#wifitesting
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Which one is better: Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 7 ?

Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 are the latest generations of wireless networking technology. Both Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 promise faster speeds, improved performance, and greater capacity than previous generations of Wi-Fi. However, there are some key differences between the two technologies that are important to understand.
One of the primary distinctions between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 is their maximum data transfer rates. Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, can reach speeds of up to 9.6 Gbps, while Wi-Fi 7, also known as 802.11be, can reach speeds of up to 30 Gbps. This means that Wi-Fi 7 is significantly faster than Wi-Fi 6.
Another difference between Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 is their capacity. Wi-Fi 6 is designed to handle a greater number of devices on a single network, allowing more devices to connect and communicate at the same time.
Wi-Fi 6 also has improved security features, including support for WPA3, the latest standard for wireless network security. Wi-Fi 7 also has advanced security features to protect the network from unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Wi-Fi 6 also has a feature called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) which enables the router to divide a channel into smaller sub-channels. This allows multiple devices to share the same channel and communicate at the same time, improving network efficiency and reducing latency.
Recent updates in Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7 is not yet an official standard and it has not been released yet. The Wi-Fi Alliance, the organization that oversees the development of Wi-Fi standards, has not announced any official plans for Wi-Fi 7. Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is the latest standard that has been announced and it is currently available for use.
Wi-Fi 7 is in its early development stages and it is expected to be released in the future. It’s worth mentioning that Wi-Fi 7 is also known as 802.11be, it is expected to be faster and more efficient than Wi-Fi 6, with speeds of up to 30 Gbps and the ability to support even more devices and handle more data traffic. Checking the official website of Wi-Fi Alliance for the latest announcements and updates on Wi-Fi 7 and other wireless networking technologies.
Conclusion:
Wi-Fi 7 is faster, more efficient, and more secure than Wi-Fi 6. With faster speeds, greater capacity, and improved security, it is the ideal choice for organizations and businesses that need to support a large number of devices and handle large amounts of data traffic. However, the availability and the price of the devices that support Wi-Fi 7 is currently limited and it may take some time for it to be widely adopted.
0 notes
Text
Wi-Fi Testing – Know how we test Access Points and improve Broadband Experience
Wifi Testing is one of the most fundamental ways to test access points and we at Alethea test it through our innovative tool to test #Wifi Access Points. We build test and measurement solutions addressing Broadband technologies space. Based out of India, our mission is to enable Perfect Broadband to Everyone, Everywhere, Everytime.
Rolling out a world-class #Wifi solution needs testing to be planned into every stage from development to deployment. Hence, you need a test solution that meets the requirements of a developer and the field engineer.
Most #Wifi networks today are only qualified with few clients for coverage with basic elements and interoperability testing. This woefully inadequate testing exposes companies to the risk of poor customer satisfaction. There are four major aspects that need to be addressed in testing before launching.
Scale: In the past, the number of #Wifi clients used to be in single digits. However, nowadays each household has 30-50 clients and public spaces such as stadiums and airports see user density of 200-300 clients per access point.
Functionality: With the release of features such as OFDMA, TWT, BSS Coloring, the testing complexity has increased. The traditional approaches to testing no longer suffice to deliver necessary test coverage.
Real Applications: Wifi started as just a 2Mbps throughput pipe. Today, we see Multigig throughput with optimizations for different types of traffic. Testing with #iperf and ping misses validating all the application-specific performance, inherent intelligence, and complexity.
Interoperability: WiCheck 6 is a new technology and any new technology rollout will see lots of interoperability issues. Testing #WiFi 6 #Accesspoints against 10s to 100s of popular new & legacy clients devices is a necessary, but extremely tedious task.
Alethea’s innovation to address these is the Distributed Device Architecture (D2A). It consists of a dedicated traffic generator/controller and different radio elements (dedicated radio test elements are called #Radioheads) that can be spatially distributed.
Each #Wi-Fi6 Radiohead supports 300+ clients across multiple bands. Multiple Radiohead can be combined to emulate 2500+ spatially distributed, stateful emulated clients.
Each of the emulated clients is capable of running a suite of around 50 applications such as video streaming, VoIP calls, browsing and malformed data packets to emulate real-world scenarios.
A specialized type of Radiohead called LinA is used to test functionality such as OFDMA and TWT.
The controller can manage 10s to 100s of real devices running different operating systems to ensure interoperability.
Our innovation is that a single product and system can address all these disparate elements and test requirements.
Scale with WiCheck 6 Radiohead
At Alethea, we combine different types of test elements into a single system. The most powerful from a scale and functionality perspective is WiCheck 6. Each WiCheck 6 Radiohead is capable of up to 300 stateful emulated clients. Each client supports real applications like video streaming and voice calls to our users and Wi-Fi security from Open to WPA3 Enterprise. With WiCheck 6, Performance measurements, stability, security and functionality can be done with different authentication mechanisms at scale with just a few clicks.
