#visibility monitoring semiconductor
Note
The thing about Affirmation Action - most people are actually just ok at their jobs, and aren't Einsteins or Ramanujans or whatever. If they meet the minimum requirements to be a surgeon you're not in particularly worse hands than you really otherwise would be, because the bulk are always going to be first standard deviation. It's just now you have a tool to prevent communities in your society from self segregating (because people get jobs through connections) into unstable subclasses and can collect data to actively monitor for things like the name disciminatory effect. You don't even cut off the upper deviations with this, either, it's just about your mixing of the middle 95 in attempt to prevent things like gangs other issues with insular ethnic or income based subclasses.
Allow me to introduce you to The O-Ring Theory of Economic Development.
The basic gist of that article is that a long, high-value production chain, where that high value doesn't kick in until the end, requires a high probability of success at each node in the chain.
What you just said is fine for an insurance salesman. It is not fine for semiconductor design and manufacturing, which is an input into the production of the entire rest of the economy.
The amount of disruption will depend on 1) the discrepancy of the input labor pool from the ideal equality politically demanded, 2) the magnitude of the imposed ethnic quotas, and 3) the degree to which the job requires abilities far from the average.
If we have a dial labeled 'ETHNIC QUOTAS' and we turn it to 1 or 2, people might not notice, and we may have disrupted hiring network effects. There's a natural amount of noise in hiring.
The problem is that the political economy of the EQ dial is not really based on liberal ethnic conflict management by light-touch reduction of hiring network effects. That was something that was more reasonable for a young liberal to believe in 2010, or might be more reasonable to believe in a small state under a firm hand, like Singapore.
The jobs which require the highest and most reliable capability will be among the best-compensated and the most prestigious.
The political economy of the EQ dial is based more on compensation and prestige. The most prestigious and well-compensated jobs will tend to be both the most unequally distributed, and the ones that suffer the most - for O-Ring reasons.
Political entrepreneurs (rhymes with "norm entrepreneurs") can see this and bring those discrepancies into high visibility to emotionally motivate voters, build consensus within their coalition to go after firms of this class, etc.
Now at this point, you might say, "Well, can't the firm just hire a bunch of underperforming personnel in order to meet the quota? And if it turns out that the firm underestimated their performance, then great, or if it turns out that wealth and social connections cause performance, then maybe their kids do very well, and the problem is solved in the next generation."
The problem is that this is a multiple-round game and the political entrepreneurs can change their actions on the next round.
If you officially hire someone to do aerospace engineering and then sideline him because you're actually just using him to fill a quota, this can be detected from other metrics, which political entrepreneurs can then use to argue that you're still "cheating," and demand more resources and concessions. They have you over a barrel.
If your production system depends on Einsteins, well, you can't just make someone into an Einstein. The social technology for that doesn't exist at this time, so political entrepreneurs can make as high of a demand as they want, because they've locked you into a contradiction.
The political entrepreneurs will always try to turn up the dial, because the amount of difference forms a gradient that they can use to gain power (like exploiting a difference in temperature, a thermal gradient, to drive a geothermal power plant), and you are depending on the other members of their coalition to not cooperate, to shut them up and make them go home.
If the mismatch is bad enough, and you turn the dial high enough, you can crash the production system as a shortage of some bottleneck resource causes a cascading failure.
At that point, you'll probably be replaced by someone who was less willing to turn the dial, and then you'll no longer be in control of the situation.
Liberals have been indulging the political entrepreneurs since 2014, but this is a mistake - their programs are not connected to real life success, which means they'll end up promoting conflict and poverty regardless of whatever they say their intentions are. Liberals should care about good things happening, which requires they be rooted in real reality, even if it's a bit uncomfortable.
8 notes
·
View notes
Photo
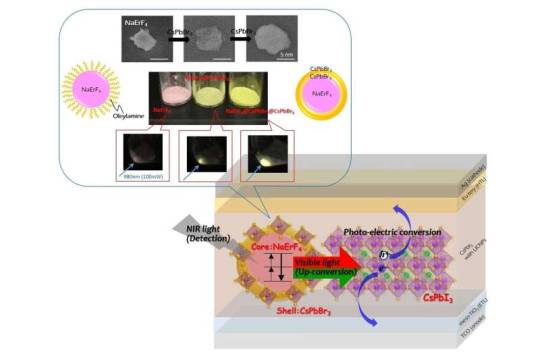
Upconverting near‐infrared light detection in lead halide perovskite with core–shell lanthanide nanoparticles
Under the JST Strategic Basic Research Program PRESTO, Associate Professor Ayumi Ishii of Teikyo University of Science with her team members has developed a new near-infrared light sensor by using a material that converts weak near-infrared light to visible light.
Near-infrared light is used in a wide range of applications on a daily basis, such as in infrared cameras (night vision cameras), infrared communication (wireless communication), optical fiber communication, remote control, and biometric authentication. The detection of weak light in the near-infrared region and improvement of sensitivity are indispensable for the advancement in optical communication technology, medical diagnosis, environmental monitoring, and other fields.
Compound semiconductors (e.g., InGaAs) having an optimal absorption band of 900–1700 nm, are used to detect light in the near-infrared region. However, these systems are expensive because of their complicated manufacturing process that involves the use of rare metals and is limited by noise interference. Moreover, such semiconductors do not exhibit visible light detection accuracy comparable to that achieved using silicon (Si) and other compounds.
Read more.
#Materials Science#Science#Perovskites#Halide perovskites#Lanthanides#Nanoparticles#Nanotechnology#Semiconductors#Core shell structures
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Improving Officer Safety and Surveillance with Low Light USB Cameras
It is more important than ever to protect law enforcement personnel while continuing to conduct efficient surveillance in today's quickly changing society. The low light USB camera is one creative option that sticks out in this endeavor. These advanced devices are revolutionizing how we approach nighttime and low-light surveillance, significantly enhancing both officer safety and operational efficiency. In this blog, we will explore how low light USB camera are making a difference and why they are becoming an essential tool in modern law enforcement.
The Role of Low Light USB Cameras in Law Enforcement
Enhanced Visibility in Low Light Conditions
Law enforcement officers often operate in challenging environments where lighting conditions can be less than ideal. Low light USB cameras are designed specifically to perform optimally in such conditions. Equipped with advanced sensor technology, these cameras can capture clear, detailed footage even in dimly lit environments. This capability is crucial for nighttime patrols, dark alleyways, and indoor surveillance where traditional cameras might struggle.
For example, the low light USB camera's enhanced sensitivity allows it to detect and record crucial details such as facial features, vehicle license plates, and suspicious activities that might otherwise go unnoticed. This heightened visibility ensures that officers have reliable footage to review, enhancing their ability to make informed decisions and respond effectively to incidents.
Integration with Modern Surveillance Systems
Another significant advantage of low light USB cameras is their seamless integration with existing surveillance systems. These cameras can be easily connected to a variety of platforms, including Raspberry Pi and other modular systems, providing a cost-effective solution for upgrading surveillance capabilities. The ability to integrate these cameras with real-time monitoring systems allows for immediate alerts and enhanced situational awareness, which is critical in high-stakes situations.
Moreover, many low light USB cameras offer features such as motion detection and automatic recording, which can be programmed to activate in response to specific triggers. This functionality ensures that officers and surveillance operators capture relevant footage without having to manually start and stop recordings, further improving efficiency and accuracy.
Key Features of Low Light USB Cameras
Superior Low-Light Performance
At the heart of a low light USB camera's effectiveness is its superior low-light performance. These cameras typically feature advanced image sensors and technologies, such as CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) sensors, which excel in capturing clear images in low-light conditions. Technologies like infrared (IR) illumination and high dynamic range (HDR) further enhance their ability to produce detailed images without compromising clarity or color accuracy.
For instance, the IMX291 USB camera, known for its exceptional low-light capabilities, can capture clear video footage in near-total darkness, making it an ideal choice for nighttime surveillance. By leveraging these technologies, law enforcement agencies can ensure that they have access to high-quality video evidence, regardless of the lighting conditions.
Durability and reliability
In addition to their low-light capabilities, low light USB cameras are built to withstand the rigors of law enforcement operations. These cameras are designed with rugged housings that protect against environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and physical impacts. This durability ensures that the cameras remain operational even in harsh conditions, providing reliable performance when it matters most.
Furthermore, low light USB cameras are often equipped with features such as thermal management systems and shock resistance, which contribute to their longevity and reliability. This robustness is crucial for maintaining continuous surveillance and ensuring that the cameras perform optimally over extended periods.
The Impact on Officer Safety
Improved Situational Awareness
One of the most significant benefits of low light USB cameras is their impact on officer safety. By providing clear and detailed video footage in low-light conditions, these cameras enhance situational awareness, allowing officers to assess and respond to potential threats more effectively. This increased visibility helps officers make better-informed decisions, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing their ability to avoid potentially dangerous situations.
