#urban farming
Text
As urban populations boom, urban agriculture is increasingly looked to as a local food source and a way to help combat inequitable food access. But little is known about how productive urban agriculture is compared to conventional, rural farming. A new study digs in, finding urban gardeners and hydroponics can meet and sometimes exceed the yields of rural farms.
“Despite its growing popularity, there’s still quite a lot we don’t know about urban agriculture, like whether the yields are similar to conventional agriculture, or even what crops are commonly grown,” says Florian Payen, an environmental scientist at Lancaster University and lead author of the study, published today in AGU’s journal Earth’s Future.
The new study compiles studies on urban agriculture from 53 countries to find out which crops grow well in cities, what growing methods are most effective, and what spaces can be utilized for growing. The researchers find that urban yields for some crops, like cucumbers, tubers and lettuces, are two to four times higher than conventional farming. Many other urban crops studied are produced at similar or higher rates than in rural settings. Cost efficiency remains an open but important question.
Most studies on urban agriculture have focused on green spaces, such as private and community gardens, parks and field growing operations. Payen’s work includes “gray” spaces — places in cities that are already built but could be used for growing, such as rooftops and building facades. In both green and gray spaces, the study examines a suite of crops grown in soils versus hydroponics, horizontal versus vertical farming, and natural versus controlled conditions.
“Surprisingly, there were few differences between overall yields in indoor spaces and outdoor green spaces, but there were clear differences in the suitability of crop types to different gray spaces,” Payen says. Certain crops like lettuces, kale and broccoli are more naturally suited to be grown vertically in indoor spaces than others. “You can’t exactly stack up apple trees in a five- or ten-layer high growth chamber,” he says, “though we did find one study that managed to grow wheat stacked up like that.”
Other crops, like watery vegetables (e.g., tomatoes) and leafy greens, performed well in hydroponic environments. And crops grown in fully controlled environments can be grown throughout the year, allowing harvests to happen more times per year than in open-air environments, which leads to higher annual yields. But scientists will need to keep studying these systems to plan cost-effective agriculture solutions.
The finding that urban agriculture can have similar or greater yields to conventional agriculture “is exactly what we have been waiting for in the urban agriculture research community,” says Erica Dorr, an environmental scientist at AgroParisTech who was not involved in the study.
836 notes
·
View notes
Text
Actually, I love that cottagecore has given Gen Z a word for "I want to have a big garden and cook my own food and keep chickens" that isn't casually invoking colonialism and manifest destiny. I get so goddamned uncomfortable every time someone refers to their urban hobby farm as a "homestead" and I'm glad to finally see it being replaced with other terms. I will buy a million books about how to live a cottagecore lifestyle if it will convince publishers to stop marketing the "homesteader" lifestyle and will get white city dwellers to stop unironically self-identifying as colonizers.
#like??? words mean things#anyway#kill the cringe#cottagecore#cottage vibes#cottage life#slow living#slow life#simple living#homesteading#urban farming#hobby farm#solarpunk#gardening#self sufficiency#farmcore#mine
848 notes
·
View notes
Photo
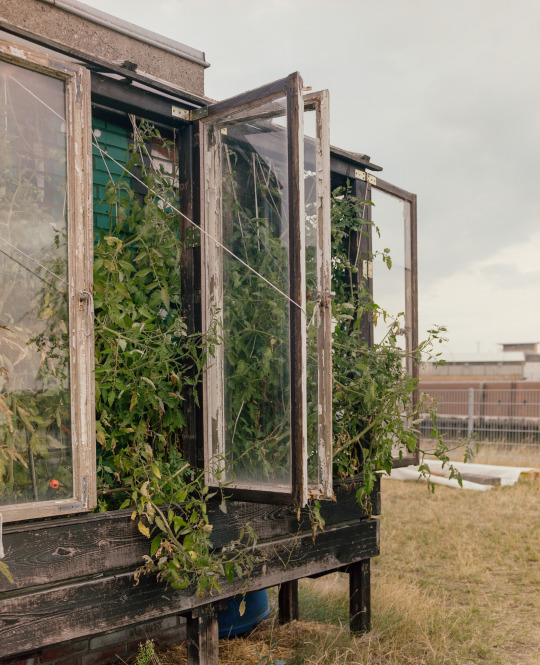
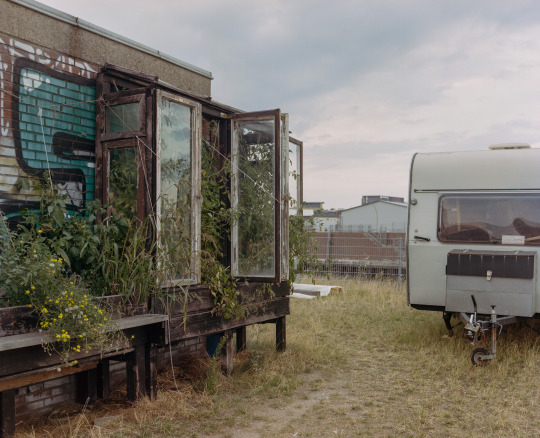



