#laravel 5.8 user auth
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Photo

Laravel-5.8: Admin Panel (Part-2) | Custom Login & Register System for User & Admin – Auth Command Here.. in this video, i have done a login and registration system with laravel auth command.. and made some changes in the registration form. source
1 note
·
View note
Text
Laravel 6.0: What You Should Know

Since the inception of Laravel 5.0 around 4.5 years ago, the Laravel ecosystem has blossomed into something that leaves users nothing to complain about, to say the least. Laravel Nova, Laravel Horizon, Laravel Echo, Laravel Scout, and Laravel Passport are just some of the tools that have been introduced since then. At the time of this writing, we’re on Laravel 5.8 and Taylor Otwell has decided to skip past 5.9 on to 6.0 on the 3rd of September. Previously, Taylor has stressed that this won’t be a major paradigm shift for Laravel and the most significant change will be the transition to semantic versioning. However, this doesn’t mean that there aren’t plenty of new features worth talking about.
Let’s dive into some of the smaller changes first.
The Smaller Things
Authorization

Authorization messages can now be made easier for users to understand. Before Laravel 6.0, the infrastructure wasn’t in place to easily give a specific response to a user when they were given an authorization-related error. The status code could be given fairly easily, but giving a custom error message was more complicated back then. Giving a custom messaged required the developer to create a new file and write their own exceptions.
Now, to get a customizable authorization response, you can simply use the Gate::inspect method when linking to the function that enables you to receive the response. Delivery of the message to the front-end is also easy to organize. Simply add $this->authorize or Gate::authorize to a suitable route or controller.
No More Default Front-End

The typical front-end setup you are given when you first start a Laravel project is now gone. This means the Vue and Bootstrap code you would usually see, would have now been removed. What it’s been replaced with is unknown. Perhaps, it hasn’t been replaced. Strangely, the make:auth command, used to provide the login system scaffolding is now not a part of the original Laravel install either. To be honest, the rationale behind this change is unclear to me. However, given Laravel’s versioning adjustment, it makes sense that third-party technologies like Vue and Bootstrap that haven’t recently undergone the same changes could cause conflict. Though, this is merely speculation.
If you want access to the old UI, you can extract a composer package that contains it with the CLI: composer require laravel/ui and php artisan ui vue --auth.
Lazy Collections

This is one of the more interesting additions. If you’re new to Laravel, Collections are tools that make it easier for you to manipulate arrays. Eloquent, one of the two main tools in Laravel used to communicate with databases, returns its queries as Collection instances. Check out the docs for Collections if you think you’re gonna lack context in a moment. https://laravel.com/docs/5.8/collections
So, what are Lazy Collections? Traditional Collections are often used for working with large amounts of data. When they run into data-heavy files, they’ll try and store all of that data at once. This may sound quick and convenient but the downside is that this is very memory-taxing. Lazy Collections solve this problem by only storing the part of the file they need, and thus, save memory usage and boost performance.
If you understand how lazy loading works then you’ll be familiar with my previous explanation. Lazy loading works the same way. When you make a request to the server with lazy loading implemented, the browser will only return the part of the web page it knows you’re going to use immediately. Then, when the user scrolls down the page or clicks on an internal link, the server will provide you the necessary content it knows you need. This way, only memory that is needed at that particular moment is being used. This method increases speed. Lazy Collections is kind of like lazy loading but with arrays from a database and not content on a webpage.
The Bigger Things
Laravel Ignition
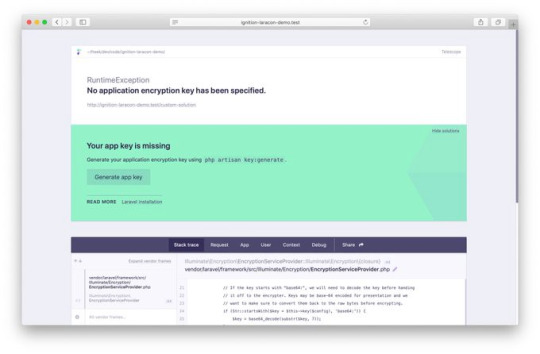
So yeah, the new error page for Laravel is called Ignition and it looks awesome. It’ll be the default error page for Laravel when 6.0 releases. However, if you don’t feel like making the switch to 6.0 just yet, that’s fine, you can still install Ignition on previous versions. Let’s talk about what Ignition brings to the table.
With Whoops (the current default Laravel error page), stack traces and relevant code snippets are shown in an error page, but this doesn’t always lead the developer to the solution. Worse, sometimes the stack traces just reference compiled paths. This can it make it difficult to find the necessary non-compiled files to fix because they aren’t listed anywhere on the error page. Thankfully, this isn’t a problem with Ignition, it can display to you the non-compiled file where the problem actually exists. By clicking on a pencil icon, you can go directly to the file in your chosen editor.
The second coolest feature of Ignition is that it can display potential solutions when displaying an error message. Most error pages just leave you with the error. For example, if the error is that you misspelled a property name, Ignition will tell you that the property has been misspelled and offer you the correct spelling. Solution suggestions can be way more sophisticated than this, I’ll link you to the source down below. Your suggestions are even customizable!
You wanna know the coolest feature? These solution suggestions are actually runnable!

Yes, really. Take a look at this short demo by one of the creators, Freek Van der Herten.
https://youtu.be/EZu0-CwTU9Q
Also, you can add your own runnable solutions too! This is great as Ignition is open source so people in the Laravel community will undoubtedly contribute their own solutions for everyone to use.
There’s a bunch of other cool features too such as creating your own tabs (yes Ignition has tabs) and sharing your error messages with other people. This is done using Flare, a tool that comes with Ignition.
For everything about Laravel Ignition and Flare, visit https://freek.dev/1441-ignition-a-new-error-page-for-laravel.
Laravel Vapor

Another big one. Laravel Vapor is a serverless deployment platform for Laravel. But wait, why do we need a deployment platform? We already have Laravel Forge, right? As beloved as Forge is amongst the Laravel community, it does have its limitations. It doesn’t have autoscaling to deal with large sudden increases in traffic that prevent your site from crashing. Also, configuration is required when OS or PHP updates occur. Vapor has autoscaling, so, you don’t have to worry about sudden spikes in your traffic causing website downtime. In addition, because of the serverless structure of Vapor, it also handles all the updates you may stress about when using Forge.