For example, a low light USB camera mounted on a patrol vehicle can capture real-time footage of a traffic stop or suspicious activity, allowing officers to monitor the situation from a safe distance. This capability enables them to evaluate the circumstances before approaching, ensuring that they are fully prepared for any potential hazards.
Evidence Collection and Accountability
Low light USB cameras also play a crucial role in evidence collection and accountability. The ability to capture clear footage in low-light conditions ensures that all interactions and incidents are documented accurately. This documentation can be invaluable for investigations, legal proceedings, and internal reviews, providing a transparent record of events and actions.
By improving the quality and reliability of video evidence, low light USB cameras help uphold accountability and integrity within law enforcement operations. This transparency not only supports investigations but also reinforces public trust in law enforcement agencies.
In summary
In conclusion, low light USB cameras are revolutionizing the way law enforcement organizations handle surveillance and the security of their officers. Their capacity to deliver crisp, comprehensive footage in difficult lighting situations boosts operational effectiveness, situational awareness, and the general safety and accountability of law enforcement activities. Low light USB cameras will probably be incorporated into more systems as technology develops, which will only serve to reinforce their importance as a necessary instrument for contemporary monitoring and law enforcement.
Investing in low light USB cameras is a strategic move that enhances the effectiveness and security of local law enforcement personnel. It goes beyond simple technological progress. These cameras are laying the groundwork for a safer, more secure future in surveillance and law enforcement thanks to their cutting-edge capabilities and tested performance.
https://www.vadzoimaging.com/product/imx291-low-light-1080p-usb-camera
0 notes
Text
Understanding X-Ray Detectors for Digital Radiography: A Comprehensive Guide
Digital radiography (DR) has revolutionized the field of medical imaging, offering enhanced image quality, faster processing times, and reduced radiation exposure compared to traditional film-based systems. At the heart of this technological advancement lies the X-ray detector, a critical component that captures the X-rays passing through the body and converts them into digital images. This blog delves into the world of X-ray detectors for digital radiography, exploring their types, working principles, and the benefits they bring to modern healthcare.
What Are X-Ray Detectors?
X-ray detectors are devices that capture and convert the X-ray energy emitted from an X-ray source into visible images. These images allow healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, ranging from broken bones to complex diseases. In digital radiography, the role of the X-ray detector is crucial as it directly influences the image quality, resolution, and overall efficiency of the imaging process.
Download PDF Brochure
Types of X-Ray Detectors in Digital Radiography
There are several types of X-ray detectors used in digital radiography, each with its unique advantages and applications:
Flat-Panel Detectors (FPDs):
Indirect Conversion Detectors: These detectors use a scintillator to convert X-rays into visible light, which is then detected by photodiodes and converted into electrical signals. Indirect conversion FPDs are widely used in general radiography due to their excellent image quality and relatively low radiation dose.
Direct Conversion Detectors: These detectors directly convert X-ray photons into electrical signals without the intermediate step of light conversion. Made from materials like amorphous selenium, direct conversion FPDs offer higher spatial resolution, making them ideal for applications requiring detailed imaging, such as mammography.
Charged-Coupled Devices (CCDs): CCDs are semiconductor devices that convert X-rays into electrical signals. Though less commonly used than FPDs, CCDs are still prevalent in specific applications like dental imaging. They offer good image quality but are often limited by their smaller size and lower sensitivity compared to FPDs.
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) Detectors: CMOS detectors are similar to CCDs but use different technology for capturing and processing X-ray images. CMOS detectors are known for their low power consumption, high speed, and durability. They are increasingly used in various medical imaging applications, including portable X-ray systems.
Photostimulable Phosphor Plates (PSP): Also known as computed radiography (CR) detectors, PSP plates store the X-ray image in a phosphor layer, which is later read out by a laser scanner. Although CR systems are less expensive than FPDs, they are gradually being replaced by more advanced digital radiography technologies due to their slower processing times.
Key Advantages of Digital Radiography with X-Ray Detectors
The transition from traditional film-based radiography to digital radiography has brought numerous benefits, largely due to advancements in X-ray detector technology:
Improved Image Quality: X-ray detectors in digital radiography provide superior image quality with better contrast resolution, enabling more accurate diagnoses.
Reduced Radiation Exposure: Digital X-ray detectors require less radiation to produce high-quality images, which enhances patient safety.
Request Sample Pages
Faster Results: The digital nature of modern X-ray detectors allows for immediate image processing and review, significantly speeding up the diagnostic process.
Enhanced Workflow Efficiency: Digital radiography systems are integrated with Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS), enabling seamless storage, retrieval, and sharing of images within healthcare networks.
Environmentally Friendly: Unlike film-based systems, digital radiography eliminates the need for chemical processing and film storage, reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
X-ray detectors are the cornerstone of digital radiography, transforming how medical images are captured, processed, and analyzed. With the ongoing advancements in detector technology, digital radiography continues to evolve, offering ever-improving image quality, patient safety, and diagnostic accuracy. As healthcare providers strive to deliver better care, understanding the different types of X-ray detectors and their benefits is essential for making informed decisions in medical imaging.
Content Source:
0 notes
Text
How Embedded Software Transforms Modern Industrial Automation

In today's rapidly evolving industrial landscape, embedded software stands out as a game-changer for modern automation. From streamlining operations to enhancing productivity, this technology is reshaping how industries function. Let’s dive into how embedded software is revolutionizing industrial automation and why it’s a crucial component for future success.
What is Embedded Software?
At its core, embedded software is specialized code designed to operate hardware devices. Unlike general-purpose software, which runs on versatile computing platforms, embedded software is tailored for specific functions within a machine or system. Think of it as the brain behind various industrial devices, orchestrating everything from machinery control to data processing.
Enhancing Efficiency with Embedded Software
One of the most significant impacts of embedded software on industrial automation is the boost in efficiency. Traditionally, industrial processes relied heavily on manual inputs and cumbersome control systems. However, embedded software automates these processes, reducing the need for human intervention and minimizing errors.
For example, in manufacturing, embedded systems can monitor production lines in real-time, adjusting parameters to ensure optimal performance. This leads to faster production cycles, higher product quality, and reduced waste. The result is a more streamlined operation where everything works in harmony, driven by precise, real-time data.
Improving Accuracy and Precision
Precision is paramount in industrial automation, and embedded software excels in this area. With the ability to process complex algorithms and execute tasks with high accuracy, embedded systems ensure that machinery and equipment perform exactly as intended.
In sectors like aerospace or semiconductor manufacturing, where even the slightest deviation can lead to significant issues, embedded software plays a crucial role. It controls and monitors various aspects of the production process, ensuring that every component meets stringent specifications. This level of precision not only enhances product quality but also improves safety and reliability.
Enabling Smart Automation
The rise of Industry 4.0 has brought with it a wave of smart technologies, and embedded software is at the forefront of this movement. By integrating with sensors, IoT devices, and other smart components, embedded systems enable more intelligent and adaptive automation solutions.
Imagine a factory where machines can predict maintenance needs before they become critical. Embedded software collects and analyzes data from sensors, identifying patterns and anomalies. This predictive capability allows for timely maintenance, reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan. Such smart automation transforms traditional setups into dynamic, responsive systems that adapt to changing conditions.
Streamlining Data Management
In industrial settings, managing vast amounts of data efficiently is crucial. Embedded software facilitates this by providing sophisticated data handling capabilities. It collects, processes, and stores data from various sources, offering insights that drive better decision-making.
For instance, in logistics and supply chain management, embedded systems track inventory levels, monitor shipments, and optimize routes in real-time. This data-driven approach enhances operational visibility and allows companies to make informed decisions quickly. The result is a more agile and responsive operation that can adapt to market demands and unforeseen challenges.
Enhancing Connectivity and Integration
Modern industrial environments are increasingly interconnected, and embedded software plays a key role in facilitating this connectivity. It enables seamless integration between various systems and devices, ensuring that they work together effectively.
Through protocols and communication standards, embedded systems link different components of an industrial setup, from production machinery to control centers. This integration streamlines workflows, improves coordination, and enables centralized control. In practice, this means fewer manual interventions and a more cohesive, efficient operation.
Supporting Scalability and Flexibility
As industries grow and evolve, the need for scalable and flexible automation solutions becomes evident. Embedded software meets this demand by offering adaptable and upgradeable systems.
Whether it's adding new features, integrating additional devices, or scaling up operations, embedded software can be adjusted to accommodate changing requirements. This flexibility ensures that industrial automation systems remain relevant and effective as technologies and business needs progress.
Driving Innovation in Industrial Automation
The role of embedded software in industrial automation extends beyond operational improvements. It drives innovation by enabling the development of new technologies and solutions.
