#ionic seperator
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Note
Due to using the ionic separator on herself, Phoebe developed some health issues after the events of frozen empire. Nothing immediately life threatening, but things that could be bad if left untreated
gb headcanon day #135
#ionic seperator#ghostbusters#dailyghostbusterheadcanons#headcanons#ghostbuster daily headcanons#phoebe spengler#phoebe spengler frozen empire#frozen empire#ghostbusters frozen empire#day 135
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Week 8 Reflection
Creating a 2D photoshop rendering
In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a digital rendering of a modified Remington Pro Ionic hair dryer.
Before the class I was really confident with the photoshop becuse I’ve had experiences with illustrator.
We followed the tutorials step by step
The linework for the hair dyer was given for this exercise. We had to convert the drawing into photoshop and adjust the hues and levels to get a clean blackline drawing with plain white backgorund.
- We did it by arranging the hues and levels under top left conner “image”
Layers and folders
creating seperate paths for each parts of the dryer
It is very important to organise everything before hand. I found it so helpful later on.
Create the mask for the main casing group by subtracting all the other parts from the overall outline. To do this, first select the outline (right click on the Parts mask, then select “Add Mask to Selection” from the drop-down options). Then, progressively subtract the other parts (right click on a part mask, the select “Subtract from Mask Selection” from the drop down options).
We need the pen tool to draw out the outline and different parts.
I started with drawing many maybe hundreds of straight lines which was the wrong way to do it.
After the suggestion by Rob, I experienced with the curves and only place minimal anchors which makes it much quicker and easier to arrange.


I could never get this to work as it always show up no pixels selected.
Instead I used the same way to create the hole on the holder.


We used brush tool to create textures. It was confusing for me the brush tool settings.
What I learnt
I learnt how to use photoshop in a sufficient way, it is important to get everything prepared and organized before hand, which includes set up folders and layers, change the page and brush settings ect,. I have also learnt to use minimum pen anchor point when tracing the ourlines, and use ctrl key to arrange it precisely afterwards. I am just getting started with texturising different materials, which I need to look up more reference photos of different mateirals.
What I found challenging
Photoshop still needs a lot of practice, which I mean a lot of little mistakes could drag you for hours trying to figure out the problem and sometimes you will have to start again. I could never get “Subtract from Mask Selection” to work, and had no idea what it means thar no pixels selected.
Conclusion
A very helpful guide(basically all we need) to complete the project 2, I enjoyed using photoshop but somehow I found Rhino more user friendly.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Juniper Publishers- Open Access Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources
Modelling of Dissolved Oxygen in Thi Vai River Water Incorporating Artificial Neural Network and Multivariable Regression
Authored by Tat Pham Van
Abstract
The water quality of watershed is one of the major concern in the operation and water quality management of watershed. The dissolved oxygen (DO) is one important element of important indicators for water bodies. This is essential demand for micro-organisms and a significant parameter of the aquatic ecosystems. In this work, we predicted the DO concentration of Thi Vai river, Viet Nam based on the relationships between the dissolved oxygen and the hydrologic parameters such as temperature, pH, turbidity, conductivity, chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD), nitrate and phosphate. The multivariate regression (MLR) technique and back-propagation neural network (BPNN) were used to establish those relationships. The study results showed that the neural network BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) with R2train = 0.96, RMSE = 0.14, GAME = 0.12) is able to predict the DO concentration accurately. The neural network BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) is a useful tool for management of environmetal quality of Thi Vai river water in Viet Nam. The DO concentration of this river water was represented by interpolated maps using Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) function. We can use those maps to perform the managerment solutions to decrease the polluted level.
Keywords: Back-Propagation Neural Network Bpnn; Dissolved Oxygen; Inverse Distance Weighted Idw
Introduction
Water scarcity in the world has been occurring more and more seriously each year [1]. Water resources in some areas are declining in both quantity and quality. It is directly linked with human welfare such as recreational activities (swimming and boating), or municipal, industrial, and private water supplies, agricultural uses including irrigation and livestock watering , the quality of water is considered to be a vital concern for mankind [2]. In addition, the assessment and management of water resources has become very complex with population growth [3]. Today, decisions on water resources management are increasingly being based on model studies [4]. Therefore, the precise determination of concentration of pollutants in water is an essential requirement to support effective management and legislation [5]. Numerous computational and statistical approaches have been applied to predict the water quality in reservoirs Liu et al. 2009, Cho et al. 2009; White et al. 2010; Lindim et al. 2011.
The dissolved oxygen (DO) is an important quality index for evaluating surface water quality because it represents for polluted level, the state of aquatic ecosystems of water bodies Chen and Liu, 2014. However, because of the influence of different factors on different waters, it is difficult to simulate DO concentrations by traditional mathematical methods [6]. In addition, limited water quality data and the high cost of water quality monitoring often pose serious problems for process-based modelling approaches. Moreover, the elements of aquatic eco-systems such as chemical,physical, and biological components are very complex and nonlinear. Which model and parameter will be used to model DO remains a question. In this regard, some traditional models, such as regression models and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models were investigated and compared He et al. 2011 applied the model MLR and ANN to forecast the daily DO variation based on water temperature (WT) and runoff in the Bow River, Canada. The results show that the ANN model outperformed MLR model [7] suggested DO = -0.18WT +0.591pH- 35.46 with the coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.4 for DO value in the River Danub [8] asserted that ANN are a relatively new concept in environmental modeling. ANNs are suitable to model nonlinear processes, such as the dynamics of DO in surface water [9]. Many kinds of networks can applied in ANNs such as Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) [10]. Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System ( MLP and ANFIS) [11]. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Generalized Regression Neural Networks (GRNN), Radial Basis Function Network (MLP and RBFN) [12]. However, according to [13-15]. ANN using Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) is the most widely used neural network for forecasting/prediction purposes. BPNN generally consists of three layers including an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer [16]. Each layer consists of neurons which are connected to the neurons in the previous and flowing layers by connection weights. These weights are adjusted according to the capability of the trained network. Input vectors and corresponding target vectors are used to train BPNNs until the models can approximate a specified minimum error or a maximum number of epochs. BPNNs with weightings, biases, a sigmoid layer, and a linear output layer can approximate any function with a finite number of discontinuities.
