#mobile application developers in Kenya
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Determined to use her skills to fight inequality, South African computer scientist Raesetje Sefala set to work to build algorithms flagging poverty hotspots - developing datasets she hopes will help target aid, new housing, or clinics.
From crop analysis to medical diagnostics, artificial intelligence (AI) is already used in essential tasks worldwide, but Sefala and a growing number of fellow African developers are pioneering it to tackle their continent's particular challenges.
Local knowledge is vital for designing AI-driven solutions that work, Sefala said.
"If you don't have people with diverse experiences doing the research, it's easy to interpret the data in ways that will marginalise others," the 26-year old said from her home in Johannesburg.
Africa is the world's youngest and fastest-growing continent, and tech experts say young, home-grown AI developers have a vital role to play in designing applications to address local problems.
"For Africa to get out of poverty, it will take innovation and this can be revolutionary, because it's Africans doing things for Africa on their own," said Cina Lawson, Togo's minister of digital economy and transformation.
"We need to use cutting-edge solutions to our problems, because you don't solve problems in 2022 using methods of 20 years ago," Lawson told the Thomson Reuters Foundation in a video interview from the West African country.
Digital rights groups warn about AI's use in surveillance and the risk of discrimination, but Sefala said it can also be used to "serve the people behind the data points". ...
'Delivering Health'
As COVID-19 spread around the world in early 2020, government officials in Togo realized urgent action was needed to support informal workers who account for about 80% of the country's workforce, Lawson said.
"If you decide that everybody stays home, it means that this particular person isn't going to eat that day, it's as simple as that," she said.
In 10 days, the government built a mobile payment platform - called Novissi - to distribute cash to the vulnerable.
The government paired up with Innovations for Poverty Action (IPA) think tank and the University of California, Berkeley, to build a poverty map of Togo using satellite imagery.
Using algorithms with the support of GiveDirectly, a nonprofit that uses AI to distribute cash transfers, the recipients earning less than $1.25 per day and living in the poorest districts were identified for a direct cash transfer.
"We texted them saying if you need financial help, please register," Lawson said, adding that beneficiaries' consent and data privacy had been prioritized.
The entire program reached 920,000 beneficiaries in need.
"Machine learning has the advantage of reaching so many people in a very short time and delivering help when people need it most," said Caroline Teti, a Kenya-based GiveDirectly director.
'Zero Representation'
Aiming to boost discussion about AI in Africa, computer scientists Benjamin Rosman and Ulrich Paquet co-founded the Deep Learning Indaba - a week-long gathering that started in South Africa - together with other colleagues in 2017.
"You used to get to the top AI conferences and there was zero representation from Africa, both in terms of papers and people, so we're all about finding cost effective ways to build a community," Paquet said in a video call.
In 2019, 27 smaller Indabas - called IndabaX - were rolled out across the continent, with some events hosting as many as 300 participants.
One of these offshoots was IndabaX Uganda, where founder Bruno Ssekiwere said participants shared information on using AI for social issues such as improving agriculture and treating malaria.
Another outcome from the South African Indaba was Masakhane - an organization that uses open-source, machine learning to translate African languages not typically found in online programs such as Google Translate.
On their site, the founders speak about the South African philosophy of "Ubuntu" - a term generally meaning "humanity" - as part of their organization's values.
"This philosophy calls for collaboration and participation and community," reads their site, a philosophy that Ssekiwere, Paquet, and Rosman said has now become the driving value for AI research in Africa.
Inclusion
Now that Sefala has built a dataset of South Africa's suburbs and townships, she plans to collaborate with domain experts and communities to refine it, deepen inequality research and improve the algorithms.
"Making datasets easily available opens the door for new mechanisms and techniques for policy-making around desegregation, housing, and access to economic opportunity," she said.
African AI leaders say building more complete datasets will also help tackle biases baked into algorithms.
"Imagine rolling out Novissi in Benin, Burkina Faso, Ghana, Ivory Coast ... then the algorithm will be trained with understanding poverty in West Africa," Lawson said.
"If there are ever ways to fight bias in tech, it's by increasing diverse datasets ... we need to contribute more," she said.
But contributing more will require increased funding for African projects and wider access to computer science education and technology in general, Sefala said.
Despite such obstacles, Lawson said "technology will be Africa's savior".
"Let's use what is cutting edge and apply it straight away or as a continent we will never get out of poverty," she said. "It's really as simple as that."
-via Good Good Good, February 16, 2022
#older news but still relevant and ongoing#africa#south africa#togo#uganda#covid#ai#artificial intelligence#pro ai#at least in some specific cases lol#the thing is that AI has TREMENDOUS potential to help humanity#particularly in medical tech and climate modeling#which is already starting to be realized#but companies keep pouring a ton of time and money into stealing from artists and shit instead#inequality#technology#good news#hope
209 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kenya Precision Agriculture Market Trends, Share, Industry, Forecast and outlook (2024-2031)

According to the January 2025 Datam Intelligence report, the Kenya Precision Agriculture Market Trends is expected to grow at a high compound annual growth rate over the 2024–2031 period, although specific historical and forecasted revenue figures are proprietary and not publicly disclosed .
Latest News & Trends Kenya’s agricultural sector is rapidly embracing digital transformation. In early 2025, the Kenyan government launched the Data for Soil Health and Innovation Challenges, inviting innovators to develop AI- and big-data–driven solutions to monitor soil fertility and boost yields across the country Complementing this, the “Third Eye” project deployed AI‐powered drones to map soil moisture and detect early pest infestations—reducing crop losses by up to 15% in pilot regions. Meanwhile, agritech platforms such as Mercy Corps’ AgriFin Digital Advisor have scaled mobile-based agronomic advice to more than 200,000 smallholders, driving precision‐tech adoption across rural Kenya
Market Segmentation The Kenyan market can be described in four key segments, each supported by quantitative insights drawn from global benchmarks:
By Technology: Guidance systems, variable-rate technology, remote sensing, crop scouting, precision irrigation, yield monitoring, financial and labor management. Globally, guidance systems accounted for the largest share of the precision‐agriculture market in 2024, while variable-rate technology is projected to grow fastest at a 13.6% CAGR through 2028
By Offering: Hardware, software, services. In 2024, the global hardware segment led with over 66% market share, owing to investments in sensors, drones, and automated machinery; software is the fastest-growing, with the global precision‐farming software market set to expand from USD 1.7 billion in 2024 to USD 3.1 billion by 2029 (12.5% CAGR)
By Application: Field mapping, yield monitoring, seeding & spraying, crop monitoring, precision irrigation, other applications. Yield monitoring held the largest global share in 2024 at over 42%, driven by farmers’ need for real-time harvest data and spatial yield analysis
By Region (within Kenya): Nairobi, Mombasa, Kisumu, Nakuru, Eldoret, Rest of Kenya. Although regional revenue breakdowns for Kenya are unpublished, global trends point to Asia Pacific as the fastest-growing region, while North America retains the largest share
Sample Link
Regional Analysis: United States & Japan
United States: The U.S. precision-farming market generated USD 2,615.0 million in revenue in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 4,865.9 million by 2030, growing at a 9.3% CAGR. Hardware led revenue in 2023, while software is the fastest-growing segment. Growth is fueled by widespread IoT and data-analytics adoption, and supported by USDA programs such as the 2023 Farm Bill’s conservation technology incentives
Japan: In 2023, Japan’s precision-farming market generated USD 278.5 million and is expected to grow at a 14.7% CAGR to USD 726.4 million by 2030. Hardware comprised the largest offering in 2023; software led growth prospects. The Smart Agriculture Promotion Act (2018) and subsidies for IoT‐enabled sensors have been key policy drivers
Key Highlights from Reports
High Growth Prospects: Kenya is pegged for a “high” CAGR through 2031, reflecting accelerating digital‐agriculture adoption .
