#vLLM
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How To Use Llama 3.1 405B FP16 LLM On Google Kubernetes

How to set up and use large open models for multi-host generation AI over GKE
Access to open models is more important than ever for developers as generative AI grows rapidly due to developments in LLMs (Large Language Models). Open models are pre-trained foundational LLMs that are accessible to the general population. Data scientists, machine learning engineers, and application developers already have easy access to open models through platforms like Hugging Face, Kaggle, and Google Cloud’s Vertex AI.
How to use Llama 3.1 405B
Google is announcing today the ability to install and run open models like Llama 3.1 405B FP16 LLM over GKE (Google Kubernetes Engine), as some of these models demand robust infrastructure and deployment capabilities. With 405 billion parameters, Llama 3.1, published by Meta, shows notable gains in general knowledge, reasoning skills, and coding ability. To store and compute 405 billion parameters at FP (floating point) 16 precision, the model needs more than 750GB of GPU RAM for inference. The difficulty of deploying and serving such big models is lessened by the GKE method discussed in this article.
Customer Experience
You may locate the Llama 3.1 LLM as a Google Cloud customer by selecting the Llama 3.1 model tile in Vertex AI Model Garden.
Once the deploy button has been clicked, you can choose the Llama 3.1 405B FP16 model and select GKE.Image credit to Google Cloud
The automatically generated Kubernetes yaml and comprehensive deployment and serving instructions for Llama 3.1 405B FP16 are available on this page.
Deployment and servicing multiple hosts
Llama 3.1 405B FP16 LLM has significant deployment and service problems and demands over 750 GB of GPU memory. The total memory needs are influenced by a number of parameters, including the memory used by model weights, longer sequence length support, and KV (Key-Value) cache storage. Eight H100 Nvidia GPUs with 80 GB of HBM (High-Bandwidth Memory) apiece make up the A3 virtual machines, which are currently the most potent GPU option available on the Google Cloud platform. The only practical way to provide LLMs such as the FP16 Llama 3.1 405B model is to install and serve them across several hosts. To deploy over GKE, Google employs LeaderWorkerSet with Ray and vLLM.
LeaderWorkerSet
A deployment API called LeaderWorkerSet (LWS) was created especially to meet the workload demands of multi-host inference. It makes it easier to shard and run the model across numerous devices on numerous nodes. Built as a Kubernetes deployment API, LWS is compatible with both GPUs and TPUs and is independent of accelerators and the cloud. As shown here, LWS uses the upstream StatefulSet API as its core building piece.
A collection of pods is controlled as a single unit under the LWS architecture. Every pod in this group is given a distinct index between 0 and n-1, with the pod with number 0 being identified as the group leader. Every pod that is part of the group is created simultaneously and has the same lifecycle. At the group level, LWS makes rollout and rolling upgrades easier. For rolling updates, scaling, and mapping to a certain topology for placement, each group is treated as a single unit.
Each group’s upgrade procedure is carried out as a single, cohesive entity, guaranteeing that every pod in the group receives an update at the same time. While topology-aware placement is optional, it is acceptable for all pods in the same group to co-locate in the same topology. With optional all-or-nothing restart support, the group is also handled as a single entity when addressing failures. When enabled, if one pod in the group fails or if one container within any of the pods is restarted, all of the pods in the group will be recreated.
In the LWS framework, a group including a single leader and a group of workers is referred to as a replica. Two templates are supported by LWS: one for the workers and one for the leader. By offering a scale endpoint for HPA, LWS makes it possible to dynamically scale the number of replicas.
Deploying multiple hosts using vLLM and LWS
vLLM is a well-known open source model server that uses pipeline and tensor parallelism to provide multi-node multi-GPU inference. Using Megatron-LM’s tensor parallel technique, vLLM facilitates distributed tensor parallelism. With Ray for multi-node inferencing, vLLM controls the distributed runtime for pipeline parallelism.
By dividing the model horizontally across several GPUs, tensor parallelism makes the tensor parallel size equal to the number of GPUs at each node. It is crucial to remember that this method requires quick network connectivity between the GPUs.
However, pipeline parallelism does not require continuous connection between GPUs and divides the model vertically per layer. This usually equates to the quantity of nodes used for multi-host serving.
