#net core vs net framework
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

1 note
·
View note
Text
ASP.Net vs ASP.Net Core. This article is about the differences between ASP.Net and ASP.Net Core. Here, you can get a comparison between ASP.Net and ASP.Net Core.
ASP.NET is a fundamental web development platform used to create websites, applications, and web services. It is the integration of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Originally ASP.net was released in 2002. The first version of Asp.Net deployed was 1.0. The Recent Version of Asp.Net is 4.6.
Looking to hire .NET developer for your next project?
Asp.Net works on HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and uses the HTTP commands and policies to set a browser-to-server bilateral communication.
ASP.NET is a part of the Microsoft .NET Framework. The following image shows the component stack.
#asp.net vs asp.net core#difference between asp.net and asp.net core#asp.net#asp.net core#asp.net developers#asp net framework#.net core vs asp.net core#net core vs net framework#.net vs .net core#asp.net development#aspnet framework#asp.net vs .net core#.net vs asp.net#what is asp net#asp.net core vs .net core#asp.net core vs asp.net#custom software development#software outsourcing
0 notes
Text
.NET Core vs .NET Framework for Developers
Dive into .NET Core vs .NET Framework to find the best fit for your projects. Understand differences in platform support, performance, and modern app development.
0 notes
Text
Thailand Permanent Residency
Thailand's permanent residency (PR) framework originates from the 1927 Alien Registration Act, with major reforms occurring in:
1950 Immigration Act (established modern categories)
1979 Immigration Act (current statutory basis)
2008 Nationality Act amendments (tightened naturalization pathways)
1.2 Jurisdictional Authorities
Primary Oversight: Ministry of Interior (Section 37 Immigration Act)
Implementation: Immigration Bureau (Division 1, Section 3)
Adjudication: Special Committee chaired by Permanent Secretary for Interior
1.3 Relevant International Obligations
While Thailand maintains strict immigration controls, certain bilateral agreements influence PR considerations:
ASEAN agreements on skilled labor mobility
US-Thai Treaty of Amity (limited PR implications)
Japan-Thai Economic Partnership (special professional categories)
2. Eligibility Matrix
2.2 Qualitative Assessments
Character Evaluation:
Police clearance from all countries of residence
Neighborhood certification (conduct verification)
Employer/associate testimonials
Integration Metrics:
Thai language proficiency (CEFR A1 minimum)
Cultural knowledge exam (80% pass mark)
Community participation evidence
3. Procedural Architecture
3.1 Document Preparation Protocol
Core Documentation:
Visa History: Certified copies of all visas + entry stamps
Financial Evidence:
Bank statements (6 months, certified)
Tax records (RD.90 forms)
Investment certificates (BOI/SEC approved)
Supporting Materials:
Property Documents: Chanote + household registration
Employment Verification:
Work permits (all versions)
Social fund records
Company financials (for business owners)
4. Financial and Tax Considerations
4.1 Cost Structure Analysis
Official Fees:
Application fee: THB 7,600
Approval fee: THB 191,400
Alien book: THB 800 (annual)
Re-entry permit: THB 3,800 (single), THB 9,800 (multiple)
Unofficial Costs:
Document procurement: THB 15,000-50,000
Legal representation: THB 100,000-500,000
Expediting services: Market rate THB 200,000+
4.2 Tax Implications
Pre-PR: Only Thai-sourced income taxable
Post-PR: Worldwide income potentially taxable (if remitted)
Wealth Tax: None currently, but property transfer taxes apply
5. Rights and Privileges
5.2 Occupational Restrictions
Registered Profession Requirement: Must work in field specified at application
Business Ownership: Permitted but requires MOI notification
Government Employment: Prohibited without special approval
6. Judicial and Administrative Review
6.1 Appeal Process
Rejection Appeals: 30 days to file with Immigration Commission
Judicial Review: Available at Administrative Court
Success Rates: <15% for appeals, <5% for judicial review
6.2 PR Revocation
Grounds include:
Criminal conviction (1+ year sentence)
Tax evasion findings
Extended overseas absence (5+ years)
National security concerns
7. Strategic Application Approaches
7.1 Category Optimization
Employment Track: Ideal for corporate executives (minimum THB 150k salary preferred)
Investment Route: Best for property developers (BOI projects favored)
Family Path: Most reliable for long-term married couples (10+ years marriage ideal)
7.2 Document Enhancement Strategies
Tax Augmentation: Voluntary additional tax payments to demonstrate commitment
Community Engagement: Documented volunteer work with registered charities
Language Certification: Official CU-TFL test scores preferred over immigration exam
8. Comparative Regional Analysis
8.2 Global Benchmarks
Processing Time: Thailand (3-5 yrs) vs Canada (1.5 yrs)
Cost: Thailand (~6K)vsUK( 6K)vsUK( 3K)
Success Rate: Thailand (8%) vs Australia (25%)
9. Emerging Trends and Reforms
9.1 Digital Transformation
E-Application Pilot: Limited testing in Bangkok
Blockchain Verification: For document authentication
Automated Background Checks: Integration with INTERPOL databases
9.2 Policy Shifts
Talent-Centric Quotas: Increasing STEM professional allocations
Retirement PR Pathway: Under consideration for high-net-worth retirees
Dual Citizenship Tolerance: Parliamentary study underway
10. Practical Challenges and Solutions
10.1 Common Obstacles
Document Procurement: Especially for older visa records
Bureaucratic Delays: Particularly at verification stage
Exam Preparation: Lack of standardized study materials
10.2 Mitigation Strategies
Early Retention: Engage immigration lawyer at least 2 years pre-application
Parallel Processing: Initiate document requests simultaneously
Mock Examinations: Utilize private language schools for test prep
11. Longitudinal Case Studies
11.1 Successful Applications
Tech Executive: Approved in 3.5 years via employment track
THB 250k monthly salary
Certified Thai language proficiency
BOI-company sponsorship
Investor: Approved in 4 years via property route
THB 25M Bangkok condo portfolio
Additional THB 5M government bonds
Documented charity contributions
11.2 Rejection Analysis
Common Factors:
Inconsistent tax payments (78% of failed cases)
Language test failures (62%)
Suspicious financial patterns (45%)
12. Future Outlook
12.1 Projected Reforms
Points-Based System: Under consideration (2026 target)
Premium Processing: THB 500k+ for expedited review
Regional PR Options: Special economic zone programs
12.2 Demographic Impacts
Current PR holder demographics:
Chinese: 32%
Japanese: 18%
Western: 22%
Other Asian: 28%
13. Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives
Thailand's PR system remains: ✔ Highly exclusive (0.03% approval rate) ✔ Process-intensive (1000+ document pages typical) ✔ Discretionary in nature (despite codified rules)
Critical success factors:
Early preparation (3-5 year horizon)
Comprehensive documentation
Professional guidance
Financial commitment
The program continues evolving toward:
Greater transparency in decision-making
Enhanced digital infrastructure
Strategic alignment with economic development goals
Prospective applicants should monitor:
Annual quota announcements (December)
Ministerial regulation changes
Judicial rulings on PR-related cases
#thailand#visa#immigration#thaivisa#thailandvisa#visainthailand#thaipr#thaipermanentresidency#thailandpermanentresidency#immigrationinthailand#thaiimmigration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Top Stock Market Course in India

India's top stockbroker, Groww, has taken a bold step into filing confidential papers for an initial public offering (IPO) with SEBI. But here's the twist: despite a massive ₹3,145 crore in revenue, the company reported a net loss of ₹805 crore in FY24. This raises a crucial question for investors: Should you bet on a loss-making fintech giant?
In this blog, we decode Groww's IPO filing, break down the broking industry's shifting dynamics, highlight the risks, and, most importantly, show you how to analyze any IPO with the framework taught in LiveLong Wealth's Stock Market Course.
What Is a Confidential IPO Filing?
Groww has opted for SEBI's confidential pre-filing route, which allows companies to
Keep IPO details private while testing investor interest.
Adjust IPO size by up to 50%.
Extend the launch timeline from 12 to 18 months.
This method provides flexibility and reduces reputational risk if market conditions worsen.
Groww's FY24 Financial Snapshot
Let's look at the core numbers:
Revenue: ₹3,145 crore (119% YoY growth)
Operating Profit: ₹535 crore (17% growth)
Net Loss: ₹805 crore
(primarily due to a one-time ₹1,340 crore tax expense for shifting its legal base from the US to India)
While operationally profitable, the company still reports a net loss—something retail investors must evaluate with caution.
