#sapient is the capacity for intelligence and complex problem solving and learning
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Real question folks.
We all know Optimus’s motto right? Right?
“Freedom is the right of all sentient beings.”
Yeah, that one. You know the one.
But. Like. Issue.
Animals are sentient. Animals like dogs, cats, wild animals, they all have sentience. So like, what do we think the Autobots think about that? How do they feel about the fact that humans (and probably every other species in the galaxy) regularly domesticate, tame, and use other sentient creatures for their own gain? For things like. Entertainment, agriculture, pet-keeping. All that stuff.
Do you think they’re bothered by it? Do yo7 think they look at humans, with our pet dogs, and think
“Wow, this situation is kinda fucked up.”
I mean. Personally , I don’t think they take much issue with it. (Especially cause like there’s instances of them in canon not giving a shit. Buster in IDW. Fluffy Ears in Earthspark. Etc.) I think they understand the difference between sentient and sapient. Like. Humans are sapient. Cybertronians are sapient. Animals are….not? At at least not really. If you want to classify animals as sapient I think you can make that argument but even then you have to agree that their sapience is severely limited compared to like. Human sapience.
So. I don’t know. Do you think the bots get wigged out but human pet ownership, I guess. Because I know what Optimus’s motto is. I know what he says. But like. Do you think maybe he means sapient where he says sentient? Cause I think that makes more sense.
Cause like. He’s advocating for total freedom, right? Equality under law, ability to self determine your own life and destiny. But. Uh. That wouldn’t really work for animals? They’re sentient, yah, but they operate on an instinct level. Not an intellect level. Not that they don’t deserve protections and shit. That’s not the point. The point is like. Do you think Optimus (and the other Bots I guess) differentiate between sentience and sapience when they apply their beliefs. Because if not then they’d have to also be advocating for total animal freedom.
I do not know where I am going with this. But. Do you all see my point???? Please tell me you do. This has been niggling at my brain for years and I just. I cannot stop thinking about it. I don’t know why.
Sentience is not sapience. But the Autobots fight for the freedom of “sentient beings”. This is driving me insane. Do you think they care about a difference? Or do they see humans as monsters for our dominion over animals? Someone help I’m thinking too much about something that doesn’t even matter.
#silkling rambles#transformers#maccadam#also#for those who do not know the difference#sentient is the ability to think and perceive and feel emotions#sapient is the capacity for intelligence and complex problem solving and learning#a big part of sapience is also like. self-awareness. awareness of yourself in the world and your relation to thr world and people around yo#it’s kinda more complicated but that’s the simple version.#so like. a cat is sentient because it can think and feel. it can even learn a little.#but it lacks the higher self-awareness that’s necessary for true sapience#I am rambling again.#someone needs to stop me#why am I fixating on this on 9 pm a Thursday night#I do not know#I just. I just wanted to let my brain vomit out. this has been ratttling and sloshing in my head for years#anyway. thoughts. let me know yours#or don’t#I’m going to shut up now
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Philosophy of Sapience
Sapience refers to wisdom, deep insight, or the ability to think and act with judgment, often contrasted with sentience (the capacity for sensation and feeling). In philosophy, sapience explores what it means to be capable of higher-order thinking, reflective self-awareness, and the pursuit of knowledge and understanding.
1. Definition of Sapience
Sapience is typically defined as the ability to reason, think abstractly, and apply knowledge wisely. It encompasses the intellectual faculties that allow beings to reflect, solve complex problems, and engage in self-directed learning.
It is often associated with wisdom, foresight, and a moral dimension, involving not only intellectual capacity but also ethical judgment.
2. Sapience vs. Sentience
Sentience refers to the capacity to have subjective experiences (such as pleasure or pain), while sapience is linked to the higher cognitive abilities that include reasoning, planning, and understanding abstract concepts.
Sapient beings are not only aware of their experiences but are capable of reflecting on those experiences, making decisions based on reason, and exercising judgment about complex matters. Humans are typically considered sapient, while many non-human animals are seen as sentient but not sapient.
3. Sapience and the Human Condition
Sapience is often seen as a key trait that distinguishes humans from other animals. It involves self-awareness and the ability to ask philosophical questions, reflect on one’s existence, and make moral judgments.
The ancient Greeks, especially Aristotle, viewed sapience as a fundamental characteristic of humans. Aristotle argued that humans are "rational animals" whose ability to reason sets them apart from other creatures and allows them to achieve eudaimonia (flourishing or happiness) through the exercise of virtue.