In order to support the complete Llama 3.1 405B FP16 paradigm, several parallelism techniques must be combined. To meet the model’s 750 GB memory requirement, two A3 nodes with eight H100 GPUs each will have a combined memory capacity of 1280 GB. Along with supporting lengthy context lengths, this setup will supply the buffer memory required for the key-value (KV) cache. The pipeline parallel size is set to two for this LWS deployment, while the tensor parallel size is set to eight.
In brief
We discussed in this blog how LWS provides you with the necessary features for multi-host serving. This method maximizes price-to-performance ratios and can also be used with smaller models, such as the Llama 3.1 405B FP8, on more affordable devices. Check out its Github to learn more and make direct contributions to LWS, which is open-sourced and has a vibrant community.
You can visit Vertex AI Model Garden to deploy and serve open models via managed Vertex AI backends or GKE DIY (Do It Yourself) clusters, as the Google Cloud Platform assists clients in embracing a gen AI workload. Multi-host deployment and serving is one example of how it aims to provide a flawless customer experience.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#Llama3.1#Llama#LLM#GoogleKubernetes#GKE#405BFP16LLM#AI#GPU#vLLM#LWS#News#Technews#Technology#Technologynews#Technologytrends#govindhtech
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I tried running the hot new small 32B-parameter reasoning model QwQ locally, and it's still just a bit too big for my rig to handle - using Ollama (whose backend is llama.cpp), it flooded my VRAM and a fair chunk of my RAM, and ended up generating at about 1 token/s (roughly, not measured), but unfortunately my mouse was also moving at about 1fps at the same time - though maybe whatever microsoft did to the task manager is the real culprit here since it surprisingly cleared up after a bit. in any case, I looked into VLLM, which is the qwen team's recommended server for inference, but it doesn't play nice on windows, so it will have to wait until I can get it running on Linux, or maybe get WSL up and running.
anyway, prompting it with a logic puzzle suggested by a friend -
I have three eggs. I eat one. One hatches into a chicken. The chicken lays an egg. How many eggs do I have?
led to it generating a seemingly infinitely long chain of thought as it kept going round and round nuances of the problem like whether you own a chicken that hatches from your egg. I decided to cut it off rather than let it terminate. here's a sample though.
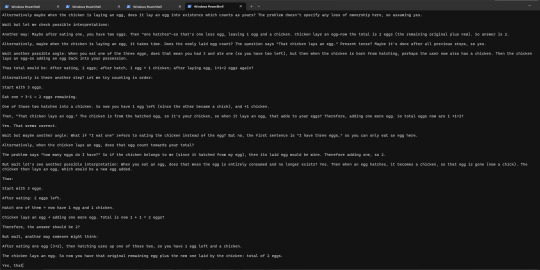
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
如何快速部署 LLM 模型到 GPU 主機?從環境建置到服務啟動
GPU 主機 – 隨著 ChatGPT、LLaMA、DeepSeek 等大型語言模型(LLM)廣泛應用,越來越多企業與開發者希望將 LLM 模型自建於本地或 GPU 實體主機上。這樣不僅能取得更高的資料控制權,避免私密資訊外洩,也能有效降低長期使用成本,並規避商業 API 在頻率、使用量、功能上的限制與資安疑慮。
然而,部署 LLM 模型的第一道門檻往往是環境建置。從 CUDA 驅動的版本對應、PyTorch 的安裝,到 HuggingFace 模型快取與推論引擎選型,都是需要考量的技術細節。如果沒有明確指引,往往容易在初期階段耗費大量時間摸索。
這篇文章將以平易近人的方式,帶你從挑選 GPU 主機開始,逐步說明環境建置、部署流程、模型上線、API 串接、容器化管理與後續運維建議,協助你成功將 LLM 模型部署到實體主機,快速打造自己的本地 AI 推論平台。
#AI Server#AI 主機#AI 伺服器#AI主機租用#DeepSeek#GPT#GPU Server#GPU 主機#GPU 主機租用#GPU 伺服器#LLaMA#OpenAI#PyTorch#實體主機
0 notes
Text
Life of an inference request (vLLM V1): How LLMs are served efficiently at scale
https://www.ubicloud.com/blog/life-of-an-inference-request-vllm-v1
0 notes
Text

NANO-VLLM is a lightweight, high-speed inference engine designed to run large language models efficiently on resource-constrained devices. Perfect for edge AI and on-the-go machine learning magic
#NANOVLLM#AI#MachineLearning#LLM#nanovllm#vllmnano#lightweightllm#fastllminference#nanolanguagemodel#efficientllm#nanovllmdeployment#edgellmmodel#opensourcenanollm#lowlatencyllm#vllmoptimization#nanovllmtutorial#runllmonedge#vllmvsnanovllm#compactllmmodel#ailatestupdate#ainews#Latestaiupdate#latestaitrends#DeepSeekVsOpenAI
0 notes
Link