Vapor’s website is very clean looking and everything seems easy to find. When you deploy a project, you can see the different stages of the deployment process loading on the UI. I find this to be very reassuring and comforting. You can also rollback your application with a click of a button. Just click on “rollback” and it’ll do just that. Pretty neat. Same deal if you want your app to undergo maintenance. Just click on the “maintenance mode” button.
Another cool feature of Laravel Vapor is that you’re able to set alarms. What do I mean by that? For example, to know when your website traffic suddenly blows up, you can set a certain amount of HTTP requests per minute, and if your website hits that limit, the alarm will go off, informing you of the surge in traffic. Taylor Otwell showcases this and other conditionals in his Laravel Vapor demo which I’ll link to below.
There’s so much to cover with Laravel Vapor and the Laravel update itself. Because of this, I didn’t really want to dive into the complexities too much in this post. To learn more about the technical aspects of Laravel 6.0, you can take a look at the release notes here https://laravel.com/docs/6.0/releases. For more info on Laravel Vapor, visit this video by Taylor Otwell https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XsPeWjKAUt0&t=362s.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Vanguard - Advanced PHP Login and User Management
New Post has been published on https://intramate.com/php-scripts/vanguard-advanced-php-login-and-user-management/
Vanguard - Advanced PHP Login and User Management

LIVE PREVIEWGet it now for only $35

Vanguard is PHP application, written in Laravel PHP framework, that allows website owners to quickly add and enable authentication, authorization and user management to their website. It is designed following latest security and code standards and it is ready for high availability websites. Although it is written in Laravel, it can be used to provide secure login, authentication, authorization and complete user management for any PHP powered website. Vanguard also comes with fully documented JSON API which allows you to easily authenticate users from your mobile (or any other) application.
It comes with almost three hundred automated tests (functional and unit), that cover all vital parts of the application and the API and ensures it’s maintainability and stability.
Version 5.0.1
Features
Secure user registration and login
Social Authentication using Facebook, Twitter and Google+
Password reset
Two-Factor Authentication
Remember Me feature on login
Login with email or username
Google reCAPTCHA on registration
Authentication Throttling (lock user account after few incorrect login attempts)
Interactive Dashboard
Unlimited number of user roles
Powerful admin panel
Unlimited number of permissions
Manage permissions from admin interface
Assign permission to roles
Easily check if user has permission to perform some action
JSON API to build any kind of applications around Vanguard
Super easy installation using installation wizard
User Activity Log
Avatar upload with crop feature
Built using Bootstrap 4
Active Sessions Management (see and manage all your active sessions)
Admins can impersonate users
Full unicode support
Client side and server side form validation
Fully customisable from settings section
Complete and detailed documentation
Fully object oriented and commented PHP and JavaScript code.
Localization support – Translate the application to any language (English, Serbian and German translations included)
Runs on PHP 7.2.5+
Flexible Plugin System
Security
CSRF Protection – all forms include CSRF token
Session Protection – highly secure Laravel session mechanism
Highly secure one-way password hashing
Server Requirements
PHP >= 7.2.5
BCMath PHP Extension
OpenSSL PHP Extension
PDO PHP Extension
Mbstring PHP Extension
Tokenizer PHP Extension
Ctype PHP Extension
XML PHP Extension
JSON PHP Extension
GD PHP Extension
Fileinfo PHP Extension
Demo and Documentation
Demo link: https://demo.vanguardapp.io
Admin Credentials
Username: admin
Password: admin123
Documentation and Support: https://milos.support-hub.io/
Discount Notifications
Subscribe to receive notifications about discounts and updates: https://vanguardapp.io/#subscribe
Changelog
Check the docs for upgrade guide.
April 8, 2020 – Version 5.0.1
Fixed installation wizard
April 5, 2020 – Version 5.0.0
Fixed custom login redirect issue Upgraded to Laravel 7 Switched to Laravel Sanctum for API authentication Replaced API transformers with Laravel's API Resources Changed API response format
September 16, 2019 – Version 4.0.1
Fixed password reset email issue Fixed avatar upload issue Updated registration and email verification flow
September 13, 2019 – Version 4.0.0
Added Plugin Support Upgraded to Laravel 6
April 1, 2019 – Version 3.2.1
Fix installation issue
March 30, 2019 – Version 3.2.0
Upgraded to Laravel 5.8 Replaced deprecated Larvel str_ and array_ helper functions
October 30, 2018 – Version 3.1.0
Upgraded to Laravel 5.7 Fixed issue with API when country_id field is null Fixed Notifications Settings update bug Improved Two-Factor Authentication by adding one more step for phone verification Added Impersonate feature
June 14, 2018 – Version 3.0.1
Minor bug-fix release to address a few mostly UI related bugs. List of changed files available inside the upgrade guide.
May 17, 2018 – Version 3.0.0
Complete frontend re-write with Bootstrap 4 Remove additional step for Twitter authentication since Twitter can provide an email now Update sizes of the avatars retreived during social authentication
March 13, 2018 – Version 2.2.0
Upgrade to Laravel 5.6 Fix issue with Authy secret key and config caching Fix issues with registration history chart Fix installation issue on PHP 7.2
December 19, 2017 – Version 2.1.1
Added ability to configure dates format across the app Added automatic session invalidation and log out of the user if he is banned by the administrator Added device info on session list page Updated dashboard chart to display data in last 365 days (instead of for current year) Extracted model factories to different files (important for testing purposes only) Fixed autoload include issue for existing websites
November 08, 2017 – Version 2.1.0
Upgrade Laravel to version 5.5 Fix glitch on User Acivity search
September 14, 2017 – Version 2.0.2
Fix avatar update issue when admin is updating avatar for some other user Disable API authentication for banned and unconfirmed users Fix country update issue which occures on some MySQL versions
August 25, 2017 – Version 2.0.1
Fix installation issues from previous version Update documentation
August 23, 2017 – Version 2.0.0
Add fully tested JSON API Fix some minor glitches related to translation
May 1, 2017 – Version 1.3.3
Fix incompatibility issues between laravel-jsvalidation package and Laravel Framework version 5.4.19+ Fix issue where country is set to null after user logs in
April 12, 2017 – Version 1.3.2
Removed zizaco/entrust package and replaced with Vanguard's native mechanism for handling roles and permissions $user->can() method now use Laravel's default authorization mechanism. For checking if user has permission defined by Vanguard, you should use $user->hasPermission('...').