Consider advancements such as autonomous robots, advanced machine learning algorithms, and real-time data analytics. These innovations are made possible by the capabilities of embedded software, which provides the foundation for these technologies to operate and deliver their full potential.
Future Trends and Developments
Looking ahead, embedded software will continue to play a pivotal role in the evolution of industrial automation. Emerging trends such as edge computing, advanced AI integration, and enhanced cybersecurity will shape the future landscape.
Edge computing, for example, involves processing data closer to where it's generated, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making. Embedded software will be instrumental in implementing these technologies, ensuring they work seamlessly within existing systems.
Similarly, as cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, embedded software will need to evolve to protect industrial systems from potential breaches. Robust security measures will be integral to maintaining the integrity and reliability of automated processes.
Conclusion
Embedded software is transforming modern industrial automation by enhancing efficiency, precision, and connectivity. Its impact is evident across various sectors, driving smarter, more adaptive, and innovative solutions. As technology continues to advance, embedded software will remain at the heart of industrial automation, shaping the future of how industries operate and thrive. Embracing these advancements will be key to staying competitive and leveraging the full potential of automation in the years to come.
To Know More About Embedded software
0 notes
Text
Fundus Camera: An Essential Equipment for Eye Examination

What is a Fundus Camera?
A fundus camera, also known as an ophthalmoscope or retinal camera, is a specialized low-power microscope used to afford high-quality imaging of the internal tissues of the living human eye, known as the fundus. The fundus refers to the interior surface of the eye opposite the lens, including the retina, optic disc, and posterior pole of the eye. Fundus cameras allow eye care professionals to non-invasively examine and document the health of the retina, optic disc and macula.
Parts
A standard fundus camera consists of the following key components:
- Illumination System: Provides controlled light to illuminate the fundus via the pupil. Koehler illumination is commonly used, allowing homogenous lighting of the fundus. Halogen or Xenon lamps are commonly used light sources.
- Optical System: Consists of lenses that magnify the light reflected from the fundus for visualization and imaging purposes. Typical magnification ranges from 15x to 60x. Wide-angle and ultra-wide angle lens options are available.
- Eye Piece: The eyepiece allows the examiner to view the magnified fundus image. Binocular eyepieces provide stereoscopic viewing.
- Digital Camera Sensor: Replaces traditional film in modern digital Fundus Camera. Charged coupled device (CCD) or complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) digital sensors capture fundus images which can be stored, analyzed and shared digitally.
- Shields/Filters: Polarization filters reduce glare from light reflections within the eye. Alignment lights and targets help with proper centration of the fundus image.
- Stand or Slit Lamp Attachment: It may sit on a stand alone or attach to an existing slit lamp biomicroscope, allowing integration with other examination equipment.
Uses and Applications of Fundus Photography
Fundus photography allows detailed examination and documentation of retinal pathologies, which is invaluable for diagnosing and monitoring many common eye diseases. Some key applications include:
- Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: Photographing the retina allows detection of microaneurysms, hemorrhages, cottonwool spots, hard exudates and neovascularization indicative of diabetic eye disease.
Optimal Fundus Photography Techniques
Careful technique is needed to obtain high quality fundus photos enabling accurate clinical evaluation:
- Pupil Dilation: Most fundus details are only visible after dilating the pupil with eyedrops to at least 6 mm. This improves illumination levels reaching the fundus.
- Centration: Centering the fundus camera lens on the pupil ensures the retina is evenly illuminated and the entire posterior pole is in view. Targeting lights assist alignment.
Get more insights on Fundus Camera
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)
#Fundus Camera#Retinal Imaging#Eye Examination#Ophthalmology#Fundus Photography#Retina#Ocular Health#Fundus Imaging#Eye Care#Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
0 notes
Text
The Essential Role of Indicators in Modern Industrial Automation
In the realm of industrial automation, where precision and efficiency are dominant, indicators play a essential role in ensuring smooth operations. These apparently simple devices provide valuable insights into the status and performance of various systems, enabling operators to make informed decisions promptly. In this blog, we'll look into the essential role of indicators in modern industrial automation, exploring their functions, types, and the significant impact they have on optimizing processes.
Understanding Industrial Automation
Before we look into the significance of indicators, let's first take hold of the concept of industrial automation. Industrial automation involves the use of control systems such as computers or robots to handle different tasks and processes in manufacturing and other industrial settings. The primary goal of automation is to improve efficiency, productivity, and safety while minimizing human intervention.
The Role of Indicators

Indicators serve as the eyes and ears of industrial automation systems, providing real-time feedback on various parameters. Whether it's monitoring temperature, pressure, flow rate, or any other critical variable, indicators play a crucial role in keeping operations running smoothly. They offer visibility into the performance of machinery and processes, allowing operators to detect anomalies and take corrective actions promptly.
Functions of Indicators
Indicators perform several essential functions in industrial automation:
Monitoring: Indicators continuously monitor key parameters to ensure they remain within specified limits. For example, in a manufacturing plant, temperature indicators can monitor the temperature of equipment to prevent overheating and potential damage.
Alerting: Indicators provide alerts or alarms when parameters deviate from the desired range. This early warning system helps operators identify issues before they escalate into major problems, minimizing downtime and preventing costly repairs.
Control: In some cases, indicators are integrated with control systems to automatically adjust settings based on real-time data. For instance, a pressure indicator can signal a control system to regulate the pressure in a hydraulic system to maintain optimal conditions.
Data Logging: Many indicators are equipped with data logging capabilities, allowing operators to record and analyze historical data. This data can be valuable for troubleshooting, process optimization, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Types of Indicators
Indicators come in various forms to suit different applications and environments:
Digital Indicators: These indicators display numerical values digitally, providing precise measurements with high accuracy. They are commonly used in industries where precise monitoring is essential, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing and semiconductor fabrication.
Analog Indicators: Analog indicators use analog displays such as meters or gauges to represent measurements. While they may not offer the same level of precision as digital indicators, they are often more cost-effective and easier to read at a glance.
Multifunction Indicators: These versatile indicators can monitor multiple parameters simultaneously, making them ideal for complex industrial processes where multiple variables need to be monitored.
Smart Indicators: Smart indicators are equipped with advanced features such as wireless connectivity, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities. They leverage technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) to provide real-time insights and optimize performance.
Impact on Efficiency and Productivity

The presence of indicators in industrial automation has a significant impact on efficiency and productivity:
Reduced Downtime: By promptly detecting issues and providing alerts, indicators help minimize downtime by enabling preventive maintenance and timely repairs.
Enhanced Safety: Indicators play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of workers and equipment by monitoring critical parameters and triggering alarms in case of deviations.
Improved Quality Control: With accurate and timely feedback from indicators, manufacturers can maintain consistent product quality by closely monitoring key parameters throughout the production process.
Optimal Resource Utilization: By monitoring energy consumption, material usage, and other resource-intensive processes, indicators help optimize resource utilization and reduce waste.
Data-Driven Decision Making: The data collected by indicators can provide valuable insights into process performance, enabling operators to make informed decisions and implement continuous improvements.
Conclusion
Indicators are necessary components of modern industrial automation systems, providing real-time feedback, alerts, and control capabilities that are essential for optimizing processes and maximizing efficiency. By investing in high-quality indicators and integrating them effectively into automation systems, industrial facilities can ensure smooth operations, minimize downtime, and stay competitive in today's fast-paced manufacturing environment.
#industrial automation#auto2mation#industrial equipment#industrial automation equipment#industrial and marine automation#industrial and marine automation equipment#industrial#automation#indicators
0 notes
Text
Advancing Non-Destructive Testing: The Asia-Pacific Industrial Computed Radiography Market | BIS Research

Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, quality, and reliability of industrial infrastructure across various sectors. Computed Radiography (CR) has emerged as a powerful NDT technique, offering superior image quality, enhanced efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing significant growth in the Industrial Computed Radiography Market, as industries increasingly adopt this advanced imaging technology.
According to BIS Research, the Asia-Pacific Industrial Computed Radiography Market is estimated to reach $19.30 million by 2033 at a growth rate of CAGR 3.49% during the forecast period 2023-2033.
Key Prominent Market Growth Drivers
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Safety Requirements:
Asia-Pacific industries like manufacturing, oil and gas, aerospace, and power generation face strict safety regulations.
Industrial computed radiography ensures compliance by accurately inspecting critical components for defects and anomalies.
Its precision in detecting flaws contributes to enhanced asset integrity and risk reduction in these regulated sectors.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency:
Industrial computed radiography offers substantial cost and time savings compared to traditional film-based methods.
Eliminating film processing chemicals and reducing image development time, CR enhances operational efficiency.
Rapid image acquisition, storage, and sharing streamline inspection processes, minimizing downtime and boosting productivity.
Technological Advancements and Image Quality:
Ongoing advancements in digital imaging sensors and software have significantly enhanced CR image quality.
