#peptide sciences
Text
0 notes
Text
youtube
0 notes
Text
What puts the electronic pep in peptides? A folded structure, according to a new study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Electron transport, the energy-generating process inside living cells that enables photosynthesis and respiration, is enhanced in peptides with a collapsed, folded structure. Interdisciplinary researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology combined single-molecule experiments, molecular dynamics simulations and quantum mechanics to validate their findings.
Continue Reading.
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

Helping Heal Bone
A 3D-printed scaffold with cryogel fibres incorporating vessel growth- and bone formation-enhancing peptides for promoting bone regeneration at the site of skull damage or defect
Read the published research article here
Image from work by Yuxuan Wei and Hao Pan, and colleagues
Zhejiang Engineering Research Center for Tissue Repair Materials, Wenzhou Institute, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
Image originally published with a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
Published in Science Advances, February 2024
You can also follow BPoD on Instagram, Twitter and Facebook
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
New publication out!
We were curious what happens with the lipid membrane if proteins are inside. As a model of membrane proteins we use transmembrane peptides with neutral and positive charge. The charges turn out to be quite crucial in the peptides influence on the lipids.
publication link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.113765…
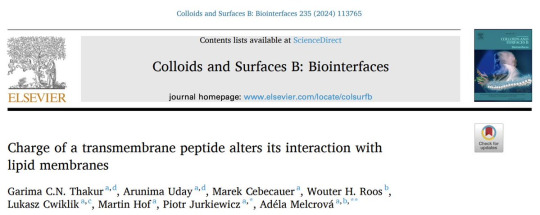
All transmembrane peptides hinder mobility of lipids around. The positive charges in the peptide make this hindering a long range influence.
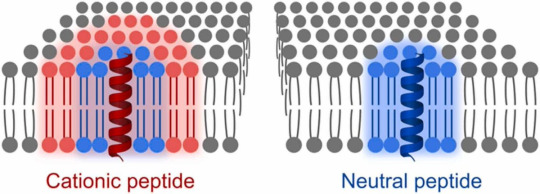
The membrane with the positive peptides then has heterogeneities in the lipid mobility. This hampers free rearrangement of lipids and leads to lower ability to seal ruptures. You can see below how the membrane stays fragmented after indentations with AFM (atomic force microscope), which is basically a very tiny tip that scans the surface of the membrane for images and can also push through it to test mechanical stability.
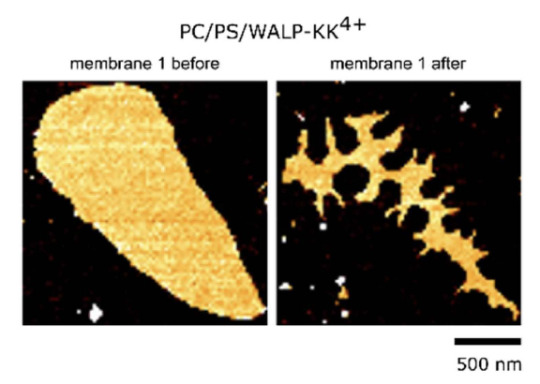
For comparison this is how it looks like with a membrane without any peptides. The mebrane seals the ruptures induced by the AFM tip and recovers its round shape. The same happens if we have a neutral, non-charged, peptide.
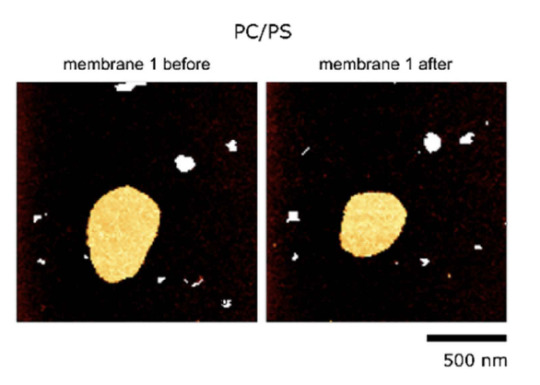
With this work we highlight the importance of including charges of proteins and peptides in membrane model studies.