March 06, 2017 – Version 1.3.1
Fixed installation issue Fixed issue with FORCE_SSL
February 18, 2017 – Version 1.3.0
Laravel 5.4 upgrade IMPORTANT: Fixed potential security issue with user avatar upload Fixed issue to don't allow banned users to log in via social networks Expanded and updated automated tests to cover all bugs and issues from above
September 30, 2016 – Version 1.2.1
Fixed bug when creating/updating users from admin panel without selected country Fixed small typos on delete user confirmation popup
September 27, 2016 – Version 1.2.0
Updated to Laravel 5.3 InnoDB is now forced storage engine for MySQL database Slightly improved design E-Mail templates updated (now using Laravel 5.3 Notifications feature) Fixed default country value Fixed n+1 problem for activity page (added missing eager loading) Fixed translation glitches Added IIS configuration file PHP 5.6.4 is now minimum PHP version required (Laravel 5.3 requirement) PHP XML extension is now requirement (Laravel 5.3 requirement) Updated and extended documentation Dropped support for HHVM, since Laravel 5.3 does not support it
March 30, 2016 – Version 1.1.2
Add missing middleware to redirect user to install page if Vanguard is not installed
March 29, 2016 – Version 1.1.1
Added German translation files Add translation for few missed strings Fix some small bugs
March 15, 2016 – Version 1.1.0
Add localization support Use social network profile image as default avatar after social auth Fix problems with pagination while browsing search results for users and activities Handle missing email from non-twitter social provider
February 18, 2016 – Version 1.0.4
Updated documentation Added option to allow redirect to custom page after login Disable access to login page for authenticated users
February 4, 2016 – Version 1.0.3
Updated documentation Fixed css glitches Added more tests
January 25, 2016 – Version 1.0.2
New design for error pages Updated installer to require Fileinfo extension
January 22, 2016 – Version 1.0.1
Add missing configuration placeholder file
January 21, 2016 – Version 1.0.0
First release
LIVE PREVIEWGet it now for only $35
0 notes
Text
Laravel Multi Auth – Lara 5.8, 5.7, 5.6 Multiple Authentication
Laravel Multi Auth – Lara 5.8, 5.7, 5.6 Multiple Authentication
Multi Laravel Authentication (auth) – Today we will show you how to create a multi auth system in laravel 5.8. Mulitple auth system means that many users can log in one application according to their role.
Multiple authentication is very important in large applications 5.6, 5.7, 5.8. Authentication is the process of recognizing user credentials.
In this multi-auth laravel system, we will create a…
View On WordPress
#laravel multi auth#laravel multi auth 5.8#laravel multi auth admin and user#laravel multi auth api#laravel multi auth github#laravel multi auth guard#laravel multi auth logout#laravel multi auth package#laravel multi auth using guard#laravel multi authentication
0 notes
Text
What’s New Features in Laravel 6.0 Release in Sep 2019
As developers, our job is not only to create applications that work but also to give them support so that they can be maintained throughout their useful life. In the case of Laravel, major updates that bring new features, improvements and corrections are made every 6 months.
However updating a project developed in Laravel from one version to another is not as complicated as it seems. Click To Tweet
In this article, we will tell you what are the most important changes and the steps to update your application from Laravel version 5.8 to 6.0.
Especially knowing that it will be an LTS version, that is, it will have support for corrections of security problems until September 2022.
What requirement we need for use of Lavarel 6.0 :
Before doing any update step, we must confirm that our application can be updated to Laravel 6.0 or not.
The version of the application to be updated is Laravel 5.8. Otherwise, you must update it to that version. Take into account that Laravel 5.9 does not exist due to the changes made to the versioning of the framework.
The production server and other environments must have PHP 7.2 or higher, as it is the new minimum requirement of Laravel 6.0 because PHP 7.1 will have active support until December 2019.
Since Laravel 6.0 announced, all need to confirm that each of the third-party packages used in the application can work with Laravel 6.0? To do this you should check their official pages or repositories.
Some recommendation
Use Git to avoid problems if something fails and you cannot solve, we recommend you create a new branch to update so that the code of your working project will be supported.
Default auth with ui:auth, make:auth Removed
Laravel team has removed default make:auth command and introduced new command which is ui:auth.
To use this package, first of all, you have to install it using the below command.
composer require laravel/ui
After installing this package you have now many commands to generate Ui code with authorization.
You can see all new commands using the below command.
php artisan ui –help
If you want to set the default as vue or react instead of bootstrap then use below command.
php artisan ui vue
php artisan ui react
Now you can make your default auth scaffolding using below command
php artisan ui:auth
If you want to generate only views then run below command.
php artisan ui:auth –views
String and Array Default Functions Removed and Moved to Package
Now there is no default helper function for array and string. All str_ and array_ helper functions have been removed and moved to a new package called helpers. You can install it in your project using the below command.
composer require laravel/helpers
Carbon 1.0 Removed and Supported Carbon 2.0
There is no support for carbon 1.x longer in Laravel 6 because now they have updated it to carbon 2.x. You can read it from here: https://ift.tt/2nGBuJS
Lazy Collection with New Cursor Method in Eloquent
Suppose you a very large dataset in your project and you want to iterate them with the condition then these will be time taking in Generator but using Lazy Collection you can do it with low memory consumption.
In the older version of Laravel return an instance of Generator, now it will return an instance of Lazy Collection.
$blogs = App\Blog::cursor();
foreach ($blogs as $blog) {
//
}
Primary Key Type Declaration in the Model
Now you can define your table primary key as a string instead of an integer using below syntax.
protected $keyType = ‘string’;
BelongsTo::update Method Update in Eloquent
Suppose you have two model attached via a belongsTo relationship and receive mass assignment then you can call update method direct on the model like below.
$comment->blog()->update([‘foo’ =>’bar’]);
$comment->blog->update([‘foo’ =>’bar’]);
Authorization Response
In older version of laravel it was very difficult to show custom error messages in default auth, but now there is new method Gate::inspect which provides the authorization responce.
$my_response = Gate::inspect(‘view’, $dashboard);
if ($my_response->allowed()) {
// User can see Dashboard…
}
if ($my_response->denied()) {
echo $my_response->message();
}
Input Facade Removed Permanently
In a very old version of Laravel, we have used the Input facade, which is work like Request facade. But now in a new will, it was removed permanently. Now if you wish to use Input::get method then you have to call it like Request::input method. All other calls to the input facade may simply be updated to use the Request facade.