The DeepSeek Researchers just released a super cool personal project named ‘nano-vLLM‘, a minimalistic and efficient implementation of the vLLM (virtual Large Language Model) engine, designed specifically for users who value simplicity, speed, and t #AI #ML #Automation
0 notes
Photo

Exciting news for AI enthusiasts and tech innovators! AMD has just announced ROCm 7, a game-changing software update focused on boosting inference performance by up to 3.5x. With support for MI350 series, new algorithms, and advanced features, AMD is leading the charge in AI acceleration. This upgrade enhances frameworks like vLLM, llm-d, and SGLang, optimizing distributed inference and multi-precision support, including FP8 and FP6. The focus on inference means faster, more efficient AI workloads—perfect for data centers, machine learning, and deep learning projects. AMD’s ROCm 7 also outperforms NVIDIA CUDA in throughput, promising a competitive edge for AI developers. Are you ready to upgrade your AI infrastructure? Discover how a custom computer build from GroovyComputers.ca can maximize these cutting-edge features and elevate your performance. Don't miss out—stay ahead in AI tech innovation! What’s your biggest AI project right now? Share below! 🚀 #AI #MachineLearning #DeepLearning #AIHardware #CustomComputerBuilds #TechInnovation #DataScience #AIaccelerator #ROCm #NVIDIAvsAMD #AIinference #GroovyComputers Visit https://groovycomputers.ca for your customized computer build today!
0 notes
Photo

Exciting news for AI enthusiasts and tech innovators! AMD has just announced ROCm 7, a game-changing software update focused on boosting inference performance by up to 3.5x. With support for MI350 series, new algorithms, and advanced features, AMD is leading the charge in AI acceleration. This upgrade enhances frameworks like vLLM, llm-d, and SGLang, optimizing distributed inference and multi-precision support, including FP8 and FP6. The focus on inference means faster, more efficient AI workloads—perfect for data centers, machine learning, and deep learning projects. AMD’s ROCm 7 also outperforms NVIDIA CUDA in throughput, promising a competitive edge for AI developers. Are you ready to upgrade your AI infrastructure? Discover how a custom computer build from GroovyComputers.ca can maximize these cutting-edge features and elevate your performance. Don't miss out—stay ahead in AI tech innovation! What’s your biggest AI project right now? Share below! 🚀 #AI #MachineLearning #DeepLearning #AIHardware #CustomComputerBuilds #TechInnovation #DataScience #AIaccelerator #ROCm #NVIDIAvsAMD #AIinference #GroovyComputers Visit https://groovycomputers.ca for your customized computer build today!
0 notes
Photo

Exploring the Open Source AI Compute Tech Stack: Kubernetes, Ray, PyTorch, and vLLM
0 notes
Text
Red Hat AI Inference Server umożliwia działanie generatywnej sztucznej inteligencji w dowolnym modelu i dowolnym akceleratorze w chmurze hybrydowej
Dzięki modelowi vLLM oraz technologiom Neural Magic, Red Hat AI Inference Server zapewnia szybsze, wydajniejsze i bardziej opłacalne mechanizmy wnioskowania sztucznej inteligencji w chmurze hybrydowej. https://linuxiarze.pl/red-hat-ai-inference-server-umozliwia-dzialanie-generatywnej-sztucznej-inteligencji-w-dowolnym-modelu-i-dowolnym-akceleratorze-w-chmurze-hybrydowej/

0 notes
Text
PyTorch/XLA 2.5: vLLM Support And Developer Improvements

PyTorch/XLA 2.5
PyTorch/XLA 2.5: enhanced development experience and support for vLLM
PyTorch/XLA, a Python package that connects the PyTorch deep learning framework with Cloud TPUs via the XLA deep learning compiler, has machine learning engineers enthusiastic. Additionally, PyTorch/XLA 2.5 has arrived with a number of enhancements to improve the developer experience and add support for vLLM. This release’s features include:
An explanation of the plan to replace the outdated torch_xla API with the current PyTorch API, which would simplify the development process. The transfer of the current Distributed API serves as an illustration of this.