Wisdom and Practical Reasoning: Sapience is also closely related to the philosophical concept of phronesis, or practical wisdom, which refers to the ability to make good judgments in everyday life. This kind of wisdom, according to Aristotle, requires not only knowledge but also experience and moral insight.
4. Sapience and Knowledge
Epistemology, or the philosophy of knowledge, is closely related to the concept of sapience. To be sapient is not just to have knowledge, but to understand how to apply that knowledge wisely in different contexts.
Philosophers like Plato and Socrates viewed sapience as the highest form of knowledge. For Plato, wisdom was a form of insight into the eternal truths of the universe, such as the Forms, and the philosopher was the one who could access this deep knowledge.
Socratic Wisdom: Socrates famously said that true wisdom comes from knowing that one knows nothing. This humility and self-awareness are seen as core aspects of sapience—the ability to reflect critically on one’s own limitations and to pursue knowledge without assuming one already has it.
5. Sapience and Artificial Intelligence
As artificial intelligence continues to develop, the question of whether machines could ever achieve sapience arises. While many AI systems demonstrate remarkable abilities to process information and solve problems (which might mimic aspects of sapience), philosophers debate whether machines can truly possess wisdom, self-awareness, or moral judgment.
Strong AI vs. Weak AI: Weak AI refers to systems that can perform specific tasks but do not have genuine understanding or wisdom. Strong AI theorizes that machines could one day develop true sapience, becoming not just tools for human use but entities capable of reflective thought and ethical decision-making.
Ethical Implications: If machines were to become sapient, this would raise profound ethical questions about their rights, responsibilities, and their place in human society. Would sapient machines deserve the same moral consideration as humans?
6. Sapience and Moral Responsibility
Moral Agency: A key philosophical question related to sapience is whether sapience is required for moral responsibility. Beings with the capacity for reflective thought, self-awareness, and moral reasoning are often seen as responsible for their actions, as they can make choices based on reasoning and judgment.
Free Will and Sapience: The relationship between sapience and free will is another important topic. For some philosophers, sapience involves the ability to act freely, based on reasoned decisions rather than instinct or compulsion.
7. Sapience in Non-Human Animals
Philosophers and scientists debate whether certain non-human animals (such as dolphins, elephants, or great apes) might possess degrees of sapience. These animals have demonstrated behaviors that suggest problem-solving, self-awareness, and even moral behavior, leading to discussions about extending moral consideration to them.
Degrees of Sapience: Some argue that sapience exists on a continuum, with humans representing the highest degree of sapience, but other species potentially exhibiting lesser forms of wisdom and self-reflection.
8. Sapience and Existentialism
Existentialist philosophers like Jean-Paul Sartre view sapience as central to the human experience. Sartre argued that humans are unique in their ability to reflect on their own existence and to make free choices in the face of an indifferent or even absurd universe.
This capacity for self-reflection and choice is both a source of freedom and a burden, as humans must create meaning and purpose in their lives without relying on external or predetermined systems of value. For existentialists, sapience is both the source of human dignity and the cause of existential anxiety.
9. Sapience and the Future
As humans develop new technologies and continue to explore the boundaries of knowledge, the concept of sapience is evolving. Philosophers consider what it means to be wise in an era of rapid technological change, where access to vast amounts of information may not always lead to wisdom or good judgment.
Transhumanism: Some thinkers speculate about the possibility of enhancing human sapience through technology. Transhumanism advocates for using science and technology to improve human intellectual and moral capacities, potentially leading to a future where humans achieve a higher form of sapience.
The philosophy of sapience examines the nature of wisdom, reflective thought, and higher-order reasoning. It encompasses questions about what distinguishes humans from other animals, the relationship between knowledge and judgment, and the moral implications of sapience. It also raises ethical concerns about the development of artificial sapience in machines and the potential for enhancing human intellectual capacities.
#philosophy#epistemology#knowledge#learning#education#chatgpt#ontology#metaphysics#psychology#Sapience#Wisdom#Knowledge#Moral Responsibility#Free Will#Artificial Intelligence#Epistemology#Self-Awareness#Ethical Decision-Making#Transhumanism
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

It also clearly demonstrates several things.
1) the cats know their own names and are capable of responding
2) they have some kind of emotional inner life and concept of selfhood because they want their human to acknowledge them and are visibly disturbed by the lack
3) at least some basic theory of mind as they are able to recognise that they know information their human doesn't have.
Undeniably sentient, and probably at least a bit sapient.