And last but not least...
This is the very first time I am the last corresponding author of a publication. I am immensely proud on myself!
#science#women in science#research#biophysics#afm#fluorescence#simulations#peptides#proteins#cell membranes#publication#collaboration#corresponding author#proud#original content
17 notes
·
View notes
Link
Recent advances in chemistry, material science, and biological research have been greatly aided by large language models (LLMs), which act as flexible foundation models for various downstream predictive or generative tasks. Researchers have proposed an LLM-based foundation model technique called AMP-Designer as a quick way to generate novel antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) with a variety of desirable features. An array of AMPs have been validated in silico tests using AMPDesigner. Results indicate that, with a 94.4% positive rate, the majority of the suggested candidates exhibit noteworthy antibacterial activity. Two candidates in human plasma demonstrated remarkable efficacy, low hemotoxicity, and stability. Forty-eight days were needed to finish the full process, which included in vitro and in vivo validation in addition to in silico design.
A significant danger to world health, bacterial antimicrobial resistance (AMR) kills millions of people each year. 1.27 million of the 4.95 million deaths connected to AMR in 2019 were caused by Gram-negative bacteria. By 2050, it is expected that this problem will result in 10 million fatalities annually. The situation is made worse by the absence of novel medications that are effective against Gram-negative bacteria that have grown resistant to widely used antibiotics.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are naturally occurring proteins that are typically between 10 and 50 amino acids long and are produced by a variety of organisms to fight off invasive invaders. AMPs have been proposed as viable substitutes for traditional small-molecule antibiotics because of their exceptional diversity in structures and functions, outstanding efficacy, and little risk of resistance development.
Continue Reading
#bioinformatics#antimicrobial resistance#foundation model#ai#llm#peptide design#global challenges#science news
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Back at it again with another funky way to make funky peptides, gotta admit I have a type. The authors didn't provide a scheme but I whipped one up anyways :)
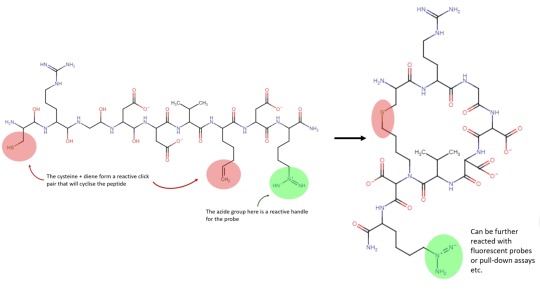
This time the approach is to forgo the traditional cyclisation methods (chemical ligation or disulphide bridging) and instead cyclise the peptide via a click reaction. So, what is a click reaction and why bother? Well click chemistry is the nickname given to a series of biorthogonal (meaning it doesn’t interfere with biological systems) azide-alkyne coupling reactions developed by Bertozzi, Meldal and Sharpless, its kinda a big deal and those folks won the 2022 Nobel prize for their work. There are a few reasons it would be useful to cyclise a peptide with click chemistry, a) its an orthogonal reaction which means that previously inaccessible functional groups could be included in cyclic peptides, b) a lot of ink has been spilled optimising, developing and expanding click chemistry so there’s a massive array of options and flexibility for future development, c) the click reaction produces a far more stable product that disulphide bridging and d) its not confined to the N/C terminus like chemical ligation usually is.
So with the background out of the way, what did these folks actually do? Well the paper is describes a protocol for creating cyclic peptide probes; i.e. a cyclic peptide that will bind to a target and is functionalised with a reactive handle so it can be visualised via a fluorophore. The paper is detailing a quite specific protocol, and what I think likely happened is that these folks were trying to create probes for their other research, but they realised the method they came up with was so effective that they should really publish it as a protocol (this would not be unusual).
