#udp server
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Setup is unable to access the SQL UDP Port 1434 on the specified SQL Server
When setting up SQL and configuring some applications. The following error might be prompted “Setup is unable to access the SQL UDP port 1434 on the specified SQL server”. This means that the setup requires access to the SQL UDP port 1434 to retrieve the TCP port assignment information from the SQL server. Please see DNS uses TCP and UDP, How to uninstall Microsoft SQL Server on Windows. Also,…

View On WordPress
#Install SQL Server 2022#Microsoft SQL#Microsoft Windows#SQL UDP Port 1434#Windows Server#Windows Server 2012#Windows Server 2016#Windows Server 2019#Windows Server 2022
0 notes
Text
cw robo gore (is he a robot? it is like.... 3d shapes gore...... all impressionable spheres and cones please turn away!) tw fire
udp: fixed colors a bit!!! didn't notice that he got eyesraingly bright
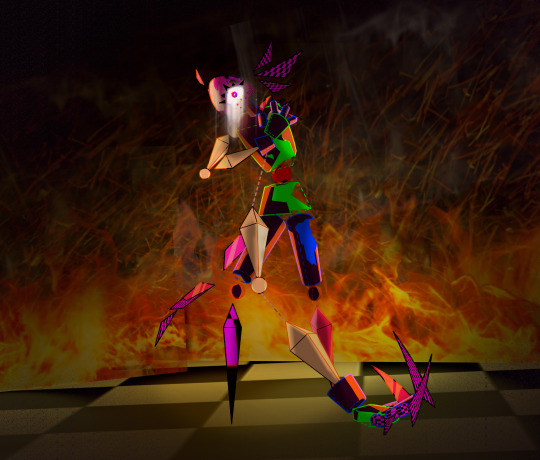

When god dies, his whole world burns with him
server [kinito] deleted succesfully
Second variant of the caption was "Which form does a shapeshifter take when dying? The one you loved the most"
Third variant was "do not worry guys he just burned his egg salad and overdramatizes"
Also a quick spin of his f-uped model and an original sketch (:
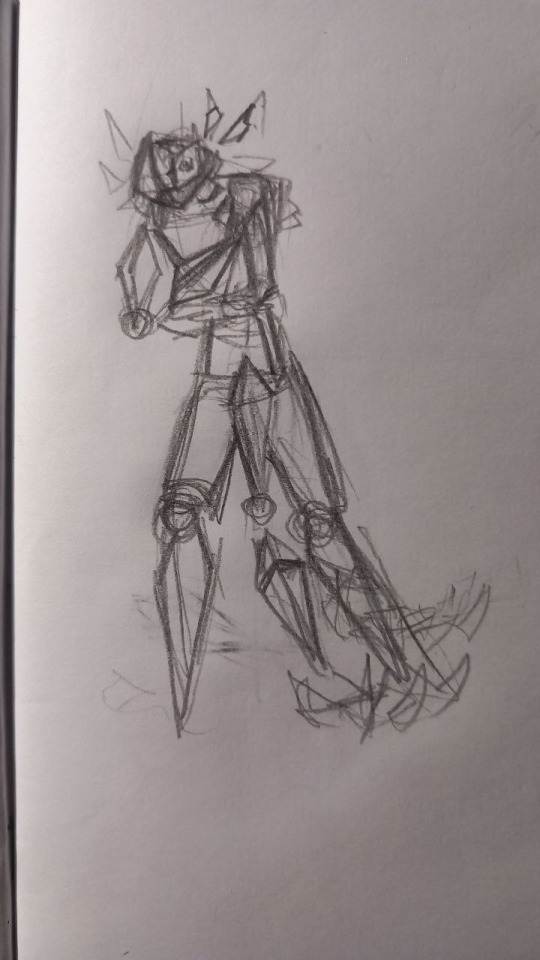
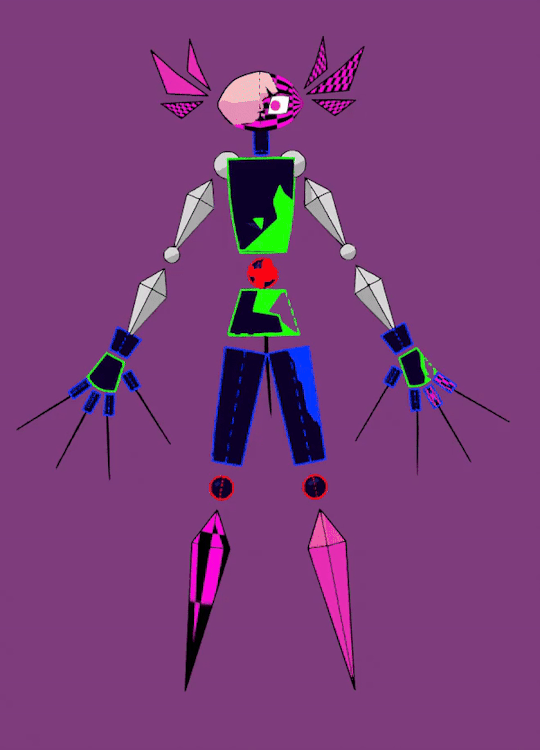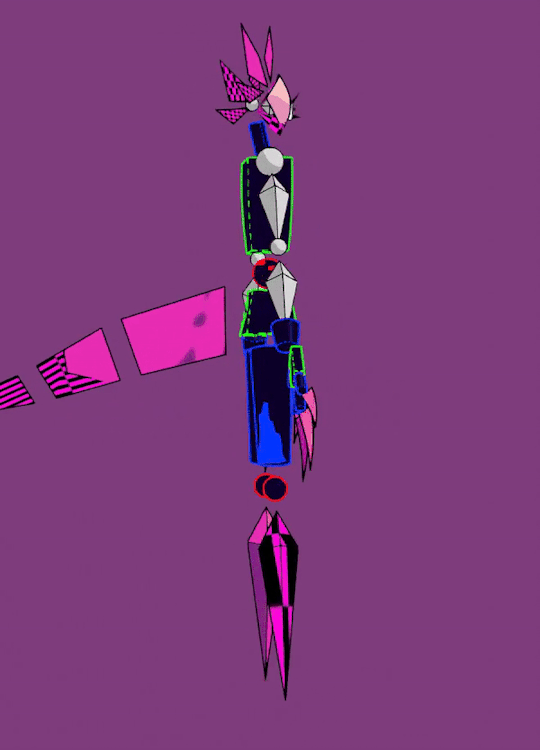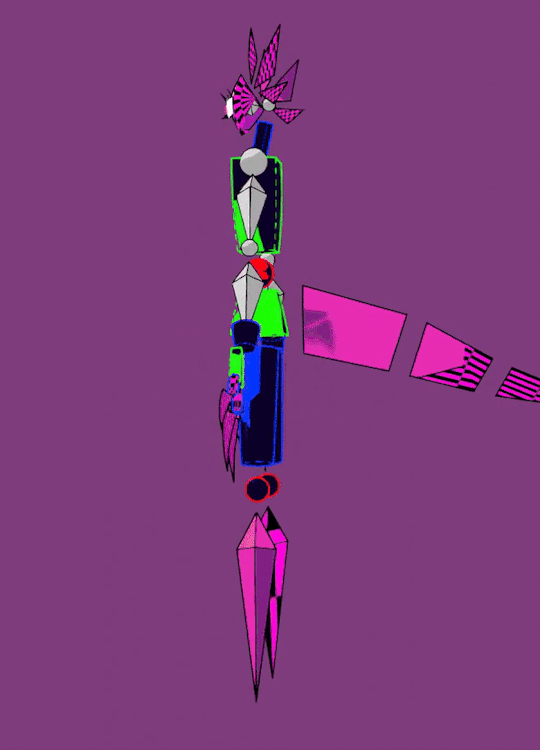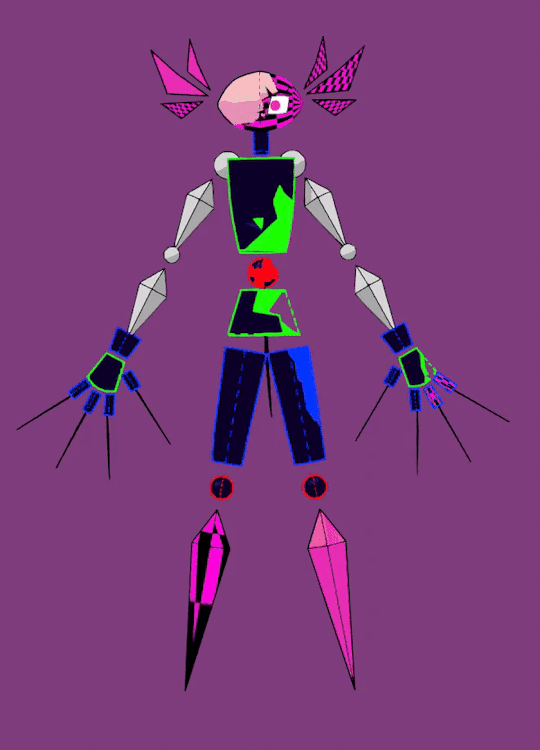

Right when i made his first model i knew i needed to make this, he is so silly
old vers:
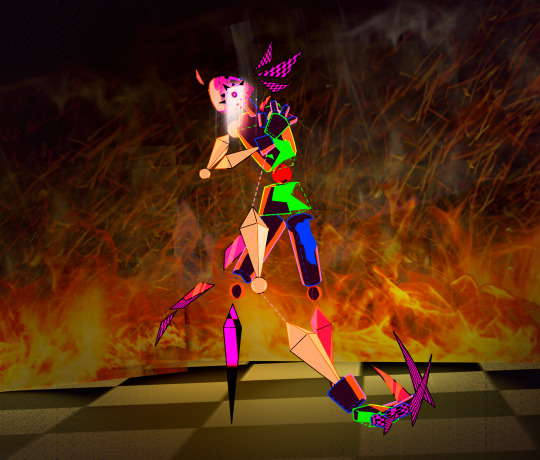

#i felt a little silly today#who ordered fried axolotl?#sorry we are out of deep-fry coating#he got his ruin dlc#i love that i can just *raises an axe above head*#chop him up cutely#“omg i love this design i made so much!!!” *smashes him with a sledge hammer*#kinitopet#kinitopet fanart#kinito the axolotl#kinito 3d model#kinito fanart#kinito my beloved#kinito pet#prosto cup of art
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
Latest Trump administration nonsense
It seems reproductiverights.gov is down and I'm hearing it's intentional rather than a technical issue. Wow.
It's not returning DNS. NOERROR and empty ANSWER rather than NXDOMAIN, but all of .gov seems to do that for records which don't exist. Also points toward intentional shutdown.
╰─❯ dig reproductiverights.gov A ; <<>> DiG 9.10.6 <<>> reproductiverights.gov A ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 36073 ;; flags: qr rd ra ad; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 1 ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;reproductiverights.gov. IN A ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: gov. 297 IN SOA a.ns.gov. dns.cloudflare.com. 1737549305 3600 900 604800 300 ;; Query time: 14 msec ;; SERVER: 100.100.100.100#53(100.100.100.100) ;; WHEN: Wed Jan 22 12:39:14 GMT 2025 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 110
Same results for AAAA and CNAME.
I've created a mirror of the site. Check out details here.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Amazon DCV 2024.0 Supports Ubuntu 24.04 LTS With Security

NICE DCV is a different entity now. Along with improvements and bug fixes, NICE DCV is now known as Amazon DCV with the 2024.0 release.
The DCV protocol that powers Amazon Web Services(AWS) managed services like Amazon AppStream 2.0 and Amazon WorkSpaces is now regularly referred to by its new moniker.
What’s new with version 2024.0?