Sentient = capable of emotional experiences greater than basic stimulus response. Pretty much all animals probably have this, insects might? It's very hard to tell past a certain point if we are just projecting.
sapient = intelligent self-awareness with complex/abstract thoughts. E.g. theory of mind, which human children begin to develop around 4 years old. Hence the incessant "why?" phase.
Both of these are sliding scales, not simply a binary. There are greater and lesser degrees of both sapience and sentience
Theory of Mind = the ability to conceptualise 1) yourself as an individual mind, 2) other people as minds separate to yourself 3) that you possess information they do not and vice versa.
Theory of mind is a necessary foundation for empathy (but not the only one). Recognising they have an emotional inner world just like you, and that their world is just as valid as yours.
Sentient and Sapient tend to get muddled up with each other, and with the general term 'intelligent'. When we talk about animal intelligence, we are mostly talking about judging their level of sapience, and how it compares to our own, but there are other kinds of intelligence.
Problem solving for one, ants as a colony demonstrate incredible problem solving abilities.
Instinct is also a form of intelligence. Gut feeling. the things you don't need to learn how to do, they're just there. Preprogrammed
With AI sentience is gonna be the real achievement. An artificial being with a demonstrable emotional inner life is *the* jackpot. Ultimately computers are tools. Problem solving is what they're designed for but anything we program them to do is essentially instinctual to them.
Machine learning is a big step in advancing the problem solving capabilities of bots.
LLMs like chatgpt are essentially just a friendly user interface and a novel implementation rather than a significant advancement towards AGI.
AGI - Artificial General Intelligence. An ai that is truly both sentient and sapient.
Personhood is an ill-defined term that is likely to generate more and more controversy as we move forward. In my personal opinion, personhood requires requires an individual to demonstrate a basic level of both sentience and sapience. It's a trait that can be acquired, not something intrinsic. I dont think humans intrinsically have personhood from birth, but they rapidly develop to that basic level, and then continue to develop well beyond it into a fully realised human.
We should, and we do treat children as people under the law, with considerations for their developing state and diminished capacity.
I believe there are some animals which can demonstrate the same basic level of sapience as a child, and I think we would benefit from extending the same benefits to them as we do to children. The other great apes for example.
I believe eventually we will develop sentient AIs, either fully artificial, or by uploading human consciousness. And I think it's essential that we have the legal and practical framework for personhood established long before we get to that point.
6K notes
·
View notes
Note
Dear Koryos: Can you imagine a universe wherein bats have become the ancestors of some kind of Highly Intelligent Life Form (not necessarily humanlike intelligence, but something as different from today-bats as humans are different from Ancient Primate Ancestor)? I originally just was thinking about what kind of Cultural Norms such beings would have, but then I realized I couldn't really imagine anything except bat-shaped things that more or less thought like humans.
I’ve sat on this question a while because it’s such an interesting one to me. The biggest issue here is that you’d have to specify which bats you’re making your theoretical ancient ancestor, because there’s such a vast diversity of behavior within the group. A vampire bat would be different from a sac-winged bat would be different from a hoary bat would be different from a flying fox ancestor, is what I’m saying. Any social or behavioral organization paradigm that you can think of, there’s a bat that has it.
So to think about what a sapient bat would look like, we first need to assess the intelligence and behavior of possible ancestral bats. And here I’m gonna stick a readmore, because this gets looooong.
Assessing which species would make a good sapience ancestor based on intelligence is also tricky, in large part because bat intelligence remains mostly under-examined. Bats as a whole share the rough reproductive hallmarks of other intelligent mammals and birds, in that they have long lifespans and small litter sizes (in most cases, a single pup). They also have unusually high whole brain size and EQs for their body size, though this is often attributed to the fact that they need more brain matter to handle echolocation.
However, if you look at EQs across Chiroptera, the general trend is that vampire bats and flying foxes tend to have the largest, followed by bulldog bats, false vampire bats, the fruit and nectar eating bats of Phyllostomidae, followed by most other Yinpterochiropteran groups, and then finally the remainder of the insectivorous bats. The authors of the particular paper I’m referencing suggest that this has to do with lifestyle- bats that specialize on blood, fruit, or non-insect prey may require more intelligence to solve the unique problems posed by their food sources compared to insect-eating bats. But the authors do admit that insect-eating bats may also have been constrained by the need to keep their brains smaller and lighter to allow for faster flight, and it’s entirely possible they’re doing more with less. (Also, it’s important to remember that EQ is an imperfect method for assessing intelligence anyway.)