Functional Testing with LinA
WiCheck 6 LinA is a specialized OFDMA tester Radiohead capable of supporting 10s of Real Wi-Fi 6 or 6E clients. These will combine with the scale offered by our WiCheck 6 Radioheads to test OFDMA capabilities, band steering, load balancing and other capabilities enabled by #Wi-Fi 6/6E rollouts. Built in sniffing capabilities ensure that you are able to have a complete understanding of the message flow.
Real Device Control
WiCheck is capable of offering a meaningful level of control & configuration of upto 200 real devices. These devices could be on different operating systems (Windows, MacOS, Android, IOS) Voice calls, Video and Browsing along with measurement applications can be run on each of these devices and meta reports generated.
Real Application Support
As can be seen above, all the different hardware elements in the test topology are delivered using Alethea’s WiCheck 6 solution and are capable of running real applications traffic. With Access Points, Controllers and Gateways becoming more intelligent in handling different types of customers and traffic streams, the ability to test these aspects becomes very important.
Ability to Combine Multiple Test Elements
With Alethea’s innovative approach, #OEMs, operators, and other ecosystem partners can now deploy comprehensive test systems that address every aspect of their verification process. Whether the system is in the lab of the field, elements of Alethea’s WiCheck system are capable of fulfilling the test requirements. All these elements are tied together and programmable and can also be used from a very accessible user interface.
Wi-Fi Testing- The Alethea Way
We believe the complexity of test tools is a major reason why developers miss to find bugs. Our approach is to reduce the ramp-up time and make the core functionality of the product easily accessible. Our workflow is kept so simple that every feature on the tool is accessible with a maximum of 3 clicks. For a Wi-Fi test engineer, the ramp-up time could be as short as a couple of hours. The modular nature of the tool also helps it adapt to new hardware/technology with minimal overhead to the users.
Making Wi-Fi Testing Simple & Effective with Alethea’s Unique Approach and Methodology
In today’s world, ensuring Scalability, Stability, Functionality and Security of Wi-Fi infrastructure is critical for meeting user expectations. Alethea’s innovative approach to #Wifi testing and the implementation of that approach as part of the WiCheck 6 test system helps our ecosystem partners meet their test requirements.
There is no other tool that can cover the ground like we do. We believe that the innovation we have demonstrated will help the ecosystem grow stronger and make #Wificonsumers happier
More information about the company & its products are available at https://www.aletheatech.com
If you want to take a quick demo, please mail us at [email protected]/
@AletheaComm
#wifitesting#wifiaccesspoints#wifi#wifi 6e#wifi solutions#wifiloadtesting wifi6scaletesting#wifilegacytesting
1 note
·
View note
Photo

Que jodida está la red ahora.... muy mal... 👎 . . . #wifi #wifitesting #pentesting #ceh (en Starbucks - Chapultepec Guadalajara) https://www.instagram.com/p/B3-ny-ogY4y/?igshid=t36irvjc9dhh
0 notes
Photo


Cable Provider Speed Test & Statistics | Best trick Cable Provider Speed Test & Statisti... https://legitnews247.com/?p=21755&feed_id=3209
#TECHNOLOGY#CABLEPROVIDERSPEEDTEST#CHECKINTERNETSPEED#INTERNETSPEEDTEST#INTERNETTEST#MYINTERNETSPEED#SPEEDTESTINTERNET#TESTMYINTERNETSPEED#WIFITEST
0 notes
Photo

Cara Jitu Mengetahui Password Wifi di Laptop dan Aplikasi HP
0 notes
Text
Hướng dẫn hack Wifi chi tiết trên điện thoại và máy tính
Wifi là một kiểu tín hiệu mạng không dây với những tiện ích cho các thiết bị di động như smartphone hoặc TV thông minh dễ dàng kết nối để trải nghiệm các tính năng cần tới internet tương đối đơn giản. Dù khoảng cách giới hạn nhưng điểm truy cập không dây (hotspot) vẫn được ưa chuộng, hack pass wifi vì thế vẫn được tìm ra dưới nhiều phương thức có cách thực hiện vô cùng đa dạng.
Router có thiết lập mật khẩu ra sao hoặc theo phương thức bảo mật WEP, WPA/WPA2 thì vẫn có một tỉ lệ cao trong việc đảm bảo thành công khi muốn truy cập vào mạng đó, tất nhiên mình sẽ không chắc chắn tuyệt đối tuy vậy bạn hãy thử làm theo nha.
Hướng dẫn hack pass Wifi trên điện thoại
Hack pass Wifi với AndroDumpper
– Bạn cần tải về ứng dụng AndroDumpper mình đã update file cài đặt ở cuối bài hướng dẫn này rồi.
– Download và cài đặt xong hay mở ứng dụng đó ra.
Giao diện sau khi bạn mở phần mềm
– Tải về 5 triệu mã Pis đã được tổng hợp và chia nhỏ cho máy điện thoại: Download ở đây.
Nếu điện thoại của bạn có cấu hình yếu thì chỉ nên chạy số lượng từ 500 mã Pis đổ lại thôi tránh tình trạng bị đơ máy phải thực hiện lại từ đầu, còn những máy điện thoại cấu hình đời cao nên chạy tầm 1 triệu Pis thôi nhé để đảm bảo tỉ lệ an toàn nhất khi sử dụng.