Conclusion
Laravel is a fast, free and open-source PHP development framework. Whose main goal is to allow you to work in a structured and fast manner. Laravel takes the monotony of web development. It provides all the tools you need to get you started programming whatever you need, it’s built to be simple and easy to learn.
The post What’s New Features in Laravel 6.0 Release in Sep 2019 appeared first on Digital Ideas.
source https://www.inpeaks.com/2019/09/26/whats-new-features-in-laravel-6-0-release-in-sep-2019/
0 notes
Link
はじめに 皆様こんにちは。OPTiM新卒1年目エンジニアの青木です。 前回は早押しボタンなんかを作っていました。 tech-blog.optim.co.jp 今回は、PHP フレームワークの Laravel を、PostgreSQL と Vue.js と組み合わせて作成する TODO アプリを通して紹介します。 このフレームワークらはこちらの記事でも密かに利用しています。 tech-blog.optim.co.jp OPTiMではあまり利用されていませんが、一���のアプリケーションで実利用されている箇所もございます。 PHPは昔のイメージからかなり避けられていていますが...今のPHPとそのフレームワークはすごく発展していてとても使いやすいので是非使っていただきたい!という気持ちがあります。 ですが、現状はあまり利用していただけなくて個人的には悲しい気持ちでいっぱいです。 そんなPHPですが、フレームワーク(LaravelやFuelPHPなど)を利用することにより未利用時よりも高速かつ安全に開発することができます。 そんなフレームワークの紹介を「TODOリストアプリケーション」を作りながら見ていきましょう。 PHPフレームワーク「Laravel」 今回ご紹介するのはPHPフレームワークの「Laravel」です。 Laravel - The PHP Framework For Web Artisans laravel.jp フレームワークの仕様に乗っかって開発することによりかなり安全で可用性のあるアプリケーションの開発が容易になります。 個人的にLaravelのいいところはズバリ 爆速安全開発 です。 本当に手早くWebアプリケーションが作れます。 今まで数人で作業していたものをたった一人で1週間もあればかなり強い物が作れます! 2019年8月5日現在のLaravel最新バージョンは「5.8」で「5.7」のマイナーアップデートとなっています。 Laravelは奇数バージョンがメインとなっており、中でもLTSとなっているのは「5.1」「5.5」となっています。セキュリティフィックス期限はLTSで3年間、一般的なリリースについては1年間のサポートとメンテナンスがされています。 このように、言語仕様だけではカバーできないセキュリティの担保もフレームワークが担ってくれることにより、PHP5以前の時代よりも遥かに強くなっています。 ここで、Googleトレンドより注目度を比較してみましょう。 実は代表的なWebフレームワークの「Ruby on Rails」や「Django」などよりもLaravelの注目度が上がってきています。 日本ではダントツで「Ruby on Rails」が多く見られます。 海外での「Laravel」の注目度が上がってきているようですね。 Laravelは機能がとても豊富です。ですからファイルサイズ的にも大きくなりますし、環境にも負担がかかってしまいます。 そんな時は「Lumen」を利用しましょう。ここではあまり解説しませんが、「Lumen」は「Laravel」の軽量版として開発されています。 とっても雑に説明するとNode.jsのExpressのような感じですね。 さて、前置きが長くなりましたが、本題に移りたいと思います。 今回の目標 PHPフレームワークLaravelで、DBを使用したSPA(Single Page Application)のTODOアプリを作ります。 またログイン認証によるユーザ管理も同時に行っていきます。 完成形 この記事の最後にはこのようなアプリケーションが出来上がります。 ユーザの新規登録・ログイン・ログアウト ログインユーザごとのTODOの表示・追加・更新・削除 最低限のView 使用する技術 PHP Laravel Vue.js PostgreSQL Docker 導入・環境構築 PHPの導入 LaravelでバージョンごとにPHPに対する要件が決められています。 現時点でのPHPの最新バージョンは「7.3.8」 現時点でのLaravelの最新バージョンは「5.8.17」 Laravel「5.8.*」で求められるPHPの要件は以下のとおりです。 = 7.1.3 BCMath PHP拡張 Ctype PHP拡張 JSON PHP拡張 Mbstring PHP拡張 OpenSSL PHP拡張 PDO PHP拡張 Tokenizer PHP拡張 XML PHP拡張 これに応じてPHPの導入を行いましょう。 ちなみにHomebrewでインストールした場合は「7.3.7」がインストールされました。こちらのバージョンでも要件を満たしておりますので大きな問題はありません。 ※ただしセキュリティ等の関係上最新バージョンを使うに越したことはありません。下調べは慎重にかつ念入りに行いましょう。 Composerの導入 Laravelを構築するためのパッケージマネージャが必要となります。 PHPの代表的なパッケージマネージャである「Composer」を導入しましょう。 curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer composer config -g repositories.packagist composer https://packagist.jp HelloWorld(プロジェクトの作成) さて、いよいよプロジェクトを作成していきます。 「Laravel」では以下の1コマンドのみでプロジェクトの新規作成が行えます。 $ composer create-project laravel/laravel Techblog_sample ビルトインサーバの起動 Laravelに標準搭載されているartisanコマンドでビルトインサーバを起動してみましょう。 簡単ですね。環境構築後からはたった3コマンドしか叩いていませんが、HelloWorld同等の画面まで出せました。 データベースの導入とAuth実装 データベースの導入を行います。 今回はPostgreSQLを利用していますが、MySQLやSQLiteなども対応しています。 PostgreSQL導入 (Docker使用) LaravelとDBの接続 Auth(認証)導入 PostgreSQL導入 (Docker使用) PostgreSQLを構築します。 こちらは皆様のお好きな方法で構��していただいて構いません。 あくまで一例として記載いたします。 データベースを開発機にそのまま構築しても良いですが、比較的構築の簡単なdocker-composeを利用して構築をしたいと思います。 docker-compose.yml version: '2' services: db: image: postgres:11-alpine ports: - "15432:5432" environment: POSTGRES_USER: "postgres" POSTGRES_PASSWORD: "password" POSTGRES_DB: "techblog" 5432/tcp データベースの構築が終わりました。 LaravelとDBの接続 LaravelとDBサーバを接続します。 こちらはデフォルトで環境変数から接続情報を取得するようになっており、環境変数を変更することにより接続情報を更新できます。 また、環境変数に存在しなかった場合はディレクトリに存在する.envファイルを参照するようになっています。 .envファイルを以下のように変更してください。各自で構築された場合は構築した際の情報に都度変更してください。 .env ... DB_CONNECTION=pgsql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=15432 DB_DATABASE=techblog DB_USERNAME=postgres DB_PASSWORD=password ... 接続確認は次のAuth作成時に確認します。 Auth(認証)導入 LaravelにAuth(認証)を追加します。 至って簡単です。 $ php artisan make:auth Authentication scaffolding generated successfully. 以上です。 試しにビルトインサーバを立ち上げ、確認をしてみましょう。 お気づきの方が既にいらっしゃるかもしれませんが、右上にログインボタンなどが現れています。 試しにログインボタンを押してみましょう。 ログイン画面が構築されています。 たった1コマンドで ログイン画面 新規登録画面 パスワードリセット画面 が実装されます。 素晴らしいですね。 ただ、いまのままですとDBにアクセス出来ていません。 以下のコマンドを入力してマイグレーション���行いましょう。 $ php artisan migrate Migration table created successfully. Migrating: 2014_10_12_000000_create_users_table Migrated: 2014_10_12_000000_create_users_table Migrating: 2014_10_12_100000_create_password_resets_table Migrated: 2014_10_12_100000_create_password_resets_table これで新規登録などが出来るようになりました。 デフォルトではセッションでログイン情報を管理します。 