#SSH key setup
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Migrate WordPress to GCP Server Using WordOps and EasyEngine
Migrating a WordPress site to Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers numerous benefits including improved performance, scalability, and reliability. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through on how to migrate WordPress to GCP using WordOps and EasyEngine, with special attention to sites created with the --wpredis flag. This guide works whether you’re migrating from a traditional hosting…
#cloud hosting#Database migration#EasyEngine#EasyEngine to WordOps#GCP#Google Cloud Platform#How to#rsync#Server migration#Server-to-server WordPress#site migration#Site migration guide#SSH key setup#SSL certificate setup#WordOps#WordOps configuration#WordPress database export#WordPress hosting#WordPress hosting migration#WordPress migration#WordPress Redis#WordPress server transfer#WordPress site transfer#WP migration tutorial#WP-CLI#wp-config
0 notes
Text
MOBATIME NTP Time Servers: Precision Time Synchronization for Secure and Reliable Networks
Network Time Protocol (NTP) Time Servers are specialized devices that distribute accurate time information across networks, ensuring all connected devices operate in unison. This synchronization is vital for applications ranging from data logging to security protocols.
MOBATIME's NTP Time Server Solutions
MOBATIME's NTP Time Servers are engineered to provide high-precision time synchronization with interfaces such as NTP and PTP (Precision Time Protocol). Equipped with crystal oscillators, these servers offer exceptional accuracy and traceability, supporting synchronization through the Global Positioning System (GPS) for both mid-sized and large infrastructure networks.
Key Features
Independent Time Reference : MOBATIME's solutions offer an autonomous, evidence-proof time source, ensuring reliable operation even without external references.
High Precision : Their time servers synchronize networks with utmost precision, providing exact time stamps essential for chronological event arrangement.
Versatility : Designed for various applications, MOBATIME's NTP Time Servers cater to diverse network environments, from simple setups to complex systems requiring master clock functionalities.
Product Highlight: DTS 4138 Time Server
The DTS 4138 is a standout in MOBATIME's lineup, offering:
Dual Functionality : It serves as both an NTP server and client, capable of synchronizing from a superior NTP server in separate networks.
Enhanced Security : Supports NTP authentication, allowing clients to verify the source of received NTP packets, bolstering network security.
User-Friendly Operation : Manageable over LAN via protocols like MOBA-NMS (SNMP), Telnet, SSH, or SNMP, ensuring safe and convenient operation.
Comprehensive Support and Services
Beyond delivering top-tier products, MOBATIME is committed to customer support. They offer training for users and regular, professional maintenance services. Their customizable maintenance models are designed to meet the specific needs of different organizations, ensuring sustained performance and reliability.
Conclusion
For organizations where precise time synchronization is non-negotiable, MOBATIME's NTP Time Servers present a dependable and accurate solution. With features like independent time references, high precision, and robust support services, MOBATIME stands out as a trusted partner in time synchronization solutions.
#mobatime#technology#ntp time server#time server technology#ptp time server#time server#network time protocol
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
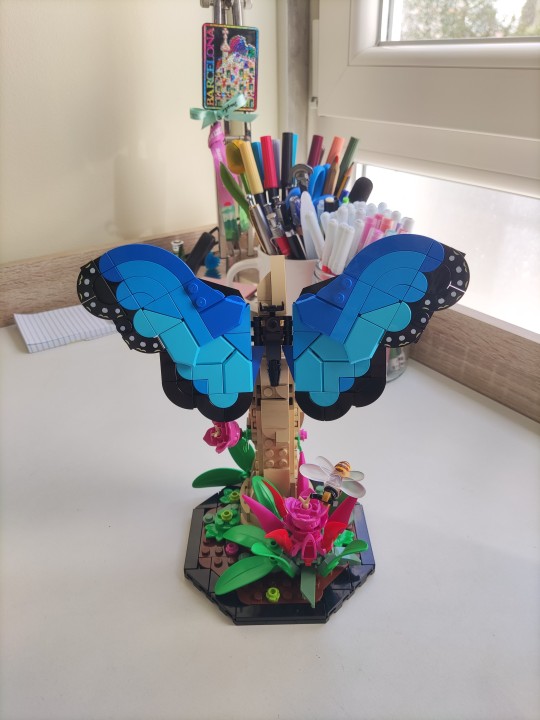
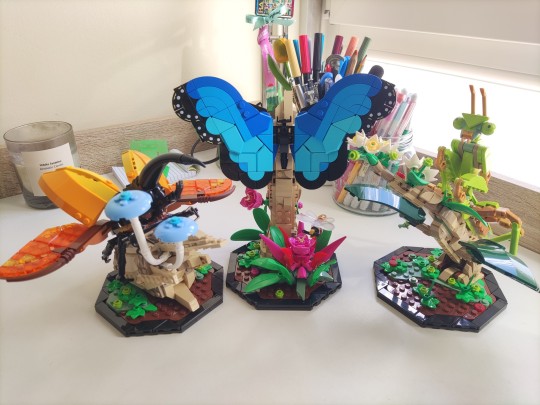



[ 1st april, 2024 • DAY 50/145 ]
we got to boop everyone~ 🥰 it was so nice 🥰❤️
-> doctor's appointment - gonna run some more tests, but everything should be fine :D
-> ES notes for classes 1, 2 and 3
-> finished ES discussion setup/tests (i. had. to. do. it. all. again. because. they. forgot. to. mention. i'd need. TO PULL NEW CODE TOMORROW FROM GITLAB 😡 SO COPY PASTE DOESN'T WORK 😡😡 NEED TO USE SSH KEY ��😡😡 AAAAAAAHHHHHHHH 😡😡😡😡😡)
-> built the last Lego model i had and it's so cute!! i love them all so much and my shelves are much happier rn 💐✨💕🌟🎉
-> sent 1000 boops and got 3 badges 🐱
#stargazerbibi#study#studyblr#100 dop#100 days of productivity#lego#student#studyspo#studyspiration#studystudystudy#aesthetic#productivity#student life#studying#studies#study blog#studygram#study motivation
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
Petalhost: The Best Magento Hosting Provider in India
When it comes to hosting your Magento-based ecommerce website, you need a hosting provider that ensures speed, reliability, and scalability. Petalhost emerges as the most trusted Magento Hosting Provider in India, offering cutting-edge hosting solutions designed specifically for Magento-powered online stores.