Resource Optimization: Chronic undernourishment (24.2% in 2016) and recurring drought risks underscore the urgency for precision solutions to boost yields and conserve inputs .
Competitive Strategies: Leading companies are pursuing M&A, partnerships, and product launches—e.g., John Deere’s 2024 FarmSight platform expansion and AGCO’s next-gen guidance systems in late 2023 .
Key Players & Competitors Major players in the Kenyan market include AGCO Corporation, Usomi, AG Junction Inc., Crop Metrics LLC, Deere & Company, Farmers Edge Inc., Grownetics Inc., Granular Inc., Crop Nuts, and Ujuzi Kilimo . The top five by market influence and recent activity are:
Deere & Company – Expanded FarmSight analytics suite in 2024.
AGCO Corporation – Launched new guidance systems in Q4 2023.
Farmers Edge Inc. – Acquired SST Development Group for USD 30 million in 2022.
Granular Inc. – Rolled out smallholder analytics tools across East Africa in 2024.
Ujuzi Kilimo – Partnered with the Kenyan government on nationwide soil-sensor networks.
Buy This Report
Conclusion Kenya’s precision agriculture market is on the cusp of a transformational leap. Strong government-led strategies, private-sector innovations, and unmet food-security needs converge to create fertile ground for digital-agriculture solutions. While precise revenue figures remain proprietary, qualitative indicators—high projected CAGRs, rapid project deployments, robust policy support—signal sustained growth. Continued collaboration among policymakers, technology providers, and farmers will be essential to harness precision agriculture’s full potential in Kenya and beyond.
0 notes
Text
Human Rabies Vaccines Market Future Landscape: Innovations, Challenges, and Global Strategies
The global Human Rabies Vaccines Market is poised for significant transformation over the next decade. With increasing efforts from international health organizations, rising awareness, and advancements in vaccine technology, the future landscape of this market is expected to evolve rapidly. The shift in public health priorities, coupled with innovations in vaccine delivery and manufacturing, will shape how the market addresses the ongoing threat of rabies.
Rabies, despite being preventable, remains a significant public health challenge, particularly in developing regions. An estimated 59,000 people die from rabies annually, mostly in Asia and Africa. The World Health Organization’s “Zero by 30” campaign aims to eliminate dog-mediated human rabies deaths by 2030. This ambitious target is acting as a major catalyst for innovation, investment, and strategic planning within the vaccine market.

Current Market Overview and Limitations
The present rabies vaccine market is dominated by a few key manufacturers and relies heavily on post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP), which must be administered promptly after exposure to the rabies virus. These vaccines are generally administered intramuscularly and require a series of doses, which can be costly and logistically challenging in resource-poor areas.
A major bottleneck in the current landscape is limited accessibility. In many rural or underserved regions, challenges such as inadequate healthcare infrastructure, lack of trained professionals, and cold chain requirements hinder widespread immunization.
Future Innovations in Vaccine Technology
The future landscape of the human rabies vaccines market is heavily dependent on technological advancements. One of the most promising developments is the creation of thermostable rabies vaccines. These vaccines do not require constant refrigeration, making them ideal for deployment in remote and tropical regions. Several biotech firms are investing in the research and development of such vaccines, which will likely see broader commercial rollout within the next five to ten years.
Single-dose and long-lasting vaccines are also on the horizon. Researchers are exploring formulations that can provide immunity with fewer doses, or even a single shot, thereby reducing the burden on healthcare systems and improving compliance rates.
Wider Adoption of Intradermal Administration
The shift from intramuscular to intradermal (ID) administration is gaining traction as a cost-effective alternative. The ID method requires a smaller volume of vaccine per dose, allowing more individuals to be treated from a single vial. This change, endorsed by the WHO, is expected to become a global standard, especially in countries with limited vaccine supply or funding.
Digital Health and Surveillance Integration
The integration of digital tools in rabies control programs will play a significant role in the future market. Applications such as mobile health (mHealth) platforms, electronic immunization registries, and real-time surveillance systems are already showing promise in improving vaccine distribution, scheduling, and follow-up.
AI-powered analytics and predictive modeling will also support public health officials in identifying high-risk zones, optimizing vaccine allocation, and monitoring the progress of elimination campaigns.
Regional Landscape: Focus on Asia and Africa
As rabies remains endemic in many parts of Asia and Africa, these regions will continue to dominate the future demand for human rabies vaccines. Countries like India, Bangladesh, Kenya, and the Philippines are ramping up efforts through national vaccination drives, educational campaigns, and government subsidies.
To support these initiatives, there is a growing trend of local vaccine production. Regional manufacturing reduces costs, ensures faster delivery, and increases responsiveness during outbreaks.
Policy Support and Global Collaboration
Global and regional partnerships are shaping the future landscape of rabies prevention. Organizations such as WHO, Gavi, UNICEF, and the Global Alliance for Rabies Control (GARC) are working closely with governments and private manufacturers to ensure that rabies vaccines are included in national immunization programs and are accessible to high-risk populations.
Funding initiatives, including outcome-based financing and pooled procurement strategies, are likely to become more widespread, helping low- and middle-income countries secure adequate vaccine supplies.
Challenges to Address
Despite a promising outlook, several hurdles remain:
Vaccine hesitancy and lack of awareness in rural populations.
Inadequate healthcare infrastructure for timely PEP administration.
High costs associated with PEP regimens, especially for travelers.
Weak animal vaccination programs, especially in stray dog populations.
Addressing these challenges will require sustained investment, stronger public education, and an integrated One Health approach that links human, animal, and environmental health strategies.
Conclusion
The future landscape of the human rabies vaccines market is marked by innovation, accessibility, and strategic collaboration. From thermostable and intradermal vaccines to AI-driven surveillance and local manufacturing, the sector is undergoing a major transformation. With coordinated global efforts, the goal of eradicating dog-mediated rabies deaths by 2030 is within reach. As stakeholders continue to align science, policy, and public health infrastructure, the market is set to not only grow but also create a lasting impact on global health outcomes.
0 notes
Text
Digital Remittance Market Overview: Trends, Growth, and Forecast
The Digital Remittance market has emerged as a transformative force in the global financial ecosystem, streamlining cross-border money transfers through advanced digital platforms. As the demand for fast, secure, and low-cost money transfers continues to rise, digital remittance services are becoming increasingly integral to global economic activity, particularly in regions with high migration flows.

Market Overview
Digital remittance refers to the transfer of money through online platforms and mobile applications without relying on traditional financial institutions. Unlike conventional remittance methods, digital remittances offer enhanced speed, lower transaction fees, and greater convenience.
