Don't wanna be here? Send us removal request.
Text
https://mintcad.com/auction
#1 Marketplace for NFT Auctions of 3D Printable Models | Mintcad
Exclusive NFT auctions for 3D printable files and models created by top artists. Sign up now to bid on these unique digital assets and collectibles!
#NFT Auctions for 3D Printable Files#NFT Auctions for 3D Printable#NFT Auctions for 3D#NFT Auctions#Marketplace for NFT Auctions of 3D Printable Models
0 notes
Text
https://mintcad.com/tools
3D Print Mechanical Tool Model NFT Downloads
Reimagine workshops with Mintcad's collection of forward-thinking hand tool, mechanical, electrical and lifting equipment model NFT downloads.
#Tool Model 3D Models#Tool Model 3D Models for Projects#Tool Model Gadget 3D Models#Best NFT Marketplace#Best 3D Print Ready Tool Model NFT Files
0 notes
Text
Future of 3D Printing: What Innovations to Expect in the Next Decade

Over the past few years, 3D printing technology has moved from being niche to now mainstream, with applications, not only groundbreaking but transformative. While the technology itself isn’t brand new, the pace of innovation has been extraordinary, and the next decade promises further radical advancements. looking ahead, it’s clear that the future of 3D printing innovations is going to continue reshaping industries, redefine manufacturing processes, and ingrain itself in the way we live our lives. So, what can we expect from this technology in the coming years?
A Revolution in Materials
A significant development in 3D printing innovations over the next decade will be the explosion of new materials. Currently, 3D printing is mostly done using plastics, resins, and metals. These materials have played an important role till now, they are only the beginning. The future will see the emergence of new composites that are stronger, lighter, and more versatile.
Biocompatible materials will revolutionize healthcare by allowing the creation of custom prosthetics, implants, and even tissues. Imagine a world where damaged organs can be replaced by 3D-printed versions tailored specifically to a patient's body. Similarly, conductive materials will introduce new possibilities in electronics, making it possible to print complex circuits and devices on demand.
Moreover, the drive towards sustainability will lead to the development of eco-friendly printing materials. Researchers are already exploring ways to use recycled plastics, organic materials, and even waste products as raw materials for 3D printing. This could dramatically reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing and contribute to a more sustainable future.

Speed and Precision: The Next Frontier
Speed and precision are two areas where 3D printing has traditionally lagged other manufacturing methods. However, significant progress is being made, and the next decade will likely see 3D printers that are not only faster but also far more precise.
Multi-material printing where most innovation is expected. The ability to print with multiple materials simultaneously, with different properties, will enable the creation of more complex and functional parts in a single print run. This will be especially valuable in industries like aerospace and automotive, where parts often need to combine different material properties.
Furthermore, high-resolution printers will allow for finer detail and more intricate designs. This will be particularly beneficial in fields like jewelry, art, and consumer goods, where aesthetics and detail are crucial. As printers become more sophisticated, the line between manufactured and 3D-printed goods will blur, making it harder to distinguish between the two.
3D Printing in Healthcare: A New Era
The impact of 3D printing on healthcare is already profound, but the next decade will take it to new heights. 3D bioprinting is perhaps the most exciting development on the horizon. This technology involves printing with cells and biomaterials to create tissues that can mimic the behavior of natural human tissues.
Soon, we could see the development of 3D-printed organs. While this might sound like something out of a science fiction novel, it's a field that is progressing rapidly. The implications are staggering, patients who once faced long waits for organ transplants could receive custom-made organs printed on demand.
Beyond organs, 3D printing will also play a crucial role in personalized medicine. The ability to print custom prosthetics, implants, and even drugs tailored to an individual's specific needs will revolutionize patient care. Imagine a world where a doctor can scan a patient's injury and print a custom cast or implant right in the clinic.
Aerospace and Automotive: The Age of On-Demand Manufacturing
The aerospace and automotive industries have been early adopters of 3D printing, and they stand to benefit enormously from the next wave. The primary advantages here are weight reduction and on-demand manufacturing.
In aerospace, weight is everything. Lighter parts mean more fuel efficiency, which is why manufacturers are constantly seeking ways to reduce the weight of their components without sacrificing strength. 3D printing allows for the creation of complex, lightweight structures that would be impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. This could lead to more fuel-efficient aircraft and spacecraft, reducing costs and environmental impact.
On-demand manufacturing is another game-changer. Rather than maintaining large inventories of spare parts, companies could print parts as needed. This would not only save on storage costs but also reduce downtime. Imagine a world where a broken-down plane or car could have its replacement part printed on-site, getting it back in service in a fraction of the time it would take to order and ship a part.
Construction: Building the Future One Layer at a Time
The construction industry is not usually associated with cutting-edge technology, but 3D printing is set to change that. 3D-printed buildings are already a reality, and the next decade will likely see this technology become more widespread.
The advantages are clear. 3D printing allows for the rapid construction of buildings, reducing both time and cost. This could be especially beneficial in areas affected by natural disasters, where quick and affordable housing solutions are desperately needed.
Moreover, 3D printing in construction could lead to more sustainable architecture. The ability to print with sustainable materials and create complex, energy-efficient designs could revolutionize the way we think about building homes and cities. Imagine living in a house that was printed to be both beautiful and energy-efficient, with a design that maximizes natural light and minimizes energy consumption.
Consumer Goods: Mass Customization and the Rise of the Home 3D Printer
The next decade will also see 3D printing become more integrated into our everyday lives, particularly in the realm of consumer goods. Mass customization is one trend that will gain traction. Consumers increasingly demand products tailored to their specific needs and preferences, and 3D printing innovations makes this possible on a scale that was previously unimaginable.
Whether it's custom-fit shoes, personalized jewelry, or even tailored electronics, the ability to customize products will become a key selling point. This shift will also give rise to a new wave of home 3D printers. As printers become more affordable and user-friendly, more people will start using them to create their own products at home. This could lead to a significant shift in consumer behavior, with more people opting to print what they need rather than buying it off the shelf.
Overcoming Challenges: Regulation, Intellectual Property, and Technical Hurdles
While the future of 3D printing is undoubtedly exciting, it's not without its challenges. Regulation will be a significant issue, particularly in fields like healthcare and aerospace, where safety is paramount. Governments and industry bodies will need to work together to establish clear guidelines to ensure that 3D-printed products meet the necessary standards.
Intellectual property (IP) is another area of concern. The ability to print almost anything raises significant challenges for IP laws, which were not designed with 3D printing in mind. Ensuring that creators and inventors are protected while allowing for innovation will be a delicate balance. Mintcad is doing its part in this area, by making ownership of design an open and controllable feature through blockchain technologies.
Finally, there are still technical challenges to overcome. While 3D printing technology has come a long way, it still has limitations, particularly regarding speed, material diversity, and resolution. However, with the rapid pace of innovation, these challenges are likely to be addressed in the coming years.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: Future of 3D Printing: What Innovations to Expect in the Next Decade
0 notes
Text
Types of 3D Printers, Materials, and Applications

