#nfsv3
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Price: [price_with_discount] (as of [price_update_date] - Details) [ad_1] An easy-to-use 1-bay personal cloud storage for NAS starters Sequential throughput at over 112 MB/s reading and 106 MB/s writing Cross-device file sharing and syncing platform. Networking Protocols - SMB1 (CIFS), SMB2, SMB3, NFSv3, NFSv4, NFSv4.1, NFS Kerberized sessions, iSCSI, HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SNMP, LDAP, CalDAV . Supported Browsers - Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Internet Explorer 10 onwards, Safari 10 onwards, Safari (iOS 10 onwards), Chrome (Android 6.0 onwards) Reliable computer backup companion for Windows/macOS and photos from mobile devices Freely access your files on the go with iOS and Android mobile apps [ad_2]
0 notes
Text
Google NetApp Cloud Volumes: Flex Volumes and Auto-tiering

Google NetApp Cloud Volumes
Google NetApp Cloud Volumes was introduced in August 2023 as the outcome of Google Cloud and NetApp’s engineering cooperation. For businesses wishing to fully leverage the cloud, this fully managed file storage service offers extensive yet user-friendly data management tools that enable great performance and excellent security.
Concerning NetApp Volumes
NetApp Volumes is a fully managed cloud-based data storage solution with highly scalable performance and sophisticated data management features.
With Google NetApp Cloud Volumes, you can manage your workloads and apps more quickly, move workloads to the cloud, and retain the features and performance of on-premises storage.
You may migrate file-based apps to Google Cloud with NetApp Volumes. Because of its built-in support for the Server Message Block (SMB) and Network File System (NFSv3 and NFSv4.1) protocols, you may continue to acquire persistent storage for your applications without having to re-architect them.
Four service levels are available from Google NetApp Cloud Volumes: Flex, Standard, Premium, and Extreme. Service levels differ in terms of capabilities, features, and performance.
They kept up the innovation since the service went live, growing their collaboration and enhancing its features. These are some of the highlights.
Announcing the service level for Flex storage
Google Cloud current Standard, Premium, and Extreme storage service levels are enhanced by the new Google NetApp Cloud Volumes Flex storage service level. You can now build a volume as little as 1GiB, a storage pool as small as 1TiB, and choose between regional storage service levels (99.99% SLA) and zonal storage service levels (99.9% availability SLA). Flex regional is now offered in Preview in seven regions, whereas Flex zonal is typically accessible in fourteen.
Meeting the demands of enterprise workloads
For businesses wishing to migrate VMware applications with a lot of storage to Google Cloud, NetApp Volumes is perfect. With Google NetApp Cloud Volumes‘ recent certification as a Google Cloud VMware Engine datastore, scalability and migration of virtual machines (VMs) can be facilitated more easily. By using volume reshaping and dynamic switching between the Premium and Extreme storage service tiers, you may optimise costs by only paying for the compute and storage nodes that you really utilise.
Furthermore, Google NetApp Cloud Volumes big volumes are currently under preview for customers running demanding workloads like electrical design automation (EDA) or high-performance computing (HPC) simulations. Large volumes are now supported by NetApp Volumes Premium and Extreme service levels, which provide performance of up to 12GiB/s and handle capacities ranging from 100GiB to 1PiB. This is a major improvement over the current Extreme performance level of 4.5GiB/s.
Novel methods for cost optimisation and data protection
NetApp Volumes make it simple to backup your data, and incremental backups can help you preserve it for a longer period of time at a lower cost. This is a supplement to current methods of data protection, such as cross-region volume replication for disaster recovery and snapshot and cloning for temporary data protection. Currently, Standard, Premium, and Extreme service levels can all access volume backups.
Auto-tiering, a new feature of Google NetApp Cloud Volumes, is currently in preview. You can configure a policy to dynamically tier data from Premium or Extreme service levels to cooler storage volumes based on file access frequency (e.g., 7 days, 30 days). The price difference between the cold storage volumes and the Premium storage volumes is about 80%1. You may now optimise your storage expenses with a “set it and forget it” strategy to track the frequency of file accesses when auto-tiering is enabled. There is no need to alter application or user behaviour for any of the data that is stored on the hot or cold tiers; it is all still available via the filesystem.
Appropriate for AI and workloads of the future
Vertex AI, Google Cloud’s machine learning platform, can be accessed through a new toolkit in Google NetApp Cloud Volumes. This platform helps you store, manage, and safeguard your data on the cloud and effortlessly connect it to Google Cloud compute capabilities to power generative AI and large language models (LLMs).
You may now access unstructured, multimodal data, such as text, audio, video, and photos, that was previously unobtainable with Google NetApp Cloud Volumes and Vertex AI. This data can be used to support scientific research, creative projects, and corporate problem-solving. Additionally, NetApp Volumes give Vertex AI applications extra levels of data security and privacy.
Consumers and analysts are paying attention
Customers who use Google NetApp Cloud Volumes to manage cloud data while lowering storage costs, enhancing performance, and fortifying data security and protection have responded incredibly well.
“Akumin, a pioneer in oncology and radiology solutions globally, relies on cutting-edge technology to provide optimal patient care. We choose Google NetApp Cloud Volumes because it is a centralised solution centrally administered from the Google Cloud panel, offering the functionality and performance Google Cloud require in a completely integrated system. We set up our storage and spun up volumes with ease, and we felt safer knowing that our data architecture was intelligent and safe thanks to NetApp and Google Cloud technologies. – Afsaan Kermani, Akumin’s Vice President of IT
Research examining the worth and advantages of adopting NetApp Cloud Volumes for Google Cloud for enterprises is presented in IDC’s “The Business Value of NetApp Cloud Volumes for Google Cloud” report.