コマンドライン(Tinker)でDBデータ確認 artisanコマンドによるデータ確認を行ってみたいと思います。 Laravelにはデフォルトでtinkerと呼ばれる対話型ツールが存在します。 こちらを利用することにより、ソースコードにする前に動作確認が出来ます。 また、Laravelに読み込まれるモジュール等が手動で読み込める状態になっているので、Laravelで開発する際はおすすめの動作確認方法です。 LaravelからDBにアクセスするために、クエリビルダを利用します。 作業をするそのまえに データベースにデータを入れるため、一旦画面上から新規登録を行ってみましょう。 しっかりと新規登録されていますね。 また、こういった事もデバッグとして利用できます。 false コマンドライン上でセッションも利用できるということですね。 独自で作成したサービスモジュールなんかも利用出来るので、是非デバッグなどにご利用ください。 テーブル設計 TODOアプリケーションを制作するに当たってテーブルを構築しなければいけません。 今回は1ユーザが複数のTODOを持てるように設計します。 テーブル設計は前項でも利用した Migration を利用します。 $ php artisan make:migration create_todos_table Created Migration: 2019_08_05_065824_create_todos_table database/migrations/2019_08_05_065824_create_todos_table.php <?php public function up() { Schema::create('todos', function (Blueprint $table) { $tablebigIncrements('id'); $tablestring('todo'); // この行を追加 $tableinteger('user_id'); $tabletimestamps(); }); } public function down() { Schema::dropIfExists('todos'); } 作成できたら、マイグレーションを実行してデータベースに反映させましょう。 $ php artisan migrate Migrating: 2019_08_05_065824_create_todos_table Migrated: 2019_08_05_065824_create_todos_table これで新たにテーブルが作成されました。 ここまで ここまではLaravelの導入、環境構築、Authの導入を行いました。 PHPでのコーディングをほぼ無しとしてここまで作れました。 次は、実際にルーティングやMVCなど、Laravelのメイン機能についてご紹介していきます LaravelのMVCとその他の機能 ルーティング コントローラ(C) ビュー(V) モデル(M) ミドルウェア ログイン後のリダイレクト先 実装するページ Authは自動で実装されるので割愛しています。 TODOアプリケーションはSPAで作成し、APIを叩いて操作を行います。 ルーティング いよいよ基盤が完成したので、ルーティングの説明に入ります。 Laravelのルーティングは routes ディレクトリ内に存在し、それぞれのファイルは用途によってプレフィックスが初期でつけられていたりします。 今回は web.php を編集していきましょう。 routes/web.php <?php Route::get('/todo', function () { return "このページはアプリケーションのページです"; }); このルーティングを追加すると、画像のように表示されます。 今回はSPAなのであまり使いませんが、SPAではないアプリケーションを作る場合は基本的にここに記述していきます。 また、 api.php に作成することで自動的に/api/のプレフィックスが付きます。任意のプレフィックスに変更したい場合は app/Provider/RouteServiceProvider.php を変更しましょう。 さて、このままではクロージャがどんどん膨れ上がって行ってしまいますので、次の工程でしっかりと分業してあげます。 コントローラ web.php がロジックでどんどん汚染されていくので、コントローラと呼ばれるもので分業していきましょう。 下記のコマンドでコントローラが自動生成されます。 $ php artisan make:controller TodoController Controller created successfully. TodoController.phpの中にメソッドを生やし、web.phpから読み込んでみましょう。 app/Http/Controllers/TodoController.php <?php namespace App\Http\Controllers; use Illuminate\Http\Request; class TodoController extends Controller { public function index() { return "コントローラからこんにちは"; } } routes/web.php <?php Route::get('/todo',TodoController::class . "@index"); 実装が出来たら、php artisan serveで見てみましょう。 いかがでしょうか。 コントローラに分割することによってルーティングによる画面や機能別にロジックを記述することが可能になりました。 ビュー では、ビューを表示してみましょう。 Laravelのビューは強力なbladeテンプレートエンジンを含んでいます。 コントローラから変数を渡し、bladeテンプレートエンジンにより表示してみます。 $ touch resources/views/todo.blade.php resources/views/todo.blade.php <?php @extends('layouts.app') @section('content') <div class="container" <div class="row justify-content-center" <h2TODO アプリケーション</h2 </div </div @endsection @から始まるものはbladeテンプレートエンジン特有のメソッドです。 今回は既に用意されているレイアウトデザインを利用します。 上記のファイル作成が終われば、TodoController.phpを変更していきます。 view()メソッドにbladeテンプレートのファイル名を記入すればviewが帰ります。 app/Http/Controllers/TodoController.php <?php namespace App\Http\Controllers; use Illuminate\Http\Request; class TodoController extends Controller { public function index() { return view('todo'); } } モデル Eloquent ORM と呼ばれる非常にシンプルかつ高機能なORMがLaravelでは提供されています。 ここでいうモデルとはEloquentモデルのことであり、Eloquent ORMの利点を最大限生かされたものです。 まずはじめに、モデルを作成しましょう。 $ php artisan make:model Todo 基本的にはこれで終わりです。 テーブル名が todos であれば、モデル名は Todo モデル名が Sample であれば、テーブル名は samples この方式で決定しています。 仮にテーブル名とモデル名を変更したい場合はモデルファイル(app/モデル名.php)のクラス変数に <?php protected $table = 'テーブル名'; と指定することが出来ます。 では、確認してみましょう。 Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection {#2981 all: [ App\Todo {#2980 id: 2, todo: "TestTest", user_id: 1, created_at: null, updated_at: null, }, ], } insert文で追加してみました。 しっかりと反映されていますね。 モデル(リレーションの定義) モデルにリレーションを定義することが出来ます。 かなり便利なので是非使っていきたいところです。 今回のリレーション内容を再確認してみましょう。 users.id と todos.user_id が紐付いていますね。 これをユーザ側のモデルからtodosを参照出来るようにモデルに定義していきます。 app/User.php <?php class User extends Authenticatable { ... 省略 public function todos(){ return $thishasMany('App\Todo'); } } これで実装が終わりです。 Tinkerで確認してみましょう。 を利用することでユーザに紐付いたTodos���ーブルのレコードを受け取ることが出来ます。 ミドルウェア ルーティングする際に、特定のページらに一定の操作を与えたい。 などのニーズに応えるのがミドルウェアです。 現状問題となっているのは、ログインしていなくても/todoにアクセス出来てしまうということです。 ログインしていないのにTodo画面へ遷移されてはとても困ります。ユーザ毎に情報を表示するのにそのユーザが誰かわからないのでエラーが出てしまいます。 かといって、毎ページ同じ動作を記述するのはとてもスマートとは言えません。 そこで、ミドルウェアの登場です。 説明よりやってみたほうが早いので、コードを記述します。 routes/web.php <?php Route::group(["middleware""auth"],function(){ Route::get('/todo',TodoController::class . "@index"); }); Route::groupの第2引数のクロージャに先程の /todo を入れてみましょう。 すると、/todoにアクセスしようとするとログイン画面へリダイレクトします。これでログイン判定が出来るのでいちいちコントローラ内部にロジックを書くことはありません。 また、ミドルウェアは自作することが出来ます。後ほどAPI作成の際にひつようになりますのでそちらで詳しく解説いたします。 