#persian folklore
Text

A prime man-eating beast of legend.
This Persian monster is the peak of its food chain, capable of killing any animal as its prey, with the notable exception of the elephant.
Elephants are the only animal that the manticores' death-bringing sting has absolutely no effect on.
#BriefBestiary#bestiary#digital art#fantasy#folklore#legend#myth#mythology#mythical creatures#monster#persian folklore#persian mythology#manticore#mythical beasts#merthykhuwar#mardykhor
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Folklore Fact - Gryphons/Griffins
Gryphons, griffins, griffons, however you prefer to spell it (I personally use gryphon) - let's talk their folklore and mythology!

(Attic pottery depicting a satyr and a griffin and an Arimaspus from around 375-350 BC, Eretria.)
You probably already know the common popular culture concept of a gryphon: a big, vicious beast that attacks people and probably eats them and/or carries people away to its nest to feed them to its babies. Not much about it has changed in legend, though in a lot of popular culture today, it has seemed to lose its divinity. Gryphons - griffins, whatever you prefer - have quite the robust history, like so many creatures of myth and folklore. Unlike some, however, they have changed very little over time.
Note that this article a general overview of concepts, not a detailed history.
Let's start with etymology, because I just love that stuff. The word "griffin" comes from the Greek word "gryps," which referred to a dragon or griffin and literally meant "curved [or] hook-nosed." Late Latin spelled it "gryphus," a misspelling of grypus, a Latinized version of the Greek (source: https://www.etymonline.com/, one of my favorite websites).
Griffins are said to have the head and wings of an eagle and body of a lion. They may or may not also have pointed ears, depending on the depiction (they more often did, overall, though the griffin of Crete is a notable exception). They were said to guard the gold in the mountains of the north, specifically the mountains of Scythia. The one-eyed Arimaspian people rode on horseback and attempted to steal the griffins' gold, causing griffins to nurture a deep hatred of and hostility toward horses.
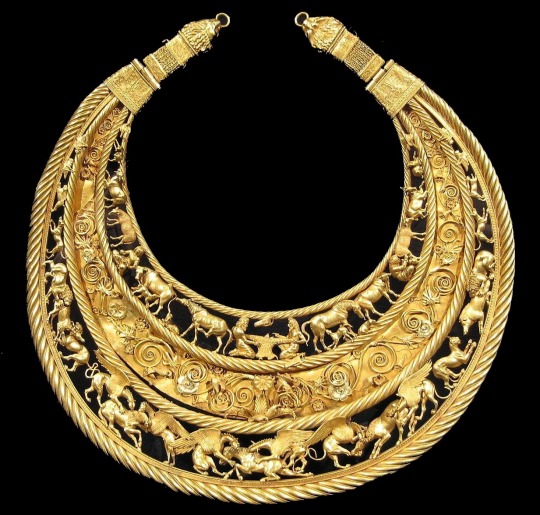

A Scythian pectoral, thought to have been made in Greece, depicting - among other things - griffins slaughtering horses. Griffins really, really hate horses.

The famous griffin in the palace of Knossos at Crete, from the Bronze Age (restored).
Griffins appear in truly ancient civilizations, not only Greece but also ancient Egypt and civilizations to the east, including ancient Sumeria. Griffins were later said to also dwell in India and guard gold in that region, and they continued to appear in art throughout ancient Persia, Rome, Byzantium, and into the Middle Ages throughout other regions such as France; they were depicted in ancient Greece with relative frequency and occasionally of considerable importance.
Griffins appeared in many ancient Greek writings, including Aristeas in the 7th century BC. Herodotus and Aeschylus preserved and continued these writings in the 5th century BC, including lines such as,
"But in the north of Europe there is by far the most gold. In this matter again I cannot say with assurance how the gold is produced, but it is said that one-eyed men called Arimaspoi (Arimaspians) steal it from Grypes (Griffins). The most outlying lands, though, as they enclose and wholly surround all the rest of the world, are likely to have those things which we think the finest and the rarest." Herodotus, Histories 3. 116. 1 (trans. Godley) (Greek historian C5th B.C.), source: https://www.theoi.com/Thaumasios/Grypes.html (a wonderful site)
Physical descriptions of the griffin were not commonplace until some later works, and even then, their appearance wasn't always agreed upon. Even the notion of griffins having wings was sometimes disputed. Some scholars even got pretty wild, claiming griffons had no wings at all but instead skin-flaps that they used to glide. They apparently hated awesome things, so it turns out there were always boring people who thought they knew everything, wanted to explain everything "logically," and generally assume they were the smartest ever while also ruining mystique. They would make great scientists today.
Griffins were, however, often said to be holy in nature. They were referred to as the "unbarking hounds of Zeus" by Aeschylus, who warned others never to approach them. Gryphons were also considered sacred to several gods, including prominently Apollo, who was said to depart Delphi each winter, flying on a griffon (griffin, gryphon, etc, I keep swapping this around, I know; my brain spells it differently because I've read way too many sources), and he also is occasionally depicted as hitching griffins to his chariot in addition to riding one. This was particularly prominent in the cults of Hyperborean Apollo, one of the many endless and fascinating cults of ancient Greece.