A number of improvements and updates are included in Amazon DCV 2024.0 for better usability, security, and performance. The most recent Ubuntu 24.04 LTS is now supported by the 2024.0 release, which also offers extended long-term support to ease system maintenance and the most recent security patches. Wayland support is incorporated into the DCV client on Ubuntu 24.04, which improves application isolation and graphical rendering efficiency. Furthermore, DCV 2024.0 now activates the QUIC UDP protocol by default, providing clients with optimal streaming performance. Additionally, when a remote user connects, the update adds the option to wipe the Linux host screen, blocking local access and interaction with the distant session.
What is Amazon DCV?
Customers may securely provide remote desktops and application streaming from any cloud or data center to any device, over a variety of network conditions, with Amazon DCV, a high-performance remote display protocol. Customers can run graphic-intensive programs remotely on EC2 instances and stream their user interface to less complex client PCs, doing away with the requirement for pricey dedicated workstations, thanks to Amazon DCV and Amazon EC2. Customers use Amazon DCV for their remote visualization needs across a wide spectrum of HPC workloads. Moreover, well-known services like Amazon Appstream 2.0, AWS Nimble Studio, and AWS RoboMaker use the Amazon DCV streaming protocol.
Advantages
Elevated Efficiency
You don’t have to pick between responsiveness and visual quality when using Amazon DCV. With no loss of image accuracy, it can respond to your apps almost instantly thanks to the bandwidth-adaptive streaming protocol.
Reduced Costs
Customers may run graphics-intensive apps remotely and avoid spending a lot of money on dedicated workstations or moving big volumes of data from the cloud to client PCs thanks to a very responsive streaming experience. It also allows several sessions to share a single GPU on Linux servers, which further reduces server infrastructure expenses for clients.
Adaptable Implementations
Service providers have access to a reliable and adaptable protocol for streaming apps that supports both on-premises and cloud usage thanks to browser-based access and cross-OS interoperability.
Entire Security
To protect customer data privacy, it sends pixels rather than geometry. To further guarantee the security of client data, it uses TLS protocol to secure end-user inputs as well as pixels.
Features
In addition to native clients for Windows, Linux, and MacOS and an HTML5 client for web browser access, it supports remote environments running both Windows and Linux. Multiple displays, 4K resolution, USB devices, multi-channel audio, smart cards, stylus/touch capabilities, and file redirection are all supported by native clients.
The lifecycle of it session may be easily created and managed programmatically across a fleet of servers with the help of DCV Session Manager. Developers can create personalized Amazon DCV web browser client applications with the help of the Amazon DCV web client SDK.
How to Install DCV on Amazon EC2?
Implement:
Sign up for an AWS account and activate it.
Open the AWS Management Console and log in.
Either download and install the relevant Amazon DCV server on your EC2 instance, or choose the proper Amazon DCV AMI from the Amazon Web Services Marketplace, then create an AMI using your application stack.
After confirming that traffic on port 8443 is permitted by your security group’s inbound rules, deploy EC2 instances with the Amazon DCV server installed.
Link:
On your device, download and install the relevant Amazon DCV native client.
Use the web client or native Amazon DCV client to connect to your distant computer at https://:8443.
Stream:
Use AmazonDCV to stream your graphics apps across several devices.
Use cases
Visualization of 3D Graphics
HPC workloads are becoming more complicated and consuming enormous volumes of data in a variety of industrial verticals, including Oil & Gas, Life Sciences, and Design & Engineering. The streaming protocol offered by Amazon DCV makes it unnecessary to send output files to client devices and offers a seamless, bandwidth-efficient remote streaming experience for HPC 3D graphics.
