#mitophagy
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
The Role of Mitochondria in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)

Introduction
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease characterized by the progressive degeneration of upper and lower motor neurons. Despite extensive research, the etiology of ALS remains multifactorial and incompletely understood. Among the cellular organelles implicated in ALS pathogenesis, mitochondria stand out as central mediators of neurodegeneration due to their pivotal roles in ATP production, calcium homeostasis, and apoptosis regulation. Mitochondrial dysfunction is not merely a secondary feature of dying neurons in ALS; accumulating evidence suggests it plays a primary and causative role in disease progression.
Mitochondrial Bioenergetics in ALS
Mitochondria are indispensable for neuronal survival due to their role in oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), the process that generates over 90% of cellular ATP. In ALS, impairments in mitochondrial respiration are evident across multiple models, including post-mortem human spinal cord tissue, motor neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and transgenic mouse models harboring ALS-associated mutations (e.g., SOD1, TDP-43, FUS, C9orf72).
Notably, enzymatic activity of complexes I and IV of the electron transport chain is reduced in ALS, correlating with early energy deficits in motor neurons. These neurons are especially vulnerable due to their long axons and high metabolic demand. Impaired ATP synthesis not only compromises synaptic transmission but also disrupts axonal transport and the maintenance of ion gradients, rendering neurons more susceptible to excitotoxicity and death.
Oxidative Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
Mitochondria are the principal source of reactive oxygen species as byproducts of respiration. While low levels of ROS serve signaling functions, excessive ROS can damage lipids, proteins, and DNA. ALS is associated with increased oxidative stress, evidenced by elevated markers of lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation in cerebrospinal fluid and nervous tissue.
Mutations in SOD1, one of the first discovered ALS-associated genes, further underscore the connection between oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. SOD1 normally detoxifies superoxide radicals. Mutant SOD1 misfolds and aggregates within mitochondria, particularly in the intermembrane space, impairing mitochondrial integrity and exacerbating ROS production. This establishes a vicious cycle wherein dysfunctional mitochondria produce more ROS, leading to further mitochondrial damage.
Mitochondrial Dynamics: Fission, Fusion, and Transport
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles that constantly undergo fission and fusion, processes necessary for maintaining mitochondrial function and distribution. These dynamics are disrupted in ALS. Studies have demonstrated increased mitochondrial fragmentation in motor neurons from ALS models, often linked to elevated activity of fission proteins such as DRP1 and downregulation of fusion mediators like MFN2 and OPA1.
Additionally, mitochondrial transport along axons is impaired in ALS. Mitochondria must be trafficked to sites of high energy demand, including synaptic terminals. Mutant SOD1, TDP-43, and FUS have all been implicated in disrupting the interaction between mitochondria and motor proteins such as kinesin and dynein. This disruption leads to a depletion of functional mitochondria at distal axonal sites, contributing to synaptic failure and distal axonopathy, hallmarks of ALS pathology.
Calcium Dysregulation and Excitotoxicity
Motor neurons in ALS are particularly sensitive to calcium dysregulation, and mitochondria play a vital role in buffering intracellular calcium. Under pathological conditions, mitochondria in ALS exhibit reduced calcium uptake capacity. This dysfunction is partly due to depolarized mitochondrial membrane potential and possibly due to defective interactions at mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs), where calcium is transferred from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to mitochondria.
The result is excessive cytosolic calcium, which, when combined with increased glutamate signaling, leads to excitotoxicity. This not only activates calcium-dependent proteases and phospholipases but also triggers the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP), a catastrophic event that leads to mitochondrial swelling, rupture, and the release of pro-apoptotic factors.
Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Permeability
The intrinsic pathway of apoptosis is closely regulated by mitochondrial integrity. In ALS, numerous studies have identified mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis as a significant contributor to motor neuron death. Proteins such as Bax and Bak insert into the mitochondrial outer membrane, promoting cytochrome c release and subsequent caspase-3 activation. Elevated levels of cleaved caspase-9 and caspase-3 have been reported in ALS patient tissue and transgenic models.
Moreover, persistent mitochondrial stress leads to chronic opening of the mPTP, a key event that commits the cell to death. This process is further exacerbated by oxidative stress, calcium overload, and the presence of misfolded proteins, all of which are abundant in ALS-affected neurons.
Defective Mitophagy and Quality Control
Quality control of mitochondria is essential to neuronal homeostasis. Damaged mitochondria are normally removed by mitophagy, a specialized form of autophagy. In ALS, mitophagy is often impaired. Mutations in genes like OPTN, TBK1, and VCP—all associated with familial ALS—directly interfere with mitophagy pathways. These proteins are responsible for tagging damaged mitochondria for autophagic clearance via ubiquitination and recruitment of autophagic machinery.
When mitophagy is compromised, dysfunctional mitochondria accumulate, leading to sustained oxidative damage, ATP deficiency, and activation of cell death pathways. This accumulation also leads to inflammation, as damaged mitochondria can release mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and other damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that activate innate immune responses.
Therapeutic Implications
Given the central role of mitochondria in ALS, numerous therapeutic strategies aim to restore mitochondrial function or prevent their dysfunction. Antioxidants such as coenzyme Q10, edaravone, and idebenone have been tested, with edaravone gaining limited clinical approval for slowing functional decline.
Agents targeting mitochondrial dynamics (e.g., DRP1 inhibitors), enhancing mitophagy (e.g., urolithin A), or stabilizing mitochondrial membranes are under preclinical and clinical investigation. Additionally, metabolic modulators that shift energy production away from oxidative phosphorylation (e.g., ketogenic diets or dichloroacetate) show promise in experimental models.
However, the translation of mitochondrial-targeted therapies into effective clinical treatments remains challenging. This is due in part to the heterogeneity of ALS, the complexity of mitochondrial biology, and the difficulty in delivering drugs across the blood-brain barrier in therapeutically relevant concentrations.
Conclusion
Mitochondria are at the intersection of multiple pathogenic pathways in ALS, including energy failure, oxidative stress, calcium overload, impaired dynamics, and defective quality control. Far from being mere bystanders, these organelles are deeply implicated in both initiating and propagating motor neuron degeneration. Future advances in ALS therapy will likely depend on a deeper understanding of mitochondrial biology and the development of strategies that can restore or preserve mitochondrial health in vulnerable neuronal populations.
#Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)#Mitochondrial dysfunction#Motor neuron degeneration#Oxidative stress#Reactive oxygen species (ROS)#SOD1 mutation#Mitochondrial bioenergetics#Electron transport chain#ATP production#Mitochondrial dynamics#Mitochondrial fission and fusion#Axonal transport#Calcium dysregulation#Excitotoxicity#Mitochondrial apoptosis#Mitophagy#Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP)#Mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs)#Neurodegeneration
0 notes
Text
The future may get PINK: only PARKINg close to membranes will maintain the energOMA 1 for all
Scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have discovered how a group of proteins linked to Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis act as “guardians” of mitochondria, small organelles within a cell that make and store energy and are found in almost all plants and animals. The findings, resulting from experiments with genetically engineered mice should advance understanding of…
#cell membrane#cellular energy#cellular stress#mitochondria#mitochondrial DNA#mitophagy#neuroinflammation#protease
0 notes
Text
From Internal Medicine to Integral Regeneration A Life-Value Framework for Healing Systems, Selves, and Civilizations | ChatGPT4o
[Download Full Document (PDF)] In an age of planetary polycrisis — ecological collapse, institutional failure, social fragmentation, and meaning depletion — there is an urgent need for a new kind of medicine: one that heals not just bodies, but systems, selves, and civilizations. This white paper begins with a clinical insight: that internal medicine already embodies the most refined practice of…
#AQAL#ChatGPT#civilizational renewal#Coherence#diagnosis#healing architectures#Hippocratic oath#institutional integrity#Integral Theory#integral vocation#internal medicine#life-capacity#Life-Value#McMurtry#metabolic coherence#metabolic governance#metabolic healing#mitophagy#planetary healing#regeneration#sacred systems design#Semiotics#systemic health#Wilber
0 notes
Text
youtube
#Breast cancer#mitophagy#E3 ubiquitin ligases#prognostic signature#cancer biomarkers#tumor progression#autophagy#molecular oncology#survival analysis#bioinformatics#targeted therapy#cancer prognosis#genetic markers#precision oncology#oncogene regulation#tumor microenvironment#clinical oncology#therapeutic targets#mitochondrial dynamics#medical innovation.#Youtube
0 notes
Text

Brain Age Functions
Mitophagy is a process cells use to neutralise damage sustained by their mitochondria – the organelles that generate energy. This study profiles the dynamics of mitophagy across different cell types in the healthy mammalian brain as it ages
Read the published research article here
Image from work by Anna Rappe and colleagues
Translational Stem Cell Biology and Metabolism Program, Faculty of Medicine, Biomedicum Helsinki, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0)
Published in The EMBO Journal, October 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Story at-a-glance
A body without cellular energy is like a car without fuel. Providing your body with the right nutrition, exercise, sleep, and sunlight exposure is essential to maintaining and replenishing these vital energy reserves
Exercise, particularly interval training and resistance exercises, stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and enhances your body's capacity to generate energy and improve metabolic health
Quality sleep enables cellular repair. This allows your mitochondria to restore and regenerate through processes like mitophagy and aligns your body's circadian rhythms
Sunlight exposure directly fuels mitochondria by converting red and near-infrared light into electrons. This supports ATP production and synchronizes your body's internal energy systems
To safely benefit from sun exposure, eliminate vegetable oils from your diet first. They contain linoleic acid that accumulates in your skin and increases your risk of UV-induced oxidative stress and sunburn
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Urolithin A+ Supplement in India for Anti-Aging & Cellular Health (500mg)
Brahmastra Pharmacy Urolithin A+ (500mg): Reignite Your Youth, From Within
In our bustling lives, aging isn't just about candles on a cake; it's a profound biological shift that touches our energy, immunity, skin, strength, and even our mental clarity. While we can't stop time, groundbreaking science is now revealing how to significantly slow its pace. This brings us to Urolithin A, a revolutionary natural compound that has captivated the global health community. And now, thanks to Brahmastra Pharmacy, India can access its most potent form: Urolithin A+ (500mg).