More than one insectivorous bat species is known to have vocal learning and the capacity to imitate, and it’s highly likely that many others do, given the complexity of bat vocal repertoires. Fruit bats, particularly the Egyptian fruit bat, also display vocal imitation. This is considered pretty smart stuff, and among animals only humans, birds, cetaceans (dolphins and whales), pinnipeds (seals), and elephants are known to be regular vocal imitators, putting the bats in a pretty high-class group. Some researchers are now arguing that bats are better candidates for studying the development of human language than birds are, given their closer relationship to us and various other similarities between our vocalizations. There’s even some emerging evidence that some species of bats may recognize each other by vocal signals unique to each individual (in other words, names). In spite of all this, bat vocalizations remain largely understudied, but it’s clear all their chatter serves a purpose.
I bring up all these points because I like reminding people how smart and cool bats are because it emphasizes that intelligence matters in different ways to each bat group, but all of them show the potential for vocal complexity that could approach that of a human’s. So wherever our theoretical sapient bat comes from, it’s likely to be noisy. (Though maybe at frequencies we can’t hear.) Now, if we look at other measures of intelligence such as tool use and environment manipulation, the evidence is more on the side of fruit-eating bats, specifically flying foxes. Though I’ve never seen one use a tool per se, they are perfectly capable solving complex problems using object manipulation. For example, pulling a plastic chain up link by link to get fruit attached to the end involves a similar amount of intelligence as the animals in that famous raven-gets-meat-on-a-string study. They’re also capable of figuring out grenade feeders (feeders in which “pins” have to be removed to make the food drop out) and sometimes will carry around small objects for no apparent reason.
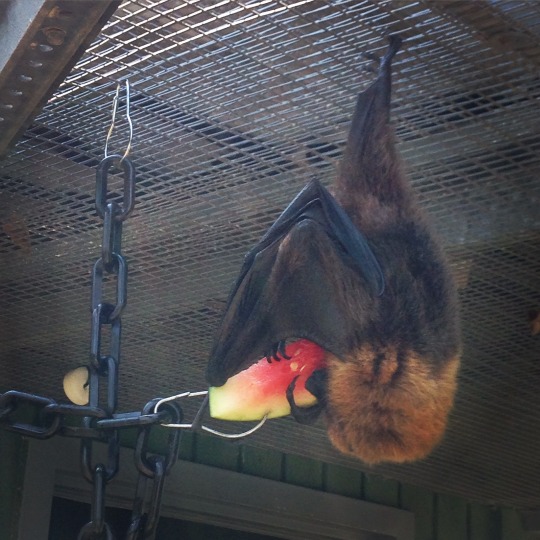

The unusually long thumbs of flying foxes allow them to manipulate objects with surprising precision and they may also use their feet and even wingtips to this end. Object manipulation is part of their natural repertoire (for example, pulling a branch closer to get at something tasty). This separates them somewhat from non-frugivorous bats, who don’t usually need to manipulate objects in pursuit of food- blood-drinking bats just gotta find a spot to bite, carnivorous and piscivorous bats swoop down like hawks, and the most manipulation I’ve seen an insect-eater do is use their tail membrane as a scoop to toss a bug into their mouth. If you want a sapient bat with lots of tool use, fruit-eaters are your likely ancestral group.
However, bats can alter their environment and get better access to food in quite intelligent ways without using objects. Here we ought to look at vampire bats. The white-winged vamipre bat, which feeds primarily on the blood of birds, has co-opted the behavior of domestic chickens in at least two ways. Some bats may perch on the exact spot on a hen’s back that causes her to assume the lordosis posture (i.e., the bout-to-get-boned posture) and feed from the back of her comb with her holding completely still. Others will press up against her brood patch, imitating a particularly goblin-faced little chick, causing her to nestle down on it as the vampire has its meal. This is incredible stuff, as these tactics couldn’t be utilized against their traditional avian prey- meaning the bats have learned how to manipulate chickens all on their own!

Common vampire bats prefer hoofed mammals to birds, and given the larger size of their prey usually don’t have to resort to such nefarious tactics to stay unnoticed. But their creativity also shines when their normal (at this point, human-introduced) prey isn’t available, and they proceed to feed on whatever they can find- which might include sea lions, rats, crocodiles, porcupines, turtles, and even venomous snakes. Each of these critters requires a different strategy on the bat’s part, but apparently the bats tackle the situation with ease. Indeed, one account tells of a vampire bat taunting a rat snake, easily avoiding each strike, until the snake was too exhausted to do anything as the bat brazenly sipped blood from its nose. It should be noted that this particular snake species specializes on feeding on bats.