urban gardening project, Hamburg
Mamiya RZ67 / Kodak Portra 160
#film camera#film photography#color film#kodak portra 160#kodakfilm#hamburg#urbanjungle#urban gardening#gardening#medium format#lensblr#documentary photography#analog photography#film#healthy#urban farming#vintage
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
There are illegal chickens??
It is illegal to keep a vegetable garden and chickens in a lot of places in America
278 notes
·
View notes
Text
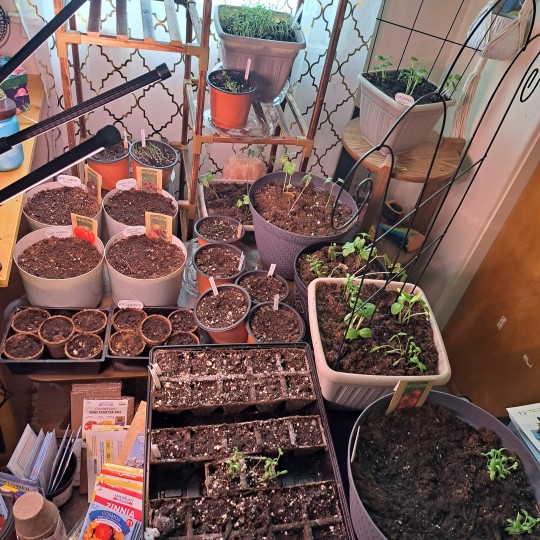
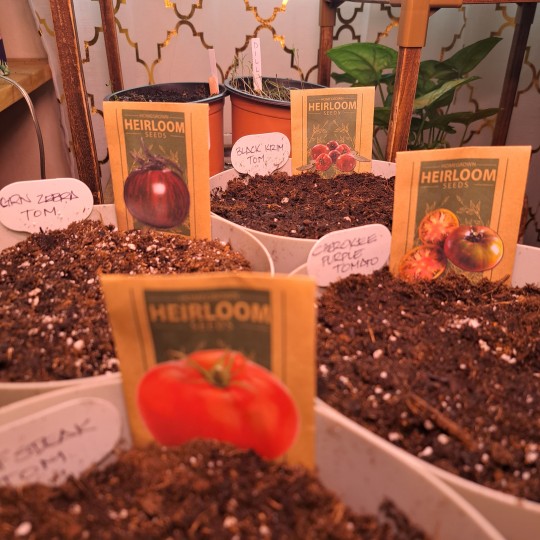
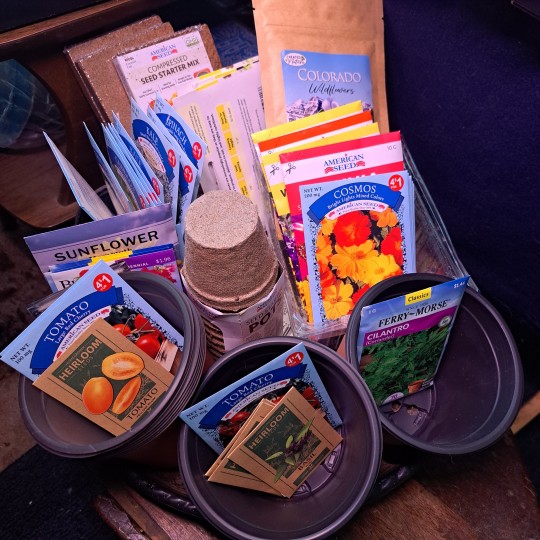





Ooooookaaaay Round 2! Transplanted all.of those morning glories that shot up into bigger pots.
Distributed Marigolds into Basil and tomato pots.
Got 8 cucumber shoots transplanted into their own pots.
Planted Hollyhock seeds and a varying variety of different tomato plants.
My craft room is over flowing!! I can't wait to get the greenhouse back up. Hopefully it will be done by April 15th!
#urban gardening#gardeners on tumblr#container gardening#urban farming#green thumb#gardenblr#cottagecore#greenblr#cottageblr#self sustainability#hollyhock#tomato plant#basil#dill#cilantro#marigolds#native wildflowers
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Good afternoon everyone~
It's cold, windy and it's been raining on and off all day but I finally got out to harvesting the sweet potatoes.
I started with the 'L' bed.

This is the bowl I'll be using to collect the spuds for this deep raised bed.
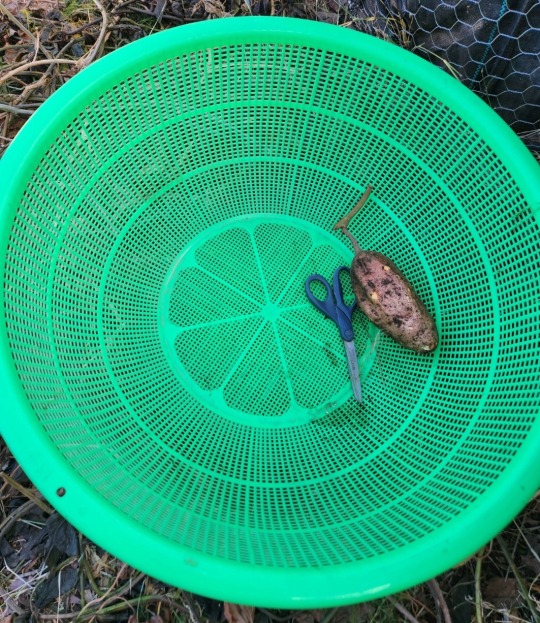

Those are full size scissors btw. This is the absolute biggest strainer I own and when I do harvesting I'm always glad to have it! Helps with carrying and washing off dirt outside so much easier!