In recent years, several researches have been conducted on water quality simulation including DO using ANNs models [17-21]. This method can predict the water quantity data with high precision and more robust [22] established an ANN model to predict total Nitrogen, total Phosphorus, total Organic Carbon, DO and Fe in deep waters of Swedish Lakes. The efficiency of regression model and ANN application in DO determination was reported in the aforementioned studies conducted for specific areas. However, to date study on predicting DO using regression and ANN models in Vietnam is limited. Thus, in this study, the application of ANN using Backpropagation Neural Network (BPNN) algorithm and multiple linear regression analysis (MLR) to model DO based on temperature, pH, turbidity, and conductivity, COD, BOD, NO3- and PO43-. Besides, we also compared the coefficients of two models (coefficient of determination - R2 and root mean square error - RMSE) to determine which model is better for predicting DO in water bodies.
Methods
Study area
Thi Vai river is a tributary of Dong Nai river system in Viet Nam. Thi Vai river basin covers an area of 625 square kilometers, starting from Nhon Tho village, Long Thanh district, Dong Nai province, which flows through Tan Thanh district,Ba Ria-Vung Tau province and Can Gio district in Ho Chi Minh city. The river basin has a length of 32km and a width of 400 to 600m. This river basin has a depth of 12-20m (the deepest area is about 60m) TTH Nguyen et al. 2017 Thi Vai river is a tidal estuary. The tidal range of this river is higher than 400cm with fast flow. The salinity of Thi Vai river varies from 24% to 32% in the rainy season, so Thi Vai river has the saline characteristics of salt.The water quality of Thi Vai river is represented by DO parameter. This parameter pointed out the decreasing tendency. This can be also explained that Thi Vai river receives not only 34,000m3 of the untreated sewage from about 200 factories along the river basin, but also it receives the large amounts of untreated sewage from residential and cattle-farming areas. A few locations with high pollution include the areas near VEDAN company and Go Dau port or Phu My port Lorenz et al. 2014.
Input data
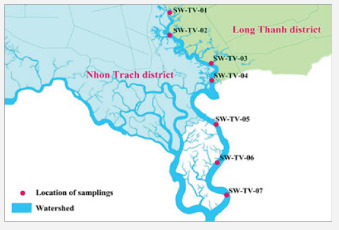
A monitoring program was also established by Centre of environmental technology and Dong Nai department of natural resources and environment. Water samples used in this work were collected by 7 monitoring stations in the period from 2010 to 2016 covering all different areas of Thi Vai river, as shown in (Figure 1) Nine physico-chemical parameters pH, temperature, disolved oxigen (DO), chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD5), conductivity (EC), turbidity, nitrate and phosphate were used as input data in the multivariate regression MLR and artificial neural network ANN model. The dataset was seperated into training set (occupied 80% of total data) and test set (20%).
Multiple linear regression model (MLR)
MLR model is used to represent the relationship between dissolved oxygen DO and physico-chemistry parameters as a linear function of several predictors [23]. MLR model was applied as well in this work to prove their impact on dissolved oxygen DO as
Where Y dependent variable (dissolved oxygen DO); xk is independent variable (kth physico-chemistry parameter); β0 regression constant; and βk coefficient of kth physico- chemistry parameter, respectively (Table 1) The abbreviation for 8 physico-chemistry parameters for predicting disolved oxygen DO. The parameter DO is used to indicate of pollution and self-cleaning capability of water bodies. Dissolved oxygen is also necessary to the organism fish, invertebrates, bacteria and plants. These use the dissolved oxygen in respiration. The biological oxygen demand (BODs) and chemical oxygen demand (CODs) consumed some of the dissolved oxygen in water. These processes can cause of decrease in dissolved oxygen DO. Oxygen is involved in the metabolism processes of various nitrogen- containing compounds. The nitrate- and phosphorus products generate the free forms of nitrate and phosphate in the water. The various forms of nitrogen and phosphorus content facilitate the development of algae. This can change the concentration of dissolved oxygen in water. The appearance of dissolved solids in the ionic form of nitrates, phosphates, etc. also changes the conductivity (EC) so the EC also indicates the DO change. In addition, some other factors also affect the DO. The biological and chemical processes can be changed as the pH changes. This affects the oxygen-consumption capability of oxygen-demanding processes. In addition, dissolved oxygen DO is influenced by natural factors such as temperature, pH, salt and several algae. The solubility of oxygen in water decreases as temperature increases. Furthermore the dissolved oxygen also decreases by the exponential function as salt levels increase. At the same time, turbidity affects the dissolved oxygen DO because of it increases the light absorption, this can increase the water temperature. Therefore the dissolved oxygen presents the important role in pollution assessment of Thi Vai river basin.The most important variables effecting on DO in Thi Vai river basin were determined based on coeffient of contribution taking the form:
Where MPxk,% is average of contribution percentage of physico-chemistry parameter kth on DO, βk regression coeffients of parameter in MLR model, xk independent variable k (Table 1).