High-definition images provide clearer visibility of defects, enabling accurate assessments by inspectors.
Digital manipulation capabilities improve diagnostic accuracy, empowering inspectors to make informed decisions.
Wide Range of Applications:
Industrial computed radiography serves diverse industries, including weldments, castings, pipelines, and turbines.
Its versatility allows efficient inspection of complex geometries and hard-to-reach areas.
CR is invaluable for inspecting structural components across various sectors, contributing to overall quality assurance.
Access More: Get FREE Detailed Report on Asia-Pacific Industrial Computed Radiography Research!
Key Market Trends and Opportunities
Growing Adoption in Developing Economies:
Rapid industrialization and infrastructure development in Asia-Pacific's developing economies drive adoption.
Focus on quality control and safety standards prompts the use of industrial computed radiography.
Benefits include higher inspection accuracy, cost reduction, and enhanced asset reliability.
Shift from Analog to Digital NDT:
Asia-Pacific sees a transition from traditional analog NDT to digital methods like computed radiography.
Advantages such as improved image quality and streamlined data analysis drive this shift.
Digital NDT presents growth opportunities for industrial computed radiography in the region.
Integration with Industry 4.0 and Automation:
Industrial computed radiography integrates with Industry 4.0 tech like IoT, AI, and robotics.
Automated CR systems with AI-enabled analysis enhance inspection speed, accuracy, and repeatability.
This convergence enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decisions in the Asia-Pacific market.
APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market Segmentation by Application
Aerospace and Defense
Automotive
Oil and Gas
Power and Energy
Security
Explosive Ordnance Disposal and Improvised Explosive Device
Electronics and Semiconductors
Food and Drugs
Transportation Infrastructure
Construction
Marine
Manufacturing
Heavy Industries
Others
Market Challenges and Future Outlook
While the Asia-Pacific Industrial Computed Radiography Industry shows promising growth prospects, there are challenges to address. These include the need for skilled personnel to operate and interpret CR systems, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and addressing concerns related to radiation safety. Overcoming these challenges through training programs, standardization efforts, and continuous technological advancements will be crucial for the widespread adoption of industrial computed radiography in the region.
Conclusion
The APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the demand for accurate, efficient, and cost-effective non-destructive testing solutions. As industries across the region embrace digital transformation and prioritize safety and quality control, the adoption of industrial computed radiography is set to rise. With ongoing technological advancements, increasing automation, and the integration of digital NDT techniques, the future of industrial computed radiography in the Asia-Pacific region looks promising, contributing to safer and more reliable industrial infrastructure.
#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market Report#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Industry#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market Trends#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market Forecast#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market Research#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market Growth#APAC Industrial Computed Radiography Market CAGR#Robotics and Automation#BIS Research
0 notes
Text
Investigating Industrial LED Lighting And Netzero Energy Solutions To Improve Illumination Efficiency
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial operations, efficiency is not just a goal; it's a necessity. As businesses strive to reduce costs, minimize environmental impact, and optimize productivity, the role of lighting solutions becomes increasingly critical. Enter Industrial LED Lighting Solutions and Netzero Energy Solutions: innovative approaches that not only illuminate workspaces but also pave the way towards sustainable and energy-efficient practices.
Industrial LED Lighting Solutions represent a paradigm shift in industrial illumination. Unlike traditional lighting technologies such as fluorescent or incandescent bulbs, LED (Light Emitting Diode) fixtures offer unparalleled efficiency and longevity. By harnessing the power of semiconductor technology, LED lights consume significantly less energy while delivering superior brightness and color rendering. This translates into lower electricity bills and reduced maintenance costs for industrial facilities.
Moreover, industrial LED lighting solutions are highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor lighting designs to meet specific operational needs. From high-bay fixtures for warehouses to task lighting for assembly lines, LED luminaires can be strategically deployed to enhance visibility, safety, and productivity in industrial environments. Advanced features such as dimming capabilities and motion sensors further optimize energy usage by adjusting light output based on occupancy and ambient light levels.
But the benefits of industrial LED lighting solutions extend beyond mere illumination. By transitioning to LED technology, businesses can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental sustainability efforts. LED fixtures have a longer lifespan and contain no hazardous materials such as mercury, making them eco-friendly alternatives to conventional lighting options. Furthermore, the efficient operation of LED lights helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and minimize the environmental impact of industrial operations.
In parallel with the adoption of industrial LED lighting solutions, many forward-thinking businesses are embracing Netzero Energy Solutions to further enhance sustainability and energy efficiency. The concept of Netzero Energy revolves around achieving a balance between energy consumption and renewable energy generation, resulting in a net-zero carbon footprint. This holistic approach involves implementing a combination of energy-saving measures, renewable energy systems, and smart technologies to minimize energy usage and maximize renewable energy production.
One of the cornerstones of Netzero Energy Solutions is energy efficiency optimization. By conducting energy audits and implementing energy-saving strategies such as lighting upgrades, insulation improvements, and HVAC system optimizations, businesses can reduce energy waste and lower their overall consumption. Industrial LED lighting solutions play a pivotal role in this process by providing efficient illumination while minimizing electricity usage.
In addition to energy efficiency measures, Netzero Energy Solutions leverage renewable energy sources to meet the remaining energy needs of industrial facilities. Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems are among the renewable energy technologies commonly deployed in Netzero Energy projects. By generating clean energy onsite, businesses can offset their grid electricity consumption and move closer to achieving energy independence.
Furthermore, advanced energy management systems and controls are essential components of Netzero Energy Solutions. These systems monitor energy usage in real-time, optimize equipment operation schedules, and enable demand response capabilities to ensure efficient energy utilization. Smart meters, building automation systems, and predictive analytics tools empower businesses to proactively manage their energy consumption and adapt to changing operational requirements.

The integration of industrial LED lighting solutions and Netzero Energy Solutions represents a holistic approach to sustainable industrial development. By combining energy-efficient lighting technology with renewable energy generation and intelligent energy management systems, businesses can reduce operating costs, enhance resilience, and minimize environmental impact. Moreover, these initiatives contribute to corporate sustainability goals, enhance brand reputation, and position organizations as leaders in the transition to a low-carbon future.
In conclusion, industrial LED lighting solutions and Netzero Energy Solutions offer synergistic opportunities for industrial facilities to optimize energy usage, reduce costs, and demonstrate environmental stewardship. By embracing these innovative approaches, businesses can illuminate their path towards a sustainable and prosperous future.
0 notes
Text
The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) market is anticipated to reach a market size of USD 104.1 billion by 2032.
RFID components like tags and readers has significantly decreased, making RFID technology more accessible and cost-effective across a broad range of industries and applications. Furthermore, continuous advancements in RFID technology have led to improvements in performance, reliability, and read range. Innovations such as the development of efficient, smaller-sized tags, enhanced read accuracy, and faster data processing capabilities have played a pivotal role in driving the widespread adoption of RFID technology.
Request Sample Report: https://datahorizzonresearch.com/request-sample-pdf/rfid-market-2190The RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven by a multitude of factors contributing to its increasing adoption across diverse industries. RFID technology offers a sophisticated means of tracking and identifying objects using radio waves, enabling real-time monitoring and inventory management with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. As a result, businesses are increasingly turning to RFID solutions to streamline operations, enhance supply chain visibility, and improve asset management processes.North America has emerged as a prominent player in the RFID market, boasting the largest share due to robust adoption across various sectors. The region’s advanced infrastructure, coupled with a strong emphasis on technological innovation, has propelled the widespread deployment of RFID systems. Furthermore, the presence of key market players and a favorable regulatory environment have further catalyzed market growth in North America, solidifying its position as a frontrunner in the global RFID landscape.Europe represents another significant market for RFID technology, characterized by increasing demand across industries such as retail, healthcare, and logistics. The region’s stringent regulations regarding product traceability and consumer safety have incentivized businesses to invest in RFID solutions to ensure compliance and improve operational efficiency. Moreover, Europe’s focus on sustainability and eco-friendly practices has spurred the adoption of RFID for enhancing supply chain visibility and reducing environmental impact through optimized inventory management and logistics operations.Looking Exclusively For Region/Country Specific Report? https://datahorizzonresearch.com/ask-for-customization/rfid-market-2190Top Companies are:· CAEN RFID· NXP Semiconductors· GAO RFID· Invengo· Infotek Software & Systems (P) Ltd (i-TEK)· Bartronics India Ltd.· Bartech Data Systems Pvt. Ltd.· Bar Code India Ltd. (BCI)· Securitag Assembly Group (SAG)· LinxensMarket Segmentations:RFID Market, By Offering (2023–2032)· Tags· Readers· Software & ServicesRFID Market, By Wafer Size (2023–2032)· 8 Inch· 12 Inch· OthersRFID Market, By Tag Type (2023–2032)· Passive· ActiveRFID Market, By Frequency (2023–2032)· Low Frequency· High Frequency· Ultra-High FrequencyRFID Market, By Form Factor (2023–2032)· Card· Implant· Key Fob· Label· Paper Ticket· Band· OthersRFID Market, By Application (2023–2032)· Agriculture· Commercial· Transportation· Healthcare· Logistics & Supply Chain· Apparel· Food· Automotive· Aerospace· Defense· Retail· Security & Access Control· Sports· Animal Tracking· TicketingBuy This Research Report: https://datahorizzonresearch.com/checkout-page/rfid-market-2190Regional AnalysisNorth America stands at the forefront of RFID adoption and market expansion, propelled by a robust retail sector and the pressing need for enhanced supply chain management. Industries spanning healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics have also embraced RFID technology for purposes ranging from inventory control to asset tracking and process optimization. This region has witnessed widespread deployment of RFID systems across retail stores, warehouses, healthcare facilities, and transportation hubs, underlining its status as a leader in RFID integration.Meanwhile, the Asia Pacific region is undergoing a surge in RFID adoption, fueled by factors such as rapid industrialization, burgeoning retail markets, and government initiatives aimed at bolstering supply chain efficiency. Key players including China, Japan, South Korea, and India are making significant contributions to the region’s RFID market. Notably, the retail sector in Asia Pacific has emerged as a pivotal adopter of RFID technology, leveraging it for inventory management, anti-counterfeiting measures, and enhancing customer experiences.