It was pretty fun digging round for the spuds and to be honest the size and shape of some of them really suprised me!
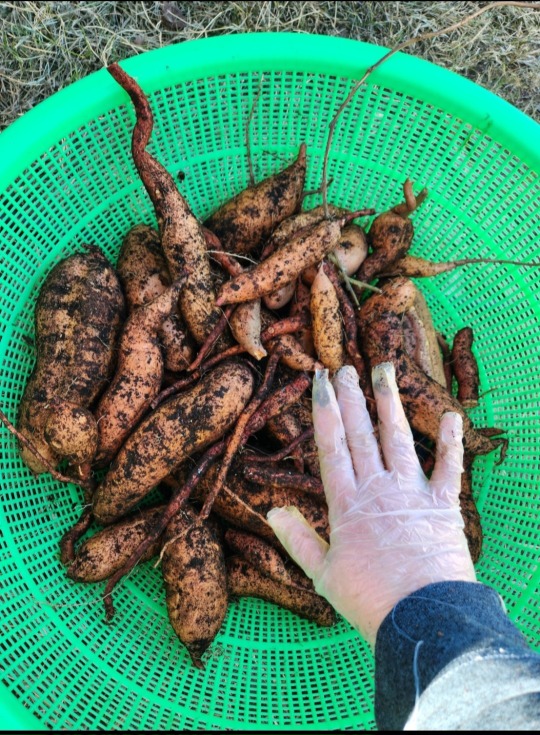

For some size comparison, my hand is right on top of them.

All cleaned out!
Next was the little round bed in the corner. I wasn't really expecting much, but it filled the bin pretty good.

I've washed the spuds off and am letting them dry off but I'll be finding a spot inside soemwhere to let them sit and cure for a bit of time. (I probably will let them cure until end of febuary.)
Curing your sweet potatoes is what makes them sweet, you can eat them right away but their said to be bitter. (I will be trying 1 potato to see if this is true!) Curing them should be done for at least 2 week in a cool dry space (around 80*f). If you under 80*f space add 7 more days.
I thought this was neat and wanted to share it. since I've not seen a sweet potato grown or dug up before

I wasn't expecting so much differance in spud size from one single root.
And one last pic,
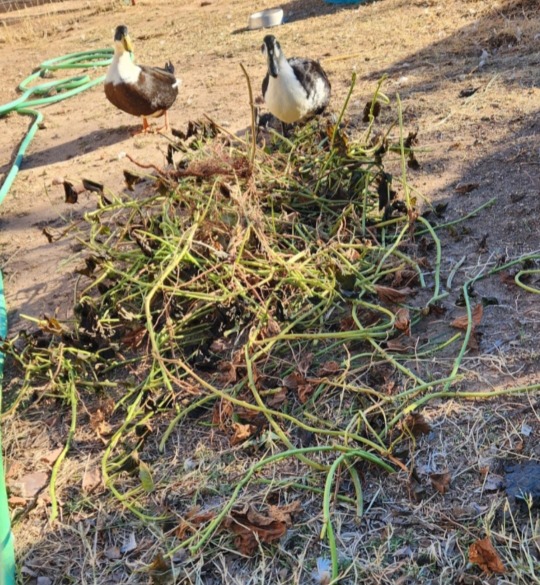

The ducks quite like the greens, while there's not much left of it I'm going to leave the vines a couple days so they can use it as enrichment/snack opportunity.
Weigh in on the spuds later!
🍠🌱Happy Homesteading and Harvesting!!
🌱🍠
1.11.2024
#self sufficient living#homesteading#thestudentfarmer#studentfarmer#self sufficiency#food#garden#gardening#low waste#duck#sustainability#smalls scale differences#urban animal keeping#urban biodiversity#urban homesteading#urban gardening#urban farming#grow what you can#simple plants to grow#multipurpose crops#right to grow#human right to clean food#right to grow food#raised garden beds#start to finish#will it grow?#food sovereignty#whole foods#first time growing#going green as can be
59 notes
·
View notes
Text