Why Choose Petalhost for Magento Hosting?
Magento is a robust ecommerce platform that demands high-performance hosting to deliver a seamless shopping experience. Petalhost understands these unique requirements and provides tailored hosting solutions that guarantee optimal performance and security for your Magento website.
1. High-Speed Servers for Lightning-Fast Performance
Slow-loading websites can drive customers away, but with Petalhost’s high-speed SSD-powered servers, your Magento store will load in the blink of an eye. This not only enhances user experience but also improves search engine rankings, ensuring more visibility for your online store.
2. 99.9% Uptime Guarantee
Downtime means lost sales and damaged customer trust. Petalhost guarantees 99.9% uptime, ensuring your Magento store remains accessible around the clock. Their state-of-the-art data centers are equipped with the latest technology to ensure uninterrupted service.
3. Robust Security Features
Ecommerce websites handle sensitive customer data, making security a top priority. Petalhost provides advanced security measures such as firewalls, DDoS protection, malware scanning, and free SSL certificates to safeguard your Magento store and protect customer information.
4. Optimized for Magento
Petalhost’s servers are specifically optimized for Magento, providing pre-configured setups that reduce the need for manual adjustments. This ensures your website runs smoothly and efficiently, regardless of traffic spikes or complex integrations.
5. Scalable Hosting Plans
As your business grows, so do your hosting requirements. Petalhost offers scalable hosting plans that allow you to upgrade your resources seamlessly without any downtime. Whether you’re running a small store or managing a large ecommerce enterprise, Petalhost has the perfect hosting solution for you.
6. 24/7 Expert Support
Petalhost’s team of Magento hosting experts is available 24/7 to assist you with any issues or queries. From initial setup to ongoing maintenance, their friendly and knowledgeable support team ensures you’re never alone.
Key Features of Petalhost’s Magento Hosting Plans
SSD Storage: High-speed solid-state drives for faster data retrieval.
Free SSL Certificate: Secure your store and build customer trust.
Daily Backups: Keep your data safe with automated daily backups.
One-Click Installation: Quickly set up your Magento store with an easy installation process.
Global Data Centers: Choose from multiple data centers for optimal performance and reduced latency.
Developer-Friendly Tools: Access SSH, Git, and other developer tools for seamless store management.
Affordable Pricing for Every Budget
Petalhost believes in offering premium Magento hosting solutions at affordable prices. Their hosting plans are designed to suit businesses of all sizes, from startups to established enterprises. With transparent pricing and no hidden fees, you get the best value for your money.
Why Magento Hosting Matters
Magento is a feature-rich platform that enables businesses to create highly customizable and scalable online stores. However, its powerful features also demand a hosting environment that can handle its resource-intensive nature. A reliable Magento hosting provider like Petalhost ensures that your website runs efficiently, providing a smooth shopping experience for your customers and boosting your online sales.
How to Get Started with Petalhost
Getting started with Petalhost’s Magento hosting is quick and hassle-free. Simply visit their website, choose a hosting plan that suits your needs, and follow the easy signup process. Their team will guide you through the setup and migration process to ensure a smooth transition.
Conclusion
If you’re looking for a reliable and affordable Magento Hosting Provider in India, Petalhost is the name you can trust. With high-speed servers, robust security, and dedicated support, Petalhost provides everything you need to run a successful Magento-based ecommerce store. Don’t let subpar hosting hold your business back. Choose Petalhost and take your online store to new heights today!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
i spent like 20 minutes trying to debug my ssh key setup, before realizing github urls are spelled like "[email protected]:$username/$repo.git" and not "[email protected]:$username/$repo.git"
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Server Security: Analyze and Harden Your Defenses in today’s increasingly digital world, securing your server is paramount. Whether you’re a beginner in ethical hacking or a tech enthusiast eager to strengthen your skills, understanding how to analyze adn harden server security configurations is essential to protect your infrastructure from cyber threats. This comprehensive guide walks you through the key processes of evaluating your server’s setup and implementing measures that enhance it's resilience. Materials and Tools Needed Material/ToolDescriptionPurposeServer Access (SSH/Console)Secure shell or direct console access to the serverTo review configurations and apply changesSecurity Audit ToolsTools like Lynis, OpenVAS, or NessusTo scan and identify vulnerabilitiesConfiguration Management ToolsTools such as Ansible, Puppet, or ChefFor automating security hardening tasksFirewall Management InterfaceAccess to configure firewalls like iptables, ufw, or cloud firewallTo manage network-level security policiesLog Monitoring UtilitySoftware like Logwatch, Splunk, or GraylogTo track suspicious events and audit security Step-by-Step Guide to Analyzing and Hardening Server Security 1. Assess Current Server Security Posture Log in securely: Use SSH with key-based authentication or direct console access to avoid exposing passwords. Run a security audit tool: Use lynis or OpenVAS to scan your server for weaknesses in installed software, configurations, and open ports. Review system policies: Check password policies, user privileges, and group memberships to ensure they follow the principle of least privilege. Analyze running services: Identify and disable unnecessary services that increase the attack surface. 2. Harden Network Security Configure firewalls: Set up strict firewall rules using iptables, ufw, or your cloud provider’s firewall to restrict inbound and outbound traffic. Limit open ports: Only allow essential ports (e.g., 22 for SSH, 80/443 for web traffic). Implement VPN access: For critical server administration, enforce VPN tunnels to add an extra layer of security. 3. Secure Authentication Mechanisms Switch to key-based SSH authentication: Disable password login to prevent brute-force attacks. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Wherever possible, introduce MFA for all administrative access. Use strong passwords and rotate them: If passwords must be used,enforce complexity and periodic changes. 4. Update and Patch Software Regularly Enable automatic updates: Configure your server to automatically receive security patches for the OS and installed applications. Verify patch status: Periodically check versions of critical software to ensure they are up to date. 5. Configure System Integrity and Logging Install intrusion detection systems (IDS): Use tools like Tripwire or AIDE to monitor changes in system files. Set up centralized logging and monitoring: Collect logs with tools like syslog, Graylog, or Splunk to detect anomalies quickly. Review logs regularly: Look for repeated login failures, unexpected system changes, or new user accounts. 6. Apply Security Best Practices Disable root login: prevent direct root access via SSH; rather,use sudo for privilege escalation. Restrict user commands: Limit shell access and commands using tools like sudoers or restricted shells. Encrypt sensitive data: Use encryption for data at rest (e.g., disk encryption) and in transit (e.g., TLS/SSL). Backup configurations and data: Maintain regular, secure backups to facilitate recovery from attacks or failures. Additional Tips and Warnings Tip: Test changes on a staging environment before applying them to production to avoid service disruptions. Warning: Avoid disabling security components unless you fully understand the consequences. Tip: Document all configuration changes and security policies for auditing and compliance purposes.