More complicated workloads that need for enterprise-level management are being moved across on-premises, hybrid cloud, and multicloud systems. Companies who wish to extend workload capabilities with cutting-edge cloud services while leveraging their current technology and expertise investments find partnerships like NetApp’s and Google Cloud’s appealing. “Research Vice President, Cloud and Edge Infrastructure Services, IDC,” Dave McCarthy
Google Cloud is eager to work with NetApp going forward and anticipate more advancements as a result of Google Cloud’s alliance.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#GoogleNetApp#googlecloud#datastorage#VMwareapplications#electricaldesignautomation#highperformancecomputing#machinelearning#VertexAI#largelanguagemodels#datasecurity#news#technews#technology#technologynews#technologytrends#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
The Network File System (NFS) is a well-proven, widely-supported and standardized network protocol used to share files between separate computer systems. The Network Information Service (NIS) is commonly used to provide centralized user management in the network. When NFS is combined with NIS, you’re able to have file and directory permissions for access control in the network. The default configuration of NFS is to completely trust the network and any machine connected to a trusted network is able to access any files that the server makes available. In Proxmox Virtualization Environment you can use local directories or locally mounted shares for storage. A directory is a file level storage that can be used to store content type like containers, virtual disk images, ISO images, templates, or backup files. In this post we discuss how you can configure NFS share on Proxmox VE for ISO images. The same process applies for any other storage purpose like storage of virtual disk images and templates. In Proxmox VE, storage configurations are located in the file /etc/pve/storage.cfg. You can list contents in /var/lib/vz/ directory: $ ls /var/lib/vz/ dump images template Within templates directory we can see iso and cache sub-directories. $ ls /var/lib/vz/template/ cache iso The table below shows a predefined directory layout to store different content types into different sub-directories Content type Subdir VM images images// ISO images template/iso/ Container templates template/cache/ Backup files dump/ Snippets snippets/ Configure NFS server Share Login to the server that will act as NFS server and configure export for ISO contents. If you’re using a ready solution with NFS feature, you can skip this steps. Install NFS server package on your Linux system. ### RHEL Based systems ### sudo yum -y install nfs-utils sudo systemctl enable --now rpcbind nfs-server sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=nfs --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload #If use NFSv3 allow the following sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=nfs3,mountd,rpc-bind --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload ### Debian Based systems ### sudo apt -y install nfs-kernel-server Let’s now configure NFS export by editing the file below $ sudo vim /etc/exports /nfs/isos *(rw,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check) In the example we’re setting /nfs/isos as NFS share for ISO images on Proxmox VE. Confirm it works after the changes by re-exporting shares: $ sudo exportfs -rrv exporting *:/nfs/isos Mount NFS ISO share on Proxmox VE server Install NFS utility packages in your Debian / Ubuntu system. sudo apt -y install nfs-common Our NFS server setup is: NFS Server IP address: 172.20.30.3 ISO Export path on NFS Server: /nfs/isos Ensure you don’t have any data inside isos directory: ls /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ On Proxmox VE, which acts as NFS client, execute the following to display RPC information of the remote NFS server. $ rpcinfo -p 172.20.30.3 program vers proto port service 100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper 100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper 100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper 100000 4 udp 111 portmapper 100000 3 udp 111 portmapper 100000 2 udp 111 portmapper 100005 1 udp 20048 mountd 100005 1 tcp 20048 mountd 100005 2 udp 20048 mountd 100005 2 tcp 20048 mountd 100024 1 udp 46068 status 100024 1 tcp 43599 status 100005 3 udp 20048 mountd 100005 3 tcp 20048 mountd 100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs 100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs 100227 3 tcp 2049 100003 3 udp 2049 nfs 100227 3 udp 2049 100021 1 udp 44453 nlockmgr 100021 3 udp 44453 nlockmgr 100021 4 udp 44453 nlockmgr 100021 1 tcp 35393 nlockmgr 100021 3 tcp 35393 nlockmgr 100021 4 tcp 35393 nlockmgr
Run the showmount to display all active folder exports in an NFS server: $ showmount -e 172.20.30.3 Export list for 172.20.30.3: /nfs/isos * Option 1: Configure mount using Proxmox pvesm (Recommended) pvesm is a powerful Proxmox VE Storage Manager command line tool. Use the tool to scan for NFS shares in the server we just configured. $ sudo pvesm scan nfs 172.20.30.3 /nfs/isos * We’re going to run commands shared below to configure NFS Storage for ISO images on our Proxmox environment. sudo pvesm add nfs NFS-iso --server 172.20.30.3 --path /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ --export /nfs/isos --content iso Where: 172.20.30.3 is the IP address of NFS server /nfs/isos is the path to the iso folder on NFS server (NFS export path) /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ path on Proxmox server where NFS share is mounted Listing contents of /etc/pve/storage.cfg after command execution. $ cat /etc/pve/storage.cfg dir: local path /var/lib/vz content iso,vztmpl,backup lvmthin: local-lvm thinpool data vgname pve content rootdir,images nfs: NFS-iso export /nfs/isos path /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ server 172.20.30.3 content iso We can confirm new lines were added to the file. With the df command you can check if mounting was successful. $ df -hT /var/lib/vz/template/iso Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 172.20.30.3:/nfs/isos nfs4 400G 39G 341G 11% /var/lib/vz/template/iso Option 2: Configure mount using /etc/fstab You can also use mount command for runtime testing if Proxmox server can access NFS server and exported directory. sudo mount -t nfs 172.20.30.3:/nfs/isos /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ To persist the configurations use /etc/fstab file. $ sudo vim /etc/fstab # Add NFS ISO share mount 172.20.30.3:/nfs/isos /var/lib/vz/template/iso nfs defaults 0 0 Unmount before testing: sudo umount /var/lib/vz/template/iso Validate mounting can be done successfully sudo mount /var/lib/vz/template/iso Check with the df command: $ df -hT /var/lib/vz/template/iso/ Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on 172.20.30.3:/nfs/isos nfs4 400G 20G 360G 6% /var/lib/vz/template/iso Login to Proxmox Web dashboard and check the status of your mount We can see a list of images available on NFS share. From here VM installation with the ISOs can begin.
0 notes
Text
DELL EMC DEE-1421 Expert - Isilon Solutions Exam Questions
The latest DELL EMC DEE-1421 Expert - Isilon Solutions Exam Questions are new updated by PassQuestion team, you can get the latest DEE-1421 questions and answers to practice for your test preparation. By using DEE-1421 Expert - Isilon Solutions Exam Questions multiple times you will be able to measure your skill level and you can determine how much effort is required to conquer the DEE-1421 real exam.It is highly recommended to go through all of our DELL EMC DEE-1421 Expert - Isilon Solutions Exam Questions so you can achieve the best results and clear the DELL EMC DEE-1421 exam on the first attempt.
DEE-1421 Expert - Isilon Solutions Exam Overview
DEE-1421 Expert - Isilon Solutions exam is a qualifying exam for the Expert - PowerScale Solutions (DCE) track. This exam has two parts, a passing score is required on both parts. • Part 1 consists of knowledge and experience-based questions • Part 2 consists of performance-based simulations
The focus of this exam is on advanced environments and workflows where a PowerScale scale-out NAS platform can be applied. Advanced networking configurations, systems integrations, security and data protection protocols are all examined as components of an appropriate PowerScale solution. Students are expected to have a deep understanding of not only course material, but of documented best practices and administration guides as well as field experience working with the PowerScale product.