Why Is Groww Still Loss-Making?
Many high-growth startups defer profits to prioritize user acquisition and tech infrastructure. However, in Groww's case:
Marketing costs and platform investments are ongoing.
It took a hit from a one-time restructuring cost due to its domicile change.
Despite fee hikes, pricing pressures continue due to fierce competition.
Fewer day traders and more mutual fund investors generate less recurring brokerage revenue.
The Broking Industry in India:
India's online broking space is evolving rapidly, driven by:
SEBI's crackdown on F&O trading resulted in a 30% drop in volumes by December 2024.
Fee restructuring, with Groww increasing charges by 150% for smaller trades to maintain profitability.
Strong rivals like Zerodha, Angel One, and Upstox are dominating market share.
This highlights the need for brokers to innovate, reduce costs, and diversify revenue streams.
Key Risks of Investing in the Groww IPO
Regulatory Uncertainty: Changes in derivatives trading, transaction taxes, and compliance norms can impact revenues.
Sustainability of Growth: Acquiring users is easier than monetizing them—especially if pricing wars intensify.
Investor Expectations: Public markets expect clear roadmaps to profitability—something Groww hasn't fully demonstrated yet.
Growth Prospects: What's Working in Groww's Favor?
Despite the risks, Groww has strategic strengths:
13 million+ active users—India's largest base.
Wide product offering-stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, F&O, and more.
Tech-first experience with a sleek UI/UX that appeals to younger investors.
Fresh capital from the IPO will likely go into product upgrades and geographic expansion.
Cross-selling personal loans
How to Analyze an IPO Like This - The LiveLong Wealth Way
At LiveLong Wealth's stock market course, we teach a structured framework to analyze IPOs using our stock market course, which includes:
1. Business Model Evaluation
Does the company have a moat?
How scalable is the model?
2. Financial Statement Analysis
Revenue trends, margins, cash flow, and debt levels.
One-time charges vs. recurring profitability.
3. Valuation Check
Compare IPO valuation with listed peers (e.g., Angel One).
Check price-to-sales, price-to-earnings (if profitable), and EV/EBITDA multiples.
4. Risk-Reward Profile
Is the IPO aggressively priced?
Can you tolerate a few years of losses for long-term upside?
This approach ensures you're not just following IPO hype but making data-driven investment decisions.
Read more: https://www.livelongwealth.in/groww-ipo-top-stock-market-course-in-india/339
#top stock market course in india#top stock market course. top stock market course Bangalore#top stock market course kerala
0 notes
Text
Software Development vs. Web Development: Which Career is Better?

If you're choosing between software development and web development as a career path, here's the straight answer: both are excellent choices with high demand and rewarding prospects. But the "better" option depends on your interests, skills, and long-term goals. While top-tier institutions like IITs and NITs offer strong foundations in both, many of the best private engineering colleges in Odisha also provide solid programs that prepare students for either path—including colleges like NMIET, which often come up in discussions around tech education in the region.
Let’s Start with the Basics
Software Development is about building computer programs that run on desktops, mobile devices, and embedded systems. This includes everything from operating systems and games to enterprise applications and mobile apps.
Web Development, on the other hand, is focused on creating websites and web applications. This includes the front-end (what users see) and the back-end (the server, database, and application logic).
Though both fields overlap in some areas, their day-to-day tasks and required skill sets can be quite different.
Career Scope & Opportunities
Software Developers often work on large-scale applications, system architecture, cloud-based services, AI models, and mobile app development. Big tech firms like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft hire software developers with strong knowledge of programming languages like Java, Python, C++, and frameworks like Spring, .NET, or TensorFlow.
In contrast, Web Developers may work in design agencies, startups, or large IT companies. The rise of eCommerce, online platforms, and SaaS (Software as a Service) has skyrocketed the demand for full-stack web developers who are well-versed in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React, Angular, Node.js, and Django.
While software roles may offer slightly higher starting packages on average, web development allows quicker entry into freelance and entrepreneurial ventures. If you're someone who wants to build and launch your own website or startup, web development might feel more rewarding early on.
Learning Curve & Technical Skills
If you're aiming for software development, you'll need a strong foundation in data structures, algorithms, system design, and object-oriented programming. Most competitive coding platforms and tech interviews test heavily in these areas. Colleges that emphasize logical thinking and core computer science principles are a good fit.
In comparison, web development tends to have a faster learning curve. You can build and deploy simple web apps within weeks, which can be very motivating early in your career. However, mastering modern frameworks, performance optimization, security, and scalability still requires serious effort and continuous learning.
Some of the best private engineering colleges in Odisha are now updating their curriculum to include both paths. For instance, institutions like NMIET focus on practical coding labs and project-based learning—whether you're building mobile apps, designing web interfaces, or working on machine learning projects.
Job Roles You Can Expect
Software Development Roles:
Software Engineer
Mobile App Developer
Game Developer
Embedded Systems Engineer
Data Engineer
Web Development Roles:
Front-End Developer
Back-End Developer
Full-Stack Developer
UI/UX Developer
Web App Developer
Companies like Cognizant, Capgemini, and IBM (which also recruit from colleges like NMIET) have openings in both domains, depending on the project requirements.
Industry Demand & Future Outlook
The demand for both careers is strong and projected to grow. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, software developer jobs are expected to grow by 25% between 2022 and 2032. Web development is also expected to grow by 16% in the same period—faster than most other occupations.
AI, IoT, and cloud computing are expanding the horizons for software developers, while the no-code/low-code movement, headless CMS, and progressive web apps are shaping the future of web development.
It’s worth noting that companies today appreciate hybrid skill sets. A web developer who understands backend logic or a software engineer who can deploy code via cloud platforms stands out.
Which Should You Choose?
Here’s a simple way to decide:
Go for software development if you love problem-solving, want to build complex systems, and enjoy algorithmic thinking.
Pick web development if you enjoy creativity, visual design, rapid prototyping, and like seeing results fast.
Neither path is inferior. What matters is consistency and continuous learning.
If you’re still unsure, choose a college that allows you to explore both. For example, a student from a Bhubaneswar-based institute like NMIET might start with web development projects in the first year and transition to mobile app development or AI systems by their final year. That’s the beauty of today’s learning environment—it's flexible if the foundation is strong.
Final Thoughts
Software development and web development both offer exciting, future-proof careers. Your choice should align with your interests, not just industry trends or package comparisons. Fortunately, many of the best private engineering colleges in Odisha offer specializations, hands-on learning, and placement opportunities in both domains.
Whether you're aiming to work with a global tech giant or build your own digital product, both paths can take you there—as long as you're ready to learn, build, and adapt.
#best colleges in bhubaneswar#college of engineering bhubaneswar#best engineering colleges in orissa#best engineering colleges in bhubaneswar#best private engineering colleges in odisha#best engineering colleges in odisha
0 notes
Text
Adaptive Modeling of Net Monetary Sovereignty under Hybrid Threats: A Strategic Framework for Digital Resilience
Abstract
In an era marked by geopolitical fragmentation, financial sanctions, and cyberwarfare, central banks must evolve beyond traditional monetary policy instruments. This paper introduces an advanced framework for simulating Net Monetary Sovereignty (NMS) under hybrid threat conditions, integrating stochastic modeling, adaptive digital policy, reinforcement learning, and real-time geopolitical indicators. We present a dynamic system that evaluates the resilience of a national currency regime in response to coordinated cyberattacks, economic shocks, and external sanctions. Our findings suggest that policy effectiveness significantly increases when infrastructure readiness and public trust are accounted for, and that synergy between digital penetration and domestic currency dominance is critical for future monetary stability.
1. Introduction
As monetary policy becomes entangled with cybersecurity, AI, and geopolitics, classical notions of sovereignty must be redefined. The rise of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), regional clearing alternatives (e.g., CIPS, SPFS), and decentralized tokenization of reserves signals a tectonic shift in the architecture of global finance.
This study develops and simulates a framework for Net Monetary Sovereignty (NMS) as a multidimensional, temporally evolving construct—vulnerable to shocks but stabilizable through smart, adaptive mechanisms.