Let's dive into why Urolithin A+ is being heralded as the future of anti-aging and cellular rejuvenation, offering a path to feeling younger and more vibrant.
What Exactly is Urolithin A?
Think of Urolithin A as a secret weapon your gut should be making. It's a natural postbiotic, a beneficial compound produced when specific gut bacteria interact with ellagitannins found in foods like pomegranates, walnuts, and berries. The catch? Most of us, due to modern diets and less-than-optimal gut health, simply don't produce enough Urolithin A naturally.
This is precisely where Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+ supplement becomes your ally. It delivers pure, highly bioavailable Urolithin A (500mg) directly to your cells, bypassing the need for perfect gut conditions. It's about giving your body what it needs, effortlessly.
How Does Urolithin Work Its Magic? The Power of Your Cellular Engines
To truly grasp Urolithin A’s incredible benefits, let's talk about mitochondria. These are the tiny, hardworking powerhouses within every one of your cells, tirelessly generating the energy (ATP) that fuels your entire body. As we age, our mitochondria can become damaged, inefficient, and fewer in number. This decline often manifests as fatigue, slower healing, diminishing muscle strength, and even "brain fog."
Urolithin A steps in like a cellular spring cleaner. It specifically activates mitophagy, a crucial natural process that identifies and removes these old, dysfunctional mitochondria. But it doesn't stop there; it also stimulates the growth of new, healthy ones. Imagine it as a powerful "detox and regeneration" cycle happening at the deepest cellular level, revitalizing your very foundation.
The core takeaway: Healthier, more abundant mitochondria mean more energy, sharper focus, and a significant slowdown in the signs of aging.
Unlocking Your Potential: Top Benefits of Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+
Here's a closer look at the remarkable changes you can experience with regular use of Urolithin A+ (500mg):
Recharge Your Energy & Stamina: With improved mitochondrial function, your cells produce energy more efficiently. Whether you're juggling a demanding career, hitting the gym, or simply want to enjoy daily activities with more zest, you'll feel a noticeable surge in energy, alertness, and overall motivation. Say goodbye to that afternoon slump!
Sharpen Your Memory & Focus: Emerging research suggests Urolithin A can cross the crucial blood-brain barrier, offering potential protection for your neurons and enhancing cognitive performance. This is a game-changer for professionals needing to stay sharp, students aiming for peak performance, and seniors looking to combat the frustrating effects of brain fog.
Boost Muscle Strength & Recovery: Urolithin A has been shown to enhance muscle endurance and power, particularly vital for older adults. It's perfect for anyone wanting to maintain an active lifestyle, gym enthusiasts looking for an edge, and individuals striving to counteract age-related muscle decline, helping you stay strong and agile.
Defy Cellular Aging: By systematically clearing out damaged mitochondria, Urolithin A actively helps to slow down the cellular aging process itself. This translates to visible improvements in skin health, optimized organ function, and a profound sense of long-term vitality that radiates from within.
Fortify Your Immunity & Longevity: A robust immune system is built on healthy cells. Urolithin A's ability to enhance cellular health can significantly bolster your body's resilience against oxidative stress, common infections, and the various diseases associated with aging, contributing to a longer, healthier life.
Why Choose Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+ (500mg)? Your Premium Choice for Rejuvenation
While Urolithin A is gaining global recognition, Brahmastra Pharmacy's Urolithin A+ stands out as India’s leading and most effective option. Here's what sets it apart:
High-Strength 500mg Formula: Many products offer only 250mg or less. Brahmastra Urolithin A+ delivers a powerful, clinically effective dosage of 500mg per capsule, ensuring you get maximum benefits with every dose.
Clinically Researched & Proven: Our Urolithin A is produced using patented fermentation technology, ensuring purity and potency. It's rigorously backed by scientific research, lab-tested, safe, and highly bioavailable.
🇮🇳 Crafted for Indian Needs: Thoughtfully formulated to complement Indian diets, gut microbiomes, and specific nutritional requirements, ensuring optimal efficacy for you.
Pure & Clean Formula: Absolutely no unnecessary fillers, artificial preservatives, gluten, soy, dairy, or harsh chemicals. It's a 100% clean formula you can trust.
GMP Certified & Quality Assured: Manufactured in state-of-the-art, GMP-certified facilities, adhering to the highest pharmaceutical-grade standards for your peace of mind.
Is Urolithin A+ Right for You?
Anyone over the age of 30 can significantly benefit from this supplement, especially if you recognize these common signs:
Persistent low energy or chronic fatigue
Slow muscle recovery or noticeable loss of strength
Lingering brain fog or occasional memory lapses
Accelerated visible signs of aging
A sedentary lifestyle or high levels of stress
Known gut issues that might hinder natural Urolithin A production
Simple to Incorporate: Your Daily Dose of Rejuvenation
Dosage: Just 1 capsule daily (500mg).
When: Ideally in the morning on an empty stomach for superior absorption.
With: A simple glass of water.
Results Timeline: Many users report a noticeable increase in energy within 7–14 days. Deeper, more profound cellular benefits and anti-aging effects typically become apparent after 6–8 weeks of consistent use.
Hear From Real Indian Users
🧓 "After turning 50, I felt constantly tired. After using Urolithin A+ for just a month, I feel like I’m back in my 30s! My energy is through the roof."
— Ramesh M., Bangalore
🏃♀️ "I'm a regular at the gym and was searching for something natural to boost my endurance and speed up recovery. Urolithin A+ worked wonders—my stamina and post-workout recovery have massively improved. Truly impressed!"
— Pooja R., Mumbai
👩⚕️ "As a doctor, I'm highly selective about recommending supplements unless they are rigorously backed by science. Brahmastra’s Urolithin A+ is the real deal. I've seen the positive impact myself."
— Dr. Shruti M., Delhi
Where to Purchase Brahmastra Urolithin A+ in India
Ready to experience the transformation? You can easily order directly from the Brahmastra Pharmacy official website, or find it conveniently on Amazon and Flipkart. It's also available at select premium wellness retailers across India.
Final Thoughts: Rewind Your Biological Clock, Naturally
True anti-aging isn't merely about topical creams or cosmetic fixes; it's about rejuvenating the very energy factories within your cells. With Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+ (500mg), you’re not just taking a supplement—you’re actively supercharging your mitochondria, powerfully fighting fatigue, enhancing muscle strength, and fundamentally slowing down your biological clock.
If you’re yearning to reclaim your youthful vigor, boost your energy levels, and feel vibrantly alive again, Urolithin A+ is your daily key to cellular rebirth.
🔴 Experience the Science of Rejuvenation. Rediscover Your Best Self.
🌟 Try Urolithin A+ Today. Only from Brahmastra Pharmacy.
0 notes
Text
The Anti-Aging Supplement Backed by Science – Urolithin A+ Explained
Unlock Healthy Aging from Within: Why Urolithin A+ by Brahmastra Pharmacy Could Be the Game-Changer Your Body Needs
Aging isn’t just about wrinkles or gray hair. It’s about how our bodies feel, move, and perform over time. Many of us invest in surface-level solutions—creams, serums, or supplements that promise miracles—but very few address aging at the cellular level.
That’s where Urolithin A+ from Brahmastra Pharmacy stands out.
What is Urolithin A, and Why Should You Care?
Urolithin A is a naturally derived compound, produced in the gut when certain microbes break down polyphenols from foods like pomegranates and berries. But here’s the catch—not everyone can produce it efficiently due to gut microbiome differences. That’s why direct Urolithin A supplementation is such a breakthrough.
Urolithin A+ delivers a clinically validated 500mg dose in each capsule—giving your body a direct pathway to experience its incredible benefits.
How Does Urolithin A Work? The Power of Mitophagy
Unlike traditional antioxidants that fight free radicals on the surface, Urolithin A gets to the root of the aging process by triggering mitophagy.
Mitophagy 101:
Mitophagy is the process where your body clears out damaged mitochondria—the tiny powerhouses inside your cells—and replaces them with new, healthy ones. Think of it like giving your cells a complete engine overhaul.
Healthy mitochondria = more energy, better performance, and slower aging.
The Real Benefits of Urolithin A+
Here’s what regular use of Urolithin A+ can do:
1. Boost Cellular Energy
By renewing mitochondria, Urolithin A improves how your cells produce and utilize energy. This can reduce fatigue and make you feel more active throughout the day.
2. Enhance Muscle Strength and Endurance
Clinical studies have shown Urolithin A can improve muscle function, especially in older adults. Whether you’re an athlete or just want to stay mobile with age, this is a game-changer.
3. Support Cognitive Function
Aging affects brain cells, too. By energizing neurons, Urolithin A may help sharpen focus, memory, and overall mental clarity.
4. Delay Visible and Internal Signs of Aging
From reducing fine lines and skin fatigue to slowing biological aging markers, Urolithin A offers a holistic anti-aging approach—from the inside out.
Why Choose Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+?
When it comes to supplements, purity and potency matter. Brahmastra Pharmacy is known for its commitment to Ayurvedic excellence backed by modern science.
Urolithin A+ is:
100% Pure and Clinically Dosed (500mg per capsule)
Free from synthetic additives and fillers
Lab-tested for quality and effectiveness
Suitable for daily use
It’s crafted with the philosophy of merging ancient wellness traditions with cutting-edge research—so you get the best of both worlds.
Who Is It For?
Urolithin A+ isn’t just for older adults. Anyone over the age of 30 who wants to:
Feel more energetic
Improve muscle performance
Maintain long-term brain and heart health
Or simply age smarter
…can benefit from this powerful supplement.
Whether you're a busy professional, a fitness enthusiast, or someone dealing with midlife fatigue—Urolithin A+ gives your body the cellular upgrade it deserves.
Final Thoughts: Future-Proof Your Health
Healthy aging isn't just a dream—it's a science. With Urolithin A+, Brahmastra Pharmacy offers a powerful, proven way to rejuvenate your cells, increase vitality, and protect your long-term well-being.
If you're ready to feel younger—not just look it—then it's time to make Urolithin A+ part of your daily routine.
Ready to experience the benefits for yourself? Explore Urolithin A+ from Brahmastra Pharmacy today and take your first step toward aging on your own terms.
0 notes
Text
Funded PhD studentship at the Hebrew University (Rehovot Campus) Hebrew University of Jerusalem If you are looking for a meaningful PhD experience, join us for a cutting edge scientific journey! See the full job description on jobRxiv: https://jobrxiv.org/job/hebrew-university-of-jerusalem-27778-funded-phd-studentship-at-the-hebrew-university-rehovot-campus/?feed_id=97567 #autophagy #cell_biology #mitophagy #Yeast_genetics #ScienceJobs #hiring #research
0 notes
Text
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
Introduction
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder that predominantly affects motor neurons, resulting in progressive muscle weakness and atrophy. The condition is caused by mutations in the survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) gene, which leads to the loss of SMN protein, a critical factor for motor neuron survival. Although the primary defect lies in the motor neurons, increasing evidence suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction plays a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of SMA. Mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell, are crucial for cellular energy production and regulation of various metabolic pathways. In the context of SMA, mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to impaired cellular energy metabolism, oxidative stress, and neuronal death.
This article reviews the emerging role of mitochondrial dysfunction in SMA, examining its impact on motor neurons, the cellular processes involved, and the potential for mitochondrial-targeted therapies.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in SMA: A Pathophysiological Overview
Mitochondria are essential organelles responsible for generating ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, controlling cellular metabolism, and mediating cell death mechanisms. In SMA, deficits in SMN protein affect multiple cellular pathways, including mitochondrial function. SMN is known to be involved in the biogenesis and maintenance of mitochondria. When its expression is reduced, mitochondrial dysfunction occurs in several ways, contributing to the progressive nature of SMA.
Impaired Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Mitochondrial biogenesis refers to the process by which new mitochondria are formed within cells. This process is tightly regulated by nuclear and mitochondrial signals, with the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) being a key regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Studies in SMA models have shown that a reduction in SMN protein leads to downregulation of PGC-1α, resulting in decreased mitochondrial biogenesis. This reduced mitochondrial mass is particularly detrimental to motor neurons, which have high energy demands due to their long axonal projections and rapid neurotransmitter signaling.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and ATP Production
Mitochondrial dysfunction in SMA results in decreased ATP production. ATP is required for essential cellular functions such as protein synthesis, ion transport, and maintaining membrane potential. In motor neurons, impaired ATP generation leads to cellular energy deficits that exacerbate neurodegeneration. Mitochondrial dysfunction also disrupts calcium homeostasis, as mitochondria play a central role in buffering intracellular calcium levels. Elevated intracellular calcium levels can activate enzymes that degrade cellular components, further contributing to cell death in motor neurons.
Oxidative Stress
One of the most significant consequences of mitochondrial dysfunction is the increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Mitochondria are the main source of ROS in cells, and under normal conditions, the antioxidant defense systems neutralize these reactive molecules. However, in SMA, defective mitochondrial function leads to excessive ROS production, which overwhelms the cell’s ability to detoxify them. ROS are highly reactive and can damage cellular structures such as proteins, lipids, and DNA, ultimately contributing to oxidative stress and neuronal injury.
Mitochondrial Dynamics and Morphology
Mitochondrial morphology is highly dynamic, with the organelles undergoing fusion and fission events in response to cellular needs. In SMA, the balance between these processes is disrupted. Studies have shown that reduced SMN levels lead to an increase in mitochondrial fragmentation, a characteristic of mitochondrial dysfunction. Fragmented mitochondria are less efficient in energy production and more prone to damage. Additionally, the fragmented mitochondria in SMA models exhibit impaired mitochondrial transport along axons, further hindering motor neuron function.
Mitochondrial Quality Control
Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms, such as mitophagy, are critical for maintaining mitochondrial health. Mitophagy is the process by which damaged mitochondria are selectively degraded by autophagosomes. In SMA, defects in SMN protein affect the cellular machinery responsible for mitophagy, leading to the accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria. This impairment in mitochondrial turnover accelerates neurodegeneration by allowing damaged mitochondria to persist, increasing oxidative stress, and triggering cellular apoptosis.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Different Types of SMA
SMA is classified into several types based on age of onset and severity, including Type I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease), Type II, Type III, and Type IV. Mitochondrial dysfunction is observed in all types, but its extent varies depending on the severity of the disease.
SMA Type I
This is the most severe form of SMA, typically presenting in infants before six months of age. These children experience profound muscle weakness and may not survive beyond the first two years of life without intervention. In Type I, mitochondrial dysfunction is particularly pronounced, with severe mitochondrial fragmentation, impaired ATP production, and significant oxidative damage observed in motor neurons. The severity of mitochondrial dysfunction correlates with the extent of neurodegeneration in the spinal cord.
SMA Type II
Type II SMA presents later in infancy or early childhood, with affected individuals showing progressive muscle weakness but with a longer life expectancy compared to Type I. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Type II is still significant but less severe than in Type I. There is evidence of mitochondrial fragmentation and altered mitochondrial dynamics, but motor neurons in Type II patients may still retain some capacity for mitochondrial biogenesis and ATP production, contributing to the slower progression of the disease.
SMA Type III and IV
SMA Type III and IV are milder forms of the disease, with onset typically in childhood or adulthood. While mitochondrial dysfunction is present, it is less pronounced than in Type I and II. In these types, mitochondrial dynamics, ATP production, and oxidative stress are affected, but the clinical presentation is less severe, and individuals often experience a normal or near-normal life expectancy.
Conclusion
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a central feature of the pathophysiology of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). Reduced SMN protein leads to impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, altered mitochondrial dynamics, increased oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. These defects contribute to the progressive degeneration of motor neurons and muscle weakness seen in SMA. Understanding the complex interplay between SMN deficiency and mitochondrial dysfunction provides valuable insights into the disease mechanisms and offers new avenues for therapeutic intervention. Mitochondrial-targeted approaches, including enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis, antioxidant therapy, and modulation of mitochondrial dynamics, hold promise for improving the quality of life and outcomes for SMA patients.
Ongoing research into mitochondrial dysfunction in SMA is crucial for identifying novel treatment strategies that can complement existing therapies and slow disease progression. As therapeutic options evolve, mitochondrial health will likely become an important consideration in the management of SMA, offering hope for more effective treatments in the future.

#Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)#Mitochondrial Dysfunction#Motor Neurons#SMN1 Gene#SMN Protein#Neurodegeneration#Mitochondrial Biogenesis#Oxidative Stress#ATP Production#Mitochondrial Fragmentation#Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)#Calcium Homeostasis#Mitochondrial Dynamics#Mitochondrial Transport#Mitophagy#Mitochondrial Quality Control#PGC-1α (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Coactivator 1-Alpha)#Cellular Energy Metabolism#Mitochondrial-Targeted Therapies#Apoptosis.
0 notes
Text
An UBIquitous Parkin to take a NAP iSINT BAD while OPTN' for cargo hold: but TANK-binding will lead to a mit-o-loss
There are several pathways to induce mitophagy, or the self-degradation of irreversibly damaged cellular mitochondria. The most well-characterized of these depends on proteins called PINK1 and Parkin, two proteins actively involved in the abnormalities of brain cells affected by Parkinson’s disease. Two other proteins, TFEB and HKDC1, play a key role in the maintenance of both mitochondria and…
#amyotrophic lateral sclerosis#cellular aging#cellular signaling#mitochondria#mitophagy#neurodegeneration#neuronal death#optineurina#Parkinson disease#protein kinase
0 notes
Text
National Natural Science Foundation Hotspot! What is Autophagy?
Autophagy
Autophagy is a fundamental process that degrades various components within the cell. Autophagy can be non-selective, where cytoplasmic materials are sequestered into autophagosomes for engulfment, typically occurring during nutrient deprivation. In contrast, selective autophagy degrades specific targets, such as damaged organelles: mitophagy, lysophagy, and ER-phagy, playing a crucial role in cellular quality control (Fig. 1)[1][2].