ログイン後のリダイレクト先 現状、新規登録・ログイン後に /home へリダイレクトしていると思います。 これはLoginController.php などが自動的にリダイレクト処理を行っているからです。 今回は/homeを利用しませんので、削除する方法を記載します。 app/Http/Controllers/Auth/LoginController.php app/Http/Controllers/Auth/RegisterController.php app/Http/Controllers/Auth/ResetPasswordController.php app/Http/Controllers/Auth/VerificationController.php - protected $redirectTo = '/home'; + protected $redirectTo = '/todo'; resources/views/home.blade.php 削除 routes/web.php name('home'); これでログイン後は /todo へリダイレクトします。 TODOアプリケーションのメイン機能実装(サーバーサイド実装) APIの実装 まずはじめにAPIの実装を行います。 今回のAPIでの認証は、セッションで行いたいと思います。 機能一覧 TODOアプリケーションを作成するに当たって、APIの機能を洗い出します。 こちらの機能を作成していこうと思います。 機能実装 まず、コントローラに定義します。 app/Http/Controllers/TodoController.php <?php use App\Todo; use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth; class TodoController extends Controller { ... 省略 public function get(){ // 全件表示 } public function post(){ // 1件追加 } public function delete(){ // 1件削除 } public function update(){ // 1件更新 } } 次に、ルーターに追加していきます。api.phpになっているので注意してください。 route/api.php <?php Route::get('/todo','TodoController@get'); Route::post('/todo','TodoController@post'); Route::delete('/todo/{id}','TodoController@delete'); Route::put('/todo/{id}','TodoController@update'); 次は確認をはさみつつ、それぞれの機能を実装していきます。 全件表示 <?php public function get(){ return response()json(Auth::user()todos()get()); } モデルの説明の時に行ったものと同じです。 1件追加 <?php public function post(Request $request){ $todo = new Todo(); $todotodo = $requesttodo; $todouser_id = Auth::id(); $todosave(); return response("OK", 200); } モデルでインスタンスを生成し、それぞれに値を当てはめてから最後にセーブをすればSQLを発行して追加処理を行ってくれます。 Todo::insert()でも同じことが行なえます。 1件削除 <?php public function delete($id){ Todo::find($id)delete(); return response("OK", 200);; } Todoのインスタンスにdeleteメソッドがありますので、それを実行すれば削除できます。 1件更新 <?php public function update(Request $request,$id){ $todo = Todo::find($id); $todotodo = $requesttodo; $todosave(); return response("OK", 200); } 追加の時とほぼ同じで、findでtodoのインスタンスを持ってくるだけで出来上がります。 APIのAuth実装 このままでは誰でもAPIにアクセスできてしまいます。 しかもコード内部で Auth::を利用しているので、ログインしていないユーザがアクセスするとエラーが発生します。 ここではそのAuth(認証)をAPIからでも行えるように変更、追記していきます。 セッションを有効化 APIではデフォルトでAuthorizedTokenを利用するような設計になっています。 今回はセッションを利用するので以下のように変更します。 app/Http/Kernel.php <?php // 省略 protected $middlewareGroups = [ 'web' [ \App\Http\Middleware\EncryptCookies::class, \Illuminate\Cookie\Middleware\AddQueuedCookiesToResponse::class, \Illuminate\Session\Middleware\StartSession::class, // \Illuminate\Session\Middleware\AuthenticateSession::class, \Illuminate\View\Middleware\ShareErrorsFromSession::class, \App\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken::class, \Illuminate\Routing\Middleware\SubstituteBindings::class, ], 'api' [ // ここを追加 \App\Http\Middleware\EncryptCookies::class, \Illuminate\Cookie\Middleware\AddQueuedCookiesToResponse::class, \Illuminate\Session\Middleware\StartSession::class, \Illuminate\View\Middleware\ShareErrorsFromSession::class, \App\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken::class, \Illuminate\Routing\Middleware\SubstituteBindings::class, // ここまで追加 'throttle:60,1', 'bindings', ], ]; // 省略 これでセッションが有効になります。 ミドルウェアの作成 デフォルトで備わっているAuthのミドル���ェアはビューに最適化されており、ログインせずにミドルウェアに到達すると /login にリダイレクトされてしまいます。 APIではリダイレクトではなく エラーメッセージ が帰ってくることを期待します。 ですのでミドルウェアを自作します。 $ php artisan make:middleware AuthApi app/Http/Middleware/AuthApi.php <?php use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth; // 省略 public function handle($request, Closure $next) { if (!Auth::check()) return response("",401,["Content-type: application/json"]); return $next($request); } use ...Auth の行が必要ですので注意してください。 app/Http/Kernel.php <?php // 省略 protected $routeMiddleware = [ // 省略 'auth.api' \App\Http\Middleware\AuthApi::class, ]; これでミドルウェアの実装完了です。 実装 先程作成したtodoのルーターに変更を加えていきます。 route/api.php <?php Route::group(["middleware" "auth.api"],function(){ Route::get('/todo','TodoController@get'); Route::post('/todo','TodoController@post'); Route::delete('/todo/{id}','TodoController@delete'); Route::put('/todo/{id}','TodoController@update'); }); これでログインしていないと401エラーを返すことになります。 フロントの実装 いよいよフロントの実装に入ります。 ここではVue.jsを利用したSPAで制作していきたいと思います。 VueJSの構築 LaravelはデフォルトでVueJSが導入されていて、 既にExampleファイルも構築されています。 Webpackも何も書かなくても初期導入されています。 したがって、npmインストールを行い、Viewを少し変更するだけでVueJSを導入できます。 $ npm i $ npm run dev $ npm run watch # ファイルの変更時、自動的にコンパイルが走る resources/views/todo.blade.php @extends('layouts.app') @section('content') <div class="container" <div class="row justify-content-center" <h2TODO アプリケーション</h2 <example-component</example-component </div </div @endsection を追加することでVue.jsの導入は完了です。 APIを叩くリクエストモジュールを作成 APIを叩く際、数が多くなってくるとごちゃごちゃになってくるので、APIを叩く機能は別に作成します。 