– Mở ứng dụng ra chọn Try Connect nó sẽ hiện lên một bảng.
Trong trường hợp hiện như thế này bạn hãy click vào Continue
– Tiếp đến nó hiện ra một số tính năng như sau, bạn chọn Brutefore nha.
– Nó sẽ hiện lên chức năng chọn tìm tới thư mục lưu file mã Pis để đọc cũng như xử lý trong quá trình hack wifi cho điện thoại.
Chọn FROM DICTIONARY
Bước cuối cùng giờ bạn chỉ cần chờ đợi để có thành quả như mình muốn mà thôi, nó sẽ hơi lâu đấy nhưng đây lại là cách hay nhất trên điện thoại tương đối hiệu quả.
Hack pass Wifi qua WPSPIN
Bạn hãy tải về phần mềm WPS hỗ trợ vào Wifi bằng mã PIN mình đã để link download ở phía cuối bài viết rồi cài đặt nó và sử dụng ngay nhé.
– Bước 1: Mở ứng dụng ra cũng như bật chức năng Wifi để quét ngay những mạng hiện có ở xung quanh bạn.
– Bước 2: Chọn một mạng Wifi mà bạn muốn thực hiện để truy cập, lời khuyên của wapmienphi.info là bạn nên chọn mạng nào mà có sóng wifi mạnh để việc vào nó sẽ diễn ra nhanh hơn không bị chậm trễ hoặc thất bại vì tín hiểu quá yếu.
Nó sẽ hiện ra giao diện như sau, nhớ mã PIN đầu tiên để tiếp tục nhé
– Bước 3: Vào WLAN (tính năng cài đặt Wifi của điện thoại), chọn mạng Wifi phía trên mà bạn vừa thực hiện ở bước trước đó. Chọn nâng cao >> Mã PIN từ điểm truy cập rồi nhập mã PIN trước đó vào ô và chọn kết nối.
Nhập mã PIN và Kết nối ngay
– Bước 4: Làm hoàn thành ba bước trên tức là bạn đã kết nối Wifi vào thành công. Bây giờ muốn hiển thị mật khẩu bạn hãy thực hiện như sau: Vào WLAN pass show chọn show display password, rồi vào Wifi chọn mạng bạn đang kết nối nó sẽ hiện ra mật khẩu. Tuy nhiên chức năng này một số điện thoại không được hỗ trợ nên nếu bạn không dùng được thì cũng đừng quá ngạc nhiên nhé.
Thông tin chung và mật khẩu đã được hiện lên
Nếu máy điện thoại không có tính năng hiển thị mật khẩu thì bạn hãy download ứng dụng Wifi Connect Manager và chọn chức năng Wifi rồi click vào WPS Push Button là được nhé.
Sử dụng WPS tự động/thủ công với WifiTest
Với cách tự động
Hiện thị các mạng wifi đang được phủ sóng
– Sau khi tải về máy và cài đặt xong bạn mở phần mềm ra và chọn bất kì một mạng wifi nào có hỗ trợ.
– Chọn bắt đầu kết nối, quá trình này mất khoảng 2 phút.
– Để xem thành công hay thất bại thì gạt thanh status của máy xuống và xem thông báo.
Với cách thủ công
– Chọn một mạng wifi mà bạn muốn với điều kiện có hỗ trợ nhé.
– Chọn vào chức năng Lấy PIN.
– Ghi nhớ lại mã PIN rồi chọn nhập Pin thủ công sau đó ấn xong để kết nối.
Sử dụng Wifi Chùa
Thực ra đây không phải là ứng dụng hack wifi nhưng với cách hoạt động lưu trữ mật khẩu được chia sẻ từ chính người dùng kèm vị trí chính xác bạn có khả năng theo dõi xác định xem mạng wifi đó có gần chỗ hiện tại của mình hay không. Từ đó việc tra cứu xem xét để truy cập modem Wifi dễ dàng phục vụ nhu cầu của bản thân nhất tương đối đơn giản.
Hướng dẫn hack pass Wifi trên máy tính
Trước tiên bạn cần phải cài đặt JumpStart và Dumpper trên máy tính của mình để bắt đầu thực hiện hai tính năng kết hợp mang lại thành công vượt qua mọi mật khẩu khó của chủ sở hữu wifi.
Tải về JumpStart 2.1.1 bản tiếng Việt tại đây. Tải về Dumpper mới nhất ở đây.
Dùng kết hợp JumpStart + Dumpper để hack Wifi
Mở ứng dụng Dumpper trên thiết bị của bạn và làm lần lượt như sau.
Chọn tất cả mạng Wifi.
Quét.
Chọn một mạng wifi có trong danh sách, ở chỗ mình có mỗi một mạng nên mình làm ví dụ thôi, bạn có thể xem bên cột tín hiệu để biết mạng nào mạnh rồi lựa chọn nhé.