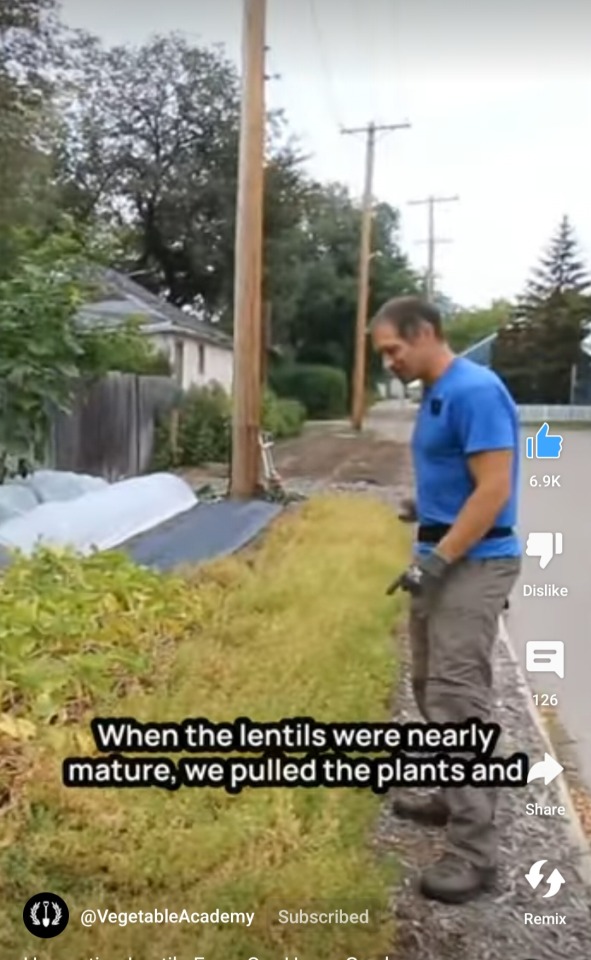
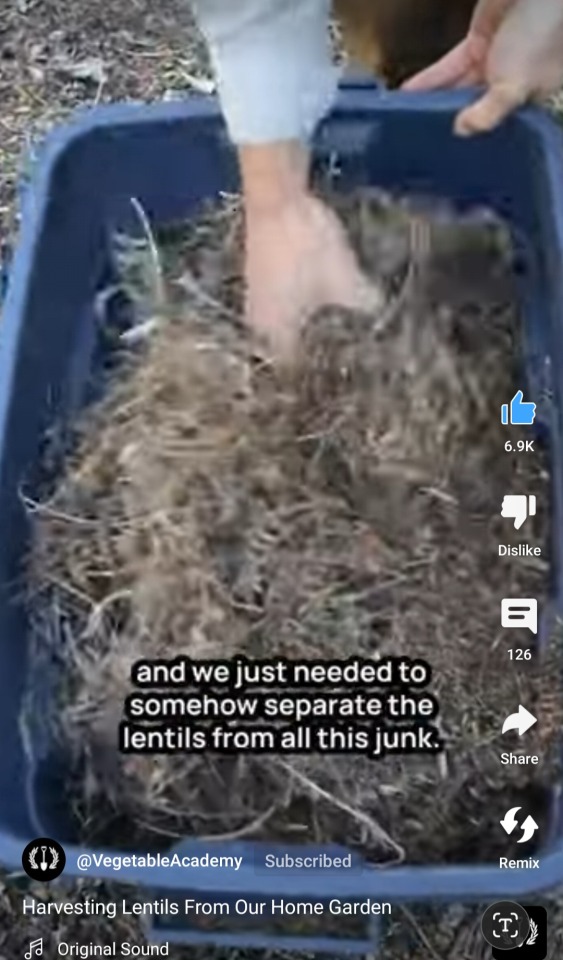





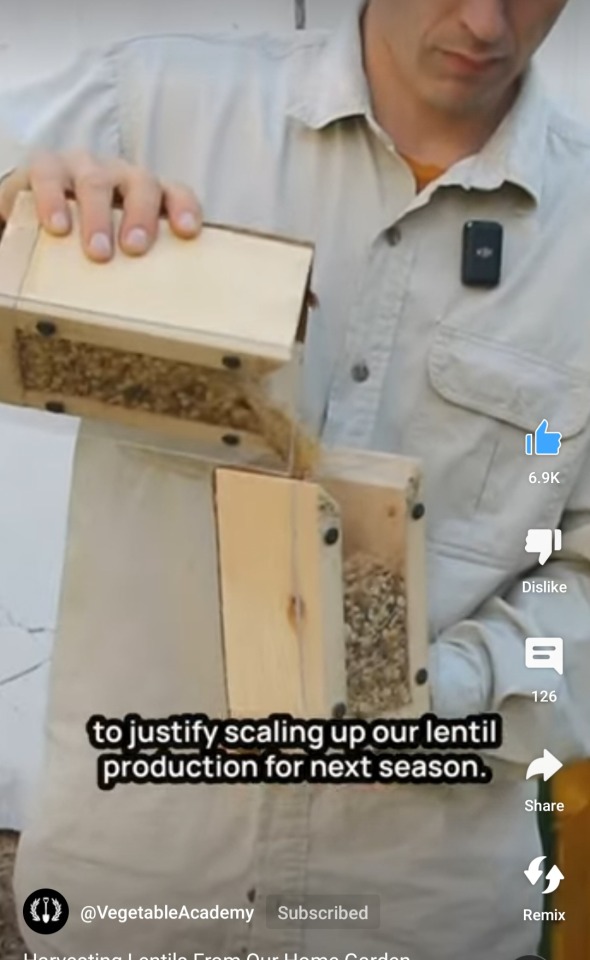
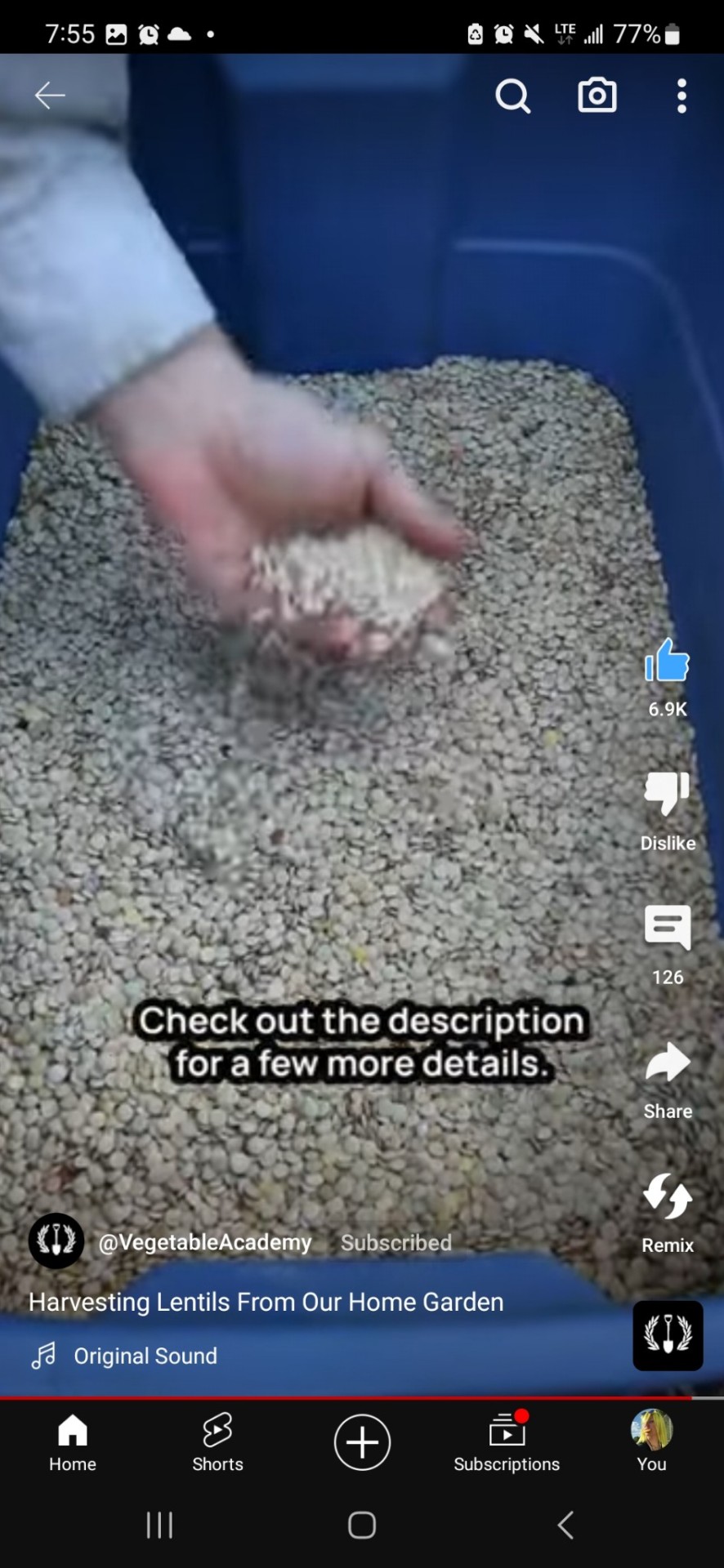
#permaculture#solarpunk#functional supply chains#garden hacks#protein farming#urban farming#green technology
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