Part 1: Duration:90 Minutes Number of Questions: 55 Questions Passing Score: 60%
Part 2: Duration: 30 Minutes Number of Questions: 5 Simulations Passing Score: 60%
A passing score is required on both parts of this exam.
Exam TopicsNetworking (16%)
• Define network routing (for example, source-based and static), Groupnets, IP subnets, and pools • Design connectivity and assess the topology (for example, NANON) • Design and configure advanced networking: LACP, VLAN, MTU, vPC, Trunk and Access, and MLAG • Assess common network services (for example, DNS, NTP, and remote support)
Tenancy, Access Management, Protocols, and Security (20%)
• Design and define multi-tenancy solutions including implementing groupnets, Access zones, networks, DNS, authenticators, and applying namespace design • Assess and design access management including AIMA (authentication and identity management and authorization), variants of Kerberos (such as AD RFC-2307, NIS, User and ID mapping, and LDAP plus share and directory), and RBAC • Identify and design protocol configurations including NFSv3, NFSv4, SMB 1.0, SMB 2.1, SMB 3.0, ACL and POSIX, advanced protocol settings, andprotocol security • Assess and implement security requirements including system hardening policies, security persistence, and compliance
Storage Management, Compliance, and Data Migrations (15%)
• Analyze and evaluate storage management requirements including onpremise and off-premise (for example, CouldPools, ECS, Azure, Amazon) and data life cycle management • Plan, assess, implement data migrations including migration methodologies (for example, DobiMigrate, technology refresh) and permissions
Performance Management (14%)
• Analyze workflow impact to define and implement data access acceleration (non-sequential data flow, streaming media, file system protection settings, and configuration design) • Assess network performance including client protocol configurations and optimization • Analyze the root cause of performance issues and evaluate cluster performance metrics
Data Protection and Recovery (14%)
• Design data replication solutions including SyncIQ and Deep Copy,Snapshots, failover and failback, and third-party applications (for example,Superna) • Identify WORM variants including Compliance mode, Enterprise mode,and SmartLock • Implement NDMP
System Management (11%)
• Assess and recommend data protection level, L3 Cache, SSD, and file pool policies • Apply system management troubleshooting tools, methodologies and design systems monitoring including alerts, events, notifications, syslog, CEE and isi commands
Systems Integration (10%)
• Gather and analyze data to determine the various system(s) requirements
View Online DEE-1421 Expert - PowerScale Solutions Exam Free Questions
An IT team is preparing to replicate a dataset from their existing primary Dell EMC Isilon cluster to a secondary cluster. Both clusters are licensed for SmartLock Enterprise and SyncIQ is used for replication. The source directory is a SmartLock directory and the target directory must be a SmartLock directory. When consulting with the IT team, what is a key consideration before running the replication policy? A. Enable WORM on the target directory after the initial synchronization. B. Allow OneFS to create the target directory automatically. C. Manually create target SmartLock directory before replicating. D. Specify the “root” user that can delete files committed to a WORM state. Answer: B
A company has three Dell EMC Isilon X2000 nodes and needs to configure two subnets on the cluster. The production subnet will only use a 10 GigE-1 port from each node. The second subnet will use both ext-1 and ext-2 ports on each node. The company will access each subnet with its SmartConnect zone name. Given that the second subnet is isolated with no route to the DNS server, how many IP addresses are needed for each subnet to accommodate the requirements? A. 3 for production and 7 for isolated B. 4 for production and 6 for isolated C. 4 for production and 7 for isolated D. 6 for production and 4 for isolated Answer: D
What enables CloudPools to achieve a recall of data from the cloud? A. Creating a HardLink file for every file whose data is archived to the cloud B. Creating a SoftLink file for every file whose data is archived to the cloud C. Creating a SmartLink file for every file whose data is achieved to the cloud D. Creating a copy file for every file whose data is achieved to the cloud Answer: C
SyncIQ policies are being configured between two Dell EMC Isilon clusters at a company’s location. In addition, the company wants the ability to perform a failover at an Access zone level. Which actions should be performed to meet the requirement? A. Create one NS record delegation per cluster. NS record should always point directly to the cluster SSIP address. B. Create one NS record delegation per SmartConnect zone. NS record should always point to an “A” record containing the zone SSIP. C. Create one NS record delegation per SmartConnect zone. NS record should always point directly to the SmartConnect zone IP address. D. Create one NS record delegation per cluster. NS record should always point to an “A” record containing the cluster SSIP address. Answer: C
A company uses the Dell EMC Isilon cluster's A200 nodes for short-team archiving of digitized film. Historical and trending information shows that the cluster capacity will reach 90% full in 60 days. To avoid the need to purchase additional A200 nodes, the company requires a solution that archives data not accessed for 18 months to a more cost-effective platform. The long-term archive data must be online and accessible. Some performance loss is acceptable. Which IT strategy provides a long-term solution that meets the requirements? A. Use data deduplication on achieved data accessed within 180 days B. Use SyncIQ to replicate the archive to the H600 nodes on the secondary cluster C. Use NDMP to backup to disk using compression and deduplication D. Use a CloudPools policy to move the target data to an ECS-powered cloud Answer: C
1 note
·
View note
Text
New Post has been published on VMware Virtualization Blog
New Post has been published on https://www.tayfundeger.com/vsan-file-services.html
vSAN File Services
Merhaba,
vSAN File Services isimli bu yazımda sizlere vSAN 7 ile birlikte gelen yeniliklerden biri olan vSAN File Services hakkında bilgi vereceğim. Daha önce vSAN 7 ile birlikte gelen yenilikleri yazmıştım. Bu yazıma aşağıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
VSAN 7 Yenilikleri
Çok kafa karıştırmadan sade bir biçimde File Services’i anlatmak istiyorum. vSAN File Services sayesinde, vSAN datastore’u kullanılarak bir NFS paylaşımı yapabiliriz. Yani bu ne demek oluyor? vSAN File Services, dosya paylaşımları sağlamak için vSAN’ın üzerine oturan bir katmandır. Şu anda SMB, NFSv3 ve NFSv4.1 dosya paylaşımlarını desteklemektedir. vSAN datastore’undan oluşturacağınız NFS paylaşımlarını bir sunucuya mount edebilirsiniz. Böylece vSAN datastore’unda bulunan kapasitesinizi NFS, SMB gibi paylaşımlar ile depolama amaçlı kullanabilirsiniz. Tüm bu yapacağınız işlemler vSAN Distributed File System yani vDFS üzerinde gerçekleşir. Bundan dolayı yaptığınız share işlemleri vSAN Storage Policy tarafından desteklenir. Yani oluşabilecek hatalardan, disk bazlı sorunlardan minimum seviyede etkilenirsiniz.
vSAN File Services
vSAN 7.0 Update 1 ile ise, SMB desteğide sunulmaya başlanmıştır. Normalde vSAN 7 ‘de sadece NFS desteği bulunuyor Update 1 ile SMB desteğide geldi. Active Directory üzerinde bulunan bir kullanıcıya yetkilendirme yapılarak paylaşımlara erişim izni verebilirsiniz. İlerleyen sürümlerde farklı desteklerinde geleceğini düşünüyorum. Açıkcası vSAN File Services’in, Tanzu ve Kubernetes gibi altyapılarda aktif olarak kullanılacağını düşünüyorum.
vSAN File Services
Ayrıca daha önceki makalelerimde Cloud Director’un kurulumunu anlatmıştım.