Backpropagation Neural Network
The back-propagation neural network BPNN is known a multi-layer feed forward network. This BPNN is trained by the training dataset while it tunes the network parameters using an error back propagation mechanis [24]. A BPNN is composed of several layers of networks, however, it is most commonly accepted as three-layer architecture BPNN I(k)-HL(m)-O(n); the input layer I(k) consists of k = 8 input neurons as physico- chemistry parameters in Table 1; the hidden layer HL(m) has m = 7 neurons; and the output layer has one neuron (with n=1) such as dissolved oxygen DO [25]. BPNN is trained with Levenberg - Marquardt algorithm. The transfer function was used in each neuron on hidden layer is tansig; for output layer the transfer function is purelin. The learning function used is learngdm. The value MSE of 2.5573 x 10-5 obtained from training process after training 10000 epochs. The neural network BPNN architecture I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) as presented in (Figure 2) was constructed successfully for predicting the DO values from 8 hydrological parameters using various sampling locations in years 2010 to 2016. The most important variables effecting on DO in BPNN architecture I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) evaluated are based on the weight coefficients taking the form,
Where RIx the relative importance of input neuron x , Σwxy wyz sum of final weights of the connection from k input neurons to m hidden neurons and the connection from m hidden neurons to n output neuron; y sum of m neurons in hidden layers, output neuron (dissolved oxygen DO).
Performance criteria
In this study, several statistical error measures were used to assess the performance of the applied models. The root mean square error (RMSE), coefficient of determination (R2) and mean absolute error (MAE) were used to provide an indication of goodness of fit between the observed and predicted values. Expressions of these error parameters are given as follows:
Where n number of observation; Yi ith observed values of dissolved oxygen DO; Y average observation value of DO; and Ŷi predicted values DO for observation ith. In addition, the t-test method of paired two sets was also applied to compare the predicted value (DOpred) from MLR and BPNN-I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) model (Table 2) with observed value DOobs, respectively.
Zoning the disolved oxygen by GIS technique
In this work the predicted values DOpred resulting from MLR and BPNN architecture I (8)-HL(7)-O(1) model and observed values DOobs were used to zone the water quality of Thi Vai river using GIS technique. For GIS technique, the Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) function is applied to interpolate the dissolved oxygen values of the river zones. The IDW function can be used to interpolate for DO values of any unmeasured locations using the measured values surrounding a prediction location taking form
Where zi observed value ith; d distance from unmeasured location to observation location ith
Results and Discussion
DO tendency through years
In general, the water quality of Thi Vai river was surveyed in years 2010 to 2016, but all did not meet the living water standards. The average results of dissolved oxygen DO and the statistical evaluation at seven locations on Thi Vai river basin are presented in (Table 2). The mean, maximum and minimum values of DO concentration as well as of other parameters have pointed out the variation range of accuracy and reliability for the observed data collecting from the survey locations. Moreover, the statistical values as the variation coefficients depicted the variation limit of water quality in different locations of Thi Vai river basin. This depended on the climate change and hydrometeorology in the river basin. The survey locations showed the change of concentration DO at the different locations corresponding to the production and living processes, as given in (Table 3).
The SW-TV-01 and SW-TV-02 locations are in far from domestic and industry areas. So these areas exhibited the highest concentration of dissolved oxygen DO in years 2015 and 2016. For five remaining locations the concentration of dissolved oxygen is lower, due to the areas are impacted from the waste sources of domestic, farming and factory areas. The lowest concentrations of DO are in the SW-TV-03 and SW-TV-04 areas, which are affected by the living waste water and fish farming as well as 200 factories along Thi Vai river basin, as given in (Table 3). In general the highest concentration of DO was found at the confluence location of Ba Ky canal and Thi Vai river. The lowest concentrations of DO are in VEDAN and Go Dau area. Because of these areas are influenced by the waste water from the factories and ships. But in these areas the water quality of this river is still in an average range and it can be improved by the closer monitoring from the units of environmental management in recent years.
DO prediction with the multilinear regression model
For data of water quality of Thi Vai river measured were collected from years 2010 to 2016, as given in Table 2, we have developed a multivariate linear relationship between DO and physico-chemistry parameters using multivariable regression techniques. The quality of multivariable models was evaluated by calculating the values of regression statistics such as R2train, Standard Error (SE), and value of multiple regression correlation between the observed DOs and predicted DOpred . values.
The best linear relationship between DO and 8 hydrological parameters can be written in the following form:
The regression results pointed out the statistical values R2train of 0.81 and RMSE of 0.32; it is satisfactory for regression- statistics standard. The contribution percentage MPxk,% of each parameter xk in regression equation (8) was calculated by using the coeffiences βk. The important effects on the dissolved oxygen DO of Thi Vai river basin were determinated by formula (2), as depicted in (Figures 3 & 4). We have also used the ANOVA statistics to compare the significant level of regression model based on value Fsig = 0.000 in confidence level α = 0.05.
Furthermore the parameter pH tends to dominate all other remaining considerations for dissolved oxygen DO in Thi Vai river (MPxk,% > 70%). The parameters can be sorted in order of influence for parameter DO: pH > temperature > conductivty > BOD > phosphate > COD > nitrate > turbility.