What is 3D Printing?
3D Printing or additive manufacturing technologies manufacture three-dimensional parts from computer-aided design (CAD) models by adding material layer by layer until the final physical part is produced. It can be done through a variety of processes where material is deposited, joined, or solidified with the aid of computer control. Materials in the form include plastics, liquids, or powder grains.
3D printing has been around since the 1980’s where it was only suitable for aesthetic protypes considered rapid prototyping but today, especially since 2019, these technologies are considered industrial- production technology, due to the precision, repeatability, and material range.
Today, professional, low-cost desktop and applications of 3D printing aid in creating geometries that were once even impossible by hand and push innovative boundaries in various industries including, jewelry, engineering, dentistry, healthcare, education, and entertainment and more. According to an article published on Statista, “the worldwide market for 3D printing products and services was valued at 12.6 Billion U.S Dollars in 2020 and the industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20% between 2020 and 2026.”
How does 3D printing Work?
Every 3D Printer starts with a CAD design file, that is sliced (converted into machine language) and sent to the Printer. Depending on the technology of your printer, the final piece might be produced layer by layer, by solidifying liquid resin or sintering powder. The final parts usually go through post-processing depending on the application.

Design
3D printable models are created with use of CAD software, 3D scanner or other. Models created with CAD software result in the fewest errors. The manual modeling process of preparing geometric data for 3D printing is like plastic arts such as sculpting. CAD models can be saved in stereolithography file format (STL), a de facto CAD file format for additive manufacturing that stores data based on triangulations of the surface of models. Other CAD formats also exist, each with different features and application such as OBJ, 3MF, AMF and more.

Slice
A Slicer software is an important part of the additive manufacturing process. Slicer algorithms convert a 3d printable model into layers that are sent to the 3D printer in machine language called G-code. A G-code file is a series on instructions that machines can understand and move the extruder in ways that prints a model layer by layer. G-code file formats are de-facto for FDM 3D printers, but Resin or SLA, MSLA printers use other formats such as photon file which are images of each layer that a laser cures the resin liquid.

3D Print
Some 3D printers use a roll of filament through a hot extruder to fuse layers into a final piece, others use a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic, others fuse small particles of polymer powder at high temperatures to build parts. Most 3D printers run unattended until the print is complete, and modern systems automatically refill the material required for the parts from cartridges.

Post-Process
Depending on the technology and the material, printed parts may require rinsing in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) to remove any uncured resin from their surface, post-curing to stabilize mechanical properties, manual work to remove support structures, or cleaning with compressed air or a media blaster to remove excess powder.
Types of 3D Printers
The three most common and established 3D printer types for plastic or metal parts are SLA, SLS and FDM. Mintcad supports all these technologies and offers a free slicer software (Jullienne) that allows encrypted 3D printing.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography was the first kind of 3D printing technology invented in the 1980’s. and is still one of the most efficient and popular technologies for professionals. SLA 3D printers use lasers to sure liquid resin into a hardened plastic, through the photopolymerizations process.
3D Printing Materials used : Liquid Resin
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is the most widely used type of 3D printing at the consumer level. FDM 3D printers work by extruding thermoplastic filaments, such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), PLA (Polylactic Acid), through a heated nozzle, melting the material and applying the plastic layer by layer to a build platform. Each layer is laid down one at a time until the part is complete.
FDM 3D printers are well-suited for basic proof-of-concept models, as well as quick and low-cost prototyping of simple parts, FDM has the lowest resolution and accuracy when compared to SLA or SLS.
3D Printing Materials used: Plastics (ABS, PLA, PVA, PET), Carbon Fiber, Steel, Silver
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
elective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high-power laser to sinter small particles of polymer powder into a solid structure. The unfused powder supports the part during printing and eliminates the need for dedicated support structures. This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including interior features, undercuts, thin walls, and negative features. Parts produced with SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling that of injection-molded parts.
3D Printing Materials used: Metals (Gold, Silver, Platinum, Titanium, Steel and Aluminum), Ceramic.
The Benefits of 3D printing
Speed
With traditional manufacturing methods it can take weeks or months to receive a part or final product of a consumable item. With 3D printing technology this time has been cut out by at least 80%. Some designs can even be printed in just a few hours for prototyping and experimentation to make time to market faster than ever before.
Cost
With 3D printing there is no requirement of expensive setups and machinery required by injection molding or machining. The same equipment can be used for prototyping and even production in some industries. As 3D printing becomes more capable of producing full function end products, it may compliment or even replace traditional manufacturing processes in low or high volumes.
Customization
From shoes to sports equipment and jewelry, we are surrounded by products made in limited uniform sizes and styles as businesses strive to standardize things to make it more economical to manufacture. With 3D printing and CAD, only the digital design needs to be changed to tailor products for consumer preferences. The concept first took to industries such as medicine and dentistry and has now entered many other industries and is beginning to grow.
New Age Design
3D printing can create complex shapes and parts, such as overhangs, microchannels, and organic shapes, that would be costly or even impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. This provides the opportunity to consolidate assemblies into less individual parts to reduce weight, alleviate weak joints, and cut down on assembly time, unleashing new possibilities for design and engineering.
Applications of 3D printing
3D printing accelerates innovation and supports startups and small businesses in a range of industries, like engineering, jewelry, dentistry, healthcare, education, entertainment, and each have their own use of 3D printer applications.
Engineering
Rapid prototyping through 3D printing technologies empowers designers in engineering to ideate and produce proof of concept and advance these concepts into production. Prototypes that are visual and functional are close to final product ideology and guides designers through a series of validation stages and finalize go to market.

Jewelry
The Jewelry industry uses CAD and 3D Printing to rapidly prototype designs, fill bespoke client needs, and produce large batches of ready to cast pieces. Digital tools allow for the creation of consistent, sharply detailed pieces without the time consuming and low finish hand wax carving.

Education
For immersive learning and advanced research, 3D printers are the go-to multifunctional tools, they encourage creativity and expose students to professional technologies supporting STEM learning and manufacturing.

Healthcare
Affordable, professional-grade desktop 3D printing helps doctors deliver treatments and devices customized healthcare to better serve each unique individual, opening the door to high-impact medical applications while saving organizations significant time and costs from the lab to the operating room.

Entertainment
High-definition physical models are widely used in sculpting, character modeling, and prop making. 3D printed parts have starred in stop-motion films, video games, bespoke costumes, and even special effects for blockbuster movies. Not only that 3D printers can print at home all kinds of toys and board-games for children and adult entertainment.