This market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years due to increased smartphone penetration, improved internet connectivity, and the growing adoption of digital financial services. Fintech innovations and partnerships with local financial institutions have also played a crucial role in expanding the reach and efficiency of these services.
Key Market Trends
Mobile-First Solutions The surge in mobile wallet usage and app-based platforms is revolutionizing how users send and receive money. Countries with a large number of unbanked individuals, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia, are seeing rapid adoption of mobile remittance services.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency Integration Blockchain technology is being used to improve transaction transparency and reduce transfer fees. Several companies are also experimenting with cryptocurrency as a remittance channel, though regulatory concerns remain a hurdle.
AI and Automation AI-driven fraud detection, personalized customer service, and automated compliance checks are helping digital remittance platforms become faster and more secure.
Government and Regulatory Support Many governments are promoting digital financial inclusion through favorable regulations and partnerships with fintech firms. This is boosting user trust and expanding market accessibility.
Remittance Corridors Expansion New and less common remittance routes are opening up, driven by increased globalization and labor mobility. Platforms are now focusing on underserved markets to gain competitive advantage.
Market Growth
The digital remittance market was valued at approximately USD 19 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13–15% through 2030. The key drivers include:
Rising international migration
Growth in disposable incomes among migrant workers
Increasing reliance on digital payment ecosystems
Expanding internet and smartphone penetration in developing nations
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific leads the digital remittance market in volume, driven by countries like India, China, and the Philippines.
North America is a key sender region, with a strong presence of migrant workers from Latin America and Asia.
Africa shows high potential for future growth, particularly with the success of mobile money solutions like M-Pesa in Kenya.
Future Forecast
Looking ahead, the digital remittance market is expected to see sustained growth driven by:
Enhanced interoperability between payment systems globally
Greater financial literacy among users in emerging markets
Integration of open banking APIs to streamline cross-border transfers
Strategic M&A activity among fintech companies aiming to scale globally
Conclusion
The Digital Remittance market is poised for exponential growth as digital transformation reshapes the financial services landscape. With ongoing innovation, evolving customer expectations, and increasing regulatory support, digital remittance platforms are not only becoming more user-friendly but also vital tools for global economic empowerment.
0 notes
Text
Africa GNSS Market Competitive Landscape and Strategic Insights to 2033
Introduction
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology has seen widespread adoption across multiple industries, including agriculture, transportation, logistics, and surveying. Africa’s GNSS market is poised for significant growth, driven by increased demand for precision positioning services, infrastructure development, and government initiatives. This article explores industry trends, key drivers, challenges, and the forecast for the African GNSS market leading up to 2032.
Market Overview
The African GNSS market is still developing but has seen notable adoption due to advancements in satellite technology, improved internet connectivity, and increasing investments in smart infrastructure. GNSS technology is used in various applications, such as land surveying, geospatial mapping, precision agriculture, fleet management, and urban planning.
𝗗𝗼𝘄𝗻𝗹𝗼𝗮𝗱 𝗮 𝗙𝗿𝗲𝗲 𝗦𝗮𝗺𝗽𝗹𝗲 𝗥𝗲𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁👉https://tinyurl.com/4t3cfe5v
Key Market Drivers
Infrastructure Development
Many African countries are investing in large-scale infrastructure projects, such as smart cities, road networks, and railway systems, which require precise geolocation services.
Agricultural Advancements
Precision farming using GNSS technology helps optimize resource utilization, improve yield, and reduce operational costs. With Africa’s agrarian economy, GNSS adoption in farming is growing rapidly.
Rising Demand for Location-Based Services (LBS)
The expansion of mobile technology and navigation-based applications has increased demand for GNSS-enabled services. This includes ride-hailing apps, logistics tracking, and emergency response systems.
Government Initiatives and Policies
Governments across Africa are implementing policies to integrate GNSS in national development plans. Programs supporting satellite navigation, mapping, and disaster management are being developed.
Improvement in Satellite Infrastructure
The deployment of regional satellite navigation systems and the use of international GNSS systems such as GPS, Galileo, and BeiDou enhance the reliability of positioning services in Africa.
Key Market Challenges
Limited Infrastructure
While urban areas have made strides in adopting GNSS, rural and remote regions still lack the necessary infrastructure to support GNSS applications effectively.
High Costs of GNSS Equipment and Services
The cost of acquiring and maintaining GNSS receivers, software, and subscription services can be a significant barrier for small-scale users.
Technical and Skills Gaps
The lack of skilled professionals in GNSS technology and applications presents a challenge to market growth. Capacity-building initiatives are needed to bridge this gap.
Regulatory and Policy Constraints
The absence of harmonized policies and regulatory frameworks across different African nations creates inconsistencies in GNSS implementation and usage.
Market Segmentation
The African GNSS market can be segmented based on application, end-user industry, and geographic region.
By Application
Navigation and Mapping: Used in urban planning, disaster management, and surveying.
Agriculture: Supports precision farming, yield monitoring, and automated machinery.
Transportation and Logistics: Fleet management, traffic control, and intelligent transport systems.
Defense and Security: Border control, surveillance, and emergency response.
Construction and Mining: Site surveying, resource tracking, and safety management.
By End-User Industry
Agriculture
Transportation and Logistics
Government and Defense
Construction and Mining
Telecommunications
Healthcare (emergency response services)
By Geography
North Africa (Egypt, Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia)
West Africa (Nigeria, Ghana, Senegal, Ivory Coast)
East Africa (Kenya, Ethiopia, Tanzania, Uganda)
Southern Africa (South Africa, Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe)
Central Africa (DR Congo, Cameroon, Chad)
Competitive Landscape
The African GNSS market is composed of international players and emerging local service providers. Key companies operating in the space include:
Trimble Inc.
Hexagon AB
Garmin Ltd.
Topcon Corporation
Septentrio NV
Fugro N.V.
ComNav Technology Ltd.
South Instruments
These players are investing in research and development, strategic partnerships, and collaborations to expand their presence in Africa.
Future Trends and Market Outlook (2024-2032)
Expansion of Local GNSS Services
Countries like South Africa, Nigeria, and Kenya are expected to enhance their GNSS infrastructure and develop local navigation services.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
GNSS will be increasingly integrated with AI, IoT, and 5G networks to improve accuracy and automation in industries such as smart agriculture and autonomous transportation.
Growing Adoption of GNSS in Disaster Management
With climate change concerns, African nations will leverage GNSS technology for early warning systems, flood monitoring, and crisis response.
Increase in Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Collaborations between governments, private firms, and international organizations will accelerate GNSS adoption and infrastructure development.
Rise in Affordable GNSS Solutions
Cost-effective GNSS solutions tailored for the African market are expected to increase accessibility and adoption among small businesses and local enterprises.
Conclusion
The Africa GNSS market is set for significant expansion over the next decade, driven by infrastructure projects, increased demand for precision-based applications, and government support. Despite challenges such as high costs and regulatory issues, ongoing developments in satellite infrastructure, training programs, and local service provisions will foster growth. With key players investing in innovation and strategic collaborations, Africa’s GNSS ecosystem is poised to become a crucial component of the continent’s digital transformation and economic development.
