidos de nitrogênio (NOₓ) com a umidade da atmosfera. Esses poluentes são liberados principalmente pela queima de combustíveis fósseis.
A diferença é que a quantidade de micropartículas de agrotóxicos encontradas na água da chuva, ainda estão em uma quantidade pequena, quando comparada à chuva ácida. “Eu não diria que é uma nova vertente da chuva ácida, mas sim, mais um poluente que estamos encontrando na água da chuva”, diz Montagner.
Eco Brasil: Alimentação saudável, sustentável e acessível
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
0 notes
Text
H5 FireKirin: A Skill-Based Revolution in Online Fish Arcade Gaming
In today’s digital world, the online gaming industry continues to expand, offering immersive experiences to video game lovers. One of the standout platforms making waves in this arena is H5 FireKirin—a browser-based fish arcade game built using advanced HTML5 technology. Unlike luck-based games, H5 FireKirin emphasizes skill, making it a refreshing choice for serious and casual gamers alike.

HTML5 Advantage: Why H5 FireKirin Needs No Download
The “H5” in H5 FireKirin signifies its HTML5 framework, meaning there's no need to download any software. Players can enjoy seamless gameplay directly from their browser, whether on a smartphone, tablet, or computer. This ease of access makes it highly attractive to modern gamers seeking instant entertainment.
Core Features of H5 FireKirin
Skill-Based Gameplay: Players rely on precision and tactics rather than pure luck.
High-Quality Visuals: Stunning graphics bring the underwater fish arcade world to life.
Immersive Sound Effects: Engaging audio enhances the gaming experience.
Multi-Device Compatibility: Fully playable on PC, mobile, or tablet.
Casino-Style Variety: Offers a mix of fish shooting, spinning reels, and other skill games.
Why is H5 FireKirin So Popular?
Since its launch in 2020, H5 FireKirin has grown in popularity, particularly among fans of online casinos and arcade shooters. Its combination of visual excellence, smooth controls, and skill-based challenges provides a competitive edge that appeals to a wide range of players.
Games You Can Play on H5 FireKirin
H5 FireKirin is not just a single game but a platform hosting multiple titles, including:
Fish shooting games
Digital fish arcade games
Slot-style spinning reels
Other skill-based mini-games
Each game is designed to test player skills, reflexes, and decision-making—perfect for those who enjoy interactive and rewarding experiences.
How to Start Playing H5 FireKirin
Getting started is simple:
Visit an online casino site that supports H5 FireKirin.
Sign up or log in.
Choose your game and start playing directly in your browser.
No apps, no installations—just pure skill-based fun.
Conclusion
Absolutely. If you're looking for a no-download, browser-based fish arcade platform where skill determines your success, H5 FireKirin is a top choice. With its impressive graphics, engaging gameplay, and casino-style excitement, it’s no surprise this platform has quickly gained a strong following among online gamers.
0 notes