#biotechnology and its applications
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Biotechnology and Its Applications Detailed Explanation Suitable for Class 12 Students
Biotechnology and Its Applications:
Introduction to Biotechnology:
Biotechnology involves using living organisms, cells, and biological systems to develop products and technologies for various applications. It merges biology with technology, providing innovative solutions in multiple fields such as agriculture, medicine, and environmental management.

1. Biotechnological Applications in Agriculture:
Biotechnology in agriculture aims to enhance food production and crop quality through several advanced techniques:
Agro-Chemical Based Agriculture: This method uses chemical fertilizers and pesticides to increase crop yields. However, it can have negative environmental impacts.
Organic Agriculture: Involves using natural methods and products for farming, promoting sustainability and reducing chemical residues in food.
Genetically Engineered Crops (GMOs): Crops are modified using genetic engineering to exhibit desirable traits such as pest resistance, drought tolerance, and improved nutritional content. Examples include Bt cotton, which produces Bt toxin to protect against specific pests, reducing the need for chemical insecticides.
Read Also: Biodiversity and Conservation - Class 12 Detailed Notes
Tissue Culture: This technique allows the growth of entire plants from small tissue samples (explants). It helps in producing a large number of genetically identical plants, known as some clones, which are beneficial for maintaining uniform crop quality.
Micro-Propagation: A form of tissue culture used to produce a large number of plants quickly. It is useful for propagating plants that do not produce viable seeds.
Somatic Hybridization: Combines different plant species at the cellular level to create new hybrid plants with desirable traits from both parent species.
2. Biotechnological Applications in Medicine:
Biotechnology has revolutionized medicine, providing advanced methods for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases:
Recombinant DNA Technology: Allows the production of therapeutic proteins and drugs in large quantities. For example, insulin used to treat diabetes is now produced using genetically engineered bacteria, making it safer and more effective than animal-derived insulin.
Gene Therapy: Involves inserting healthy genes into a patient's cells to treat genetic disorders. It offers potential cures for diseases like cystic fibrosis and certain types of cancer.
Vaccines: Biotechnology has enabled the development of new vaccines, such as the recombinant hepatitis B vaccine, which is produced using yeast cells.
3. Transgenic Animals:
Transgenic animals are genetically modified to carry genes from other species. They serve various purposes, including:
Research: Studying gene functions and disease mechanisms in transgenic animals helps scientists understand human diseases better.
Pharming: Producing valuable proteins and drugs in the milk, eggs, or blood of transgenic animals, which can then be harvested and purified for medical use.
Improving Livestock: Enhancing traits like growth rate, disease resistance, and milk production in farm animals.
4. Ethical Issues:
Biotechnology raises several ethical and moral concerns:
Safety of GMOs: There is ongoing debate about the potential health risks and environmental impacts of genetically modified crops and animals.
Genetic Discrimination: The use of genetic information by employers or insurance companies could lead to discrimination against individuals based on their genetic predisposition to certain diseases.
Moral Implications: Genetic modifications in humans, such as designer babies, spark ethical questions about the extent to which humans should interfere with natural processes.
Conclusion:
Biotechnology offers immense potential to solve some of the world's pressing challenges in food production, healthcare, and environmental conservation. However, it is crucial to address the ethical and safety issues associated with its applications to ensure responsible and sustainable use of this powerful technology.
This more detailed overview should help Class 12 students understand the scope and implications of biotechnology and its applications in a comprehensive yet accessible manner.
#biotechnology and its applications#applications of biotechnology#biotechnology and its applications notes#biotechnology and its applications class 12#biotechnology and its applications ppt#biology#vavaclasses#science#chemistry#11thclass#botany#class 8#foundation#9thclass#11th class#Class 12
1 note
·
View note
Text
"If you're hoping that reef-restoring coral larvae will settle down in damaged reefs, you can't just sit around and wait for it to happen. You have to get out there and entice the larvae, which is exactly what a new algae-based gel is designed to do.
While we may think of coral reefs' "skeletons" as being composed solely of calcium carbonate produced by coral polyps, much of the material is in fact generated by what are known as crustose coralline algae.
Along with contributing greatly to the structural integrity of reefs, the algae-produced calcium carbonate also serves as a home to planktonic coral larvae. Once those formerly free-swimming organisms settle in and become polyps, they start producing reef-building calcium of their own.
It's a good arrangement for the coral, but it also benefits the algae.
Not only does the reef itself provide the algae with protection from the elements, the coral polyps also emit ammonia which the algae feed upon. It is therefore in the algae's best interest to entice any coral larvae that may be swimming past in the water column. In order to do so, the algae release metabolite chemicals that attract the larvae.
Led by Dr. Daniel Wangpraseurt, scientists at UC San Diego's Scripps Institution of Oceanography have now incorporated those metabolites into a gel that can be applied to degraded coral reefs. Called SNAP-X, the substance reportedly boosts coral larval settlement by up to 20 times as compared to untreated surfaces.
If the algae metabolites were just applied to the coral on their own, they would soon dissipate in the water, leaving the coral larvae unable to follow them to their source. For that reason, the researchers started by encasing the chemical molecules in durable silica nanoparticles. Those particles were then suspended within a biocompatible liquid blend of gelatin methacrylate and polyethylene glycol diacrylate.
When that liquid is sprayed or painted onto a surface – such as a piece of dead coral – then exposed to ultraviolet light, it polymerizes into a hydrogel form. That gel is capable of clinging to the surface for up to one month while immersed in flowing water, gradually releasing its larvae-attracting nanoparticles as it does so.
Initial lab tests showed that application of SNAP-X resulted in a six-fold increase in larval settlement. Subsequent tests that more accurately simulated the water flow on coral reefs, however, produced the 20-times figure.
It should be noted that all of the tests conducted so far have involved a single type of coral, but Wangpraseurt believes the technology should work on other species with a few tweaks.
"I think this material is a breakthrough that can hopefully make a big contribution to coral restoration," he says. "Biomedical scientists have spent a lot of time developing nanomaterials as drug carriers, and here we were able to apply some of that knowledge to marine restoration."
A paper on the research was recently published in the journal Trends in Biotechnology."
-via New Atlas, May 26, 2025
#coral#conservation#ocean#marine biology#ecosystem#ecosystem restoration#ecology#marine science#marine life#coral reef#science news#tidalpunk#biotechnology#good news#hope
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
In a major stride towards sustainable industrial fermentation, a team of researchers at Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in The Netherlands, has unveiled pioneering advancements in the purification of isopropanol and acetone from the fermentation of waste gases. The study, published in the Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, introduces novel processes that promise to elevate the efficiency and viability of large-scale production. Isopropanol and acetone have a combined global market of $10 billion. Both chemicals are important industry solvents, and isopropanol also has significant applications as a pharmaceutical ingredient due to its low toxicity. Conventional production relies on fossil carbon-dependent methods, which are becoming less favorable as stricter environmental regulations come into place.
Continue Reading.
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
RADICAL LIFE EXTENSION:
### Key Areas of Research and Approaches:
1. **Genetic Engineering**:
- **CRISPR and Gene Editing**: Technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 allow scientists to modify genes associated with aging and age-related diseases. By editing or repairing genes, it may be possible to slow down or reverse aging processes.
- **Telomere Extension**: Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with age. Research is exploring ways to extend or maintain telomere length to delay cellular aging.
2. **Senescence and Cellular Repair**:
- **Senolytics**: These are drugs designed to selectively eliminate senescent cells, which accumulate with age and contribute to tissue dysfunction and chronic diseases. Removing these cells can improve health and extend lifespan.
- **Stem Cell Therapy**: Stem cells have the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs. Research is ongoing to harness stem cells for repairing age-related damage and restoring function.
3. **Metabolic and Dietary Interventions**:
- **Caloric Restriction**: Studies have shown that reducing calorie intake without malnutrition can extend lifespan in various organisms. Researchers are investigating the mechanisms behind this and developing drugs that mimic the effects of caloric restriction.