Medieval bestiary depiction of a griffin slaughtering a horse.
Even by the Middle Ages, gryphons still hated and slaughtered horses and guarded gold, elements that certainly persisted throughout their legends. They also killed men and carried them away to their nests, similar to the manner in which Aeschylus warned people to stay away from gryphons even back when. We can obviously assume griffons were never cuddly, so that isn't much of a change.
Griffins also did not entirely lose their divine relations even into the Middle Ages. Christianity often used positive portrayals of griffins to represent and uphold certain positive tenets of Christian faith; likewise, they became important symbols of medieval heraldry, used to represent a Christian symbol of divine power, as well as general courage, strength, and leadership, especially in a military sense. The depiction of the griffin as a powerful and majestic creature - killing horses and men or not - throughout its history is no doubt because they are a combination of two beasts often considered noble symbols of bravery, power, and divinity: the lion and the eagle, kings of land animals and birds, respectively.
That's a general overview! As you can see, griffins aren't always so bad, at least not compared to some of the other creatures out there from folklore and myth.
( If you like my blog, be sure to follow me here and sign up for my free newsletter for more folklore and fiction, including books!
Free Newsletter - maverickwerewolf.com (info + book shop) — Patreon — Wulfgard — Werewolf Fact Masterlist — Twitter — Vampire Fact Masterlist — Amazon Author page )
#folklore#mythology#gryphon#griffin#fantasy creature#gryphons#griffins#griffon#folklore fact#folklore thursday#greek myth#myth#persian myth#medival#medieval folklore#history
66 notes
·
View notes
Text

Wait till they (bigoted conservative right wing white supremacists) realize the Cinderella, Snow White, many fairy tales and folk tales ALL have origins from MANY places that aren't from Europe/originated from stories from pre-European & peasant folk/are recurring tropes and narratives from across the globe (sorry there was a typo here😔 but i meant to say check the Motif Index on Folk Literature and the study of folklore, it's a branch of anthropology, and studies literature and oral traditions that are shared by humanity across ages!)
and they're simply clamoring for the white washed versions because they don't know how to step out of their bubble
The One Thousand and One Nights, and various versions of Cinderella are said to have Persian/Arab and Chinese roots! And there's even a Cinderella story in ancient Egypt!
And from just looking up fairy tale as a term, ancient India has the Jataka, a collection of stories about Buddha reincarnated as different people, and this is described as one of the best surviving fairytale compilations
And regarding the Shanameh, the heroine Rudaba is described with long raven hair and such. But I won't spoil it: here's the Iran online site where Shanameh fairy tale is:
https://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/rudaba
Another online site, with lots of Islam literature, where Rudāba's story is:
#fairytale#black mermaid#little mermaid#poc#cinderella#rapunzel#persian#fuck bigots#fuck whitewashing#whitewashing#islam literature#literature#folklore#folktales
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
A dragon from Librum Prodigiosum ! The Jawzahr dragon, this immortal beast comes from Persian mythology! After being banished, he chases the sun and moon, causing eclipses- though the celestial bodies always escape!

#digital art#digital illustration#fantasy#art#folklore#mythology#librum prodigiosum#monster#mythical creatures#creature#artists on tumblr#mythology art#dragon art#dragon#jawzahr#mythologyart#persian mythology
84 notes
·
View notes
Text







Images from the Siyah Qalam, 15th century.
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Page of Swords. Art by Lisa Hunt, from the Animals Divine Tarot.
Anahita
#Lisa Hunt#Animals Divine Tarot#Page of Swords#Page#Swords#Minor Arcana#Tarot#Folklore#Persian#Iran#Anahita#Animals#Birds#Peacock#Racial Diversity
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Creature Feature III: Mishmashed Mayhem we look at 3 different creatures from mythology and folklore that are the fusion of different creatures into one.
#mythical creatures#myth#mythology#arthurian mythology#folklore#sumerian mythology#persian mythology#egyptian mythology
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is the meaning of Nevruz for Turkic People?
History of NevruzSignificance of NevruzCustoms and TraditionsSymbolism of NevruzModern CelebrationsVideo: The Sound of the Proto-Turkic languageYou may also like
Nevruz (or Newroz) is a spring festival celebrated by the Turkic people and many other communities around the world. The word “Nevruz” comes from two Persian words, “nev” meaning “new” and “ruz” meaning “day”. Thus, the festival is…

View On WordPress
#Celebrations#Cultural Festivals#Customs#Folklore#History#Kurdish#Mythology#Nevruz#New Year#Newroz#Origins#Persian#Spring Equinox#Traditions#Turkic
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
@tracle0 that gryphon art you tagged me in sparked a little research excursion and I now have gryphons in LofM! Do you remember my little soot dragon? Sadly, they don't feature anymore, because little gryphons have replaced them.
I do still have dragons, but I'll be saving the soot dragons for a different story (sequel, maybe? Or different universe altogether, I haven't decided!) The gryphons are more in line with the origin myths and folklore and history I'm pulling from than the somewhat western dragons I was envisioning :]
#anywho i love them#thank you!!!#kaatibawrites#lofm.wip#my worldbuilding has roots in arabian and persian and egyptian myth and folklore and tales etc#on purpose haha#trying to show a side of fantasy that is less western u know?#im loving it a lot#and gryphon type creatures were in ancient persin myths#called shirdal!
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
One Thousand and One Nights





A beautiful edition of “One Thousand and One Nights” revised for youth by Dr. Lauckhard and published by Dr. Hofmann in 1878 Leipzig, Germany. With many colourful illustrations and aesthetic decor.
The Genesis of “One Thousand and One Nights” is as exciting as the frame story. Throughout the history there where different kinds of versions and translations. The European version is morally revised and was appropriated culturally in the 18th century. Paradoxically it also influenced the Arabic version in playing the erotica dramatically down, so today we can not really tell how the primeval unspoiled Indian version must have been, but one thing is for sure: The fascination of this magical work ✨
#literature#book cover#world literature#classic literature#oriental literature#orientalism#one thousand and one nights#Tausend und eine Nacht#Shehrezad#Arabian Nights#Arabic#Persian#Indian#orientalischer Traum#oriental poet#oriental#19th century#folklore#fairy tales#tales#oriental cult#culture#oriental heritage
6 notes
·
View notes
Text