Chạy JumpStart.
Nếu có cửa số này bị hiện lên thì chọn Tiếp tục nhé.
Nó sẽ hiện lên thông báo xử lý quá trình kết nối bạn cần chờ một chút.
Nếu thành công sẽ có giao diện như thế này.
Muốn xem mật khẩu wifi đó là gì bạn quay lại phần hồ sơ của Dumpper là được nhé.
Hack pass Wifi với JumpStart
Cách này sẽ lâu hơn và kém hiệu quả so với cách đầu tiên tuy nhiên cũng nên thử vì biết đâu một trong hai phương pháp này giúp bạn có được mật khẩu Wifi xung quanh.
Mở JumpStart lên, chọn tự động nhập PIN vào điểm truy cập Wifi > Next. (Nhớ bỏ dấu tích tự động chọn mạng Wifi đi nhé)
Chọn một mạng Wifi trong danh sách bấm Next, các bước sau chỉ cần chờ đợi kết quả mà thôi.
Như vậy mình đã hướng dẫn xong cách phá mật khẩu Wifi qua hai phần mềm JumpStart và Dumpper trên máy tính rồi đấy việc còn lại bạn chỉ cần thử xem độ may mắn của mình có kết nối thành công được hay không mà thôi.
Trên đây là toàn bộ những gì mà Wap Miễn Phí chia sẻ tới mọi người bí kíp để hack mật khẩu Wifi ở những dòng máy, thiết bị đã được công bố ở diễn đàn cũng như mạng xã hội được đông đảo người dùng công nhận, hy vọng rằng sẽ nhận được sự ủng hộ bằng cách chia sẻ nhiệt tình nó nhé.
source https://wapmienphi.info/hack-pass-wifi.html
0 notes
Text
Linksys en Tweakers zoeken vijf wifitesters
Ons hele digitale leven als tweaker is afhankelijk van de kwaliteit van het wifisignaal. Heeft een vakantiebestemming geen wifi, dan gaan de meeste tweakers ergens anders heen. Wij tweakers zijn nu eenmaal gehecht aan een goede verbinding en Linksys weet dit als geen ander. https://goo.gl/SE7ZkD
0 notes
Text
Linksys en Tweakers zoeken vijf wifitesters
Ons hele digitale leven als tweaker is afhankelijk van de kwaliteit van het wifisignaal. Heeft een vakantiebestemming geen wifi, dan gaan de meeste tweakers ergens anders heen. Wij tweakers zijn nu eenmaal gehecht aan een goede verbinding en Linksys weet dit als geen ander. http://dlvr.it/NYj5BF
0 notes
Text
The Future of In-Flight Wi-Fi: How Scale Testing Can Ensure Smooth Deployment

In the 21st century, Wi-Fi has become an integral part of our daily routine needed in every sector of industry. Wi-Fi as a technology introduced in the early 2000s has grown with each passing day and is evolving rapidly. With initial speeds from 100kbps in the early 2000s Wi-Fi can generate a speed of Gbps in seconds from anywhere in the world. Any information on any topic about Wi-Fi is available just in our fingerprints from any look and corner of the world and has certainly made our life easier and faster. With Wi-Fi showing high signs of improvement in all industries, the connectivity inside the aircraft is still not as up to the mark. That is why many experts say that it is the market of the 21st century and has valued it at 5.5 billion dollar market in 2022 which is expected to increase by 15% in the next few years. Connecting to the internet from an aircraft for a decade was something we had only imagined, thanks to the evolving Wi-Fi technology we are now able to get good and better connections throughout the journey. Even though the time of journey and spacious seats are a concern, the Wi-Fi connectivity in the last few years has certainly improved. Many of the market leaders are investing in In-flight connectivity as there is a high increase in high-definition streaming, data-loaded applications and connected networks everywhere. In the past few years, many carriers have started to deploy inflight Wi-Fi to their fleets to make the overall flight experience better. Wi-Fi has been a major looked criterion for people whenever they are about to book a ticket and with this high increase in demand and need for Wi-Fi, it has become a must to install Wi-Fi in their planes but to deploy Wi-Fi in the aircraft is a lot of investment, time taking process which has to be done with a lot of testing to make sure to provide the best Wi-Fi to all the passengers. Before deployment, it is very necessary to test the performance and experience of the Wi-Fi and so testing at scale is a mandatory process to make sure that it caters to a large number of users at a single point in time. Therefore testing at scale ensures all the problems can be looked at and the best Wi-Fi with the best performance can be installed in the aircraft.
The deployment can be done as per the requirement after the large-scale testing to provide a high-quality connection to all the users without any interruption. At Alethea Communications Technologies, we test inflight Wi-Fi at scale before the deployment process to make sure that all the users get a seamless connection for a memorable flight journey.
To know more - Visit Us
0 notes
Text
Log Analysis using AI/ML for Broadband

Log Analysis using Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning [AI/ML] for Broadband
Whenever you hear about “Log analysis”, we picture a developer, going through 1000s of lines of logs to figure out a problem. Does it always have to be like this? Our topic of discussion is what can Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning [AI/ML]do to help us in Log analysis.