Read Full Report:-https://www.uniprismmarketresearch.com/verticals/information-communication-technology/africa-gnss.html
0 notes
Text
GIS in Agriculture: Transforming Farming with Spatial Intelligence
Introduction:
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are revolutionizing agriculture by providing farmers and agribusinesses with critical spatial data to enhance decision-making. By integrating GIS in agriculture with farming practices, it helps improve crop management, optimize land use, and increase productivity. This article explores the role of GIS, its benefits, and real-world case studies demonstrating its impact.
The Role of GIS in Agriculture:
GIS is a powerful tool that allows farmers to collect, analyze, and interpret spatial data for better farm management. Some essential uses of GIS technology in agriculture involve:
Precision Farming: GIS enables precise mapping of soil properties, water availability, and crop health, allowing farmers to apply fertilizers and pesticides only where needed, reducing costs and environmental impact.
Crop Monitoring and Yield Prediction: Satellite imagery and remote sensing data help monitor crop growth and predict yield, enabling better planning for harvests and market supply.
Soil Mapping and Analysis: GIS-based soil analysis provides insights into soil fertility, moisture levels, and erosion risks, assisting in selecting suitable crops and irrigation methods.
Water Resource Management: GIS helps in efficient irrigation planning by mapping water sources, analyzing drainage patterns, and preventing overuse of water resources.
Disaster Management and Risk Assessment: GIS assists in tracking climate patterns, identifying areas prone to drought, flooding, or pest infestations, and implementing preventive measures.
Case Studies:
Case Study 1: Precision Farming in Punjab, India
Company/Institution: Punjab Agricultural University & ICAR
Challenge: Farmers in Punjab were experiencing declining soil fertility and excessive fertilizer use, leading to reduced crop yields and environmental degradation.
Solution: The Punjab Agricultural University, in collaboration with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), introduced a GIS-based precision farming system. GIS mapping was used to analyze soil fertility and moisture levels, enabling targeted application of fertilizers and irrigation.
Outcome: The project resulted in a 15% increase in crop yield and a 20% reduction in input costs. Additionally, groundwater depletion was mitigated by implementing optimized irrigation strategies.
Case Study 2: Water Management in California, USA
Company/Institution: University of California, Davis
Challenge: California’s Central Valley, a major agricultural region, faced severe water scarcity due to prolonged droughts and inefficient irrigation systems.
Solution: The University of California, Davis, partnered with local farming cooperatives to implement a GIS-based irrigation management system. This system used satellite imagery and field sensors to track soil moisture levels and optimize water distribution.
Outcome: Farmers reduced water wastage by 25% while maintaining crop health. The project also helped detect leaks and inefficiencies in irrigation infrastructure, leading to significant water conservation.
Case Study 3: Disaster Preparedness for Maize Farmers in Kenya
Company/Institution: Kenyan Agricultural Research Institute (KARI)
Challenge: Kenyan maize farmers frequently suffered from droughts and pest infestations, particularly the Fall Armyworm, leading to severe crop losses.
Solution: KARI developed a GIS-based early warning system that integrated weather forecasts, pest monitoring data, and satellite imagery. Farmers were alerted via mobile applications and local extension services about potential threats, allowing them to take preventive measures.
Outcome: Maize losses due to pests and extreme weather were reduced by 30%, significantly improving food security for thousands of smallholder farmers.
Conclusion:
GIS technology is transforming agriculture by enhancing precision, sustainability, and resilience. By integrating spatial intelligence into farming practices, GIS not only improves productivity but also helps conserve resources and mitigate risks. The real-world case studies presented here demonstrate how GIS is enabling data-driven decision-making in agriculture, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable farming systems worldwide. As technology continues to advance, GIS will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of agriculture.
0 notes
Text
In this episode, Midnight Mike and the team dive into the first segment with casual banter about technological nostalgia, including a deep dive into Steve Jobs' legacy and his influence on the evolution of computers and user experience. They also discuss the interplay between innovation and difficult personalities in leadership, drawing parallels to other notable figures like Stanley Kubrick and Christian Bale. The conversation flows into lighter anecdotes about editing and content creation challenges, humorously highlighting tech's role in modern life.
The second segment shifts to a discussion on political and current events, with a heavy focus on AI's integration into defense and intelligence. Topics include the CIA's increasing reliance on AI, the potential risks of AI in surveillance, and its applications in espionage. The hosts critically analyze recent developments and implications for national security, contrasting U.S. advancements with China's dominance in AI-powered surveillance. They also touch on controversies like the management of California's wildfires and broader climate policies, linking systemic issues to political leadership.
Finally, in the third segment, the podcast explores strange news and listener calls. Highlights include a story about a giant metallic ring that fell from the sky in Kenya, sparking debates on aerospace debris and unexplained phenomena. They also discuss unique job opportunities, like driving the "Peanut Mobile," and laugh at absurd headlines, such as scams involving celebrity impersonators. Wrapping up, the hosts discuss bizarre cultural moments, including controversial political hearings and outlandish conspiracy theories.
0 notes
Text
Open Call for the EU Youth Empowerment Fund (YEF)

Youth-Led Action for the SDGs 2024: Open Call for Grant Applications(Up to €5,000 in grant available) The European Union, in partnership with the Global Youth Mobilization (GYM) and the “Big Six” youth organizations, is excited to announce the launch of the Open Call for the EU Youth Empowerment Fund (YEF) through the Global Youth Mobilization. Click here to learn more about this opportunity and apply. About Youth-Led Action for the SDGs 2024 This initiative aims to empower young people to drive positive change in their communities by providing micro-grant funding for innovative, youth-led solutions that advance the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Benefits of Youth-Led Action for the SDGs 2024 - Individual Young People and Informal Groups: €500 to €1,500 - Registered Youth Organizations: €3,000 to €5,000 Youth-Led Action for the SDGs 2024 Requirments Young individuals aged 14 to 30 from eligible countries: - Africa: Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, São Tomé and Príncipe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe. - Asia: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China (People’s Republic of), India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Kiribati, Kyrgyzstan, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Maldives, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Tokelau, Tonga, Turkmenistan, Tuvalu, Uzbekistan, Vanuatu, Viet Nam, Yemen. - Europe: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia. - Latin America and the Caribbean:Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Cuba, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Grenada, Guatemala, Guyana, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela. - Middle East: Palestine. - Oceania: Nauru, Niue, Tokelau, Tuvalu. What They Are Looking For Projects addressing global challenges aligned with the SDGs, especially those led by or for underrepresented young people, including those from lower socio-economic backgrounds, those facing gender equality issues, and individuals with disabilities. We are particularly interested in projects focusing on climate change and environmental sustainability. Selection Process A diverse panel of young individuals will review and score applications. Successful applicants will be notified within two months and will need to sign a grant agreement and submit their banking information. Unsuccessful applicants will receive feedback to help strengthen future submissions. Capacity-Building Support To assist applicants, we offer a series of capacity-strengthening webinars and resources, including sample application answers and FAQs. These are designed to help applicants submit the best possible projects. Application Date and Process - Click on the link to the application website to apply. Application Deadline 21 July, 2024 Scholarship Application Portal View details of Youth-Led Action for the SDGs 2024 Apply for Youth-Led Action for the SDGs 2024 Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Week 12: Crowdsourcing

In the midst of a period that is marked by an increasing frequency and severity of emergencies, ranging from environmental catastrophes to global health crises, crowdsourcing has emerged as a powerful instrument for the purpose of mobilising resources, gathering information, and stimulating innovation. This collaborative approach makes use of the numerous abilities and points of view of individuals from all over the world, so giving a method that is both flexible and adaptive in order to address complex and urgent issues. (Desai, Kuderer & Lyman 2020) An examination of the various applications of crowdsourcing in crisis management is presented in this essay. These applications are illustrated through prominent examples, and the study also discusses the inherent challenges and variables that need to be taken into consideration.