- **Rapamycin and mTOR Inhibition**: Rapamycin, a drug that inhibits the mTOR pathway, has been shown to extend lifespan in animal models. It is being studied for its potential to delay aging in humans.
4. **Regenerative Medicine**:
- **Tissue Engineering**: Creating replacement tissues and organs using bioengineering techniques can address age-related degeneration and organ failure.
- **3D Bioprinting**: This technology allows for the creation of complex tissues and organs layer by layer, potentially providing replacements for damaged or aging body parts.
5. **Artificial Intelligence and Biotechnology**:
- **AI in Drug Discovery**: AI is being used to accelerate the discovery of new drugs and therapies for aging-related conditions.
- **Biomarkers of Aging**: Developing accurate biomarkers to measure biological age and the effectiveness of anti-aging interventions.
6. **Cryonics and Mind Uploading**:
- **Cryonics**: The practice of preserving bodies or brains at extremely low temperatures with the hope that future technology can revive and rejuvenate them.
- **Mind Uploading**: A speculative concept where a person's consciousness is transferred to a digital substrate, potentially allowing for indefinite existence in a virtual environment.
### Ethical and Societal Considerations:
- **Equity and Access**: Ensuring that life-extending technologies are accessible to all, not just the wealthy.
- **Overpopulation**: Addressing the potential impact on global population and resources.
- **Quality of Life**: Ensuring that extended life is accompanied by improved health and well-being, not just prolonged existence.
### Current Status:
While significant progress has been made in understanding the biology of aging, most radical life extension technologies are still in the experimental stages. Human trials are ongoing for some interventions, but widespread application is likely still years or decades away.
Radical life extension remains a highly interdisciplinary field, combining insights from genetics, biotechnology, medicine, and computational science. The ultimate goal is to not only extend human lifespan but to ensure that those additional years are lived in good health and vitality.
#future#cyberpunk aesthetic#cyberpunk artist#futuristic#futuristic city#cyberpunk city#cyberpunkart#concept artist#digital art#digital artist#live forever#forever life
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Genetic engineering: CRISPR and beyond
In genetic engineering, we find ourselves amidst a scientific revolution with the advent of revolutionary technologies like CRISPR-Cas9. However, our journey into the intricate landscape of genetic manipulation is far from complete. This post delves into the nuanced world of genetic engineering, exploring cutting-edge technologies and their remarkable potential in shaping the future of medicine and biotechnology.
CRISPR-Cas9: Precision at the Molecular Level
CRISPR-Cas9, a revolutionary genome editing tool, stands for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9. It utilizes a guide RNA (gRNA) to target specific DNA sequences, and the Cas9 protein acts as molecular scissors to cut the DNA at precisely defined locations. This break in the DNA prompts the cell's natural repair machinery to make changes, either through non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) or homology-directed repair (HDR). CRISPR-Cas9's precision allows for gene knockout, modification, or insertion with remarkable accuracy.
Beyond CRISPR: Emerging Technologies
While CRISPR-Cas9 has dominated the field of genetic engineering, numerous promising technologies have emerged on the horizon. These include CRISPR-Cas variants like CRISPR-Cas12 and CRISPR-Cas13, which offer unique advantages such as smaller size, increased specificity, and targeting of RNA. Additionally, base editing techniques, such as adenine base editors (ABEs) and cytosine base editors (CBEs), enable the direct conversion of one DNA base into another without causing double-strand breaks, expanding the range of genetic modifications possible.
Applications in Medicine
The implications of these advancements are profound, particularly in medicine. Genetic engineering can potentially treat various genetic disorders, from cystic fibrosis to sickle cell anemia, by correcting disease-causing mutations at their source. Precision medicine, tailored to an individual's genetic makeup, is becoming increasingly feasible, allowing for personalized therapies with minimal side effects.
Ethical Considerations and Regulation
As we venture further into the genetic frontier, we must acknowledge the ethical considerations surrounding genetic engineering. The ability to modify the human germline, with implications for future generations, raises ethical dilemmas that necessitate rigorous oversight and regulation. The international community is developing guidelines to ensure responsible use of these powerful tools.
Future Directions and Challenges
While genetic engineering offers immense promise, it is not without its challenges. Off-target effects, unintended consequences, and the potential for creating designer babies are among the issues that demand careful consideration. Researchers and ethicists must work in tandem to navigate this uncharted territory.
References
Doudna, J. A., & Charpentier, E. (2014). The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science, 346(6213), 1258096.
Anzalone, A. V., Randolph, P. B., Davis, J. R., Sousa, A. A., Koblan, L. W., Levy, J. M., … & Liu, D. R. (2019). Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature, 576(7785), 149-157.
Kime, E. (2021). CRISPR and the ethics of gene editing. Nature Reviews Genetics, 22(1), 3-4.
This post only scratches the surface of the profound transformations occurring in genetic engineering. The relentless pursuit of knowledge and ethical exploration will shape the future of this field as we continue to unlock the intricate secrets of our genetic code.

#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#genetics#genetic engineering#crispr#ethical genetics
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand Board of Investment
The Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) is a pivotal government agency tasked with promoting investment in Thailand, both from domestic and foreign sources. Established in 1966, the BOI plays a crucial role in driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and enhancing Thailand's competitiveness in the global market. By offering a range of incentives, streamlined services, and strategic support, the BOI attracts high-value investments across various sectors. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the BOI, covering its legal framework, incentive schemes, application process, and strategic considerations for investors.
Legal Framework and Mission of the BOI
The BOI operates under the Investment Promotion Act B.E. 2520 (1977), which grants it the authority to provide incentives and support to qualified investments. The BOI's mission is to:
Promote Investment: Attract domestic and foreign investment in targeted industries and regions.
Enhance Competitiveness: Strengthen Thailand's position as a regional hub for trade and investment.
Foster Innovation: Support research and development (R&D), technology transfer, and sustainable practices.
Facilitate Business: Streamline regulatory processes and provide comprehensive support services to investors.
The BOI is governed by a board chaired by the Prime Minister, with members from key ministries and private sector representatives, ensuring a balanced approach to investment promotion.
Key Incentives Offered by the BOI
The BOI offers a range of incentives to attract and support investments in targeted industries. These incentives are designed to reduce costs, enhance competitiveness, and facilitate business operations. Key incentives include:
1. Tax Incentives
Corporate Income Tax (CIT) Exemptions: Projects may receive CIT exemptions for up to 8 years, with possible extensions for projects in advanced technology or R&D.
Import Duty Exemptions: Exemptions on import duties for machinery, raw materials, and components used in production.
Dividend Tax Exemptions: Dividends paid from exempted profits are also exempt from taxation.
2. Non-Tax Incentives
Land Ownership: Foreign investors may own land for promoted projects, subject to BOI approval.
Work Permits and Visas: Simplified procedures for obtaining work permits and visas for foreign executives, experts, and technicians.
Repatriation of Funds: Permission to repatriate investment capital, profits, and dividends.
3. Sector-Specific Incentives
Targeted Industries: Enhanced incentives for industries such as biotechnology, digital technology, renewable energy, and advanced manufacturing.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs): Additional incentives for investments in SEZs, including infrastructure support and reduced regulatory requirements.
4. Additional Benefits
Investment Promotion Zones: Incentives for investments in designated zones, such as the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC).
Green Initiatives: Additional benefits for projects that promote environmental sustainability and energy efficiency.
Targeted Industries and Strategic Sectors
The BOI focuses on promoting investments in industries that align with Thailand's economic development goals. Key targeted industries include:
Advanced Technology and Innovation:
Biotechnology, nanotechnology, and advanced materials.
Digital technology, including software development, data centers, and cybersecurity.
Sustainable Industries:
Renewable energy, such as solar, wind, and biomass.
Environmental management and waste-to-energy projects.
High-Value Manufacturing:
Automotive and aerospace industries.
Electronics and electrical appliances.
Services and Infrastructure:
Tourism and hospitality, including medical tourism.
Logistics and transportation, particularly in the EEC.
Agriculture and Food Processing:
High-tech agriculture and food innovation.
Halal food production and export.