Persian Miku!?
In traditional Mazani clothing from persia!
More info⬇️⬇️
Mazandaran province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Sari . Located along the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and in the adjacent Central Alborz mountain range.Mazandaran is a major producer of farmed fish, and aquaculture provides an important economic addition to traditional dominance of agriculture. Another important contributor to the economy is the tourism industry, as people from all of Iran enjoy visiting the area.
Language: The population is overwhelmingly Mazandarani, with a minority of Gilaks, Azerbaijanis, Kurds, Georgians, Armenians, Circassians, Turkmen and others, Mazandarani people have a background in Tabari ethnicity and speak Mazandarni.
Culture( literature) : In the Persian epic, Shahnameh, Mazandaran is mentioned in two different sections. The first mention is implicit, when Fereydun sets its capital in a city called Tamishe near Amol:
بیاراست گیتی بسان بهشت.................... به جای گیا سرو گلبن بکشت
از آمل گذر سوی تمیشه کرد .............. نشست اندر آن نامور بیشه کرد
And when Manuchehr is returning to Fereydun's capital, Tamisheh in Mazandaran (known as Tabarestan), after his victory over Salm and Tur.
Arash the Archer is a heroic archer-figure of Iranian mythology. According to Iranian folklore, the boundary between Iran and Turan was set by an arrow launched by Arash, after he put his own life in the arrow's launch. The arrow was traveling for days before finally landing on the other side of the Oxus on the bark of a walnut tree hundreds of miles away from the original launch site atop a mountain
Music and dance:
Music in this region relates to the lifestyle of the inhabitants, and the melodies revolve around issues such as the forests, cultivation or farming activities and herding. The most famous dance of this area is the Shomali dance, not forgetting the stick dance that the men perform. Popular music in the province, known as the Taleb and Zohre, Amiri Khani and Katuli.
Cuisine :
The cuisine of the province is very rich in seafood due to its location by the Caspian Sea, and rice is present in virtually every meal. Mazandarani cuisine is diverse between regions; the cuisine of coastal regions is different from mountainous regions, as people in the Alborz usually use the indigenous herbs and coastal people use the dishes of fish and Caspian Mazandaran rice with vegetables.
#art#design#anime#fashion#fanart#miku#hatsune miku#vocaloid miku#miku fanart#persian#ancient persia#mazani clothing#twitter#artists on tumblr#my art#illustration#vocaloid#traditional clothing#traditional costume#miku challenge#international miku
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Performances in Teheran.
A man dressed as the folklore character Hajji Firuz performs in Tehran on March 14, 2023, ahead of the Nowruz New Year festival.
1 note
·
View note
Text
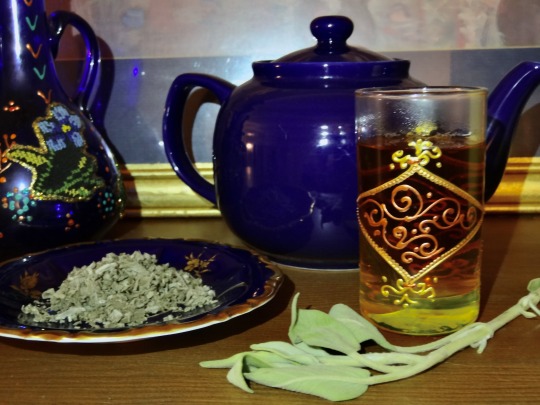