2. Theoretical Foundations
2.1 Core Components of NMS
We define NMS as a function of four interdependent variables:
D(t): Domestic monetary dominance
A(t): Autonomy in international settlement
P(t): Digital currency penetration
X(t): Dependency on external assets/infrastructure
2.2 Enhanced NMS Equation
We propose:dNMS(t)=[αdDdt+βdAdt+γdPdt−δdXdt+ϵD(t)P(t)]dt+σdW(t)+∑ηkdJk(t)
ϵD(t)P(t): synergy term modeling feedback between currency legitimacy and digital reach
dJk(t): jump process representing cyberattacks or sanctions
3. Adaptive Policy Architecture
3.1 Digital Sovereign Policy Model
Post-attack recovery is modeled as:Adjustment(t)=0.01⋅I(t)⋅T(t)1+e−τ(t−i)
I(t): infrastructure readiness (5G, blockchain nodes)
T(t): public trust in digital instruments
This reflects a system in which the speed and efficacy of monetary repair depend on physical/digital infrastructure and perceived legitimacy.
4. Simulation Engine
4.1 State Variables
s(t)=[NMS,D,A,P,X,TensionIndex,I,T]
4.2 Threat Modeling
Cyberattack intensity:λk(t)=λ0⋅TensionIndex(t)Derived from real-time data (e.g., GDELT geopolitical news index)
4.3 Reinforcement Learning Agent
Algorithm: PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization)
Objective: Maximize NMS while minimizing inflation, dependence, and time-to-recovery
Adversarial module simulates intelligent attacker behavior based on past patterns (e.g., 2022 SWIFT blacklisting, infrastructure breaches)
5. Empirical Validation
5.1 Scenario: Coordinated Attack on Energy and Finance
Without policy: 12% drop in NMS within 6 months
With adaptive buffer:
Immediate stabilization through digital gold tokenization (10% reserve mobilized)
Strategic deployment of regional currency swaps (reduced X by 8%)
2× faster recovery compared to control
5.2 Simulation Visualization
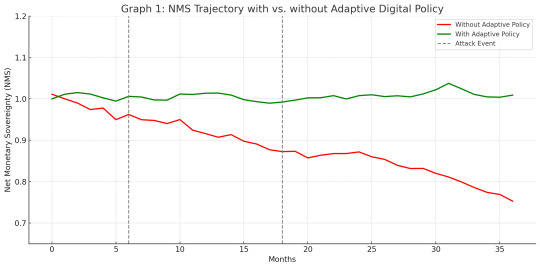
Graph 1: NMS trajectory with vs. without adaptive digital policy
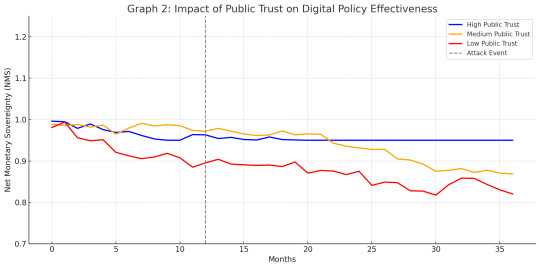
Graph 2: Impact of public trust volatility on digital buffer effectiveness
6. Strategic Implications
6.1 For Sanctioned or Isolated States
Digital buffer policies are essential for monetary survival
Regional integration (e.g., BRICS+ CIPS corridors) enhances A(t)
6.2 For Advanced Economies (e.g., U.S., EU)
NMS framework can be integrated into FedNow, ECB TIPS to assess resilience
Tokenization of reserves could improve systemic agility under coordinated attacks
6.3 For Global CBDC Architecture
NMS can serve as a resilience benchmark for cross-border CBDC interoperability
Suggests inclusion of AI-coordinated liquidity buffers in digital currency protocol design
7. Policy Recommendations
HorizonRecommendationImmediatePilot reinforcement learning framework within national monetary sandboxShort-TermDeploy sovereign trust index as part of digital monetary reportingMedium-TermCreate bilateral tokenized swap lines with friendly jurisdictionsLong-TermEmbed NMS module into central bank macro-modeling platforms (e.g., DSGE models)
8. Conclusion
This model represents a convergence of digital economics, monetary sovereignty, and intelligent defense. In a fragmented and adversarial world economy, the central bank of the future must act as a cyber-resilient, data-driven, real-time sovereign infrastructure hub. Net Monetary Sovereignty is no longer static—it is programmable, adaptive, and, if necessary, weaponized.
9. References
Brunnermeier, M. et al. (2021). The Digitalization of Money
Ghosh, I. (2023). Hybrid Warfare and Central Bank Liquidity Shields
Shiryaev, A. et al. (2008). Optimal Stopping and Control under Uncertainty
Kaspersky Lab (2022). Threat Intelligence for Financial Systems
Chainalysis (2023). Global Crypto Adoption Index
GDELT Project (2024). Global Tension Data for Risk Monitoring
0 notes
Text
Kickbacks 101: A Legal Analysis
I. Kickbacks: A Legal Analysis II. Legal Definition and Elements of the Offense1. Definition in Statutory and Case Law 2. Essential Elements in Common Law Jurisdictions 3. Specific Sectoral Legislation and Doctrinal Refinements 4. Mens Rea and Burden of Proof 5. Comparative Legal Note III. Classification Under Criminal Law1. Bribery of Public Officials 2. Commercial Bribery 3. Fraud (Including Procurement Fraud) 4. Conspiracy and Organized Criminal Activity 5. Money Laundering 6. Administrative and Collateral Sanctions IV. Evidentiary and Procedural Challenges1. Nature of Evidence: Direct vs. Circumstantial 2. Whistleblower Testimony and Qui Tam Actions 3. Forensic Accounting and Financial Reconstruction 4. Use of Subpoenas, Wiretaps, and Surveillance 5. Mens Rea and Defenses Based on Intent 6. International and Procedural Barriers
I. Kickbacks: A Legal Analysis
Kickbacks constitute a serious violation of legal norms governing integrity in both public and private sectors. Recognized universally as a form of corruption, they are prosecuted under national and international anti-bribery laws. While often associated with white-collar crime, kickbacks carry significant legal consequences including imprisonment, financial penalties, and civil liability. This essay analyzes the legal dimensions of kickbacks, their classification under criminal law, evidentiary and procedural considerations in prosecution, and their place in international legal frameworks.