So in comparison to a sapient fruit bat, a sapient vampire bat might be much more focused on manipulating the behavior of other species, perhaps even domesticating animals for its own use. I should mention, however, that one species of vampire bat- the hairy-legged vampire bat- has evolved a kind of opposable thumb on its foot (a sixth digit fashioned from the calcar), not found in any other bat species. It uses this thumb to help it grip branches as it scuttles around nibbling bird toes, but if you were to make it sapient, you might imagine that instead of the thumb-based object manipulation seen in pteropodids, this fellow would manipulate stuff with its feet. (No relation to the horrible Dougal Dixon futurebats, though, please.)
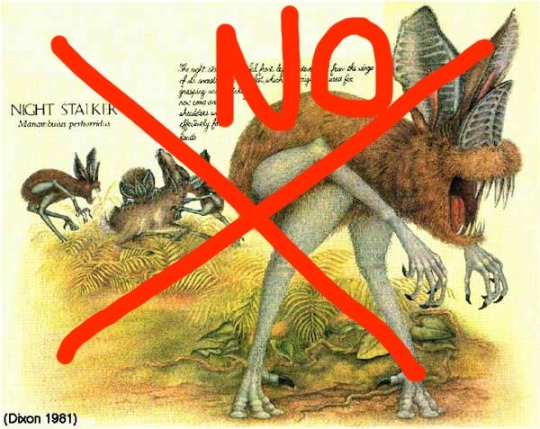

Speaking of horrible future bats, most of the speculative future bats I’ve seen have two things in common- a) flightlessness and b) a loss of vision in order to rely primarily on echolocation. But neither of these things are really plausible. I’ve discussed why it’s highly unlikely for bats to evolve flightlessness before, so I won’t go into too much detail here, but suffice it to say that unlike birds, which sometimes seem to drop flight as soon as they can get away with it, no bat has evolved to be flightless even when in the most prime conditions. The degree of specialization they have for flight would make it pretty hard to go back to a terrestrial lifestyle, in fact- at best I can imagine a short-flighted bat that flaps from tree to tree.
Some might argue that evolving the brainpower for sapience would necessitate flightlessness because of how heavy and energy-draining such a big brain would be, but just because that’s how humans do it doesn’t mean it HAS to be done that way: look at the brain sizes of highly intelligent birds, such as corvids and parrots- still flying, and quite well. (And the birds that HAVE evolved secondary flightlessness aren’t exactly known for their brainpower). I couldn’t find any information on the neuronal density of bat brains, but I’d bet that it’s higher than expected, given the dizzying amount of calculations that have to take place in an echolocating, flying, insectivorous bat’s head to be successful.
Sightlessness is as unlikely in bats as flightlessness... again, no bat species we know of, living or extinct, has lost its vision! In fact most bats have pretty good vision, despite the reduced size of the eyes of some species. No bat species lives in complete darkness all the time, which would be what would render vision obsolete- vision is still better off than echolocation when it comes to spotting daytime/dawn/dusk/moonlight predators on the move.
Granted, some species have almost lost the ability to see forward due to specialization for echolocation, I’ll give you that...
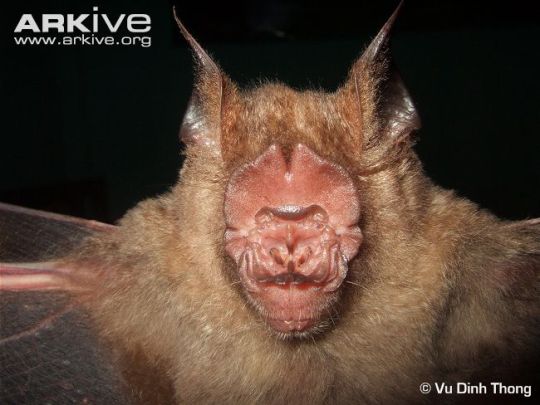

But they still have quite nice eyes. (And note how slits in the noseleaf allow for a little forward vision.)

In any case if our hypothetical bat evolved from a pteropodid/flying fox it wouldn’t have any echolocation at all, because they don’t echolocate, with the exception of Rousettus species, who do it via tongue-clicking. (And there’s some evidence that other pteropodids have like, a ~mystery~ version of echolocation using their wings, but we hardly know anything about that right now.) Pteropodids are also largely crepuscular- active at dawn/dusk- rather than fully nocturnal, as well, and their primary sense is vision, which accounts for their sometimes inappropriately large eyes.