[ID: A Moroccan teaglass with a bundle of sage, a saucer of dried sage, a deep blue-purple teapot, and a Palestinian vase in the background. End ID]
شاي المريمية / Shay al-maryamiyya (Palestinian sage tea)
Palestinian sage is a common after-dinner beverage and digestive aid made from black tea and three-lobed wild sage (Salvia fruticosa syn. Salvia triloba L.). In the Levant, this variety of sage is known as "مَرْيَمِيَّة" ("maryamīyya") or, more dialectically, "مَرْمَرِيَّة" ("marmariyya").
Terminology and etymology
The term "maryamīyya" likely derives from the Aramaic "מרייא" ("marvā"), meaning "common sage" (Salvia officinalis). The modern form of the word in Arabic—as well as in Persian, in which "مریم گلی" ("maryam goli") is “sage” or "garden sage"—was also influenced by a folkloric association between sage and the مَرْيَم (Maryam) of the Bible (Mary, mother of Jesus). Dr. Tawfiq Kanaan, for example, says that Mary sat on a stone to rest after a walk in the hot summer sun, and used a few leaves from a sage plant to dry her forehead: this is how the plant got its pleasant scent, and why it is still named after Mary. The dialectical pronunciation "marmariyya" then arises through an assimilation of the second syllable to the first.
"Maryamīyya" is perhaps also related to the obsolete Arabic مَرْو ("marw"), meaning "fragrant herbs" [1]. This Arabic term is derived from the Aramaic מַרְוָא / ܡܲܪܘܵܐ ("marwā"), which refers to wild marjoram or za'tar (Origanum syriacum; syn. Origanum maru) and is related to words for fragrant herbage, marjoram, and grass (Ciancaglini; see also Aramäische Pflanzennamen, p. 193). The Aramaic is itself a borrowing from the southwest Middle Persian "𐭬𐭫𐭥𐭠" (transliterated: mlw'; pronounced /marw/) [2], which survives in several New Persian words: see for example "مرغ" ("margh"), "a species of grass of which animals are exceedingly fond"; and "مرو" ("marv"), "a fragrant herb." (Interestingly, the related Sanskrit मरुव "maruva" ultimately gives the English "marjoram" by way of Latin and Old French.)
[1] The term may also refer to the genus Maerua (to which it gives its name), and in particular the species Maerua crassifolia.
[2] See also Müller-Kessler, p. 10, and note 41 on p. 29; MacKenzie, p. 55.
Sage and Palestinian Culture
Three-lobed sage is one of the "most deeply rooted plants in the Palestinian traditional culture and ethnobotany," being the second-most-mentioned of all foraged plants (after za'tar) in a survey conducted in 2008. The connection of three-lobed sage to Maryam leads to its use in creating protective blessings at various rituals from birth until death; in the Galilee, it is burned to guard against the evil eye and to expel demons at births, weddings, and at the graves of holy people. When consumed, it is believed to help with many ailments including stomach complaints, eye diseases, and insomnia, and is used to treat livestock as well as humans.
Maryamiyya is not commonly grown as a garden herb in Palestine; rather, it is foraged from its wild range across the mountains of the West Bank, where it scents the air. Like za'atar and labna, using maryamiyya for culinary purposes is connected to Palestinian identity throughout all regions, with some people asserting that every Palestinian household must have some in stock.
Tea made with the addition of sage is perhaps the most popular herbal tea in Palestine, especially in the winter: though mint, chamomile, and aniseed are also commonly infused in water and drunk. Other varieties of sage grow in Palestine and are produced and exported by Palestinian farmers [1], but Gustaf Dalman noted in the early 20th century that three-lobed sage was the most important variety:
Of the spicy-smelling labiate flowers, which assume a significant role in the flora of Palestine, numerous sage varieties bloom in the spring. Among these the Salvia triloba, with violet flower heads on a tall shrub, is not the most colorful but is the best known, called in the north 'ēzaqān [عِيزَقَانْ] and in the south miryamīye, mēramīye thus connecting it with the Virgin Mary. (trans. Nadia Abdulhadi Sukhtian)
During the spring, sage leaves are collected and air-dried for use in tea throughout the whole year. Tea may also be made from fresh leaves, but some people consider dried to be superior. Dried maryamiyya leaves are purchased by Palestinian refugees and expatriates wherever they are. Food is thus tied to locality, memory, resistance, and terroir—a groundedness in land that considers aspects as diverse and interconnected as soil, climate, and politics. A concept of terroir in agriculture and cooking brings out how products "register[] origin and provenance."
[1] Today, the vast majority of Palestinian herb exports are to the United States, but Palestinian farmers are not able to export goods themselves—they rely on Israeli distributors and exporters, which cuts into their profits and curtails their autonomy.
Criminalizing Foraging
Ali-Shtayeh et al. noted in 2008 that the gathering of wild edible plants had been in decline in the Palestinian territories throughout preceding decades, with many young people lacking the cultural knowledge to identify and prepare wild plants. They mention several possible reasons for the decline, including an increase in intensive agriculture, improvement in national networks of roads, and the fact that some middle-aged people associate foraging with times of poverty. But we should also consider the fines, arrests, and potential imprisonment that Palestinians risk when foraging wild plants for food as a likely cause for the decline in the practice.
There are two strains of law relevant to the criminalization of foraging in "Israel" and the occupied Palestinian territories (the West Bank and Gaza: henceforth "OPT"). The first consists of primary laws which establish the right of representatives of the Israeli government to declare a plant to be a protected "natural value" (ערכי טבע), and lay out the maximum penalties people can be charged with for causing "harm" ("פג'עה") to a protected plant; the second comprises secondary declarations in the form of lists of which plants are considered protected.
The 1963 Natural Parks and Nature Reserve Law (חוק גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע, תשכ"ג - 1963) belongs to the first strain. It empowered the Minister of Agriculture to declare a plant to be protected within "Israel," subject to the approval of a government council (ch. 5, 40-42); and declared that harming a plant was an offence punishable by up to three months' imprisonment (chapter 6).
In the text of the law, "harm" is specifically defined to include "picking," "קטיפה," and "gathering," "נטילה." No systematic distinction is established based on how much of the plant was harvested, and whether the plant was foraged for personal or commercial purposes. Nor is there any qualification of what qualities a plant should have to be considered "protected," or any obligation for the government to pursue or present scientific evidence that a given plant is overharvested.
In 1969, The Decree on the Protection of Nature (צו בדבר הגנה על הטבע) (Military Order no. 363) gave similar authority to the occupying military, and criminalized foraging in the OPT. Military orders are enforced by military courts, whereas offenders in "Israel" go through civil courts.
Several plants were already on the list of protected natural values at this time, but they were not commonly foraged for food. 1977 proved a signal year in this regard: with the "Proclamation of National Parks and Nature Reserves" [אכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערבי טבע י מוגנים), תשל״ח -1977], Minister of Agriculture Ariel Sharon (אריאל שרון) added za���tar ("אזוב מצוי") and maryamiyya ("מרוה משולשת") to the list. The inclusion of these plants, and especially za'tar, was more disastrous and insulting than previous bans on foraging had been. Za'tar, besides being a source of food and income for many poor or disabled Palestinians, has immense cultural significance in Palestine.
Arab Palestinians—and only Arabs—were arrested, fined, and even imprisoned, with no clear correspondence between the amount they had foraged and their sentencing. Most of the recorded court cases in "Israel" deal with za'tar, though court cases in legal databases show that Palestinians were also fined and tried for foraging maryamiyya (FN 38). An atmosphere of intimidation prevailed, with many habitual foragers feeling newly afraid to leave their homes.
In 1998, a new National Parks, Natural Reserves, National Sites and Memorial Sites Law [חוק גנים לאומיים, שמורות טבע, אתרים לאומיים ואתרי הנצחה, תשנ"ח-1998] replaced the prior National Parks law (of 1992, which had itself replaced the aforementioned 1963 law). It removed the necessity for an ecological council to approve the Minister's declaration of a "protected" status, and increaed the maximum prison time for a violation of the law to three years. Throughout all periods, however, the penalty usually imposed has been a fine.
Since the imposition of the harsher law, two notable updates have been made to the list of protected plants: the 2005 list of Protected Natural Assets) [אכרזת גנים לאומיים, שמורות טבע, אתרים לאומיים ואתרי הנצחה (ערכי טבע מוגנים), התשס״ה–2005] replaced the 1979 list, and added عَكُوب ('akoub; "עכובית הגלגל"), a culturally important and commonly foraged thistle. [1] Za'tar and maryamiyya remained on the list. The 2005 declaration also specifies that the species on the list are protected if they are wild, but not if they are cultivated (section 3). This provision allows Israeli farmers to profit from the farming and sale of za'tar.
The second notable update came in 2019: the Nature and Parks Authority (שרשות הטבע והגנים) announced that it would redact the absolute ban on harvesting za'tar, maramiyya, and 'akoub, instead setting a maximum allowable amount for household consumption and cracking down on the sale of these plants, rather than on foraging itself.
Activists believe this partial measure to have occurred as a result of legal and public pressure instigated by an open letter which human rights lawyer Rabea Eghbariah sent the Israeli Attorney General and Environmental Protection Minister requesting that za'tar, 'akkoub, and maryamiyya be removed from the "protected" list in advance of their foraging seasons, noting the inconsistency in sentencing and the law's disproportionate criminalization of Palestinians. (The specific cultural importance of these three plants is attested by the fact that they, among the dozens of species considered "protected," form the basis of Eghbariah's complaint.) The Nature and Parks Authority (NPA), however, insisted that an independent assessment, and not public criticism, had led them to announce the change in policy. And fines levied at Palestinian foragers did continue despite the announced change in policy, at least through March 2020.
Nor is the change complete in scope, even if it were being upheld. Eghbariah notes that "It is not yet clear if the change will also apply [in the West Bank] - and there it is a parallel system, less transparent and much more predatory. The enforcement is much worse, including the confiscation of cars, and the judgment is in a military court. We will continue to monitor."
[1] Eghbariah writes that the "Protected Natural Values Declaration (Amendment No. 2) (Judea and Samaria), 1978" added za'tar and maramiyya to the list in the OPT, and the "Protected Natural Values Declaration (Amendment No. 2) (Judea and Samaria), 2004" added 'akoub. I have been unable to find or independently verify the text of either declaration. From a list of secondary legislation related to military orders, I believe the declaration being amended is "הכרזה בדבר ערכי טבע מוגנים (יהודה והשומרון), התשל"ג - 1973".