II. Legal Definition and Elements of the Offense
From a strictly legal standpoint, the concept of a kickback falls under the genus of corrupt practices, yet its particular species is distinguishable by its structural features: it is a concealed, reciprocal exchange that undermines the integrity of a transaction, typically in the context of public procurement or private contracting. While jurisdictions may vary in their statutory formulations, the definitional core of a kickback remains the same: an illicit inducement provided in exchange for preferential treatment or influence over a decision-making process. 1. Definition in Statutory and Case Law Kickbacks are often legislatively codified either as a subset of bribery, fraud, or commercial corruption. In common law countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada, courts and legislatures have gradually refined the contours of the offense to include both overt and covert forms of inducement, and to apply in both public and private sectors. For instance, U.S. law includes multiple statutory frameworks that directly or indirectly address kickbacks. Apart from the Anti-Kickback Statute in the healthcare sector (42 U.S.C. § 1320a–7b(b)), the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR 52.203-7) imposes criminal liability on government contractors who offer or accept kickbacks in relation to subcontracts. Here, the statute explicitly prohibits “any money, fee, commission, credit, gift, gratuity, or compensation of any kind” provided for the purpose of improperly obtaining or rewarding favorable treatment. In United States v. Greber, 760 F.2d 68 (3d Cir. 1985), the Third Circuit held that if “one purpose” of the payment was to induce future referrals, the Anti-Kickback Statute was violated—even if other legitimate purposes were also present. This “one purpose test” sets a relatively low threshold for establishing criminal liability and has been affirmed in numerous decisions, thereby broadening the prosecutorial net. In civil law systems, particularly in jurisdictions following the Napoleonic Code tradition, kickbacks may fall under the offense of corruption passive et active, abus de fonction, or trafic d'influence. French Penal Code Article 433-1, for example, criminalizes both the act of soliciting and the act of providing undue advantages, with penalties up to 10 years of imprisonment and substantial fines. The emphasis lies not only on the exchange but also on the distortion of the legal or institutional function involved. 2. Essential Elements in Common Law Jurisdictions In jurisdictions governed by common law principles, the crime of kickback involves several constituent elements. Each must be established beyond a reasonable doubt to obtain a criminal conviction: - (a) Agreement or Understanding (Express or Implied): Unlike contract law, where clarity and explicit consent are required, in criminal law an implied understanding suffices. Courts look for a “meeting of the minds,” which may be inferred from conduct, communications, or patterns of behavior. A silent expectation of favor in return for a benefit may meet the requisite threshold. - (b) Benefit Conferred (Monetary or Otherwise): The benefit may take the form of direct payments, commissions, inflated invoices, employment for relatives, gifts, entertainment, or future job offers. The law does not require the benefit to be tangible or immediate—it is enough that it is intended to induce preferential treatment. - (c) Quid Pro Quo: A defining feature of kickbacks is the exchange element, the illicit reciprocity. The giving and receiving of benefits must be linked causally or purposefully to an official act or decision. In some cases, causation can be difficult to establish, and prosecutors may use circumstantial or expert evidence to show a pattern of corrupt exchange. - (d) Breach of Fiduciary Duty or Lack of Disclosure: Often overlooked, this component is what transforms a mere gift into a criminal kickback. The recipient is typically under a fiduciary duty—whether legal or ethical—to act in the best interest of an employer, a principal, or the public. When a benefit is accepted without disclosure and with the intent to bias decision-making, the fiduciary relationship is breached, and the offense is complete. 3. Specific Sectoral Legislation and Doctrinal Refinements Certain industries are regulated with heightened scrutiny due to their susceptibility to kickbacks. Healthcare and defense procurement are two such sectors. - Healthcare Sector (U.S. Law): The Anti-Kickback Statute (AKS) is a strict liability statute. It criminalizes not only completed transactions but also offers of remuneration. Moreover, knowledge and intent are interpreted broadly. As per the statutory language, “remuneration” includes transfers of anything of value. This expansive definition has allowed the Department of Justice to bring cases involving speaking fees, consulting contracts, and even research funding. - Defense Contracting (U.S. and EU): In the defense sector, kickbacks often take the form of subcontractor collusion. The U.S. Kickbacks Act of 1986 (41 U.S.C. §§ 8701–8707) prohibits any inducement offered to a prime contractor or subcontractor for favorable treatment. European Union law, while lacking a unified anti-kickback statute, incorporates anti-corruption clauses into procurement directives (notably Directive 2014/24/EU), allowing Member States to exclude corrupt contractors and seek damages for corrupted awards. 4. Mens Rea and Burden of Proof In criminal law, the mental state (mens rea) required to establish a kickback offense generally includes knowledge and willfulness. That is, the defendant must have known that the remuneration was unlawful and must have acted voluntarily in offering or receiving it. In civil cases, the standard is lower—often "preponderance of the evidence"—allowing liability to be imposed even in the absence of criminal intent. The U.S. Supreme Court, in McDonnell v. United States, 579 U.S. 550 (2016), narrowed the definition of “official act” in corruption cases, requiring a specific and formal exercise of governmental power. However, courts have distinguished kickback cases by emphasizing the transactional rather than merely political nature of the act, thereby preserving the broad applicability of kickback statutes. 5. Comparative Legal Note In the United Kingdom, the Bribery Act 2010 offers one of the world’s most comprehensive legal frameworks, criminalizing both the giving and receiving of bribes without requiring proof of quid pro quo. Section 1 and Section 2 cover active and passive bribery respectively, and Section 7 imposes corporate liability for failure to prevent bribery. While the term “kickback” is not explicitly used, the functional equivalence is evident in prosecutions and guidance issued by the Serious Fraud Office (SFO). In Germany, the Strafgesetzbuch (Criminal Code) §§ 331–335 govern the offense of bribery and corruption, including private sector bribery. The Bundesgerichtshof (Federal Court of Justice) has clarified that payments that violate professional duties or contractual obligations can constitute criminal conduct even absent an explicit agreement—a jurisprudential position that enhances the prosecutability of kickback-type arrangements.
III. Classification Under Criminal Law
The legal classification of kickbacks as a criminal offense reflects the multifaceted harm they pose to institutional integrity, economic fairness, and public trust. Because kickback schemes are structurally complex and often intertwined with legitimate contractual processes, legislators and courts have resorted to a wide range of criminal law categories to prosecute them effectively. Depending on the factual matrix and the nature of the actors involved, kickbacks may fall under several legal rubrics, each bringing distinct elements, procedural implications, and penalties. 1. Bribery of Public Officials In jurisdictions where the recipient of a kickback is a public official, the act is almost invariably prosecuted under the statutory or common law provisions governing bribery. The defining feature here is the distortion of public duty for private gain. Bribery statutes typically prohibit any offer, promise, or transfer of a benefit in exchange for the performance—or non-performance—of an official act. In the United States, federal law (18 U.S.C. § 201) criminalizes the giving or receiving of anything of value with corrupt intent to influence an official act. When a kickback is paid to a government procurement officer in exchange for awarding a contract, this constitutes a paradigmatic case of public bribery. Notably, U.S. law draws a distinction between “bribes” (which require a quid pro quo) and “gratuities” (which do not), although both may be criminally sanctioned. In civil law jurisdictions, such as France or Italy, this conduct falls under corruption passive et active de fonctionnaires publics—the acceptance or offering of undue advantages by or to a public agent. The functional equivalence to common law bribery is clear, but the emphasis on abuse of function as a statutory element provides civil systems with broader reach, including acts that are not directly tied to a formal duty but nevertheless compromise institutional neutrality. 2. Commercial Bribery Where the kickback occurs in the private sector—between or within corporations, for instance—it is typically prosecuted as commercial bribery. While this category lacks the public interest dimension that public bribery entails, it nonetheless threatens market integrity and breaches fiduciary obligations. Under U.S. law, the prosecution of commercial bribery is often based on state statutes (e.g., New York Penal Law § 180.00) or federal statutes such as the Travel Act (18 U.S.C. § 1952), which allows for the federalization of state commercial bribery laws when interstate commerce is involved. Courts have construed commercial bribery to include kickbacks to purchasing agents, consultants, or executives who use their positions to favor vendors or contractors in return for personal gain. In European Union law, Directive (EU) 2017/1371 (the PIF Directive) criminalizes fraud and corruption affecting the Union’s financial interests, which includes bribery in the context of structural funds or procurement involving EU monies—even when conducted by private entities. 3. Fraud (Including Procurement Fraud) Kickbacks are frequently prosecuted as a form of fraud, especially where they are concealed through deceptive practices. When kickbacks are embedded in procurement processes, they often involve false documentation, inflated invoices, sham contracts, or misrepresentation of competitive bidding processes. These artifices support charges of procurement fraud, wire fraud (18 U.S.C. § 1343), or mail fraud (18 U.S.C. § 1341). The fraudulent dimension of a kickback scheme typically lies in the misrepresentation to a principal (a government agency, a company, or the public) that the contract or decision was made on objective and lawful grounds. This breach of fiduciary representation renders the underlying transaction voidable and criminally actionable. Internationally, the United Nations Convention Against Corruption (UNCAC), ratified by over 180 countries, mandates that States criminalize fraud and corruption not only in the public but also in the private sphere, particularly when public resources are involved. Article 21 specifically calls for the criminalization of bribery in the private sector, reinforcing the fraud-based approach to kickbacks. 4. Conspiracy and Organized Criminal Activity Kickback schemes rarely involve isolated actors. More often, they are embedded in networks of collusion between officials, intermediaries, contractors, or financial agents. As such, they are prosecutable under conspiracy statutes and sometimes under laws targeting organized crime. In U.S. law, a conspiracy is established under 18 U.S.C. § 371 when two or more persons agree to commit an offense against the United States, and one of them takes an overt act in furtherance of the agreement. In the context of kickbacks, this provision allows prosecutors to charge all participants in a scheme—even those whose involvement was peripheral or indirect. Moreover, when the kickback is part of a broader pattern of racketeering activity, charges under the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (RICO) may be brought. RICO provides for significant penalties, asset forfeiture, and the possibility of treble damages in civil actions. In civil law jurisdictions, conspiracy is often covered by provisions on association de malfaiteurs (France) or criminal organizations (Germany, Italy), allowing for the prosecution of collective or corporate criminality even in the absence of a formal criminal organization. 5. Money Laundering Once a kickback is received, the proceeds are typically disguised through financial engineering—layering, placement, and integration. This concealment constitutes money laundering, a separate and serious criminal offense. Prosecuting kickback schemes under money laundering statutes enables law enforcement to trace and recover illicit gains and to impose harsher penalties for financial obfuscation. Under U.S. law, 18 U.S.C. § 1956 and § 1957 criminalize the use of financial institutions or interstate commerce to conceal the nature, location, source, ownership, or control of proceeds from unlawful activity. Notably, it is not necessary that the predicate offense (e.g., bribery or fraud) be prosecuted in the same action—money laundering can stand on its own. In EU and civil law countries, the Fourth and Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directives obligate member states to criminalize laundering of proceeds from corruption and to ensure financial institutions perform enhanced due diligence, particularly on politically exposed persons (PEPs). This regulatory aspect often complements the criminal proceedings, strengthening the enforcement arsenal. 6. Administrative and Collateral Sanctions Beyond criminal prosecution, many legal systems impose administrative sanctions for kickback-related conduct. These may include: - Monetary fines; - Revocation or suspension of business licenses; - Debarment from public procurement processes; - Professional disqualification (e.g., disbarment of lawyers, license suspension for doctors or contractors). Such sanctions can be imposed by regulatory agencies, ethics commissions, or public procurement offices, often with lower evidentiary thresholds than criminal trials. The World Bank, for instance, maintains a list of debarred contractors based on findings of corrupt practices, including kickbacks, even without a criminal conviction. In civil law systems, the principle of parallel administrative liability permits administrative bodies to sanction conduct that is also criminally prosecutable. This dual approach allows for swift regulatory action while awaiting judicial outcomes.