Predictability of BPNN model
The neural network BPNN with architecture I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) in (Figure 2) was constructed by Levenberg-Marquardt converging algorithm with neurons on input layer such as pH, temperature, COD, BOD, EC, turbidity, NO3- and PO43-. This neural network I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) was proceeded by using 10000 epochs. The results of prediction in BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) are presented in (Figure 5). The correlation value R2train of 0.9624 between the observed DOobs and predicted DOpred values is extremely high, as showed in (Figure 4a). It means that the approximation 96.24% of variation in DO is explained by variation in 8 physico- chemistry parameters. Thereby the discrepancy between blue (observed DOobs) and red (predicted DOpred resulting from ANN model) line is insignificant. This is presented clearly by bestfit capability (Figure 5b). In other words, the ANN model I(8)- HL(7)-O(1) pointed out the high predictability and reliability. In neural network BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) the neurons on input layer pointed out the important effects in the training process of this neural network, as showed in (Figure 5). The value RI of 18.65% was calculated by formula (3). The parameters can be also sorted in order of influence for parameter DO: phosphate > conductivty > pH > COD > BOD > nitrate > turbility.
Assessment of the accuracy of prediction methods
The models BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) and MLR (with k = 8) were tested by using the statistical values such as coefficients R2train of 0.96, R2test of 0.9211 for BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) and R2train . of 0.811, R2test of 0.4423 for MLR model, as exhibited in (Figure 6). Moreover values RMSE for BPNN and MLR model are also used to indicate the predictability. In addition the global absolute mean of errors GAMEs for models MLR and BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) were close to zero, as shown in (Table 4). These suggest that the BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) model produces the less error. The results are also used to imply that the predictability of BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) was better than MLR model. This finding was consistent with the studies proposed by [19,26,27]. To assess the efficiency of each model, the method t-test paired two samples for means was also used to evaluate the difference between the observed DOobs, with predicted DOpred .values, as given in (Table 4). The results of t-test paired two samples showed that the difference between models MLR and BPNN is insignificant at confident level at 95%.
Mapping disoved oxygen using GIS technique
In this study, the IDW function of GIS technique was used to interpolate the DO values surrounding the observed DOobs and predicted DOpred values from MLR and BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) model. The interpolated values resulting from IDW function were used to make the map of water quality in Thi Vai river basin. The maps of water quality of two years 2015 and 2016 were used to compare between the DO values from models, as exhibited in (Figure 7). In part of Thi Vai river, in particular, the location of VEDAN area and other areas near Phu My and Thermal Power Plant are in decline, appropriate measures should be taken to minimize pollution. In general, the water quality of Thi Vai river is at average level up to the regulated standards. A few locations are polluted by the discharge of effluents from residential, factory and farming area such as location SW-TV-05 and SW- TV-06 in 2015. But the water quality of the locations SW-TV-05 and SW-TV-06 in 2016 was improved emphatically. Due to the environmental management of Thi Vai river by the authorities in 2016 was carried out efficiently. The effluent from the factories along Thi Vai river basin causes the water area herein to be unsafe for water supply. In addition, the fish farming also affects the water quality such as locations SW-TV-03 and SW-TV-02. Furthermore, the water quality of Thi Vai river is also impacted by the tidal change [26-29].
Conclusions
The MLR and BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) model were then constructed successfully to predict the DO parameter in Thi Vai river. From MLR model the important effect of physico-chemistry parameters for Thi Vai river basin were also determined. This can help the environmental managers to produce the law of environmental monitoring. The predicted DOpred values resulting from BPNN I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) turn out to be a good agreement with the observed DOobs values. This BPNN can be used to be superior to the multilinear regression MLR model. The application of the neural network I(8)-HL(7)-O(1) is more appropriate for predicting the dissolved oxygen DO. The GIS techniques is also a very efficient tool to make the interpolated maps by IDW function.
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/ijesnr/index.php
#Environmental Sciences#Natural Resources#juniper publishers publons#Juniper Publishers Indexing Sites List#sustainability#atmosphere#water
0 notes
Text
Twelfth Week
This week I had a math exam, so I didn’t come in on monday. What I did this week was test the efficacy of my seperation of our product from the unwanted salt. My plan was to do this via solubility, because our salt is ionic while our product is most definitely not - pretty basic General Chemistry concept. Earlier this month when I ran my solubility tests, I found that a mixture of Toluene:Methanol worked really well as dissolving our product. When dissolving our actually formed products with this with the toluene:methanol mixture though it worked to a certain extent, in that I lowered it by 10%, but I wasn’t able to completely separate out all of the salt. There was still some amount (~2%) left over. Not sure where this part of the project is going right now though, as Bryon would like to scale up the actual reaction before continuing to explore this.
In personal news, Scots Fest is this weekend, and I’m not looking forward to it. I have a lot of organic chemistry studying to do, and TKE always has a lot to do during the weekend, so it’ll be kind of a drag. Though getting to experience it with all the new brothers will be nice. I’m really just ready at this point for easter break to hit.
0 notes
Link
Water occurs in nature "pure" and what ever be the source always contains impurities either in solution or in suspension. The determination of these impurities makes analysis of water necessary and removal and control of these impurities make water treatment essential.
Water sources:
The various sources of water can be broadly classified as:
a) Rain water
b) Surface water (River, Streams, Ponds, Lakes and Reservoirs)
c) Ground water (Springs, Shallow wells and Deep wells)
of the above, logically rain water is the purest but even this collects and dissolves atmospheric gasses and impurities in air. Further, once in contact with the earth's crust, the rain water will gradually dissolve various materials.