resources/js/api.js "use strict" const send = (method,uri,data={} { const url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8000' + uri return new{ var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open(method, url); xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8" { try{ const res_json = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText) resolve(res_json) }catch (e) { resolve(xhr.responseText) } } { console.log(xhr.status); console.log("error!"); }; xhr.send(data); }) } const api = { getTodoList(){ return send("GET","/api/todo"); }, postTodo(todo){ return send("POST","/api/todo",todo); }, updateTodo(id,todo){ return send("PUT","/api/todo/" + id,todo); }, deleteTodo(id,data){ return send("DELETE","/api/todo/" + id,data); } } export default api APIを叩くためのメソッド send を用意して、下段にAPIをリストのように記述することで新たにAPIが増えても追加しやすいようにします。 コンポーネントの実装 では、駆け足でコンポーネントを作成していきましょう。 今回はLaravelの紹介なのでフロント実装の部分は大幅にカットします。 以下のソースコードをまるごとコピーすれば動作すると思います。 resources/js/components/ExampleComponent.vue <template <div class="container" <div class="row justify-content-center" <div class="col-md-8" <div class="card" <div class="form-group" <input type="text" class="form-control" id="inputtodo" v-model="todo_form" <button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" @click="addTodo"Add</button </div </div <div class="card" v-for="todo in todos" <div class="card-header" <button type="button" class="btn btn-danger" @click="deleteTodo(todo.id)"Delete</button <button type="button" class="btn btn-info" @click="updateTodo(todo.id)"Update</button <input type="text" class="form-control" id="todo" v-model="todo.todo" </div </div </div </div </div </template <script import api from "../api.js" export default { data(){ return { active_todo: null, todo_form:"", todos:[] } }, methods:{ addTodo(){ let data = {todo:this.todo_form} data._token = document.getElementsByName('csrf-token')[0].content; api.postTodo(JSON.stringify(data)).then((){ this.getTodoList() }) }, deleteTodo(id){ let data = {} data._token = document.getElementsByName('csrf-token')[0].content; api.deleteTodo(id,JSON.stringify(data)).then((){ this.getTodoList() }) }, updateTodo(id){ let data = {todo:this.todos.filter((v){return v.id === id})[0].todo} data._token = document.getElementsByName('csrf-token')[0].content; api.updateTodo(id,JSON.stringify(data)).then((){ this.getTodoList() }) }, getTodoList(){ api.getTodoList().then((result){ this.todos = result }) } }, mounted() { this.getTodoList() console.log('Component mounted.') } } </script それぞれの機能ごとに method を用意して、dataやv-modelなどを駆使してAPIを叩きます。 APIを叩いた後はすかさずthis.getTodoListを行っていますが、これは変更を適応するためです。 完成 TODOリストが完成しました。 最後に いかがでしたでしょうか。 記事が長くなってしまいましたが、実際に記述したソースコードはほんの一部分だけです。 こちらにアプリケーションのソースコードを載せております。 GitHub - optim-corp/techblog-laravel-todo-sample Auth(認証)やAPIの作成、SPAの実装までこの量で出来てしまいます。 この記事の通りに実装を行えば上記のTodoアプリケーションが出来上がりますが、バリデーションチェック等の エラーハンドリングを全く行っておりません(特にAPI部分) ので、ご注意ください。 最後になりましたが、「Laravelを使って爆速Webアプリケーション開発を行っていこう!」という言葉を残して締めくくりたいと思います。 ありがとうございました。 OPTiMでは様々な分野で活躍できるエンジニアを募集しております。 今回のようなWebアプリケーションも然り、機械学習やクラウド系インフラ周りまであらゆる分野で活躍出来る場があります! 興味がある方は是非弊社採用ページにてご覧ください! www.optim.co.jp また、夏季インターンシップも募集しておりますので、合わせてご覧ください。 www.optim.co.jp
0 notes
Text
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch - e23 - Adding a Custom Middleware
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e23 – Adding a Custom Middleware
[ad_1]
Now that we know how to apply one of the default middlewares, let’s take the time to create our own custom middleware for our app. Follow along as we talk about all of the ways you can add a middleware, from global, to web groups to individual routes.
For the best experience, follow along in our interactive school at https://www.coderstape.com
Resources
Course Source Code
https://github.com…
View On WordPress
#Laravel#laravel 5 auth#laravel 5.8#laravel 5.8 authentication#laravel 5.8 custom middleware#laravel 5.8 feature#laravel 5.8 features#laravel 5.8 global middleware#laravel 5.8 middleware#laravel 5.8 multi auth#laravel 5.8 user auth#laravel 5.8 user authentication#laravel auth#laravel authentication#laravel custom middleware#laravel from the ground up#laravel global middleware#laravel middleware#laravel registration#laravel route group middleware
0 notes
Text
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch - e24 - URL Helpers - Laravel
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e24 – URL Helpers – Laravel
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e24 – URL Helpers – Laravel
[ad_1]
In this episode, we explore the 3 URL Helpers offered by Laravel out of the box and refactor our project to use them.