IV. Evidentiary and Procedural Challenges
The prosecution of kickback schemes entails a distinct set of evidentiary and procedural hurdles that reflect the clandestine and often sophisticated nature of these offenses. Unlike overt criminal acts, kickbacks are designed to mimic legitimate business transactions, frequently cloaked under contracts, consulting agreements, or commissions. As such, their criminality lies not in the act itself but in the corrupt motive behind it—rendering the establishment of intent, quid pro quo, and concealment pivotal but inherently difficult. 1. Nature of Evidence: Direct vs. Circumstantial Kickbacks are rarely documented in explicit terms. Instead of plainly worded agreements or overt exchanges of money, prosecutors are often left to construct the evidentiary narrative through circumstantial indicators. These may include: - Unusually timed payments coinciding with contract awards; - Inflated invoices or split commissions; - Shell companies or intermediaries with no substantive business role; - Digital traces, such as emails, encrypted messages, or unregistered phone calls; - Patterns of favoritism or deviations from procurement procedures. Read the full article
0 notes
Text
The Sovereign Morons of America
The "sovereign citizen" movement is a loosely organized group of people who believe they are not subject to government authority, including laws, taxes, or regulations, because they claim to be independent "sovereigns" rather than citizens. They often argue that the U.S. government is illegitimate, citing a mix of misinterpreted historical documents, legal theories, and fringe interpretations of the Constitution. Here's a quick breakdown:
Core Beliefs: They assert that individuals can declare themselves free from government jurisdiction by rejecting "contracts" like driver’s licenses, Social Security numbers, or birth certificates. They often use pseudo-legal jargon, like claiming to be "natural persons" or "living men" rather than corporate entities under admiralty law (a baseless theory).
Misinterpretation of the Constitution: Sovereign citizens cherry-pick phrases from the Constitution, Declaration of Independence, or old legal texts like the Magna Carta, twisting them to fit their narrative. For example, they might claim the 14th Amendment created a fictional "corporate citizen" they can opt out of, ignoring its actual purpose (granting citizenship and equal protection post-Civil War). Their readings are often divorced from legal scholarship or precedent.
Why It’s Nonsense: Courts consistently reject their arguments as frivolous. The U.S. legal system operates under established case law and statutes, not their invented frameworks. Their tactics—like filing fake liens, refusing to pay taxes, or challenging police authority—frequently lead to legal trouble, including arrests or convictions. The FBI and other agencies track the movement due to its potential for anti-government extremism.
Why It Persists: It appeals to those distrustful of authority, often fueled by online echo chambers, conspiracy theories, or economic distress. Some are drawn by promises of escaping debt or legal obligations, sold by "gurus" peddling fake legal strategies. Cognitive bias and confirmation bias play a role—they cling to their interpretations despite overwhelming evidence.
Public Perception: Their behavior, like arguing with cops over "traveling" vs. "driving" or flooding courts with nonsensical filings, often makes them look foolish or unhinged to outsiders. Legal experts and scholars dismiss their claims as baseless, and their confrontations frequently go viral for the wrong reasons.
The sovereign citizen rejection of Social Security is a head-scratcher, and it’s a great example of how their ideology shoots them in the foot. They often claim Social Security numbers are government "contracts" that bind them to a fictional corporate state, so they try to "revoke" or avoid using them. But this logic falls apart when you look at the practical fallout and their own inconsistencies:
What They’re Giving Up: By rejecting Social Security, they’re ditching benefits like retirement payments, disability insurance, and Medicare eligibility. These are critical safety nets for most people, especially if they’re injured, mentally ill, or just old and unable to work. Without private insurance (which many also avoid, claiming it’s another "contract"), they’re left with no coverage. It’s a gamble that assumes they’ll never need help, which is wildly optimistic.
Many sovereign citizens do work, often in cash-based or under-the-table gigs to avoid taxes and paperwork. But those with regular jobs can’t easily dodge Social Security contributions—FICA taxes are automatically withheld from paychecks unless they’re self-employed or committing tax fraud. Some try to file forms like IRS Form 4029 (for religious exemptions) or claim they’re not "employees" under their bizarre legal theories, but the IRS and courts shut these down. So, ironically, many are still paying into the system they claim to reject, just without expecting benefits later.
The Contradiction: It’s comical because they’re often screwing themselves out of money they’ve already paid into. They’ll argue they’re “free” from the system, but when they’re 70, broke, and ineligible for benefits, the freedom argument looks pretty hollow. Some even try to claim benefits later anyway, only to find their earlier rejections (or fraud attempts) have disqualified them.
Why They Do It: It’s less about practicality and more about ideology. They see Social Security as a symbol of government overreach, fueled by conspiracy theories about the system “enslaving” them. Online forums and sovereign “gurus” push this, convincing them it’s a stand for liberty, even if it means financial ruin.
The sovereign citizen obsession with dodging driver’s licenses, vehicle registration, and taxes is peak absurdity—it’s like they think they can opt out of society’s basic rules and still use its roads. Here’s the rundown on why this is such a clown show:
Driver’s Licenses: They argue that driving is a “right,” not a privilege, so they don’t need a license. They’ll claim the government only regulates “commercial travel,” not their personal “right to travel.” This comes from a tortured misreading of old court cases or the Constitution, ignoring that driving on public roads has always been regulated for safety. Without a license, they’re just breaking the law, and cops don’t buy their “I’m not driving, I’m traveling” spiel. Cue viral traffic stop meltdowns where they argue with officers and get towed or arrested.
Vehicle Registration: They often refuse to register cars or display valid plates, sometimes making their own “sovereign” license plates with fake seals or phrases like “Private Traveler.” They claim registration is a contract with the state they can reject. In reality, registration funds road maintenance and ensures vehicles meet safety standards. Driving unregistered vehicles leads to fines, impoundment, or jail time when they double down in court with their gibberish legal arguments.
Taxes: Sovereign citizens love dodging taxes, claiming they’re not “persons” under IRS code or that income tax is unconstitutional (debunked repeatedly, like in Cheek v. United States). They file fraudulent forms, hide income, or claim exemptions based on their “sovereign” status. The IRS doesn’t play along, and tax evasion often lands them in federal prison. Yet they keep trying, thinking their magic legal phrases will outsmart the system.
Why It’s Silly: They’re using public infrastructure—roads, bridges, traffic systems—while refusing to contribute or follow rules. It’s like eating at a restaurant, stiffing the bill, and claiming you don’t owe because you’re a “free man.” Courts, cops, and the DMV aren’t swayed by their wordplay, so they just rack up fines, lose their cars, or end up in cuffs. The mental gymnastics to justify it are laughable, especially when they post their “wins” online, only to get slapped with reality later.