Application Process for BOI Promotion
The process of applying for BOI promotion involves several steps, each requiring careful preparation and adherence to regulatory requirements. Below is a detailed breakdown:
1. Determine Eligibility
Identify the appropriate BOI category and incentives based on your business activities and investment plans.
Ensure that your project aligns with the BOI's targeted industries and strategic goals.
2. Prepare Required Documents
Business Plan: Detailed plan outlining the project's objectives, scope, and financial projections.
Financial Statements: Audited financial statements for existing companies or pro forma financials for new ventures.
Technical Specifications: Details of machinery, technology, and production processes.
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): For projects with potential environmental impacts.
3. Submit the Application
Submit the application through the BOI's online portal or at a BOI office.
Pay the application fee, which varies depending on the project size and complexity.
4. Review and Approval
The BOI reviews the application, including the project's feasibility, economic impact, and compliance with regulations.
Additional information or clarifications may be requested during the review process.
5. Receive BOI Promotion Certificate
If approved, the BOI issues a Promotion Certificate, detailing the incentives and conditions.
The certificate must be registered with the relevant government agencies to activate the incentives.
6. Compliance and Reporting
BOI-promoted projects are subject to periodic reporting and compliance checks.
Ensure that all conditions and requirements are met to maintain the incentives.
Strategic Considerations for Investors
To maximize the benefits of BOI promotion, investors should consider the following strategies:
Sector Alignment:
Align your investment with the BOI's targeted industries and strategic goals.
Research the specific incentives and requirements for your sector.
Comprehensive Planning:
Develop a detailed business plan that outlines the project's objectives, scope, and financial projections.
Consider the long-term impact of the investment and potential for expansion.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance:
Ensure compliance with Thai laws and regulations, including environmental and labor standards.
Seek legal advice to navigate the complexities of BOI promotion and regulatory requirements.
Partnerships and Collaboration:
Form strategic partnerships with local businesses, research institutions, and government agencies.
Leverage local expertise and networks to enhance the project's success.
Sustainability and Innovation:
Incorporate sustainable practices and innovative technologies into the project.
Explore opportunities for R&D and technology transfer to enhance competitiveness.
Recent Developments and Trends
Thailand's investment landscape is evolving, with several trends and developments shaping the BOI's strategies:
Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC):
The EEC is a flagship initiative to develop the eastern region into a hub for advanced industries and innovation.
The BOI offers enhanced incentives for investments in the EEC, including infrastructure support and streamlined regulations.
Digital Transformation:
The BOI is promoting investments in digital technology, including artificial intelligence, blockchain, and fintech.
Digital infrastructure projects, such as data centers and smart cities, are prioritized.
Sustainability and Green Initiatives:
There is growing emphasis on sustainable investments, including renewable energy, waste management, and green manufacturing.
The BOI offers additional incentives for projects that promote environmental sustainability.
Post-Pandemic Recovery:
The BOI is implementing measures to support economic recovery, including incentives for healthcare, biotechnology, and supply chain resilience.
Efforts to attract foreign investment and boost domestic industries are intensified.
Conclusion
The Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) is a vital institution for promoting investment and driving economic growth in Thailand. By offering a range of incentives, streamlined services, and strategic support, the BOI attracts high-value investments across various sectors. Understanding the BOI's legal framework, incentive schemes, and application process is essential for investors seeking to capitalize on the opportunities in Thailand. As the country continues to evolve its investment landscape, staying informed and proactive will remain key to achieving long-term success. Whether you are a domestic entrepreneur or a foreign investor, the BOI provides a robust platform for realizing your investment goals and contributing to Thailand's economic development.
#thailand#thai#corporate#thailandboardofinvestment#thailandboi#thaiboi#boi#boardofinvestment#corporateinthailand#businessinthailand#business
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
News on Fall Boosters
(I focus on Novavax for reasons previously discussed on this blog, searchable via its tag.)
June 14, 2024 - Novavax Submits Application to U.S. FDA for Updated Protein-based 2024-2025 Formula COVID-19 Vaccine
Novavax's JN.1 vaccine has demonstrated broad cross-neutralizing antibodies against multiple variant strains, including KP.2 and KP.3, indicating the potential to protect against forward drift variants.
June 27, 2024 - U.S. CDC & ACIP Recommend Use of Authorized and Approved 2024-2025 COVID-19 Vaccines
Today the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted unanimously in favor of a universal recommendation for the use of 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccines ... Novavax intends to provide doses of our 2024-2025 COVID-19 vaccine at the start of the vaccination season and upon EUA by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Aug. 14, 2024 - COVID is surging again. Here’s the latest on new variants, updated vaccines, and masking
Novavax, an American biotechnology company, had already developed a JN.1-targeted vaccine and the company said it wouldn’t have time to change the formulation before the fall. Novavax’s vaccine is the only protein-based COVID-19 vaccine
[I disagree with Mark Sawyer, MD's quote in the article that “It’s important to have Novavax as an option because some people are still concerned about mRNA”. I in particular have no issue with "mRNA tech", have taken it, and am familiar with it due to having worked on some of the earliest science-journalistic reporting about it. Many choose Novavax for other reasons, again, discussed previously / elswhere, and will continue to as long as it confers equal or better protection vs mRNA options.]
Is it time to wear a mask again? ... Sawyer also recommends masking while traveling or in high-risk situations.“ If you’re in a community where the virus is surging, as so many people are, it is smart to wear a mask if you’re in indoor, crowded conditions,” he says.
[*For some of us it isn't "again"; we didn't stop in any situation where it was "smart" to.]
Despite COVID not being a seasonal illness, new vaccines are still being offered on a seasonal schedule. Updated boosters are again expected in September.
#covid#article#masking#vaccines#covid vaccines#covid boosters#boosters#get vaccinated#get boosted#Novavax
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
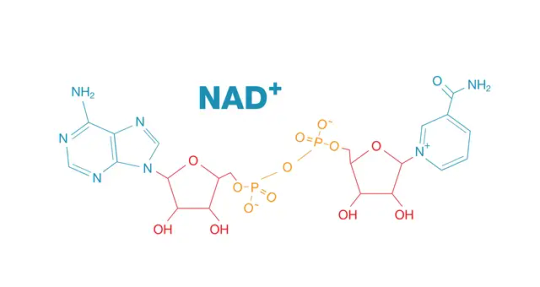
🔬 Unveiling the Wonders of NAD⁺: The Molecule Behind Energy, Aging, and Longevity
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) is an essential coenzyme found in all living cells, playing a central role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and healthy aging. NAD⁺ switches between its oxidized (NAD⁺) and reduced (NADH) forms to power critical biological processes—especially ATP production through glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.

🔍 Historical Milestones: Discovered in the early 20th century, NAD⁺ research gained momentum with key breakthroughs:
1930s–50s: Identified role in fermentation and DNA repair.
2000s: Discovery of Sirtuins and NAD⁺ biosynthetic pathways (e.g., via nicotinamide riboside) opened new therapeutic possibilities.
⏳ NAD⁺ & Aging: NAD⁺ levels decline with age, impairing mitochondrial function and DNA repair. Studies show that restoring NAD⁺ can reverse age-related metabolic dysfunction, enhance Sirtuin activity, and reduce cellular senescence—potentially slowing aging at the cellular level.
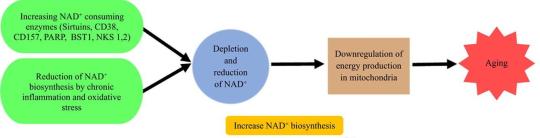
Figure: Reasons for the decrease of NAD+ in the body during aging (DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.08.003)
❤️ More Health Benefits:
Metabolism: Boosts energy use and nutrient absorption.
Heart health: Improves cardiac output and function in preclinical studies.
Vascular protection: Activates Sirtuins (especially SIRT1), which are protective against cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.

🚀 Real-World Applications:
NAD⁺ supplements.
Exercise: Enhances NAD⁺ synthesis through NAMPT activation.
Diet and fasting: B3-rich foods and intermittent fasting can help maintain NAD⁺ levels.