For the best experience, follow along in our interactive school at https://www.coderstape.com
Resources
Course Source Code
https://github.com/coderstape/laravel-58-from-scratch
Hit us up on Twitter with any…
View On WordPress
#laravel 5 auth#laravel 5.8#laravel 5.8 authentication#laravel 5.8 feature#laravel 5.8 features#laravel 5.8 multi auth#laravel 5.8 named resource routes#laravel 5.8 named routes#laravel 5.8 user auth#laravel 5.8 user authentication#laravel auth#laravel authentication#laravel from the ground up#laravel middleware#laravel named resource routes#laravel named routes#laravel registration#laravel route group middleware#laravel routing with parameters
0 notes
Text
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch - e21 - Artisan Authentication - Register, Login & Password Reset - Laravel
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e21 – Artisan Authentication – Register, Login & Password Reset – Laravel
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e21 – Artisan Authentication – Register, Login & Password Reset – Laravel
[ad_1]
It’s time for us to talk about registering users, login in users and resetting passwords. Up until now, a very daunting task, but with Laravel, it’s as simple as running php artisan make auth and everything just works. Let’s working on adding authentication to our Laravel…
View On WordPress
#authentication in laravel#laravel 5 auth#laravel 5.8#laravel 5.8 auth tutorial#laravel 5.8 authentication#laravel 5.8 feature#laravel 5.8 features#laravel 5.8 multi auth#laravel 5.8 user auth#laravel 5.8 user authentication#laravel 5.8 what&039;s new#laravel auth#laravel auth role#laravel authentication#laravel authorization#laravel from the ground up#laravel login#laravel middleware#laravel register user#laravel registration#laravel reset password
0 notes
Text
Laravel 5.8 || Email Verification || Laravel tutorial - Laravel
Laravel 5.8 || Email Verification || Laravel tutorial – Laravel
Laravel 5.8 || Email Verification || Laravel tutorial – Laravel
[ad_1]
In this video we will use laravel 5.8 to make auth and migrate. After that we will implement MustVerifyEmail functionality in our User Model.
Why confirm email Verification?
Conformation email verification is the most accurate way to tell whether the email is valid or not.
This can be odd for an existing email list, since it…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
As developers, our job is not only to create applications that work but also to give them support so that they can be maintained throughout their useful life. In the case of Laravel, major updates that bring new features, improvements and corrections are made every 6 months.
However updating a project developed in Laravel from one version to another is not as complicated as it seems.
Click To Tweet
In this article, we will tell you what are the most important changes and the steps to update your application from Laravel version 5.8 to 6.0.
Especially knowing that it will be an LTS version, that is, it will have support for corrections of security problems until September 2022.
What requirement we need for use of Lavarel 6.0 :
Before doing any update step, we must confirm that our application can be updated to Laravel 6.0 or not.
The version of the application to be updated is Laravel 5.8. Otherwise, you must update it to that version. Take into account that Laravel 5.9 does not exist due to the changes made to the versioning of the framework.
The production server and other environments must have PHP 7.2 or higher, as it is the new minimum requirement of Laravel 6.0 because PHP 7.1 will have active support until December 2019.
Since Laravel 6.0 announced, all need to confirm that each of the third-party packages used in the application can work with Laravel 6.0? To do this you should check their official pages or repositories.
Some recommendation
Use Git to avoid problems if something fails and you cannot solve, we recommend you create a new branch to update so that the code of your working project will be supported.
Default auth with ui:auth, make:auth Removed
Laravel team has removed default make:auth command and introduced new command which is ui:auth.
To use this package, first of all, you have to install it using the below command.
composer require laravel/ui
After installing this package you have now many commands to generate Ui code with authorization.
You can see all new commands using the below command.
php artisan ui –help
If you want to set the default as vue or react instead of bootstrap then use below command.
php artisan ui vue
php artisan ui react
Now you can make your default auth scaffolding using below command
php artisan ui:auth
If you want to generate only views then run below command.
php artisan ui:auth –views
String and Array Default Functions Removed and Moved to Package
Now there is no default helper function for array and string. All str_ and array_ helper functions have been removed and moved to a new package called helpers. You can install it in your project using the below command.
composer require laravel/helpers
Carbon 1.0 Removed and Supported Carbon 2.0
There is no support for carbon 1.x longer in Laravel 6 because now they have updated it to carbon 2.x. You can read it from here: https://ift.tt/2nGBuJS
Lazy Collection with New Cursor Method in Eloquent
Suppose you a very large dataset in your project and you want to iterate them with the condition then these will be time taking in Generator but using Lazy Collection you can do it with low memory consumption.
In the older version of Laravel return an instance of Generator, now it will return an instance of Lazy Collection.
$blogs = App\Blog::cursor();
foreach ($blogs as $blog) {
//
}
Primary Key Type Declaration in the Model
Now you can define your table primary key as a string instead of an integer using below syntax.
protected $keyType = ‘string’;
BelongsTo::update Method Update in Eloquent
Suppose you have two model attached via a belongsTo relationship and receive mass assignment then you can call update method direct on the model like below.
$comment->blog()->update([‘foo’ =>’bar’]);
$comment->blog->update([‘foo’ =>’bar’]);
Authorization Response
In older version of laravel it was very difficult to show custom error messages in default auth, but now there is new method Gate::inspect which provides the authorization responce.
$my_response = Gate::inspect(‘view’, $dashboard);
if ($my_response->allowed()) {
// User can see Dashboard…
}
if ($my_response->denied()) {
echo $my_response->message();
}
Input Facade Removed Permanently
In a very old version of Laravel, we have used the Input facade, which is work like Request facade. But now in a new will, it was removed permanently. Now if you wish to use Input::get method then you have to call it like Request::input method. All other calls to the input facade may simply be updated to use the Request facade.
Conclusion
Laravel is a fast, free and open-source PHP development framework. Whose main goal is to allow you to work in a structured and fast manner. Laravel takes the monotony of web development. It provides all the tools you need to get you started programming whatever you need, it’s built to be simple and easy to learn.
The post What’s New Features in Laravel 6.0 Release in Sep 2019 appeared first on Digital Ideas.
via Digital Ideas
0 notes