The rapid collection and dissemination of information is an immediate and practical application of crowdsourcing that can be utilized during times of need. During times of natural disasters, social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook have become increasingly important means for receiving information that is up to the minute. Those who live in areas that have been affected are able to share their own experiences with regard to the level of destruction, the immediate needs, and the current status of safety. (Desai, Kuderer & Lyman 2020) This information distribution from the bottom up has the potential to improve official reporting, thereby providing a more comprehensive picture of the matter. One outstanding example is the Ushahidi platform, which was initially developed to record instances of violence that occurred in Kenya during the elections that took place in 2008. Ushahidi has been utilized all over the world to collect information from the general population during times of emergency, such as the earthquake that occurred in Haiti in 2010 and the tsunami that occurred in Japan in 2011. As a result of collecting data from a variety of sources, Ushahidi helps to validate information and improve decision-making, hence reducing the amount of erroneous information that is distributed. (Meier 2012)
When a crisis is occurring, it is absolutely necessary to distribute resources as quickly as possible. Platforms that facilitate crowdsourcing make this process more effective by enabling a wide range of individuals to contribute resources, including money and materials. It is important to note that crowdfunding platforms like GoFundMe and Kickstarter have been essential in the process of raising financial support for relief efforts that are urgently needed. This demonstrates the power of collective action by allowing for the quick accumulation of modest contributions from a considerable number of individuals. These platforms assist the aggregation of these contributions. During the COVID-19 epidemic, a large number of crowdfunding initiatives were launched in order to provide assistance to healthcare workers, supply personal protective equipment (PPE), and finance research endeavors. As a result of the success of these efforts, the effectiveness and potential of crowdsourcing in terms of mobilizing resources during times of global crisis have been demonstrated. (Mollick 2014)
The utilisation of the collective intelligence of the global community is what makes crowdsourcing a useful tool for fostering innovation. With the ability to issue open solicitations for responses to specific challenges brought about by crises, governments and organisations have the opportunity to communicate their needs. This method not only speeds up the process of finding solutions to problems, but it also brings in a diverse range of perspectives and technical knowledge.
Through the utilisation of crowdsourcing, it has been demonstrated that it has the capability to significantly enhance disaster management and recovery efforts. The strategy offers a flexible and adaptive approach to dealing with the complex challenges that are brought about by crises. This is accomplished by harnessing the combined strength of individuals. The strength of collective action during times of urgency is demonstrated by crowdsourcing, which encompasses actions such as the collection of information, the mobilization of resources, the resolution of any problems that may arise, and the coordination of volunteer efforts.
References
Desai, A, Kuderer, NM & Lyman, GH 2020, ‘Crowdsourcing in Crisis: Rising to the Occasion’, JCO Clinical Cancer Informatics, no. 4, pp. 551–554.
Meier, P 2012, 'Crisis Mapping in Action: How Open Source Software and Global Volunteer Networks Are Changing the World, One Map at a Time', Journal of Map & Geography Libraries, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 89-100.
Mollick, E 2014, 'The dynamics of crowdfunding: An exploratory study', Journal of Business Venturing, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 1-16.
0 notes
Text
How to become a designer in Kenya 2024

The design industry is rapidly growing in Kenya and globally. The number of professional designers in Kenya has tripled in the last decade. One thing is for sure, Kenyans are creative. As many Kenyans discover they want to join the design industry, they have no idea where to start. In this article you will get the information you need to know how to become a designer in Kenya.
Introduction
In Kenya mist Universities and colleges don't offer design classes and the design industry until recently wasn't considered a serious profession. For example if you want to pursue UI design in Kenya, it is not easy to get any large institution offering UI design classes. Most of the top designers in Kenya are self taught. Before diving in, it is good to understand the different types of design. This will help you choose the design industry you want to pursue.
Types of designs
- Graphic Design- Graphic design involves creating visual concepts using computer software or by hand to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, or captivate consumers. Graphic designers work on a wide range of projects, including branding, advertising, packaging, and print materials. - UI (User Interface) Design- UI design focuses mainly on the look and feel of a digital product, such as websites, mobile apps, and software interfaces. UI designers design every visual aspect that you see when you launch an application, software or website. They aim to create intuitive, visually appealing interfaces that enhance user experience and usability. - UX (User Experience) Design- UX design involves the overall experience of users when interacting with a product or service. UX designers conduct user research, create wireframes and prototypes, and collaborate with UI designers and developers to ensure a seamless and enjoyable user experience. - Web Design- Web design is a branch of the design industry that specializes in creating visually appealing and functional websites. Web designers work with various design elements, including layout, color schemes, typography, and imagery, to create engaging online experiences. - Motion Design- I am sure at one point of your life you were very curious about how animations are created. Motion design deals with creating animations, videos, and other moving graphics for a many purposes, such as branding, advertising, and entertainment. They use animation software such as blender to bring static designs to life and engage viewers through dynamic storytelling. - Product Design- Product designers create the visuals you see on products. They focus on the design and development of physical products, such as consumer electronics, furniture, and appliances. Through collaborating with marketers, and manufacturers to create products that are functional, aesthetically pleasing, and marketable. - Interior Design- Interior design in Kenya is considered a lady profession. Interior designers specialize in creating functional and aesthetically pleasing interior spaces for homes, offices, restaurants, and other environments. By considering factors such as layout, lighting, color schemes, and furniture selection they are able to create cohesive and harmonious interiors. - Fashion Design: One of the most famous design Industry for the Kenyan youths, fashion designers create clothing, footwear, and accessories for various markets, including haute couture, ready-to-wear, and mass market. They sketch designs, select fabrics, and oversee the production process to bring their creative vision to life. - Architectural Designer: Architectural designers focus on the design and planning of buildings and structures by creating architectural drawings, 3D models, and renderings to visualize proposed designs and collaborate with architects and engineers to ensure feasibility and functionality.
Choosing a design Industry
Having known the different types of design, its time to choose a design industry to pursue. Here are the things to consider when choosing a design industry: - The first thing to consider is your interests, passions, and strengths. Consider what aspects of design excite you the most and where your natural talents lie. Look at what you have been loving throughout your life. - Do thorough research on the responsibilities, skills, and requirements associated with the type of design industry you want. Research on different examples of work in each field to get a sense of what the day-to-day work entails. - What is your long-term career goals and aspirations? You need to consider the type of work environment you envision yourself in, whether it's working for a design agency, freelancing, or starting your own design business. Consider the earning potential and job opportunities associated with each design specialization. - Evaluate your existing skills and education background to determine which type of design aligns best with your strengths and background. Some design specializations such as architectural design require specific technical skills or formal education, while others may be more accessible to self-taught individuals. - Reach out to professionals working in different design fields for advice and insights. - Research the market demand for different types of design skills in the job market. Consider factors such as industry trends, emerging technologies, and evolving consumer preferences when assessing the demand for specific design specializations. YOU MIGHT LIKE : HOW TO START FREELANCING IN KENYA
How to learn Design in Kenya
To learn design is easy. Once you have chosen the type of industry you want, its time to start learning. But how do you learn design in Kenya. Here are the different ways to learn designing in Kenya.