Warning: Never expose unnecessary services to the internet; always verify exposure with port scanning tools. Summary Table: Key Server Security Checks Security AspectCheck or ActionFrequencyNetwork PortsScan open ports and block unauthorized onesWeeklySoftware UpdatesApply patches and updatesDaily or WeeklyAuthenticationVerify SSH keys,passwords,MFAMonthlyLogsReview logs for suspicious activityDailyFirewall RulesAudit and update firewall configurationsMonthly By following this structured guide,you can confidently analyze and harden your server security configurations. Remember, security is a continuous process — regular audits, timely updates, and proactive monitoring will help safeguard your server against evolving threats. Ethical hacking principles emphasize protecting systems responsibly, and mastering server security is a crucial step in this journey.
0 notes
Text
Secure DevOps: How Cloud DevOps Services Improve Application Security

In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are under pressure to innovate quickly without compromising on security. Customers expect new features, faster updates, and high availability—yet the rise of cloud computing and microservices has also expanded the attack surface for cyber threats.
That’s where Secure DevOps, also known as DevSecOps, enters the scene. It blends the agility of DevOps with proactive, embedded security practices. When powered by Cloud DevOps Services, organizations can automate and enforce security across every stage of the development lifecycle—from code to deployment and beyond.
This article explores how Cloud DevOps Services improve application security, why traditional methods fall short, and how businesses can implement a secure-by-design DevOps culture without sacrificing speed or scalability.
⚙️ What Is Secure DevOps?
Secure DevOps is the integration of security practices directly into the DevOps workflow. Instead of treating security as a final checkpoint, Secure DevOps makes it a shared responsibility for developers, operations teams, and security professionals alike.
Key principles include:
Shift-left security (testing early in the development process)
Automation of security checks in CI/CD pipelines
Continuous monitoring and incident response
Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) with secure configurations
By embedding security into development from the start, Secure DevOps ensures that vulnerabilities are identified and resolved early—before they make it into production.
🔍 Why Traditional Security Approaches Don’t Work in the Cloud Era
In legacy IT environments, security teams operated in silos. Applications were developed over months or years and then handed off to security for review before deployment.
This approach simply doesn’t work in the age of:
Cloud-native apps
Microservices architecture
Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
When developers are pushing changes daily or even hourly, security can’t be an afterthought. Manual reviews and firewalls at the perimeter are no longer sufficient.
Cloud DevOps Services help bridge this gap—by embedding security checks into automated workflows and ensuring protection across the entire stack.
🔐 How Cloud DevOps Services Improve Application Security
Let’s explore the major ways Cloud DevOps Services enhance security without slowing down innovation.
1. Integrating Security into CI/CD Pipelines
Modern Cloud DevOps Services help businesses set up secure, automated CI/CD pipelines that:
Scan code for vulnerabilities as it's committed
Run container and dependency scans before builds
Perform automated security tests as part of the deployment process
Tools like Snyk, SonarQube, Aqua Security, Trivy, and Checkmarx can be integrated with GitHub, GitLab, Jenkins, or Azure DevOps to detect vulnerabilities before the code ever goes live.
These early-stage checks ensure:
Secure coding practices
Up-to-date and trusted dependencies
No hard-coded secrets or misconfigurations
2. Securing Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC)
With IaC, developers define cloud infrastructure using code—Terraform, CloudFormation, or ARM templates. But that infrastructure can include:
Public-facing storage buckets
Open security groups
Unencrypted volumes
Cloud DevOps Services scan IaC templates for misconfigurations before provisioning. This prevents insecure setups from ever reaching production.
They also enforce policies-as-code, automatically blocking non-compliant deployments—like allowing unrestricted SSH access or deploying to unauthorized regions.
3. Enforcing Identity and Access Management (IAM)
In the cloud, identity is the new perimeter. Poorly configured IAM roles are among the top causes of cloud data breaches.
Cloud DevOps Services enforce:
Least privileged access to services and data
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Federated identity integration with SSO providers (like Okta or Azure AD)
Secrets management through services like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault
By automating and monitoring access rights, these services reduce the chances of privilege escalation or unauthorized access.
4. Container Security and Orchestration Hardening
Containers have revolutionized how applications are built and deployed—but they bring their own security challenges. Misconfigured containers or unpatched base images can expose sensitive data.
Cloud DevOps Services help secure containers by:
Scanning images for known vulnerabilities
Enforcing signed and verified images
Setting up runtime security policies using tools like Falco or Kubernetes admission controllers
Monitoring for drift between deployed and intended configurations
In orchestrated environments like Kubernetes, Cloud DevOps teams also:
Enforce namespace isolation
Secure K8s API access
Use network policies to limit pod communication
5. Automated Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Secure DevOps is not just about prevention—it’s also about real-time detection and response.
Cloud DevOps Services set up:
Centralized logging with tools like ELK Stack, Fluentd, or CloudWatch
SIEM integration (e.g., with Splunk, Azure Sentinel, or AWS Security Hub)
Alerting systems tied into Slack, Teams, or email
Automated incident response through playbooks or runbooks
This allows businesses to respond to threats in minutes, not days.
6. Continuous Compliance and Auditing
Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, or PCI DSS, compliance in the cloud is complex—and often a moving target.
Cloud DevOps Services simplify compliance by:
Mapping policies to compliance frameworks
Generating automated audit logs and reports
Enforcing controls via code (e.g., blocking non-compliant configurations)
Continuously scanning environments for violations
This helps businesses stay audit-ready year-round—not just during compliance season.
🚀 Getting Started with Secure Cloud DevOps
To begin your Secure DevOps journey, start with:
Assessing your current DevOps pipeline
Identifying security gaps
Choosing the right Cloud DevOps partner or tools
Building a roadmap for automation and policy enforcement
Training teams to adopt a security-first mindset
Remember, Secure DevOps isn’t a one-time project—it’s a culture shift supported by the right cloud tools, automation, and expertise.