Cloud Director 10 Kurulumu Bölüm 2 – NFS
Bu kurulumda NFS paylaşımı olarak Windows’u kullanmıştım. Eğer sizlerin vSAN 7 ve sonraki versiyonlara sahip bir altyapınız bulunuyor ise, burada vSAN File Services’i kullanıp Cloud Director kurulumunda NFS paylaşımını vSAN üzerinden verebiliriz. Böylece NFS için ekstra olarak bir sunucu bulundurmak zorunda kalmayacaksınız veya NFS sunucu yönetimi ile uğraşmayacaksınız.
vSAN File Share‘in bazı limitasyonları bulunmaktadır. Bunları kısaca sıralayacak olursak;
vSAN Cluster’ında maintenance mode’a alınan bir ESXi host olduğunda, o ESXi host üzerinde bulunan File Service VM otomatik olarak power off olur ve silinir. Maintenance mode’dan çıkarıldığında ise Virtual machine tekrar deploy edilir.
vSAN 7.0 Update 1, 32 File Share ve 32 File Server (ESXi node) desteklemektedir.
vSAN File Shares kullanarak oluşturduğunuz NFS paylaşımını ESXi host’a ekleyip üzerinde Virtual Machine barındırmamalısınız. Bu işlem unsupported ‘dır.
Önemli: 2 node vSAN ve Stretched Cluster support edilmemektedir. Bu vSAN 7 versiyonu için geçerlidir. İlerleyen versiyonlarda bu destek gelebilir.
vSAN File Services aktif etmek için öncelikle vSAN Cluster’ını seçiyoruz ve Configure > vSAN Services bölümüne giriş yapıyoruz.
vSAN Services bölümüne giriş yaptığımızda File Services bölümünde Enable butonuna basıyoruz.
Introduction bölümünde vSAN File Services’in nasıl çalıştığını anlatan bilgiler yer alıyor. Aynı şeyleri yukarıda da anlattım. Burada da göreceğiniz üzere File Services vDFS’in üzerinde çalıştığı için oldukça güvenlidir. Storage Policy’de belirlemiş olduğunuz ayarlar aynı zamanda File Services içinde geçerli olduğu için bize maksimum koruma sağlamaktadır.
File Services’i kullanabilmeniz için static bir IP adresine ihtiyacınız bulunmaktadır. Çünkü burada bir file share oluşturacağınız için bu file share’a ulaşabilmesi için bir IP gerekli. Örneğin Linux bir sunucuya NFS mount ederken burada belirteceğiz IP adresini kullanacaksınız. Aşağıdaki gereksinimleri karşılamayı unutmayın.
Static IP address
Subnet mask ve Gateway
DNS server (geçerli bir A kaydı)
Reverse DNS lookup
Next ile devam ediyoruz.
File Services’i kullanabilmeniz için File Service Agent’i download etmeniz gerekir. Burada Automatic approach seçeneğini seçerseniz en son çıkan File Services Appliance’i otomatik olarak download eder. Ancak siz kendiniz manuel olarak download etmek isterseniz Manual approad seçeneğini seçip ilerleyebilirsiniz. Ben Automatic approach seçeneğini seçiyorum ve OVF dosyasını download ediyorum. Bu işlemi yaptıktan sonra File Service agent bölümü bir daha karşınıza çıkmaz.
Next ile devam ediyorum.
Ben DNS üzerinde vsanfs isminde bir A kaydı oluşturdum ve bunun Reverse DNS kaydınıda yaptım. File Service domain bölümünde DNS üzerinde oluşturduğunuz ve vSAN File Share için kullanacağınız ismi giriyoruz. DNS ve DNS Suffixes bölümünü dolduruyoruz. Directory Service bölümünü isterseniz yapılandırabilirsiniz. Kimlik doğrulama için bir Active Directory domain’ini kullanabilirsiniz. Kerberos kimlik doğrulamasıyla bir SMB dosya paylaşımı veya NFSv4.1 dosya paylaşımı oluşturmayı planlıyorsanız, vSAN File Services için bir Active Directory domain’i yapılandırmanız gerekir. Ben şuan için bunu seçmiyorum.
Next ile devam ediyoruz.
Networking bölümünde File Services‘in kullanacağı network, subnet mask ve gateway’i belirtiyoruz. Ben test ortamımda dedicated bir portgroup belirtmedim ancak sizler production ortamında kullanacaksanız dedicated bir portgroup belirtmenizi tavsiye ederim. Ayrıca Distributed Switch versiyonunun 6.6.0 veya daha üst bir sürüme sahip olmalıdır. Ben burada Standard switch üzerinde konfigurasyon yaptığım için default olarak bırakıyorum ve Next ile devam ediyorum.
Son olarak IP pool bölümünde deploy edilecek olan File Service Agent üzerine IP’lerin belirlenmesi gerekiyor. vSAN Cluster’ınızda kaç adet ESXi host bulunuyor ise o kadar File Service Agent deploy edilecek ve bu sunucuların herbirinin bir IP adresi ve DNS kaydı olması gerekmektedir. Belirteceğiniz her IP adresinin DNS üzerinde mutlaka bir kaydı olması gerekmektedir. Autofill butonuna bastığınızda IP adreslerini sıralı bir biçimde dolduracaktır. Lookup DNS butonuna bastığınızda ise yazmış olduğunuz IP adreslerinin DNS üzerindeki karşılıklarını otomatik olarak yazacaktır. Tüm bilgileri doldurduktan sonra Next butonu ile devam ediyoruz.
Son olarak yapmış olduğumuz işlemlerin kısa bir özetini görüyoruz ve Finish butonu ile işlemi başlatıyoruz.