Shoppe Black’s Ultimate List of Black Owned Farms and Food Gardens🥦🥬
#shoppe black#gardening#herbs#reading#container gardening#black farmers#black gardeners#garden resources#urban farming#horticulture#permaculture#black owned farms#rootwork
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
"In Washington D.C., a sophisticated sewage treatment plant is turning the capital’s waste into a form of capital: living capital that is fertilizing the gardens of farms of the Mid-Atlantic region and saving vast quantities of resources.
Described by the workers’ there as a “resource recovery plant,” D.C. Water run a biogas plant and high-quality fertilizer production in the course of their dirty duty to ensure the city’s waste finds a safe endpoint.
The nation’s capital is exceptional at producing waste from the toilet bowls of the 2.2 million people who live, work, and commute through the city and its suburbs.
Reporting by Lina Zeldovich reveals that rather than trucking it all to a landfill, D.C. Water extract an awful lot of value from the capital crap, by looking at it as a resource to send through the world’s largest advanced wastewater treatment plant, which uses a “thermal hydrolysis process” in which it is sterilized, broken down, and shipped off for processing into “Bloom,” a nitrogen-rich, slow-release fertilizer product.
The other “Black Gold”
At their facility in southwest Washington, huge aeration tanks percolate the poo of everyone from tourists to the President. After it’s all fed into enormous pressure cookers where, under the gravity of six earth atmospheres and 300°F, the vast black sludge is rendered harmless.
Next this “Black Gold,” as Zeldovich described it, is pumped into massive bacterial-rich tanks where microbes breakdown large molecules like fats, proteins, and carbs into smaller components, shrinking the overall tonnage of sewage to 450 tons per day down from 1,100 at the start of the process.
This mass-micro-munching also produces methane, which when fed into an onsite turbine, generates a whopping 10 megawatts of green energy which can power 8,000 nearby homes. [Note: Natural gas (which is mostly methane) is definitely greener than coal and oil, but it still causes a significant amount of emissions and greenhouse gases.] The 450 tons of remaining waste from the D.C. feces are sent into another room where conveyor belts ring out excess fluid before feeding it through large rollers which squash it into small congregate chunks.
D.C. Water sends this to another company called Homestead Gardens for drying, aging, and packaging before it’s sold as Bloom.
“I grow everything with it, squashes, tomatoes, eggplants,” Bill Brower, one of the plant’s engineers, tells Zeldovich. “Everything grows great and tastes great,” he adds.
“And I’m not the only one who thinks so. We’ve heard from a lot of people that they’ve got the best response they’ve ever seen from the plants. Particularly with leafy greens because that nitrogen boost does well with leafy plants. And the plants seem to have fewer diseases and fewer pests around—probably because Bloom helps build healthy soils.”
While farms around the country are facing nutrient depletion in soils from over-farming, turning to synthetic fertilizers to make up the difference, introducing more such thermal hydrolysis plants could truly revolutionize the way humans look at their feces—as a way of restoring the country’s soils rather than polluting them. As Mike Rowe would say, it only takes a person who’s willing to get their hands dirty."