Need for Automated Log Analysis
In large-scale systems, the seemingly obvious way of log analysis is not so scalable. A broadband network managed by an operator like Comcast, having 100s of Wi-Fi Access Points and Routers/Switches and 4G/5G small cells, from multiple equipment providers, say Commscope, Aruba, or CISCO. Collection of logs at multiple nodes, there are GBs of data created every minute.
The possible issues are hidden, they may not be something as obvious as a crash. It may be a problem that occurred and went away and could not be detected, other than the fact that there were several complaints received by the Network Operators. These systems are developed by multiple developers (100(0)s), so it is difficult to be analyzed them by a single person. They pull out modules from various third parties and make extensive use of the open source. And then the parts of the systems are on continuous upgrade cycles. So there is a clearly established need for automated log analysis in large-scale networks through the use of smart log analysis techniques.
Mapping Log Analysis problem to Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning [AI/ML] problem
Machine learning sees the problems in two ways:
supervised
unsupervised.
Supervised learning is applicable if we have a labeled data set i.e. input data, where we know the label (or value). With this data, we can train the model. After Training, the model can take the new input and predict the label (or value).
Unsupervised learning means we do not have labeled data sets. The model classifies data into different classes. When the new data arrives, it finds the correlation with the existing classes and puts it into one of those classes.
For log analysis, we are basically looking for anomalies in the log, something that is not normally expected. We may or may not have labeled data sets, and accordingly, we need to pick supervised or unsupervised learning.
Anomaly Detection algorithms. For supervised algorithms, we will have data sets, where each set is labeled as “normal” or “Anomaly”. For unsupervised algorithms, we need to configure the model for two classes only, “Normal” or “Anomaly”.
A combined approach is good for the broadband use case, where both can be used. For clear anomalous behaviour we can use supervised methods. And when creating an exhaustive labeled data set may not be possible, we can fall back to unsupervised.
These algorithms exist already and there are open-source implementations as well. (refer References)
Mapping Logs to Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning [AI/ML] input
There are many ongoing online logs coming from various nodes. The only way to make a data set is to time-slice them, into smaller log snippets. Using each snippet we have to convert it into a data set.
Now the logs are distributed, coming from switches, routers, SysLogs and Pcaps, and Others. Do we need different models for each kind of log? No. The logs have to be given to a single Model as only then the correlation between different logs can be harnessed.
The logs are unstructured text, can we use (Natural Language Processing) Models to extract data sets from the logs. The answer is again “No”. For NLP models, the text is preprocessed to get features like the number of times a word is repeated, the different words followed by each other, and other features. There are pre-trained models which can do this and have been trained over the entire Wikipedia text! But these can not be used for logs, as logs have technical context and not the natural language.
Since logs have an underlying structure, we can view the log snippets as a series of predefined events. This way we can retain the information in each log. It also helps aggregate different kinds of logs, as we can consider the logs having different sets of events. The model will be trained by understanding based on events that are happening in a given time window and can then detect anomalies.
Constructing Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning [AI/ML] Training data set from Logs
Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning [AI/ML] works on vectors/matrices of numbers and additions and multiplications of these numbers. We can not feed these events directly to the model. They need to be converted into numbers. (Gradient Descent and Logistic Regression works with finding derivatives. Deep learning is Matrix multiplications and lots of it. Decision Trees or Random forests partition the data on numbers.)
For computer vision and image processing use cases, these numbers are the RGB value of each pixel in the image. For tabular data, the text is converted into numbers by assigning ordered or unordered series.
One option is to associate each event with an identifier number and give vectors of these identifiers to the model, along with a timestamp. However, synchronizing/aggregating this will be an issue as we will start getting these vectors from each node. Also one event may happen multiple times, in the snippet, so handling of these vectors will become complex.
So a better method is to collate vectors from each node for a given time slice and then go with the count of each kind of event in a master vector.
We explain the approach below in detail. The approach is derived from this popular paper, for more details please refer https://jiemingzhu.github.io/pub/slhe_issre2016.pdf)
1.Log Collection –
In broadband systems, we have multiple sources of logs (SysLog, Air captures, wired captures, Cloud Logs, Network element i.e. switches/Routers/Access Points logs). We need to first be able to gather logs from each of the sources.
We need to make an exhaustive list of all sources as
[S1, S2, S3.. Sn]
2.Event Definition – For each source, we need to come up with predefined event types. In the networking world, broadly event types in the logs, can be defined as follows
Protocol message
Errors/Alerts
Each Type is one event type
Layer
Management
Each Type is one event type
Control
Each Type is one event type
Data
Each Type is one Event type
State Change
Error Alerts
Each Type is one event type
Module
Each Critical Log Template is an event type
Each State Transitions is an event type
Errors/Alerts
Each type of Error/Alert is one event type each Leaf node corresponds to a different event
With this analysis, for each source, we come up with a list of events, as follows
[S1E1, S1E2, S1E3,.. S1Em,
S2E1, S2E2, S2E3,.. S2En,
… ,
SnE1, SnE2, SnE3,.. SnEp]
3.Log to Event conversion – Each line of the time series log will have a constant part and a variable part. The constant part is what we are interested in. Variable parts like IP addresses, source and destination are variable and need to be ignored. We need to parse logs for the constant parts, to check if the log has any event or not, and record only the event. Then the log snippet taken over a window of time will start looking like something like this for a source.