File Service’in oluşturulma işlemi biraz zaman almaktadır. Çünkü File Service Agent’in download edilip her host üzerine import edilme işlemi ve bunlara IP atama işlemleri zaman alabilmektedir. Kurulumun tüm detaylarını tasks üzerinden takip edebilirsiniz.
File Service üzerinde yapmış olduğumuz ayarların hepsini vSAN Cluster > Configure > vSAN Services bölümü altında görebilirsiniz.
File Service başarılı bir şekilde aktif hale geldikten sonra Cluster altında ESX Agent isimli bir Resource Pool oluşacaktır. Bu Resource Pool altında vSAN File Service Agent’ları çalışacaktır.
Peki File Service’i aktif ettik, bunu bir sunucuya nasıl mount edebiliriz onu göstermek istiyorum.
vSAN Cluster > Configure > File Shares bölümüne giriş yapıyoruz ve burada Add butonuna basıyoruz.
General bölümünde vSAN File Share ile ilgili bazı bilgiler yazmamız isteniyor. Name bölümünde paylaşımın ismini belirtiyoruz. Protocol olarak NFS seçiyoruz. Versions olarak ben default bırakıyorum ancak siz isterseniz sadece NFS 3 veya NFS 4.1 seçebilirsiniz. Storage Policy bölümünü default olarak bırakıyorum. Çünkü bu share yani paylaşım için özel bir policy belirtmedim.
Oluşturacağınız bu paylaşıma isterseniz bir kota belirtebilir hatta belirtmiş olduğunuz sınıra geldiğine size uyarı vermesini sağlayabilirsiniz. Ben burada kota olarak 10 GB, warning olarak ise 5 GB tanımladım. Label bölümünde ise isterseniz bu paylaşımı ne amaç ile kullanacağınızı belirtebilirsiniz.
Next butonu ile devam ediyorum.
Oluşturduğunuz bu paylaşıma hangi IP’lerin erişeceğiniz belirtebilirsiniz. Ben burada Allow access from any IP seçiyorum. Herhangi bir IP kısıtlaması olmaksızın tüm IP’lerden bu paylaşıma bağlantı sağlanabilsin. Eğer isterseniz Customize net access seçeneğini seçerek bir IP bloğu belirtebilirsiniz.
Next ile devam ediyoruz.
Tüm işlemleri tamamladıktan sonra Finish butonu ile işlemi tamamlıyoruz.
Paylaşımımız başarılı bir şekilde oluştu. Şimdi ben bu paylaşımı bir Windows sunucuya mount edeceğim. Altyapımda Linux bir sunucu olmadığı için Linux üzerinde test edemiyorum maalesef 🙂
Copy Path butonuna bastığınız bu paylaşımın adresini kopyalayabilirsiniz.
Windows sunucum üzerinde aşağıdaki komutu çalıştırıyorum.
[php]
mount -o nolock vsanfs1.tayfundeger.local:/vsanshare z:
[/php]
mount -o nolock yazıp daha sonrasında copy path bölümüne bastığımda kopyalanan path’i yapıştırıyorum. Komutun sonuna ise drive ismini belirtiyorum.
vSAN File Services kullanarak oluşturduğumuz paylaşımı Windows sunucuma mount ettim.
Son olarak vSAN File Shares bölümünde, doluluk oranlarınız görebilirsiniz.
vSAN File Shares ilerleyen zamanlarda çok aktif kullanacağımızı düşünüyorum. Çünkü container mimarilerinde NFS paylaşımlarına ihtiyacımız bulunabiliyor. Böyle bir durumda eğer vSAN kullanıyorsanız vSAN File Shares‘i kullanabilir ve böylece işlerinizi hızlı/basit bir şekilde çözebilirsiniz. Ayrıca oluşturacağınız bu File Share, vSAN Storage Policy ile korunduğu için oluşabilecek hatalardan minimum seviyede etkilenirsiniz.
Umarım faydalı olmuştur.
İyi çalışmalar.
0 notes
Text
Willscott/go-NFS: Golang NFSv3 server
https://github.com/willscott/go-nfs/ Comments
0 notes
Text
用 flock 防止指令同時間重複執行
flock(1) 是個好用的工具,可以避免指令同時重複執行。基本的用法是:
flock /tmp/example.lock /usr/bin/example
從這邊的 /tmp/example.lock 可以看出是透過檔案系統層的鎖實做的,也因為這樣的���計,所以用在 NFS 上時,可以規劃出跨機器的鎖定機制。(不過要注意舊版的 NFSv2/NFSv3 是可以刻意不跑 lock daemon 的,這樣就爛掉了 XD)
配合 crontab 執行時,-n 也是常用的選項,用在「這次沒跑也沒關係」的東西上,通常用在是計算出來後丟到 cache 內的程式,跑比較久的時候就跳過這次…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
如何保证NFS文件锁的一致性?
阿里妹导读:在存储系统中, NFS(Network File System,即网络文件系统)是一个重要的概念,已成为兼容POSIX语义的分布式文件系统的基础。它允许在多个主机之间共享公共文件系统,并提供数据共享的优势,从而最小化所需的存储空间。本文将通过分析NFS文件锁状态视图一致性的原理,帮助大家理解NFS的一致性设计思路。
文件锁
文件锁是文件系统的最基本特性之一,应用程序借助文件锁可以控制其他应用对文件的并发访问。NFS作为类UNIX系统的标准网络文件系统,在发展过程中逐步地原生地支持了文件锁(从NFSv4开始)。NFS从上个世界80年代诞生至今,共发布了3个版本:NFSv2、NFSv3、NFSv4。
NFSv4最大的变化是有“状态”了。某些操作需要服务端维持相关状态,如文件锁,例如客户端申请了文件锁,服务端就需要维护该文件锁的状态,否则和其他客户端冲突的访问就无法检测。如果是NFSv3就需要NLM协助才能实现文件锁功能,但是有的时候两者配合不够协调就会容易出错。而NFSv4设计成了一种有状态的协议,自身就可以实现文件锁功能,也就不需要NLM协议了。
应用接口
应用程序可以通过 fcntl()…
from 如何保证NFS文件锁的一致性? via KKNEWS
0 notes
Quote
NFSv3 の固定ポート NFSv3 クライアントのサポートが必要な場合、固定ポートを使うのが良いでしょう。デフォルトでは NFSv3 による rpc.statd や lockd の制御にはランダムな一時ポートが使われます。ファイアウォールを通して NFSv3 の制御ができるようにするには固定ポートを定義する必要があります。/etc/sysconfig/nfs を編集して STATDARGS を設定してください: /etc/sysconfig/nfs STATDARGS="-p 32765 -o 32766 -T 32803" rpc.mountd は /etc/services を読み込んで通常の状態では同じ固定ポート 2048 に bind されます。しかしながら、明示的に定義する必要があるときは /etc/sysconfig/nfs を編集して RPCMOUNTDARGS を設定してください: /etc/sysconfig/nfs RPCMOUNTDARGS="-p 20048" 上記の変更を加えたら、複数のサービスを再起動してください。最初に設定オプションを /run/sysconfig/nfs-utils (参照: /usr/lib/systemd/scripts/nfs-utils_env.sh) に書き出して、二番目に新しいポートで rpc.statd を再起動し、最後に新しいポートで lockd (カーネルモジュール) をリロードします。次のサービスを再起動してください: nfs-config, rpcbind, rpc-statd, nfs-server。 再起動後、サーバーで rpcinfo -p を使って固定ポートが思い通りにいってるか確認してください。クライアントから rpcinfo -p を使えば本当に同じ固定ポートを使っているか明らかになります。
NFS - ArchWiki https://wiki.archlinux.jp/index.php/NFS
0 notes
Text
Smbitinabox causes 3,144 counties files in USA to be exposed and accessed worldwide including foreign country cities
The following links shows over 3,144 exposed files on Google to access from small to large corporations that will allow Cyber Criminals to extract all exposed data from forbidden hidden files. These files are sensitive financial data, personal records, sensitive data, and highly confidential information. Malware programs are being written to extract these 3,144 counties that host servers to extract exposed files and steal data.