If you found this article helpful support designers on Mintcad and print your first 3D printable design file using Mintcad’s free slicer software today. Share this 3D printing guide on your social media or with your friends and colleagues who want to get started today.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: Types of 3D Printers, Materials, and Applications
0 notes
Text
Print Ready Component 3D Models and NFTs – Mintcad
Cut design time with downloadable component model NFT files from Mintcad. 3D print precision mechanical parts, electronics, structures, molds & tools!
#Ready Component 3D Models#Component 3D Models for Projects#Component Gadget 3D Models#Best NFT Marketplace#Best 3D Print Ready Component Model NFT Files
0 notes
Text
https://mintcad.com/gadgets
Best 3D Printable Gadget Model NFT Files – Mintcad
Imagine it then print it! Bring innovative gadget inventions to reality with ready-to-print 3D model NFT files for electronics, robots, tools & hobby items.
#Printable Gadget 3D Models#Printable Gadget 3D Models for Projects#Printable Gadget 3D NFT Models#Best NFT Marketplace#Best 3D Printable Gadget Model NFT Files
0 notes
Text
Popular NFT Myths Debunked

Non-Fungible Token (NFTs) and blockchain technology have given rise to numerous myths due to the volatility and nascent stage of the industry. Like many technological innovations throughout history, anything new and exciting first goes through and manic period when the world is just starting to learn about its potential. While the early enthusiasm may wane, the true potential of NFTs to create real digital assets remains strong and will likely unfold over the coming decade. Nobody can argue the innate nature of NFTs to create real digital assets, this is a technological feature that is here to stay. In this article we will discuss five of the most famous myths surrounding these technologies and debunk them, shedding light on the truths that will become clearer with time.
NFTs Are Just Expensive JPEGS
Many people associate NFTs solely with costly JPEGs or graphic images. Their perception is often shaped by high-profile sales, such as the Bored Ape Yacht Club images that sold for millions of dollars. This may lead to the misconceptions that NFTs are merely overpriced pictures, prompting some to view the enthusiasm for NFTs as irrational.
Debunked: While many NFTs are digital art pieces, NFTs can represent ownership of a wide range of digital and physical assets, including 3D Printable files, virtual real estate, and even real-world items like property deeds. The value comes from their uniqueness, verifiable ownership, and provenance.
NFTs Have No Real-World Utility
People find it hard to believe the disruption can occur through NFT and the Blockchain and has no real-world application other than gimmickry. This is quite a difficult myth surrounding the technology and the same was said about personal computers in the 80’s and early 90’s.
Debunked: NFTs have numerous real-world applications beyond art. They can be used for digital identity verification, ticketing for events, 3D printing, intellectual property rights management, and more. Their blockchain-based nature ensures transparency and security.
NFTs Are Just a Fad
NFTs experience an extraordinary surge in 2021, with transaction volume at $20 Billion for the year. Entering 2022 this volume dwindles and stabilized at just 20% of it’s peak over the next two years. Despite the decline the underlying technology is maturing significantly and is reminiscent to the trajectory of Dot-com companies in 1999 and the current stage of AI companies.
Debunked: While the hype around NFTs has surged and waned, the underlying technology represents a significant advancement in how we manage digital ownership and intellectual property. Industries ranging from gaming to real estate are integrating NFTs, indicating long-term potential and utility. Mintcad is doing its part by making 3D printables, revolutionary digital assets.
Anyone Can Copy an NFT, So They’re Worthless
There is a common misconception that NFTs can easily be plagiarized since they’re considered digital assets freely available to view search and download on the internet.
Debunked: Copying the image associated with an NFT doesn’t replicate ownership of the NFT itself. The value of an NFT lies in its verifiable ownership and provenance through blockchain metadata, not the ability to view or download the associated file. Mintcad goes a step further by storing underlying 3D Printable files on IPFS a decentralized database, downloads are impossible, and 3D prints are encrypted.
Creating NFTs Is Complicated and Costly
Most designers and artists get disheartened when they think about stepping into the world of digital assets, they need not be. Companies like Mintcad and OpenSea are working hard, to make creating NFTs for your designs and art easier than ever.
Debunked: While some platforms charge high fees for minting NFTs, many others offer affordable (Polygon chain) or even free options. The process of creating NFTs has been streamlined, with user-friendly platforms that guide creators through the steps without requiring deep technical knowledge. Minting NFTs for 3D printables on Mintcad takes less than 55 seconds.
Benefits of 3D Printable NFTs on Mintcad
Scalable Income Potential: 3D Printable designers can create NFTs for their files and earn passively through a pay-per-print model.
Secured Intellectual Property: They enable creators to establish control over their designs and creations.
Creator Empowerment: NFTs allow artists and creators to monetize their work directly and receive royalties on secondary sales.
Transparency and Security: Blockchain technology ensures that transactions are transparent and secure, reducing the risk of fraud.
True Digital Ownership: Decentralized databases ensure that underlying 3D Printable files are un-downloadable and remain income generating digital assets.
By addressing these myths and highlighting the real benefits, it becomes clear that NFTs are more than just a passing trend—they are a transformative technology with wide-reaching implications.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: Popular NFT Myths Debunked
0 notes
Text
3D Printing In Classroom: A Hands-On Approach To STEM Education
The education system is continuously evolving through technological advancements paving way for better education and intellectual citizens of tomorrow. Online learning, EdTech innovations, gamification and immersive learning have reshaped the way concepts are taught, making education a more fun and an engaging experience. 3D printing is a novel addition to the technological spectrum of contemporary educational system. With the introduction of 3D printing in education, educational institutions can give a better understanding of complex concepts especially in STEM that encompasses the disciplines of Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics. The 3D Printing Market in Education Sector size is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 23.49% between 2022 and 2027.
In this blog we give you a brief overview of how integrating 3D printing in STEM education can enhance the overall learning experience for students while diving into the benefits of 3D printing in education.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is the process of converting your digital CAD files, like the .STL format into a three-dimensional physical object. The digital files are created using CAD software and then printed using a slicer software. The 3D printing slicer software slices the digital file into multiple layers and generates a geometric code that instructs the 3D printer to follow a certain path to print the object. The object is printed layer by layer hence making it a part of the additive manufacturing process.
What are the Benefits of 3D Printing in Education?
Education in a STEM discipline requires more practical knowledge and hands-on training to understand the concepts better. There is an evident difference between theoretical bookish knowledge and what one learns via practical experimentation. And this is where the use of 3D printing in education comes into play.

Enhancing student engagement
Picture two scenarios: First one is where the teacher is reading out paragraphs from the textbook and drawing certain diagrams on the board to explain a scientific concept. Second scenario is where the teacher comes with the physical objects in hand to explain you the concepts.
Now which scenario would keep the students engaged and intrigued in knowing more about the subjects? The second one, obviously!
The hands-on nature of 3D printing in STEM education captures students' attention, fostering a deeper interest in STEM subjects and promoting active participation in the learning process.
Give Room to Creativity & Innovation
Students are encouraged to think creatively and solve real-world problems by designing and prototyping solutions using 3D printing technology. 3D printing is like providing students with a blank canvas and a set of vibrant colors, allowing them to paint their imaginative ideas into tangible reality.
For instance, in a physics class, students might create a working model of a simple machine like a lever or pulley, exploring innovative ways to improve its efficiency.

Hands-on Practical Training of Subjects
3D printing allows students to apply theoretical concepts from STEM subjects to tangible projects, reinforcing understanding through hands-on experience.
In an engineering class, students can design and manufacture mechanical parts using 3D printing, providing practical insights into the product development lifecycle.
Improve Problem Solving & Critical Thinking Skills of Students
The natural synergy between 3D printing and STEM education lies in their shared focus on problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity. Utilizing 3D printing in the classroom can bridge the gap between theoretical concepts and real-world applications, making STEM subjects more engaging and relevant for students. Students tasked with designing a functional prosthetic limb ing 3D printing must overcome challenges relating to materials, ergonomics and functionality.