🔚 Final Thoughts
Security is no longer optional in a world where applications run in the cloud and threats evolve daily. The key is to build security into your DevOps processes—not bolt it on after the fact.
With Cloud DevOps Services, you get the best of both worlds:
Rapid innovation
Continuous delivery
Enterprise-grade security
Whether you're a startup or an enterprise, investing in Secure DevOps means protecting your applications, your data, and your reputation—without slowing down your growth.
Security doesn’t have to come at the cost of speed. With Secure DevOps, you get both.
#azure devops consultant#devops as a service companies#devops as a service#devops service providers#devops solution#devops expert
0 notes
Text
Automate Linux Administration Tasks in Red Hat Enterprise Linux with Ansible
System administration is a critical function in any enterprise IT environment—but it doesn’t have to be tedious. With Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and Ansible Automation Platform, you can transform manual, repetitive Linux administration tasks into smooth, scalable, and consistent automated workflows.
🔧 Why Automate Linux Administration?
Traditional system administration tasks—like user creation, package updates, system patching, and service management—can be time-consuming and error-prone when performed manually. Automating these with Ansible helps in:
🔄 Ensuring repeatability and consistency
⏱️ Reducing manual errors and downtime
🧑💻 Freeing up admin time for strategic work
📈 Scaling operations across hundreds of systems with ease
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool that enables you to define your infrastructure and processes as code. It is agentless, which means it doesn't require any additional software on managed nodes. Using simple YAML-based playbooks, you can automate nearly every aspect of Linux administration.
💡 Key Linux Admin Tasks You Can Automate
Here are some of the most common and useful administration tasks that can be automated using Ansible in RHEL:
1. User and Group Management
Create, delete, and manage users and groups across multiple servers consistently.
2. Package Installation & Updates
Install essential packages, apply security patches, or remove obsolete software across systems automatically.
3. Service Management
Start, stop, restart, and enable system services like Apache, NGINX, or SSH with zero manual intervention.
4. System Configuration
Automate editing of config files, setting permissions, or modifying system parameters with version-controlled playbooks.
5. Security Enforcement
Push firewall rules, SELinux policies, or user access configurations in a repeatable and auditable manner.
6. Log Management & Monitoring
Automate setup of log rotation, install monitoring agents, or configure centralized logging systems.
🚀 Benefits for RHEL Admins
Whether you're managing a handful of Linux servers or an entire hybrid cloud infrastructure, Ansible in RHEL gives you:
Speed: Rapidly deploy new configurations or updates
Reliability: Reduce human error in critical environments
Visibility: Keep your system configurations in version control
Compliance: Easily enforce and verify policy across systems
📚 How to Get Started?
To start automating your RHEL environment:
Install Ansible Automation Platform.
Learn YAML syntax and structure of Ansible Playbooks.
Explore Red Hat Certified Collections for supported modules.
Start small—automate one task, test, iterate, and scale.
🌐 Conclusion
Automation is not just a nice-to-have anymore—it's a necessity. Red Hat Enterprise Linux with Ansible lets you take control of your infrastructure by automating Linux administration tasks that are critical for performance, security, and scalability. Start automating today and future-proof your IT operations.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Text
Top 5 Security Misconfigurations Causing Data Breaches

In the ever-escalating arms race of cybersecurity, headlines often focus on sophisticated malware, nation-state attacks, and zero-day exploits. Yet, time and again, the root cause of devastating data breaches isn't a complex, cutting-edge attack, but rather something far more mundane: a security misconfiguration.
These are the digital equivalent of leaving your front door unlocked, the windows open, or a spare key under the doormat. Simple mistakes or oversights in the setup of software, hardware, networks, or cloud services create gaping vulnerabilities that attackers are all too eager to exploit. Getting the basics right is arguably the most impactful step you can take to protect your assets.
Here are the top 5 security misconfigurations that commonly lead to data breaches:
1. Default, Weak, or Unmanaged Credentials
What it is: Using default usernames and passwords (e.g., admin/admin, root/root), not changing credentials after initial setup, or enforcing weak password policies that allow simple, guessable passwords. It also includes failing to disable old user accounts.
How it leads to a breach: Attackers use automated tools to try common default credentials, brute-force weak passwords, or leverage stolen credentials from other breaches. Once inside, they gain unauthorized access to systems, data, or networks.
Real-world Impact: This is a perennial favorite for attackers, leading to widespread compromise of routers, IoT devices, web applications, and even corporate networks.
How to Prevent:
Change All Defaults: Immediately change all default credentials upon installation.
Strong Password Policy: Enforce complex passwords, regular rotations, and most critically, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all accounts, especially privileged ones.
Least Privilege: Grant users only the minimum access required for their role.
Regular Audits: Routinely review user accounts and access privileges, disabling inactive accounts promptly.
2. Unrestricted Access to Cloud Storage Buckets (e.g., S3 Buckets)
What it is: Publicly exposing cloud storage containers (like Amazon S3 buckets, Azure Blobs, or Google Cloud Storage buckets) to the internet, often accidentally. These can contain vast amounts of sensitive data.
How it leads to a breach: Misconfigured permissions allow anyone on the internet to read, list, or even write to the bucket without authentication. Attackers simply scan for publicly exposed buckets, download the data, and exfiltrate it.
Real-world Impact: This has been the cause of numerous high-profile data leaks involving customer records, internal documents, proprietary code, and financial data.
How to Prevent:
Principle of Least Privilege: Ensure all cloud storage is private by default. Only grant access to specific users or services that absolutely need it.
Strict Access Policies: Use bucket policies, IAM roles, and access control lists (ACLs) to tightly control who can do what.
Regular Audits & Monitoring: Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to continuously scan for misconfigured buckets and receive alerts.
3. Open Ports and Unnecessary Services Exposure
What it is: Leaving network ports open that shouldn't be (e.g., remote desktop (RDP), SSH, database ports, old services) or running unpatched services that are exposed to the internet.
How it leads to a breach: Attackers scan for open ports and vulnerable services. An exposed RDP port, for example, can be a direct gateway for ransomware. An unpatched web server on a commonly used port allows for exploitation.
Real-world Impact: This is a common entry point for ransomware attacks, network intrusion, and data exfiltration, often facilitating lateral movement within a compromised network.
How to Prevent:
Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems using firewalls and VLANs.
Port Scanning: Regularly scan your own network externally and internally to identify open ports.