But anyways, onto the chemistry. To create cyclic probes the researchers incorporated 2 orthogonal click reactivities into the linear sequence, a thiol-ene reaction to generate the cycle and a classical azide-alkyne for the probe functionality. The scheme does all the talking really (and was a bitch to draw) but nonetheless I think that it’s a neat demonstration of the expanding tools available for synthesising tricky peptides and versatility of click chemistry.
References:
LeValley PJ , Ovadia EM , Bresette CA , Sawicki LA , Maverakis E , Bai S , Kloxin AM . Design of functionalized cyclic peptides through orthogonal click reactions for cell culture and targeting applications. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018 Jun 19;54(50):6923-6926. doi: 10.1039/c8cc03218a. PMID: 29863200; PMCID: PMC7433322.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Future of Skincare: How Peptide Research is Revolutionizing Anti-Aging Treatments
Peptides are small chains of amino acids that play a crucial role in the health and rejuvenation of our skin. These unique molecules are the building blocks of larger proteins, such as collagen and elastin, which are essential for maintaining the skin's structural integrity and youthful appearance. By delving into the science behind peptides, we can better understand how they can be harnessed to combat the signs of aging and promote a more radiant, youthful complexion.
Peptides are composed of varying numbers of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. The specific sequence and arrangement of these amino acids determine the unique properties and functions of each peptide. In the context of skin care, peptides can act as signaling molecules, communicating with skin cells and triggering a cascade of beneficial responses. They can stimulate the production of collagen, elastin, and other essential skin components, helping to restore the skin's natural resilience and firmness.
The potential benefits of peptides in reversing the signs of aging and promoting a youthful appearance are numerous. By stimulating the production of essential skin components, peptides can help improve skin elasticity, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and enhance the overall radiance and smoothness of the skin. As the field of peptide research continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective peptide-based skincare solutions emerge, offering a promising alternative to traditional anti-aging treatments.
Key Takeaways
Peptides play a crucial role in skin rejuvenation by stimulating collagen production and promoting youthful, radiant skin.
The emergence of peptide-based skincare represents a paradigm shift in anti-aging treatments, offering a more targeted and effective approach.
Peptides are key in maintaining optimal moisture levels for a healthy glow, addressing skin hydration at a cellular level.
Peptides are effective in reducing wrinkles and smoothing the signs of aging, providing a more youthful appearance.
Customized peptide formulations allow for tailored skincare to address individual skin needs, maximizing efficacy and results.
The Emergence of Peptide-Based Skincare: A Paradigm Shift in Anti-Aging Treatments

In recent years, the skincare industry has witnessed a remarkable shift towards the use of peptide-based products, as consumers and skincare experts alike have recognized the remarkable potential of these small but mighty molecules. The growing popularity of peptide-based skincare is a testament to the advancements in peptide research and the increasing demand for natural, science-backed solutions to combat the signs of aging.
The rise of peptide-based skincare can be attributed to the growing body of scientific evidence demonstrating the efficacy of these compounds in improving skin health and appearance. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms by which peptides interact with skin cells, they have been able to develop more targeted and effective formulations that can address a wide range of skin concerns, from wrinkles and fine lines to dullness and loss of elasticity.
This shift towards more science-backed, targeted approaches to anti-aging treatments has been driven by the growing consumer demand for natural, non-invasive skincare solutions. Consumers are increasingly seeking out products that are not only effective but also gentle on the skin and free from harsh chemicals. Peptide-based skincare products, with their ability to harness the power of natural, bioactive compounds, have become a popular choice for those seeking a more holistic and sustainable approach to skin rejuvenation.
Peptides and Collagen Production: Unlocking the Key to Youthful, Radiant Skin
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin's elasticity, firmness, and overall youthful appearance. As we age, the natural production of collagen begins to decline, leading to the formation of fine lines, wrinkles, and a loss of skin elasticity. This is where peptides come into play, offering a powerful solution to this age-old problem.