Teaching Complex Subjects in an Easy Way
3D printing proves invaluable in visualizing geometric shapes and figures, making abstract concepts more tangible for students studying geometry.
In mathematics, students can create 3D-printed models of geometric shapes to understand spatial relationships, turning abstract theorems into tangible objects.
Preparation for Future Technologies
Exposure to 3D printing enhances students' familiarity with advanced technologies, contributing to their overall technological literacy. Acquiring skills related to 3D printing prepares students for future careers in industries where additive manufacturing is increasingly prevalent, such as manufacturing, design, and healthcare.
Conclusion
3D printing helps elevate the learning experience for students in various sectors like art, design, science projects, mathematics, etc. Mintcad supports printing your NFTs and we have our homemade Jullienne slicing software. Our slicing software is free to use and hence anyone who wants to print their digital files can use Jullienne to slice their digital file and connect with any 3D printer of your choice. Give your kids an engaging learning experience by leveraging 3D printing in education.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: 3D Printing In Classroom: A Hands-On Approach To STEM Education
0 notes
Text
Why Mintcad Created Its Own 3D Printing Slicer?

3D printing has revolutionized the engineering industry as it reduces production time, increasing the opportunities for innovation. Your digitally created Computer Aided Designs turn into real, physical products with a 3D printer.
But do you know how your CAD software communicates with a 3D printer or how the files stored locally are sent to your 3D printer? Machines understand only the machine language and hence you need some coded instructions commanding the 3D printer to print your 3D printable models. You need an intermediate communicating tool which is a slicing software.
Slicing software gets the digital file from the CAD software and accordingly instructs the 3D printer on how to print the design to obtain the intended output. To better understand this, let’s picture you’re on a business trip to a foreign country but do not know their native language. This makes it difficult for you to communicate with the locals of that place and get your work done. So, you seek the help of a local person who understands both your language and the natively spoken one, thereby communicating your message to the people there and getting your work done. Slicing software is analogous to that intermediator who translates your message to the locals.
Let’s look over how a 3D printing Slicer works and how it’s a crucial asset to a 3D printing platform or a 3D printable NFT marketplace.
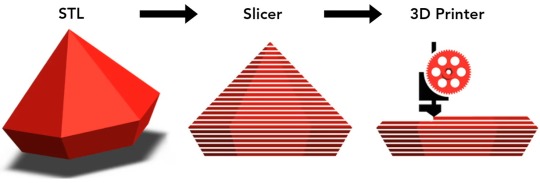
What is a Slicing Software?
A slicing software is a crucial tool in the world of 3D printing. Technically speaking, the 3D printing slicer converts the STL file (Stereolithography or Standard Tessellation Language) into the G-code that commands the printer. It takes 3D printable models, formats like a .STL or .OBJ from a CAD software, and breaks it down into individual layers, much like slicing a loaf of bread.
These layers are then translated into vector instructions for the 3D printer, guiding it on how to build the object layer by layer. The software determines factors such as layer thickness, print speed, and support structures, ensuring that the final printed object matches the digital design. In essence, a slicer serves as the bridge between the digital design and the physical creation, making 3D printing possible.
There are many 3D printing slicing softwares available in the market including both free and paid versions. Cura, PrusaSlicer, Simplify3D and Slic3r are a few commonly used best 3D printer slicer softwares.
Mintcad comes integrated with our own homemade 3D printing slicer that makes it easy for people to slice the NFTs and make them print ready. Our proprietary slicing software Jullienne is free to use and is compatible with all types of 3D printers available in the market.

Parts of a Slicer Software
The slicing software has two major front end and back-end components i.e., the GUI and the logical algorithmic component respectively.
Front-End GUI
The Graphical User Interface component of the slicer is the one that helps the user to visualize the design and interact with the software. You can move, scale, rotate and change the settings for your 3D digital model.
Here you can view the complex 3D models into their layers.
Back-End Logic
The back end of the slicer converts the digital file and automatically generates the geometric code or the G-code which gives the necessary instruction to execute the print option.
Post the G-code generation, the slicing algorithm follows the geometric instructions and slices the 3D model into its 2D slices.
How Does Our 3D Printer Slicer Software - Jullienne Work?
You must first purchase a print from the many 3D printable NFTs that are listed on Mintcad. Learn how to buy a single print.
Once your purchased print is loaded onto our slicer the model is sliced into G-code layers that can be viewed in different anatomical directions - the coronal, axial, and sagittal planes.
Each slice is individually sent for the print operation.
Technically, the slicer converts the .STL file into a G-code that includes step by step instruction for the 3D printer on how to print.
The 3D printing is done in layers where each layer sits on another supporting layer below. However, if there are any hanging layers you can add an external supporting layer using the graphical elements like skirt, brim and raft.
You can add a single outline known as skirt surrounding the object on the print bed without actually touching the object.
A brim made of a few concentric layers gets attached to the edges of the 3D model and extend from the print bed. It keeps the print in place preventing warping while the printer works on the part.
A 3D printing support raft is a bit wider than the first layer of the print and placed beneath the object to print. It functions as the base support of the print.
All three graphical elements are easily detachable and hence the output print is an exact replica of the input file.
You can further set various print settings like the layer heights, infill percent, speed of printing, optimized print path, temperature of the extruder, filament diameter, nozzle diameter, print bed shape, etc.
Finally, you can connect it to your 3D printer and start printing.