Disable Unnecessary Services: Remove or disable any services, applications, or protocols that are not strictly required.
Strict Firewall Rules: Implement "deny by default" firewall rules, only allowing essential traffic.
Patch Management: Keep all exposed services and applications fully patched.
4. Missing or Inadequately Configured Security Headers/Web Server Settings
What it is: Web applications and servers often lack crucial security headers (like Content Security Policy, X-XSS-Protection, HTTP Strict Transport Security) or are configured insecurely (e.g., directory listings enabled, verbose error messages, default server banners).
How it leads to a breach: These omissions can expose users to client-side attacks (Cross-Site Scripting - XSS, Clickjacking), provide attackers with valuable reconnaissance, or allow them to enumerate files on the server.
Real-world Impact: Leads to website defacement, session hijacking, data theft via client-side attacks, and information disclosure.
How to Prevent:
Implement Security Headers: Configure web servers and application frameworks to use appropriate security headers.
Disable Directory Listings: Ensure web servers don't automatically list the contents of directories.
Minimize Error Messages: Configure web applications to provide generic error messages, not detailed technical information.
Remove Default Banners: Conceal server and software version information.
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): Deploy and properly configure WAFs to protect against common web exploits.
5. Insufficient Logging and Monitoring Configuration
What it is: Not enabling proper logging on critical systems, misconfiguring log retention, or failing to forward logs to a centralized monitoring system (like a SIEM). It also includes ignoring security alerts.
How it leads to a breach: Without adequate logging and monitoring, organizations operate in the dark. Malicious activity goes unnoticed, attackers can dwell in networks for extended periods (dwell time), and forensic investigations after a breach are severely hampered.
Real-world Impact: Lengthens detection and response times, allowing attackers more time to exfiltrate data or cause damage. Makes it difficult to reconstruct attack paths and learn from incidents.
How to Prevent:
Enable Comprehensive Logging: Log all security-relevant events on servers, network devices, applications, and cloud services.
Centralized Log Management (SIEM): Aggregate logs into a Security Information and Event Management system for correlation and analysis.
Define Alerting Rules: Configure alerts for suspicious activities and ensure they are reviewed and acted upon promptly.
Regular Review: Periodically review logs and audit trails for anomalies.
The common thread running through all these misconfigurations is often human error and oversight compounded by increasing system complexity. While cutting-edge AI and advanced threat detection are crucial, the simplest and most impactful wins in cybersecurity often come from getting the fundamentals right. Regularly auditing your environment, enforcing strict policies, and embracing automation for configuration management are your best defenses against these common, yet devastating, vulnerabilities. Don't let a simple oversight become your next breach.
0 notes
Text
Is Your Cloud Really Secure? A CISOs Guide to Cloud Security Posture Management

Introduction: When “Cloud-First” Meets “Security-Last”
The cloud revolution has completely transformed how businesses operate—but it’s also brought with it an entirely new battleground. With the speed of cloud adoption far outpacing the speed of cloud security adaptation, many Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) are left asking a critical question: Is our cloud truly secure?
It’s not a rhetorical query. As we move towards multi-cloud and hybrid environments, traditional security tools and mindsets fall short. What worked on-prem doesn’t necessarily scale—or protect—in the cloud. This is where Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) enters the picture. CSPM is no longer optional; it’s foundational.
This blog explores what CSPM is, why it matters, and how CISOs can lead with confidence in the face of complex cloud risks.
1. What Is Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)?
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a framework, set of tools, and methodology designed to continuously monitor cloud environments to detect and fix security misconfigurations and compliance issues.
CSPM does three key things:
Identifies misconfigurations (like open S3 buckets or misassigned IAM roles)
Continuously assesses risk across accounts, services, and workloads
Enforces best practices for cloud governance, compliance, and security
Think of CSPM as your real-time cloud security radar—mapping the vulnerabilities before attackers do.
2. Why Traditional Security Tools Fall Short in the Cloud
CISOs often attempt to bolt on legacy security frameworks to modern cloud setups. But cloud infrastructure is dynamic. It changes fast, scales horizontally, and spans multiple regions and service providers.
Here’s why old tools don’t work:
No perimeter: The cloud blurs the traditional boundaries. There’s no “edge” to protect.
Complex configurations: Cloud security is mostly about “how” services are set up, not just “what” services are used.
Shadow IT and sprawl: Teams can spin up instances in seconds, often without central oversight.
Lack of visibility: Multi-cloud environments make it hard to see where risks lie without specialized tools.
CSPM is designed for the cloud security era—it brings visibility, automation, and continuous improvement together in one integrated approach.
3. Common Cloud Security Misconfigurations (That You Probably Have Right Now)
Even the most secure-looking cloud environments have hidden vulnerabilities. Misconfigurations are one of the top causes of cloud breaches.
Common culprits include:
Publicly exposed storage buckets
Overly permissive IAM policies
Unencrypted data at rest or in transit
Open management ports (SSH/RDP)
Lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Default credentials or forgotten access keys
Disabled logging or monitoring
CSPM continuously scans for these issues and provides prioritized alerts and auto-remediation.
4. The Role of a CISO in CSPM Strategy
CSPM isn’t just a tool—it’s a mindset shift, and CISOs must lead that cultural and operational change.
The CISO must:
Define cloud security baselines across business units
Select the right CSPM solutions aligned with the organization’s needs
Establish cross-functional workflows between security, DevOps, and compliance teams
Foster accountability and ensure every developer knows they share responsibility for security
Embed security into CI/CD pipelines (shift-left approach)
It’s not about being the gatekeeper. It’s about being the enabler—giving teams the freedom to innovate with guardrails.
5. CSPM in Action: Real-World Breaches That Could Have Been Avoided
Let’s not speak in hypotheticals. Here are a few examples where lack of proper posture management led to real consequences.
Capital One (2019): A misconfigured web application firewall allowed an attacker to access over 100 million customer accounts hosted in AWS.
Accenture (2021): Left multiple cloud storage buckets unprotected, leaking sensitive information about internal operations.
US Department of Defense (2023): An exposed Azure Blob led to the leakage of internal training documents—due to a single misconfiguration.
In all cases, a CSPM solution would’ve flagged the issue—before it became front-page news.
6. What to Look for in a CSPM Solution
With dozens of CSPM tools on the market, how do you choose the right one?
Key features to prioritize:
Multi-cloud support (AWS, Azure, GCP, OCI, etc.)