0 notes
Text
InGaAs Photodiode Sensor Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast 2030
In the realm of optical sensing, where precision meets innovation, a remarkable technology has been quietly making waves – the InGaAs photodiode sensor. Behind this unassuming name lies a world of possibilities, where light is not just detected but decoded with unparalleled accuracy and sensitivity. Join us as we delve into the dynamic landscape of the InGaAs photodiode sensor market, exploring its evolution, applications, and the transformative potential it holds for diverse industries.
The Essence of InGaAs Photodiode Sensors
At the heart of InGaAs photodiode sensors lies a semiconductor compound known as Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs), renowned for its unique optical properties that enable the detection of near-infrared (NIR) light. Unlike traditional silicon-based photodiodes, InGaAs photodiodes exhibit exceptional sensitivity to wavelengths beyond the visible spectrum, making them indispensable for a wide range of applications in fields such as telecommunications, spectroscopy, and aerospace.
Request Sample Report: https://www.snsinsider.com/sample-request/3185
Market Dynamics and Trends
The InGaAs photodiode sensor market is characterized by a steady growth trajectory, driven by increasing demand for high-performance sensing solutions across diverse industries. Key factors driving market growth include advancements in sensor design, manufacturing techniques, and integration capabilities, as well as the growing adoption of NIR spectroscopy for industrial process monitoring, environmental sensing, and medical diagnostics.
One notable trend within the InGaAs photodiode sensor market is the miniaturization of sensors and the development of compact, lightweight modules tailored for portable and handheld applications. This trend reflects the growing need for on-the-go sensing solutions in fields such as food safety, pharmaceuticals, and consumer electronics, where real-time analysis and quality control are paramount.
Applications and Innovations
The versatility of InGaAs photodiode sensors is reflected in their myriad applications across various industries. In telecommunications, for instance, these sensors play a critical role in optical fiber communications, enabling high-speed data transmission over long distances with minimal signal loss. Similarly, in spectroscopy, InGaAs photodiodes are employed for chemical analysis, material characterization, and environmental monitoring, offering unparalleled sensitivity and spectral range.
Moreover, the integration of InGaAs photodiode sensors with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is unlocking new possibilities for intelligent sensing and data analytics. By leveraging AI algorithms to analyze sensor data in real-time, researchers and engineers can extract valuable insights, identify patterns, and optimize process parameters with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their remarkable capabilities, InGaAs photodiode sensors face challenges related to cost, performance optimization, and compatibility with existing infrastructure. Additionally, the stringent regulatory requirements governing certain industries, such as healthcare and aerospace, pose barriers to market entry and product adoption.
However, amidst these challenges lie abundant opportunities for innovation and growth. As sensor manufacturers continue to refine their fabrication techniques and develop new materials, the cost of InGaAs photodiode sensors is expected to decline, making them more accessible to a broader range of applications and industries. Furthermore, advancements in packaging technologies, such as hermetic sealing and ruggedization, are expanding the deployment possibilities of InGaAs photodiode sensors in harsh environments and demanding operating conditions.
The Future of InGaAs Photodiode Sensors
As we gaze into the future of the InGaAs photodiode sensor market, one thing is clear: the potential for innovation and impact is boundless. With advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and interdisciplinary collaboration, InGaAs photodiode sensors will continue to push the boundaries of what's possible in optical sensing, enabling new discoveries, enhancing productivity, and improving quality of life across the globe.
In conclusion, the InGaAs photodiode sensor market represents a convergence of cutting-edge science, engineering, and imagination. From its humble beginnings to its transformative potential, the journey of InGaAs photodiode sensors illuminates the profound impact of light on our understanding of the world and our ability to harness its power for the greater good. As we embrace the possibilities of intelligent sensing and exploration, let us embark on a journey of discovery and innovation, guided by the brilliance of InGaAs photodiode sensors.
Access Full Report Details: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/ingaas-photodiode-sensor-market-3185
0 notes
Text
Digital Screen Types – The Technologies
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp & Wechat: +86 18038197291
www.xygledscreen.com
One of the first electronic displays was the Cathode Ray Tube (CRT), invented in 1897. In 1922, CRTs became commercially available. The CRT is a simple screen device with an electron "gun" that shoots electrons at a phosphorus-coated glass screen, thus creating an image on the outside visible area. These screen types were the first televisions and computer monitors.
That was just the beginning.
Moving Forward – Here and Now
Improvements include a wide range of digital screen types that are more efficient, have superior images and amaze consumers. To know more about digital screen technologies, a deeper appreciation of them is critical. Whether one is a video enthusiast, consumer, or marketer, a basic knowledge of screen technology is essential.
The first technology to forcibly step forward in the market was the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD). To this day, LCDs are the most common display type in the market today for televisions, computers, smartphones, security monitors, and more. They are inexpensive to fabricate and have good image quality. LCDs have poor viewing at angles and limited color spectrums.
LCDs create images by modulating light with liquid crystals. The crystal's alignment changes when an electric field activates under digital control. Pixels are the result (tiny areas of illumination).
Presented images are manipulated digitally to create light and color of the pixels. Because the pixels are close and minute, a clear picture accurately depicts graphics, videos, and photos. LCDs comprise the lion's share of the screen market, from televisions to computer monitors and tablets to smartphones.
Organic Light-Emitting Diodes (OLED) have taken hold among videophiles. OLEDs have better contrast, superior image quality, better viewing at angles, and faster responses than LCDs (quick changing of pixel colors). However, OLEDs are expensive to fabricate, with costs passed on to consumers. They have a susceptibility to screen scaring (damage).
Organic thin films are the OLED's light-emitting layers. Transparent conductors, typically made with zinc or tin oxide, act as electrodes controlling the film's current flow. A plastic or glass substrate forms the base layer, and a polymer protection layer seals the environment out.
This complex organic light-emitting diode screen technology relies on several scientific principles. But the outline of OLED is plain. In organic thin films, images created on the visible screen appear when an electric current is applied and digitally manipulated. Color filters and drivers control colors, contrast, graphics, and images. Drivers, especially, control current flows. A backplane has integrated circuits to control single pixels.
Quantum Dot LED (QLED) is a newer innovation that has yet to prove itself to consumers. By using quantum dots, image quality improves. The color range and crisp brightness outpace LCDs. Screen scaring reduces, and durability increases. Still outstanding is a more market-ready price point.
Often confused with OLEDs, QLED technology has similarities and differences. A variant of LCDs combines with QLEDs using quantum dots to improve image quality.
Quantum dots are tiny semiconductor nanocrystals that produce color and light. A backlight shines through a layer of blue quantum dots. The digitally controlled blue light converts to green and red, providing a broad spectrum of color. Thus, outpacing LCD screens. Like an LCD, QLEDs have a liquid crystal layer controlling the light that passes through the pixels. Color filters refine colors, driver circuits control current throughout the screen, and backplane integrated circuits control each pixel.
Plasma displays are unique and primarily used for giant televisions and digital signage. They have excellent color representation, great viewing at angles, deep blacks, and the whitest whites. Plasma screens have fast response times with little or no blurring. These screens are power-hungry, heavy, and thick, so they aren't used in smaller devices (smartphones, tablets, desktop screens).
The"Pros and Cons"
LCDs are an inexpensive alternative to OLEDs. Consumers already accept LCDs, and manufacturers want to keep costs down for their devices. The downside is that innovation has outclassed LCDs in clarity, definition, and color by a wide margin.