Peptides have the remarkable ability to stimulate the production of collagen, the very foundation of healthy, youthful skin. By acting as signaling molecules, peptides can communicate with skin cells and trigger the synthesis of new collagen fibers, as well as prevent the breakdown of existing collagen. This dual-pronged approach helps to maintain and even enhance the skin's natural collagen levels, resulting in a more plump, firm, and radiant complexion.
The impact of increased collagen levels on the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles is truly remarkable. As the skin's structural integrity is reinforced, the visible signs of aging begin to diminish. Fine lines and wrinkles become less pronounced, and the skin takes on a more youthful, smooth, and even texture. Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated the efficacy of peptide-based treatments in boosting collagen synthesis, with participants reporting a significant improvement in the overall appearance and firmness of their skin.
Peptides and Skin Hydration: Maintaining Optimal Moisture Levels for a Healthy Glow

Maintaining optimal skin hydration is essential for a healthy, youthful appearance. As we age, the skin's natural ability to retain moisture can diminish, leading to dryness, dullness, and an overall lack of radiance. This is where peptides come into play, offering a powerful solution to the challenge of maintaining optimal skin hydration.
Peptides play a crucial role in regulating the skin's natural moisture balance. By interacting with specific receptors on the surface of skin cells, peptides can enhance the skin's ability to retain water and prevent dehydration. This, in turn, leads to a more plump, supple, and radiant complexion, as the skin is able to maintain its optimal moisture levels.
The benefits of improved skin hydration go beyond just a more youthful appearance. When the skin is properly hydrated, it is better equipped to function at its best, with improved barrier function, reduced sensitivity, and a more even tone and texture. Peptides can work synergistically with other hydrating ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid, to create a comprehensive skincare solution that addresses the multifaceted needs of aging skin.
Peptides and Wrinkle Reduction: Smoothing the Signs of Aging for a More Youthful AppearanceAs we age, the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles can become a source of concern for many individuals. Fortunately, peptides offer a promising solution to this common skin care challenge. By targeting the underlying mechanisms that contribute to the formation of wrinkles, peptides can help smooth and firm the skin, resulting in a more youthful and rejuvenated appearance.
The mechanisms by which peptides can reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles are multifaceted. Some peptides work by stimulating the production of collagen and elastin, the structural proteins that provide the skin with its firmness and elasticity. By boosting the synthesis of these essential components, peptides can help plump and smooth the skin, diminishing the visibility of wrinkles and expression lines.
#Peptide Research#Scientific Innovation#Top-Tier Peptides#Research Products#Peptide Science#Scientific Excellence
0 notes
Text
Folded Peptides and Buddhist Philosophy
Daily writing promptScour the news for an entirely uninteresting story. Consider how it connects to your life. Write about that.View all responses
In the ceaseless hum of daily news, punctuated by crises and breakthroughs, a recent scientific advancement offers an unexpected opportunity for philosophical reflection.