Real-time visibility and alerts
Auto-remediation capabilities
Compliance mapping (ISO, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, etc.)
Risk prioritization dashboards
Integration with services like SIEM, SOAR, and DevOps tools
Asset inventory and tagging
User behavior monitoring and anomaly detection
You don’t need a tool with bells and whistles. You need one that speaks your language—security.
7. Building a Strong Cloud Security Posture: Step-by-Step
Asset Discovery Map every service, region, and account. If you can’t see it, you can’t secure it.
Risk Baseline Evaluate current misconfigurations, exposure, and compliance gaps.
Define Policies Establish benchmarks for secure configurations, access control, and logging.
Remediation Playbooks Build automation for fixing issues without manual intervention.
Continuous Monitoring Track changes in real time. The cloud doesn’t wait, so your tools shouldn’t either.
Educate and Empower Teams Your teams working on routing, switching, and network security need to understand how their actions affect overall posture.
8. Integrating CSPM with Broader Cybersecurity Strategy
CSPM doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s one pillar in your overall defense architecture.
Combine it with:
SIEM for centralized log collection and threat correlation
SOAR for automated incident response
XDR to unify endpoint, application security, and network security
IAM governance to ensure least privilege access
Zero Trust to verify everything, every time
At EDSPL, we help businesses integrate these layers seamlessly through our managed and maintenance services, ensuring that posture management is part of a living, breathing cyber resilience strategy.
9. The Compliance Angle: CSPM as a Compliance Enabler
Cloud compliance is a moving target. Regulators demand proof that your cloud isn’t just configured—but configured correctly.
CSPM helps you:
Map controls to frameworks like NIST, CIS Benchmarks, SOC 2, PCI, GDPR
Generate real-time compliance reports
Maintain an audit-ready posture across systems such as compute, storage, and backup
10. Beyond Technology: The Human Side of Posture Management
Cloud security posture isn’t just about tech stacks—it’s about people and processes.
Cultural change is key. Teams must stop seeing security as “someone else’s job.”
DevSecOps must be real, not just a buzzword. Embed security in sprint planning, code review, and deployment.
Blameless retrospectives should be standard when posture gaps are found.
If your people don’t understand why posture matters, your cloud security tools won’t matter either.
11. Questions Every CISO Should Be Asking Right Now
Do we know our full cloud inventory—spanning mobility, data center switching, and compute nodes?
Are we alerted in real-time when misconfigurations happen?
Can we prove our compliance posture at any moment?
Is our cloud posture improving month-over-month?
If the answer is “no” to even one of these, CSPM needs to be on your 90-day action plan.
12. EDSPL’s Perspective: Securing the Cloud, One Posture at a Time
At EDSPL, we’ve worked with startups, mid-market leaders, and global enterprises to build bulletproof cloud environments.
Our expertise includes:
Baseline cloud audits and configuration reviews
24/7 monitoring and managed CSPM services
Custom security policy development
Remediation-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Network security, application security, and full-stack cloud protection
Our background vision is simple: empower organizations with scalable, secure, and smart digital infrastructure.
Conclusion: Posture Isn’t Optional Anymore
As a CISO, your mission is to secure the business and enable growth. Without clear visibility into your cloud environment, that mission becomes risky at best, impossible at worst.
CSPM transforms reactive defense into proactive confidence. It closes the loop between visibility, detection, and response—at cloud speed.
So, the next time someone asks, “Is our cloud secure?” — you’ll have more than a guess. You’ll have proof.
Secure Your Cloud with EDSPL Today
Call: +91-9873117177 Email: [email protected] Reach Us | Get In Touch Web: www.edspl.net
Please visit our website to know more about this blog https://edspl.net/blog/is-your-cloud-really-secure-a-ciso-s-guide-to-cloud-security-posture-management/
0 notes
Text
Red Hat OpenStack Administration I (CL110) – Step into the World of Cloud Infrastructure
In today’s digital-first world, the need for scalable, secure, and efficient cloud solutions is more critical than ever. Enterprises are rapidly adopting private and hybrid cloud environments, and OpenStack has emerged as a leading choice for building and managing these infrastructures.
The Red Hat OpenStack Administration I (CL110) course is your first step toward becoming a skilled OpenStack administrator, empowering you to build and manage a cloud environment with confidence.
🔍 What is Red Hat OpenStack Administration I (CL110)?
This course is designed to provide system administrators and IT professionals with hands-on experience in managing a private cloud using Red Hat OpenStack Platform. It introduces key components of OpenStack and guides learners through practical scenarios involving user management, project setup, instance deployment, networking, and storage configuration.
🎯 What You’ll Learn
Participants of this course will gain valuable skills in:
Launching Virtual Instances: Learn how to deploy VMs in OpenStack using cloud images and instance types.
Managing Projects & Users: Configure multi-tenant environments by managing domains, projects, roles, and access controls.
Networking in OpenStack: Set up internal and external networks, routers, and floating IPs for connectivity.
Storage Provisioning: Work with block storage, object storage, and shared file systems to support cloud-native applications.
Security & Access Control: Implement SSH key pairs, security groups, and firewall rules to safeguard your environment.
Automating Deployments: Use cloud-init and heat templates to customize and scale your deployments efficiently.
👥 Who Should Attend?
This course is ideal for:
Linux System Administrators looking to enter the world of cloud infrastructure.
Cloud or DevOps Engineers seeking to enhance their OpenStack expertise.
IT Professionals preparing for Red Hat Certified OpenStack Administrator (RHCOSA) certification.
Prerequisite: It's recommended that attendees have Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) skills or equivalent experience in Linux system administration.
🧱 Key Topics Covered
Introduction to OpenStack Architecture Understand components like Nova, Neutron, Glance, Cinder, and Keystone.
Creating Projects and Managing Quotas Learn to segment cloud usage through structured tenant environments.
Launching and Securing Instances Deploy virtual machines and configure access and firewalls securely.
Networking Configuration Build virtual networks, route traffic, and connect instances to external access points.
Provisioning Storage Use persistent volumes and object storage for scalable applications.
Day-to-Day Cloud Operations Monitor usage, manage logs, and troubleshoot common issues.
🛠 Why Choose Red Hat OpenStack?
OpenStack provides a flexible platform for creating Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) environments. Combined with Red Hat’s enterprise support and stability, it allows organizations to confidently scale cloud operations while maintaining control over cost, compliance, and customization.