🔮 The Future: Ongoing research aims to optimize NAD⁺ delivery, personalize supplementation strategies, and explore its full potential in regenerative medicine and anti-aging therapies.
NAD⁺ is more than just a coenzyme—it's a cornerstone of cellular health and a promising target in the science of aging and longevity.
Sources: Cell Metab (2010), Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2021), Science (2015), J Adv Res (2022), Sci Rep (2023), Plast Reconstr Surg (2022), and more.
At Xi'an Innov Biotechnology, we provide high-quality NAD+ and other anti-aging ingredients like liposomal Vitamin C and glutathione—perfect for cutting-edge supplements and skincare.
#nutrition#supplements#nad+#health#health and wellness#antiaging#anti aging#aging#vitamin#healthy aging#advice#health & fitness#aging gracefully#aging in place
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Culturing Bacteria in a Petri dish With Agar; an experiment/observation

Today's post is quite different from the usual;
So, we had to do a project in the educational institution I study in; Which was growing bacteria in a Petri dish with agar.
Today, the results came in, but our professor insisted that we have to throw the dishes in the bin. I didn't give up there; after talking to her for a short amount of time, she accepted that I can take the dish with me to my flat, and have a look at it with microscope.
I still cannot comprehend why other students were disgusted by them; they are beyond wonderful.
Allow me to explain this astonishing journey:
What exactly is agar?
Well, agar, derived from the minute aquatic organism known as seaweed or algae, specifically the types Gelidium or Gracilaria, is a widely employed gelling agent. Found abundantly in the coastal regions of East Asia, particularly Japan and South Korea, it undergoes a process of cleaning and extraction to obtain agar in its usable forms of dry strips, flakes, or powdered consistency.
Now, when it comes to the realm of cell and bacterial culture, agar assumes a pivotal role as a solidifying and gelling medium within culture media. Its remarkable gel-forming properties allow for the creation of a three-dimensional matrix, offering an ideal environment for the growth and sustenance of cells and bacteria alike. Nutrients and metabolites find efficient transfer within this agar-based culture medium, while its structural integrity ensures the confinement of cells to designated areas.
Agar's utilization in cell and bacterial culture provides a multitude of advantages, including its ease of implementation, stability, and facilitation of cell separation procedures. The versatility of agar finds application in diverse fields, from microbiology to biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries.
Bacteria can be found on any surface, anywhere.
I decided to pick them up from my shoe soles.
After extracting bacteria from the soles of the shoes, I cultured them in an agar-containing Petri dish. After one week, I observed bacterial and fungus growth in this environment. Here are some images I captured with my microscope:
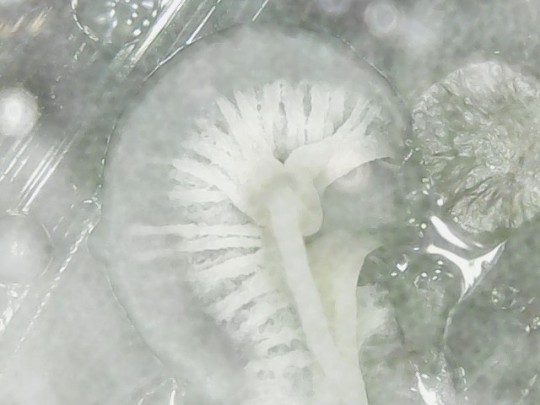

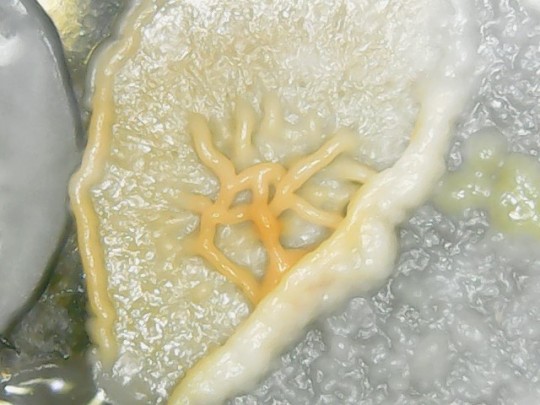
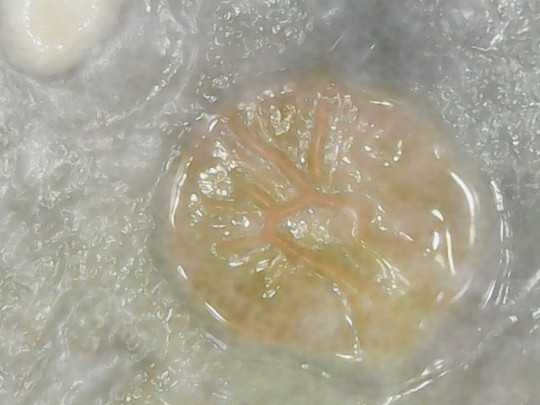
Wonderful, aren't they?
ND
#bacteria#fungus#deduction#tumblr#deducter#deduce#deductive reasoning#science of deduction#tumblrpost
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand SMART Visa
1.1 Statutory Foundations
Established under Royal Decree on SMART Visa B.E. 2561 (2018)
Amended by Ministerial Regulation No. 377 (2021) expanding eligible sectors
Operates within Thailand 4.0 Economic Model under BOI oversight
1.2 Governance Structure
Primary Authority: Board of Investment (BOI)
Interagency Coordination:
Immigration Bureau (visa issuance)
Digital Economy Promotion Agency (DEPA) for tech qualifications
Ministry of Higher Education for academic validation
Technical Review Committees:
Sector-specific panels (12 industries)
Investment verification unit
2. Eligibility Criteria & Qualification Pathways
2.1 SMART-T (Experts)
Compensation Thresholds
Base Salary: Minimum THB 200,000/month (USD 5,800)
Alternative Compensation:
Equity valued at 25% premium to cash salary
Performance bonuses (capped at 40% of base)
2.2 SMART-E (Entrepreneurs)
Startup Metrics
Revenue Test: THB 10M+ ARR
Traction Test: 50,000 MAU
Funding Test: Series A (THB 25M+)
Accelerator Requirements:
DEPA-certified programs
Minimum 6-month incubation
3. Application Process & Technical Review
3.1 Document Authentication Protocol
Educational Credentials:
WES/IQAS evaluation for foreign degrees
Notarized Thai translations (certified by MFA)
Employment Verification:
Social security cross-check (home country)
Three professional references (direct supervisors)
3.2 Biometric Enrollment
Facial Recognition: 12-point capture system
Fingerprinting: 10-print electronic submission
Iris Scanning: Optional for Diamond tier
4. Privilege Structure & Compliance
4.1 Employment Rights Framework
Permitted Activities:
Primary employment with sponsor (≥80% time)
Academic collaboration (≤20% time)
Advisory roles (max 2 concurrent)
Restrictions:
Local employment outside specialty
Political activities
Unapproved commercial research
4.2 Dependent Provisions
Spousal Work Rights:
General employment permitted
No industry restrictions
Child Education:
25% tuition subsidy at partner schools
University admission priority
4.3 Mobility Features
Airport Processing:
Dedicated SMART lanes at 6 airports
15-minute clearance guarantee
Re-entry Flexibility:
Unlimited exits
72-hour grace period
5. Sector-Specific Implementations
5.1 Biotechnology
Special Privileges:
Lab equipment duty waivers
Fast-track FDA approval
50% R&D tax deduction
5.2 Advanced Manufacturing
Incentives:
Robotics import tax exemption
Industrial land lease discounts
THB 500K training subsidy
5.3 Digital Infrastructure
Cloud Computing:
VAT exemption on services
30% energy cost reduction
Cybersecurity:
Liability protections
Gov't certification fast-track
6. Compliance & Monitoring
6.1 Continuous Reporting
Quarterly:
Employment verification
Investment maintenance
Annual:
Contribution assessment
Salary benchmarking
6.2 Renewal Process
Documentation:
Updated financials
Health insurance (USD 100K)
Performance metrics
Fees:
THB 10,000 renewal
THB 1,900 visa stamp
7. Emerging Developments
7.1 2024 Enhancements
Blockchain Specialist Category
Climate Tech Fast-Track
EEC Regional Expansion
7.2 Pending Reforms
Dual Intent Provision
Skills Transfer Mandate
Global Talent Pool
8. Strategic Application Approach
8.1 Pre-Submission Optimization
Compensation Restructuring
Patent Portfolio Development
Professional Endorsements
8.2 Post-Approval Planning
Tax Residence Strategy
Asset Protection
Succession Planning
9. Risk Management
9.1 Common Rejection Reasons
Document Issues (32%)
Qualification Gaps (28%)
Financial Irregularities (19%)
9.2 Operational Challenges
Banking Restrictions
Healthcare Access
Cultural Integration
#thailand#immigration#visa#immigrationinthailand#immigrationlawyers#thai#thaivisa#immigrationlawyersinthailand#thailandsmartvisa#smartvisa#smartvisainthailand#thaismartvisa
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fulbright Scholarship Results Are Out – Congratulations to the Awardees!