-via Good News Network, November 23, 2021
Note: You can buy this fertilizer yourself here!
#older news but still relevant#you can go buy this fertilizer yourself!#sewage#sanitation#fertilizer#sustainability#circular economy#sustainable agricuture#nitrogen#waste#waste management#waste disposal#good news#hope#hope posting#washington dc#dc#united states#district of columbia#urban farming#solarpunk#urban gardening#environmentalism#farming#rooftop garden#gardening#edible gardening#toilet#soil#soil quality
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
Farmer Technologie
#urban farming#Farmer Technologie#farmers#amazing#video#strange#weird#funny concept#funny tumblr#my video#omg#laugh#hilarious#funny#lol
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a conversation with Civil Eats, lead author Jason Hawes, a Ph.D. student at the University of Michigan, said this his team compiled “the largest data set that we know of” on urban farming. It included 73 urban farms, community gardens, and individual garden sites in Europe and the United States. At each of those sites, the research team worked with farmers and gardeners to collect data on the infrastructure, daily supplies used, irrigation, harvest amounts, and social goods.
That data was then used to calculate the carbon emissions embodied in the production of food at each site and those emissions were compared to carbon emissions of the same foods produced at “conventional” farms. Overall, they found greenhouse gas emissions were six times higher at the urban sites—and that’s the conclusion the study led with.
But not only is 73 a tiny number compared to the data that exists on conventional production agriculture, said Omanjana Goswami, an interdisciplinary scientist at the Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS), but lumping community gardens in with urban farms set up for commercial production and then comparing that to a rural system that has been highly tuned and financed for commercial production for centuries doesn’t make sense.
“It’s almost like comparing apples to oranges,” she said. “The community garden is not set up to maximize production.”
In fact, the sample set was heavily tilted toward community and individual gardens and away from urban farms. In New York City, for example, the only U.S. city represented, seven community gardens run by AmeriCorps were included. Brooklyn Grange’s massive rooftop farms—which on a few acres produce more than 100,000 pounds of produce for markets, wholesale buyers, CSAs, and the city’s largest convention center each year—were not.
And what the study found was that when the small group of urban farms were disaggregated from the gardens, those farms were “statistically indistinguishable from conventional farms” on emissions. Aside from one high-emission outlier, the urban farms were carbon-competitive.
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
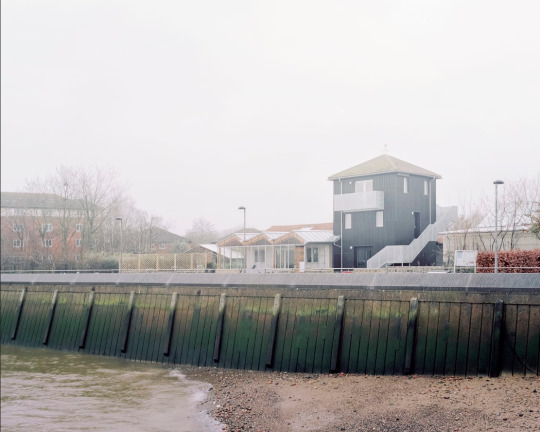
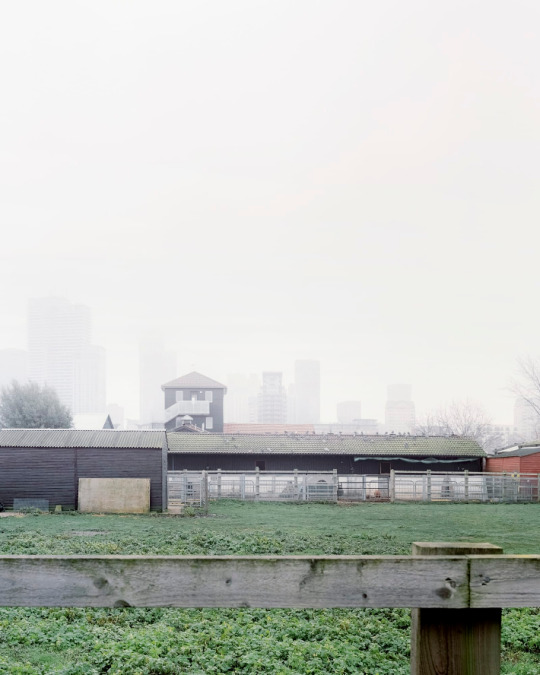
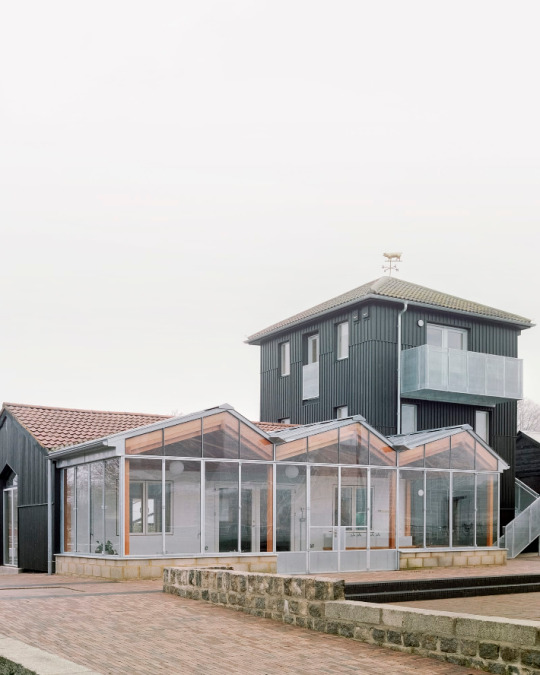
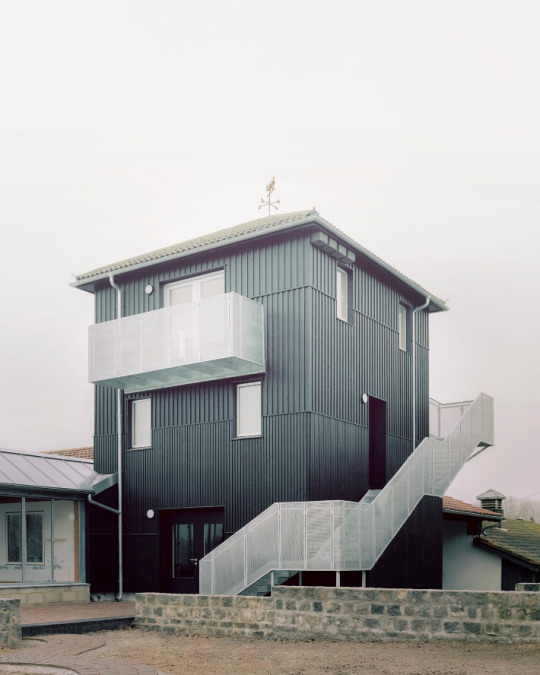
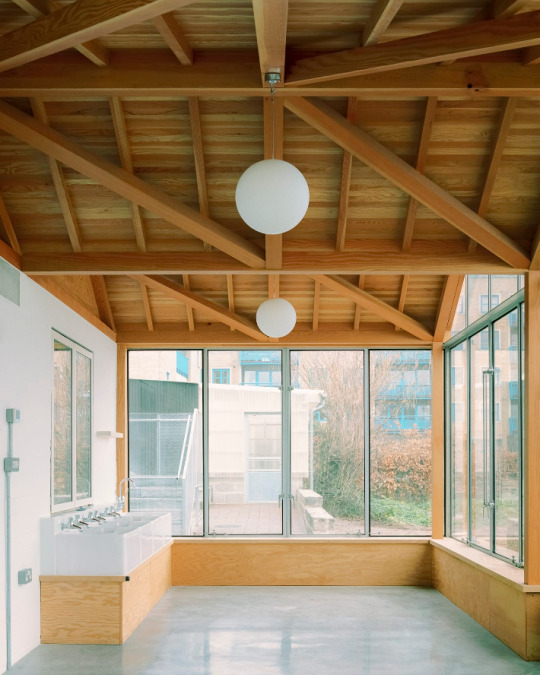
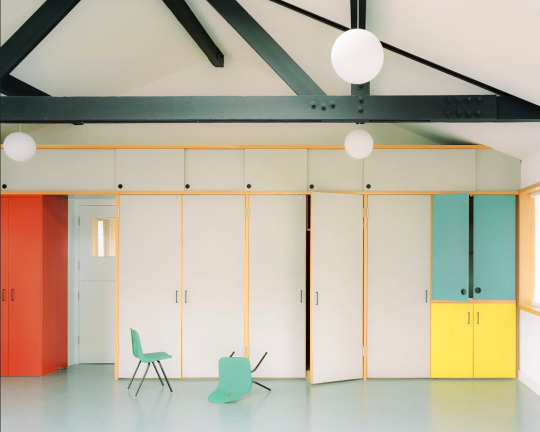
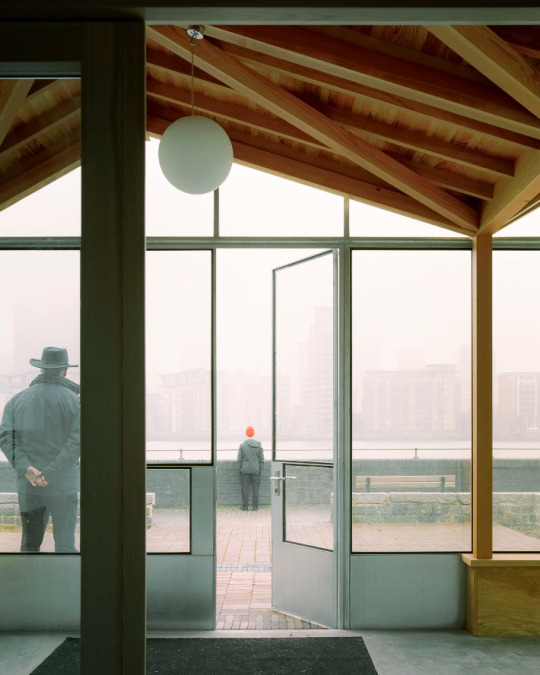