[ID: Light shone through a blue glass vase is cast over the bundle of sage and glass of tea. End ID]
"Preservation" and Green Colonialism
Of course, Palestinians and activists also suspect that the underlying purpose of the ban is to starve and intimidate Palestinians, rather than any real concern with nature. Israeli botanist Nativ Dudai points out that foraging causes much less harm to these plants than Israeli bulldozers do. Samir Naamneh, who sells foraged produce, also dismisses the environmentalist excuse for the ban on foraging:
We feel, and we know, and we’re sure, that the laws are made, on principle, against the Arab residents of the country, to hurt their livelihoods. It’s part of the pressure that Israel puts on us to starve us out.
The 1977 decision to add za'tar and maryamiyya to the protected plants list was ostensibly taken in accordance with a report submitted by a group of Israeli ecologists, which suggested that the species were in danger due to over-foraging. However, Israeli forager Yatir Sade (יתיר שדה) suggests that the converse may be true, and that the people who wrote the report might have taken their cues from the government.
On June 20, 1977, the inauguration of the Begin (בגין) Cabinet marked the first time that a right-wing party had held a majority in the Knesset; this dramatic change in Israeli politics would come to be called "המהפך" ("HaMahapakh"), "the revolution" or "the upheaval."
Sade's research reveals that, about a week later, on June 27, 1977, a team of ecologists at the NPA submitted a list of species to the Legal Bureau at the Ministry of Agriculture (משרד החקלאות), suggesting that they be declared protected. The list is accompanied by a letter of legal advice signed by a partner in the law firm Reva, Shein, Katz & Co. This initial suggested list did not include four species which would end up on the final 1977 list, all of them important culinary and medicinal herbs among Palestinians and Bedouin Arabs: babonj (בבונג / بابونج / golden chamomile), maryamiyya, za'tar, and ss'atr barriyy (صعتر بري / קורנית מקורקפת / Persian hyssop). [1]
But about four months later, on October 16, another letter was sent on behalf of the same law firm, requesting that these four species be added to the "protected" list, and that the standard procedure for adding them be expedited. Accordingly, on November 2, only a few days after receiving the letter, the Minister's office published the final declaration, with golden chamomile, maryamiyya, za'tar, and Persian hyssop newly added. The new Minister of Agriculture Ariel Sharon (אריאל שרון), part of the First Begin Cabinet and co-founder, with Menachem Begin, of the right-wing party HaLikud (הליכוד), signed the new declaration. It therefore seems likely that these plants were added to the list for political reasons and precisely because of their importance to Palestinian Arabs, rather than from any ecological concern.
It is also relevant that the 1963 and 1998 laws which criminalized foraging also laid out guidelines for the creation of national parks, nature reserves, and military and state memorial land. The text of the 1998 law, in particular, describes the goals behind creating these sites, and gives the council it establishes the authority to do anything necessary to promote those goals. These goals include to "protect natural and heritage sites" ("הגן על ערכי הטבע והמורשת"); to "maintain international scientific relations" in the field of nature conservation ("קיים קשרים מדעיים בין-לאומיים") ; to promote education about conservation among youth and students (7. (א)); and to promote travel and tourism (14. (א)).
Many discourses and strategies can here be seen operating together. The creation of nature reserves, state heritage sites, and military memorial land all within the text of the same law explicitly connects environmentalism to patriotism; creates special reasons for bringing land under state control, and imposing special codes of behavior on this land (i.e., natural and heritage sites); connects environmentalism to state ownership and control of land, and connects both to the education of youth and the creation of the ideal Israeli civic subject; uses environmentalism to promote Israel internationally as a scientific authority, a responsible steward of land (unlike the indigenous population), and thus a legitimate state; and sanitizes and 'advertizes' Israel internationally by associating sites of destruction, annexation, and ethnic cleansing with the concepts of environmental protection, natural beauty, preservation, and heritage.
Israel frequently declares land a "nature reserve" as a method of annexation, only to later build settlements on it (see Karimi-Schmidt p. 369 ff). Palestinians are forbidden from foraging certain plants within nature reserves (other plants are forbidden for foraging everywhere), and from constructing on them; they are thus alienated from this land, and dissociated from the ways in which they have long related to it. Yatir Sade points out that the four plants added to the original 1977 draft of the protected species list are typically harvested out in open areas, rather than within yards and villages; declaring these areas nature reserves, or arresting Arabs who enter them under suspicion of foraging, prevents Palestinians from moving freely, and from claiming any connection to the land. [3]
The "Green Patrol" (HaSayeret HaYeruka / הסיירת הירוקה), the enforcement unit for the NPA, was founded in 1976 by then-Minister of Agriculture Aharon Ozan and director of the Israel Land Administration Meir Zore, for the specific purpose of policing "open areas" (שטחים פתוחים) which had been declared state land, and preventing Palestinians from "tresspassing" ("הסגות גבול") or illegally building in these areas. [4] Through these strategies, land is appropriated for the state's and settlers' purposes under the guise of environmentalism.