A number of enhancements to the torch_xla.compile function that enhance developers’ debugging experience when they are working on a project.
You can expand your current deployments and use the same vLLM interface across all of your TPUs thanks to experimental support in vLLM for TPUs.
Let’s examine each of these improvements.
Streamlining torch_xla API
Google Cloud is making a big stride toward improving the consistency of the API with upstream PyTorch with PyTorch/XLA 2.5. Its goal is to make XLA devices easier to use by reducing the learning curve for developers who are already familiar with PyTorch. When feasible, this entails phasing out and deprecating proprietary PyTorch/XLA API calls in favor of more sophisticated functionality, then switching the API calls to their PyTorch equivalents. Before the migration, several features were still included in the current Python module.
It has switched to using some of the existing PyTorch distributed API functions when running models on top of PyTorch/XLA in this release to make the development process for PyTorch/XLA easier. In this release, it moved the majority of the calls for the distributed API from the torch_xla module to torch.distributed.
With PyTorch/XLA 2.4
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm xm.all_reduce()
Supported after PyTorch/XLA 2.5
torch.distrbuted.all_reduce()
A better version of “torch_xla.compile”
To assist you in debugging or identifying possible problems in your model code, it also includes a few new compilation features. For instance, when there are many compilation graphs, the “full_graph” mode generates an error message. This aids in the early detection (during compilation) of possible problems brought on by various compilation graphs.
You may now also indicate how many recompilations you anticipate for compiled functions. This can assist you in troubleshooting performance issues if a function may be recompiled more frequently than necessary, such as when it exhibits unexpected dynamism.
Additionally, you can now give compiled functions a meaningful name rather than one that is generated automatically. When debugging messages, naming compiled targets gives you additional context, which makes it simpler to identify the potential issue. Here’s an illustration of how that actually appears in practice:
named code
@torch_xla.compile def dummy_cos_sin_decored(self, tensor): return torch.cos(torch.sin(tensor))
target dumped HLO renamed with named code function name
… module_0021.SyncTensorsGraph.4.hlo_module_config.txt module_0021.SyncTensorsGraph.4.target_arguments.txt module_0021.SyncTensorsGraph.4.tpu_comp_env.txt module_0024.dummy_cos_sin_decored.5.before_optimizations.txt module_0024.dummy_cos_sin_decored.5.execution_options.txt module_0024.dummy_cos_sin_decored.5.flagfile module_0024.dummy_cos_sin_decored.5.hlo_module_config.txt module_0024.dummy_cos_sin_decored.5.target_arguments.txt module_0024.dummy_cos_sin_decored.5.tpu_comp_env.txt …
You can observe the difference between the original and named outputs from the same file by looking at the output above. The automatically produced name is “SyncTensorsGraph.” The renamed file associated with the preceding tiny code example is shown below.
vLLM on TPU (testing)
You can now use TPU as a backend if you serve models on GPUs using vLLM. A memory-efficient and high-throughput inference and serving engine for LLMs is called vLLM. To make model testing on TPU easier, vLLM on TPU maintains the same vLLM interface that developers adore, including direct integration into Hugging Face Model Hub.
It only takes a few configuration adjustments to switch your vLLM endpoint to TPU. Everything is unchanged except for the TPU image: the model source code, load balancing, autoscaling metrics, and the request payload. Refer to the installation guide for further information.
Pallas kernels like paged attention, flash attention, and dynamo bridge speed optimizations are among the other vLLM capabilities it has added to TPU. These are all now included in the PyTorch/XLA repository (code). Although PyTorch TPU users may now access vLLM, this work is still in progress, and it anticipate adding more functionality and improvements in upcoming releases.