Why Choose Mintcad’s Jullienne Slicer Software?
Mintcad is a holistic niche NFT marketplace where you can mint NFTs for your CAD files, sell your NFTs and also allow people to print it for a one-time fee. Printing an NFT or a digital 3D model requires connecting to a slicer software as an intermediary step. Instead of hunting for an external slicing software, you can get the work done on the Mintcad platform itself and for free of cost.
Here are a few reasons why Jullienne stands out as a good 3D printing slicing software:
i) Protecting Your Intellectual Property:
JULLIENNE ensures that your 3D NFT models don't need to be downloaded, allowing you to make money without sacrificing your intellectual property. This feature safeguards your creations and empowers you to profit while maintaining control over your digital assets.
ii) Supports 3D Printable NFTs:
Jullienne steps into the future by supporting 3D printable NFTs. Whether you've just acquired a Mintcad NFT or paid for a one-time print, load the file onto our slicer, and effortlessly send print commands remotely. Monitor your masterpiece in the making from anywhere.
iii) Customizable - Add Your Own Printer:
Tailor Jullienne to fit your 3D printing arsenal. While it's already prepped for most printer configurations, you have the power to add any custom printer to your toolkit, ensuring compatibility with your unique printing setup.
iv) Project Management - Never Lose Your Prints:
Bid farewell to the fear of losing print settings. Jullienne is your project vault, securely storing all your print data. Easily revisit settings, review past prints, and learn from each project, ensuring every print is a masterpiece.
v) G-code Playback - See Your Print in Action:
Witness your creation come to life with Jullienne's integrated layer playback. Visualize each layer's printing process, offering endless opportunities for optimization. See the magic unfold before your eyes, layer by layer.
vi) Access Anytime, Anywhere:
Embrace flexibility with Jullienne's browser-based app, granting you access to your files from any computer with just your login credentials. Your 3D printing projects are at your fingertips, anytime and anywhere.
vii) Real-Time Updates Without Additional Packages:
Stay informed with Jullienne's real-time updates, all without the hassle of installing extra packages. Receive notifications and insights as your prints progress, ensuring a smooth and informed 3D printing experience.
viii) Cross-Platform Compatible:
Experience Jullienne's versatility across browsers. Whether you prefer Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge, access your slicer effortlessly, breaking down platform barriers for a unified user experience.
ix) Free Of Cost
You do not need to burn a hole in your pocket to get your digital 3D model converted into a format that your 3D printer can print. You can easily and quickly do it via Mintcad’s proprietary Jullienne slicing software at free of cost.
x) User-Friendly UI/UX:
Experience an intuitive journey with Jullienne’s user-friendly interface. Navigating through your 3D printing projects becomes a breeze, making the entire process seamless and enjoyable for users of all levels.
Conclusion
A 3D printing slicer software serves as a great asset in getting your NFTs printed by converting the digital NFTs into printer understandable g-codes. Mintcad is a pioneer in integrating a proprietary slicing software into the NFT 3D printing platform making the entire process a breeze for the end users. Explore Mintcad’s slicing software Jullienne and print out some cool stuff today.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: Why Mintcad Created Its Own 3D Printing Slicer?
0 notes
Text
https://mintcad.com/household
One-Stop for Household 3D Printing
Mintcad offers the top digital marketplace for household 3D model NFTs, featuring ready-to-print home goods, organizers, furnishings, decor & lights!
#Household 3D Models for Printing Lessons#Household 3D Models for Projects#Household 3D Models#Best NFT Marketplace
0 notes
Text
Building The Future: How 3D Printing Is Shaping The Next Generation Of Engineers

Just imagine you have designed a cool toy on a computer and now there is some magical wand that turns your design into a physical toy in your hands. That’s the power of 3D printing! With 3D printing technology, your digital design like CAD drawings and blueprints becomes a physical product that you can touch and feel.
Right from enhanced production speeds to reduction in costs and streamlining the supply chains with rapid innovations, CAD designs complimented with 3D printing in engineering industry is shaping a great future for engineers.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing in the realm of additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary process that creates physical objects by layering material on top of each other.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Firstly, design the object you want to create using a special computer aided design software. You can design anything from a toy to a tool or even complex parts of engineering machines.
The slicer software then takes your design and slices it into thin layers, like slicing a cake into multiple layers. Each slice represents a layer of your object.
The 3D printer starts building the object layer by layer by adding material (such as plastic or metal) one layer at a time. According to stats, metal makes up a major portion of the market for 3D printing materials, accounting for more than 48% of global revenue.
Once the printing is complete, you have a real, tangible object that matches the design created on the computer.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Engineering
Between 2022 and 2027, the size of the global 3D printer market is anticipated to increase by $24 Billion to $49.16 Billion at a CAGR of 23.49%.
The rise in 3D printing market owes to the lucrative benefits it brings especially in the engineering industry. Let’s ponder over a few benefits below:
1. Precision and Customization in Manufacturing:
Precision takes center stage as 3D printing allows engineers to create intricate designs with unparalleled accuracy. The ability to customize each component to exact specifications ensures a perfect fit, catering to the unique needs of every project.
Example: Imagine an engineer using 3D printing to create a custom-designed bone implant. With precision down to the millimeter, the implant fits perfectly, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
More than 75% of American patients with damaged skulls from disease or trauma had their implants made by Oxford Performance Materials' 3D printer, according to the company.
2. Cost-Effective Prototyping and Rapid Iteration:
Gone are the days of costly and time-consuming prototyping. 3D printing enables engineers to swiftly create prototypes at a fraction of the traditional cost. This agility facilitates rapid iteration, allowing designers to test and refine their ideas promptly.
Example: A product designer creates a CAD model of a new smartphone casing. Through 3D printing, multiple iterations are rapidly produced, allowing the design team to assess each version's ergonomic feel and aesthetic appeal before finalizing the product.
3. Reducing Material Waste and Environmental Impact:
Embracing sustainability, 3D printing minimizes material waste by building layer upon layer only where needed. This eco-friendly approach not only reduces environmental impact but also contributes to resource conservation in the manufacturing process.
More 3D printing might cut waste by up to 95%.
Example: In architectural engineering, CAD is employed to design a building with intricate support structures. 3D printing these components minimizes material waste by constructing them layer by layer, aligning precisely with the CAD design, promoting sustainability in construction.
4. Enhanced Design Capabilities and Complex Geometries:
Engineers are liberated from the constraints of traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing empowers them to explore intricate and complex geometries that were once deemed challenging or impossible. This newfound design freedom sparks innovation across various engineering disciplines.
Example: A mechanical engineer uses CAD to design a complex gear system for a robotics project. 3D printing brings this intricate design to life, enabling the creation of gears with non-traditional shapes, optimizing performance and efficiency.
5. Accelerated Product Development Cycles:
Time is of the essence in the competitive landscape of engineering. 3D printing slashes product development timelines by streamlining the manufacturing process. This acceleration allows engineers to bring concepts from design to reality swiftly, staying ahead in the race of innovation.
Example: A car manufacturer utilizes CAD to model a new engine component. Through 3D printing, prototypes are rapidly produced and tested, allowing for quick iterations until the optimal design is achieved. This agile process significantly shortens the product development cycle.
Use Cases of CAD & 3D Printing in the Engineering Sector
In the ever-evolving landscape of CAD engineering, 3D printing continues to push boundaries, opening up new avenues for innovation with plethora of 3D printing projects for engineers. By 2026, it’s anticipated that the market for CAD software and on-demand parts services will have tripled.
Let's explore the cutting-edge applications and new uses for 3D printing in engineering industry:
Customized Prosthetics and Orthopedics:
Harnessing the power of engineering CAD design, engineers can now create personalized prosthetic limbs and orthopedic implants tailored to an individual's unique anatomy. This not only enhances comfort for the user but also improves overall functionality and integration with the body.