In much the same way, the list of protected species is ultimately about using environmental science to cement state authority. Irus Braverman points out that endangered species lists function as a means of regulation, not least by being ostensibly objective: "their global power, mobility, and ubiquity derive from their configuration as scientific, technical, and quantitative, and therefore as neutral and apolitical." The protected species list thus joins other "environmental infrastructures," such as renewable energy and agricultural technologies, as a "mechanism[] for land appropriation and dispossession" of the indigenous population: together, these infrastructures make up a strategy that is alternately called greenwashing, green grabbing, and green colonialism.
[1] Letter regarding the declaration of national parks and nature reserves (protected natural values), 1977, from Ofir Katz to Tovi R. [מכתב בנושא אכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערכי טבע מוגנים) תשל"ז-1977, מאופיר כץ לטובי ר'], 6/27/1977. In: Proclamation of National Parks and Nature Reserves (Protected Natural Values), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development [אכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערכי טבע מוגנים), משרד החקלאות ופיתוח הכפר], January 1965–October 1982. State Archives, ISA-moag-moag-00119qy, pp. 164-175.
[2] Letter regarding a proposal to declare national parks and nature reserves (protected natural values), 1977, from Ofir Katz to Tovi R., [מכתב בנושא הצעה לאכרזת גנים לאומיים ושמורות טבע (ערכי טבע מוגנים) תשל"ז-1977] 10/24/1977. In: Proclamation of National Parks and Nature Reserves (Protected Natural Values), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development, January 1965–October 1982. State Archives, ISA-moag-moag-00119qy, p. 160.
[3] Yatir Sade, Master's thesis, pp. 68-9. Personal communication.
[4] Sade points out that Yehuda Reva (יהודה רווה), another partner of the law firm that provided legal advice on the matter of the 1977 protected species list, was also prominent in helping the Green Patrol expropriate Palestinian land and property within the bounds of Israeli law (Master's thesis, p. 44, FN 34).
Foraging and Food Sovereignty
The disastrous effect of these strategies and regulations should not be understated—but nor should their power to control Palestinians' behavior be overstated. Palestinians reference specific plants in writing and in art (including ceramics and tatreez), bring dried herbs to family members abroad, purchase or grow important culinary plants wherever they live in the diaspora, and continue to forage plants despite harassment and the risk of fines and arrest. Plants are an important way of symbolizing, and of practicing, resistance, resilience, and rootedness in history and in the land.
Foraging can be a strategy of reconnection in defiance of dispossession. Rochelle Davis notes that Palestinians often visit the villages from which they were displaced in order to gather grape leaves and herbs, “ingesting the place by consuming the land’s produce” (p. 172). Through this practice, as Anne Meneley puts it, "[e]ating becomes an act of momentary repossession."
The message boards on PalestineRemembered.com attest to this practice. When Mouttaz Ammoura returned to الطيرة (Al-Tira), the village from which his family was displaced, he noted maramiyya as the one plant he brought back with him:
Now I live in Canada, but far-away from AL-TIRA. When I came back, I brought with me some sand, maramieh, few stones, & water from Tirat Haifa. Yes, I brought all of that to remember al-Tira & to have it close to my hart back in Canada.
In an interview conducted in a Palestinian refugee camp in 1998, women demonstrate this same association of plant life with place:
They spoke of the names of land plots around ~ Tjzim (Wadi al-Nahel, Durat al-Qamar, Shana), and the act of naming evoked an aura of magic for those who remembered the places [...]. They also related to the wild plants. The women, who felt we had shifted to familiar ground, called out the names — khubeize (mallow), ‘aqub (tumble thistle), maramiyyeh (sage), za’atar (thyme).
Mirna Bamieh's Palestine Hosting Society put on an Edible Wild Plants Table, which registered the connection of foraging to place, local knowledge, and temporality. The project, which focused on "identifying the names, forms, locations and availability of wild plants in Palestine’s nature," involved a menu created from foraging in the mountainous regions of Palestine during the blooming season "from mid-January until the end of February."
Foraging is also one strategy among many that Palestinians use—alongside instituting agricultural innovations, creating native seed banks, educating about Palestinian cuisine, and seeking out contracts with foreign markets—to attain food self-sufficiency and sovereignty. It is therefore both a symbolically defiant strategy, and a practical one. Palestinians illustrate a belief in the illegitimacy of Israel's laws and claims, and insist on the primacy of their relationship to the land, when they forage for food.
When asked whether he believed that 2020 would bring the promised relaxation in criminalization of foragers, Samir Naamneh, who has been repeatedly fined, arrested, and tried over the past decades, told Dror Foyer (דרור פויר):
"We'll live and see, but it won't change anything for me: whether it's allowed or not, I'm going to forage. I do the work I love, and I'm at peace with myself. The fact that I'm making a statement to the State of Israel and their law—that's enough for me."
Donate to an evacuation fund
Donate eSims
Palestinian heirloom seeds
Ingredients:
250g filtered water
2.5g (1 1/2 tsp) high-quality loose leaf black tea
4g (1 1/2 Tbsp) dried three-lobed sage, or substitute another variety of sage
Sugar, to taste (optional)
Dried three-lobed sage can be purchased from a Palestinian brand such as Al-'Ard or Yaffa (not "Jaffa").
Instructions:
1. Combine tea with just-boiled water and steep for two minutes.
2. Add sage and steep for another minute.
3. Pour into tea glasses and serve hot.
Times and quantities are geared towards producing a tea that is mild enough to be enjoyed without sugar. Adjust as per preference.
293 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here’s the Karkadann, from Indian and Persian mythology! Said to roam grasslands and act in a similar manner to unicorns, this creature is believed to be based on the Indian Rhinoceros!