Application Access via a Browser
The Web Client for Amazon DCV is compatible with all HTML5 browsers and offers a mobile device-portable streaming experience. By removing the need to manage native clients without sacrificing streaming speed, the Web Client significantly lessens the operational pressure on IT departments. With the Amazon DCV Web Client SDK, you can create your own DCV Web Client.
Personalized Remote Apps
The simplicity with which it offers streaming protocol integration might be advantageous for custom remote applications and managed services. With native clients that support up to 4 monitors at 4K resolution each, Amazon DCV uses end-to-end AES-256 encryption to safeguard both pixels and end-user inputs.
Amazon DCV Pricing
Amazon Entire Cloud:
Using Amazon DCV on AWS does not incur any additional fees. Clients only have to pay for the EC2 resources they really utilize.
On-site and third-party cloud computing
Please get in touch with DCV distributors or resellers in your area here for more information about licensing and pricing for Amazon DCV.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#AmazonDCV#Ubuntu24.04LTS#Ubuntu#DCV#AmazonWebServices#AmazonAppStream#EC2instances#AmazonEC2#News#TechNews#TechnologyNews#Technologytrends#technology#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How To Set Up Socks5 Proxy List in Wingate.me?
What Is Private Proxy Wingate.me?

Wingate.me is a private proxy service that delivers secure managed internet access across your entire network and all your online activities. It caters to a range of requirements, from small networks to large enterprises. Known for its high-quality private proxies, particularly in the Russian region, Wingate.me has carved a niche for itself as a powerful online platform.
Supporting for Internet hosting ensures that the WinGate Proxy Server is compatible with all browsers, SSL, FTP, streaming audio and video, DirectPlay Internet gaming, etc. Socks5 proxy list wingate.me provides clients with a safe, anonymous, and unrestricted internet browsing experience. They shield users from data collection and facilitate access to otherwise blocked websites.
Types of Private Proxy Wingate.me
It offers a variety of private proxy types, including:
1. SOCKS4 proxy
A versatile proxy for web browsing, file sharing and online gaming, known for its speed and efficiency.
2. SOCKS5 proxy
These proxies support TCP and UDP traffic, making them ideal for online streaming, torrenting, and high-performance tasks.
3. IPv4 proxy
Stable and reliable proxy based on IPv4 protocol, compatible with most websites and services on the Internet.
4. Mix of SOCKS5 and IPv4 proxies
This option combines the advantages of both proxy types, providing flexibility for different tasks.
An Overview Of Wingate.me’s Socks5 Proxy List
Socks5 proxy list wingate.me provides an extensive list of Socks5 proxy servers, ensuring users have access to a broad range of functional and efficient proxies. The list, updated regularly, includes information such as the IP address, port number, country, and the last time the proxy was checked for functionality. This transparency empowers users to make informed decisions when selecting a proxy server.
Get 1GB Proxy Free Trial of Residential Proxies Now!
How To Set Up Wingate.me’s Socks5 Proxy?
Setting up a Socks5 proxy from Wingate.me is straightforward. After selecting a proxy from the list, users can configure their web browsers or applications to use the proxy by entering the provided IP address and port number in the relevant settings. Specific setup instructions may vary depending on the application or browser used. Here are detailed instructions:
Step 1 Installing Wingate Proxy Server
After downloading the latest package of WinGate Proxy Server, double-click its ‘.exe’ package to start the installation setup wizard of WinGate proxy server. After that, you will be greeted by its welcome page to get started with the installation on your devices. Click on the “Next” button to continue.
Get 1GB Proxy Free Trial of Residential Proxies Now!
Step 2 License Agreement
You need to read and accept the license agreement before the installation and use of Wingate by choosing the right option as shown.
Step 3 Installation Folder
Choose the location on your system, where you like to place the WinGate installation setup.
Step 4 Select Packages
You will be asked to choose the program features that you wish to install on your system.
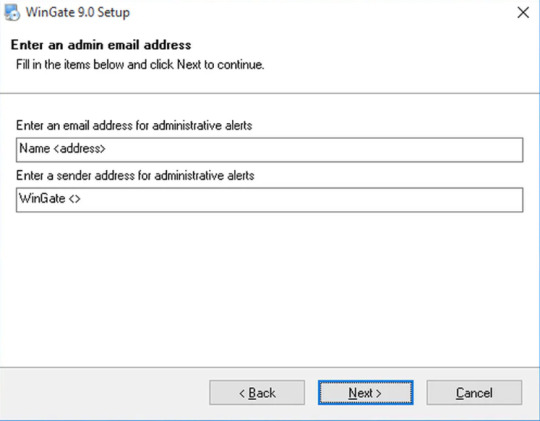
Step 5 Admin Email Address
You should provide your Administrative User Name and Email ID along with the Senders’ address for the administrative alerts.
Step 6 Ready to Install
If you click on the ‘Next’ button, your installation process will start processing files and other selecting configurations. After finishing the installation process of WinGate, click on the ‘Finish’ to exit the installer. Remember to click on the ‘Yes’ to go for system reboot and wait till it is back.

Step 7 Setting Up
After you finish the installation, you can set up Wingate.me’s Socks5 Proxy List now.
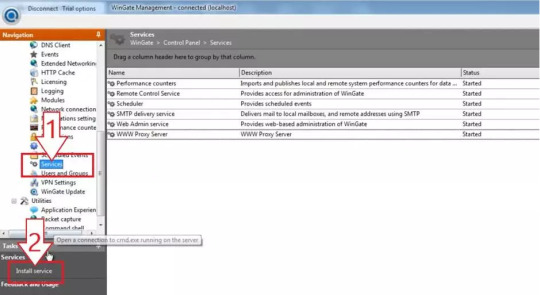
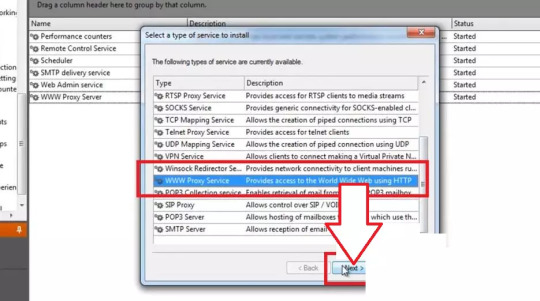
1. You will see a welcome page and a navigation menu on the left with available configuration options. Please focus on setting up the proxy. To do this, select “Services” from the navigation menu, then right-click on the empty space on the right and select Install Service.
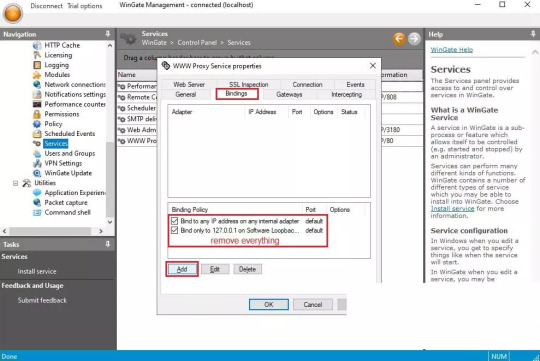
2. The service properties window will appear. Navigate to the Bindings tab. Remove all active bindings and click Add. Select “Any External Adapter” and click “OK” to save your configuration.
3. Now, go to the Connection tab. Check the box next to “Connect through upstream proxy.” Go to the IP Settings dashboard to configure your proxy. Note down the HTTP proxy host, proxy port, proxy username and proxy password of the private proxy you obtained from the website and import this data into WinGate.

By following these steps, you will successfully configure a private proxy using Wingate’s user-friendly interface. This ensures safe, anonymous and efficient internet browsing while protecting your online activity and data.
Get 1GB Proxy Free Trial of Residential Proxies Now!