The Fulbright Program, hooked up in 1946, stands as one of the maximum prestigious international instructional exchange projects, aiming to foster mutual information between the USA and other nations. Each year, thousands of scholars, college students, and professionals from around the globe are decided on to take part in this program, embarking on possibilities for superior studies, college lecturing, and graduate have a look at in the U.S. The choice technique is pretty aggressive, reflecting this system's commitment to academic excellence and cultural alternate.

Fulbright Scholarship Result Requirement
Recent Developments in the Fulbright Program
As of March 2025, several noteworthy events have spread out within the Fulbright community:
Funding Freeze and Its Implications
In February 2025, the U.S. State Department initiated a brief pause on spending to study its programs and sports. This decision has drastically impacted programs like Fulbright, Gilman, and Critical Language global scholarships. Consequently, many students who depend upon State Department funding have located themselves stranded, both inside the U.S. And abroad, facing monetary uncertainties. This abrupt investment freeze has affected over 12,500 American college students and professionals presently abroad or scheduled to participate in State Department programs within the subsequent six months. Additionally, extra than 7,four hundred global contributors in U.S.-based applications were affected.
AP NEWS
2025 U.S.-ASEAN Visiting Scholar (USAS) Program Nominees
Despite the funding challenges, the Thailand–United States Educational Foundation (Fulbright Thailand) introduced the interview results for the 2025 Fulbright U.S.-ASEAN Visiting Scholar (USAS) Program. Four prominent nominees had been decided on:
Professor Dr. Montarop Yamabhai: Professor of Molecular Biotechnology at Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima.
Dr. Orawan Sriboonruang: Knowledge Management Manager on the Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization Regional Centre for STEM Education, Bangkok.
Assistant Professor Dr. Piya-on Numpaisal, MD.: Associate Dean on the Institute of Medicine, Suranaree University of Technology, Nakhon Ratchasima.
Dr. Totsanat Rattanakaew: Agricultural Research Officer, Expert degree, on the Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, Bangkok.
These nominees will continue to the final choice method carried out with the aid of the U.S. Mission to ASEAN in Jakarta.
FULBRIGHTTHAI.ORG
Fulbright 2025 Cohort Selection in Pakistan
The United States Educational Foundation in Pakistan (USEFP) discovered the choice of the Fulbright 2025 cohort. From 1,a hundred ninety applications spanning a hundred thirty five universities, 88 applicants had been chosen—70 for grasp's applications and 18 for Ph.D. Applications. This cohort's choice underscores the program's willpower to academic advantage and management capability.
USEFP NEWSLETTER
Understanding the Fulbright Selection Process
The Fulbright selection system is meticulous, designed to pick out applicants who now not handiest excel academically however also reveal ability for leadership and a commitment to fostering mutual know-how. Key components of the selection process encompass:
Project Proposal & Grant Purpose: Evaluators check the nice and feasibility of the proposed undertaking, such as its relevance to the host country and its ability impact.
Applicant Qualifications: This encompasses the candidate's academic and professional report, relevant education, accomplishments, extracurricular activities, and language education if required.
Contribution to the Fulbright Mission: Reviewers don't forget how the candidate and their task will enhance the Fulbright purpose of selling mutual understanding amongst international locations via network engagement and other activities.
FULBRIGHT ONLINE
Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
The recent funding freeze affords considerable challenges for current and potential Fulbright scholars. The uncertainty surrounding monetary support has left many in precarious conditions, highlighting the need for clean conversation and contingency making plans.
Despite these challenges, the Fulbright Program keeps to provide worthwhile opportunities. For example, the Fulbright U.S. Scholar Program for the 2025-2026 cycle is about to release, presenting over four hundred awards across six world regions. The utility system is scheduled to begin in February 2025, with a closing date in September 2024.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand SMART Visa
Thailand's Smart Visa program is a specialized initiative designed to attract highly skilled professionals, investors, entrepreneurs, and startup founders to the Kingdom. Launched in 2018, the Smart Visa aims to bolster Thailand's economic growth by fostering innovation, technology development, and foreign investment. Unlike traditional visas, the Smart Visa offers extended stay periods, work authorization, and streamlined immigration processes, making it an attractive option for high-value individuals. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the Thailand Smart Visa, covering its eligibility criteria, application process, benefits, and strategic insights for prospective applicants.
Legal Framework for the Smart Visa
The Smart Visa program is governed by the Immigration Act B.E. 2522 (1979) and related regulations. It is administered by the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) in collaboration with the Immigration Bureau and other government agencies. The Smart Visa is part of Thailand's broader strategy to position itself as a regional hub for technology, innovation, and investment.
Key objectives of the Smart Visa program include:
Attracting Talent: Encouraging highly skilled professionals to work and contribute to Thailand's economy.
Promoting Investment: Facilitating foreign investment in targeted industries.
Supporting Startups: Fostering innovation and entrepreneurship through startup support.
Enhancing Competitiveness: Strengthening Thailand's competitiveness in the global market.
Types of Smart Visas
The Smart Visa program is divided into four categories, each catering to a specific group of applicants:
1. Smart T (Talent)
Eligibility: Highly skilled professionals with expertise in targeted industries.
Requirements:
Minimum monthly salary of THB 200,000 (or THB 120,000 for certain sectors).
At least three years of experience in the relevant field.
Employment with a Thai company or organization in a targeted industry.
2. Smart I (Investor)
Eligibility: Investors committing capital to technology-driven or innovative businesses.
Requirements:
Minimum investment of THB 20 million in a Thai business.
Investment in one of the targeted industries, such as digital technology, biotechnology, or renewable energy.
3. Smart E (Executive)
Eligibility: Executives of companies operating in targeted industries.
Requirements:
Minimum monthly salary of THB 200,000.
Senior position in a Thai company or subsidiary in a targeted industry.
4. Smart S (Startup)
Eligibility: Founders of innovative startups approved by a recognized Thai incubator or accelerator.
Requirements:
Innovative business model with high growth potential.
Approval from a recognized Thai startup incubator or accelerator.
Application Process
The Smart Visa application process involves several steps, each requiring careful preparation and adherence to legal requirements. Below is a detailed breakdown:
1. Determine Eligibility
Identify the appropriate Smart Visa category based on your qualifications and objectives.
Ensure that you meet the eligibility criteria, including salary, investment, or startup approval requirements.
2. Gather Required Documents
Passport: Valid for at least six months with sufficient blank pages.
Proof of Qualifications: Academic certificates, professional licenses, and employment contracts.
Financial Evidence: Bank statements, investment documents, or salary slips.
Business Documents: Company registration, tax ID, and list of shareholders (for Smart I and Smart E applicants).
Startup Approval: Letter of approval from a recognized Thai startup incubator or accelerator (for Smart S applicants).
3. Submit the Application
Submit the application through the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) or the One Start One Stop Investment Center (OSOS).
Pay the application fee, which varies depending on the visa category.
4. Review and Approval
The BOI reviews the application and conducts due diligence to verify the applicant's eligibility.
If approved, the BOI issues a Smart Visa endorsement letter.