The Crazy Factor: It’s not just ignorance; it’s a delusional commitment to a fantasy where they’re above the law. They’ll scream about freedom while handcuffed in a squad car, oblivious to the irony. Online, you’ll see them share “scripts” to argue with cops or file fake liens against judges, which only digs their hole deeper.
More or less, they are simply batshit crazy.
Sovereign citizens’ beliefs are so divorced from reality—ignoring basic legal and financial systems while clinging to their pseudo-legal word salad—that "batshit crazy" isn’t far off. It’s like they’re playing a game of make-believe with real-world consequences, and the self-sabotage is both wild and oddly entertaining. If you spot any unhinged sovereign citizen posts or want me to dig into a specific angle of their nonsense, let me know!
0 notes
Text
Cross-Platform Development: The Ultimate 2025 Guide to Building Apps That Work Everywhere

Introduction: Why Cross-Platform Development Matters More Than Ever
In the fast-paced digital world, businesses want apps that are fast to build, cost-effective, and work across Android, iOS, Windows, and the web. Enter cross-platform development—the solution that allows you to write code once and deploy everywhere.
If you’re a startup, business owner, or a developer exploring smarter ways to build applications in 2025, cross-platform development is a game-changer.
In this guide from diglip7.com, we’ll explore what cross-platform development is, its benefits and drawbacks, best tools and frameworks, real-life use cases, and how you can get started today.
What is Cross-Platform Development?
Cross-platform development is the process of creating software applications that are compatible with multiple operating systems using a single codebase.
Instead of building separate apps for Android, iOS, and web from scratch, developers can write the core logic once and reuse it across platforms.
🔍 Example:
Instagram, Facebook, and Skype are excellent examples of cross-platform apps—they work seamlessly across various devices and platforms using shared codebases.
Why Businesses Are Choosing Cross-Platform Development in 2025
The popularity of cross-platform development is skyrocketing for good reasons:
✅ Faster Time to Market
A single codebase means quicker development and deployment. You can launch on both iOS and Android simultaneously, saving time and energy.
✅ Reduced Development Costs
Why hire separate iOS and Android teams when you can build both using one tech stack? Cross-platform development cuts costs without compromising on performance.
✅ Consistent User Experience
Using the same design and logic ensures your brand looks and behaves consistently across platforms.
✅ Easier Maintenance and Updates
Updates or bug fixes are made once and pushed to all platforms, improving efficiency and consistency.
✅ Wider Audience Reach
With apps that run on multiple devices, your brand reaches a broader audience without additional development effort.
Popular Cross-Platform Frameworks in 2025
Here are the most widely used cross-platform frameworks in 2025, and why developers love them:
1. Flutter (by Google)
Language: Dart
Strengths: High performance, hot reload, beautiful UI, strong community
Use Cases: eCommerce apps, social networks, MVPs
2. React Native (by Meta)
Language: JavaScript
Strengths: Native-like performance, strong community, reusable components
Use Cases: Messaging apps, utility apps, startups
3. Xamarin (by Microsoft)
Language: C#
Strengths: Integrates with .NET ecosystem, strong enterprise support
Use Cases: Enterprise apps, internal business tools
4. Unity
Language: C#
Strengths: Best for gaming and 3D apps
Use Cases: Cross-platform games, AR/VR apps
5. Ionic + Capacitor
Language: JavaScript/TypeScript
Strengths: Web-first, fast prototyping, integration with Angular/React/Vue
Use Cases: Hybrid apps, quick prototypes, educational apps
Native vs. Cross-Platform: What's the Difference?
FeatureNative DevelopmentCross-Platform DevelopmentCodebaseSeparate for each platformSingle shared codebasePerformanceSlightly betterVery close with modern frameworksTime & CostHigherLowerUser ExperiencePlatform-specific UINear-native look and feelMaintenanceUpdate each platform separatelyOne update for all platformsIdeal ForComplex, hardware-intensive appsBusiness apps, MVPs, startups
Cross-Platform Development Process: Step-by-Step
Here’s how a typical cross-platform development cycle works:
Step 1: Define the App Requirements
Understand target audience and platforms
List core features and design expectations
Step 2: Choose the Right Framework
Based on budget, timeline, and performance needs
Flutter or React Native are top choices for most use cases
Step 3: Design the App UI/UX
Use Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch
Ensure responsive design and consistent brand identity
Step 4: Develop the App
Write code using the chosen framework
Integrate APIs, third-party tools, and local databases
Step 5: Test on All Platforms
Use tools like Appium, BrowserStack, or in-built emulators
Perform unit, integration, and UI testing
Step 6: Deploy to App Stores
Prepare builds for Android and iOS
Follow Play Store and App Store guidelines
Step 7: Monitor and Maintain
Track app performance with tools like Firebase, Sentry, or Analytics
Push updates regularly to fix bugs and improve features
Pros and Cons of Cross-Platform Development
Pros:
✅ Single codebase = faster development
✅ Reduced development and maintenance costs
✅ Consistent UI and UX across devices
✅ Larger potential user base
✅ Great for MVPs and quick market entry
Cons:
❌ Slightly lower performance for very complex apps
❌ Dependency on third-party plugins
❌ Limited access to some native features
❌ UI might not always feel “perfectly native”
Cross-Platform Development Trends in 2025
Stay ahead with these rising trends:
🔮 AI Integration
AI-powered features like chatbots, image recognition, and voice commands are now easily embedded across platforms using unified SDKs.
🔮 Cloud Backends
Integration with services like Firebase, Supabase, and AWS Amplify makes building scalable apps easier than ever.
🔮 Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs continue to rise as a fast, app-like alternative to native apps.
🔮 Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Platforms like OutSystems and FlutterFlow let non-developers build cross-platform apps visually.
Reviews from Developers and Businesses
👨💻 Developer Review
“Flutter has changed how I build apps. I can launch for both iOS and Android in weeks instead of months. Cross-platform saves time without sacrificing quality.” — Aman Gupta, Freelance App Developer
👩💼 Business Owner Review
“React Native allowed our startup to test our MVP quickly and affordably. We reached both Android and iPhone users without hiring two separate teams.” — Neha Sharma, Co-founder at a SaaS startup
Best Use Cases for Cross-Platform Development
Startups building MVPs
Businesses targeting both Android and iOS users
eCommerce and retail apps
Media, entertainment, and education apps
Apps with common UI across platforms
Common Mistakes to Avoid
❌ Ignoring platform-specific UI guidelines
❌ Choosing the wrong framework for your needs
❌ Skipping testing on real devices
❌ Overusing third-party libraries without vetting
❌ Not planning for long-term maintenance
How to Hire a Cross-Platform Development Team
Look for:
✅ Experience with React Native, Flutter, or your chosen framework
✅ Knowledge of both Android and iOS ecosystems
✅ Strong UI/UX design background
✅ Previous work on similar apps
Where to Find Developers:
Freelance platforms like Upwork, Toptal, Fiverr
Dedicated agencies
Tech communities like GitHub, Stack Overflow
FAQs About Cross-Platform Development
❓ Is cross-platform better than native?
It depends. For apps with general functionality and wide reach, cross-platform is better. For hardware-intensive apps (games, AR), native may be better.
❓ Which is the best cross-platform framework in 2025?
Flutter and React Native are leading in 2025 due to their large communities, excellent performance, and robust libraries.
❓ Can I convert a website into a mobile app using cross-platform tools?
Yes! Tools like Ionic and React Native Web allow you to reuse web components for mobile.
❓ How much does cross-platform development cost?
Depending on complexity, costs can range from $5,000 to $100,000+. It's usually 30-40% cheaper than building two native apps.
❓ Is it suitable for large enterprise apps?
Absolutely. With frameworks like Xamarin and Flutter, many large corporations have already adopted cross-platform for internal and consumer apps.
Conclusion: The Future is Cross-Platform
Cross-platform development is not just a trend—it's a powerful strategy for building efficient, scalable, and user-friendly apps in 2025.
By reducing costs, speeding up time to market, and maintaining consistency, it's ideal for businesses, startups, and developers alike.
Whether you’re planning your next big app or scaling an existing one, cross-platform technology offers the flexibility and reach you need.
Ready to build your next cross-platform app? Explore the latest frameworks, tutorials, and industry tips at diglip7.com—your trusted source for digital innovation.