Various (Majour) impurities:
The major impurities of water can be classified in three main groups:
1) Non-ionic and undissolved
2) Ionic and Dissolved
3) Gaseous 1) Non-ionic Impurities: These are mainly, salt, mud, dirt and other suspended matter, micro-organisms, bactiria and other organic matter, oil and corrosion products. It goes without saying that drinking water and most industrial water supplied should be clear and organic-free. 2) Ionic and dissolved Impurities: Any salt which dissolves in water disassociates into positively charged ions called "Cations" and negetively charged ions called "Anions". Since these permit the water to conduct electricity, these salts are called electrolytes. Some of the most common Cations in water are: Calcium, Magnesium, Sodium and Iron, and rarely Ammonium, Potassium and Manganese. These cations are associated with Anions like Bicarbonates, Carbonates, Hydroxides (the sum of which is termed as Alkalinity), Sulfates and Chlorides. Presence of Nitrites and Phosphates is normally not very common. In the water treatment field, the preferred method of expression of these dissolved impurities is in terms of Equivalent Calcium Carbonate, abbrevated to as "CaCO3". This is because Calcium Carbonate is a good common denominator as it has a molecular weight of 100, which facilitates calculations. Moreover, in this form of analysis, the sum of Cations or total Cation always equals the total Anions. Quantitatively, these are expressed in parts per million or milligram/ltr. One part per million equals one ten thousandth of one percent (0.0001%). One part per million means one part in a million parts, for example, one liter in a million liters of water or one Kg in a million Kgs of water. Of all the dissolved impurities, hardness is perhaps the most troublesome. Hardness is due to compounds of Calcium and Magnesium. On heating water caontaining these salts, Carbon Dioxide is released from solution and the Bicarbonates are converted into Carbonates which are insoluble and form scales and deposites. Other salts of Calcium and Magnesium like Sulfates and Chlorides have lower solubility than Sodium salts and participated out at high temperatures. Bicarbonates of Calcium and Magnesium are known as the "Alkaline hardness" or "Temporary hardness" and chlorides, sulfates, nitrates etc., of Calcium and Magnesium are known as "Neutral" or "Permanent hardness". Sodium salts are highly soluble but can be corrosive if present in large quantities such as Sodium Chloride or Sodium Bicarbonate. Dissolved Silica is another troublesome impurity, especially in water fed to Boilers of very high temperatures and pressures. Even in lower pressure boilers, it could form a very hard type of scale by acting as a binding agent. The natural water contains solid, liquid and gaseous impurities and therefore, this water cannot be used for the generation od steam in the boilers. The impurities present in the water should be removed before it'suse in steam generation. The necessity for reducing the corrosive nature & quantity of dissolved and suspended solids in feed water has become increasingly important with the advent of high pressure, critical & supercritical boilers. Impurities in water: The impurities present in the feed water are classified as given below - -- Undissolved and suspended solid materials. -- Dissolved salts and minerals. -- Dissolved gases. -- Other materials (as Oil, Acid) either in mixed or unmixed forms.
A. Undissolved and suspended materials: Turbidity and sediments:
Turbidity in the water is suspended insoluble matter including coarse particles (mud, sediment, sand etc.,) that settle rapidly on standing. Amounts range from almost zero in most ground waters and 60,000 ppm in muddy and turbulent river water. The turbidity of feed water should not exceed 5 ppm. These materials can be removed by settling, coagulation and filtration. Their presence is undesirable because heating or evaporation produces hard stony scale deposits on the heating surface and clog the fluid system. Both are objectionable as they cause damage to the boiler system. B. Dissolved salts and minerals: a) Calcium and Magnesium salts: The calcium and Magnesium salts present in the water in the form of carbonates, bicarbonates, sulfates and chlorides. The presence of these salts is recognized by the hardness of water (Hardness of water is tested by soap test). The hardness of water is classified as temporary and permanent hardness. The temporary hardness is caused by the bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium and can be removed by boiling. The boiling converts the soluble bicarbonates into less soluble carbonates which can be removed by simple blow down method. The permanent hardness of the water is caused by the presence of chlorides, sulfates and nitraes of calcium and magnesium and they cannot be removed just by boiling because they form a hard scale on heating surfaces. A standard amount of measurement of hardness is taken as being the amount of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) in th water and is referred to in part per million (ppm) or grains per gallon (grains/gallon*17.1=ppm). b) Sodium and Potassium salts: These are extremly soluble in water and do not deposit unless highly concentrated. Their presence is troublesome as they are alkaline in nature and accelerated the corrosion. c) Chlorides: Majority of the chlorides cause increased corrosive action of water. d) Iron: Most common soluble iron in water is ferrous bicarbonate. The water cantaining ferrous bicarbonate deposits become yellowish and reddish sediments of ferric hydroxide if exposed to air. Majority of ground surface water contains less than 5 ppm but even 0.3 ppm can create trouble in feed water system by soft scale formation and accelerating