5. Visa Issuance
Present the endorsement letter and supporting documents to the Thai Immigration Bureau.
Pay the visa fee and receive the Smart Visa.
6. Registration and Reporting
Upon arrival in Thailand, register your address with the Immigration Bureau.
Submit periodic reports as required by the visa conditions.
Benefits of the Smart Visa
The Smart Visa offers a range of exclusive benefits designed to attract and retain high-potential individuals and businesses:
Extended Stay Periods:
Smart Visa holders can stay in Thailand for up to 4 years, with the option to renew.
This is significantly longer than traditional visas, which typically allow stays of 1 year or less.
Work Authorization:
Smart Visa holders are authorized to work in Thailand without the need for a separate work permit.
This simplifies the process for professionals and executives employed by Thai companies.
Multiple Entries:
The Smart Visa allows unlimited entries and exits from Thailand, providing flexibility for international travel.
Family Inclusion:
Spouses and children of Smart Visa holders are eligible for dependent visas, allowing them to live and study in Thailand.
Streamlined Processes:
The Smart Visa application process is faster and more efficient than traditional visa routes.
Dedicated support is available through the BOI and OSOS.
Tax Incentives:
Smart Visa holders may be eligible for tax exemptions or reductions on personal income earned in Thailand.
Strategic Considerations for Applicants
While the Smart Visa offers numerous advantages, prospective applicants should consider the following factors to maximize their chances of success:
Industry Alignment:
Ensure that your qualifications, experience, and business activities align with Thailand's targeted industries.
Research the specific requirements and opportunities in your field.
Documentation:
Prepare comprehensive and accurate documentation to support your application.
Ensure that all documents are translated into Thai and certified by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs if necessary.
Professional Assistance:
Engage a qualified immigration lawyer or consultant to navigate the complexities of the application process.
Seek professional advice on tax planning, compliance, and long-term stay options.
Long-Term Planning:
Consider your long-term goals and how the Smart Visa can support your personal and professional objectives in Thailand.
Plan for potential extensions, family inclusion, and career development.
Compliance:
Adhere to all visa conditions, including reporting requirements and restrictions on employment.
Stay informed about changes in immigration policies and regulations.
Recent Developments and Trends
Thailand's Smart Visa program has undergone several updates to enhance its appeal and effectiveness:
Expansion of Targeted Industries:
The Thai government has expanded the list of targeted industries to include emerging sectors such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and fintech.
This expansion reflects Thailand's commitment to fostering innovation and attracting global talent.
Digital Transformation:
The BOI has introduced online application platforms and digital services to streamline the Smart Visa process.
These initiatives improve transparency and efficiency, making it easier for applicants to navigate the system.
Increased Focus on Startups:
The Smart S category has been strengthened to attract more innovative startups and foster Thailand's startup ecosystem.
Partnerships with leading Thai and international incubators are enhancing support for startup founders.
Post-Pandemic Recovery:
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, Thailand has implemented measures to facilitate business travel and attract high-value individuals.
These measures include reduced quarantine requirements and fast-track visa processing for Smart Visa holders.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many benefits, the Smart Visa program is not without challenges:
Stringent Eligibility Criteria:
The program's high standards may exclude some qualified individuals and businesses.
Applicants must meet specific salary, investment, or startup approval requirements.
Limited Awareness:
Many potential applicants are unaware of the Smart Visa and its benefits, limiting its reach.
Increased awareness and outreach efforts are needed to attract a diverse pool of talent.
Administrative Complexity:
The application process, while streamlined compared to traditional visas, can still be complex and time-consuming.
Applicants must navigate multiple steps and provide extensive documentation.
Dependence on BOI Approval:
The BOI's approval process is subjective and may result in inconsistencies.
Applicants must demonstrate their value and alignment with Thailand's strategic priorities.
Conclusion
The Thailand Smart Visa is a transformative initiative that reflects the country's commitment to innovation, technology, and foreign investment. By offering extended stay periods, work authorization, and streamlined processes, the Smart Visa provides a compelling opportunity for highly skilled professionals, investors, executives, and startup founders to contribute to Thailand's economic growth. However, the program's stringent eligibility criteria and administrative complexities require careful planning and preparation. By understanding the requirements, leveraging professional assistance, and aligning with Thailand's strategic priorities, prospective applicants can unlock the full potential of the Smart Visa and achieve their personal and professional goals in the Kingdom. As Thailand continues to evolve its immigration policies, the Smart Visa will remain a cornerstone of its efforts to attract global talent and investment.
#thailand#thailandsmartvisa#thaismartvisa#smartvisa#smartvisainthailand#thai#visa#thaivisa#immigration#thaiimmigration
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand SMART Visa
Thailand's Smart Visa program is a groundbreaking initiative designed to attract highly skilled professionals, investors, entrepreneurs, and startup founders to the Kingdom. Launched in 2018 by the Thai government, the Smart Visa aims to bolster Thailand's economic growth by fostering innovation, technology development, and foreign investment. Unlike traditional visas, the Smart Visa offers a host of exclusive benefits, including extended stay periods, work authorization, and streamlined immigration processes. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the Thailand Smart Visa, covering its eligibility criteria, application process, benefits, and strategic considerations for prospective applicants.
Overview of the Thailand Smart Visa
The Smart Visa is a specialized visa category tailored to meet the needs of high-potential individuals and businesses in targeted industries. It is part of Thailand's broader strategy to position itself as a regional hub for technology, innovation, and investment. The program is administered by the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) in collaboration with the Immigration Bureau and other government agencies.
The Smart Visa is divided into four categories, each catering to a specific group of applicants:
Smart T (Talent): For highly skilled professionals in targeted industries.
Smart I (Investor): For investors in technology-driven businesses.
Smart E (Executive): For executives of companies operating in targeted industries.
Smart S (Startup): For founders of innovative startups.
Eligibility Criteria
Each Smart Visa category has specific eligibility requirements, but all applicants must meet the following general criteria:
Targeted Industries: Applicants must work in or invest in one of Thailand's targeted industries, which include:
Digital technology and software development
Advanced manufacturing and automation
Biotechnology and medical technology
Renewable energy and environmental technology
Food and agriculture technology
Tourism and hospitality innovation
Qualifications and Experience:
Smart T: Applicants must possess specialized skills and at least three years of experience in their field.
Smart I: Investors must commit a minimum of THB 20 million in a Thai business.
Smart E: Executives must hold a senior position in a company operating in a targeted industry.
Smart S: Startup founders must have an innovative business model and secure approval from a recognized Thai startup incubator or accelerator.
Financial Requirements: Applicants must demonstrate sufficient financial resources to support themselves and their dependents during their stay in Thailand.
Health Insurance: Applicants must have health insurance coverage of at least USD 50,000 for the duration of their stay.
Application Process
The Smart Visa application process involves several steps, each requiring careful preparation and documentation. Below is a detailed breakdown:
1. Pre-Application Preparation
Identify the appropriate Smart Visa category based on your qualifications and objectives.
Gather all required documents, including proof of qualifications, financial statements, and health insurance.
2. Submission of Application
Submit the application through the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) or the One Start One Stop Investment Center (OSOS).
Pay the application fee, which varies depending on the visa category.
3. Review and Approval
The BOI reviews the application and conducts due diligence to verify the applicant's eligibility.
If approved, the BOI issues a Smart Visa endorsement letter.
4. Visa Issuance
Present the endorsement letter and supporting documents to the Thai Immigration Bureau.
Pay the visa fee and receive the Smart Visa.
5. Registration and Reporting
Upon arrival in Thailand, register your address with the Immigration Bureau.
Submit periodic reports as required by the visa conditions.
Benefits of the Smart Visa
The Smart Visa offers a range of exclusive benefits designed to attract and retain high-potential individuals and businesses:
Extended Stay Periods:
Smart Visa holders can stay in Thailand for up to 4 years, with the option to renew.
This is significantly longer than traditional visas, which typically allow stays of 1 year or less.
Work Authorization:
Smart Visa holders are authorized to work in Thailand without the need for a separate work permit.