Local colleges
Enroll to a college that offers classes for the type of design you want to learn. Unfortunately in Kenya most top universities don't offer design courses. But many private colleges offer design courses. One of the best colleges to learn design is Kenya College of Interior Design.
Online Courses
One of the best way to learn design in Kenya is learning online. Most of the online courses have been carefully trimmed to suit everyone. The best online courses to learn design in Kenya are: - Coursera - The coursera design course is one of the sought out online course in the world. They offer various Design courses designed to fit your needs. Curated from top educational institutions and industry leaders, their selection of Design courses aims to provide quality training for everyone. They also give you a legitimate certificate upon approval of the courses. - Udemy- competing back to back with coursera, udemy offers one of the best competitive online design course in the market today. - Domestica - Alison-graphic design - Skill share
Free resources
Having no money to learn design should not stress you. You can learn design by utilizing free design resources available in the internet. I have written a comprehensive guide on where to find and utilize free design resources HERE.
Conclusion
The journey to become a designer is not hard and anyone can become a designer if they want. It is important to understand that design is an ever-evolving field, so make sure you commit to lifelong learning and skill development. Take additional courses, attend workshops, or pursue certifications to expand your knowledge and stay competitive in the industry. Read the full article
1 note
·
View note
Text
Elevate Your Business with Eujim Solutions: Your Trusted Software Development Partner

Are you ready to take your business to the next level in the digital world? Look no further than Eujim Solutions – your go-to software development company in Kenya. With their stellar reputation for excellence and innovation, they're here to be your trusted partner in crafting top-notch software solutions designed specifically for your business needs.
At Eujim Solutions, they're not just in the business of creating software – they're dedicated to building lasting relationships with their clients. Since their inception in 2018, their team of over 30 experts has been committed to delivering scalable, cost-effective solutions that drive real results for businesses just like yours. Whether you're a startup, small business, or large enterprise, they have the skills and flexibility to bring your vision to life.
Their wide range of services covers everything from software development and UI/UX design to digital marketing, IT consultancy, cybersecurity, and staff augmentation. Whether you need a web application, mobile app, or something in between, they've got you covered with their robust tech stack, including Swift, Kotlin, HTML, JavaScript, Java, Python, MySQL, and MongoDB – ensuring versatility and proficiency in every project.
But what truly sets Eujim Solutions apart is their unwavering commitment to your satisfaction. They believe in going above and beyond to exceed your expectations, offering round-the-clock support and maintenance to ensure your software solution continues to perform at its best.
So why wait? Partner with Eujim Solutions today and unlock the full potential of your business in today's digital landscape. Let them help you elevate your brand, streamline your operations, and drive growth with bespoke software solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Get in touch with them now to discover how Eujim Solutions can empower your business to thrive in the digital age. Together, let's embark on a journey of innovation and success.
0 notes
Text
Kenya cards and payments Market : A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In the heart of East Africa lies Kenya, a nation not only known for its breathtaking landscapes but also for its dynamic and evolving financial landscape. One of the pivotal components of this landscape is the cards and payments market, a sector that has undergone significant transformations over the years.
Historical Perspective
The journey of Kenya's cards and payments market is akin to a captivating narrative. From the early days of barter systems to the introduction of paper currency, the evolution has been profound. The advent of plastic cards, especially credit and debit cards, marked a significant leap forward, bringing convenience to the fingertips of consumers.
Current Scenario
As of today, Kenya's cards and payments market is a bustling ecosystem with various stakeholders. Leading banks, financial institutions, and fintech startups play crucial roles in shaping the landscape. The range of payment methods is diverse, including traditional cards, digital wallets, and the ubiquitous mobile money platforms.
Digital Transformation
The technological wave has not spared the financial sector in Kenya. The rapid digitization has led to a paradigm shift in how transactions are conducted. Mobile payments, in particular, have gained immense popularity, making financial services more accessible to the unbanked and underbanked populations.
Regulatory Landscape
In the pursuit of a robust financial system, Kenya has implemented stringent regulations. Government policies focus on ensuring the security and integrity of transactions. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for all players in the cards and payments arena.
Market Trends
The cards and payments market in Kenya is a dynamic space with several trends shaping its trajectory. Contactless payments, blockchain applications, and the integration of artificial intelligence are some of the key trends that demonstrate the industry's forward-looking approach.
Challenges
However, like any thriving sector, the cards and payments market in Kenya faces challenges. From issues related to cybersecurity to the need for constant innovation, industry players are navigating a landscape filled with complexities.
Opportunities
Despite challenges, the market presents vast opportunities for growth. The untapped potentials lie in expanding financial inclusion, developing innovative products, and collaborating with global players to enhance cross-border transactions.
Consumer Behavior
Understanding the psyche of the consumer is crucial in the financial arena. Consumer preferences, influenced by factors like convenience and security, dictate the choice of payment methods. This insight is invaluable for industry players seeking to tailor their services to meet customer expectations.
Case Studies
Examining successful case studies within Kenya's cards and payments market provides insights into strategies that have worked. Whether it's a novel approach to digital banking or a revolutionary mobile payment solution, these cases offer valuable lessons.
Future Outlook
Peering into the future, the cards and payments market in Kenya is poised for further growth. Technological advancements, coupled with strategic collaborations, are expected to redefine the landscape, making financial services more inclusive and efficient.
Global Comparisons
Drawing comparisons with global payment trends is essential to understand Kenya's position in the broader context. Analyzing similarities and differences sheds light on areas where the market can learn from or contribute to global best practices.
Sustainable Practices
In an era where sustainability is paramount, the cards and payments market in Kenya is exploring environmentally friendly and ethical practices. The integration of green technologies and adherence to ethical standards are becoming increasingly significant considerations.
Impact on Businesses
The influence of the cards and payments market extends beyond individual consumers. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly impacted, with the efficiency and accessibility of payment systems playing a crucial role in their operations and growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Kenya's cards and payments market is not just a financial engine but a reflection of the nation's progress. The journey from traditional transactions to the digital era is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of the industry. As Kenya charts its course into the future, the cards and payments market will continue to be a cornerstone of economic development.
To gain more information on the Kenya cards and payments market forecast, download a free report sample
0 notes
Text
React Native or Flutter-Know the pros and cons of both to make a choice
If you look around you, almost everyone is using smartphone apps these days. With so many mobile users everywhere, it’s obvious that companies will look for solutions to make the apps even more user-friendly than before. This is where React Native and Flutter step in; they are both hybrid frameworks that help you develop apps.
Knowing their features and advantages will help you see why more and more startups are turning towards these for creating apps.
React Native vs Flutter-which should you opt for?
React Native is unarguably one of the leading open-source frameworks using a JavaScript library for creating cross-platform applications. It was created by Facebook engineers and it combines the best features of native development and React for building user interfaces. Apps like Instagram, Uber Eats, Pinterest, etc were developed on this platform. You can create apps using JavaScript alone and these can be downloaded on Apple Store and Google Play Store. A big reason why engineers prefer React JS eCommerce framework is that it lets them focus more on products instead of struggling with the framework.
