Text
"you should be at the club" incorrect "you should be at pirate weekend at the renn fair" well this we cannot refute.
18K notes
·
View notes
Text
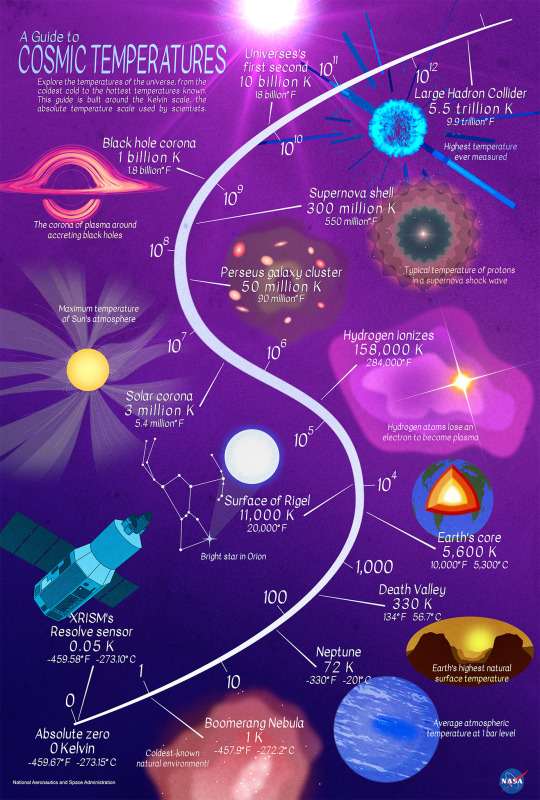
A Tour of Cosmic Temperatures
We often think of space as “cold,” but its temperature can vary enormously depending on where you visit. If the difference between summer and winter on Earth feels extreme, imagine the range of temperatures between the coldest and hottest places in the universe — it’s trillions of degrees! So let’s take a tour of cosmic temperatures … from the coldest spots to the hottest temperatures yet achieved.
First, a little vocabulary: Astronomers use the Kelvin temperature scale, which is represented by the symbol K. Going up by 1 K is the same as going up 1°C, but the scale begins at 0 K, or -273°C, which is also called absolute zero. This is the temperature where the atoms in stuff stop moving. We’ll measure our temperatures in this tour in kelvins, but also convert them to make them more familiar!
We’ll start on the chilly end of the scale with our CAL (Cold Atom Lab) on the International Space Station, which can chill atoms to within one ten billionth of a degree above 0 K, just a fraction above absolute zero.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Just slightly warmer is the Resolve sensor inside XRISM, pronounced “crism,” short for the X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission. This is an international collaboration led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) with NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). Resolve operates at one twentieth of a degree above 0 K. Why? To measure the heat from individual X-rays striking its 36 pixels!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Resolve and CAL are both colder than the Boomerang Nebula, the coldest known region in the cosmos at just 1 K! This cloud of dust and gas left over from a Sun-like star is about 5,000 light-years from Earth. Scientists are studying why it’s colder than the natural background temperature of deep space.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Let’s talk about some temperatures closer to home. Icy gas giant Neptune is the coldest major planet. It has an average temperature of 72 K at the height in its atmosphere where the pressure is equivalent to sea level on Earth. Explore how that compares to other objects in our solar system!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
How about Earth? According to NOAA, Death Valley set the world’s surface air temperature record on July 10, 1913. This record of 330 K has yet to be broken — but recent heat waves have come close. (If you’re curious about the coldest temperature measured on Earth, that’d be 183.95 K (-128.6°F or -89.2°C) at Vostok Station, Antarctica, on July 21, 1983.)
We monitor Earth's global average temperature to understand how our planet is changing due to human activities. Last year, 2023, was the warmest year on our record, which stretches back to 1880.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
The inside of our planet is even hotter. Earth’s inner core is a solid sphere made of iron and nickel that’s about 759 miles (1,221 kilometers) in radius. It reaches temperatures up to 5,600 K.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We might assume stars would be much hotter than our planet, but the surface of Rigel is only about twice the temperature of Earth’s core at 11,000 K. Rigel is a young, blue star in the constellation Orion, and one of the brightest stars in our night sky.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We study temperatures on large and small scales. The electrons in hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, can be stripped away from their atoms in a process called ionization at a temperature around 158,000 K. When these electrons join back up with ionized atoms, light is produced. Ionization is what makes some clouds of gas and dust, like the Orion Nebula, glow.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We already talked about the temperature on a star’s surface, but the material surrounding a star gets much, much hotter! Our Sun’s surface is about 5,800 K (10,000°F or 5,500°C), but the outermost layer of the solar atmosphere, called the corona, can reach millions of kelvins.
Our Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft to fly through the corona in 2021, helping us answer questions like why it is so much hotter than the Sun's surface. This is one of the mysteries of the Sun that solar scientists have been trying to figure out for years.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Looking for a hotter spot? Located about 240 million light-years away, the Perseus galaxy cluster contains thousands of galaxies. It’s surrounded by a vast cloud of gas heated up to tens of millions of kelvins that glows in X-ray light. Our telescopes found a giant wave rolling through this cluster’s hot gas, likely due to a smaller cluster grazing it billions of years ago.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Now things are really starting to heat up! When massive stars — ones with eight times the mass of our Sun or more — run out of fuel, they put on a show. On their way to becoming black holes or neutron stars, these stars will shed their outer layers in a supernova explosion. These layers can reach temperatures of 300 million K!