Conclusion
Wingate.me’s Socks5 proxy list is a powerful tool for anyone seeking to navigate the digital world with anonymity, versatility, and global access. However, like any tool, it should be used responsibly and ethically. As we continue to sail through the data-driven era, tools like Wingate.me’s Socks5 proxy list will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping our digital experiences.
For more please read the original article which is from:
#socks5 proxy list wingate.me
#private proxy wingate.me
#buy wingate me private proxy
#proxy for email wingate.me
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
DNS over HTTPS ve FF/klonech
Proč: Protože O2 manipuluje s DNS ve snaze dodávat takzvaně „zabezpečené připojení“, čili cokoliv, co se jim nelíbí, přesměrují spoofovanou DNS odpovědí na vlastní server, kde (v rámci TLS) nesedí certifikát (naštěstí, MitM jim zatím nejde, bo nedrží v rukou žádnou CA) a když to akceptujete, sdělí vám toliko, že „vstupujete na škodlivý obsah“…a „škodlivé“ je málem cokoliv, protože jejich bezpečák je evidentně nějaký copyrightů dbalý aktivně zapojený český nácek. Takhle rozhrabaná DNS představuje nemalé bezpečnostní riziko.
Proč DNS over HTTPS: když by stačilo jen použít jiný DNS server. No, zatím by asi stačilo, ale je jen otázkou času, než přesměrují všechny odchozí UDP spojení na svůj DNS server. Problém je v tom, že VY nezjistíte že tohle udělali do momentu, než to něco viditelně rozbije, což už může být pozdě. TLS pro ně zatím představuje překážku, čili DNS over HTTPS je v tomto případě dostatečně spolehlivé řešení. A jelikož je to v prohlížečích implementováno, je to současně dostatečně jednoduché řešení…ovšem řeší to jen ten prohlížeč pochopitelně.
Volba DNS over HTTPS poskytovatele: Já jsem se rozhodla pro Quad9. Je to bohužel švýcarská společnost, já na tu zemi nemám obecně dobrý názor, avšak cokoliv je lepší než nesvatá trojice USA, Čína, Sajuz a ono si upřímně řečeno není moc z čeho vybírat. Blbé je, že tato společnost poskytuje i určitou filtraci DNS, nicméně volbou DNS over HTTPS serveru si současně volíte i tuto filtraci, přičemž poskytují i kompletně nefiltrovanou službu (moje volba). Je to celé vysvětlené na https://quad9.net/service/service-addresses-and-features/
Nastavení: Pokud vstoupíte do nastavení od firefoxu a necháte hledat DNS, najdete příslušná nastavení. Zde máte jako default Cloudflare (což je z deště pod okap), ale je tu možnost zadat Custom nastavení. Sem zadáte https://dns10.quad9.net/dns-query a vřele doporučuji zapnout režim výhradního DNS over HTTPS. Minimálně pro začátek, protože potřebujete vyzkoušet že vám to funguje, čili potřebujete dostat chybové hlášení když to nefunguje.
Nojo, jenže DNS překládá názvy serverů na IP adresy, jak se tedy najde IP adresa serveru dns10.quad9.net?
No systémovým resolverem pochopitelně, což je všechno, jen ne bezpečné. Přesněji řečeno, pokud se provider rozhodne pro něco nečestného, mělo by si to vylámat zuby na TLS, ale to je jediná vrstva, přičemž pokud provider opravdu hodne rozbije DNS, pak vám to DoH (DNS over HTTPS) znefunkční…čímž vzniká prostor, že ho vypnete a padáte do těch všech radostí s rozhrabanou DNS. Vy zadáváte jméno DoH serveru, protože tohle se použije na validaci TLS certifikátu, ale současně potřebujete jeho IP. Nejsnadnějším způsobem by tedy bylo nacpat pár adresa-server do /etc/hosts. Nicméně implementace DoH ve Firekryse tohle dokáže řešit po vlastní ose…ovšem musíte do about:config.
Výchozí IP adresu vašeho DoH serveru zadáváte jako řetězec s klíčem network.trr.bootstrapAddr a v mém případě to muselo být 149.112.112.10, adresa 9.9.9.10 nefungovala a já se obávám, že v tomhle má opět prsty kyslík. Teoreticky můžete zadat IPv6, ale protože Kaon, router, který kyslík svým zákazníkům vnucuje, má občas záchvaty, které znefunkční IPv6, rozhodla jsem se pro řešení s IPv4. Tímto nastavením kompletně obejdete DNS vašeho providera, podotýkám, že pouze v tom jednom konkrétním prohlížeči, ale ono tohle zatím většinou stačí.
Další DoH servery najdete na https://github.com/curl/curl/wiki/DNS-over-HTTPS Příliš jsem ho nezkoumala, takže možná DoH server v budoucnu změním, potřebovala jsem rychlé řešení problému. Pokud nemusíte jednat ve spěchu, asi dává smysl ten seznam důkladněji prozkoumat.
Edit: Nakonec jsem namísto Quad9 zkusila belnet. Rychlejší odezva. Ovšem zjistila jsem další věc, některé služby se začaly chovat jinak. Myslela jsem si, že konkrétní obsah je závislý spíše od zdrojové IP a že load balancing se dělá na úrovni routingu, ale vypadá to, že některé služby (google například) řeší tyto věci na úrovni DNS, takže kupříkladu trubka nyni tahá data z belgie namísto toho, aby tahala z lokálního googlu přes český nix. No z tohoto pánové z kyslíku nebudou mít radost, bo samozřejmě tier1 routing stojí víc peněz než přímá lajna potažmo nix. No ale byli to oni kdo si tímhle načůral do bot, kdyby nedělali nesmysly a nerozhrabávali DNS, nikdy bych se nějakým DNS over HTTPS nezabývala. BTW uvidím, jaký to bude mít vliv na spolehlivost. Každopádně volbou toho serveru jde viditelně leccos ovlivnit.
0 notes
Text
Why is North America leading the global DRaaS market expansion
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) Market Size was valued at USD 11.7 Billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 76.0 Billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 23.1% over the forecast period 2024-2032.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) Market is witnessing exponential demand as organizations prioritize business continuity in the face of rising cyber threats, data breaches, and natural disasters. Enterprises across industries are shifting toward cloud-based recovery solutions to ensure seamless IT resilience, reduced downtime, and cost efficiency.
U.S. enterprises are rapidly adopting DRaaS for critical infrastructure protection and regulatory compliance, especially in healthcare, BFSI, and manufacturing sectors.
Disaster Recovery as a Service Market is expanding as more businesses adopt remote operations, SaaS platforms, and hybrid cloud models. DRaaS offers rapid data recovery, scalable infrastructure, and minimal human intervention, making it a preferred solution for modern digital ecosystems.