Flutter is another extensively-used open-source framework much like React Native that makes use of dart technology for creating apps. Unlike React, this was developed by Google engineers. It was launched in 2017 and continues to grow rapidly to become popular among developers. Countries like Canada, Japan, China, Bangladesh, Kenya, and Jordan prefer this framework.
React Native vs Flutter Language:
React Native makes use of JavaScript but Flutter uses Dart. Dart is harder to learn than JavaScript, and you will find few developers who know Dart well. This makes React Native JC eCommerce a little bit more popular. Writing codes using Dart takes more time because of its object-oriented concept. React JS, on the contrary, is easy to pick up and developers can access many resources. In case of a problem, developers can also reach out to a very wide community.
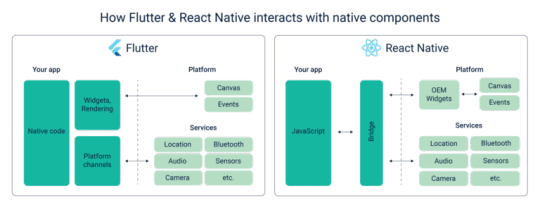
React Native vs Flutter Architecture:
React JS uses a JavaScript bridge, which is a runtime environment enabling communication with native components. This requirement to combine JS code with native modules may slow down the app in certain cases, but otherwise, the performance isn’t impacted. Flutter has most of the necessary components and there’s no need for a bridge. Since it offers key channels and protocols, apps tend to be more stable. Flutter uses Skia architecture while React Native uses Flux architecture. Flutter has a BLoC architecture which has a few benefits. It is robust, testable, and simple. Its main principle is building complex products from simple blocks. So, BLoC architecture can lessen the time needed to familiarize oneself with the project; this makes Flutter appealing for commercial projects that must be completed within shorter deadlines.
React Native vs Flutter Installation:
Because of differences in their architecture, the installation speeds of these two frameworks can be different. When you already know JavaScript, you implement the node package manager to set up React Native quickly, using minimal effort. Flutter, on the other hand, doesn’t use program bridges. You must download the entire binary from the Github repository for its installation. Besides, you will need an additional zip file to install Mac OS. The involvement of multiple steps makes installation for Flutter a tad slower.
React Native vs Flutter Development:
React is known for quick development time and ready-to-use components. This saves a lot of time during the development process. It can deliver new functions to the supported platforms right away, thus saving time. It has many features to streamline and speed up development, like the Hot Reload feature. This lets developers make changes and see instant results; it is now called Fast Refresh.
Flutter is one of the quickest frameworks for creating apps, but its development time lags behind React Native. When you use Flutter, you must add distinct code files for iOS and Android systems; this is limited only to apps that need complex user interfaces. At the same time, Flutter can access many third-party libraries having ready-to-use elements. This helps to reduce development time. The Hot Restart feature lets you view changes right away.
React Native vs Flutter installation:
React Native is very easy to set up and creates packages, unlike Flutter. It offers only device access APIs and user interface rendering features and the framework depends on third-party libraries.
React Native vs Flutter Performance:
React Native is written in JavaScript and developers must combine native with extra interactions to get desired results. The architecture for React is composed of two parts, native and JavaScript; so, you need a JS bridge for interacting with native components. This explains why the speed may be slower at times. Flutter, on the other hand, is written in the Dart language which lets you compile codes faster than JS. So, Flutter can display animations at a very high speed. In terms of performance, Flutter-created apps are known for their high performance. There may be problems affecting the speed in which case Flutter makes certain recommendations. Flutter recommends reducing building costs and applying widgets or effects only when these are really needed.
React Native vs Flutter Documentation:
While the documentation for React Native may not be that impressive, developers consider this user-friendly because there are popular topics and guides allowing users to find whatever they need. In comparison, Flutter has perfectly-structured documentation that can answer all your queries. What it lacks in terms of development speed, it compensates in terms of documentation.
React Native vs Flutter Features:
React Native has an exciting Fast Refresh feature that guarantees fast coding. Users can build apps for multiple platforms using a single codebase. Flutter eCommerce open-source also has a Hot Reload feature, rich widgets for designing an appealing UI, community support, and a single code base to develop many apps. The framework is easy to learn and can be accessed by developers from all kinds of backgrounds.
React Native vs Flutter Major Use Cases:
Besides Facebook, Messenger, and Instagram, React Native has catered to some big players like Walmart, along with startups like Huiseoul, SoundCloud Pulse, and Townske. Flutter was created as part of Google’s services, like Google Ads but now has started catering to big names like Groupon, Alibaba Group, and The New York Times.
React Native Vs Flutter UI:
The user interface is one of the key elements of any framework that focuses on cross-platform development. When the framework isn’t able to manage the UI, the app won’t have the look or feel of a native app. React Native is supported by fundamental components like loading buttons and icons. Flutter doesn’t have third-party options; rather, it provides many out-of-the-box elements. While React’s UI elements wrap up the native ones, the framework must have a bridge to make this happen. Flutter acts in a different way, drawing UI elements from scratch.
React Native vs Flutter Development Time:
React Native developers have many resources, designs from different sources, and libraries to choose from, whereas Flutter is comparatively new. This is why you must spend a lot of time assembling the development team.
React Native vs Flutter code reusability: If you compare React Native codebase with that of Flutter, you will find Flutter’s codebase to be more reusable. Flutter allows developers to change any line in the codebase, reuse it for another purpose, or define new logic seamlessly. Its intuitive and graphic coding interface makes its code easy to reuse.
React Native vs Flutter Recruitment:
Hiring developers is one of the bigger challenges when you must develop apps. According to Glassdoor surveys, the costs of hiring developers for React Native are slightly higher than for Flutter. Since JavaScript is a far more popular programming language, you will get more developers easily who know how to use this. Dart is less popular but that hasn’t stopped flutter from being one of the top cross-platform app development tools in the market. So, it’s no surprise that the developer pool is fast watching up.
React Native vs Flutter Popularity:
If you look at both frameworks in terms of popularity, React Native is found to be more popular because of wider adoption. An analysis of Flutter vs React Native popularity shows that Flutter is new, and even though it managed to catch the attention of app developers, it has a long way to go. Dart is a new language which is why its adoption rate is a bit lower among developers.
React Native vs Flutter Community Support:
React Native was released in 2015 on GitHub and continues to be a popular framework supported by a vast community of users. In comparison, Flutter is new with a smaller community to date. But, more and more app developers are taking to it.
React Native vs Flutter Quality Assurance:
React Native lets developers make use of many third-party tools for testing such as Jest and Detox to overcome its shortcomings. As far as Flutter goes, Google has incorporated many testing features within Flutter, but third-party test tools are limited in number.
React Native vs Flutter release:
React Native’s release is manual and quite standard but Google has facilitated the release of Flutter, providing high flexibility right from fast-lane implementation to automated release.