OLED technology is the standard bearer of all LED-based screen designs. It produces higher-quality images, has better contrast, and has fast response times. Unfortunately, screen scaring occurs too often, and prices have yet to be accessible to many consumers. QLEDs are an improvement to some degree because of less screen scaring, but their price point remains high.
Digital Screen Types in Development
The miniLED, also called microLED, is a working model offering even more improvements than the standard screens. Once entering the market, high costs will ensue while even more technologies are evolving. The next screen innovations will solve many problems with the original screen types.
MiniLEDs and microLEDs are sometimes called mLED or µLED. They use arrays of microscopic LEDs, creating elements within each pixel. This means each pixel is "self-emissive." The result is wide viewing angles, perfect black, and high-contrast graphics and pictures. Their most significant selling points are durability, energy efficiency, and eliminated screen scaring. These LED variants will move into production soon, and production costs will lower as the technology matures. First adopters will encourage more investment and improvements in this near-perfect technology.
Direct View LED technologies fork from micro-LEDs with larger LEDs. The screens are more affordable for the mass market by pedaling back on ultra-small LEDs. Customers will especially favor them when on a budget.
Completely transparent LED film can add images on windows for storefronts and signage. Further developments in flexible LED promise greater functionality for wearables and smartphones.
Cutting Edge Digital Screen Technologies
Consumers are about to face sweeping changes in the screens they love. These technologies surpass the rectangular screens that have been in use for many decades. These innovations will adapt to the consumer, be interactive, and immersive. Prototypes and some stumbling efforts have made strides, but they have yet to take hold.
Retinal display devices that project images to the eye's retina are under development. Many theoretical variations may soon come to the market. This technology will provide hands-free information in real-time. There are health and ethical issues that still need to be explored more.
Biometric displays are in their infancy. Locking and unlocking doors and cell phones is only the start. Under development are physiological tracking sensors for eye movement, and heart rate monitors may include emotion-aware devices that adapt to the user experience.
Long seen in science fiction, holographic displays have already attracted consumers' attention. These three-dimensional (3D) prototypes are already stunning but too bulky. The future of holographic displays may be developed in many formats like televisions, monitors, and small screens. Rendering holographic images on table tops and room spaces may become common.
Visuals are entertaining and communicate ideas and stories. The screens we use at work, at home, and for pleasure have evolved in our lifetimes. The early televisions rendered images in black and white, and the first computer monitors were monochrome. Today, screens are on the verge of a reality-like appearance. From tube televisions to flatscreens, LCD to QLEDs, and all the variations, there is no way to know what tomorrow will bring – the future is now.
0 notes
Text
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Market Size Growth Set to Surge Significantly during 2024-2031

Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, becoming a pivotal component in modern manufacturing processes. MES is a comprehensive software solution that plays a crucial role in managing and optimizing manufacturing operations on the shop floor. Its primary objective is to enhance production efficiency, reduce errors, and provide real-time insights into the manufacturing process. As industries increasingly embrace automation and digitization, the MES market is poised for continued expansion. The concept of MES is widely recognized and used in manufacturing sectors such as automotive, semiconductor, electronics, food processing, pharmaceuticals, aerospace, medical devices, and textiles. Elements such as scheduling, maintenance management, quality, time, and attendance fall within the scope of MES and are used in all industries.
To Know the Global Scope and Demand of the Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) Market | Request for Sample PDF: https://www.sanglobalresearch.com/enquiry/manufacturing-execution-systems-mes-market
One of the key drivers propelling the growth of the MES market is the relentless pursuit of operational excellence by manufacturing enterprises. MES enables companies to streamline their production processes, improve overall efficiency, and minimize waste. By providing real-time visibility into production metrics, MES empowers decision-makers to make informed choices, optimize resource utilization, and reduce production costs. The demand for MES solutions is further fueled by the need for better compliance with regulatory standards and industry norms, ensuring that manufacturers adhere to quality and safety standards.
Moreover, the growing trend of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has been a significant catalyst for the MES market's expansion. As manufacturing facilities embrace the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, sensors, and data analytics, MES becomes the linchpin connecting these technologies. MES not only facilitates communication between various manufacturing components but also helps in harnessing the power of data for predictive analytics and proactive decision-making. The ability of MES to foster connectivity and data-driven insights positions it as a crucial enabler for the digital transformation of manufacturing processes.
However, the MES market does face certain restraints that could impact its growth trajectory. Implementation costs and the complexity of integrating MES with existing systems pose challenges for some businesses. Small and medium-sized enterprises, in particular, may find the initial investment in MES implementation daunting. Additionally, concerns about data security and the potential disruptions during the transition phase can act as deterrents for organizations considering MES adoption. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, collaboration with experienced MES providers, and a phased approach to implementation.
Despite the hurdles, the MES market is poised for growth due to various favorable factors. The increasing demand for customized and configurable MES solutions tailored to specific industry requirements is creating new opportunities for market players. MES vendors are focusing on developing user-friendly interfaces and scalable solutions to cater to a diverse range of manufacturing environments. The emphasis on scalability ensures that MES can adapt to the evolving needs of businesses, making it a sustainable and future-proof investment.
Furthermore, the emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly manufacturing practices is driving the adoption of MES. Manufacturers are leveraging MES capabilities to monitor and optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and adhere to environmental regulations. As businesses increasingly recognize the importance of corporate social responsibility, MES becomes a strategic tool for aligning manufacturing operations with sustainable practices.
In conclusion, the Manufacturing Execution Systems market is witnessing robust growth driven by factors such as the pursuit of operational excellence, the advent of Industry 4.0, and the demand for sustainable manufacturing practices. While challenges such as implementation costs and integration complexities exist, the overall trajectory of the MES market is positive. As industries continue to prioritize efficiency, connectivity, and sustainability, MES will remain a crucial technology in the evolving landscape of modern manufacturing.
Market segment by players, this report covers
ABB
Accenture
Andea Solutions
Aptean
Dassault Systemes
Emerson
Eyelit
Fujitsu
GE Digital
HCL Technologies
Honeywell
IBASEt
Krones
Market Segmentation
The Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) market is split by Type and by Application. For the period 2024-2031, the growth among segments provides accurate calculations and forecasts for consumption value by Type, and by Application in terms of value.
Market Segment by Type
On-Premises
On-Demand
Hybrid
Market Segment by Application
Beverages or Brewing Industrial
Refineries and Petrochemicals
Pharmaceuticals
Chemicals and Specialty Chemicals
Automotive
Machine or Plant Construction
Metal or Paper
Market segment by regions, regional analysis covers
North America (United States, Canada, and Mexico)
Europe (Germany, France, UK, Russia, Italy, and Rest of Europe)
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Southeast Asia, Australia and Rest of Asia-Pacific)
South America (Brazil, Argentina and the Rest of South America)
Middle East & Africa (Turkey, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of Middle East & Africa)
Our More Reports:
Marketing Automation Market: https://sanglobalresearch.com/report/marketing-automation-market/3032
Software Consulting Market: https://sanglobalresearch.com/report/software-consulting-market/3020
Customer Data Platform Market: https://sanglobalresearch.com/report/customer-data-platform-market/3016
Visit Our Blogs:
Thank you for reading the report. The report can be customized as per the requirements of the clients. For further information or query about customization, please reach out to us, and we will offer you the report best suited for your needs.
About Us:
At San Global Research Report, we pride ourselves on our commitment to quality and accuracy. Our team of experienced researchers utilizes a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to ensure that our findings are both accurate and reliable. With a strong emphasis on responsiveness, transparency, and collaboration, we work closely with our clients to understand their objectives and deliver actionable insights. Learn more about our research approach and how it can benefit your business.
Contact Us:
Address: Gera Imperium Rise, Phase 2 Hinjewadi, Pune, India
San Global Research | Web: http://www.sanglobalresearch.com
Direct Line: +91 9209275355
E-mail: [email protected]
0 notes
Text
"Detecting Beyond the Visible: Unveiling the Power of InGaAs Photo Diode Sensors"
An InGaAs photodiode sensor is a type of semiconductor device that is specifically designed to detect and measure near-infrared (NIR) light. It is widely used in various applications, including telecommunications, spectroscopy, industrial process control, and scientific research.
The key characteristic of an InGaAs photodiode sensor is its sensitivity to wavelengths in the near-infrared spectrum, typically ranging from around 900 to 1700 nanometers. This makes it ideal for detecting light that is beyond the visible range but within the near-infrared region. InGaAs sensors are particularly sensitive to longer wavelengths, which allows for detection of light that is absorbed or transmitted by certain materials or substances.
One of the primary applications of InGaAs photodiode sensors is in telecommunications. In fiber optic communication systems, which use light signals to transmit data, InGaAs sensors are employed for monitoring the intensity and quality of the optical signals. They can convert the optical signals into electrical signals that can be processed and analyzed for data transmission and reception.