Photo by RF._.studio on Pexels.com
The revelation of new insights into…

View On WordPress
#curiosity#dailyprompt#dailyprompt-2021#folding peptides#interconnected#meaning#molecular dynamics simulations#patience#peptides#purpose#quantum mechanics#Raffaello Palandri#Research#science#understanding#Universe#wisdom#wonder
0 notes
Text

shout out to this random blank graph i found on a paper this afternoon for being the funniest fucking thing i've ever seen in an article
#“yeah out of all the antimicrobial peptides we've tried out this is the best one”#“the survival rate of the larvae when injected with it is [REDACTED]”#science#biology
0 notes
Video
youtube
Southern California Center for Anti-Aging (aka Anti-Aging Center at Make You Well)
23211 Hawthorne Blvd Suite 200-A Torrance,
CA 90505
424-247-4962
SEMAGLUTIDE PEPTIDE THERAPY FOR WEIGHT LOSS | OZEMPIC AND WEGOVY WEIGHT LOSS DOCTORS
Hi everybody, thank you for being here today with me. So what's all this hype about the Semaglutide peptide known as Ozempic and Wegovy - the weight loss medications that are blowing up on the internet and going viral on social media. They're being touted as Miracle weight loss medications and now everybody ran out to get them. So what is the big deal? I'm dr. Judy Gold Stone. I am an obesity medical specialist with the anti-aging Center and make you well and I'm going to share with you my two best weight loss tips at the end of this video. So please be sure to stick around. And back to Ozempic and Wegovy - They aren't exactly the miracle weight-loss drugs, that everybody sang but they do work better with less side effects than any other medication approved for weight loss of till now they're both the same thing of peptide called semi latitude 72 has been around for a while and in 2017 the FDA approved it as a treatment for diabetes. St4 on those jumping were noted to be losing pretty significant amounts of weight. So in 2021 the FDA approved, something creative for weight loss and that drug was called Lugo V. They are both the same thing. The only difference is the dosage of the similitude, it's higher in were bovie. So your best office just thinking of it as so many fortitude. How does it cause weight loss? Well, it mimics a natural hormone which lowers blood sugar causes, the feeling of fullness and slows the rate of which food empties out of the stomach that all leads to feeling full and a decreased appetite. So people eat a lot less Another great thing about 70. Good to, you know, sembach and we'll go visit. The same thing is that there are no Jitters or staying up late at night. Right thinking of the older medications. The older medications, the best, you can hope to get was about 5 to 10% of your body weight, lost at the end and a good diet and exercise, people are losing up to 15 to 20% of their initial body weight within a year. That's better than anything and almost like a gastric bypass surgery. The side effects are pretty minimal, nausea! Vomiting and constipation diarrhea. There can be in a rare event and acute pancreatitis or a gallbladder attack. Gallbladder test can happen to anybody losing significant amounts of weight. I'm so confident in these medications that I even have my own daughter taking it. Now there are a couple people who should not use it for medical reasons. So please be sure to check with your physician before you start jumping on a medical weight loss plan. It can be very expensive as I'm sure. You know, it can cost 1200 to 1500 dollars per month without insurance and insurance companies have very strict fight. Materia about who they will approve, 470, good tubes. So approval doesn't happen that often since so sympathetic, and we'll go VR so hard to get. Now I use a compounding pharmacy, which does make something with to the exact same chemical structure as Exempted or would go. Lea to same selling with you and a much more reasonable price. It's taken as a subcutaneous injection. That means just below the skin. It's easy to do and painless And remember, you have to combine it with exercise and a good weight loss program to get the best results. Most people, unfortunately will regain the weight, they lost within a year. That's just the sad fact about weight loss and this is where the two tips that I promise to give you come in. I learned these tips from my weight loss, patient number one is accountability patients team in and setting in so many ways. They said, I need to pay the money. I need to have something to report to. I need accountability. Otherwise, you just go back to your old habits and regain all the weight that you lost. And the second tip is support only you care and we care about your weight loss, pretty much nobody else really does, they're not going to encourage you. But at the anti-aging Center at make you, well, first, we customize a weight loss program for you, with exercise, we do a medical evaluation And, We give you the support that you need every week you come in and get your cellular to the injection. We counsel you and you have them much better chance to keep that weight off permanently because we haven't maintenance program where we keep you coming back for that, support that you need. We promise to get your cheerleaders for life. Weight Loss Doctors in Los Angeles
#youtube#weigh loss#peptides#petide therapy#medical weight loss#torrance california weight loss clinics#science and weight loss
0 notes
Text
University of Central Florida College of Medicine researcher Renee Fleeman is on a mission to kill drug-resistant bacteria, and her latest study has identified a therapy that can penetrate the slime that such infections use to protect themselves from antibiotics.
In a study published in Cell Reports Physical Science, Fleeman showed that an antimicrobial peptide from cows has potential for treating incurable infections from the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Continue Reading.