With CL110, you're not just learning commands—you're building the foundation to manage production-grade cloud platforms.
💡 Final Thoughts
Cloud computing isn't just the future—it's the now. Red Hat OpenStack Administration I (CL110) gives you the tools, skills, and confidence to be part of the transformation. Whether you're starting your cloud journey or advancing your DevOps career, this course is a powerful step forward. For more details www.hawkstack.com
0 notes
Text
How To Create EMR Notebook In Amazon EMR Studio

How to Make EMR Notebook?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) has incorporated Amazon EMR Notebooks into Amazon EMR Studio Workspaces on the new Amazon EMR interface. Integration aims to provide a single environment for notebook creation and massive data processing. However, the new console's “Create Workspace” button usually creates notebooks.
Users must visit the Amazon EMR console at the supplied web URL and complete the previous console's procedures to create an EMR notebook. Users usually select “Notebooks” and “Create notebook” from this interface.
When creating a Notebook, users choose a name and a description. The next critical step is connecting the notebook to an Amazon EMR cluster to run the code.
There are two basic ways users associate clusters:
Select an existing cluster
If an appropriate EMR cluster is already operating, users can click “Choose,” select it from a list, and click “Choose cluster” to confirm. EMR Notebooks have cluster requirements, per documentation. These prerequisites, EMR release versions, and security problems are detailed in specialised sections.
Create a cluster
Users can also “Create a cluster” to have Amazon EMR create a laptop-specific cluster. This method lets users name their clusters. This workflow defaults to the latest supported EMR release version and essential apps like Hadoop, Spark, and Livy, however some configuration variables, such as the Release version and pre-selected apps, may not be modifiable.
Users can customise instance parameters by selecting EC2 Instance and entering the appropriate number of instances. A primary node and core nodes are identified. The instance type determines the maximum number of notebooks that can connect to the cluster, subject to constraints.
The EC2 instance profile and EMR role, which users can choose custom or default roles for, are also defined during cluster setup. Links to more information about these service roles are supplied. An EC2 key pair for cluster instance SSH connections can also be chosen.
Amazon EMR versions 5.30.0 and 6.1.0 and later allow optional but helpful auto-termination. For inactivity, users can click the box to shut down the cluster automatically. Users can specify security groups for the primary instance and notebook client instance, use default security groups, or use custom ones from the cluster's VPC.
Cluster settings and notebook-specific configuration are part of notebook creation. Choose a custom or default AWS Service Role for the notebook client instance. The Amazon S3 Notebook location will store the notebook file. If no bucket or folder exists, Amazon EMR can create one, or users can choose their own. A folder with the Notebook ID and NotebookName and.ipynb extension is created in the S3 location to store the notebook file.
If an encrypted Amazon S3 location is used, the Service role for EMR Notebooks (EMR_Notebooks_DefaultRole) must be set up as a key user for the AWS KMS key used for encryption. To add key users to key policies, see AWS KMS documentation and support pages.
Users can link a Git-based repository to a notebook in Amazon EMR. After selecting “Git repository” and “Choose repository”, pick from the list.
Finally, notebook users can add Tags as key-value pairs. The documentation includes an Important Note about a default tag with the key creatorUserID and the value set to the user's IAM user ID. Users should not change or delete this tag, which is automatically applied for access control, because IAM policies can use it. After configuring all options, clicking “Create Notebook” finishes notebook creation.
Users should note that these instructions are for the old console, while the new console now uses EMR Notebooks as EMR Studio Workspaces. To access existing notebooks as Workspaces or create new ones using the “Create Workspace” option in the new UI, EMR Notebooks users need extra IAM role rights. Users should not change or delete the notebook's default access control tag, which contains the creator's user ID. No notebooks can be created with the Amazon EMR API or CLI.
The thorough construction instructions in some current literature match the console interface, however this transition symbolises AWS's intention to centralise notebook creation in EMR Studio.
#EMRNotebook#AmazonEMRconsole#AmazonEMR#AmazonS3#EMRStudio#AmazonEMRAPI#EC2Instance#technology#technews#technologynews#news#govindhtech
0 notes
Text
Kubernetes vs. Traditional Infrastructure: Why Clusters and Pods Win
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, agility, scalability, and reliability are not just nice-to-haves—they’re necessities. Traditional infrastructure, once the backbone of enterprise computing, is increasingly being replaced by cloud-native solutions. At the forefront of this transformation is Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration platform that has become the gold standard for managing containerized applications.
But what makes Kubernetes a superior choice compared to traditional infrastructure? In this article, we’ll dive deep into the core differences, and explain why clusters and pods are redefining modern application deployment and operations.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Before drawing comparisons, it’s important to clarify what we mean by each term:
Traditional Infrastructure
This refers to monolithic, VM-based environments typically managed through manual or semi-automated processes. Applications are deployed on fixed servers or VMs, often with tight coupling between hardware and software layers.
Kubernetes
Kubernetes abstracts away infrastructure by using clusters (groups of nodes) to run pods (the smallest deployable units of computing). It automates deployment, scaling, and operations of application containers across clusters of machines.
Key Comparisons: Kubernetes vs Traditional Infrastructure
Feature
Traditional Infrastructure
Kubernetes
Scalability
Manual scaling of VMs; slow and error-prone
Auto-scaling of pods and nodes based on load
Resource Utilization
Inefficient due to over-provisioning
Efficient bin-packing of containers
Deployment Speed
Slow and manual (e.g., SSH into servers)
Declarative deployments via YAML and CI/CD
Fault Tolerance
Rigid failover; high risk of downtime
Self-healing, with automatic pod restarts and rescheduling
Infrastructure Abstraction
Tightly coupled; app knows about the environment
Decoupled; Kubernetes abstracts compute, network, and storage
Operational Overhead
High; requires manual configuration, patching
Low; centralized, automated management
Portability
Limited; hard to migrate across environments
High; deploy to any Kubernetes cluster (cloud, on-prem, hybrid)
Why Clusters and Pods Win
1. Decoupled Architecture
Traditional infrastructure often binds application logic tightly to specific servers or environments. Kubernetes promotes microservices and containers, isolating app components into pods. These can run anywhere without knowing the underlying system details.
2. Dynamic Scaling and Scheduling
In a Kubernetes cluster, pods can scale automatically based on real-time demand. The Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) and Cluster Autoscaler help dynamically adjust resources—unthinkable in most traditional setups.