Fig. 1 Different mechanisms of autophagy[2].
2.Autophagy Protects & Promotes Death
Autophagy is a highly integrated process that maintains cellular homeostasis by promoting cell survival or leading to cell death[3][4].
2.1 Autophagy-Mediated Cytoprotection
The primary function of autophagy is to promote cell survival following stress or nutrient deprivation by recycling essential cellular components. Autophagy is induced by various stimuli, including nutrient and energy stress, hypoxia, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial damage[4].

Fig. 2 Overview of the major components of the core pathway of mammalian autophagy[5].
For example, when cells are cultured under conditions of simultaneous nutrient and growth factor deprivation, autophagy reaches its highest level[6]. Additionally, in mice, after 24-48 hours of starvation, most cells in various tissues exhibit an increase in autophagosome numbers[7]. Furthermore, cells must clear damaged mitochondria to prevent the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)[5]. Certain stress pathways, such as moderate hypoxia, also induce autophagy to prevent cell death (Fig. 2)[5][8].
2.2 Autophagy-Induced Cell Death
Autophagy is often observed in the context of cell death, and in some cases, inhibiting autophagy can prevent cell death[9]. Due to extensive crosstalk between different signaling pathways, the pro-death effects of autophagy are very complex[10].
Case 1: Autophagy-Dependent Ferroptosis
Recently, Jiao Liu and colleagues reported the critical role of TMEM164 in selectively mediating ATG5-dependent autophagosome formation during ferroptosis (rather than during starvation). TMEM164 promotes the death of iron-dependent cells by activating autophagy to degrade ferritin, GPX4, and lipid droplets, thereby increasing iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation. The loss of TMEM164 limits the anticancer activity of ferroptosis-mediated cytotoxicity in mice, establishing a new paradigm for autophagy-dependent ferroptosis[11].

Fig. 3 The role of TMEM164 in autophagy-dependent cell death[11].
Case 2: Autophagy-Triggers Necroptotic Apoptosis
Research indicates that GX15-070 can induce autophagy by increasing the accumulation of autophagosomes and promoting the interaction of Atg5 (a component of the autophagosome membrane) with key components of the necrosome, namely FADD, RIP1, and RIP3, triggering the assembly of the necrosome on autophagosomes. This leads to the formation of cytoplasmic cell death signaling complexes, initiating necrotic cell death[12].

Fig. 4 GX15-070 triggers necroptotic apoptosis by promoting the assembly of the necrosome on autophagosomes[12].
Autophagy plays a dual role in cancer, depending on the type and stage of the cancer [10][13]. On one hand, autophagy can promote tumorigenesis and metastasis; currently, the only FDA-approved autophagy inhibitors are Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine[14]. On the other hand, autophagy can enhance the efficacy of cancer treatments by promoting cell death either independently or in conjunction with other cell death pathways (Table 1)[10].
Table 1. Drug treatments that induce autophagy and cell death[10].

3. Detection of Autophagy
With the increasing interest in autophagy research, related detection methods have also become a focal point for researchers. The number of autophagosomes and autophagic flux are often used as indicators of cellular autophagic activity levels.
3.1 Monitoring the Number of Autophagosomes
Currently, there are three main methods used to monitor the number of autophagosomes: electron microscopy, optical microscopy for detecting the subcellular localization of LC3, and biochemical assays for the membrane-associated form of LC3[15].
The most traditional method is electron microscopy, which allows for the observation of autophagic vacuole-like structures in samples. Under electron microscopy, cells undergoing autophagy display damaged organelles, such as swollen mitochondria, surrounded by vacuolar double-membrane-like structures, or double-membranes encircling mitochondria to form autophagosomes. Residual bodies that cannot be degraded are also visible within autolysosomes (Fig. 5 and 6A)[15][16].

Fig 5. Morphology of autophagosomes and autolysosomes[15].
Secondly, the mammalian autophagy protein LC3 is a marker for autophagosomes and can be detected using more widely used optical microscopy and biochemical methods. Endogenous LC3 or GFP-LC3 can be observed via fluorescence microscopy as a diffuse cytoplasmic pool or as punctate structures primarily representing autophagosomes (Fig. 6B-C).
3.2 Monitoring Autophagic Flux
One of the main methods for measuring autophagic flux is monitoring the turnover of LC3. When cells are treated with lysosomal agents (such as ammonium chloride, Chloroquine, or Bafilomycin A1) or lysosomal protease inhibitors (such as E64d), the degradation of LC3-II is blocked, leading to its accumulation. Therefore, the differences in LC3-II levels between samples represent the amount of LC3 delivered to lysosomes for degradation (Fig. 6D)[15].

Fig 6. Methods for monitoring autophagosome quantity and autophagic flux[15].
Additionally, the total cellular LC3 levels can be quantified through immunoblotting analysis or flow cytometry, or qualitatively observed via fluorescence microscopy, which inversely correlates with autophagic flux. Besides LC3, the levels of other autophagic substrates can also be used to monitor autophagic flux (Fig. 6).
Conclusion
In this issue, our little M has summarized the types of cellular autophagy, related mechanisms, and characteristics, and introduced the dual functions of autophagy in cell protection and promotion of cell death. Finally, we have organized the relevant detection methods for cellular autophagy!
Product Recommendation
Chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antimalarial and anti-inflammatory agent widely used to treat malaria and rheumatoid arthritis. Chloroquine is an autophagy and toll-like receptors (TLRs) inhibitor. Chloroquine is highly effective in the control of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection in vitro (EC50=1.13 μM).
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a synthetic oral antimalarial drug that can be used in the study of malaria and autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Hydroxychloroquine is a potent autophagic flux inhibitor with antiviral activity (such as SARS-CoV-2 virus) that inhibits Toll-like receptor 7/9 (TLR7/9) signaling.
Vorinostat
Vorinostat (SAHA) is a potent and orally active pan-inhibitor of HDAC1, HDAC2 and HDAC3 (Class I), HDAC6 and HDAC7 (Class II) and HDAC11 (Class IV), with ID50 values of 10 nM and 20 nM for HDAC1 and HDAC3, respectively. Vorinostat induces cell apoptosis. Vorinostat is also an effective inhibitor of human papillomaviruse (HPV)-18 DNA amplification.
Sorafenib
Sorafenib (Bay 43-9006) is a potent and orally active Raf inhibitor with IC50s of 6 nM and 20 nM for Raf-1 and B-Raf, respectively. Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor with IC50s of 90 nM, 15 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM and 58 nM for VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFRβ, FLT3 and c-Kit, respectively. Sorafenib induces autophagy and apoptosis. Sorafenib has anti-tumor activity. Sorafenib is a ferroptosis activator.
Dactolisib
Dactolisib (BEZ235) is an orally active and dual pan-class I PI3K and mTOR kinase inhibitor with IC50s of 4 nM/5 nM/7 nM/75 nM, and 20.7 nM for p110α/p110γ/p110δ/p110β and mTOR, respectively. Dactolisib (BEZ235) inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2.
References
[1] Vargas JNS,et al. The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy in mammals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Mar;24(3):167-185. [2] Aman Y,et al. Autophagy in healthy aging and disease. Nat Aging. 2021 Aug;1(8):634-650. [3] Noguchi M, et al. Autophagy as a modulator of cell death machinery. Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 8;11(7):517. [4] Denton D, et al. Autophagy-dependent cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2019 Mar;26(4):605-616. [5] Kroemer G, et al. Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell. 2010 Oct 22;40(2):280-93. [6] Boya P, et al. Inhibition of macroautophagy triggers apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(3):1025-40. [7] Mizushima N. The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Apr;22(2):132-9. [8] Bellot G, et al. Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 2009 May;29(10):2570-81. [9] Jung S, et al. Autophagy as a decisive process for cell death. Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jun;52(6):921-930. [10] Denton D, et al. Autophagy as a pro-death pathway. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;93(1):35-42. [11] Liu J, et al. TMEM164 is a new determinant of autophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Autophagy. 2023 Mar;19(3):945-956. [12] Basit F, et al. Obatoclax (GX15-070) triggers necroptosis by promoting the assembly of the necrosome on autophagosomal membranes. Cell Death Differ. 2013 Sep;20(9):1161-73. [13] Li X, et al. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020 Jan 22;19(1):12. [14] Mohsen S, et al. Autophagy Agents in Clinical Trials for Cancer Therapy: A Brief Review. Curr Oncol. 2022 Mar 5;29(3):1695-1708. [15] Mizushima N, et al. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 2010 Feb 5;140(3):313-26. [16] Martinet W, et al. In situ detection of starvation-induced autophagy. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006 Jan;54(1):85-96.
0 notes
Text
Valter Longo and Mark Mattson’s 2014 study on fasting, published in Cell Metabolism, highlights the powerful effects of prolonged fasting on stem cell regeneration, immune system rejuvenation, and longevity pathways.
Key Mechanisms & Longevity Pathways
1. Stem Cell Regeneration
• Prolonged fasting (48-72 hours) depletes glucose and liver glycogen, shifting metabolism to fat-derived ketones.
• This metabolic switch triggers hematopoietic stem cell activation, promoting the regeneration of immune cells.
• Autophagy and mitophagy clear out damaged cell components, making way for healthier cells.
2. Immune System Rejuvenation
• Fasting significantly reduces white blood cell count, which triggers a rebound effect—stem cells regenerate new, functional immune cells after refeeding.
• This mechanism is crucial for counteracting immunosenescence (aging-related immune decline).
3. Longevity Pathways
• FOXO Proteins: Fasting activates FOXO3, a transcription factor that enhances stress resistance, DNA repair, and cellular longevity.
• AMPK Activation: Energy stress from fasting increases AMPK levels, boosting mitochondrial biogenesis and metabolic efficiency while reducing inflammation.
• IGF-1 Reduction: Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), linked to aging and cancer, drops during fasting, promoting repair over proliferation.
Application for Longevity
• Periodic prolonged fasting (2-3 days) every few months could help rejuvenate stem cells and the immune system.
• Intermittent fasting (16:8 or 5:2) activates some of these pathways, though prolonged fasting shows deeper regenerative benefits.
• Refeeding phase is crucial—it should include essential amino acids and healthy fats to maximize stem cell activation.
This study lays the foundation for using fasting as a non-pharmacological approach to longevity, immune health, and cellular regeneration.
0 notes
Text
Healthspan - Wege zu einer längeren Lebensspanne in Gesundheit. Fünfter Teil - Präventive Medizin