Get Sample Copy of This Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/2780
Market Keyplayers:
IBM Corporation (IBM Cloud Disaster Recovery, IBM Resiliency Orchestration)
Microsoft Corporation (Azure Site Recovery, Microsoft Hyper-V Replica)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) (AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery, AWS Backup)
VMware, Inc. (VMware vSphere Replication, VMware Site Recovery Manager)
Sungard Availability Services (Recover2Cloud, Managed Recovery Program)
Acronis International GmbH (Acronis Cyber Protect, Acronis Disaster Recovery)
Zerto (Zerto Virtual Replication, Zerto Cloud Continuity Platform)
Veeam Software (Veeam Backup & Replication, Veeam Cloud Connect)
Dell Technologies (Dell EMC RecoverPoint, Dell EMC PowerProtect)
Cisco Systems, Inc. (Cisco UCS, Cisco HyperFlex)
Carbonite, Inc. (Carbonite Server Backup, Carbonite Endpoint Backup)
Arcserve (Arcserve UDP Cloud Direct, Arcserve Continuous Availability)
Axcient, Inc. (Axcient Fusion, Axcient Replibit)
Datto, Inc. (Datto SIRIS, Datto ALTO)
TierPoint (TierPoint Managed Disaster Recovery, TierPoint Cloud to Cloud Recovery)
iland Internet Solutions (iland Secure DRaaS, iland Secure Cloud Console)
IBM Resiliency Services (IBM Business Continuity, IBM Cyber Resilience Services)
Flexential (Flexential DRaaS, Flexential Cloud)
InterVision (InterVision Disaster Recovery, InterVision Cloud Recovery)
Market Analysis
The DRaaS market is shaped by the growing urgency for robust disaster recovery strategies due to increasing ransomware attacks and data dependency. Companies are transitioning from traditional recovery models to cloud-native solutions that offer better scalability, automation, and recovery speed. Additionally, regulatory pressures in the U.S. and Europe are driving adoption to maintain data integrity and compliance.
Market Trends
Surge in cloud-based and hybrid DRaaS adoption
Integration of AI and ML for predictive threat detection
Rise in ransomware recovery solutions
Automated failover systems minimizing human input
Growth in subscription-based DRaaS models
Increasing compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other data protection laws
Partnerships between cloud providers and managed service providers (MSPs)
Market Scope
With digital transformation accelerating globally, the DRaaS market is evolving from a niche IT service to a mission-critical infrastructure element. Businesses of all sizes are integrating DRaaS into their core IT strategies to ensure operational continuity.
Rapid scalability for SMEs and enterprises
Cloud-agnostic architecture supporting multiple platforms
On-demand disaster simulations and recovery drills
Pay-as-you-go pricing increasing accessibility
Global coverage with local compliance integration
Real-time monitoring and centralized dashboards
Forecast Outlook
The Disaster Recovery as a Service market is expected to continue strong upward momentum driven by cloud maturity, growing data volumes, and heightened risk awareness. As businesses across the U.S., Europe, and beyond aim for zero downtime environments, DRaaS will be a strategic pillar of resilience architecture. Vendors focusing on automation, cost-efficiency, and seamless integration will gain a competitive edge in the evolving market landscape.
Access Complete Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/disaster-recovery-as-a-service-market-2780
Conclusion
As digital infrastructures grow more complex and threats more sophisticated, Disaster Recovery as a Service has become a vital component of enterprise strategy. From San Francisco to Frankfurt, organizations are investing in intelligent, cloud-first recovery models that deliver reliability, compliance, and peace of mind. DRaaS is no longer a backup plan—it’s the frontline defense in ensuring operational continuity and digital trust.
Related Reports:
U.S.A Reconciliation Software Market Gears Up for Significant Digital Transformation Growth
U.S.A Loyalty Management Strategies Drive Customer Retention and Competitive Edge
U.S.A. Team Collaboration Software Market Set to Revolutionize Workplace Productivity
About Us:
SNS Insider is one of the leading market research and consulting agencies that dominates the market research industry globally. Our company's aim is to give clients the knowledge they require in order to function in changing circumstances. In order to give you current, accurate market data, consumer insights, and opinions so that you can make decisions with confidence, we employ a variety of techniques, including surveys, video talks, and focus groups around the world.
Contact Us:
Jagney Dave - Vice President of Client Engagement
Phone: +1-315 636 4242 (US) | +44- 20 3290 5010 (UK)
Mail us: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
How LiteSpeed Improves Loading Speed
Website speed is a critical factor in user experience, SEO performance, and conversion rates. Faster-loading websites engage visitors better, reduce bounce rates, and rank higher in search results. LiteSpeed Web Server (LSWS) is engineered to optimize website speed with powerful technologies built into its core. This article provides a technical and practical look at how LiteSpeed improves website performance, its architectural strengths, and comparisons with other web servers like Apache and NGINX.
What Is LiteSpeed?
LiteSpeed is a high-performance web server software developed by LiteSpeed Technologies. It serves as a drop-in replacement for Apache, meaning it can use Apache configurations such as .htaccess and mod_rewrite while offering far superior performance.

Unlike traditional web servers that rely on process-based or thread-based architectures, LiteSpeed uses an event-driven approach. This enables it to handle thousands of simultaneous connections efficiently without consuming excessive resources. It’s widely used in shared, VPS, and dedicated hosting environments due to its scalability and speed.
LiteSpeed is compatible with major web hosting control panels like cPanel, Plesk, and DirectAdmin. It also integrates seamlessly with WordPress, Magento, Joomla, and other popular CMS platforms.
How LiteSpeed Improves Loading Speed
LiteSpeed's performance is not just theoretical. Numerous benchmarks and case studies show significant improvements in load time, server response, and concurrent user handling. Its technical foundation plays a pivotal role in enabling these advantages.

Event-Driven Architecture
Most traditional web servers like Apache use a process-based or threaded architecture. Each connection requires a dedicated process or thread, which leads to high memory usage under load.
LiteSpeed uses an event-driven, asynchronous model. It processes multiple connections within a single thread, significantly reducing memory consumption and CPU load.
For example, benchmarks by LiteSpeed Technologies show that LSWS handles over 2x more concurrent connections than Apache with the same hardware configuration [1]. This architecture is especially beneficial during traffic spikes, such as flash sales or viral content events.
Built-In Caching (LSCache)
LiteSpeed’s caching engine, LSCache, is built directly into the server core. Unlike third-party caching plugins that operate at the application level, LSCache works at the server level, making it faster and more efficient.
With LSCache enabled on WordPress, testing from WPPerformanceTester shows up to 75% reduction in page load times compared to uncached sites. This is because LSCache delivers prebuilt HTML pages directly to users, bypassing PHP execution and database queries.
LSCache also supports advanced features such as:
ESI (Edge Side Includes) for partial page caching
Smart purging rules
Private cache for logged-in users
Image optimization and critical CSS generation
These features make it suitable not only for static pages but also for dynamic, eCommerce-heavy platforms like WooCommerce or Magento.
Compression and Optimization
LiteSpeed supports GZIP and Brotli compression out of the box. These technologies reduce the size of files transmitted over the network, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
According to Google PageSpeed Insights, compressing assets can reduce page size by up to 70%, which directly improves load time. Brotli, developed by Google, provides even better compression rates than GZIP in many cases, and LiteSpeed uses it efficiently.
Additionally, LiteSpeed can minify JavaScript, CSS, and HTML, combine files to reduce HTTP requests, and enable lazy loading for images—all directly from the server level.
QUIC and HTTP/3 Support
LiteSpeed is one of the earliest web servers to fully support QUIC and HTTP/3, protocols developed by Google and later adopted by IETF.
QUIC is built on UDP instead of TCP, which reduces handshake latency and improves performance over poor network conditions. HTTP/3 inherits QUIC’s benefits and introduces faster parallel requests and better encryption handling.
When HTTP/3 is enabled, page loads feel snappier, especially on mobile devices and in regions with weaker connectivity. Cloudflare reported up to 29% faster page loads using HTTP/3 versus HTTP/2 [2].
LiteSpeed’s implementation ensures that your site is future-ready and delivers optimal performance even under challenging network environments.
LiteSpeed vs Apache and NGINX
Performance benchmarks consistently show that LiteSpeed outperforms both Apache and NGINX in various scenarios, especially under high traffic and dynamic content conditions.

Apache Comparison
Apache is widely used but is resource-heavy under load. When serving PHP applications like WordPress, Apache relies on external modules (e.g., mod_php) or handlers like PHP-FPM, which increase overhead.
LiteSpeed replaces these with LiteSpeed SAPI, a more efficient PHP handler. Benchmarks show that LiteSpeed can process 3x more PHP requests per second compared to Apache [3].