InGaAs photodiode sensors also find application in spectroscopy, which involves the measurement and analysis of the interaction between light and matter. The near-infrared spectrum contains valuable information about the composition and characteristics of various materials. InGaAs sensors enable precise and accurate detection of near-infrared light, making them suitable for spectroscopic analysis in fields such as environmental monitoring, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and material characterization.
In industrial process control, InGaAs photodiode sensors are utilized for monitoring and control of various processes that involve near-infrared radiation. For example, in manufacturing processes that require precise temperature measurements or monitoring of chemical reactions, InGaAs sensors can accurately measure the thermal radiation or specific wavelengths associated with the process, providing valuable data for control and optimization.
Scientific research also benefits from the use of InGaAs photodiode sensors. In fields such as astronomy, atmospheric studies, and bioimaging, where the detection of near-infrared light is crucial, these sensors enable scientists to gather valuable data and insights.
The advantages of InGaAs photodiode sensors include their high responsivity and sensitivity in the near-infrared spectrum, low noise levels, and fast response times. They offer excellent performance in low-light conditions and can operate at high speeds, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Additionally, InGaAs sensors are often designed to be compact and rugged, allowing for easy integration into various systems and environments.
In conclusion, InGaAs photodiode sensors play a critical role in detecting and measuring near-infrared light in a variety of applications. Their sensitivity, reliability, and fast response make them valuable tools in telecommunications, spectroscopy, industrial process control, and scientific research. The use of InGaAs sensors enables precise measurements and analysis of near-infrared radiation, contributing to advancements in technology, research, and various industries.
Read more @ https://techinforite.blogspot.com/2023/06/unveiling-power-of-ingaas-photo-diode.html
0 notes
Text
Qualcomm attempts to revive its IoT fortunes with Aware, a powerful device-to-cloud platform
Overview Of the Qualcomm Aware platform
Qualcomm announced the launch of its Aware platform- an API-rich, device-to-cloud technology platform to enable industrial digital transformation. A key strength of the Aware platform is energy-efficient real-time location services, which is a great fit with asset visibility applications such as asset tracking and condition monitoring.
The Qualcomm Aware platform integrates Qualcomm’s hardware with location technology assets from Skyhook (#cellular+Wi-Fi+#GNSS) and PoLTE (cellular: #4G & #5G) acquired in May 2022 and February 2023 respectively. Through these acquisitions, Qualcomm Aware platform enables energy-efficient location tracking for battery-operated sensor devices used in supply chain visibility applications. Along with the location services, The Qualcomm Aware platform also offers additional software capabilities such as connectivity management, end-to-end security and feature-rich open #API tools for solution developers and system integrators to seamlessly integrate with ERP and cloud systems across vertical industries.
Softening demand, market fragmentation and supply chain complexities underpin Qualcomm #SaaS move
As the semiconductor market increasingly faces stiff competition, as the cost of radio chipsets and modems continues to depreciate annually. Demand for #IoThardware has also dwindled as enterprise IoT adoption is disrupted due to various global market uncertainties triggered by the #US-China trade wars, the #COVID-19 pandemic, and more recently Russia-Ukraine war. These market uncertainties have also exposed vulnerabilities in the industrial supply chain due to the lack of visibility in global value chains and the concentration of production in a few countries. IoT IC chipset market growth has suffered in the last few years across all regions except for #China which accounts for a large majority of the IoT chipset/module sales driven by smart meter(enerygy and water) and smart city applications.
The above market conditions have accelerated communication chipset and module vendors need to strengthen their hardware portfolio with value-added software and to move up the value chain and ensure a larger share of revenues from enterprise #digital #transformation. With the Aware platform, #Qualcommis creating a one-stop-shop for device-to-cloud solutions by strategically partnering with device OEMs such as #ikotec and #Sodaq.
Qualcomm Aware platform attempts to address the technology market fragmentation and complexities of device-to-cloud data management, and low-power, low-cost location tracking, a key criterion for battery-operated sensor devices. The Aware platform will play a significant role in enabling supply chain visibility in enterprises that are undertaking digital transformation of their operations by implementing sensor networks. These sensor networks will allow enterprises to gather new data streams that offer real-time actionable insights to continuously improve operational visibility and control.
The Qualcomm Aware platform helps simplify the provisioning and commissioning of connected field devices when implemented, using multiple wireless connectivity technologies at scale across geographical locations and environments. The platform’s positioning technology will help field technicians automatically tag the location of devices during the installation process. Device location data is not only important for tracking mobile assets but also is an essential data point when installing stationary assets. In vertical IoT applications like smart meters, #streetlights, power transformers, industrial containers, feed silos, etc, tagging the precise location of field assets is an essential data requirement while provisioning the connected assets. The location data of fixed assets are integrated into enterprises' #GIS and subsequently used for periodic maintenance and other field service operations.
Skyhook and PoLTE location technology merged into a powerful device-to-cloud platform
Founded in 2007, Skyhook is a Boston, US-based location software that offers positioning technology using #WiFi, cellular, and #GNSS signals, or a combination of these wireless technologies to calculate device geo-location in the cloud. The accuracy and precision of the geolocation vary depending on the environment and wireless network technology.
PoLTE based in Dallas, Texas, is a location technology company founded in 2005. PoLTE, #proprietary #Cloud #location over cellular (C-LOC) technology leverages carriers' terrestrial LTE and 5G networks to offer real-time location services.
Both these cloud-based location technologies require a small firmware upgrade in device hardware to install a software agent that analyses signals from already deployed networks (Wi-Fi, cellular, and GNSS). This data is transmitted to the cloud to calculate near real-time geolocation of the device.
PoLTE and Skyhook achieve this using powerful cloud solvers leveraging either cellular and/or short-range wireless (Wi-Fi & #BLE) network scan data to compute accurate location data in the cloud. For example, a Wi-Fi-enabled device uses network scan information (eg. signal strength) from multiple Wi-Fi access points to compute the location of the device. Similarly, in the case of cellular networks, the device location is computed using measurement data obtained from cellular radio towers. The devices transmit network characteristics with an accurate time stamp to the cloud where powerful algorithms use data points either from a single network or in the case of hybrid solvers using multiple networks to compute the location with accuracy varying from a few centimetres to 10’s of meters.
Qualcomm Aware platform embeds these two powerful #geolocationtechnologies in PoLTE and Skyhook to their Qualcomm IoT modem chipsets. Integration of PoLTE and Skyhook technologies brings together their strengths in cellular and WiFi network geolocation to the Aware platform. This enables Qualcomm to offer #energy-efficient geolocation services, by transferring the location processing workload from the device to the cloud. This is a crucial requirement for battery-operated sensor devices that need to operate autonomously in the field for several years to create a strong business case and a positive return on investment (ROI) for various digital transformation projects.
One-Stop-Shop device to cloud platform will help reduce solution time to market
Vendors offering digital supply chain solutions using Qualcomm chipsets will gain the most value as they can quickly integrate Qualcomm’s Aware platform as an off-the-shelf solution to its asset visibility solution stack. This will help IoT device OEMs, system integrators and solution providers to accelerate their solution time to market. The platform's capabilities reduce complexities in device provisioning and commissioning, connectivity management, and security of IoT devices at scale.
Qualcomm Aware will potentially help reduce fragmentation and offers enterprises an end-to-end solution. The Aware platform is a device-to-cloud service that comes with integrated devices, global data connectivity, device management, tracking and sensing #modules, and developer-friendly cloud APIs.
As part of the Aware platform launch, Qualcomm has also announced a developer device, the Qualcomm QT S110 tracker which uses the #MDM9205 modem. The device is designed for global multi-modal supply chain visibility needs and comes pre-integrated with Aware Cloud. Qualcomm plans to add three new deviceswhich include:
Aware Thin Tracker, a credit card-sized tracker for shipment logistics.
Aware Cellular Label, a smart label for tracking parcels.
Aware Sensor, a low-cost inclinometer for pole tilt monitoring.
Analyst view: Opportunity in Enterprise Supply chain visibility-“You cannot improve what you don’t measure”
To improve industrial supply chains, enterprises are increasingly demanding near real-time visibility in the form of geolocation and condition of field assets. Furthermore, supply chain visibility will play a crucial role for industries to transition from existing linear to more #sustainable and #circular supply chains. The need for reliable and real-time data on assets and processes has become a critical requirement to plan, strategise and execute the necessary changes. Qualcomm aware platform has identified six asset-intensive industry verticals- construction, energy & utilities, healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and retail. However, over time the demand for digital tools that help transition to circular/sustainable supply chains will be felt across all industries.
Broader market segmentation for potential opportunities in enterprise asset visibility can be briefly summarised as follows.