the corrosion. e) Manganese: It also occurs in similar form and it is also equally troublesome. f) Silica: Most natural water contains silica from 1 to 100 ppm. Its presence is highly objectionable as it forms very hard scale in Boilers and forms insoluble deposits in turbine blades. In modern high pressure boilers its presence is reduced as low as 10-50 ppb. g) Microbiological Growth: Various growth occur in surface water (lake & river). The micro-organisms include diatoms, molds, bacterial slimes, algae, manganese & sulphate reducing bacteria and many others. These can cause coating on Heat Exchanger and clog the flow passages and reduce the heat transfer rates. h) Colour: Surface waters from swampy areas become highly colored due to decaying vegetation. Colour of feed water is objectionable as it causes foaming in Boilers and may interfere with treatment processes. It is generally removed by chlorination and absorption by activated carbon. C. Dissolved Gases: a) Oxygen: It presents in surface water in dissolved form with variable percentage depending upon the water temperature and other solid contents in water. Its presence is highly objectionable as it corrosive to iron, zinc, brass and other minerals. It causes corrosion and pitting of water lines, boiler tubes. Its effect is furthur accelerated at high temperatures. b) Carbon Dioxide: The river water contains 50 ppm and well water contains 2 to 50 ppm of C02. It also causes the corrosion of stream, water and condensate lines, It also helps to accelerate the corrosive action of oxygen. wThe other gases are H2S, CH4, N2, and many others but their percentages are negligible, therefore, their effects are not discussed here. D. Other minerals: a) Free Mineral Acid: Usually present as Sulphuric or hydrochloric acid and causes corrosion. The presence is reduced by neutralization with alkalis. b) Oil: Generally, the lubricating oil is carried with steam into the condenser and through the feed system to the Boiler. It causes sludge, scale and foaming in Boilers. It is generally removed by strainers and baffle seperators. The effects of all the impurities present in the water are the scale formation on the different parts of the boiler system and corrosion. The scale formation reduces the heat transfer rates and clog the flow passage and endager the life of the equipments by increasing the temperature above safe limit. The corrosion phenomenon reduces the life of the plant rapidity. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to reduce the impurities below a safe limit for the proper working of the power plant. C. Dissolved Gases: The atmosphereic gases found in naturally occuring waters, only two Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen, are the main causes of many corrosion related problems.
0 notes
Text
Grundlagen Leise Haartrockner Test Techniken Die Am Besten Sind
Ich bin Juliana - willkommen auf meiner Seite über Haartrockner Test. Denn bei einem regelmäßig beruflich genutzten aufsatz haartrockner kommen letztendlich ganz andere Kriterien für einen Kauf zum Einsatz als bei einem nur selten verwendeten aufsatz haartrockner. Im Gegensatz zum herkömmlichen Haarföhn, hat dieser eine antistatische Wirkung. Nur, weil Sie die Rechnung für Haarfön oder Haartrockner später bezahlen, wird natürlich nicht der Haarfön oder Haartrockner später ausgeliefert. Keratin haartrockner, Ideal Für keratin haarglättung, brasilianische haarglättung. (Art# 178724) REMINGTON AC9096 Seien Sie bereit für umwerfende Styles mit seidig-glattem und super glänzend aussehendem glattes Haar, Locken oder einfach nur Haare trocknen - ab sofort perfektionieren Sie Ihren Look mit der Silk Silk Produktserie besteht aus unserem professionellsten und schnellsten Haarglätter für Ergebnisse wie beim Friseur, dem leistungsstarken Silk Haartrockner sowie den drei innovativen Silk Stylern für seidig glänzende Locken und Wellen. Haartrockner Fön Babyliss PRO BAB6510IE , BAB 6510 IE , BAB6510 Caruso Ionic NEU. Wichtig, auch der Haartrockner sollte zu Ihren Haaren passen.
Haartrockner Friseur
TIPP Dyson 305967
Haartrockner Preis
Valera Ionen Haartrockner
Der Oster Pro Power hat zwei Gebläsestufen und drei Temperaturstufen, eine seperate Kaltlufttaste und 1600 Watt. Das Haar trocknet deutlich schneller als mit gängigen Föhnen. Tatsächlich gibt es aber beim Haartrockner selbst einige Unterschiede: Er ist nicht mehr so steinschwer wie der alte. Die Ionen-Technologie bleibt übrigens bei jeder Einstellung aktiv.
Ein guter Föhn muss vor allem handlich, leicht und gut zu bedienen sein. 2100 Watt, mit der gleichen Leistung wie ein 2400 Watt starker Haartrockner, für schnelles Trocknen. Strom sparen: Haartrockner sind wahre Stromfresser.
youtube
Sicher einkaufen.-Frisuren von Vidal Sassoon - Bilder - -Ohnehin sind Frisuren von Vidal Sassoon bis heute wahre Dauerbrenner - natürlich vor allem unter den Kurzhaarfrisuren-Atome? Hm nun haben wir ordentlichen Kabelsalat und ich frag mich ob das besser ist. Dann probieren Sie die neue Technologie doch einfach aus. Profi Haartrockner - Ionen Haartrockner ✅ Desweiteren pflegen sie das Haar und glätten die äußere Schuppenschicht für glänzendes Haar. Im Oktober 2010 ×-Hotel-Haartrockner Produkte Aliseo-Black Mambo 1875.
BaByliss D 372 E Haartrockner Retra Cord 2000 mit Kabelaufwicklung Fön D372E. Der Satin Hair 7 Haartrockner/Föhn mit einzigartigem IONTEC wurde speziell entwickelt, um Austrocknung und... Abhängig vom Reisehaartrockner-Material kann auch das Gewicht dadurch beeinflusst werden. 3.4. Komfort & Haartrockner-Zubehör. Bei Kauf eines Dyson Supersonic Haartrockner Weiß/Silber oder Anthrazit/Fuchsia ohne Box im Dyson Onlineshop erhalten Sie einen gratis Dyson Aufbewahrungsbeutelim Wert von 30,00 €. Aktionszeitraum: 30.05.2018 bis zum 30.06.2018 und solange der Vorrat reicht.