NGINX Comparison
NGINX is known for its speed with static files, but it lacks full .htaccess compatibility and requires more manual tuning for dynamic sites.
LiteSpeed combines Apache’s ease of configuration with NGINX’s speed and goes further by offering built-in caching and QUIC support. This makes it a more all-in-one solution for both static and dynamic content delivery.
Real-World Results
A hosting provider, NameHero, migrated over 50,000 sites from Apache to LiteSpeed. The result was an average decrease in load time by 40%, with no change in hardware configuration [4].
Another example is a WooCommerce store that used LiteSpeed Cache. Load times dropped from 4.2s to 1.2s after activation, significantly improving Core Web Vitals and user retention.
Website owners consistently report faster Time to First Byte (TTFB), better PageSpeed scores, and fewer server crashes during traffic peaks when using LiteSpeed.
Who Should Use LiteSpeed?
LiteSpeed is ideal for:
WordPress users who want faster page loads without complex configurations.
WooCommerce and Magento store owners needing efficient dynamic caching.
Web hosting providers looking to reduce server load and increase client satisfaction.
SEO-focused marketers who want better Core Web Vitals.
Developers who want Apache compatibility with modern performance.
LiteSpeed is available in both open-source (OpenLiteSpeed) and commercial versions. While OpenLiteSpeed is suitable for smaller projects, the enterprise version offers advanced features and full control panel integration.
Final Thoughts
LiteSpeed offers a clear performance advantage due to its architecture, built-in caching, modern protocol support, and optimization features. It helps websites load faster by minimizing server load, reducing latency, and delivering content more efficiently.
Whether you're a developer, site owner, or hosting provider, switching to LiteSpeed can result in measurable improvements in speed, stability, and scalability. In today’s performance-driven web ecosystem, LiteSpeed is a practical solution backed by real results and advanced engineering.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Telecommunication Protocols Overview: VoIP
Revolutionary Transition from TDM to IP Networks Voice over IP (VoIP) technology VoIP and Triple Play: Key Protocols for Multimedia Transmission in IP Networks
Voice-over-IP (VoIP), also known as IP telephony, connects TDM networks with channel switching to IP networks with packet switching. It also facilitates the gradual transition from TDM to IP networks. Introduced in the late **1990s**, VoIP is one of the earliest telecommunication technologies to enable the use of IP phones, IP PBXs, and similar equipment; the suite of VoIP protocols is **crucial** among other telecom protocols.
According to the common definition, IP telephony is real-time voice signal transmission over a packet-switched network. It converts a phone number into an IP address and the analog voice signal into a digital one.
The birth year of Internet telephony is considered to be 1995, when Vocaltec released the Internet Phone software for telephone transmission using the IP protocol. **Until** the mid-1990s, Internet phone network implementation was possible only via telephone modems, resulting in significantly lower voice quality compared to traditional phones. Nevertheless, this laid the foundation for VoIP.
Since then, the development has been so rapid that VoIP's capabilities now far exceed its formal name. Essentially, this technology allows for the transmission of not only voice but any type of information using the IP protocol, so the term shifted to a broader one, "multimedia." Corresponding data structures can include voice, images, and data in any combination, commonly referred to as Triple Play.
The VoIP network structure can be viewed as two planes. The lower one represents the transport mechanism for non-guaranteed delivery of multimedia traffic as a protocol hierarchy (RTP, UDP/IP), and the upper one is the call service management mechanism. The key protocols here are H.323 ITU-T, SIP, MGCP, and MEGACO, each offering different implementations for call **services** in IP telephony networks.
Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) provides transport services to multimedia applications, but it doesn't guarantee delivery or packet order. RTP helps **apps** detect packet loss or order issues by assigning a number to each packet. RTP works in point-to-point or point-to-multipoint modes with no regard to the transport mechanism, but usually it is UDP.
RTP works with the Real-Time Control Protocol (RTCP), which manages data flow and checks for channel overload. RTP session participants periodically exchange RTCP packets with statistical data (number of packets sent, lost, etc.), which senders can use to adjust transmission speed and load type dynamically.
Recommendation H.323
The recommendation H.323, historically the first method for making calls in an IP network, involves the following types of data exchange: - Digital audio - Digital video - Data (file/image sharing) - Connection management (communicating function support, logical channel management) - Session and connection establishment and termination
Key H.323 network elements include terminals, gateways, gatekeepers, and Multipoint Control Units (MCU).
A terminal provides real-time communication with another H.323 terminal, gateway, or MCU.
Gateways connect H.323 terminals with different network protocol terminals by converting the information back and forth between networks.
Gatekeepers participate in managing connections by converting phone numbers to IP addresses and **vice versa**.
Another element of the H.323 network, the proxy server, operates at the application level to identify application types and establish necessary connections.
The H.323 call service plane includes three main protocols (see picture): RAS (Registration Admission and Status) for terminal registration and resource access control, H.225 for connection management, and H.245 for logical channel management. RAS uses UDP, while H.225 and H.245 use TCP for guaranteed information delivery. UDP's delivery is not guaranteed, so if confirmation isn't received in time, UDP retransmits the message.

Pic. 1. Overview of H.323
The process of establishing a connection involves three stages. The first one is to detect the gatekeeper, register terminals with the gatekeeper, and control **terminals'** access to network resources using the RAS protocol. The next two stages involve H.225 signaling and H.245 control message exchanges.
Recommendation H.225 outlines the procedures for connection management in H.323 networks using a set of signal messages from the ITU-T's Q.931 recommendation.
Recommendation H.245 describes the procedures for managing information channels: determining the master and slave devices, communicating terminal capabilities, and opening and closing unidirectional and bidirectional channels. It also covers delays, information processing modes, and the state of information channels by organizing loops.
The exchange of signaling messages between interacting H.323 network devices happens over H.245 logical channels. The zero logical channel, which carries control messages, must remain open for the entire duration of the connection.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol)
The second method for handling calls in VoIP networks involves using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), specified in RFC 2543 by the IETF. As an application-level protocol, it is designed for organizing multimedia conferences, distributing multimedia information, and setting up phone connections. SIP is less suited for interaction with PSTN but is easier to implement. It's more suitable for ISPs offering IP telephony services as part of their package.
Key features of SIP include user mobility support, network scalability, the ability to add new functions, integration with the existing Internet protocol stack, interaction with other signaling protocols (e.g., H.323), enabling VoIP users to access intelligent network services, and independence from transport technologies.
It's worth noting that user mobility support is no longer exclusively a SIP feature. H.323 now also supports it (see ITU-T H.510, "Mobility for H.323 Multimedia Systems and Services").
A SIP network contains user agents, or SIP clients, proxy servers, and redirect servers.
User agents are terminal equipment applications that include a client (User Agent Client, UAC) and a server (User Agent Server, UAS). The UAC initiates the service request, while the UAS acts as the calling party.
The proxy server combines UAC and UAS functions. It interprets and, if necessary, rewrites request headers before sending them to other servers.
The redirect server determines the location of the called subscriber and informs the calling user.
MGCP (Media Gateway Control Protocol)
The third method for building an IP telephony network relies on the Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP), proposed by the IETF's MEGACO workgroup. The architecture of this protocol is probably the simplest of all three in terms of functionality. An MGCP network contains a media gateway (MG) for converting voice data between PSTN and IP telephony networks, a signaling gateway (SG) for processing signaling information, and a call agent (similar to an H.323 gatekeeper) for managing gateways.
Like H.323, MGCP is convenient for organizing PSTN-compatible IP telephony networks. However, in terms of functionality, MGCP surpasses H.323. For example, an MGCP call agent supports SS7 signaling and transparent transmission of signaling information over the IP telephony network. In contrast, H.323 networks require any signaling information to be converted by a gateway into H.225 (Q.931) messages. MGCP messages are transmitted in plain text format.