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Jeremy Schnittman
We couldn’t explore cosmic temperatures without talking about black holes. When stuff gets too close to a black hole, it can become part of a hot, orbiting debris disk with a conical corona swirling above it. As the material churns, it heats up and emits light, making it glow. This hot environment, which can reach temperatures of a billion kelvins, helps us find and study black holes even though they don’t emit light themselves.
JAXA’s XRISM telescope, which we mentioned at the start of our tour, uses its supercool Resolve detector to explore the scorching conditions around these intriguing, extreme objects.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/CI Lab
Our universe’s origins are even hotter. Just one second after the big bang, our tiny, baby universe consisted of an extremely hot — around 10 billion K — “soup” of light and particles. It had to cool for a few minutes before the first elements could form. The oldest light we can see, the cosmic microwave background, is from about 380,000 years after the big bang, and shows us the heat left over from these earlier moments.

Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
We’ve ventured far in distance and time … but the final spot on our temperature adventure is back on Earth! Scientists use the Large Hadron Collider at CERN to smash teensy particles together at superspeeds to simulate the conditions of the early universe. In 2012, they generated a plasma that was over 5 trillion K, setting a world record for the highest human-made temperature.
Want this tour as a poster? You can download it here in a vertical or horizontal version!
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Scott Wiessinger
Explore the wonderful and weird cosmos with NASA Universe on X, Facebook, and Instagram. And make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
tumblr being all adults nowadays is so funny because my mutuals are either unemployed chainsmokers or Ezra, Bioengineering PHD Candidate at University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
#this one goes out to astrogeekery 'C' punkpresentmic. youre getting an astrophysics phd right?#<- prev 🥺#haven’t applied to PhD positions yet boss o7#currently an assistant researcher w my astrophysics bachelor’s tho :^)
135K notes
·
View notes
Photo





i noticed there aren’t any transparent gifs of the minecraft parrots (to my knowledge) so i made my own! (feel free to use without credit- please don’t take credit though!!)
they work as discord emojis too!

44K notes
·
View notes
Text
Thank you women who use he/him. For everything
17K notes
·
View notes
Text
so cool when i say hi to a cat and they do a big stretch like i dont think that has anything to do with the words i just said to you i said but i think its awesome that you got long
25K notes
·
View notes
Text

The rarest cryptid of them all
I'm officially back from the little break I went on! I was feeling stressed and unsatisfied with my art for a hot second, but now l'm actually excited to be back and I can't remember the last time I had so much time working on something :')
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
me & my close king friend decided to start a drag haus as brothers hehe
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo






cancel your plans we’re thinking about the pale blue dot voyager pic tonight
#space#the Saturn image was taken by Cassini from ~900 million miles away!#the Voyager 1 “pale blue dot” image was taken from ~3.7 BILLION miles away—out past the orbit of neptune
128K notes
·
View notes
Text
the idea that restrooms, locker rooms, etc need to be single-sex spaces in order for women to be safe is patriarchy's way of signalling to men & boys that society doesn't expect them to behave themselves around women. it is directly antifeminist. it would be antifeminist even if trans people did not exist. a feminist society would demand that women should be safe in all spaces even when there are men there.
88K notes
·
View notes
Text

9K notes
·
View notes
Text
11K notes
·
View notes
Text
11K notes
·
View notes