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
"A team at Northwestern University has come up with the term “dancing molecules” to describe an invention of synthetic nanofibers which they say have the potential to quicken the regeneration of cartilage damage beyond what our body is capable of.
The moniker was coined back in November 2021, when the same team introduced an injection of these molecules to repair tissues and reverse paralysis after severe spinal cord injuries in mice.
Now they’ve applied the same therapeutic strategy to damaged human cartilage cells. In a new study, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, the treatment activated the gene expression necessary to regenerate cartilage within just four hours.
And, after only three days, the human cells produced protein components needed for cartilage regeneration, something humans can’t do in adulthood.
The conceptual mechanisms of the dancing molecules work through cellular receptors located on the exterior of the cell membrane. These receptors are the gateways for thousands of compounds that run a myriad of processes in biology, but they exist in dense crowds constantly moving about on the cell membrane.
The dancing molecules quickly form synthetic nanofibers that move according to their chemical structure. They mimic the extracellular matrix of the surrounding tissue, and by ‘dancing’ these fibers can keep up with the movement of the cell receptors. By adding biological signaling receptors, the whole assemblage can functionally move and communicate with cells like natural biology.
“Cellular receptors constantly move around,” said Northwestern Professor of Materials Sciences Samuel Stupp, who led the study. “By making our molecules move, ‘dance’ or even leap temporarily out of these structures, known as supramolecular polymers, they are able to connect more effectively with receptors.”
The target of their work is the nearly 530 million people around the globe living with osteoarthritis, a degenerative disease in which tissues in joints break down over time, resulting in one of the most common forms of morbidity and disability.
“Current treatments aim to slow disease progression or postpone inevitable joint replacement,” Stupp said. “There are no regenerative options because humans do not have an inherent capacity to regenerate cartilage in adulthood.”
In the new study, Stupp and his team looked to the receptors for a specific protein critical for cartilage formation and maintenance. To target this receptor, the team developed a new circular peptide that mimics the bioactive signal of the protein, which is called transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGFb-1).
Northwestern U. Press then reported that the researchers incorporated this peptide into two different molecules that interact to form supramolecular polymers in water, each with the same ability to mimic TGFb-1...
“With the success of the study in human cartilage cells, we predict that cartilage regeneration will be greatly enhanced when used in highly translational pre-clinical models,” Stupp said. “It should develop into a novel bioactive material for regeneration of cartilage tissue in joints.”
“We are beginning to see the tremendous breadth of conditions that this fundamental discovery on ‘dancing molecules’ could apply to,” Stupp said. “Controlling supramolecular motion through chemical design appears to be a powerful tool to increase efficacy for a range of regenerative therapies.”"
-via Good News Network, August 5, 2024
#nanotechnology#osteoarthritis#arthritis#medical news#science news#cell biology#molecular biology#cartilage#good news#hope
704 notes
·
View notes
Text
Meet AlphaPeptDeep: a Deep Learning Framework for Predicting Peptide Properties from Sequences
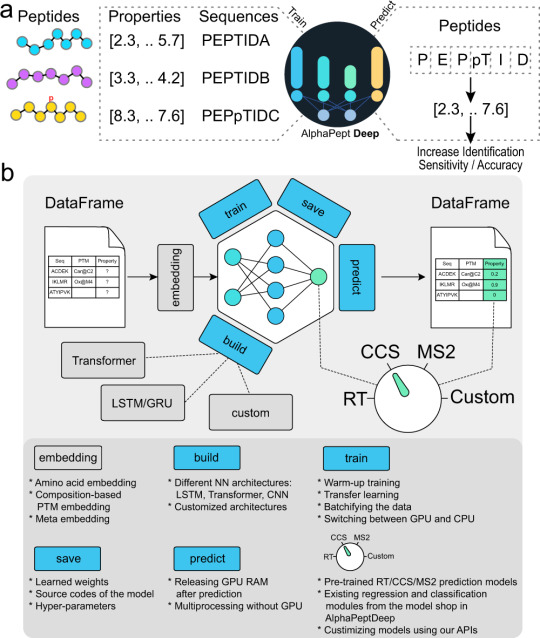
A research team at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry has developed AlphaPeptDeep. AlphaPeptDeep is a Python framework built on the PyTorch deep learning library that can learn and predict peptide properties. AlphaPeptDeep additionally includes a plug-in capability that allows non-experts to develop models with just a few lines of code. AlphaPeptDeep may also indicate additional sequence-based features, as demonstrated with a Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) peptide prediction model.