[T1, E2
T2, Nil
T3, E2
T4, E4]
4.Frequency transform – Invert the parsed log to find event frequency. Basically in a given time window how many times an event happened. So if the window goes from Time 1 to Time 4.

Going for multiple time slices it will look like this

The window can be fixed with timer intervals. These can be non-overlapping or sliding. Sliding windows can give better results, but maybe more computationally intensive.
For balancing computation load, it is advisable to do edge compute i.e. derive the Event Count Matrix separately from each source.
5.Event Frequency Matrix – Once the event count matrix is being fetched from each source, they should be all combined at a central place, before being fed to the ML world.
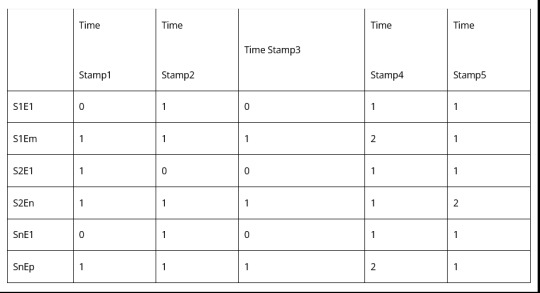
Highlighted Part is the final Matrix that is an input to the ML system. Each window is fed with a timestamp. So it becomes a time series input vector. Set of these vectors will make a data set. So finally now we have the data set for log analysis!
Resources
[1] AI/ML Theory Machine Learning by Stanford University
[2] Applied AI/ML Tutorial Deep Learning For Coders—36 hours of lessons for free
[3] Log Analysis AI/ML Research Paper Experience Report: System Log Analysis for Anomaly Detection
[4] LogPai/Loganaly (logpai/loglizer: A log analysis toolkit for automated anomaly detection [ISSRE’16])
[5] AICoE/LAD (AICoE/log-anomaly-detector: Log Anomaly Detection – Machine learning to detect abnormal events logs)
Request a Call
0 notes
Text
Why WiFi in Stadiums need rigorous testing?

The Role of WiFi in Social Media Engagement
With the proliferation of smartphones and tablets, users in stadiums demand high data rates to engage with other fans across multiple social networks be it Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or Snapchat. The expectation is of pervasive connectivity. Fans come to the stadium not only to view their favorite football/tennis/rugby/cricket match live but also to share their experiences with their friends and family instantly. During the 2014 Football world cup final in Rio, over 32 million tweets and 280 million interactions on Facebook were recorded from within the Maracana stadium through the period of the game. Now, imagine the number of social media interactions from stadiums in 2017. Providing free WiFi in stadiums has become a game changer for sports clubs, leagues, and entertainment operators to engage with their fans and to build their brands. Loss of connectivity now has a tangible commercial cost that goes far beyond mildly disgruntled fans. Venues have to validate their network’s robustness to ensure a superior multimedia experience for their fans.
How Deploying WiFi Can Benefit Venue Owners and Customers
Large crowds and significant multimedia usage demand a high-density wireless deployment. Connected stadiums are crucial to provide compelling fan experience and a profitable & sustainable digital future for clubs. The WiFi service benefits different user groups with multiple applications:
To enhance Fan experience and fill as many seats as possible
Streamed instant replays
Real-time scores
Live travel and parking data
Connect with family and friends on social networks without losing connectivity
2. To generate revenue through apps
In-seat food and beverage ordering
Selling merchandise
Selling tickets for future games
3. To promote the brand
Real-time promotions
Digital signage
Engage with people outside the stadium
4. To carry out operations effectively
Reliable high-speed press box Internet access
Ticketing and point-of-sale transaction processing
Challenges in providing Stadium WiFi with acceptable QoS
There may be tens of thousands of people in the stadium watching their favorite team playing a match and sharing their experiences on social media creating massive bandwidth requirements for video and data applications. There are also other critical applications where WiFi is mandatory today like ticketing, digital signage and stadium security. With these scenarios and conflicting demands, providing high QoS to all users is tricky. Below are the technical challenges to provide In-stadium WiFi with secure access and acceptable user experience:
Security – Having a single network used by thousands of fans, employees, leagues and contractors requires a high level of security for monetary transactions and other confidential data transfers. Is the network secure enough for all the activities?
High bandwidth applications – High speed access is mandatory for a good user experience when streaming replays, sharing high quality images on social media etc. Are these possible on the network at stadium scale?
Scalability – Thousands of users may access the network concurrently within the stadium. Is the infrastructure scalable to withstand the traffic?