This simplifies the process for professionals and executives employed by Thai companies.
Multiple Entries:
The Smart Visa allows unlimited entries and exits from Thailand, providing flexibility for international travel.
Family Inclusion:
Spouses and children of Smart Visa holders are eligible for dependent visas, allowing them to live and study in Thailand.
Streamlined Processes:
The Smart Visa application process is faster and more efficient than traditional visa routes.
Dedicated support is available through the BOI and OSOS.
Tax Incentives:
Smart Visa holders may be eligible for tax exemptions or reductions on personal income earned in Thailand.
Strategic Considerations for Applicants
While the Smart Visa offers numerous advantages, prospective applicants should consider the following factors to maximize their chances of success:
Industry Alignment: Ensure that your qualifications, experience, and business activities align with Thailand's targeted industries.
Documentation: Prepare comprehensive and accurate documentation to support your application, including proof of qualifications, financial resources, and health insurance.
Professional Assistance: Engage a qualified immigration lawyer or consultant to navigate the application process and address any challenges.
Long-Term Planning: Consider your long-term goals and how the Smart Visa can support your personal and professional objectives in Thailand.
Compliance: Adhere to all visa conditions, including reporting requirements and health insurance obligations, to maintain your Smart Visa status.
Recent Developments and Trends
Since its launch, the Smart Visa program has undergone several updates to enhance its appeal and effectiveness:
Expansion of Targeted Industries: The Thai government has expanded the list of targeted industries to include emerging sectors such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and fintech.
Digital Transformation: The BOI has introduced online application platforms and digital services to streamline the Smart Visa process.
Increased Focus on Startups: The Smart S category has been strengthened to attract more innovative startups and foster Thailand's startup ecosystem.
Partnerships with Incubators: The BOI has partnered with leading Thai and international incubators to identify and support high-potential startups.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many benefits, the Smart Visa program is not without challenges:
Stringent Eligibility Criteria: The program's high standards may exclude some qualified individuals and businesses.
Limited Awareness: Many potential applicants are unaware of the Smart Visa and its benefits, limiting its reach.
Administrative Complexity: The application process, while streamlined compared to traditional visas, can still be complex and time-consuming.
Dependence on BOI Approval: The BOI's approval process is subjective and may result in inconsistencies.
Conclusion
The Thailand Smart Visa is a transformative initiative that reflects the country's commitment to innovation, technology, and foreign investment. By offering extended stay periods, work authorization, and streamlined processes, the Smart Visa provides a compelling opportunity for highly skilled professionals, investors, executives, and startup founders to contribute to Thailand's economic growth. However, the program's stringent eligibility criteria and administrative complexities require careful planning and preparation. By understanding the requirements, leveraging professional assistance, and aligning with Thailand's strategic priorities, prospective applicants can unlock the full potential of the Smart Visa and achieve their personal and professional goals in the Kingdom. As Thailand continues to evolve its immigration policies, the Smart Visa will remain a cornerstone of its efforts to attract global talent and investment.
#thailand#thailandvisa#thaivisa#visa#thai#thailandsmartvisa#smartvisa#smartvisainthailand#thaiimmigration#immigrationinthailand
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thailand Smart Visa
Thailand’s Smart Visa program, launched in 2018, is a specialized visa initiative designed to attract highly skilled professionals, investors, entrepreneurs, and startup founders to contribute to the country’s economic development. The program aims to position Thailand as a hub for innovation and technology by offering a streamlined visa process, extended stay periods, and a range of benefits tailored to the needs of high-potential individuals and businesses. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the Thailand Smart Visa, covering its eligibility criteria, application process, benefits, and strategic implications for prospective applicants.
1. Overview of the Thailand Smart Visa
The Smart Visa is part of Thailand’s broader strategy to drive economic growth through targeted industries, including digital technology, advanced manufacturing, biotechnology, and renewable energy. The program is administered by the Thailand Board of Investment (BOI) in collaboration with other government agencies, such as the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Immigration Bureau.
The Smart Visa is available in four categories:
Smart T (Talent): For highly skilled professionals in targeted industries.
Smart I (Investor): For investors in targeted industries.
Smart E (Executive): For executives of companies operating in targeted industries.
Smart S (Startup): For founders of startups in targeted industries.
Each category has specific eligibility criteria and benefits, but all are designed to facilitate long-term stays and support the growth of Thailand’s innovation-driven economy.
2. Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for the Smart Visa vary by category but generally include the following requirements:
2.1 Smart T (Talent)
Applicants must possess expertise in a field relevant to Thailand’s targeted industries.
They must have a work contract or employment offer from a company in Thailand.
The minimum annual salary requirement is THB 200,000 (approximately USD 6,000).
2.2 Smart I (Investor)
Applicants must invest at least THB 20 million (approximately USD 600,000) in a targeted industry.
The investment must be made in a BOI-promoted project or a company operating in a targeted industry.
2.3 Smart E (Executive)
Applicants must hold a senior executive position (e.g., CEO, CTO) in a company operating in a targeted industry.
The company must be BOI-promoted or engaged in activities that align with Thailand’s economic development goals.
2.4 Smart S (Startup)
Applicants must be founders or co-founders of a startup in a targeted industry.
The startup must be endorsed by a government agency or incubator recognized by the BOI.
3. Application Process
The Smart Visa application process involves several steps, which are coordinated by the BOI and other relevant agencies.
3.1 Pre-Approval
Applicants must first obtain pre-approval from the BOI by submitting the required documents, such as:
A completed application form.
Proof of qualifications, expertise, or investment.
A letter of endorsement from the employer, investor, or startup incubator.
3.2 Visa Issuance
Once pre-approved, applicants can apply for the Smart Visa at a Thai embassy or consulate. The required documents include:
The BOI’s pre-approval letter.
A valid passport.
Proof of financial stability (e.g., bank statements).
A medical certificate.
3.3 Visa Extension
The Smart Visa is initially valid for up to four years, with the possibility of extension. Extensions are granted based on continued compliance with the program’s requirements.
4. Benefits of the Smart Visa
The Smart Visa offers a range of benefits designed to attract and retain high-potential individuals and businesses. Key benefits include:
4.1 Extended Stay Period
The Smart Visa allows holders to stay in Thailand for up to four years, significantly longer than standard visas. This provides stability and continuity for professionals, investors, and entrepreneurs.
4.2 Multiple Entries
Smart Visa holders are granted multiple-entry privileges, allowing them to travel in and out of Thailand without the need for additional visas or re-entry permits.
4.3 Work Permit Exemption
Smart Visa holders are exempt from the requirement to obtain a separate work permit, simplifying the process of working in Thailand.
4.4 Family Inclusion
Smart Visa holders can include their spouse and children in the visa application, allowing the entire family to reside in Thailand.
4.5 Fast-Track Immigration
Smart Visa holders benefit from fast-track immigration services at major airports, reducing waiting times and enhancing convenience.
4.6 Tax and Investment Incentives
In some cases, Smart Visa holders may be eligible for tax incentives or other benefits under Thailand’s investment promotion policies.
5. Strategic Considerations for Applicants
Prospective Smart Visa applicants should carefully evaluate the program’s requirements and benefits to determine its suitability for their needs. Key considerations include:
5.1 Alignment with Targeted Industries
Applicants should ensure that their skills, investments, or business activities align with Thailand’s targeted industries. The BOI provides detailed guidelines on eligible sectors, which include:
Digital technology and software development.
Advanced manufacturing and robotics.
Biotechnology and medical technology.
Renewable energy and environmental technology.
5.2 Long-Term Commitment
The Smart Visa is designed for individuals and businesses with a long-term commitment to Thailand. Applicants should be prepared to contribute to the country’s economic development and comply with the program’s requirements.
5.3 Financial and Legal Planning
Applicants should seek professional advice on financial and legal matters, such as tax obligations, investment structures, and compliance with Thai regulations.
5.4 Networking and Collaboration
Thailand’s innovation ecosystem offers numerous opportunities for networking and collaboration. Smart Visa holders should actively engage with local businesses, government agencies, and research institutions to maximize their impact.