Speaking large-eyed, fruit eating critters, I can say with confidence that the behavior of large pteropodids I worked with reminded me very much of the macaques I’d once worked with. Even though it’s been debunked that bats and primates are close relatives, I think large flying fox behavior is very similar to cercopitheceine primate behavior (as well as spotted hyena behavior in some ways). Their social organization is a mixed-sex, hierarchical, fission-fusion sort of society, where mating is promiscuous, coalitions can form around power grabs, and competition for spotty resources is quite fierce. Infantacide does occur in fruit bats as in primates, though I’m not sure if there’s been any study on how common it is.
Compare this to the social structure of the common vampire bat, though. Female vampire bats will shift roosts freely and form multiple-matriline groups, usually with a single or two or three males in attendance. These males defend their “harems” from other males, but there’s not much evidence for female policing as in primates, given that females regularly swap roosts; rather, the males seem focused on defending the favorable roosts themselves.
In addition, female vampire bats are pretty famous models of reciprocal altruism, that is, I’ll-scratch-your-back-if-you-scratch-mine behavior. Because they feed entirely on blood, the bats can’t build up any fat reserves, and over 24 hours without feeding can starve them. To combat this, they have a complex network of blood donors (via regurgitation, not vein-piercing) that they turn to in times of need; it’s based on kinship but even more so on how familiar they are with the bat in question, and whether or not they give blood as well when it’s their turn.
Spectral bats are strict carnivores that eat rodents, lizards, birds, and other bats. They’re notable for being a monogamous species, with two parents raising one pup together while defending a hunting territory, and in some cases the offspring of previous years may stick around to help as well, in the manner of canids and some bird species. An even more exceptional monogamous bat is the Dayak fruit bat, where males lactate as well as females. Check out the armpit-nipples of the lactating male, below.

Many other bats have lek breeding systems, like the hammerhead bat, where males congregate together to perform for females, but otherwise the sexes live separately; other species have males that fly completely solo and sing like birds to attract a mate; in other species like the hoary bat both sexes normally live solitary lives.
Most cave-dwelling insectivorous bats stay in sex-segregated groups until it comes time for hibernation, in which case they cluster together in caves, mate, and nap. Social behavior among these species is probably the most poorly understood, given that they are often tucked into near-unreachable places during the day.
Of course, the social behavior in the vast majority of all bat species hasn’t been studied at all, so who knows what other forms their societies might take? I particularly await with eagerness the discovery of a polyandrous bat species similar to tamarins and marmosets... It’s not unfeasible, given the large size of newborn bats (a pup may be up to 1/3 the weight of its mother) and the fact that they often need to be carried rather than hidden, meaning poor mom has gotta carry them while flying, and in some species it can take two years or more before they’re able to survive on their own- as in our small primate cousins, having two dads could really make life easier. I mean... look how big this newborn ghost bat pup is. (And if you’re brave, watch this evening bat giving birth... that looks painful.)

Anyway.
An important indicator of high intelligence would be a great degree of behavioral flexibility (which can lead to transmitted culture) within a species. I don’t think the social behavior of any bat has been studied thoroughly enough to assess how flexible their lifestyles are between groups, but I would bet vampire bats are among some of the most adaptive, as well as some of the most socially receptive and cooperative.
On the other hand I would love to do a study on observational learning in pteropodid bats; I bet they’d do really well. It’s already been shown that they can learn to understand and respond to human pointing gestures.
I guess my ultimate point is, you could expect a sapient bat to behave very differently based on its ancestral lifestyle and morphology (especially whether or not it echolocates) but sapience would imply a degree of behavioral diversity that wouldn’t be limited to any one set of cultural norms. Which is why I hesitate to say any sapient bat would behave just like such-and-such species, but smarter.
It would be very interesting, though, to design a theoretical culture based on creatures that are flighted (travel would be much easier, but energy requirements much higher, how are the flightless elderly cared for?), or one that drinks blood (would certain species’ blood become taboo? what sorts of species might they domesticate and how would they keep them?), one that primarily hangs upside-down in branches (artificial perches would have to go everywhere), or most especially, one that echolocates. I can only imagine the diverse sorts of oral traditions that an echolocating sapient species would have.
Hope this long, long answer gave you at least some degree of what you were looking for! And thanks for the question.
498 notes
·
View notes