Interference – Accessing a network that contains 10s to 100s of access points in and around the stadium used by 1000s of users with varied traffic applications is an RF nightmare. How is it possible to model the kind of traffic that is normal in a stadium environment and account for such interference?
Roaming – People move from one place to another within stadiums and expect uninterrupted connectivity. Is the infrastructure is validated for such scenarios?
Multiple Captive Portal logins – Fans on entering the stadium login to the captive portal to access free WiFi in the stadium. Is the infrastructure capable of handling 100’s of secured captive portal logins simultaneously?
Solution to address the challenges
Alethea offers test and measurement solutions in connectivity space. Our flagship product WiCheck model the sort of environment that a fan will encounter in a stadium. Each WiCheck box can emulate up to 256 real users and allows you to validate end user experience on your network using real applications & real life scenarios
What can be validated with WiCheck?
Security – supports all standard security options from WEP, WPA2 Enterprise, 802.1x to SIM based authentication and captive portal authentication
Applications – run multiple real applications – Facebook, Streaming, Twitter, YouTube, Google, Skype & more
Scalability – supports up to 256 real users per box. Increasing the number of emulated users is as easy as adding more boxes
Interference – WiCheck loads up channels with whatever traffic you require. That makes it the ideal tool to set up interference and test devices & APs under difficult network conditions
Roaming – Tests the network’s roaming capabilities
Captive Portal – Objectively measure scalability & usability of captive portal solution
Request a call
Download Brochure
1 note
·
View note
Text
#wifilegacytesting#wifi solutions#wifiaccesspoints#wifitesting#wifitestingwithrealapplications#bestwifitesttools
0 notes
Text
Hướng dẫn hack Wifi chi tiết trên điện thoại và máy tính
Wifi là một kiểu tín hiệu mạng không dây với những tiện ích cho các thiết bị di động như smartphone hoặc TV thông minh dễ dàng kết nối để trải nghiệm các tính năng cần tới internet tương đối đơn giản. Dù khoảng cách giới hạn nhưng điểm truy cập không dây (hotspot) vẫn được ưa chuộng, hack pass wifi vì thế vẫn được tìm ra dưới nhiều phương thức có cách thực hiện vô cùng đa dạng.
Router có thiết lập mật khẩu ra sao hoặc theo phương thức bảo mật WEP, WPA/WPA2 thì vẫn có một tỉ lệ cao trong việc đảm bảo thành công khi muốn truy cập vào mạng đó, tất nhiên mình sẽ không chắc chắn tuyệt đối tuy vậy bạn hãy thử làm theo nha.
Hướng dẫn hack pass Wifi trên điện thoại
Hack pass Wifi với AndroDumpper
– Bạn cần tải về ứng dụng AndroDumpper mình đã update file cài đặt ở cuối bài hướng dẫn này rồi.
– Download và cài đặt xong hay mở ứng dụng đó ra.
Giao diện sau khi bạn mở phần mềm
– Tải về 5 triệu mã Pis đã được tổng hợp và chia nhỏ cho máy điện thoại: Download ở đây.
Nếu điện thoại của bạn có cấu hình yếu thì chỉ nên chạy số lượng từ 500 mã Pis đổ lại thôi tránh tình trạng bị đơ máy phải thực hiện lại từ đầu, còn những máy điện thoại cấu hình đời cao nên chạy tầm 1 triệu Pis thôi nhé để đảm bảo tỉ lệ an toàn nhất khi sử dụng.
– Mở ứng dụng ra chọn Try Connect nó sẽ hiện lên một bảng.
Trong trường hợp hiện như thế này bạn hãy click vào Continue
– Tiếp đến nó hiện ra một số tính năng như sau, bạn chọn Brutefore nha.
– Nó sẽ hiện lên chức năng chọn tìm tới thư mục lưu file mã Pis để đọc cũng như xử lý trong quá trình hack wifi cho điện thoại.
Chọn FROM DICTIONARY
Bước cuối cùng giờ bạn chỉ cần chờ đợi để có thành quả như mình muốn mà thôi, nó sẽ hơi lâu đấy nhưng đây lại là cách hay nhất trên điện thoại tương đối hiệu quả.
Hack pass Wifi qua WPSPIN
Bạn hãy tải về phần mềm WPS hỗ trợ vào Wifi bằng mã PIN mình đã để link download ở phía cuối bài viết rồi cài đặt nó và sử dụng ngay nhé.
– Bước 1: Mở ứng dụng ra cũng như bật chức năng Wifi để quét ngay những mạng hiện có ở xung quanh bạn.
– Bước 2: Chọn một mạng Wifi mà bạn muốn thực hiện để truy cập, lời khuyên của wapmienphi.info là bạn nên chọn mạng nào mà có sóng wifi mạnh để việc vào nó sẽ diễn ra nhanh hơn không bị chậm trễ hoặc thất bại vì tín hiểu quá yếu.