The links to the 3,144 cities exposed files can be found below:
The exposed files are over 2 Million confidential files that can be accessed on Google at the following link ( Over 2 Million exposed files worldwide)(2019). Most file systems have methods to assign permissions or access rights to specific users and groups of users. These permissions control the ability of the users to view, change, navigate, and execute the contents of the file system. The way it looks the wrong commands was applied to these file systems, which employees was given administrator access to secure these files, but did not do.costTwo types of permissions are very widely used: traditional Unix permissions date back many decades to the earliest days of Unix. They are universally available on all Unix and Linux derived platforms. Access Control Lists (ACLs) are more recent in origin and are universally used on Microsoft Windows based file systems where the file system supports user permissions (mainly NTFS and ReFS), and are also now commonly used and widely available in most common Unix and Linux based systems, although not necessarily all. They are generally capable of far more detailed fine-tuning of permissions than the traditional Unix permissions, and permit a system of access control which traditional ACLs cannot provide. On Unix and Linux based systems, the standard type of ACL is that defined by the POSIX standard (POSIX ACLs) but other variants exist such as NFS v3 and v4 ACLs, which work slightly differently (NFSv3 ACLs or NFSv4 ACLs).Where multiple systems are available within the same operating system, there is usually a way to specify which will be used for any given file system, and how the system should handle attempts to access or modify permissions that are controlled by one of these, using commands designed for another. The usual solution is to ensure at least some degree of awareness and inter-operability between the different commands and methods. The cost on securing these files will be over $100 Billion as Billions of dollars are already lost because Cyber Criminals can download and extract the financial, hospital data, businesses sensitive data, large corporations data, and many more sensitive data that can be extracted. The SMBITINABOX can be founded all over Google that is scattered Worldwide on popular networks which allow Cyber Criminals to download any file they want at the following link ( SMBITINABOX scattered all over Google for any Cyber Criminal to access )(2019).
#nbc news#breaking news#tech news#local news#news#america#world news#nbc#abc news#msnbc news#msnbc#msn#cnn news#politics#us politics#technology#- google news#microsoft#life#latest news#united states#foreign policy#cybersecurity#bbc news - world#bbc news - home#wgnmorningnews#pc world#zdnet#linux#us navy
0 notes
Text
How to Export an NFSv4 Server to External Networks
We ever discussed fixing ports used by NFSv3 so that it can be easily exported to external networks. For NFSv4.1 or higher, things are much easier. The ports for mountd, statd, and lockd are not required in a pure NFSv4 environment. We have less ports to control or allow for connections. Only port 111 and 2049 need to be taken care of for NFSv4. » Read more How to Export an NFSv4 Server to External Networks from SysTutorials.
0 notes
Text
New Virtual Instruments software improves NAS, flash models
Version 5.3 of Virtual Instruments' Load DynamiX 5 software supports time-based NFSv3 workloads, eases preconditioning of flash arrays and improves the user interface. from rsstechygods http://searchstorage.techtarget.com/news/450417077/New-Virtual-Instruments-software-improves-NAS-flash-models
0 notes
Text
In our previous articles we walked you through the installation of XCP-ng Hypervisor and how to manage XCP-ng Hypervisor with XenCenter | XCP-ng Center. Once the hypervisor and management from XenCenter is configured, configuration of networking and storage repositories can be performed. In Xen virtualization Storage Repository is the place for your VM disks (VDI SR) and storage of ISO files. In this guide we look at how you can configure ISO Library Storage Repository in Xen and upload some ISO files to it. There are two types of ISO SR that can be configured in Xen: NFS ISO – This SR type handles CD images stored as files in ISO format available as an NFS share. Windows File Sharing (SMB/CIFS) – This SR type handles CD images stored as files in ISO format available as a Windows (SMB/CIFS) share. Configure new ISO Storage Repository in Xen We’ll be using XenCenter/XCP-ng Center in this setup but Xen Orchestra can also be used to achieve the same. NFS Server is needed for the storing ISO images. We’ll configure NFS share on a Linux server. Step 1: Install NFS Server Use the commands below to install NFS Server on Ubuntu / Debian system: # Debian / Ubuntu sudo apt update sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server -y Install NFS Server on CentOS / RHEL 8 / CentOS 7: sudo yum -y install nfs-utils Once NFS Server is installed use the commands below to enable the service: sudo systemctl enable --now rpcbind nfs-server Step 2: Configure NFS Share Create ISO Library directory in your NFS Server: sudo mkdir -p /mnt/isos Configure NFS Share by editing the file /etc/exports $ sudo vim /etc/exports # Examples /mnt/isos *(rw,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check) #Allow access from any IP /mnt/isos 192.168.20.0/24(rw,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check) #Allow access only from hosts in subnet 192.168.20.0/24 /mnt/isos 192.168.20.10/24(rw,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check) #Allow access only from single host IP 192.168.20.10 Export your shares $ sudo exportfs -rrv exporting 192.168.20.0/24:/mnt/isos On CentOS NFS Server If you have Firewalld running allow NFS service: sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=nfs --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload #If use NFSv3 allow the following sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=nfs3,mountd,rpc-bind --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --reload Step 3: Add ISO Storage Repository Open your XenCenter/XCP-ng Center console and click “Storage” > “New SR” on the toolbar. In the next screen choose “ISO library“ Give the storage repository a name. The default can be used without renaming. Enter NFS share path inside “Share Name” box. Example: 192.168.20.2:/mnt/isos Where: 192.168.20.2 is the IP Address of NFS server /mnt/isos is the path to ISO files directory as exported in NFS server. For Windows File Sharing SMB/CIFS the share name will have format like \server\sharename Confirm storage repository has been added and visible. Step 4: Add ISO files to NFS share Let’s download some ISO files to the NFS share. Switch to nfs share directory: sudo su - cd /mnt/isos Download ISO files to the directory. See below examples; # Ubuntu 22.04 ISO wget https://releases.ubuntu.com/jammy/ubuntu-22.04-live-server-amd64.iso # Rocky Linux 8 Minimal ISO wget https://download.rockylinux.org/pub/rocky/8/isos/x86_64/Rocky-8.6-x86_64-minimal.iso # Debian 11 netinstall ISO wget https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current/amd64/iso-cd/debian-11.3.0-amd64-netinst.iso Confirm if ISO files can be seen on the XCP-ng server end: In our next guide we’ll discuss installation of Linux and Windows virtual machines from the ISO files in the ISO Library.