A) Indoor/Campus Asset Visibility
Visibility (location and condition) of assets within the premises of a building or a campus. This includes tracking movement and condition of assets/goods within building facilities such as factories, warehouses, hospitals, retail shops, transportation hubs, construction sites, educational institutions etc. The requirement for asset visibility in indoor environments are as follows-
Have a higher density of assets in indoor environments with location tracking and condition-monitoring at the item level and/or aggregate level (pallets, containers, Re-usable transport units).
Indoor asset visibility solutions today are dominated by short-range wireless connectivity technologies deployed as campus networks. Over the years, #RFID and to some extent BLE have gained mainstream adoption across key industry verticals such as Retail & apparel, logistics, manufacturing, and health care.
Location accuracy requirements for of indoor asset tracking can vary from a few centimetres to meters.
Short-range wireless connectivity technologies such as RFID, #UWB, Wi-Fi, and BLE are popular technology choices for enabling asset visibility indoors,
Cellular network technologies such as #NBIoT, #LTEM and 5G and non-cellular LPWAN LoRaWAN are increasingly gaining indoor coverage, especially through the deployment of private networks.
Qualcomm Aware platform fit- Low: Qualcomm Aware platform currently does not support RFID and BLE 2 dominant connectivity technologies used in indoor asset visibility. Native support of the RFID, BLE and UWB on the Aware platform would help enterprises with legacy asset visibility systems benefit from cloud applications and expand their indoor asset visibility use cases enabled by new capabilities enabled by technologies such as Wi-Fi-6, UWB and 5G.
B) Outdoor Asset Visibility
The demand for Asset visibility in outdoor environments is often for high-value assets or assets transported in the aggregate form in pallets, boxes or containers. The requirement of asset visibility for outdoor environments are as follows-
Item-level tracking of assets is mostly implemented through an edge gateway (parent) embedded with cellular and GNSS connectivity that is linked to multiple trackers (child) used to monitor either individual items or at aggregate levels when assets are being transported.
Location accuracy for outdoor asset visibility typically varies from a few 10’s of meters to hundreds of meters with the data transmission frequency of a few times a day. Sensors such as temperature sensors, vibration sensors, level sensors, humidity/moisture sensors, and pressure sensors are typically used to monitor the condition of goods while in transit.
Devices use public connectivity network infrastructure and require reliable regional coverage and/or even multi-regional coverage for use cases such as multi-modal container tracking.
Low-cost asset tracker devices use RFID, BLE and #Zigbee to track at the item level.
Asset trackers using #LPWA network technologies such as 5G (LTE-M, NB-IoT) and LoRa and Sigfox have emerged as popular technology choices to offer simple, low-cost outdoor tracking solutions at the item and/or aggregate level without the need for gateways devices.
Qualcomm Aware platform fit- High: Provides strong value proposition in this segment as the Aware platform offers an Off-the-shelf solution that will help enterprises transition from legacy outdoor asset visibility solutions using cellular technologies such as 2G/3G networks that are expected to be sunset soon to more energy efficient technologies such as #CAT1, LTE-M and NB-IoT. The simplicity and TCO benefits from low-power, low-cost, outdoor asset trackers will also help replace existing complex point-to-point tracking systems and also stimulate new demand for asset visibility.
C) Seamless Indoor and Outdoor Asset visibility
End-to-end supply chain visibility requires seamless tracking of goods or assets as it moves through factory floors to warehouses to end-customer locations and in some cases returned back.
Changing environments present several challenges as no single location tracking technology is suitable for seamless indoor and outdoor tracking. Asset visibility application requirements also vary depending on the environment.
Relatively more complex solution designs to address application and business use-case requirements.
Leverages a combination of private/campus networks and public network infrastructure for device connectivity.
To enable seamless indoor and outdoor tracking capability use multi-radio connectivity hardware using a combination of short-range wireless technologies such as RFID, Wi-Fi, BLE and UWB for indoor environments and WAN technologies for cellular, GNSS and non-cellular LPWA for outdoor environments to mitigate connectivity network coverage limitations.
Qualcomm Aware platform fit- Medium: In this segment, connectivity technology limitations contribute to solution design challenges that have a direct impact on device/solution complexity from multi-radio hardware, cost, implementation complexity, data silos, integration challenges etc that directly impacts enterprise adoption. The Qualcomm Aware platform’s growth in this segment will depend on indoor network coverage of cellular (4G/5G) and Wi-Fi to drive adoption or the platform will require plug-ins, and integrations with indoor asset visibility solution providers to offer end-to-end supply chain visibility.
Conclusion and Recommendations:
As briefly explained above, application requirements for location technologies vary depending on the industrial supply chain process, interoperability with existing systems, location/environment, the total cost of ownership, ease of implementation and several other factors. Qualcomm’s Aware platform currently supports Wi-Fi, Cellular and GNSS network technologies and does not include BLE and RFID two popular location technologies used in indoor location services. The platform also does not support emerging location technologies such as UWB and LoRaWAN. These limitations can be potentially addressed by leveraging the open APIs to integrate data generated from connectivity technologies currently not supported by the platform.
Qualcomm’s acquisition of Skyhook and PoLTE and its integration into the Qualcomm Aware platform also validate the value and demand for cloud-based location technologies. However, Qualcomm through this strategic acquisition has also created problems for several of its competitors. Over the years, Skyhook and PoLTE had developed strategic partnerships with several chipset vendors including #Mediatek, #Unisoc, #Altair Semi, #Nordic Semiconductor, and #Sequans Communications that have embedded their location technology in their chipsets to offer similar geolocation services. it’s unclear after the acquisition of PoLTE and Skyhook, how these chipset vendors will mitigate the impact on its continuity of geolocation service. In the short term, the affected chipset vendors can potentially switch to other cloud-based location software technology providers such as #Google, #Here, #unwired labs, and #Ubudu, which offer similar indoor and outdoor geolocation solutions.
The Qualcomm Aware platform will directly compete with connectivity platforms and solutions from large telecom operators such as #AT&T, #Verizon, #Vodafone, #DeutscheTelekom, #Orange Etc that offer similar enterprise asset visibility solutions. That said, the Qualcomm Aware platform also helps other regional telecom operators with similar ambitions to offer end-to-end solutions will be able to quickly develop their asset visibility offerings and significantly reduce their solution time to market.
Finally, the acquisition of Skyhook and PoLTE by Qualcomm highlights the need for the industry to collaborate on an open-source, standards-based low-power location technology for sensor devices that are agnostic of connectivity technology and radio-chipset vendor. Such an open-source standards-based solution will foster a multi-vendor cloud-based location technology supplier and chipset supplier ecosystem, enabling interoperability and reducing the risks of vendor lock-in for end customers.
#IoT#digitaltransformation#supplychain#visibility#LPWA#technology#assettracking#strategy#GTM#assetvisibility#qualcomm
1 note
·
View note
Text
Drive with Confidence: Navigating the Thriving Automotive Defogger System Market
Automotive defogger systems are a crucial part of any vehicle, ensuring that the driver's visibility is not impaired during cold or humid weather. These systems work by heating the rear windshield and removing any condensation or frost buildup, providing a clear view for the driver. The defogger system typically consists of a set of electrical wires that heat the windshield, a control switch, and a timer. Depending on the make and model of the vehicle, the system may also include sensors to monitor humidity and temperature levels.
One of the key benefits of automotive defogger systems is improved safety for drivers. Fogged or misty windows can obstruct the driver's view, leading to potential accidents. The defogger system eliminates this risk by quickly clearing up any condensation or frost buildup, allowing the driver to see the road clearly. Moreover, it also prevents the need for drivers to manually wipe or clean the windshield, which can be a distraction while driving.
Request For The Sample Copy of The Report @ https://www.persistencemarketresearch.com/samples/32173
Automotive defogger systems are generally low maintenance and can last for several years. However, like any other part of the vehicle, they may require repair or replacement if damaged or malfunctioning. Regular cleaning of the windshield and proper use of the defogger system can extend its lifespan and improve its effectiveness. With the increasing demand for safety features in vehicles, automotive defogger systems are becoming an essential component for manufacturers to include in their models.
About us: –
Persistence Market Research is a U.S.-based full-service market intelligence firm specializing in syndicated research, custom research, and consulting services. Persistence Market Research boasts market research expertise across the Healthcare, Chemicals and Materials, Technology and Media, Energy and Mining, Food and Beverages, Semiconductors and Electronics, Consumer Goods, and Shipping and Transportation industries. The company draws from its multi-disciplinary capabilities and high-pedigree team of analysts to share data that precisely corresponds to clients’ business needs.
Contact Us:
Persistence Market Research
Address – 305 Broadway, 7th Floor, New York City, NY 10007 United States
U.S. Ph. – +1-646-568-7751
USA-Canada Toll-free – +1 800-961-0353
Sales – [email protected]
0 notes