Nó sẽ hiện ra giao diện như sau, nhớ mã PIN đầu tiên để tiếp tục nhé
– Bước 3: Vào WLAN (tính năng cài đặt Wifi của điện thoại), chọn mạng Wifi phía trên mà bạn vừa thực hiện ở bước trước đó. Chọn nâng cao >> Mã PIN từ điểm truy cập rồi nhập mã PIN trước đó vào ô và chọn kết nối.
Nhập mã PIN và Kết nối ngay
– Bước 4: Làm hoàn thành ba bước trên tức là bạn đã kết nối Wifi vào thành công. Bây giờ muốn hiển thị mật khẩu bạn hãy thực hiện như sau: Vào WLAN pass show chọn show display password, rồi vào Wifi chọn mạng bạn đang kết nối nó sẽ hiện ra mật khẩu. Tuy nhiên chức năng này một số điện thoại không được hỗ trợ nên nếu bạn không dùng được thì cũng đừng quá ngạc nhiên nhé.
Thông tin chung và mật khẩu đã được hiện lên
Nếu máy điện thoại không có tính năng hiển thị mật khẩu thì bạn hãy download ứng dụng Wifi Connect Manager và chọn chức năng Wifi rồi click vào WPS Push Button là được nhé.
Sử dụng WPS tự động/thủ công với WifiTest
Với cách tự động
Hiện thị các mạng wifi đang được phủ sóng
– Sau khi tải về máy và cài đặt xong bạn mở phần mềm ra và chọn bất kì một mạng wifi nào có hỗ trợ.
– Chọn bắt đầu kết nối, quá trình này mất khoảng 2 phút.
– Để xem thành công hay thất bại thì gạt thanh status của máy xuống và xem thông báo.
Với cách thủ công
– Chọn một mạng wifi mà bạn muốn với điều kiện có hỗ trợ nhé.
– Chọn vào chức năng Lấy PIN.
– Ghi nhớ lại mã PIN rồi chọn nhập Pin thủ công sau đó ấn xong để kết nối.
Sử dụng Wifi Chùa
Thực ra đây không phải là ứng dụng hack wifi nhưng với cách hoạt động lưu trữ mật khẩu được chia sẻ từ chính người dùng kèm vị trí chính xác bạn có khả năng theo dõi xác định xem mạng wifi đó có gần chỗ hiện tại của mình hay không. Từ đó việc tra cứu xem xét để truy cập modem Wifi dễ dàng phục vụ nhu cầu của bản thân nhất tương đối đơn giản.
Hướng dẫn hack pass Wifi trên máy tính
Trước tiên bạn cần phải cài đặt JumpStart và Dumpper trên máy tính của mình để bắt đầu thực hiện hai tính năng kết hợp mang lại thành công vượt qua mọi mật khẩu khó của chủ sở hữu wifi.
Tải về JumpStart 2.1.1 bản tiếng Việt tại đây. Tải về Dumpper mới nhất ở đây.
Dùng kết hợp JumpStart + Dumpper để hack Wifi
Mở ứng dụng Dumpper trên thiết bị của bạn và làm lần lượt như sau.
Chọn tất cả mạng Wifi.
Quét.
Chọn một mạng wifi có trong danh sách, ở chỗ mình có mỗi một mạng nên mình làm ví dụ thôi, bạn có thể xem bên cột tín hiệu để biết mạng nào mạnh rồi lựa chọn nhé.
Chạy JumpStart.
Nếu có cửa số này bị hiện lên thì chọn Tiếp tục nhé.
Nó sẽ hiện lên thông báo xử lý quá trình kết nối bạn cần chờ một chút.
Nếu thành công sẽ có giao diện như thế này.
Muốn xem mật khẩu wifi đó là gì bạn quay lại phần hồ sơ của Dumpper là được nhé.
Hack pass Wifi với JumpStart
Cách này sẽ lâu hơn và kém hiệu quả so với cách đầu tiên tuy nhiên cũng nên thử vì biết đâu một trong hai phương pháp này giúp bạn có được mật khẩu Wifi xung quanh.
Mở JumpStart lên, chọn tự động nhập PIN vào điểm truy cập Wifi > Next. (Nhớ bỏ dấu tích tự động chọn mạng Wifi đi nhé)
Chọn một mạng Wifi trong danh sách bấm Next, các bước sau chỉ cần chờ đợi kết quả mà thôi.
Như vậy mình đã hướng dẫn xong cách phá mật khẩu Wifi qua hai phần mềm JumpStart và Dumpper trên máy tính rồi đấy việc còn lại bạn chỉ cần thử xem độ may mắn của mình có kết nối thành công được hay không mà thôi.
Trên đây là toàn bộ những gì mà Wap Miễn Phí chia sẻ tới mọi người bí kíp để hack mật khẩu Wifi ở những dòng máy, thiết bị đã được công bố ở diễn đàn cũng như mạng xã hội được đông đảo người dùng công nhận, hy vọng rằng sẽ nhận được sự ủng hộ bằng cách chia sẻ nhiệt tình nó nhé.
from Wap Miễn Phí https://ift.tt/2zXUXJh via https://wapmienphi.info
0 notes