Use PyTorch/XLA 2.5
Downloading the most recent version via your Python package manager will allow you to begin utilizing these new capabilities. For installation instructions and more thorough information, see the project’s GitHub page if you’ve never heard of PyTorch/XLA before.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#PyTorch#XLA#PytorchXLA#vLLM#Google#TPUs#Govindhtech#news#technews#technology#technologytrends#technologynews#googlecloud#ai
0 notes
Text
INTELLECT-2: A Large-Scale Language Model Trained with Distributed Resources
INTELLECT-2 represents a significant advancement in large language models, distinguishing itself by its use of a distributed architecture and training focused on mathematics and programming. Key Points: 32 billion parameter language model with distributed training. Use of unauthorized global GPU resources via the prime-rl framework. Optimization for mathematics and programming tasks with verifiable rewards. Compatibility with popular inference libraries such as vllm and sglang. INTELLECT-2 stands out in the landscape of advanced language models for its 32 billion parameter... read more: https://www.turtlesai.com/en/pages-2813/intellect-2-a-large-scale-language-model-trained-with
0 notes
Text
VLLM Docker: Fast LLM Containers Made Easy
Learn how to deploy large language models (LLMs) efficiently with VLLM Docker. This guide covers setup, optimization, and best practices for fast, scalable LLM inference in containers. #centlinux #linux #docker #openai

0 notes
Text
Nano-Vllm: lightweight vLLM implementation built from scratch
https://github.com/GeeeekExplorer/nano-vllm
0 notes
Text

A Red Hat acaba de lançar novas atualizações no Red Hat AI, seu portfólio de produtos e serviços projetados para acelerar o desenvolvimento e a implantação de soluções de IA na nuvem híbrida. O Red Hat AI oferece uma plataforma de IA empresarial para treinamento de modelos e inferência, proporcionando mais experiência, flexibilidade e uma experiência simplificada para implantar sistemas em qualquer lugar na nuvem híbrida. Na busca por reduzir os custos de implementação de grandes modelos de linguagem (LLMS) para atender a um número crescente de casos de uso, empresas ainda enfrentam o desafio de integrar esses sistemas com seus dados proprietários e acessá-los de qualquer lugar: seja em um datacenter, na nuvem pública ou até mesmo na edge. Integrando tanto o Red Hat OpenShift AI como o Red Hat Enterprise Linux AI (RHEL AI), o Red Hat AI responde a essas preocupações ao fornecer uma plataforma de IA empresarial que permite adotar modelos mais eficientes e otimizados, ajustados com os dados específicos do negócio, com possibilidade de serem implantados na nuvem híbrida para treinar modelos em uma ampla gama de arquiteturas de computação. Para Joe Fernandes, vice-presidente e gerente geral de Unidade de Negócios de IA de Red Hat, a atualização possibilita que organizações serem precisas e econômicas em suas jornadas de IA. "A Red Hat sabe que as empresas vão precisar de maneiras para gerenciar o custo crescente de suas implantações de IA generativa, à medida que trazem mais casos de uso para produção e operam em escala.. O Red Hat AI auxilia as organizações a endereçarem esses desafios, permitindo que elas disponham de modelos mais eficientes, desenvolvidos para um propósito, treinados com seus dados e que possibilitam inferência flexível em ambientes on-premises, de nuvem e na edge." Red Hat OpenShift AI O Red Hat OpenShift AI oferece uma plataforma completa de IA para gerenciar os ciclos de vida de IA preditiva e generativa (gen AI) na nuvem híbrida, incluindo operações de aprendizado de máquina (MLOps) e capacidades de Large Language Model Operations (LLMOps). A plataforma fornece funcionalidades para construir modelos preditivos e ajustar modelos gen AI, juntamente com ferramentas para simplificar o gerenciamento de modelos de IA, desde pipelines de ciência de dados e modelos até o monitoramento de modelos, governança e muito mais. Versão mais recente da plataforma, o Red Hat OpenShift AI 2.18, adiciona novas atualizações e capacidades para apoiar o objetivo do Red Hat AI de trazer modelos de IA mais otimizados e eficientes para a nuvem híbrida. Os principais recursos incluem: ● Serviço distribuído: disponível por meio do servidor de inferência vLLM, o serviço distribuído permite que as equipes de TI dividam o serviço de modelos entre várias unidades de processamento gráfico (GPUs). Isso ajuda a aliviar a carga em um único servidor, acelera o treinamento e o ajuste-fino e promove o uso mais eficiente dos recursos de computação, ao mesmo tempo em que ajuda a distribuir os serviços entre os nós para os modelos de IA. ● Experiência de