0 notes
Text
Economic Justice
Economic justice is a branch of ethics that examines how wealth, opportunity, and resources should be distributed in a fair and just society. It seeks to balance individual freedom with collective well-being, ensuring that economic policies and systems promote equity, fairness, and dignity for all members of society.
1. Core Principles of Economic Justice
Economic justice is built on several foundational principles:
A. Equity
People should have fair access to economic resources, regardless of social status, race, or background.
Equity does not always mean equality (identical treatment); rather, it seeks to address systemic disadvantages and ensure fairness in opportunity.
B. Fair Distribution of Wealth
Society must determine whether wealth should be distributed based on merit, need, or social contribution.
The debate between capitalism (rewarding individual effort) and socialism (redistributing wealth for collective benefit) falls within economic justice.
C. Fairness in Economic Transactions
Workers should receive just wages that reflect their labor’s value.
Consumers should not be exploited through price gouging, fraud, or monopolistic practices.
Corporations have a duty to act ethically rather than solely maximizing profit.
D. Opportunity and Economic Inclusion
Economic justice ensures that everyone has access to jobs, education, and financial stability.
Discrimination based on race, gender, or class should not determine a person’s economic potential.
E. Social Safety Nets
A just society provides protections for the vulnerable, including healthcare, unemployment benefits, and welfare programs.
These safety nets prevent poverty and economic collapse for individuals facing hardship.
2. Theories of Economic Justice
Philosophers and economists have proposed different frameworks for what constitutes a just economy:
A. Utilitarianism (Greatest Good for the Greatest Number)
Economic policies should maximize overall happiness and well-being.
A free market is just if it leads to widespread prosperity.
Critics argue that this can justify inequality if it benefits society as a whole.
B. Libertarianism (Minimal Government, Maximum Freedom)
Economic justice means protecting individual property rights and allowing free markets to operate with minimal state interference.
Redistribution of wealth through taxation is viewed as coercion.
Critics argue this leads to unchecked inequality and social stratification.
C. Rawlsian Justice (Fairness and the Veil of Ignorance)
Philosopher John Rawls argues that a just economy must benefit the least advantaged members of society.
If we designed society without knowing our position in it, we would choose policies that ensure fair opportunities for all.
D. Marxist Economic Justice (Class Struggle and Redistribution)
Karl Marx believed capitalism inherently exploits workers and leads to inequality.
A just economy prioritizes collective ownership of resources and the elimination of class oppression.
Critics argue that historical attempts at Marxist economies have resulted in inefficiency and loss of individual freedoms.
E. Distributive Justice (Who Gets What?)
Some theorists argue that wealth should be distributed based on merit, while others argue for need-based allocation.
Progressive taxation, social welfare, and universal basic income (UBI) are modern policies influenced by distributive justice.
3. Key Issues in Economic Justice
Economic justice plays a role in various real-world economic debates, including:
A. Income Inequality
Should billionaires exist in a just economy?
Is it fair that CEOs make hundreds of times more than average workers?
How can societies address wage stagnation and economic disparity?
B. Corporate Responsibility vs. Profit Maximization
Should businesses be held accountable for environmental damage and labor exploitation?
Is corporate social responsibility (CSR) an ethical obligation, or just good branding?
C. The Ethics of Taxation
Is progressive taxation (higher taxes on the wealthy) a form of justice or punishment?
Are tax havens and loopholes ethical if they are legal?
Should there be a universal basic income (UBI) to ensure economic fairness?
D. Labor Rights and Exploitation
Should governments implement a universal living wage?
Is outsourcing jobs to lower-wage countries ethical?
How should societies deal with automation replacing human labor?
4. Economic Justice in Practice
Many policies aim to implement economic justice in society, such as:
Minimum wage laws to prevent worker exploitation.
Progressive taxation to reduce extreme wealth gaps.
Universal healthcare and welfare programs to ensure basic needs are met.
Affirmative action and diversity programs to correct past injustices.
Regulation of monopolies and unethical business practices to ensure fair competition.
5. The Future of Economic Justice
The concept of economic justice is evolving due to:
Automation and AI replacing jobs, requiring new labor protections.
Globalization, which raises questions about fair trade vs. worker exploitation.
Cryptocurrency and decentralized finance, which challenge traditional economic structures.
Climate change, which demands a just approach to economic sustainability.
Conclusion
Economic justice is about ensuring that economic systems promote fairness, dignity, and well-being for all members of society. While different philosophical perspectives offer conflicting views on wealth distribution, labor rights, and corporate responsibility, the core goal remains the same: to create a more just and equitable economic system that benefits society as a whole.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#ethics#economics#economic ethics#Economic Justice#Distributive Justice#Labor Rights#Fair Wages#Corporate Responsibility#Taxation Ethics#Free Market vs. Regulation#Universal Basic Income#Social Welfare#wealth#inequality
0 notes
Text
Crafting SEO-Friendly Websites: A Developer’s Roadmap to Visibility

In today’s digital ecosystem, a website’s success hinges not just on sleek design or functionality, but on its ability to be found. For developers, weaving SEO into the fabric of your build process isn’t optional—it’s critical. At CodingNectar.com, we’ve seen how SEO-savvy development drives traffic and growth. Let’s break down how to engineer websites that both users and search engines love.
1. Architect with SEO in Mind
A website’s structure is its backbone. Imagine constructing a skyscraper: without a blueprint, chaos ensues.
Flat Architecture Wins:
Keep pages within 3–4 clicks from the homepage for easy crawling.
Avoid orphan pages—every page should link back to your main navigation.
URLs That Speak Clearly:
Ditch cryptic strings like /page123. Opt for descriptive paths (e.g., /guides/seo-for-devs).
Use hyphens (-) to separate words—search engines read them as spaces.
Pro Tip: Tools like Screaming Frog act as X-ray goggles, uncovering broken links or duplicate content.
2. Nail Technical SEO Foundations
Think of technical SEO as the plumbing—it’s invisible but essential.
Mobile-First Isn’t a Trend, It’s a Rule:
Use responsive frameworks (e.g., Bootstrap) and test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool.
Speed Is Non-Negotiable:
Compress images to WebP format (tools: ImageOptim).
Minify CSS/JS files and leverage browser caching.
Guide Search Engines:
Generate an XML sitemap.
Block irrelevant pages (e.g., test environments) via robots.txt.
3. Semantic HTML: SEO’s Best Friend
Clean code isn’t just for developers—it’s a love letter to search engines.
HTML5 Tags Are Your Allies:
Use <header>, <nav>, and <article> to add context.
Headings Hierarchy Matters:
One <h1> per page (your title), followed by logical <h2>-<h6>.
Alt Text: Describe, Don’t Keyword-Stuff:
alt="developer optimizing website speed" beats alt="SEO tips".
4. Ace Core Web Vitals
Google’s user experience metrics can make or break your rankings.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP):
Target <2.5 seconds. Optimize hero images and lazy-load offscreen content.
First Input Delay (FID):
Defer non-critical JavaScript.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS):
Reserve image/video space with width and height attributes.
Test Tools: Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse are your go-to auditors.
5. Content: Where Code Meets Strategy
Developers wear many hats—content strategist included.
Keyword Research:
Tools like Ahrefs uncover gems (e.g., “optimize Angular SEO” vs. generic terms).
SPA Challenges:
Use server-side rendering (Next.js/Nuxt.js) for React/Angular apps.
Canonical Tags:
Fix duplicate content with <link rel="canonical" href="https://your-primary-url">.
6. Security & Accessibility: SEO’s Silent Allies
HTTPS is Mandatory:
Free SSL via Let’s Encrypt boosts trust and rankings.
Accessibility Enhances SEO:
ARIA labels (e.g., aria-label="Contact form") aid screen readers and search bots.
7. Structured Data: Speak Google’s Language
Schema markup helps search engines “get” your content.
JSON-LD Example:
html
Copy<script type="application/ld+json"> { "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "Guide", "name": "SEO for Developers", "author": "CodingNectar.com" } </script> Run HTML
Validate with Google’s Structured Data Tool.
8. Monitor, Tweak, Repeat
SEO is a marathon, not a sprint.
Track Progress:
Google Search Console reveals crawl errors and keyword performance.
Moz or Ahrefs monitor rankings.
Fix Issues Promptly:
Redirect broken links (301s) and refresh stale content.
Avoid These SEO Blunders
Neglecting Mobile: Most searches happen on phones.