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics seeks to gain an unbiased assessment of all the proteins present in a particular system. This difficult analytical process necessitates sophisticated liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC/MS) instruments downstream with bioinformatic analysis pipelines. Deep learning (DL) techniques have grown in potency over the last decade and are becoming increasingly valuable for MS-based proteomics. In proteomics, the identification includes matching fragmentation spectra (MS2) and other features to a set of peptides. Bioinformatics can now predict peptide properties for every amino acid sequence and compare them to real observed data. This can significantly boost statistical confidence in peptide identifications.
Continue Reading
#bioinformatics#proteomics#peptides#deep learning#machinelearning#100daysofcode#scicomm#stem#science news
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Lasso peptides are a really cool family of peptides that have a very unique knotted structure and are chronically understudied and poorly understood. Lasso peptides get their name from the way the N-terminus wraps back around the peptide chain and forms an isopeptide bond with the carbonyl of a Glu/Asp residue, forming a literal lasso like shape:

This is a deceptively tricky reaction to study, let alone replicate. At the minute, most studies done on identifying and isolating these molecules use overexpression, chemical or even biosynthetic strategies are inaccessible, which is a real shame because the unusual topologies of these peptides gives them excellent protease resistance and much better pharmacokinetics than linear, or even standard cyclic peptides.
More detailed images of the peptides reveal some interesting quirks of how they adopt this unique shape:

This stick model on the left show the whole lasso peptide, with the section forming the ring highlighted in green. The sequence that is ‘lasso’d’ so to speak is quite interesting, and is shown on the right. The C terminal tryptophan-phenylalanine motif is common among lasso peptides and acts as a ‘stopper’ and provides a, frankly massive, steric barrier to unfolding the lasso. The encapsulated section is comprised of glycine which is pretty easy to rationalise because glycine doesn’t have a side chain, thus making it the most suitable for threading through a ring. I’ve also highlighted the proline, which is also common among lasso peptides, it is though that the proline is important to preorganising the lasso before the ring is completed, proline is a much more restricted amino acid than the others and often adopts this role as a conformational guide.
Its worth remembering just how tight this whole arrangement is, threading a peptide though a 7 residue ring is no small feat, and here’s the space filling model to highlight that fact:

There is no wiggle room at all, and that is key to understanding why these things are so hard to make, they incur a huge entropic and steric penalties for being in these tightly wound conformations and aren’t offsetting that by forming covalent bonds or massive protein scale stabilising interactions. As such I think they’re pretty remarkable and definitely worth studying more.
References:
1. Tan, S., Moore, G., and Nodwell, J. (2019) Put a bow on it: Knotted antibiotics take center stage. Antibiotics 8, 117.
2. Liu, T., Ma, X., Yu, J., Yang, W., Wang, G., Wang, Z., Ge, Y., Song, J., Han, H., Zhang, W., Yang, D., Liu, X., and Ma, M. (2021) Rational generation of lasso peptides based on biosynthetic gene mutations and site-selective chemical modifications. Chemical Science 12, 12353–12364.
3. Structure, bioactivity, and resistance mechanism of streptomonomicin, an unusual lasso peptide from an understudied halophilic actinomycete. Chemistry & Biology. Cell Press.
4 notes
·
View notes