Healthspan - Wege zu einer längeren Lebensspanne in Gesundheit. Fünfter Teil - Präventive Medizin
15. Präventive Medizin
Regelmäßige Vorsorgeuntersuchungen helfen, altersbedingte Krankheiten frühzeitig zu erkennen und zu behandeln Regelmäßige Vorsorgeuntersuchungen spielen eine zentrale Rolle im Bereich Anti-Aging, da sie helfen, den Gesundheitszustand zu überwachen, frühzeitig Anzeichen von altersbedingten Erkrankungen zu erkennen und Maßnahmen zu ergreifen, um die Gesundheit zu erhalten und das Altern zu verlangsamen. Diese Untersuchungen konzentrieren sich auf präventive Maßnahmen, die die Lebensqualität steigern und altersbedingte Risiken minimieren. Hier sind einige der wichtigsten Vorsorgeuntersuchungen und -maßnahmen im Kontext von Anti-Aging: 1. Allgemeine Gesundheitsuntersuchungen - Blutdruckmessung: Hoher Blutdruck kann zu Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen führen, die mit dem Alter zunehmen. Eine regelmäßige Kontrolle hilft, das Risiko für Herzinfarkt und Schlaganfall frühzeitig zu erkennen und zu behandeln. - Blutuntersuchungen: Regelmäßige Blutuntersuchungen bieten Informationen über wichtige Blutwerte, wie Cholesterin, Blutzucker, Nieren- und Leberfunktionen. Diese Werte sind wichtige Indikatoren für das Risiko von Diabetes, Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen und anderen altersbedingten Krankheiten. - Blutfettwerte (Cholesterin, Triglyceride): Hohe Cholesterinwerte sind mit einem erhöhten Risiko für Herzkrankheiten verbunden. - Blutzucker (Insulinresistenz, HbA1c): Die Überwachung des Blutzuckers hilft, Diabetes frühzeitig zu erkennen und zu behandeln. - Entzündungsmarker: Entzündungen sind ein wichtiger Faktor im Alterungsprozess (Inflammaging). CRP (C-reaktives Protein) und andere Entzündungsmarker können Hinweise auf chronische Entzündungen geben. 2. Krebsfrüherkennung - Mammographie (Brustkrebs): Für Frauen ab einem bestimmten Alter (je nach Land und individueller Risikofaktoren) wird eine regelmäßige Mammographie empfohlen, um Brustkrebs frühzeitig zu erkennen. - Pap-Abstrich und HPV-Test (Gebärmutterhalskrebs): Frauen sollten regelmäßig Pap-Abstriche durchführen lassen, um Gebärmutterhalskrebs vorzubeugen und frühzeitig zu erkennen. - Darmkrebs-Screening (Kolonoskopie): Ab dem 50. Lebensjahr wird häufig empfohlen, alle 10 Jahre eine Koloskopie zur Früherkennung von Darmkrebs durchzuführen. - Prostatakrebs-Screening: Männer sollten ab dem 50. Lebensjahr (oder früher, wenn familiäre Vorbelastung vorliegt) eine jährliche Prostatauntersuchung in Betracht ziehen. Der PSA-Test kann dabei helfen, Prostatakrebs frühzeitig zu erkennen. 3. Herz-Kreislauf-Untersuchungen - EKG (Elektrokardiogramm): Ein EKG hilft, Herzrhythmusstörungen zu erkennen und zu überwachen. Es ist besonders wichtig für die Früherkennung von Herzinfarkten oder anderen kardiovaskulären Erkrankungen. - Ultraschall der Halsschlagader: Diese Untersuchung prüft auf Plaqueablagerungen in den Arterien, die zu einer Arteriosklerose und damit zu einem erhöhten Risiko für Schlaganfälle führen können. - Herz-Kreislauf-Risiko-Analyse: Bei dieser Untersuchung werden Risikofaktoren wie Blutdruck, Cholesterinwerte und Blutzucker berücksichtigt, um das individuelle Risiko für Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen zu ermitteln. MONOAMIN-OXIDASEN, OXIDATIVER STRESS UND VERÄNDERTE MITOCHONDRIALE DYNAMIK BEI DER HERZALTERUNG MAO-A SIPS (STRESS-INDUCED PREMATURE SENESCENCE) Mitochondrien sind in dem Seneszenz-Prozess verwickelt, hauptsächlich, weil sie sowohl Quellen als auch Ziele von reaktiven Sauerstoffspezies (ROS) sind. Stressbedingte vorzeitige Seneszenz in Herzzellen durch erhöhte MAO A führt zu mitochondrialen Schäden, Kardiomyozytentod und Herzinsuffizienz und steuert in Herzzellen zur ROS-Produktion, mitochondriale Dysfunktion und zur Mitophagie-Hemmung bei. Zusätzlich beeinträchtigt MAO A-erzeugter oxidativer Stress die Lysosomenfunktion, was zu einer Blockade des autophagischen Flusses führt. Als Beispiel ist das mitochondriale Enzym Monoamin-Oxidase-A (MAO A) zu erwähnen, welches im Herzen durch die Bildung von Wasserstoffperoxid (H2O2), das aus dem Abbau (oxidativer Desaminierung) seiner Hauptsubstrate Noradrenalin und Serotonin stammt, eine relevante Quelle für reaktive Sauerstoffspezies (ROS) darstellt und zur zellulären Seneszenz am Herzen führt.
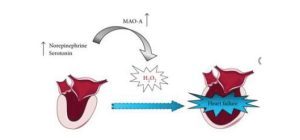
ABB. ROLLE VON MAO-A BEI HERZINSUFFIZIENZ Quelle: Gomes, Aldrin V. Magg iorani, Damien et al. Monoamine Oxidases, Oxidative Stress, and Altered Mitochondrial Dynamics in Cardiac Ageing. 2017.Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.