Surrey Docks Farm, London - Pup Architects
#Pup Architects#architecture#design#building#modern architecture#interiors#minimal#interior design#farm#urban farming#south london#london#river thames#fog#quayside#metal cladding#timber#beautiful design#industrial#british architecture
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Alright, I don’t post much, but I have a question for some of you out there listening. I’m gardening out of my apartment & can’t use the dirt/backyard space because of lease agreement. What is y’all’s best recommendations for a raised bed/standing bed?
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
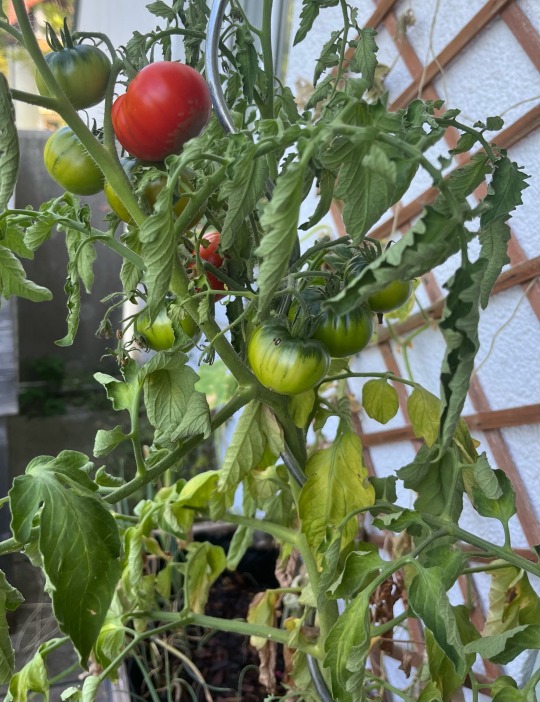
~ Welcome to the August Garden~