0 notes
Text
Gros problèmes entre le BTRFS et le NFSv4
Bonjour à tous.
Petit article aujourd'hui pour parler d'un souci, j'espère que ça servira d'avertissement pour certains qui tomberaient dans le même piège que moi.
Le ton est volontairement humoristique, car quand on a ce genre de couille, il vaut mieux en rire, ou du moins, essayer.
C'est assez relié avec les tutos sur les partages nfs déjà disponibles sur ce blog, donc pour ceux qui dormiraient au fond de la classe, prenez note.
Alors, comme vous avez pu le lire, j'ai récemment mis en place un système de partage assez simple mais néanmoins complexe (WTF?) au niveau de mon serveur de fichier et de mes systèmes là ou je travail en tant qu'administrateur système.
Alors comme ce matin j'ai vécu un véritable apocalypse et empêché une équipe de travaillé pendant 30 minutes, je préfère avertir les têtes brûlées qui voudrait un jour tenter de faire les mêmes conneries que moi.
Ne faites pas comme moi, gardez toujours à l'esprit que quelque chose en développement, même si il parait très cool tout ça, N'EST PAS STABLE!
Quand j'ai formaté mon serveur à l'installation de Debian, j'ai pris la décision d'utiliser le BTRFS comme système de fichier. Pour ceux qui dormais ces 5 dernières années, le BTRFS est annoncé comme le successeur des systèmes journalisés comme la série des ext. Il est en développement depuis 2007 et considéré comme stable depuis mars 2009. Oui mais...

On peut se demande, pourquoi ce système si miraculeux, n'équipe donc pas toutes nos distributions linux actuelles? Lui qui annonces vers performance de +500% en compressé comparé à son camarade ext4, reste irrémédiablement dans l'ombre.
Le fait est que malgré tout le travail et les avancées faites sur son sujet, il n'en reste pas moins un système de fichier en développement, non complet et inapplicable à certaine situation.
Mon exemple est le suivant. Voici mon ancienne infrastructure, que vous connaissez bien, vous les deux ou trois qui suivez mon blog :
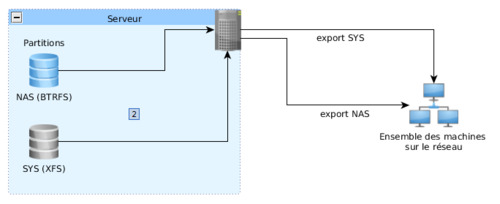
Comme vous le voyez, j'ai fais le choix du BTRFS et j'exporte en NFSv4 au cotés de la partition du Système linux, transportant la racine du système, sur une partition en XFS.
La première fois que j'ai tenté ce montage, j'ai été confronté à un problème assez étrange. En effet, la partition du NAS, en BTRFS, une fois monté en en NFS, provoquait un très très très gros ralentissement. En temps normal, un hdparm -t sur la partition NAS donnait une vitesse de lecture variant entre 1 et 5 Mo/s, contrairement aux 110 Mo/s dont j'ai habitude. Suspectant un problème inhérent au fait de dédoubler un lien nfs partant d'une même source et allant vers une même destination, je me suis donc décidé à essayer de ne tourner qu'avec une seule exportation, limitant dans le même coup les erreurs de démontages sur les postes clients, et j'ai donc donné vie au tutoriel d'hier (ou d'avant hier, je sais plus). Bref, donc cette configuration fut modifiée et j'ai pu aboutir au bout de quelques recherches à l'ensemble suivant :
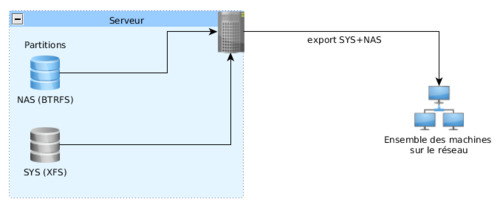
Hier soir je clos définitivement l'affaire, prépare à distance mes systèmes, et, prévoyant, met mon réveil plus tôt pour être premier au boulot, on sait jamais.
Ce matin, les 4 premiers postes démarrent sans encombre et je vais me fumer une cigarette, certes matinale mais néanmoins méritée pour célébrer ma victoire sur cette hérésie qu'est l'infrastructure de développement local standard des sociétés de développement web d'aujourd'hui.
En revenant de cette délicieuse cigarette, le 5e poste est allumé et...

D'un coup, tout les systèmes commencent à ralentir.
Suspectant un ralentissement du réseau, je cherche d'abord dans ce sens, avant de me rendre compte que mes hdparm ne passent plus. Chaque consoles ouvertes avec lesquelles je lance un hdparm me lâchent, et me guide désespérément vers la triste réalité que me réserve le /var/log/syslog.
Pour la faire courte, toute la couche BTRFS avait sauté d'un coup à la suite de l'appel nfsv4 du 5e poste. Je me retrouve avec une énorme erreur kernel, révélée en fait par le hdparm.
Je me retrouve donc à devoir repasser sur notre vieux serveur de fichier, celui qui crash dès qu'une porte claque trop fort.

Ouaip, donc un conseil :
LE BTRFS EN NFSv4 POUR LE PARTAGE MASSIF, ON ÉVITE!
Et moi je reformate ma partition de serveur en ext4. Ça m'apprendra a faire des expériences.