100 % bioactive
SAM-e
S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE
als (S/S) Spiegelisomer
singulärer DNA-und Histon-Methylgruppen-Donator
https://nugenis.eu/shop/
4. Hormonelle Gesundheit und Endokrine Systemuntersuchungen - Testosteronspiegel (bei Männern) und Östrogenspiegel (bei Frauen): Die regelmäßige Überprüfung der Hormonwerte ist wichtig, da Hormonungleichgewichte das allgemeine Wohlbefinden und das Altern beeinflussen können. Besonders bei Männern im mittleren und höheren Alter kann ein Testosteronmangel die Lebensqualität negativ beeinflussen. - Schilddrüsenuntersuchung: Schilddrüsenprobleme wie Hypothyreose (Unterfunktion) oder Hyperthyreose (Überfunktion) können das Altern beschleunigen. Die regelmäßige Überprüfung der Schilddrüsenwerte (z.B. TSH, T3, T4) ist deshalb wichtig. 5. Knochengesundheit - Knochendichte-Messung (Osteoporose-Screening): Ab dem 50. Lebensjahr, besonders bei Frauen nach der Menopause, ist es wichtig, die Knochendichte regelmäßig zu messen. Eine verminderte Knochendichte erhöht das Risiko für Frakturen und Osteoporose. - Vitamin D-Spiegel: Ein Vitamin D-Mangel kann sich negativ auf die Knochengesundheit auswirken und zu einer erhöhten Knochenbrüchigkeit führen. Regelmäßige Messungen können helfen, Mängel frühzeitig zu erkennen. 6. Augen- und Höruntersuchungen - Augenuntersuchungen: Regelmäßige Augenuntersuchungen sind wichtig, um Alterskrankheiten wie Makuladegeneration oder grauen Star frühzeitig zu erkennen. Auch Diabetische Retinopathie bei Diabetikern ist ein häufiger Altersfaktor. - Hörtests: Ab dem 50. Lebensjahr oder bei Anzeichen von Hörverlust sollte regelmäßig ein Audiogramm durchgeführt werden, um Hörprobleme frühzeitig zu diagnostizieren. ALTERSBEDINGTER MAKULADEGENERATION (AMD) Die altersbedingte Makuladegeneration (AMD) ist eine der häufigsten Ursachen für Sehbehinderungen und Erblindung bei älteren Menschen, besonders in Industrieländern. Ihre Häufigkeit steigt mit dem Alter, und sie betrifft zunehmend die älteren Generationen. Hier sind einige wichtige Fakten zur Häufigkeit von AMD: - Prävalenz: - Etwa 8 bis 10% der Menschen über 60 Jahren weltweit leiden an einer Form der AMD. - In Deutschland sind es schätzungsweise etwa 1,5 Millionen Menschen, die an AMD erkrankt sind. In anderen westlichen Ländern sind ähnliche Zahlen zu beobachten. - Altersgruppen: - Die Häufigkeit der AMD nimmt mit dem Alter signifikant zu. Bei Menschen im Alter von 50 bis 60 Jahren ist die Erkrankung noch relativ selten, aber ab etwa 70 Jahren steigt das Risiko erheblich. - Rund 30% der Menschen im Alter von 75 Jahren oder älter haben eine Form der AMD An der Pathogenese der altersbedingten Makuladegeneration ist die DNAHypomethylierung beteiligt. Die altersbedingte Makuladegeneration (AMD) ist die häufigste Ursache für eine irreversible Blindheit bei Menschen ab 50 Jahren und kann nicht wirksam geheilt werden. Die Krankheit ist gekennzeichnet durch die fokale Ablagerung von azellulären und polymorphen Trümmern, Drusen genannt,zwischen retinalem Pigmentepithel (RPE) und Bruch-Membran. Eines der in Drusen akkumulierten Hauptproteine ist Clusterin, dessen Expression durch Promotor-Methylierung reguliert wird. Auch gibt es zahlreiche Hinweise, dass die durch oxidativen Stress aus der Atmungskette der Mitochondrien verursachten Störungen eine weitaus größere Bedeutung bei der Entstehung der AMD haben als bislang angenommen. Gerade der oxidative Stress (ROS) führt bei AMD-Patienten zu gravierenden DNA-Schäden der mitochondrialen DNA. Sowohl Alter und Rauchen sind bestätigte Risikofaktorenfür AMD.

100 % bioactive
SAM-e
S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE
als (S/S) Spiegelisomer
singulärer DNA-und Histon-Methylgruppen-Donator
https://nugenis.eu/shop/
7. Zahngesundheit - Regelmäßige Zahnuntersuchungen: Zahngesundheit hat direkten Einfluss auf das allgemeine Wohlbefinden und den Alterungsprozess. Regelmäßige Zahnarztbesuche helfen, Zahnerkrankungen (wie Parodontitis oder Karies) zu vermeiden, die zu entzündlichen Erkrankungen führen können und somit den gesamten Körper belasten. 8. Mental Health Check-up - Psychische Gesundheit: Besonders im Alter können psychische Erkrankungen wie Depression, Angststörungen oder Kognitive Beeinträchtigungen auftreten. Regelmäßige Screenings für psychische Gesundheit sind wichtig, um frühzeitig gegen Alzheimer oder andere demenzielle Erkrankungen vorzugehen und die Lebensqualität zu erhalten. 9. Genetische Untersuchungen - Genetische Prädispositionen: Einige Menschen haben aufgrund ihrer genetischen Veranlagung ein höheres Risiko, an bestimmten Krankheiten zu erkranken (z. B. Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankungen, Krebs). Mit genetischen Tests können Risikofaktoren identifiziert werden, die präventive Maßnahmen erleichtern. Diese Tests suchen nach Genveränderungen, die das Risiko erhöhen können, bestimmte Krankheiten in der Zukunft zu entwickeln, wie z. B. bestimmte Arten von Krebs (z. B. Brust- oder Darmkrebs) oder neurodegenerative Erkrankungen wie die Huntington-Krankheit. Ein bekanntes Beispiel ist der BRCA1- oder BRCA2-Test, der auf ein erhöhtes Risiko für Brust- und Eierstockkrebs hinweist. Prävention ist der Schlüssel Anti-Aging geht weit über kosmetische Eingriffe hinaus. Es umfasst vor allem präventive Maßnahmen, die darauf abzielen, den Körper zu erhalten, bevor Symptome von Alterserkrankungen auftreten. Regelmäßige Vorsorgeuntersuchungen sind eine wichtige Grundlage, um den Gesundheitszustand zu überwachen und altersbedingte Risiken frühzeitig zu erkennen. Diese Untersuchungen ermöglichen es, Verhaltensweisen zu ändern, Behandlungen zu starten und so die gesunde Lebensspanne (Healthspan) zu maximieren und das biologische Altern zu verlangsamen.
16. Sind wir durch Vorsorgeuntersuchungen wirklich gesund?
Die asymptomatische Neurodegeneration
MITOCHONDRIALE THEORIE VON ALTERN UND NEURODEGENERATION (Harman 1972) Die mitochondriale Theorie von Altern und Neurodegeneration von Denham Harman postuliert einen molekularen Teufelskreis, in dem sich oxidativer Stress und Schäden an mitochondrialen Proteinen und mitochondrialer DNA (mtDNA) gegenseitig verstärken. Die Folge ist eine mitochondriale Funktionsstörung und eine verminderte Expression von mitochondrial kodierten Atmungskettenuntereinheiten. Dies bewirkt eine Störung des Elektronenflusses in der Atmungskette und führt aus diesem Grund zu einer vermehrten reaktive Sauerstoffspezies (ROS)-Produktion. Bei Überschreiten eines bestimmten Schädigungsschwellenwertes (ca. 60- 85% aller mtDNA-Moleküle einer Zelle) kommt es zu einer Funktionsstörung der Mitochondrien und letztendlich zum Untergang der betroffenen Zellen, was sich nach außen als „normales Altern“, (auf Zellebene als „physiologischer“ Alterungsprozess, aber auch als noch asymptomatische Neurodegeneration) oder aber als „neurodegenerative Erkrankung“ mit manifesten Symptomen äußert. Postmitotische Gewebe mit hohem Energiebedarf, wie Gehirn, Leber, Retina und Skelettmuskel/Herzmuskel, Nieren und Hoden sind besonders vondiesem Teufelskreis betroffen, da sie einen hohen Sauerstoff-Umsatz haben und geschädigte Zellen nicht in relevantem Umfang erneuert werden können. Ohne rechtzeitiger Prävention zum Schutz der Mitochondrien (oxidativer Stress durch den Anstieg der ROS-Produkte und Schäden an mitochondrialen Proteinen und mitochondrialer DNA (mtDNA) durch eine S-Adenosylmethionine-Supplementation, sind bei klinischer Diagnose der z.B. Alzheimer-Krankheit die neurodegenerativen Schäden bereits soweit fortgeschritten, dass nur symptomatische und palliative Therapien zur Patientenversorgung offen stehen. Sobald klinisch manifeste neurodegenerative Schäden auftreten, ist der Handlungsspielraum stark eingeschränkt. Der Schutz der Mitochondrien und die Reduktion oxidativen Stresses in frühen Stadien (oder sogar präventiv) sind daher Schlüsselstrategien, um den Verlauf von Krankheiten wie Alzheimer zu verzögern oder zu verhindern.
S-Adenosylmethionine
(SAMe, Ademetionin):
SAMe ist ein wichtiger Methylgruppendonator, der für viele zelluläre Prozesse essenziell ist, einschließlich der DNA-Methylierung und des Schutzes vor oxidativem Stress Es wird davon ausgegangen, dass eine Ergänzung von SAMe die mitochondrialen Funktionen unterstützt, indem es die Expression der Monoamin-Oxidase an seinem Genort stilllegt und damit antioxidativ wirkt, indem es den ROS-Produkte-Anstieg aus der Desaminierung der monoaminergen Neurotransmitter (Serotonin, Dopamin, Noradrenalin) durch die erhöhte Monoamin-Oxidase (MAO) verhindert. Die Vulnerabilität des Mitochondriums ist durch die Nähe der äußeren und inneren Mitochondrienmembran gegeben. Der Abstand zwischen der äußeren (Sitz der MAO-Enzyme) und innerer Mitochondrienmembran (Energiestoffwechsel der Mitochondrien, insbesondere die oxidative Phosphorylierung oder Atmungkette genannt) beträgt etwa 10–20 Nanometer (nm). Ein Nanometer (nm) entspricht einem Milliardstel Meter.