6. Challenges and Limitations
While the Smart Visa offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges and limitations:
6.1 Stringent Eligibility Criteria
The program’s eligibility criteria are highly selective, limiting access to a relatively small pool of highly skilled professionals, investors, and entrepreneurs.
6.2 Limited Awareness
Despite its potential, the Smart Visa program remains relatively unknown to many prospective applicants. Greater awareness and promotion are needed to attract a wider range of candidates.
6.3 Bureaucratic Hurdles
The application process can be complex and time-consuming, particularly for applicants unfamiliar with Thailand’s regulatory environment.
6.4 Competition from Other Countries
Thailand faces competition from other countries in the region, such as Singapore and Malaysia, which offer similar visa programs with attractive benefits.
7. Case Studies: Smart Visa in Action
7.1 BOI-Promoted Manufacturing Facility
A Japanese automotive parts manufacturer established a facility in Thailand with BOI promotion. The company received exemptions from foreign ownership limits and tax incentives, enabling it to operate efficiently and competitively in the Thai market.
7.2 Joint Venture in the Tourism Sector
A European hotel chain formed a joint venture with a Thai partner to operate a luxury resort in Phuket. The partnership allowed the foreign company to comply with the FBA’s restrictions while benefiting from the local partner’s market knowledge and connections.
7.3 Expat Acquiring a Condominium in Bangkok
An expatriate working in Bangkok obtained a mortgage to purchase a freehold condominium. The borrower negotiated a favorable interest rate and used currency hedging to manage exchange rate risks.
8. Conclusion
The Thailand Smart Visa program represents a significant step forward in the country’s efforts to attract global talent, investment, and innovation. By offering extended stay periods, work permit exemptions, and other benefits, the program provides a compelling value proposition for high-potential individuals and businesses. However, prospective applicants must carefully evaluate the program’s requirements and challenges to determine its suitability for their needs. By understanding the eligibility criteria, gathering strong documentation, and seeking professional assistance, applicants can maximize their chances of success. For those facing the daunting prospect of separation from their loved ones, the Smart Visa offers a path to hope and reunification, provided they navigate the process with care and diligence.
#thailand#immigration#thai#thaivisa#thailandsmartvisa#smartvisa#visainthailand#thailandvisa#immigrationinthailand#smartvisainthailand
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Decoding the Pharmacological Symphony of Turkey Tail Mushroom: An In-Depth Analysis of its Chemical Composition, Immunomodulatory Mechanisms, and Implications in Cancer Therapeutics 🍄🔬
Salutations, esteemed Tumblr intellectuals! Brace yourselves for a cerebral sojourn into the pharmacological labyrinth of Turkey Tail Mushroom, an exploration that transcends the ordinary and delves into the intricate interplay of its chemical constituents, the sophisticated mechanisms of immunomodulation, and the far-reaching implications of its therapeutic potential in the intricate landscape of cancer biology. Prepare your minds for an expedition into the realms of molecular complexity, immune orchestration, and therapeutic promise. Grab your favorite scientific journal, a pen, and perhaps a lab coat, for this journey is not for the faint of intellectual heart. ☕📚
Chemical Symphony: An Elaborate Choreography of Bioactive Compounds:
In the molecular ballet of Turkey Tail, bioactive compounds are the principal dancers, each executing a meticulously choreographed routine. Polysaccharopeptides (PSPs), intricate glycoproteins with immunomodulatory acumen, command attention. Through the fine-tuned modulation of immune responses, these compounds stimulate various facets of the immune system, orchestrating an elaborate dance that amplifies the body's ability to recognize and eliminate neoplastic cells. Concurrently, beta-glucans, linear glucose polymers, contribute to this biochemical ballet by fine-tuning immune cell responses, enhancing the overall antitumor immune surveillance.
Navigating the Anti-Tumor Terrain: A Molecular Expedition:
Our scientific cartography navigates the expansive anti-tumor terrain mapped out by Turkey Tail's polysaccharides. The inhibitory effects on tumor growth and metastasis are akin to molecular fortifications against cancer progression. Through intricate mechanisms involving the activation of natural killer cells, cytotoxic T cells, and macrophages, Turkey Tail emerges as a sentinel, curbing the unchecked proliferation of malignant cells. Additionally, its antioxidative prowess, rooted in compounds like ergosterol peroxide, further shields cellular structures from oxidative stress, a nexus in carcinogenesis.
Immersive References: Nourishment for the Inquisitive Intellect:
1. Stamets, P. (2012). "Turkey Tail: Old Medicine, New Hope." Integrative Medicine: A Clinician's Journal, 11(1), 54–59.
- Stamets' exposé weaves a tapestry connecting ancient medicinal wisdom with contemporary insights, shedding light on Turkey Tail's multifaceted potential.
2. Wasser, S. P. (2011). "Current findings, future trends, and unsolved problems in studies of medicinal mushrooms." Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89(5), 1323–1332.
- Wasser's comprehensive review acts as a meta-analysis, synthesizing the current knowledge landscape of medicinal mushrooms, positioning Turkey Tail within the broader discourse.
3. Sun, J. E., Ao, Z. H., Lu, Z. M., Xu, H. Y., Zhang, X. M., & Dou, W. F. (2002). "Antihyperglycemic and antilipidperoxidative effects of dry matter of culture broth of Inonotus obliquus in submerged culture on normal and alloxan-diabetes mice." Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 95(2-3), 285–292.
- In the realm of metabolic interactions, this study offers a glimpse into the potential implications of Turkey Tail compounds in managing hyperglycemia and lipid peroxidation.
4. Kidd, P. M. (2000). "The use of mushroom glucans and proteoglycans in cancer treatment." Alternative Medicine Review, 5(1), 4–27.
- Kidd's magnum opus serves as a compendium, dissecting the applications of mushroom-derived compounds in cancer therapeutics, providing a nuanced understanding.
Empowering the Community: A Call for Translational Excellence:
Knowledge is a potent elixir, yet its administration demands finesse. As we unlock the mysteries of Turkey Tail Mushroom, let us champion translational excellence, bridging the realms of bench and bedside. Always, without exception, seek the counsel of healthcare professionals, for personalized insights into the delicate interplay of molecular intricacies. Our collective journey extends beyond unraveling the pharmacological nuances; it's a clarion call to empower our community with the technical acumen to navigate the dynamic expanse of cancer research. 🌐💚

Your musings on this intricately detailed exploration are most welcome!

#science#biology#college#education#school#student#medicine#doctors#health#healthcare#mushrooms#turkey tail#chemistry#cancer#cancer treatment
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
✨STUDY HARD NOVEMBER✨


By channeling my current efforts into my studies, I'm manifesting the future I desire.
-----------------------------------------------
•Biology
1. Biotechnology: Principles and Processes ✅
2. Biotechnology and Its Applications ✅
3. Principles of Inheritance and Variation
4. Molecular Basis of Inheritance
5. Organisms and Populations
6. Ecosystem ✅
7. Biodiversity and Conservation ✅
•Chemistry
1. Chemical Kinetics ✅
2. Coordination Compounds ✅
3. Haloalkanes and Haloarenes ✅
4. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
5. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
6. Amines ✅
7. Biomolecules ✅
•Physics
1. Electric Charges and Fields ✅
2. Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance ✅
3. Current Electricity ✅
4. Moving Charges and Magnetism ✅
5. Magnetism and Matter ✅
6. Electromagnetic Induction ✅
7. Alternating Current ✅
8. Electromagnetic Waves ✅
9. Ray Optics and Instruments ✅
10. Wave Optics ✅
11. Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter ✅
12. Atoms ✅
13. Nuclei ✅
14. Electronic Devices ✅
#pray for me bruh😭#i can do this#i have to do this#i MUST do this#do or die#girlblogging#girlboss#dark academia#light academia#chaotic academia#academi#desi academia#desi tumblr#desi tag#study motivation#board exams#cbseboard#cbse class 12#I HAVE GOT THIS#yeah I haven't studied phy AT ALL cause idk man i don't understand the numerical part urgh am dum'
22 notes
·
View notes