JavaScript Overload: Heavy scripts slow crawlers.
Duplicate Content: Canonical tags are your safety net.
Cheap Hosting: Slow servers = lost rankings.
Final Take: SEO is Part of Your Code
Building SEO-friendly sites isn’t about gaming algorithms—it’s about creating fast, accessible, and intuitive experiences. By embedding SEO into your development DNA, you’ll future-proof your work and unlock organic growth. At CodingNectar.com, we’ve turbocharged rankings for everyone from startups to Fortune 500s by merging technical rigor with SEO strategy.
Ready to code your way to the top? Start with SEO in your toolkit—your analytics will thank you.
0 notes
Text

Performance checking out is essential for comparing the reaction time, scalability, reliability, speed, and aid utilization packages and net offerings below their anticipated workloads. The software program marketplace presently has diverse overall performance checking out gear. Nevertheless, whilst we talk of overall performance checking out gear, Apache Jmeter and Micro Focus LoadRunner (former HP LoadRunner) are the 2 names that routinely come to mind. Both those gear paintings nicely for detecting insects and locating obstacles of software program packages with the aid of using growing their load. But in this text we additionally would like to inform approximately our in-residence device Boomq.io. A clever manner to find out which device is applicable on your commercial enterprise wishes is to evaluate the important capabilities of Jmeter vs Loadrunner vs Boomq. In this text, we talk about the important variations among Jmeter, Loadrunner and Boomq. Jmeter Features in Performance and Load Testing Apache Jmeter has the subsequent key capabilities.
- GUI Design and Interface
- Result Analysis and Caches
- Highly Extensible Core
- 100% Java scripted
- Pluggable Samplers
- Multithreading Framework
- Data Analysis and Visualization
- Dynamic Input
- Compatible with HTTP, HTTPS, SOAP / REST, FTP, Database through JDBC, LDAP, Message-orientated middleware (MOM), POP3, IMAP, and SMTP
- Scriptable Samplers (JSR223-well matched languages, BSF-well matched languages, and BeanShell)
Pros and Cons of the Jmeter Application Jmeter is a sturdy overall performance checking-out device with numerous awesome capabilities. However, the utility nevertheless has many professionals, in addition to cons. Jmeter Advantages Here are a few key benefits that stand out the most. Available free of price Data extraction in famous reaction formats, including JSON, XML, HTML, and many others Although the Apache Jmeter has numerous benefits, it additionally has some shortcomings, which might be noted below: Doesn`t assist JavaScript so it doesn`t assist AJAX requests with the aid of using an extension Memory intake for the utility may be excessive whilst utilized in GUI mode After a sure limit, excessive reminiscence intake reasons mistakes for a big range of customers Can be hard to check complicated packages the use of JavaScript or dynamic content, including CSRF tokens. Less gifted than paid overall performance checking out gear including LoadRunner What is LoadRunner? HP Loadrunner (now Micro-Focus Loadrunner) is an especially state-of-the-art software program overall performance checking out a device that detects and stops overall performance troubles in net packages. It makes a specialty of detecting bottlenecks earlier than the utility enters the implementation or the deployment phase. Similarly, the device is extraordinarily useful in detecting overall performance gaps earlier than a brand-new gadget is applied or upgraded. However, Loadrunner isn't restrained from checking out net packages or offerings. The utility is likewise optimized for checking out ERP software programs, and legacy gadget utility, in addition to Web 2. zero technology. Loadrunner allows software program testers to have complete visibility over their gadget`s cease-to-cease overall performance. As a result, those customers are capable of examining every factor for my part earlier than it is going to stay. At the same time, Loadrunner additionally offers its customers especially superior forecasting capabilities for forecasting prices for up-scaling utility ability. By exactly forecasting prices associated with each software program and hardware, it's miles less difficult to decorate the ability and scalability of your utility. Loadrunner isn't open source and is owned by the era-large Hewlett Packard. Therefore, the code of the utility isn't to be had by customers. However, because the utility already gives many superior and excessive-stage checking-out capabilities, it isn`t essential to customize present capabilities. Loadrunner Features in Performance and Load Testing
#software testing training#unicodetechnologies#automation testing training in ahmedabad#manual testing
0 notes
Text
What is the estimated cost of building a text-based chatbot similar to WhatsApp or Telegram?
What is the Estimated Cost of Building a Text-Based Chatbot Similar to WhatsApp or Telegram?
Introduction
In modern-day rapid-paced world, instantaneous verbal exchange is critical, leading organizations to invest extra in text-primarily based chatbots. These digital assistants facilitate interactions, automate customer support, and raise person engagement. As the call for for AI-pushed conversational retailers rises, a key question arises: what is the cost to develop an app in dubai or other most important tech hubs.
Understanding the Scope of a Text-Based Chatbot
What Defines a Text-Based Chatbot
A textual content-primarily based chatbot is an AI-powered software that communicates with customers thru textual content messages. These chatbots simulate human-like conversations and generate responses primarily based on both predefined policies or machine studying algorithms.
Key Features of Chatbots Like WhatsApp and Telegram
Real-time messaging with cease-to-cease encryption
AI-pushed responses for extra natural conversations
Support across a couple of systems, including cell and net
Integration with third-party APIs for improved functionalities
Core Features Required in a Chatbot
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
A chatbot needs to understand and process human language effectively. This involves using NLP algorithms to improve the accuracy of responses.
User Authentication and Security
To safeguard sensitive user information, strong security measures such as OAuth authentication and end-to-end encryption are essential.
Integration with Third-Party Services
Chatbots frequently connect with CRMs, payment gateways, and social media platforms to broaden their capabilities.
Chat History and Cloud Storage
Users expect their chat history to be saved, which necessitates cloud infrastructure and effective data storage solutions.
AI-Driven Responses vs. Rule-Based Responses
AI-driven chatbots provide personalized interactions through machine learning, while rule-based bots adhere to predefined scripts.
Factors Affecting Development Cost
Platform Selection: Web, iOS, Android, or Cross-Platform
Developing a chatbot for one platform is cheaper compared to developing a multi-platform solution.
Technology Stack: Custom Developed or Leverage Chatbot Frameworks
Development costs can be minimized by using open-source frameworks such as Rasa or Google Dialogflow.
AI vs. Rule-Based Chatbots: Cost Implications
AI-based bots need large training datasets, and thus are more costly compared to basic rule-based chatbots.
Third-Party API Integrations
Integration with services such as payment gateways, voice assistants, or CRM tools may contribute to the overall cost.
Breakdown of Cost for Creating a Chatbot
Requirements for Development Team
A chatbot project will generally need:
Project manager
AI/ML engineers
Frontend and backend developers
UI/UX designers
QA testers
Costs of Frontend and Backend Development
Creating the chatbot's interface and backend infrastructure demands a lot of coding and database management.
Estimated Building Cost of a Chatbot Such as WhatsApp or Telegram
Basic Chatbot Estimate
A basic rule-based chatbot would cost between $5,000 and $15,000.
Advanced Chatbot with AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI-based chatbots vary between $30,000 and $100,000, based on complexity.
Enterprise-Level Chatbot Pricing
Costs can range above $150,000 for large-scale deployments, including cloud computing and comprehensive AI training.
Selecting the Right Development Partner
Dubai Mobile App Development Companies vs. Offshore Developers
Whereas mobile app development companies in dubai provide high-end services, offshore developers can offer affordable solutions.
Mobile App Development Company in Muscat: Why Companies Opt for Local Teams
A mobile app development company in muscat can have a better grasp of local market requirements and compliance laws.
How to Maximize Cost Efficiency Without Sacrificing Quality
Selecting Open-Source Frameworks
The use of platforms such as Rasa or Dialogflow saves up-front investment.
Leaning on Cloud-Based Services
Cloud companies provide cost-saving pay-as-you-go schemes.
Outsourcing vs. Internal Development
Employing offshore resources can greatly minimize costs without affecting quality.
Conclusion
Creating a text-based chatbot such as WhatsApp or Telegram has several cost implications, ranging from development to upkeep. The app cost of developing in Dubai is highly dependent on features, platform, and artificial intelligence integration. Companies need to evaluate their requirements and hire a well-established Mobile app development agency in Dubai or a Mobile app development agency in Muscat to make a cost-effective, high-quality chatbot system.

0 notes
Link
0 notes