React Native vs Flutter Future:
According to Statista, developers preferring Flutter eCommerce app has gone up from only 30% in 2019 to a whopping 42% in 2021. React Native, on the contrary, seems to have lost preference during this period. If you consider Flutter vs React Native future prospects, it appears that Flutter has a better market ahead, but React Native is slowly catching up. If you were to look at their future prospects, the recent trends provide some interesting insights. In the last 3 years, Flutter seems to have raced past React Native in terms of user preferences. Google has also been encouraging the growth of an enthusiastic community for supporting this framework. In doing so, it has released many updates for it. Today, the number of Flutter-developed apps has crossed 500,000! The key improvements for Flutter are support for folding phones, international text inputs, desktop platforms, and quicker image decoding in the web version. At the same time, React Native has also undergone some key changes and the most recent upgrades include a new status bar API, better compatibility with C++17 and M1 users, and hotkeys on the iOS debug menu. The Meta community too has been involved in bringing notable improvements to this platform. So, you can be rest assured React Native isn’t going to lag behind Flutter in any respect.
Now, when it comes to making a choice between the two, developers may be finding it challenging. They are both robust when employed intelligently for a project. Which is the right for you in 2023 depends largely on the type of app and its size.
The truth is both React Native and Flutter are top-of-the-line frameworks for creating cross-platform apps and choosing one over the other can be a hard decision to make. Each has its advantages and drawbacks; depending on the app type and use case, you should take a final call. Both React Native and Flutter resolve the problem of building distinct codes for platforms like iOS and Android. Today, it’s possible to build an app for multiple platforms using just one code.
When choosing the right framework, developers in the US, Canada, Australia, Germany, and Japan consider their requirements, experience, and business needs. For instance, if they already know JavaScript in programming, they will probably opt for React Native. However, if they target a stable and quicker performance, they will probably find Flutter more convenient. Regardless of the framework they have opted for, it’s imperative that they test the application before they release it.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Earn with us get 5usd welcome bonus
Introduction: In today’s digital era, mobile applications and artificial intelligence tools are transforming the way we live, work, and learn. One company spearheading this technological revolution is CKings Capital, a dynamic tech firm based in Kenya. With a primary focus on mobile app development and providing AI tools for students, CKings Capital offers an exciting opportunity through its Affi…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Mobile App Development in Kenya
Mobile App Development in Kenya Plays a major role. A mobile application is a category of application software created specifically to run on mobile devices like smartphones and tablets.Similar services to those accessed on PCs are routinely made available to consumers through mobile applications. Apps are frequently compact, separate software components with limited functionality and its App Store,which has thousands of programmes available, helped make this use of app software popular in the beginning.
A connection is used by a simple mobile application to communicate with external computing resources.The process of creating software applications for mobile devices is known as mobile application development. A mobile app or mobile application is a software programme made specifically for use on small, wireless computing devices like tablets and smartphones as opposed to being developed for use on desktop or laptop computer applications.
Deviating from the integrated software systems often seen on PCs are mobile applications. Instead, each app only offers a few isolated and restricted features, like a game, calculator, or mobile web browsing. Applications may have avoided multitasking due to the early mobile devices’ constrained hardware capabilities, but now that consumers may choose what their devices are capable of, their specialisation is part of what makes them desirable.
Design of Mobile app Development in Kenya :
There are many mobile app developments in Kenya which are provided by Best mobile app Developers in Kenya , catering to businesses of all sizes and budgets. Here are some of the most popular services:
Mobile Responsive Design in Kenya : APPs are optimised for viewing on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, because of mobile responsive design services. This service covers creating a website that can adapt to multiple screen sizes and is optimised for mobile devices.
Mobile App Design in Kenya : Businesses seeking to sell things online should take advantage of mobile app website design services. These services involve creating and designing an online store, integrating payment processors, and setting up systems for managing shipping and inventory.
Custom App Design in Kenya : The custom app design services provided by several Kenya organisations are catered to the individual requirements of each client. Design thoughts, mockups, and revisions are frequently part of this service until the client is satisfied with the finished item.
Application services in Kenya : Businesses may feel confident that their app is being maintained and updated on a regular basis thanks to application maintenance services. These services consist of bug patches, backups, and security upgrades.
Application Redesign in Kenya : Businesses who currently have an app but wish to update or improve its appearance might use application redesign services. The app will be completely redesigned, with a fresh layout, colour scheme, and content.
Process of Mobile App Development in Kenya :
These are just a few examples of the mobile app development services offered in Kenya .The Best app developer in Kenya should be chosen after careful consideration of the demands and objectives of your company.
We are the best company to provide Mobile App development in Kenya , and we follow tight rules to complete projects on time and with high quality.
Research: We keep our strategies in front of the curve in our continual efforts to promote innovation by doing extensive research before making an investment.
Layout: We may methodically bring your concepts to life and create a lovely finished product by demanding perfection and excitement during the designing stage.
Development & Testing: Create and design reliable mobile apps with a motivated team after a comprehensive testing procedure to visually bring digital concepts to life.
Organising: Projects are simpler when there is extensive planning. The best basis for any difficult task is diligent and sensible planning.
Completion: Modern analytical techniques are used by our team to monitor and guarantee that the project is completed successfully and on time.
Our services in Mobile app development in Kenya
Android Application Design in Kenya
Blackberry Application Design in Kenya
Windows Application Design in Kenya
Android Application Design in Kenya : Applications for devices running the Android operating system are developed using the Android design process. According to Google, using the Android software development kit (SDK), Android apps may be created using Kotlin, Java, and C++ languages,” however utilising additional languages is also an option.
Blackberry Application Design in Kenya :Including the help of the BlackBerry Development Platform, you can create strong, specialised, and secure mobility solutions for nearly any use case. Email, text messaging, web surfing, and phone service are all available on Blackberry. It is a complete wireless email solution that enables wireless synchronisation of your Outlook inbox, calendar, contacts, and tasks.
Windows Application Design in Kenya : The process of designing desktop applications involves making programmes that run locally on computers. Desktop apps can be made using programming languages including Java, C#, C++, Python, Ruby, and JavaScript. You can use these programmes to assist you with a variety of routine tasks, including internet browsing, calendar management, and music shopping. The majority of these programmes can be launched by first selecting the Start button, then selecting the desired app’s icon.
How much does cost of Mobile App Development in Kenya
The size of the app, the features and functionalities required, the degree of customization necessary, the developer’s experience, and location all have a significant role in the price of mobile app development in Kenya . In general, there are various different costs involved in creating a app in Kenya
Mobile App Design: These costs cover the price of developing the App visual design, which includes the layout, colour scheme, typography, and other graphical components.
Development: This includes the price of building the front-end and back-end features of the app, such as constructing and integrating databases, user interfaces, e-commerce features, and bespoke programming.
Generation of content: This involves the price of writing copy, producing photos, producing videos, and adding other types of material to the website.
Supporting and assisting: This includes the price of continuing app upkeep, updates, and technical support.
How to get Mobile app Development in Kenya ?
If you are looking to get Mobile app development in Kenya then we are here to help you with affordable costing. Our Developers are experts in Android, blackberry, windows and other platforms. Please reach out to Webivalue- we are a top 10 mobile app development company in Kenya . Feel free to share your requirements at [email protected] or visit webivalue.com and touch with our experts.
0 notes
Text
Everything You Need to Know about Google’s Latest Products (Pixel 4, Pixel 4 XL, Buds)
Learn everything about the products including the prices and specs as analysed by the best mobile application developers in Kenya
0 notes