#nfsv4#nfsv3#nfs#mount#partage#linux#ubuntu#debian#it's#a#trap#connerie#developpement#instable#stable
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
New Post has been published on VMware Virtualization Blog
New Post has been published on https://www.tayfundeger.com/vsan-7-lisanslama-modeli.html
VSAN 7 Lisanslama Modeli

Merhaba,
VSAN 7 Lisanslama Modeli isimli bu yazımda sizlere VSAN 7 ‘nin lisanslama methodları hakkında bilgi vereceğim. Daha önce yazmış olduğum VSAN ile ilgili makalelere aşağıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
https://www.tayfundeger.com/kat/VSAN
Daha önce VSAN 6.5 ile ilgili lisans detaylarını paylaşmıştım. Bu yazıma aşağıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
vSAN 6.5 Lisans Detayları
VSAN 7 Lisanslama Modeli
Bu yazımda da benzer şeyleri yazacağım aslında. VSAN ‘ın lisanslama işlemleri CPU soket bazlı yapılmaktadır. Yani her CPU için lisans almanız gerekmektedir. Cluster’da kaç adet ESXi host var ise onlar için VSAN lisansı almanız gerekmektedir. Örneğin 2 soketli 4 adet fiziksel sunucunuz var. Burada 8soketlik bir lisans almanız gerekmektedir. Hangi lisansı alacağınızı ise aşağıda görebilirsiniz.
Ancak kullanacağınız veya tercih edeceğiniz konfigurasyona göre lisanslama modeli değişebilir. Örneğin ROBO konfigurasyonunda farklı lisanslama modeli var iken, 4 node’dan oluşan bir VSAN’da farklı lisanslama modeli bulunmaktadır. Elbette tercih edeceğiniz lisansa göre sahip olacağınız özelliklerde farklı olacaktır. Bundan dolayı lisanslama konusunda dikkatli davranmanızı öneririm. Seçeceğiniz lisansa göre bir maliyette çıkacağını unutmayın 🙂 Her şey toz pembe değil yani 🙂
VSAN 7 Lisanslama Modeli
Deduplication ve Compression ile RAID-5/6 Erasure coding özelliklerini kullanabilmeniz için, All Flash VSAN kullanmanız gerekiyor. Eğer VSAN kullanıyorsanız kesinlikle kullanmanızı tavsiye edeceğim özellikler bunlar. VSAN’da gerçek performansı bu özellikleri kullandığınız zaman anlayabiliyorsunuz. Bu özellikler Hybrid VSAN konfigürasyonlarında desteklenmez. Deduplication ve Compression, RAID-5/6 Erasure coding ve All Flash VSAN ile ilgili aşağıdaki makalelerimi inceleyebilirsiniz.
VSAN – All Flash ve Hybrid
VSAN – Raid 5/6 Erasure Coding
VSAN 6.2 – Deduplication ve Compression
VSAN Standard, Advanced, Enterprise sürümleri CPU (soket) başına, VDI başına veya VM başına lisanslanır. Enterprise Plus sürümü yalnızca CPU başına lisanslanır. Bu dört VSAN sürümü bağımsız lisanslar olarak mevcuttur ve VMware vSphere’e dahil değildir. Mixed bir mimariniz var ise buna hem server hemde VDI dahil ise CPU başına VSAN lisansı alınmalıdır. Ancak burada bu yazacaklarıma dikkat etmeniz gerekiyor.
Bir VSAN Cluster’ınız var ve bu cluster’ın içerisinde VSAN olmayan, VSAN datastore’unu kullanmayan ESXi host’lar bulunuyor ise, bunlarıda VSAN için lisanslamanız gerekiyor. Yani VSAN Cluster’ı içerisinde bulunan her ESXi host, VSAN ile lisanslanması gerekmektedir.
Hangi VSAN versiyonunda hangi özellik bulunduğunu merak ediyorsanız aşağıdaki resimi inceleyebilirsiniz.

VSAN 7.0’de File Services özelliği tanıtıldı. VSAN File Services, dosya paylaşımları sağlamak için vSAN’ın üzerine bulunan bir katmandır. Şu anda NFSv3 ve NFSv4.1 dosya paylaşımlarını desteklemektedir. VSAN File Services, VSAN nesnelerini bir araya getirerek temel ölçeklenebilir dosya sistemini sağlayan VSAN Distributed File System (vDFS) ‘den oluşur. Bu konu ile ilgili ayrıca bir makale zaten yazacağım.
VSAN 7 Yenilikleri
Bu yazımda VSAN yeniliklerine çok değinmeyeceğim çünkü daha önce bu konu ile ilgili bir yazı yazmıştım. Bu yazıma yukarıdaki linkten ulaşabilirsiniz.
VSAN, uzak ofis ve şube (ROBO) uygulamaları için mükemmel bir çözümdür. ROBO için VSAN lisansları, sanal makine başına (VM başına) fiyatlandırılır ve 25 lisanslık paketler halinde satılır. 25’li bir lisans paketi, birden çok konumda paylaşılabilir. Örneğin, her biri 5 sanal makine çalıştıran 5 uzak ofisiniz bulunuyor. Bu yaklaşım, dağıtım esnekliği sağlar ve genellikle uzak ofislerde bulunan daha küçük altyapıların maliyetini en aza indirmeye yardımcı olur.
Her uzak ofis, VSAN for ROBO lisanslama modeli kapsamında maksimum 25 sanal makine ile sınırlıdır. Uzak bir ofiste 25’ten fazla sanal makine çalışıyorsa, CPU lisansı başına VSAN Standard veya Advanced veya Enterprise kullanılmalıdır. Tek bir site’da bir VSAN cluster’ında çalışan sanal makine sayısı 25 veya daha az olduğu sürece, ROBO Standard veya Advanced veya Enterprise için VSAN ile herhangi bir sayıda ESXi host lisanslanabilir. ROBO lisansları için VSAN ile başlamak ve ardından uzak bir ofis 25 sanal makineyi aştığında kesintisiz olarak CPU lisansı başına VSAN Standard, Advanced veya Enterprise’a geçmek mümkündür. Uzak ofis veya şube ofisinin tanımı, birincil veri merkezi dışındaki herhangi bir uzak fiziksel konumdur. VM başına ROBO lisansları için VSAN’dan CPU başına VSAN Standard, Advanced, Enterprise ve Enterprise Plus lisanslarına yükseltme / dönüştürme yolu olmadığına dikkat etmek önemlidir.
Umarım faydalı olmuştur.
İyi çalışmalar.
0 notes