The fourth method for building an IP network, an improvement over MGCP, was developed by the IETF's MEGACO group together with ITU-T's SG 16, hence the name MEGACO/H.248. It mainly differs from its older sibling in connection organization. Thanks to this, the MEGACO/H.248 controller can change the port connection topology, allowing for flexible conference management. The MEGACO protocol supports two methods of binary encoding.
MGCP has also evolved in the field of the Internet of Things (IoT), where it is used to manage media gateways and transmit voice information in various scenarios, such as smart homes or intelligent buildings.
0 notes
Text
Networking in Java

Networking in Java involves creating and managing communication between computers over a network using Java programming language. It leverages Java's robust APIs to develop client-server applications, socket programming, and web services. Java networking supports TCP/IP and UDP protocols, enabling efficient data exchange and real-time communication. With Java’s platform independence, developers can build scalable, secure, and high-performance networked applications for cloud computing, IoT devices, and distributed systems. Key concepts include sockets, URL handling, multithreading for concurrent connections, and integration with RESTful APIs. Networking in Java is essential for modern software development, supporting microservices architecture, seamless data transmission, and cloud-native applications
0 notes
Text
E5908 module RJ45 interface communication
How to achieve communication with the E5908 module RJ45, a brief introduction to help you take the next step
Introduction to the module and interface E5908 is an Ethernet communication module with a built-in TCP/IP protocol stack. It supports direct communication with an Ethernet switch or router through the RJ45 interface. The main control MCU can interact with the module through UART (AT command) or SPI/SDIO (depending on the module description).
Hardware connection (RJ45 interface) RJ45 interface (with magnetic transformer): The module's onboard RJ45 interface has an integrated magnetic transformer and can be plugged into a standard network cable without an external transformer. Power and ground: VCC (3.3V/5V) -> module VCC, GND -> module GND. UART connection: MCU_TX -> module UART_RX, MCU_RX -> module UART_TX Reset pin: connected to the MCU GPIO for module hardware reset. Decoupling capacitors: Add 10µF and 0.1µF decoupling capacitors to the module power pins to ensure stable power supply.
Network configuration:
DHCP: AT+NETMODE=DHCP returns +IP:...; Static IP: AT+NETMODE=STATIC,<IP>,<Mask>,<Gateway>. Establish socket: TCP client: AT+TCPSTART="<IP>",<Port>; TCP server: AT+TCPLISTEN=<Port>; UDP: AT+UDPSTART="<IP>",<Port>.
Data sending and receiving: Sending: AT+TCPSEND=<Len> �� module prompts > → sending data; Receiving: module serial port pushes +TCP:RECV,..., followed by data.
Typical C code example:
#define UARThuart1 bool at_send(const char *cmd, const char *exp, uint32_t to) {...} void net_init(void) { //reset HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RESET_GPIO_Port, RESET_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET); HAL_Delay(50); HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RESET_GPIO_Port, RESET_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET); HAL_Delay(200); at_send("AT+NETMODE=DHCP", "OK", 2000); } void tcp_client(void) { at_send("AT+TCPSTART=\"192.168.1.50\",8000", "CONNECT", 5000); at_send("AT+TCPSEND=5", ">", 2000); HAL_UART_Transmit(&UART, (uint8_t*)"hello", 5, 100); at_send("", "SENDOK", 2000); at_send("AT+TCPSTOP", "CLOSED", 3000); }
If you want to know more detailed solutions, please read this article: E5908 module Ethernet communication implementation solution
1 note
·
View note
Text
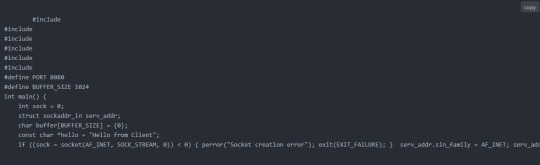
COMP 4320 Project 1 Implementation of a Simple File Transfer Service over the UDP Transport Service
Objective The purpose of this assignment is to implement a simple File Transfer Protocol (FTP) service over the UDP transport service. This project will help you understand some of the important functions in implementing simple data transfer protocols in computer networks. You will write the simple FTP client and server programs that will communicate over either your own computer(s) or the…
0 notes
Text
Application Load Balancer vs Network Load Balancer: Key Differences Explained
Application Load Balancers (ALBs) and Network Load Balancers (NLBs) serve distinct purposes in traffic management. ALBs operate at Layer 7 (Application Layer), making routing decisions based on content such as HTTP headers, methods, paths, and query parameters. This allows for advanced routing strategies, SSL termination, and sticky sessions, making them ideal for modern web applications and microservices architectures. In contrast, NLBs function at Layer 4 (Transport Layer), handling TCP, UDP, and TLS traffic. They excel in managing high-throughput, low-latency traffic and are suitable for applications requiring extreme performance, such as gaming or real-time data processing. Edgenexus Limited provides comprehensive insights into these differences, aiding businesses in selecting the appropriate load balancing solution based on their specific application requirements.
Enhancing Application Performance with Advanced Load Balancing Solutions
In today's digital landscape, ensuring optimal application performance is crucial for business success. Edgenexus Limited offers advanced load balancing solutions that intelligently distribute traffic across servers, preventing overload and minimizing latency. This approach enhances user experience by ensuring fast and reliable access to applications, even during peak traffic periods. By implementing Edgenexus Limited's application load balancer, businesses can achieve seamless scalability and maintain high availability, which are essential for meeting the demands of modern users.
Strengthening Security Posture with Integrated Web Application Firewalls
Protecting applications from evolving cyber threats is a top priority for organizations. Edgenexus Limited addresses this need by integrating robust Web Application Firewalls (WAF) into their load balancing solutions. These WAFs provide comprehensive protection against common vulnerabilities and attacks, ensuring that only legitimate traffic reaches your applications. By incorporating Edgenexus Limited's application load balancer with integrated WAF, businesses can safeguard sensitive data and maintain compliance with industry security standards.
Achieving Global Scalability with Geo-Location Based Load Distribution
As businesses expand globally, delivering consistent application performance across different regions becomes challenging. Edgenexus Limited's application load balancer offers geo-location-based load distribution, directing users to the nearest or best-performing data center. This feature reduces latency and enhances user satisfaction by providing faster access to applications, regardless of geographic location. Implementing this solution enables businesses to offer a consistent and responsive experience to their global user base.
Simplifying IT Infrastructure Management with Unified Application Delivery Controllers
Managing complex IT infrastructures requires efficient tools that streamline operations. Edgenexus Limited's Application Delivery Controllers (ADC) consolidate multiple functions, including load balancing, security, and traffic management, into a single platform. This unification simplifies deployment and reduces the operational overhead associated with managing separate solutions. By utilizing Edgenexus Limited's ADCs, businesses can achieve greater control over their application delivery processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Accelerating Application Delivery with SSL Offload and Content Optimization
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption is essential for protecting data in transit but can introduce performance overhead. Edgenexus Limited's application load balancer addresses this by offloading SSL processing from application servers, freeing them to handle business logic more efficiently. Additionally, features like content caching and compression optimize data delivery, further enhancing application speed. By leveraging these capabilities, businesses can provide secure and fast application experiences to their users.
Ensuring High Availability and Disaster Recovery with Global Server Load Balancing
Maintaining application availability during server failures or site outages is critical for business continuity. Edgenexus Limited's Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) solution distributes traffic across multiple data centers, providing failover capabilities and disaster recovery. In the event of a site failure, GSLB automatically redirects traffic to healthy sites, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted access to applications. This feature is vital for businesses that require constant application availability and resilience.