Topology-Optimized Components:
CAD combined with 3D printing allows engineers to optimize the internal structures of components through generative design. This results in lightweight yet structurally robust parts, minimizing material usage and improving overall performance.
Advanced Heat Exchangers for Electronics:
Engineers are leveraging 3D printing to design intricate heat exchangers for electronics. The precise control offered by engineering CAD designs allow for the creation of complex, space-efficient designs that enhance cooling efficiency in electronic devices.
Bioprinting for Tissue Engineering:
The integration of CAD design in bioprinting enables the creation of 3D-printed tissues and organs. This revolutionary approach holds tremendous potential in the field of regenerative medicine, allowing for the fabrication of functional biological structures.
Microscale Devices for Electronics:
CAD design paired with 3D printing facilitates the creation of microscale devices with intricate features. This is particularly beneficial in the electronics industry, where miniaturization is crucial for developing advanced sensors, actuators, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Architectural Models and Prototypes:
In the realm of architecture and construction, CAD-driven 3D printing is revolutionizing the creation of detailed architectural models and prototypes. This allows architects to visualize and test designs before full-scale construction, saving time and resources.
More than 68% of companies using 3D printing use it for prototyping and pre-series manufacturing.
Complex Tooling and Jigs:
Engineers are utilizing 3D printing to craft custom tooling and jigs through CAD design. These specialized tools aid in manufacturing processes, ensuring precision and efficiency in tasks such as assembly, welding, and quality control.
Integration in Education:
CAD-driven 3D printing is becoming a cornerstone in engineering education. Students can bring their CAD designs to life, gaining hands-on experience in prototyping and product development, fostering a deeper understanding of engineering principles.
As the fusion of CAD and 3D printing continues to evolve, these new applications exemplify the transformative impact on the field of engineering, ushering in an era of unprecedented possibilities and innovation.
In this transformative landscape, Mintcad stands as a beacon, providing a user-friendly platform to seamlessly transition from CAD design to 3D printing. With Mintcad, the process becomes not just a technological marvel but a user-centric journey, empowering engineers to unlock the full potential of their designs and witness innovation materialize layer by layer. The future of CAD engineering and 3D printing is not only promising but, with Mintcad, it's also accessible and exciting.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: Building The Future: How 3D Printing Is Shaping The Next Generation Of Engineers
0 notes
Text
Have Your Content Get Stolen Through Lazy Minting NFTs

Are you a passionate Computer aided designer, digital artist, or a content creator? Every piece you create, consists of your time, sweat and wisdom. However, a nightmare for any artist or designer is to witness their intellectual property succumb to theft or forgery. Non-fungible tokens(NFTs) emerge as a promising solution for designers to register and authenticate their creations on the blockchain and showcase it to the world, yet there is a dark side to the process of minting NFTs.
Bots and scammers have found ways to steal original artworks and create NFTs without the creator's knowledge. This surge in spam, theft and other malicious activities gained momentum with the introduction of the lazy minting feature in 2021. Before you NFTs are even minted on the blockchain they’ve already been copied.
Here’s all you need to know about lazy minting NFTs and how your content is at the risk due to the feature. We also share tips on how you can safeguard your content from being stolen by minting 3D printable CAD files on Mintcad’s NFT platform.
Why Do You Need NFTs for Intellectual Property?
Firstly, let’s understand what an NFT is. In simple terms, NFTs or Non-Fungible Tokens, indicate a unique digital identifier attached to a content file whether it’s a 3D printable CAD file or other forms of digital content. It represents the authenticity and the genuine ownership of the underlying art. They allow digital property to form digital assets by registering their ownership on the blockchain. The process of converting a digital file into a non-fungible digital asset by assigning it a unique token on the blockchain is known as minting.
The unique feature about NFTs is their non-fungibility ie. you cannot exchange two NFTs for a single NFT as you can with fiat currency. These are non-interchangeable and irreplaceable. You can transfer the ownership if you sell your NFT or even rent it out to users for single use through custom smart contracts.
The digital asset’s metadata and underlying file is stored on a decentralized database such as IPFS which makes it nearly impossible to edit or modify the record unless the owner transfers or burns (deletes) it. No one can steal their work and claim it to be theirs ensuring CAD security with NFTs.
What is Lazy Minting of NFTs?
If you have read Mintcad’s article on how to mint your first NFT, you have a fair idea about minting NFTs. However, minting NFTs is a pricey procedure as creators must pay an upfront gas fee to mint their NFT on the blockchain. This creates an entry barrier for most of the creators who do not want to commit a good sum of money and risk before testing the waters.
Lazy minting or gasless minting emerged as a solution to this. Gasless minting does not mean you can mint NFTs without a gas fee. It simply implies that you assign a placeholder for your NFT to be minted later. Your NFT will not appear on the blockchain unless it is minted nor does its metadata and underlying file get stored on the IPFS.
Nevertheless, your NFT gets listed on the marketplace, but when a buyer places an order to buy the NFT, the NFT gets minted on the blockchain. Thus, the buyer bears the minting charges or the gas fees along with the cost of NFT.
How Lazy Minting poses a threat to digital content creators?
Lazy minting makes entering the NFT market a breeze for anyone who wants to list and sell their NFTs. It removes initial expenses allowing anyone to create NFTs for free, but if you haven’t minted your design yet, anyone can download the file from centralized databases and mint it before you can, making your NFT a copy.
This not only benefits the artists and designers but also the scammers who are successfully pulling off NFT scams.
Content theft is one of the major drawbacks of lazy minting NFTs. As the initial minting is free of cost, scammers steal content creators’ works and create an NFT for it, listing it on the marketplaces for sale. Sometimes the original creator does not even know that their work is being stolen and sold without their knowledge.
One of the top NFT marketplaces, OpenSea has even admitted, “Over 80% of the NFTs created with our "free minting tool" are 'plagiarized works, fake collections, and spam'.”
Lazy minting which was assumed to be a boon for the designers has allowed art thieves to exploit the entire system with virtually zero risk.
Real-world Examples of Lazy Minting NFT leading to content theft
Aja Trier, an artist faced a new and overwhelming challenge when she discovered that her popular Vincent Van Gogh-style paintings had been transformed into almost 86,000 NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). These digital tokens were being sold on OpenSea, without Aja's knowledge.
The issue arose because these NFTs were created using a method known as "lazy minting" on OpenSea. Lazy minting allows users to list NFTs for sale without completing the transaction on the blockchain until a buyer comes along. This feature became a problem because scammers exploited it to list numerous stolen items in the hope of finding buyers.
The method involved bots scraping art from online galleries or using keyword searches on Google Images to create collections with automatically generated descriptions. OpenSea, due to its popularity and less rigorous vetting system, became a hotspot for such activities.
Solution to Content Theft Caused by Lazy Minting
Though lazy minting looks lucrative on the surface allowing you to easily enter the NFT market it is putting your CAD assets at the risk of theft. At Mintcad we do not support lazy minting, we want to protect your design IPs with NFTs and believe the original creators should remain safe in this novel marketplace.
With lazy minting, the metadata of your CAD file gets stored only on a database like AWS, however when you mint your NFTs on Mintcad, we store your data on the decentralized database like IPFS. This ensures that the ownership of your NFT gets secured on the blockchain.
Along with this we are also working on an AI-based geometric recognition algorithm that recognizes the NFTs already minted and rejects the request on re-minting. This ensures that your CAD assets do not get stolen or forged.
We are working towards algorithm updates that restrict minting NFTs for content that violate any copyrights. We are taking every step to secure the digital assets of our content creators and enable them to leverage the benefits of NFTs.
If you are looking to secure the ownership of your 3D printable CAD files, mint NFTs for your CAD files on Mintcad, get them listed for sale or allow 3D printing enthusiast to print your file for a small fee that you as a creator earn.
NFT Minting on Mintcad
To mint your NFT, you must choose an appropriate NFT marketplace, Mintcad serves as a no-code solution to mint NFTs via smart specialized contracts.
Mintcad is one of the best NFT platforms to mint your 3D printable CAD files, list them for sale or allow your designs to be printed. You can learn more about how to mint your first 3d printable NFT on Mintcad.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: Have Your Content Get Stolen Through Lazy Minting NFTs
0 notes
Text
How NFTs Are Revolutionizing The 3D Printing Industry