3. Resilience and Self-Healing
Kubernetes watches your workloads continuously. If a pod crashes or a node fails, the system automatically reschedules the workload on healthy nodes. This built-in self-healing drastically reduces operational overhead and downtime.
4. Faster, Safer Deployments
With declarative configurations and GitOps workflows, teams can deploy with speed and confidence. Rollbacks, canary deployments, and blue/green strategies are natively supported—streamlining what’s often a risky manual process in traditional environments.
5. Unified Management Across Environments
Whether you're deploying to AWS, Azure, GCP, or on-premises, Kubernetes provides a consistent API and toolchain. No more re-engineering apps for each environment—write once, run anywhere.
Addressing Common Concerns
“Kubernetes is too complex.”
Yes, Kubernetes has a learning curve. But its complexity replaces operational chaos with standardized automation. Tools like Helm, ArgoCD, and managed services (e.g., GKE, EKS, AKS) help simplify the onboarding process.
“Traditional infra is more secure.”
Security in traditional environments often depends on network perimeter controls. Kubernetes promotes zero trust principles, pod-level isolation, and RBAC, and integrates with service meshes like Istio for granular security policies.
Real-World Impact
Companies like Spotify, Shopify, and Airbnb have migrated from legacy infrastructure to Kubernetes to:
Reduce infrastructure costs through efficient resource utilization
Accelerate development cycles with DevOps and CI/CD
Enhance reliability through self-healing workloads
Enable multi-cloud strategies and avoid vendor lock-in
Final Thoughts
Kubernetes is more than a trend—it’s a foundational shift in how software is built, deployed, and operated. While traditional infrastructure served its purpose in a pre-cloud world, it can’t match the agility and scalability that Kubernetes offers today.
Clusters and pods don’t just win—they change the game.
0 notes
Link
#configuration#encryption#firewall#IPmasking#Linux#networking#OpenVPN#Performance#PiVPN#Privacy#RaspberryPi#remoteaccess#Security#self-hosted#Server#Setup#simplest#systemadministration#tunneling#VPN#WireGuard
0 notes
Text
🔧 Red Hat Enterprise Linux Automation with Ansible
Empowering IT Teams with Simplicity, Speed, and Security
🌟 Introduction
In the evolving world of IT, where speed, consistency, and security are paramount, automation is the key to keeping up. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), paired with Ansible, provides a powerful solution to streamline operations and reduce manual effort — enabling teams to focus on innovation rather than repetitive tasks.
What is Ansible?
Ansible is an open-source automation tool by Red Hat. It’s designed to manage systems, deploy software, and orchestrate complex workflows — all without needing any special software installed on the managed systems.
Key Features:
Agentless: Works over SSH — no agents required.
Human-Readable: Uses simple YAML syntax for defining tasks.
Efficient: Ideal for managing multiple servers simultaneously.
Scalable: Handles environments from small to enterprise-scale.
🔄 Why Automate Red Hat Enterprise Linux?
RHEL is a foundation of many enterprise IT environments. Automating RHEL with Ansible helps: BenefitDescription
⏱ Speed Up OperationsTasks that take hours can be completed in minutes.
📋 Ensure ConsistencyEliminate errors caused by manual setup.
🔒 Improve SecurityApply and enforce security policies across all systems.
🔄 Simplify UpdatesAutomate patching and system maintenance.
☁️ Support Hybrid EnvironmentsSeamlessly manage on-prem and cloud infrastructure.
📌 Use Cases for RHEL Automation with Ansible
1. System Provisioning
Quickly set up RHEL systems with the necessary configurations, user access, and services — ensuring a consistent baseline across all servers.
2. Configuration Management
Apply and maintain settings like firewall rules, time synchronization, and service configurations without manual intervention.
3. Patch Management
Automatically install system updates and security patches across hundreds of machines, ensuring they remain compliant and secure.
4. Application Deployment
Automate the deployment of web servers, databases, and enterprise applications with zero manual steps.
5. Security & Compliance
Enforce enterprise security policies and automate compliance checks against industry standards (e.g., CIS, PCI-DSS, HIPAA).
💼 Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform (AAP)
For enterprises, Red Hat offers a more robust version of Ansible through the Ansible Automation Platform, which includes:
Visual Dashboard: Manage and monitor automation through a UI.
Role-Based Access Control: Assign permissions based on user roles.
Automation Hub: Access certified playbooks and modules.
Analytics: Get insights into automation performance and trends.
It’s built to scale and is fully integrated with RHEL environments, making it ideal for large organizations.
📊 Business Benefits
Organizations using RHEL with Ansible have seen:
Increased productivity: Less time spent on routine tasks.
Fewer errors: Standardized configurations reduce mistakes.
Faster time to deploy: Systems and applications are ready faster.
Better compliance: Automated reporting and enforcement of policies.
🚀 Conclusion
Red Hat Enterprise Linux + Ansible isn’t just about automation — it’s about transformation. It enables IT teams to work smarter, respond faster, and build a foundation for continuous innovation.
Whether you're managing 10 servers or 10,000, integrating Ansible with RHEL can transform how your infrastructure is built, secured, and maintained.
For more info, Kindly follow: Hawkstack Technologies
0 notes
Photo
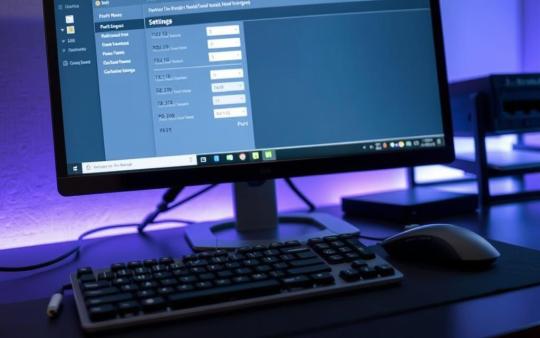
https://pcport.co.uk/how-to-check-the-port-number-on-your-computer/ Today's digital world demands understanding your computer's network setup. A port number is key, linking different applications and processes over the network. Every IP address can handle up to 65,535 ports, enabling many connections at once. This article will show you how to find your computer's port number.Whether you're on Windows or Mac, we’ve got you covered. By learning these steps, you'll better manage network connections and boost security. From common ports like 80 (HTTP) and 22 (SSH)
0 notes