Welchen Haartrockner Kaufen
Durch die ThermoProtect-Temperatureinstellung soll es zu weniger Haarschäden kommen. Kunden sind einfach rund um zufrieden mit BaByliss Haartrockner nach dem Test. Es liegen noch keine Bewertungen für "Clatronic Haartrockner Profi F鰊 mit Diffuser HDT 2939 in Schwarz mit 2000 Watt" vor. Temperaturstufen und Leistung von Ionen-Haartrocknern. Dafür verfügt er über hochwertige Technik, die Ihnen auch auf Reisen oder beim Sport ein solides Fönergebnis garantieren kann. Die meisten Haartrockner sind mit Kipp- oder Schiebeschaltern ausgestattet. Föhns und Haartrockner werden in den verschiedensten Ausführungen angeboten. Preiswerter Profi-Haartrockner mit kräftigem (1950 Watt) und langlebigem Kollektormotor in Friseur-Salon Qualität.
TIPP Profi Haartrockner Leise
Dieser Haartrockner mit einer professionellen Leistung von 2000 W erzeugt einen starken Luftstrom. Welche Vorteile die einzelnen Typen haben, zeigen wir Ihnen in einer detaillierten Aufstellung. Es ist noch keine Bewertung für Remington DB 4110 OP Retro Pink Lady Haartrockner abgegeben worden. Passt auf fast alle AC- und DC-Haartrockner. Auch hier lohnt tuhocphp.com/jeromekafj578/geruchtekuche-am-brodeln-uber-ionen-funktion-beim-fon/ sich beim Online-Kauf ein Blick in die Kundenbewertungen oder die direkte Frage an den Verkäufer. Nach Staubsaugern und Handtrocknern wollen die Briten jetzt auch in den Föhn-Markt frische Luft pusten - mit neuer Technik und einem Modell, das zehnmal teurer als ein herkömmlicher Haartrockner ist. Wichtig ist, dass die Bedienung bequem erfolgen kann und das Gewicht angenehm in der Hand liegt. Ghd Air Wanderlust Haartrockner.
Eine zu große Hitze sorgt jedoch auch immer für Schäden am Haar, sodass bei der Wahl des Haartrockners besondere Aufmerksamkeit und Sorgfalt gefragt ist. Da man bei dem Haartrockner die Temperatur so gut regulieren kann, wird das ihr Haar schonen und es wird noch lange schön aussehen 🙂 Braun Satin Hair 7 HD 780 SensoDryer Haartrockner professioneller Haartrockner. Als Frau braucht man einen Haartrockner und warum Ionen Haartrockner für Dich vorteilhaft sind, wollen wir dir hier verraten. Glanz und Geschmeidigkeit sind weitere positive Nebeneffekte. Diese Möglichkeit ist nämlich nicht bei allen elektronischen Geräten, die sehr praktisch sind und als Werbeträger in Frage kommen, in dieser Vielfalt möglich. Dadurch wird eine statische Aufladung des Haars verhindert - die Haare stehen also nach dem Föhnen nicht ab.
0 notes
Text
WATER TREATMENT - BASIC WATER CHEMISTRY
Water occurs in nature "pure" and what ever be the source always contains impurities either in solution or in suspension. The determination of these impurities makes analysis of water necessary and removal and control of these impurities make water treatment essential.
Water sources:
The various sources of water can be broadly classified as:
a) Rain water
b) Surface water (River, Streams, Ponds, Lakes and Reservoirs)
c) Ground water (Springs, Shallow wells and Deep wells)
of the above, logically rain water is the purest but even this collects and dissolves atmospheric gasses and impurities in air. Further, once in contact with the earth's crust, the rain water will gradually dissolve various materials.
Various (Majour) impurities:
The major impurities of water can be classified in three main groups:
1) Non-ionic and undissolved
2) Ionic and Dissolved
3) Gaseous 1) Non-ionic Impurities: These are mainly, salt, mud, dirt and other suspended matter, micro-organisms, bactiria and other organic matter, oil and corrosion products. It goes without saying that drinking water and most industrial water supplied should be clear and organic-free. 2) Ionic and dissolved Impurities: Any salt which dissolves in water disassociates into positively charged ions called "Cations" and negetively charged ions called "Anions". Since these permit the water to conduct electricity, these salts are called electrolytes. Some of the most common Cations in water are: Calcium, Magnesium, Sodium and Iron, and rarely Ammonium, Potassium and Manganese. These cations are associated with Anions like Bicarbonates, Carbonates, Hydroxides (the sum of which is termed as Alkalinity), Sulfates and Chlorides. Presence of Nitrites and Phosphates is normally not very common. In the water treatment field, the preferred method of expression of these dissolved impurities is in terms of Equivalent Calcium Carbonate, abbrevated to as "CaCO3". This is because Calcium Carbonate is a good common denominator as it has a molecular weight of 100, which facilitates calculations. Moreover, in this form of analysis, the sum of Cations or total Cation always equals the total Anions. Quantitatively, these are expressed in parts per million or milligram/ltr. One part per million equals one ten thousandth of one percent (0.0001%). One part per million means one part in a million parts, for example, one liter in a million liters of water or one Kg in a million Kgs of water. Of all the dissolved impurities, hardness is perhaps the most troublesome. Hardness is due to compounds of Calcium and Magnesium. On heating water caontaining these salts, Carbon Dioxide is released from solution and the Bicarbonates are converted into Carbonates which are insoluble and form scales and deposites. Other salts of Calcium and Magnesium like Sulfates and Chlorides have lower solubility than Sodium salts and participated out at high temperatures. Bicarbonates of Calcium and Magnesium are known as the "Alkaline hardness" or "Temporary hardness" and chlorides, sulfates, nitrates etc., of Calcium and Magnesium are known as "Neutral" or "Permanent hardness". Sodium salts are highly soluble but can be corrosive if present in large quantities such as Sodium Chloride or Sodium Bicarbonate. Dissolved Silica is another troublesome impurity, especially in water fed to Boilers of very high temperatures and pressures. Even in lower pressure boilers, it could form a very hard type of scale by acting as a binding agent. The natural water contains solid, liquid and gaseous impurities and therefore, this water cannot be used for the generation od steam in the boilers. The impurities present in the water should be removed before it'suse in steam generation. The necessity for reducing the corrosive nature & quantity of dissolved and suspended solids in feed water has become increasingly important with the advent of high pressure, critical & supercritical boilers. Impurities in water: The impurities present in the feed water are classified as given below - -- Undissolved and suspended solid materials. -- Dissolved salts and minerals. -- Dissolved gases. -- Other materials (as Oil, Acid) either in mixed or unmixed forms.