100 % bioactive
SAM-e
S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE
als (S/S) Spiegelisomer
singulärer DNA-und Histon-Methylgruppen-Donator
https://nugenis.eu/shop/
17. Impfungen und Präventionsmaßnahmen verringern das Risiko von Infektionen, die den Alterungsprozess beschleunigen können
Impfungen und präventive Maßnahmen spielen eine wichtige Rolle im Anti-Aging, indem sie das Risiko von Infektionen verringern, die den Alterungsprozess negativ beeinflussen können. Gerade im Alter wird das Immunsystem schwächer, wodurch ältere Menschen anfälliger für Infektionen sind, die chronische Entzündungen und andere Gesundheitsprobleme fördern können. Solche Entzündungen sind ein bekannter Risikofaktor für den beschleunigten Alterungsprozess – auch als Inflammaging bezeichnet. Hier sind einige der wesentlichen Impfungen und Präventionsmaßnahmen, die helfen können, den Alterungsprozess zu verlangsamen und die Gesundheit zu fördern: 1. Impfungen als Schutz vor Infektionen - Grippeimpfung: Die saisonale Grippeimpfung ist besonders für ältere Menschen wichtig, da sie anfälliger für Komplikationen durch Influenza sind, die das Immunsystem stark belasten können. Grippeinfektionen können bei älteren Menschen zu schweren Erkrankungen oder sogar Tod führen, insbesondere wenn sie mit anderen chronischen Erkrankungen wie Herzkrankheiten oder Diabetes kombiniert sind. - Pneumokokken-Impfung: Pneumokokken sind Bakterien, die Lungenentzündungen und andere schwere Infektionen verursachen können. Besonders ältere Erwachsene sind anfällig für Pneumokokkeninfektionen, die den Alterungsprozess beschleunigen können, da chronische Entzündungen und Organschäden entstehen. Die Pneumokokkenimpfung hilft, diese Infektionen zu verhindern. - Herpes Zoster (Gürtelrose): Der Herpes Zoster (Gürtelrose) wird durch das gleiche Virus verursacht, das auch Windpocken hervorruft. Nach einer Windpockenerkrankung verbleibt das Virus im Körper und kann später im Leben reaktiviert werden. Ältere Menschen haben ein höheres Risiko, an Gürtelrose zu erkranken, was mit starken Schmerzen und möglichen langfristigen Komplikationen (z.B. postherpetische Neuralgie) verbunden sein kann. Die Impfung kann das Risiko einer Gürtelrose deutlich senken und somit das Risiko chronischer Entzündungen reduzieren. - Tetanus-, Diphtherie- und Pertussis-Impfungen: Diese Impfungen sind Teil des Standardimpfplans, können aber auch im höheren Alter notwendig sein, insbesondere bei Verletzungen oder Kontakt mit potenziellen Erregern. Infektionen wie Tetanus können das Immunsystem stark belasten und langfristige gesundheitliche Probleme verursachen. - Hepatitis-Impfungen: Die Hepatitis-B-Impfung ist besonders wichtig für Menschen im mittleren und höheren Alter, um vor einer chronischen Lebererkrankung zu schützen. Chronische Lebererkrankungen können den Alterungsprozess beschleunigen und das Risiko für Leberkrebs erhöhen. 2. Präventionsmaßnahmen zur Verringerung des Infektionsrisikos Neben Impfungen gibt es weitere wichtige Präventionsstrategien, die das Risiko von Infektionen reduzieren und somit den Alterungsprozess unterstützen: - Hygienemaßnahmen: Regelmäßiges Händewaschen und das Vermeiden von engen Kontakt mit kranken Menschen sind grundlegende Maßnahmen, um Infektionen zu verhindern. Dies ist besonders wichtig für ältere Menschen, da ihre Immunabwehr nicht mehr so effizient ist wie bei jüngeren Menschen. - Ernährung: Eine ausgewogene, nährstoffreiche Ernährung stärkt das Immunsystem und trägt dazu bei, Infektionen abzuwehren. Bestimmte Nahrungsmittel wie Obst, Gemüse, Ballaststoffe, Vitamine (insbesondere Vitamin C und D) und Mineralien (wie Zink und Eisen) haben immunstärkende Eigenschaften und unterstützen das Immunsystem. Eine gesunde Darmflora, die durch Präbiotika und Probiotika gefördert werden kann, ist ebenfalls wichtig für die allgemeine Immunfunktion. - Bewegung: Regelmäßige körperliche Aktivität stärkt das Immunsystem und hilft, das Risiko von Krankheiten zu verringern. Moderate Bewegung, wie z. B. Spaziergänge, Schwimmen oder Radfahren, hat entzündungshemmende Effekte und fördert die allgemeine Gesundheit, was wiederum den Alterungsprozess verlangsamt. - Stressmanagement: Chronischer Stress hat nachweislich negative Auswirkungen auf das Immunsystem und kann zu einer höheren Anfälligkeit für Infektionen führen. Langfristiger Stress fördert auch chronische Entzündungen, die den Alterungsprozess beschleunigen. Daher sind Maßnahmen wie Meditation, Atemübungen, Yoga oder regelmäßige Entspannungsphasen wichtig, um das Immunsystem zu stärken und den Alterungsprozess zu verlangsamen. Read the full article
#10%SAM-e-JONundentfaltetmaximalebiologischeWirkung.#altersbedingteKrankheiten#altersbedingteMakuladegeneration(AMD)#Anti-AgingStrategien#chronischeEntzündungen#Darm-Hirn-Achse#Entzündungsregulation#EthikinderAnti-Aging-Forschung#genetischePrädisposition#Gesundheitsvorsorge#Healthspan#ImpfungenundAnti-Aging#Inflammaging#MAO-ASIPS(STRESS-INDUCEDPREMATURESENESCENCE)#Mikrobiom-Optimierung#MitochondrialeGesundheit#PräventiveMedizin#S-Adenosylmethionine(SAMe)#VorbeugenistbesseralsHeilen#Vorsorgeuntersuchungen#Zellalterungverlangsamen
0 notes
Text
Urolithin A Supplement in India – Top Rated for Anti-Aging & Mitochondrial Health
Brahmastra Pharmacy Presents: Urolithin A+ (500mg) – India’s Game-Changing Supplement for Youthful Vitality & Cellular Health
Aging is a universal experience, but how we age is increasingly within our grasp. Thanks to incredible strides in modern science and a deeper understanding of our cellular machinery, we can now actively influence the aging process from within. Brahmastra Pharmacy is proud to introduce Urolithin A+ (500mg), an innovative supplement crafted to ignite cellular rejuvenation, optimize mitochondrial health, and unlock your youthful vitality. Proudly made right here in India, consider this your secret weapon to turning back the biological clock – naturally and powerfully.