The Computer-Aided Design (CAD) industry is finally witnessing a tailwind of technological advancements that are nothing short of breathtaking. The industry, now at the forefront of the tech race, is witnessing cutting-edge solutions that make designing, manufacturing, and precision manufacturing easier than ever.
3D printing? It's nothing if not magic. If watching bits turn into atoms doesn’t melt your heart, I don’t know what would. The tech is revolutionary for jewellery designers, engineers, and manufacturers, transforming digital designs into tangible realities. The digital backbone for their work, allowing creators to easily design highly complex shapes and structures that were difficult or near impossible through traditional methods. It has kicked off a new era where anything can be tailored, ideas can be brought to life promptly, and making things more affordable than ever.
In a world where 3D printing is the protagonist, where is the plot twist? Anybody can duplicate your designs and sell it under their own label. How do we fix this problem? NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are here to save the day. The latest of innovations, the third version of the internet (WEB 3.0), decentralizes and makes intellectual property ownership possible in the digital world.
If 3D printing brings designs to life, an NFT in CAD introduces authority to the designs. Through smart contracts, a complex cryptographic set of rules on the blockchain, each design file turns into a one-of-a-kind asset. 3D printables become unique and ownable digital assets.
Let’s explore in detail the future of Computer-Aided Design and how NFT marketplaces are revolutionizing the industry.
Recent Challenges in CAD Industry
In the realm of CAD and 3D printing, there's a big problem. Picture this, you've invested a significant amount of time and crafted an intricate design, but when it's out there, you're not reaping the full financial benefits for your hard work. There isn't an ideal platform where you can securely share and sell your designs while maintaining control. Some designers, especially in jewellery, are paid measly sums for their fantastic work. Even the folks making the actual 3D files hardly make money selling the files themselves. Imagine developing a revolutionary programming language, but most of the recognition and financial gains go to the entity that uses it, leaving you with minimal returns.
Now, the existing solutions have their own complications. Some allow people to freely download designs, and the original designers receive no compensation once their hard work is disseminated.
Others send you the fully printed 3D model, but it takes an eternity, and if you're a designer without a fleet of high-tech printers, you must share your design with other companies to get it printed and delivered to the buyer. It's like sharing your groundbreaking code with another company to implement. There's also the option of hiring freelance designers, but that's an expensive affair for everyone involved. Clients must invest substantially, and designers end up working tirelessly without much opportunity for career growth.
In this tech-savvy world, there's a dire need for a sophisticated platform where designers can securely share their digital creations, earn rightful compensation, and streamline the entire process. like creating a space where tech innovators finally get the recognition and financial rewards they deserve, without all the unnecessary complexities.
How Can NFT Marketplaces Revolutionize CAD Industry?
In a landscape where CAD designers invest substantial time and effort, the conventional models often fall short in compensating them adequately. With the introduction of NFTs - the revolutionary digital tokens built on blockchain technology, you can not only validate ownership but transform digital designs into tangible, 3D printable assets. The challenges of royalty tracking, ownership control, and fair compensation find solutions in the cryptographic magic of NFTs.
What are NFTs or Non-Fungible Tokens?
Imagine you've meticulously crafted a sophisticated digital blueprint, perhaps a futuristic jewellery design or an intricate mechanical engineering prototype. Now, imagine you digitally sign your name on this creation, in a way that can never every be modified and becomes part of your design’s core metadata.
Your new NFT shows, "This unique 3D model is my creation, and its authenticity is digitally etched in stone for eternity." It's your means of leaving a distinguishable, un-editable mark in the digital landscape of the 3D printable world. Non-Fungible Tokens(NFTs) become the anti-matter for your designs, now stored on the inter-planetary file system.
So, when you create a piece of digital art or anything cool on your computer, minting an NFT is like getting a virtual autograph on it. It says, "Hey, this is the original, and there's no other exactly like it," making your digital things extra special and one-of-a-kind!
To learn more about NFTs, checkout our article about what are Non-Fungible Tokens.
Significance of the Integration of NFTs in CAD
Authenticity in a Digital Landscape
Our team at Mintcad proudly unveils the ultimate solution. The first and best NFT marketplace tailor-made for 3D printable NFTs. Here, you can create Non-Fungible Tokens for your 3D printables, registering your design on the blockchain, granting ownership over intellectual property and transforming it into bona fide digital assets.
A Marketplace of Possibilities
Your newly tokenized CAD creations will gain visibility among a diverse audience. The top NFT marketplaces like Mintcad becomes a digital gallery, showcasing your designs to a global network of art enthusiasts, potential collaborators, and industry influencers. It's a stage where your work will be recognized and celebrated in our online community.
Mintcad introduces a plethora of revenue channels, from auctions, fixed-priced listings, and payment for single prints. As designers, you have the flexibility to choose how you want to present your digital assets, providing a dynamic marketplace for buyers, manufacturers, enthusiasts and creators alike. You can learn more about listing types on our article, How to list your first NFT on Mintcad.
Monetization Opportunities
NFTs not only amplify the visibility of your 3D printable designs, but also opens doors to monetization opportunities. As your designs gain recognition on Mintcad, they become more than just digital art – they become potential sources of income. Collectors and enthusiasts can print your designs once using Mintcad very own slicer software, offering a unique avenue for artists and designers to earn from every print without having your file downloaded.
Designers own the underlying files they create and allow other users to 3D print them for a fee they decide, all through the power of smart contracts. Users can also sell the digital assets to buyers through auctions, fixed priced listing and more. This ensures fair compensation and open transactions, empowering designers to monetize their talents effortlessly.
Providing Scalability to Designers with Mintcad: The Resale Revolution
A notable aspect of 3D printable NFTs, especially on Mintcad, is the emergence of the secondary market tailored for you assets. Much like artists relish ongoing royalty payments from the perpetual sale and resale of their creations, CAD designers utilizing Mintcad can now partake in a continuous percentage share with every transaction involving their digital assets. This transformative feature not only introduces a scalable recurring revenue stream for designers but also acts as a dynamic incentive, fostering the generation of high-quality and innovative designs. We stand for royalties.
Teamwork Makes the Dream Work
The best NFT platforms aren't just about one designer and their masterpiece, they're about teamwork. Imagine an artist in Japan teaming up with a tech whiz in Brazil to create something amazing. With Mintcad, you can easily team up globally, fostering collaboration and connecting creative minds across the world. It's like the Avengers of design, where different skills unite to create something bigger and better than before.
Future-Proofing Creativity
As we navigate the integration of NFTs in CAD, it's not merely a trend but a strategy for future-proofing creativity. Just as Uber transformed transportation and Spotify revolutionized music consumption, Mintcad urges designers to be the trailblazers of change in the future of CAD.
By registering intellectual property on the blockchain and creating 3D printable NFTs early on Mintcad, designers become architects of the future. The platform incentivizes creativity, attracting users to your creations and adding value to lives. It's not just a marketplace, it's a digital revolution that has already begun.
The Impact: A Revolutionary Future for CAD Files
NFTs don't just turn design files into a scalable career option, they transform them into and outlet for human innovation and evolution. This new paradigm reveals unprecedented possibilities for monetization and collaboration, positioning Mintcad as the gateway to a transformative journey in the world of WEB 3.0 and 3D printing.
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: How NFTs Are Revolutionizing The 3D Printing Industry
0 notes
Text
NFT Marketplaces To Watch Out For In 2024