#librum prodigiosum#this is a drawing from Librum Prodigiosum!#digital art#digital illustration#fantasy#art#folklore#mythology#monster#mythical creatures#creature#rhinoceros#rhinoceros art#karkadann#indian mythology#persian mythology#mythology art#mythologyart
32 notes
·
View notes
Note
In the Hybrid AU, would Gojo be a rabbit or another cat hybrid? Because you’ve got Rabbit Gojo who’s using his cute looks to his advantage but also secretly horny all the time and wants to breed little cute bunnies inside you. Then you’ve got Catoru, who’s the pamper type who loves making mischief and knocking things off the table just for funnsies.
Yes, Avy and I talked about this a few weeks back, and came to a consensus that he’d definitely be a bunny! (pampered Catoru gives me fuzzy feelings too. Because he’s pretty like one of those persian cats with blue eyes.) I do think it’s funny that baby rabbits are called kits/kittens, too.
+breeding, dubious consent, hybrids, fem!reader
Gojo’s a smart and silly little bun bun, who definitely uses his cuteness to get what he wants! He may have an adorable twitchy nose, whiskers, and fuzzy ears. His bouncing around during JJK 0 is his version of zoomies, which is what tricked you into taking him home.
Yet, he causes nothing but trouble. Digging through stuff around the house, constantly eating your snacks, bothering your curtains and sheets, and taunting the neighbors’ dogs. You thought you were getting a sweet, innocent bunny, not Bugs Bunny.
If he can’t work his way out of something on his own, he’s confident his luck will get him out of any trouble he causes. Always laughing away the problem because he has “lucky rabbit’s feet”.
He loves it when you scratch the top of his head and groom him. He’s super-fast and can fight well, so you don’t have to worry about him getting into fights with other hybrids. In fact, wolf-dog hybrid Suguru is his best friend.
He really likes sweets and fruits too. Gojo would inhale them if you let him, reminding you of the folklore of rabbits making rice cakes on the moon. With Gojo’s sweet tooth, you can see why it became a legend.
He’s bonded himself to you, so he loves to cuddle up with you for daily naps and tries to groom you. However, he’s really bad about keeping you up during the late hours and early morning when he’s the most awake before sleeping throughout the day like an innocent lil’ fuzzy.
Gojo scent marks you, constantly dragging his chin over your head and against your belongings to let others know you’re a part of his territory. He gets pouty, grumpy, and clingy when you’re around other rabbit hybrids. He also has really bad personal space issues, circling around you and yapping away to get your attention (because he considers you his mate!).
He wants to breed his cute little bunnies in you. He wonders, “How many kits can humans have at one time?” Two? Three? Six? Sometimes those shows on TV have 9! He thinks 6 is a good overall goal number. To start, anyway.
He's going to think about it all day, every day. There's a reason the saying "breed like rabbits exists". He gets so hard thinking about you. You don't even have to do anything. The idea of breeding you with his babies, a daydream of little yous with the same bunny ears as him is enough to make him want to mount you.
You think playing with his fluffy tail, watching it flick back and forth, and rubbing his fuzzy white ears is a cute way to tease him but all you’re doing is working up an already horny mind that was ready to mount you as soon as you rolled out of that bed in the morning.
If you pet him one more time, he’s going to grab you, pull you into his lap, and use his thick legs to part yours. You barely touched your bunny, but he’s already hard and pulling out his dripping cock to breed you. It’s your fault for starting it, doe! And if you try to wiggle away, he thinks you’re just playing a game with him. Weren’t you just grooming him?
Gojo will treat you so well most of the time though. He knows how to use his tongue to groom you, especially down there, and he is aware he has you when you start to make pretty little moans for him. He’ll have you soaking wet and choking up before he thinks about breeding you with his cute little fluffballs. You’re not even going to think about it when he presses his weight against your back, bites hard on your shoulder, and start to thrust like he's possessed.
He’ll keep going into you’re overstimulated and begging for rest, but he keeps his arms wrapped around you to stop all your squirming, begging not just yet, one more time, doe. It’s always one more time with him during his rut. One more orgasm, one more thrust, one more kit--please, please, please, doe--he knows you can.
#gojo x reader#gojo satoru x reader#satoru x reader#jjk smut#notsfw#adelssmut#tw: hybrids#tw: hybrid au
562 notes
·
View notes
Text
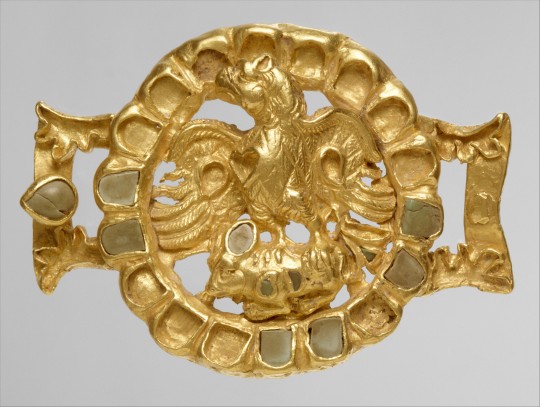
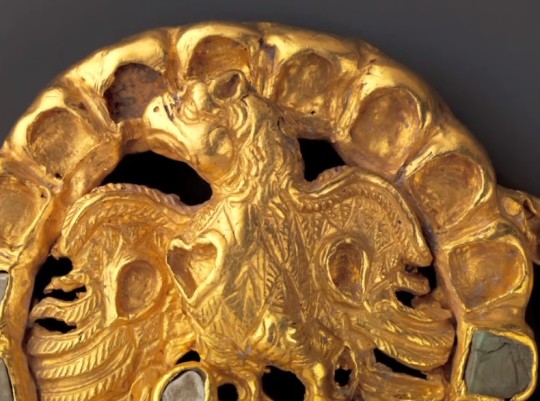
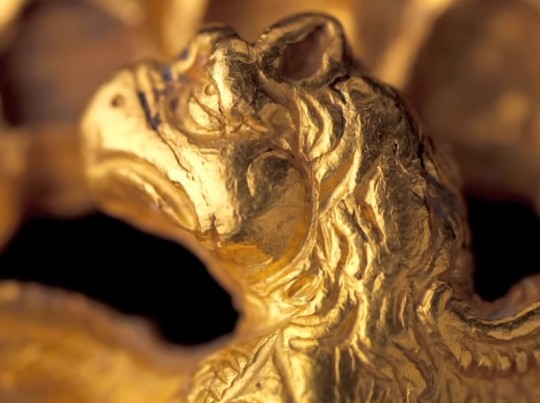