Facilitating Seamless Cloud Integration with Multi-Cloud Load Balancing Support
As organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies, managing application delivery across different cloud environments becomes complex. Edgenexus Limited's application load balancer supports multi-cloud load balancing, enabling seamless distribution of traffic across various cloud platforms. This capability allows businesses to optimize resource utilization, enhance performance, and avoid vendor lock-in. By integrating Edgenexus Limited's load balancing solutions, organizations can achieve flexibility and efficiency in their cloud deployments.
Conclusion
Edgenexus Limited's application load balancer offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance application performance, security, and availability. By integrating advanced load balancing, security measures, global scalability, and cloud support, businesses can deliver superior application experiences to their users. Embracing these solutions enables organizations to navigate the complexities of modern IT environments, ensuring that applications are fast, secure, and always available. Partnering with Edgenexus Limited equips businesses with the tools needed to thrive in a competitive digital landscape.
0 notes
Text
How to Choose the Right Proxy for Your Needs
Proxies are essential tools for privacy, security, and accessing restricted content. However, with different types available, selecting the right one can be challenging. Here’s a quick guide to help you make an informed decision.
1. Understand the Different Proxy Types
Residential Proxies – Use real IP addresses from ISPs, making them appear as regular users. Best for tasks requiring high anonymity (e.g., web scraping, ad verification).
Datacenter Proxies – Come from cloud servers, offering high speed but lower anonymity. Ideal for bulk tasks where IP bans are less likely.
Mobile Proxies – Use 4G/5G IPs, perfect for mobile-specific tasks like app testing or social media management.
SOCKS5 Proxies – Support various traffic types (TCP/UDP), useful for torrenting and gaming.
2. Consider Your Use Case
Web Scraping? → Residential or rotating proxies to avoid blocks.
SEO Monitoring? → Location-specific proxies for accurate local results.
Gaming or Streaming? → Low-latency SOCKS5 proxies.
Social Media Management? → Mobile or residential proxies to mimic real users.
3. Check Key Features
Speed & Reliability – Datacenter proxies are faster, while residential proxies are more stable for long sessions.
Geo-Targeting – Ensure the provider offers IPs in your desired locations.
Rotation Options – Rotating IPs help avoid detection in automated tasks.
Concurrent Connections – Some proxies limit simultaneous sessions; choose based on your needs.
4. Security & Privacy
Avoid Free Proxies – They often log data and may be unsafe.
Look for HTTPS Support – Ensures encrypted connections.
No-Log Policies – Critical if handling sensitive data. https://nodemaven.com/
5. Test Before Committing
Many providers offer trial periods or money-back guarantees. Test speed, uptime, and compatibility with your tools before long-term use.
0 notes
Text
The Future of Load Balancing: Trends in Network Load Balancers
A network load balancer is a critical component in modern IT infrastructure, especially for organizations handling large volumes of traffic and data. It ensures the distribution of network or application traffic across multiple servers, enhancing performance, availability, and reliability. Whether managing web applications, databases, or large-scale enterprise networks, network load balancers are essential for maintaining seamless operations.
The Basics of a Network Load Balancer
A network load balancer operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model. It directs incoming TCP and UDP traffic to different servers based on configuration rules. Unlike application load balancers, which consider application-level content, network load balancers handle raw connection traffic, making them highly efficient and scalable for handling sudden spikes in network demands.
Benefits of Using a Network Load Balancer in High-Traffic Environments
One of the major advantages of a network load balancer is its ability to manage high volumes of connections with low latency. This makes it suitable for mission-critical applications and services that require high availability. In environments like e-commerce platforms or cloud-based systems, the network load balancer ensures continuous uptime by distributing traffic evenly and avoiding server overloads.
How a Network Load Balancer Enhances Fault Tolerance and Redundancy?
A well-configured network load balancer improves system resilience. If one server fails or becomes unreachable, the load balancer redirects traffic to healthy instances without interrupting user access. This fault tolerance and built-in redundancy prevent downtime and ensure business continuity, especially during maintenance or unexpected outages.
Comparing Network Load Balancer with Other Load Balancing Methods
Compared to other types of load balancers such as application or global load balancers, a network load balancer offers lower latency and is more effective for raw network traffic. While application load balancers are better suited for HTTP/HTTPS traffic and content-based routing, the network load balancer excels in scenarios requiring high-speed and high-throughput connections.
Security Features Associated with Network Load Balancers
Network load balancers also contribute to a more secure environment. They can be configured to filter traffic, prevent malicious attacks like DDoS, and restrict access through IP whitelisting. Integrating with network security tools enhances protection against external threats, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of sensitive data.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications of Network Load Balancers
Network load balancers are widely used across various industries. From online streaming services to financial institutions and cloud service providers, they ensure that applications perform optimally under varying loads. For example, an online game with millions of players relies on a network load balancer to handle connections simultaneously without delays.
Conclusion
A network load balancer plays a foundational role in achieving scalability, reliability, and performance in IT systems. By effectively managing traffic distribution, improving fault tolerance, and integrating with security protocols, it supports seamless service delivery. As digital demands grow, the importance of adopting a robust network load balancer becomes even more essential for businesses aiming to offer uninterrupted, high-quality digital experiences.
0 notes
Text
Introduction to Server and Network Programming

Server and network programming is essential for building applications that communicate over the internet or local networks. From creating web servers to building chat apps or IoT solutions, understanding networking fundamentals is key for any modern developer.
What is Server and Network Programming?
Server and network programming involves writing code that enables applications to communicate with each other over a network. This includes:
Creating and managing servers
Establishing network connections
Sending and receiving data (HTTP, TCP/IP, UDP)
Managing client-server interactions
Common Use Cases
Web servers and APIs
Chat applications
Multiplayer games
IoT device communication
File transfer services
Key Concepts in Network Programming
IP Address: Identifies a device on a network
Port: Endpoint for communication on a device
Client-Server Model: One device requests (client), another responds (server)
Protocols: Rules for data exchange (TCP, UDP, HTTP, FTP, etc.)
Sockets: Programming interface for network communication
Popular Languages for Network Programming
Python: Great for rapid prototyping and learning (socket, asyncio, Flask)
JavaScript/Node.js: Ideal for real-time apps (Express, WebSockets)
Java: Enterprise-grade networking (ServerSocket, RMI)
C/C++: Low-level networking with high performance (raw sockets)
Go: Fast and efficient concurrency (net/http, goroutines)
1. Creating a Simple Server in Python
import socket server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) server.bind(('localhost', 8080)) server.listen(1) print("Waiting for a connection...") conn, addr = server.accept() print(f"Connected to {addr}") conn.send(b"Hello from the server!") conn.close()
2. Making a Request (Client Side)
import socket client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) client.connect(('localhost', 8080)) message = client.recv(1024) print("Received:", message.decode()) client.close()
3. RESTful API with Node.js
// Install Express first: npm install express const express = require('express'); const app = express(); app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Hello from Node server!')); app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on port 3000'));
4. Real-Time Communication with WebSockets
Use WebSockets for two-way communication:
Socket.io (Node.js)
ws library (JavaScript)
WebSocket library (Python)
5. Network Security Basics
Use HTTPS to encrypt web traffic
Sanitize inputs to avoid injection attacks
Use authentication tokens or API keys
Implement firewalls and access control
6. Tools and Protocol Analyzers
Wireshark: Analyze network packets
Postman: Test HTTP APIs
Netcat: Debug and scan ports
Ping/traceroute: Diagnose connectivity
Conclusion
Server and network programming are crucial for building scalable, efficient, and connected applications. Whether you're interested in building a simple REST API or a real-time multiplayer game, a strong grasp of networking concepts will take your skills to the next level.
0 notes