It is now the month of red! Look at this morning’s harvest.
My summer sown broccoli are looking so good. It’s my first attempt, so I’m very excited to see if we get any florets before the first frost.

My first cabbage is also almost ready to be harvested and the tomatoes are giving us a steady stream of fruits now. Hopefully they will keep it up well into September.


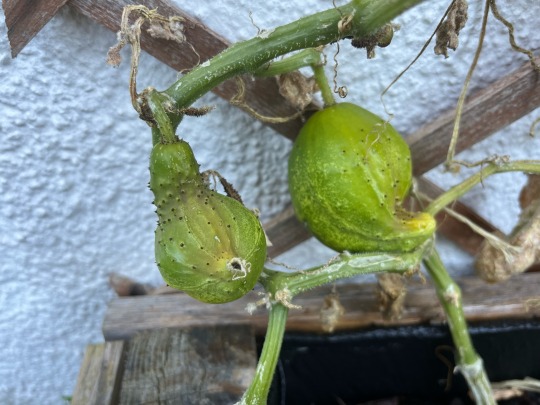
We are getting to the end of cucumber season. All that’s left of my plants are these little deformed ones, but I bet they will still be absolutely delicious!

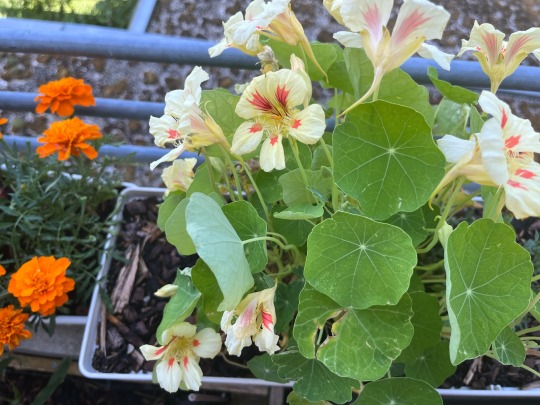
As for some color, my yellow nasturtiums have finally started blooming en masse. Next to them you can see that the marigolds are also still going strong 💪🏻

Next month will probably look a lot more bare, as our first frost date is at the beginning of October.
Until next time,
~L
#cottagecore#farmcore#balcony garden#urban farming#gardening#homesteading#vegetables#grandmacore#homestead
72 notes
·
View notes
Text

Lemon drop rooster. 🍋🐓🟨 (commissions available)🐔
#chicken#chicks#chick#chickens#poulet#poultry#poultry farming#farmers market#urban farming#fresh eggs#chicken art#chickens of tumblr#chicken painting#hens#hen#happy hens#chicken noodle soup#rooster#roosters#backyard chickens#chicken coop#pop art#contemporary art#fine art#folk art#modern art#basquiat#abstract expressionism#julian schnabel#pollo
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
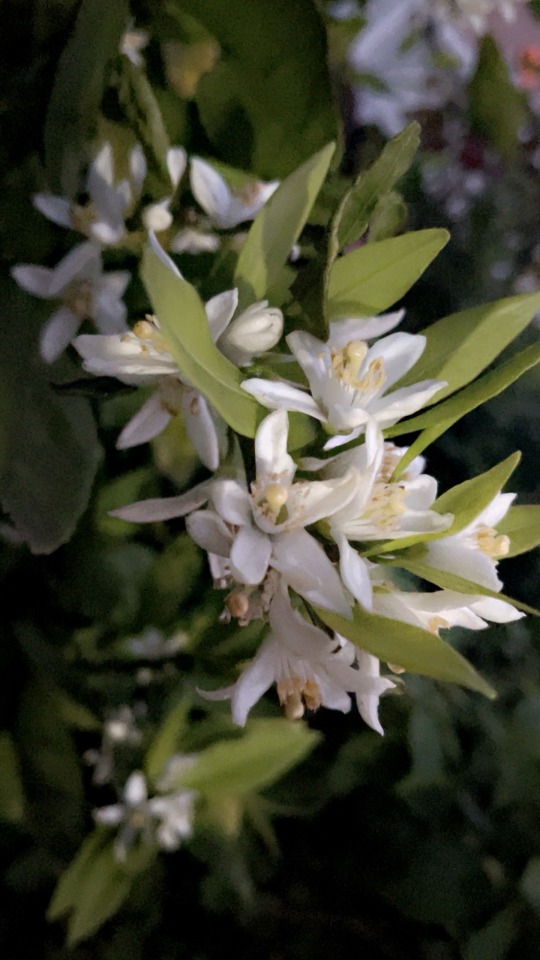

Snapped this pic at 5:30 this morning the sun is starting to rise and my orange trees are in full bloom . The scent is amazing
17 notes
·
View notes