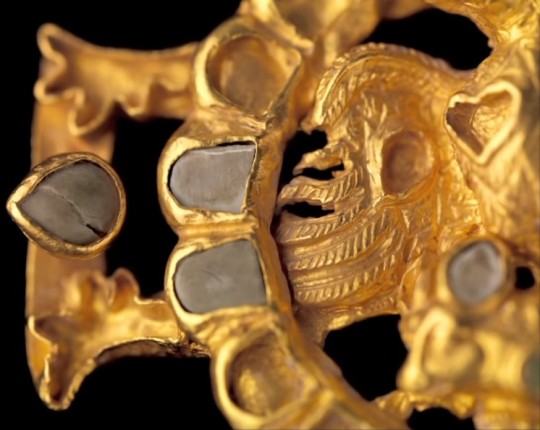

Gold clasp of eagle, possibly belonging to the House of Karen, 1st-2nd C. CE. Found in Nahavand. The House of Karen seems to have been descended from the Parni, who were themselves an offshoot of the Scythians. Ernst Herzfeld wrote that this item probably belonged to their house.
"House of Karen (Middle Persian: Kārēn; Parthian: 𐭊𐭓𐭍𐭉, romanized: Kārēn; Persian: کارن, romanized: Kārin or Kāren), also known as Karen-Pahlav (Kārēn-Pahlaw) was one of the Seven Great Houses of Iran during the rule of Parthian and Sassanian Empires. The seat of the dynasty was at Nahavand, about 65 km south of Ecbatana (present-day Hamadan, Iran). Members of House of Karen were of notable rank in the administrative structure of the Sassanian empire in multiple periods of its four century-long history.
The Karens, Karan-Vands, Qarinvand dynasty or Karen-Pahlevi as they are also called, claimed descent from Karen, a figure of folklore and son of the equally mythical Kaveh the Blacksmith. Their historical origin however may be that the Karens, along with the House of Mihran, were descended from the Arsacids. According to Movses Khorenatsi, this descent was via one of the three sons of Phraates IV, also named Karen. The fact that Karen may also have been among the family names of the Arsacid dynasty may give credence to this theory.
The first verified reference to the Karenas was during the Arsacid era, specifically as one of the feudal houses affiliated with the Parthian court. In this they were similar to the House of Suren, the only other attested feudal house of the Parthian period. Following the conquest of the Parthians, the Karenas allied themselves with the Sassanids, at whose court they were identified as one of the so-called "Parthian clans". The Armenian Kamsarakan family was a branch of the House of Karen."
-taken from Wikipedia
youtube
#scythian#iranian#ancient persia#ancient history#history#art#antiquities#museums#archaeology#heart symbol#Youtube
206 notes
·
View notes