What are NFTs?
Suppose you borrow $100 from your friend, you need to pay him back with the exact same value, but not necessarily the exact same bill. You can return two $50 bills or ten $10 bills, it’s fungible. Although when you borrow a friend’s car, you cannot return a different car, thus a car is considered non fungible, collectible and is unique. Non-fungibility is a physical asset’s unique property. NFTs are unique, they cannot be exchanged or traded equivalently unlike money.
NFTs or Non-Fungible Tokens are cryptographic assets minted (created) through blockchain technology, and have unique identification codes and meta-data, which makes each of them distinguishable. They can be transferred to other wallets, traded on the blockchain or leased to someone through a special smart contract with a time horizon.
NFTs are minted as smart contracts that assign ownership and manage their transferability. When someone creates or mints an NFT, they execute code stored in smart contracts that conform to different standards, such as ERC-721. This information is added to the blockchain where the NFT is being managed. The minting process, from a high level, has the following steps that it goes through:
Creating a new block
Validating information
Recording information into the blockchain
Use Cases of NFTs
Authenticity and Ownership - As the blockchain can permanently store information about the product. NFT smart contracts can be used to check for the rarity, owner, and authenticity of the products. This can be applied to real estate, music items, videos, and more.
Digital Content - The most common use of NFTs today is digital content. Content creators see their profits enhanced by NFTs, as they power a creator economy where creatives maintain ownership over their content on platforms where they are publicised. An NFT could represent a key that unlocks access to a certain service or piece of content. This would allow some content creators to monetize their work for the first time ever. At Mintcad users can create an NFT for CAD files for the first time.
Gaming Items - NFTs are changing the gaming industry from its roots. From game developers to players, NFTs have caught interest for their benefits to both. For example, an NFT could represent a character in a game. The NFT would be stored on a blockchain and would be transferable to another player if the original owner decides to sell it. These can be applicable to other game items as well. This is where the major development towards the Metaverse is happening.
Domain Names - NFTs provide your domain with an easier-to-remember name. It works like a website domain name, making its IP address more memorable and valuable, usually based on length and relevance.
Loyalty points or rewards - A company could issue NFTs that can be redeemed for discounts or special offers. It would give customers an incentive to keep using the company’s products or services.

What’s the size of the NFT Market?
Global NFT transaction volumes are on pace to surpass last year's peak soon, but the monthly declines beginning 2022 are troubling for the once-scintillating market. Total sales hit $37 billion as of the first week of May, according to a report from blockchain analysis firm, Chainalysis, compared with $40 billion for all of 2021.
There are around 15,000 to 50,000 NFTs being bought and sold every week. The right to the first-ever tweet was converted into an NFT, and sold for a record $2.9 million, by Twitter founder Jack Dorsey.
This tweet just said, "just setting up my twttr."
How to buy an NFT?
We can buy or sell NFTs through an NFT Marketplace. These are eCommerce platforms like Amazon or eBay where different products are listed by sellers, and buyers.
NFTs for digital assets can be stored, traded, and displayed to a large audience, an evolved business model is developing through these Marketplaces.
Three Simple steps to buy an NFT:-
Purchase Ethereum. (Since most NFTs are Ethereum-based tokens, most marketplaces for these collectibles accept primarily ETH tokens as payment.)
Connect your Wallet to an NFT Marketplace. There are many marketplaces to trade on.
Create, Sell, Buy or Lease the NFT.
Types of NFT Marketplaces.
Digital Collectibles: Examples of NFTs in such a marketplace are Computer aided design files for 3D Printing, game/trade cards, trophies of wins, and unique videos of rare gaming moments, which are digitized as a non-fungible token or NFT.
Example:- Opensea
Gaming: Blockchain Games use NFT marketplaces in two ways. Some blockchain games collaborate with gaming marketplaces to allow tokenization of their in-game assets into NFTs. Then, there are pure NFT marketplace-centred games that are exclusively built on the concept of tradable collectibles. Such games are modelled after traditional games like football, racing, strategy, arcade, and even virtual worlds.
Example:- Axie Infinity
Real Estate: It is an online platform for fractional real estate where investors and agents can collaborate with each other to buy and sell their assets. It gives access to high-end, unique, and in-demand properties which can be converted into non-fungible tokens and crowd funding.
Music: The music industry may have finally started taking NFTs more seriously. A number of artists have launched music projects that have garnered fan attention and generated millions of dollars in revenue. Entire music albums or specific songs can be converted into NFTs and sold or leased (per listen) directly via special NFT marketplaces.
Example:- Airnfts
Investment Projects: In this model, the NFT marketplace can function like a stock market, and allow the users to buy/sell specific NFTs via trading. In some of the advanced and regulated NFT marketplace, such transactions can also have legal validity, similar to real estate.
Metaverse: A metaverse NFT marketplace is a technical concept of creating and integrating NFT assets into the virtual spaces of the metaverse. The metaverse is considered a parallel universe where avatars (representing the unique identity of users) can perform activities similar to the real world with the use of VR headsets.
Example:- Cryptovoxels, Decentraland
Top 10 NFT Marketplaces in 2023
1. OpenSea
2. Mintcad
3. SuperRare
4. Jump.trade
5. Rarible
6. Axie Infinity
7. Nifty Gateway
8. Solanart
9. Binance
10. NBA Top Shot
This content is originally published on Mintcad's Website: NFT Marketplaces To Watch Out For In 2024
0 notes
Text
https://mintcad.com/educational
Educational 3D Models for Printing Lessons & Projects
Enliven STEM lessons using 3D printing and Mintcad's collection of education 3D model NFTs. Covering science, tech, engineering, art and math!
#Educational 3D Models for Printing Lessons#Educational 3D Models for Projects#Educational 3D Models#Best NFT Marketplace
0 notes
Text
https://mintcad.com/healthcare
Healthcare NFT Models for 3D Printing – Mintcad
Print customized medical devices, anatomical models, orthotics and more with healthcare NFT files from Mintcad's digital marketplace. Revolutionize medicine!
#Healthcare NFTs Models for 3D Printing#Healthcare NFTs 3D Printable#Healthcare NFT Models#Best NFT Marketplace
0 notes
Text
https://mintcad.com/architecture
Architecture NFTs and Stunning 3D Printable Models
Bring your architecture visions to life with MintCad's expansive collection of architecture NFTs and 3D printable model files for visualization and printing.
0 notes