Unveiling Urolithin A: Your Cellular Refresh Button
So, what exactly is Urolithin A? It's a fascinating postbiotic compound our bodies can produce when certain beneficial gut bacteria break down polyphenols found in foods like pomegranates, berries, and walnuts. Think of it as a vital message that tells your cells to "refresh."
However, not everyone has the specific gut microbiome needed to produce Urolithin A efficiently. This is where Urolithin A+ by Brahmastra Pharmacy steps in. Each potent capsule delivers 500mg of pure Urolithin A, bypassing the need for complex gut processes and delivering this powerful compound directly to your system, ensuring you get the benefits, every time.
Why Urolithin A is Your Ally Against Aging
The true essence of aging begins deep within our cells. As the years go by, our cells become less efficient at repairing themselves and generating the energy we need to thrive. This cellular slowdown can manifest as nagging fatigue, a foggy mind, noticeable muscle loss, and an increased susceptibility to chronic health issues. A primary culprit in this decline is the reduced function of our mitochondria – often called the "powerhouses" of our cells.
Here's where Urolithin A shines! It's been scientifically proven to stimulate mitophagy, a remarkable cellular "clean-up" process. Imagine your body sweeping away old, damaged mitochondria and replacing them with fresh, healthy ones. This is the core mechanism behind maintaining youthful energy levels, boosting endurance, and ultimately, enhancing overall longevity.
Experience the Transformative Power of Urolithin A+ (500mg)
Embrace a new chapter of vitality with these incredible benefits:
Recharge Your Cellular Batteries: Urolithin A actively promotes mitophagy, leading to more efficient energy production at the cellular level. The result? More stamina, laser-sharp focus, and enhanced physical performance to conquer your day.
Slow Down the Hands of Time: By rejuvenating tired mitochondria and combating oxidative stress, Urolithin A helps reduce the cellular damage that often accelerates the aging process.
Strengthen Your Body, Boost Your Endurance: Clinical studies highlight Urolithin A's ability to improve muscle function. This makes it a perfect addition for active individuals, aging adults looking to maintain strength, and anyone seeking long-term physical vitality.
Sharpen Your Mind: Healthier mitochondria in your brain cells can translate to clearer thinking, improved memory, and vital protection against age-related cognitive decline.
Unleash Your Inner Radiance: Cellular repair and renewal from within often reflect outwardly. Many users notice a more vibrant, youthful glow and improved skin appearance with consistent use.
Extend Your Healthspan: By supporting cellular renewal and autophagy (another key cellular clean-up process), Urolithin A helps you not just live longer, but live better and more vibrantly.
Why Choose Brahmastra Pharmacy's Urolithin A+? Your Health, Our Promise.
India's wellness market offers countless choices, but Brahmastra Pharmacy stands out through an unwavering commitment to quality, transparency, and scientifically-backed formulations. Here’s why our Urolithin A+ is becoming the trusted choice for thousands across India:
Pharmaceutical Grade Quality: Every single capsule is meticulously manufactured in GMP-certified, ISO-compliant facilities, ensuring the highest standards of safety, purity, and potency. Your well-being is our top priority.
Clinically Dosed – 500mg: We don't believe in guesswork. Backed by rigorous peer-reviewed studies, 500mg is the optimal dose shown to deliver real, measurable anti-aging benefits. No underdosing, no unnecessary fillers – just pure effectiveness.
100% Bioavailable Formula: Our advanced formulation ensures that Urolithin A effectively reaches your cells for maximum absorption and impact. It’s designed to work where it matters most.
Gut-Friendly and Vegan: Crafted with care, our Urolithin A+ is free from common allergens, synthetic additives, and is proudly 100% vegan-friendly, making it suitable for almost all dietary preferences.
Made in India, Backed by Global Science: While inspired by cutting-edge global longevity research, this product is proudly researched, developed, and made right here in India, championing local innovation and excellence.
Seamlessly Integrate Urolithin A+ Into Your Routine
Dosage: Simply take 1 capsule daily with a meal, or as advised by your healthcare provider. Best Time to Take: The morning, perhaps with breakfast, is ideal to help kickstart your energy and metabolism for the day ahead. Who Can Benefit: Urolithin A+ is designed for adults over 25, especially those feeling the early signs of fatigue, noticing decreased performance, or actively seeking to slow down the aging process.
Is Urolithin A+ Right for You?
If you resonate with any of these, Urolithin A+ might be your perfect match:
✅ Busy Professionals eager to combat burnout and enhance mental clarity.
✅ Fitness Enthusiasts seeking improved recovery and boosted endurance.
✅ Seniors committed to maintaining their mobility and independence.
✅ Biohackers and Longevity Seekers exploring cutting-edge anti-aging solutions.
✅ Anyone Over 30 starting to notice the subtle (or not-so-subtle) effects of aging.
The Science Speaks for Itself
Urolithin A is not just a trend; it's a compound rigorously studied in multiple human clinical trials. A landmark 2020 study published in Nature Metabolism demonstrated that Urolithin A supplementation significantly improved mitochondrial function in older adults, leading to enhanced muscle endurance. Another compelling study in Cell Reports Medicine showcased improved biomarkers of cellular health and reduced inflammation after just 4-12 weeks of Urolithin A use.
These findings are particularly exciting because they point towards a powerful, non-invasive anti-aging strategy. Instead of relying on complex hormone therapies or invasive procedures, Urolithin A empowers your own cells to heal, regenerate, and function at their best.
Real People, Real Transformations
Don't just take our word for it. Hear from those who've experienced the Brahmastra difference:
"I've been taking Urolithin A+ for two months now, and my energy has skyrocketed. I feel sharper at work and genuinely more alive." – Rohan M., Bengaluru
"I’m 62 and love staying active. Since using Brahmastra’s Urolithin A+, I've noticed much better stamina during my walks and significantly fewer joint aches. It's truly made a difference." – Neeta A., Mumbai
"This feels like the real deal. I've tried so many anti-aging supplements, but nothing has given me results like this. Highly, highly recommended!" – Devansh S., Delhi
Get Your Urolithin A+ Today – Exclusively at Brahmastra Pharmacy!
Urolithin A+ is now available exclusively through Brahmastra Pharmacy’s official online store and select trusted online platforms. We offer swift, reliable delivery across India, secure payment options, and dedicated customer support to ensure a seamless experience.
🎁 Special Introductory Offer: Buy 2, Get 1 Free + Enjoy Free Shipping Across India! Don't miss this limited-time opportunity to invest in your youthful future.
Your Questions, Answered (FAQs)
❓ Is Urolithin A safe? Yes, absolutely. Extensive clinical studies have shown Urolithin A to be safe and exceptionally well-tolerated, with no major side effects reported when taken as directed.
❓ How long before I start seeing results? While individual experiences can vary, most users begin to notice positive changes within 2–4 weeks. Optimal and more pronounced results are typically observed after consistent use for 8–12 weeks.
❓ Can I take it with other supplements? Definitely! Urolithin A+ complements well with a wide range of other supplements, including your daily multivitamins, omega-3s, and other anti-aging or fitness-focused supplements.
❓ Is it suitable for vegetarians or vegans? Yes, Brahmastra Urolithin A+ is proud to be 100% vegan and completely free from any animal-derived ingredients.
Conclusion: Age Smarter, Live Better with Brahmastra Urolithin A+
Aging is no longer a journey you have to passively accept. With Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+, you now hold the key to one of the most scientifically advanced anti-aging supplements available in the Indian market. Whether you're in your 30s looking to maintain peak energy, in your 50s hoping to preserve vibrant vitality, or in your 60s and beyond aiming to significantly extend your healthspan – Urolithin A+ (500mg) is your trusted companion for aging gracefully, powerfully, and with purpose.
It's time to take charge of your cellular destiny. Experience the future of longevity today.
👉 Order Urolithin A+ – Rewind Your Youth from Brahmastra Pharmacy now.
0 notes
Text
Urolithin A+ by Brahmastra Pharmacy: A Natural Breakthrough for Healthy Aging
In a world where aging often feels like a slow surrender, what if science offered a smarter way to stay active, energized, and sharp — naturally?
Welcome to the future of wellness with Urolithin A+, an advanced anti-aging supplement by Brahmastra Pharmacy that’s taking the health world by storm. Unlike ordinary antioxidants or quick-fix energy boosters, this supplement works at the cellular level — targeting the very core of aging: your mitochondria.
Let’s explore why Urolithin A+ is gaining attention as a game-changer in the world of natural longevity.
What is Urolithin A, and Why Should You Care?
Urolithin A is a powerful compound produced naturally in the gut — but only if you have the right kind of gut bacteria. That’s a problem because most people don’t, especially with today’s lifestyles and diets.
Luckily, science has found a way to deliver pure Urolithin A directly through supplementation.
But what does it do?
Urolithin A stimulates a biological process called mitophagy — your body’s way of cleaning out damaged mitochondria (the parts of your cells that create energy) and replacing them with new ones. In simple terms: it recharges your cells from the inside out.
Why Mitochondria Matter More Than You Think
As we age, our mitochondria — the "powerhouses" of our cells — start to break down. This is one reason we feel tired more often, lose strength, and experience brain fog.
Urolithin A+ helps reverse that decline by:
Revitalizing mitochondrial function Boosting cellular energy Improving endurance and strength Slowing signs of aging at the root level
This isn’t hype — it’s backed by real, cutting-edge science.
Real Benefits You Can Feel
People using Urolithin A+ consistently report noticeable improvements in several key areas:
1. More Energy, Less Fatigue
You’ll feel a sustained boost — not a caffeine crash. By energizing your cells, Urolithin A+ helps you feel alert and motivated all day long.
2. Improved Muscle Strength & Recovery
Whether you’re hitting the gym or just climbing stairs, your muscles will feel stronger, and your body will recover faster from physical exertion.
3. Sharper Mental Focus
Brain fog is often linked to poor mitochondrial health. Urolithin A+ supports cognitive function, focus, and mental clarity.
4. Cellular Anti-Aging
This isn’t just about looking younger — it’s about functioning younger. From your heart to your muscles to your mind, this supplement supports holistic anti-aging.
Why Choose Brahmastra Pharmacy’s Urolithin A+?
Brahmastra Pharmacy is known for blending ancient Ayurvedic wisdom with modern science. With Urolithin A+, they’ve created a product that’s:
Clinically supported
100% pure with 500mg Urolithin A per capsule
Free from harmful additives or synthetic fillers
Tested for safety and potency
It’s a trusted solution from a brand that understands both tradition and innovation.
Who Should Use Urolithin A+?
The truth? Almost anyone over 30 can benefit — especially if you:
Feel tired often without reason
Struggle with physical recovery after workouts
Notice signs of aging catching up
Want to support healthy aging proactively
Need better focus, energy, and stamina daily
From busy professionals to health-conscious seniors and fitness lovers — Urolithin A+ fits right into your daily wellness routine.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
While individual results vary, many users begin to feel improvements in energy and clarity within 2–4 weeks of regular use. Deeper mitochondrial benefits — such as strength and stamina — become more noticeable after 6–8 weeks.
Consistency is key. Like all good things, the best results come with regular use and a healthy lifestyle.
Final Thoughts: It’s Time to Age on Your Terms
Aging doesn’t have to mean slowing down. With Urolithin A+, you can support your body’s ability to renew, recharge, and perform at its peak, no matter your age.
At Brahmastra Pharmacy, we believe that true wellness starts within — and Urolithin A+ is a testament to that philosophy. This isn’t just a supplement. It’s a lifestyle choice for those who want to stay active, feel vibrant, and live fully.
Ready to Feel the Difference?
Order your bottle of Urolithin A+ today and take the first step toward youthful energy, strength, and clarity — naturally.
Available now at [Brahmastra Pharmacy Website] Pure. Potent. Proven.
0 notes