A. Undissolved and suspended materials: Turbidity and sediments:
Turbidity in the water is suspended insoluble matter including coarse particles (mud, sediment, sand etc.,) that settle rapidly on standing. Amounts range from almost zero in most ground waters and 60,000 ppm in muddy and turbulent river water. The turbidity of feed water should not exceed 5 ppm. These materials can be removed by settling, coagulation and filtration. Their presence is undesirable because heating or evaporation produces hard stony scale deposits on the heating surface and clog the fluid system. Both are objectionable as they cause damage to the boiler system. B. Dissolved salts and minerals: a) Calcium and Magnesium salts: The calcium and Magnesium salts present in the water in the form of carbonates, bicarbonates, sulfates and chlorides. The presence of these salts is recognized by the hardness of water (Hardness of water is tested by soap test). The hardness of water is classified as temporary and permanent hardness. The temporary hardness is caused by the bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium and can be removed by boiling. The boiling converts the soluble bicarbonates into less soluble carbonates which can be removed by simple blow down method. The permanent hardness of the water is caused by the presence of chlorides, sulfates and nitraes of calcium and magnesium and they cannot be removed just by boiling because they form a hard scale on heating surfaces. A standard amount of measurement of hardness is taken as being the amount of Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) in th water and is referred to in part per million (ppm) or grains per gallon (grains/gallon*17.1=ppm). b) Sodium and Potassium salts: These are extremly soluble in water and do not deposit unless highly concentrated. Their presence is troublesome as they are alkaline in nature and accelerated the corrosion. c) Chlorides: Majority of the chlorides cause increased corrosive action of water. d) Iron: Most common soluble iron in water is ferrous bicarbonate. The water cantaining ferrous bicarbonate deposits become yellowish and reddish sediments of ferric hydroxide if exposed to air. Majority of ground surface water contains less than 5 ppm but even 0.3 ppm can create trouble in feed water system by soft scale formation and accelerating the corrosion. e) Manganese: It also occurs in similar form and it is also equally troublesome. f) Silica: Most natural water contains silica from 1 to 100 ppm. Its presence is highly objectionable as it forms very hard scale in Boilers and forms insoluble deposits in turbine blades. In modern high pressure boilers its presence is reduced as low as 10-50 ppb. g) Microbiological Growth: Various growth occur in surface water (lake & river). The micro-organisms include diatoms, molds, bacterial slimes, algae, manganese & sulphate reducing bacteria and many others. These can cause coating on Heat Exchanger and clog the flow passages and reduce the heat transfer rates. h) Colour: Surface waters from swampy areas become highly colored due to decaying vegetation. Colour of feed water is objectionable as it causes foaming in Boilers and may interfere with treatment processes. It is generally removed by chlorination and absorption by activated carbon. C. Dissolved Gases: a) Oxygen: It presents in surface water in dissolved form with variable percentage depending upon the water temperature and other solid contents in water. Its presence is highly objectionable as it corrosive to iron, zinc, brass and other minerals. It causes corrosion and pitting of water lines, boiler tubes. Its effect is furthur accelerated at high temperatures. b) Carbon Dioxide: The river water contains 50 ppm and well water contains 2 to 50 ppm of C02. It also causes the corrosion of stream, water and condensate lines, It also helps to accelerate the corrosive action of oxygen. wThe other gases are H2S, CH4, N2, and many others but their percentages are negligible, therefore, their effects are not discussed here. D. Other minerals: a) Free Mineral Acid: Usually present as Sulphuric or hydrochloric acid and causes corrosion. The presence is reduced by neutralization with alkalis. b) Oil: Generally, the lubricating oil is carried with steam into the condenser and through the feed system to the Boiler. It causes sludge, scale and foaming in Boilers. It is generally removed by strainers and baffle seperators. The effects of all the impurities present in the water are the scale formation on the different parts of the boiler system and corrosion. The scale formation reduces the heat transfer rates and clog the flow passage and endager the life of the equipments by increasing the temperature above safe limit. The corrosion phenomenon reduces the life of the plant rapidity. Therefore, it is absolutely necessary to reduce the impurities below a safe limit for the proper working of the power plant. C. Dissolved Gases: The atmosphereic gases found in naturally occuring waters, only two Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen, are the main causes of many corrosion related problems.
via Blogger http://bit.ly/2UCZvBh
0 notes