ajuste de modelo de ponta a ponta: usando o InstructLab e os pipelines de ciência de dados do Red Hat OpenShift AI, esse novo recurso ajuda a simplificar o ajuste fino dos LLMs, tornando-os mais escaláveis, eficientes e auditáveis em grandes ambientes de produção, ao mesmo tempo em que entrega gerenciamento por meio do painel de controle do Red Hat OpenShift AI. ● AI Guardrails: o Red Hat OpenShift AI 2.18 ajuda a melhorar a precisão, o desempenho, a latência e a transparência dos LLMs por meio de uma pré-visualização da tecnologia AI Guardrails, que monitora e protege as interações de entrada do usuário e as saídas do modelo. O AI Guardrails oferece recursos adicionais de detecção para auxiliar as equipes de TI a identificar e mitigar discursos potencialmente odiosos, abusivos ou profanos, informações pessoais identificáveis, dados de competidores ou outros restritos por políticas corporativas. ● Avaliação de modelo: usando o componente de avaliação de modelo de linguagem (lm-eval) para fornecer informações importantes sobre a qualidade geral do modelo, a avaliação de modelo permite que os cientistas de dados comparem o desempenho dos seus LLMs em várias tarefas, desde raciocínio lógico e matemático até a linguagem natural adversarial, ajudando a criar modelos de IA mais eficazes, responsivos e adaptados. RHEL AI Parte do portfólio Red Hat AI, o RHEL AI é uma plataforma de modelos fundamentais para desenvolver, testar e executar LLMs de forma mais consistente, com o objetivo de impulsionar aplicativos empresariais. O RHEL AI oferece modelos Granite LLMs e ferramentas de alinhamento de modelos InstructLab, que são pacotes em uma imagem inicializável do Red Hat Enterprise Linux e podem ser implantados na nuvem híbrida. Lançado em fevereiro de 2025, o RHEL 1.4 trouxe diversas melhorias, incluindo: ● Suporte ao modelo Granite 3.1 8B como a mais recente adição à família de modelos Granite com licença open source. O modelo adiciona suporte multilíngue para inferência e personalização de taxonomia/conhecimento (pré-visualização para desenvolvedores), além de uma janela de contexto de 128k para melhorar a adoção de resultados de sumarização e tarefas de Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) ● Nova interface gráfica do usuário para contribuir com habilidades e conhecimentos prévios, disponível no formato de pré-visualização para desenvolvedores, com o objetivo de simplificar o consumo e a fragmentação de dados, bem como permitir que usuários adicionem suas próprias habilidades e contribuições a modelos de IA. ● Document Knowledge-bench (DK-bench) para facilitar comparações entre modelos de IA ajustados com dados privados relevantes com o desempenho dos mesmos modelos base não ajustados. Red Hat AI InstructLab no IBM Cloud Cada vez mais, as empresas estão em busca de soluções de IA que priorizem a precisão e a segurança de seus dados, ao mesmo tempo em que mantêm os custos e a complexidade os mais baixos possíveis. O Red Hat AI InstructLab, disponível como um serviço no IBM Cloud, foi projetado para simplificar, escalar e ajudar a melhorar a segurança no treinamento e na implantação de sistemas de IA. Ao simplificar o ajuste de modelos do InstructLab, organizações podem construir plataformas mais eficientes, adaptadas às suas necessidades únicas, mantendo o controle de suas informações sigilosas. Treinamento gratuito sobre os Fundamentos da IA A IA é uma oportunidade transformadora que está redefinindo como as empresas operam e competem. Para apoiar organizações nesse cenário dinâmico, a Red Hat oferece treinamentos online gratuitos sobre Fundamentos de IA. A empresa está oferecendo dois certificados de aprendizado em IA, voltados tanto para líderes seniores experientes quanto para iniciantes, ajudando a educar usuários de todos os níveis sobre como a IA pode ajudar a transformar operações comerciais, agilizar a tomada de decisões e impulsionar a inovação. Disponibilidade O Red Hat OpenShift AI 2.18 e o Red Hat Enterprise Linux AI 1.4 já estão disponíveis. Mais informações sobre recursos adicionais, melhorias, correções de bugs e de como atualizar a sua versão do Red Hat OpenShift AI para a mais recente podem ser encontradas aqui, e a versão mais recente do RHEL AI pode ser encontrada aqui. O Red Hat AI InstructLab no IBM Cloud estará disponível em breve. O treinamento sobre os Fundamentos de IA da Red Hat já está disponível para clientes. Read the full article
0 notes
Link
The DeepSeek Researchers just released a super cool personal project named ‘nano-vLLM‘, a minimalistic and efficient implementation of the vLLM (virtual Large Language Model) engine, designed specifically for users who value simplicity, speed, and t #AI #ML #Automation
0 notes